Coronary Artery Disease Detection Based on a Novel Multi-Modal Deep-Coding Method Using ECG and PCG Signals
Abstract
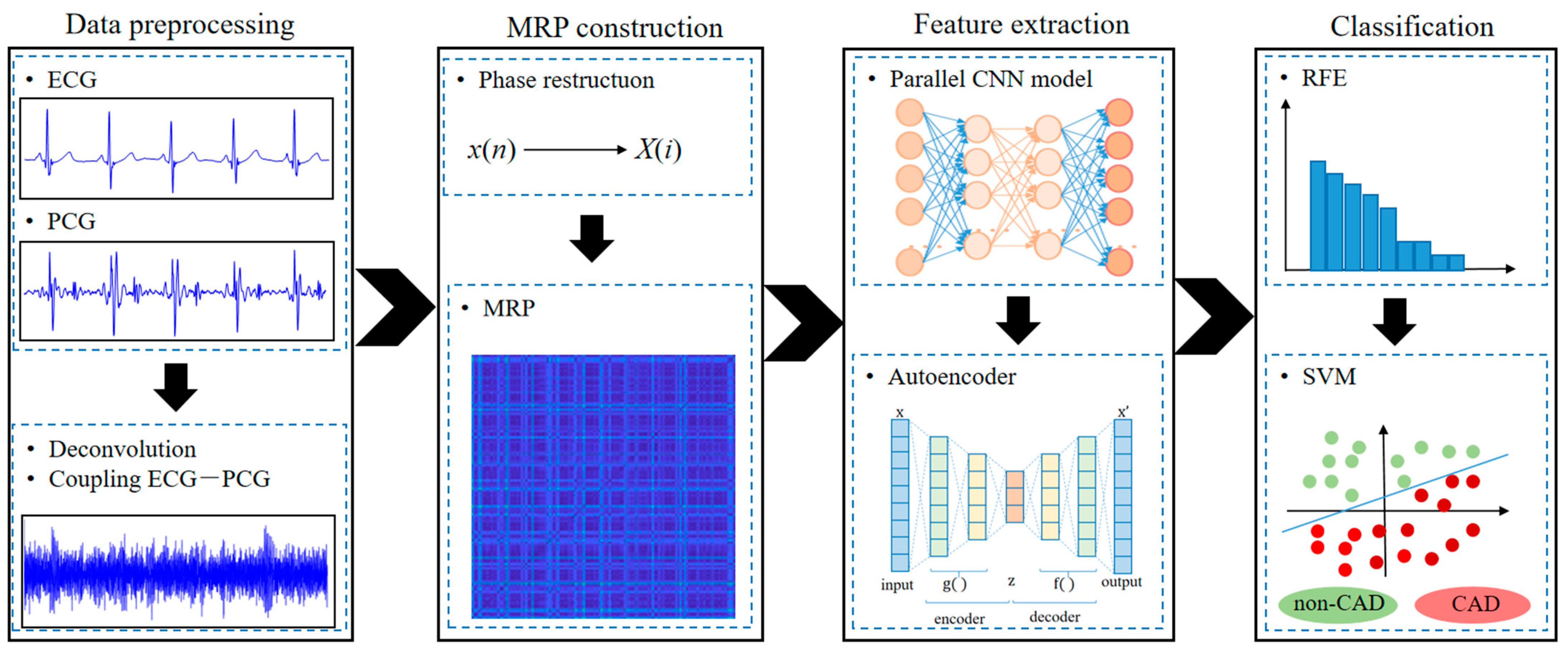
:1. Introduction
- A novel multi-modal learning method by considering both ECG and PCG signals is proposed to detect CAD.
- The multi-modal deep-coding information involves ECG, PCG and ECG-PCG coupling deep-coding MRP features.
- The proposed method constructs MRPs to quantify the nonlinear dynamic characteristics of ECG, PCG and their deconvolution signals, and builds the integrating deep learning network to code multi-modal deep-coding features and reduce feature dimension.
- A combination of optimal multi-modal features and SVM classifier is used for final classification, and the result indicates superiority of the multi-modal learning method.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Data Pre-Processing
2.2.1. Data Denoising
2.2.2. ECG-PCG Coupling Signal Evaluation
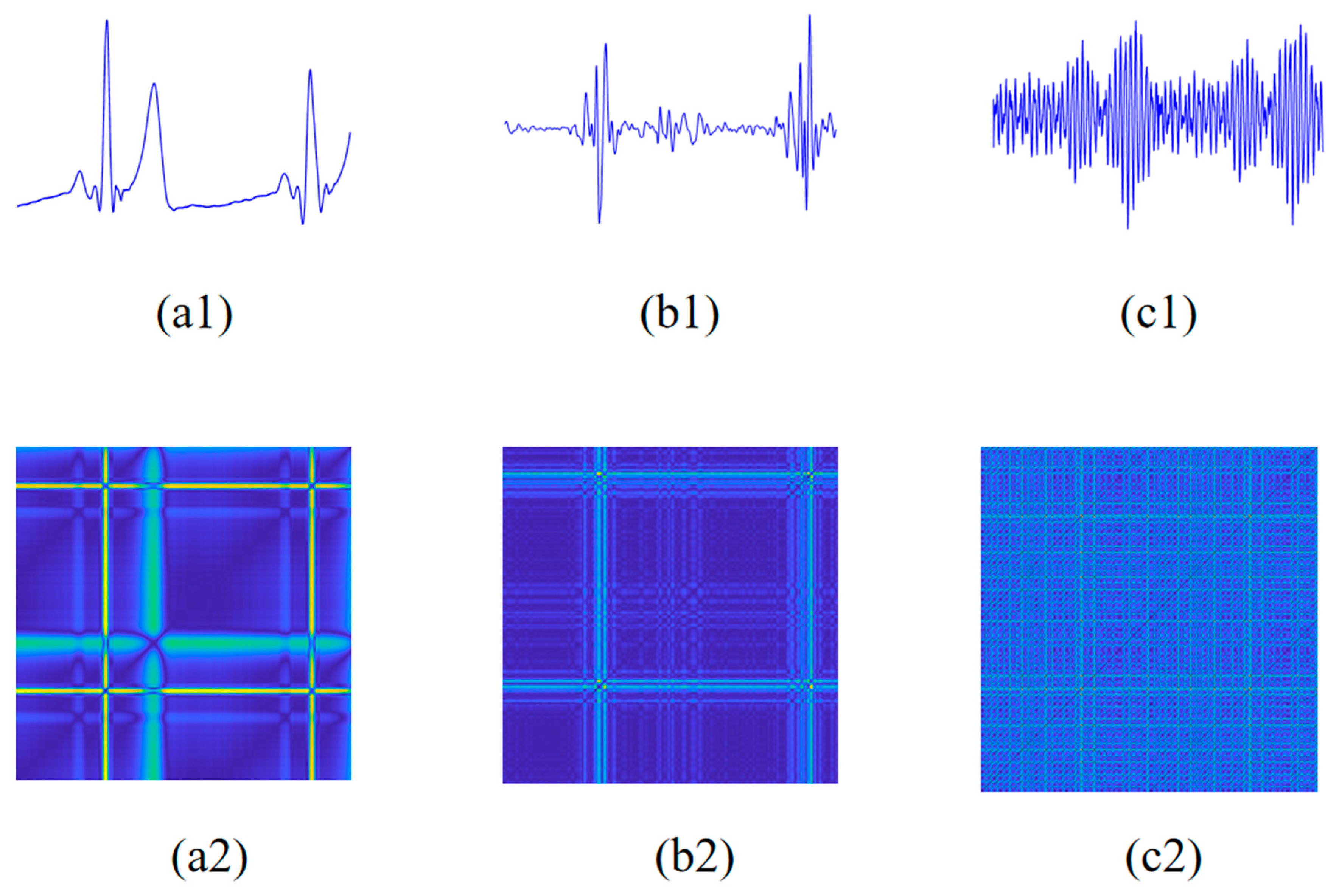
2.3. Modified Recurrence Plot
2.3.1. Phase Space Reconstruction
2.3.2. Modified Recurrence Plot Construction
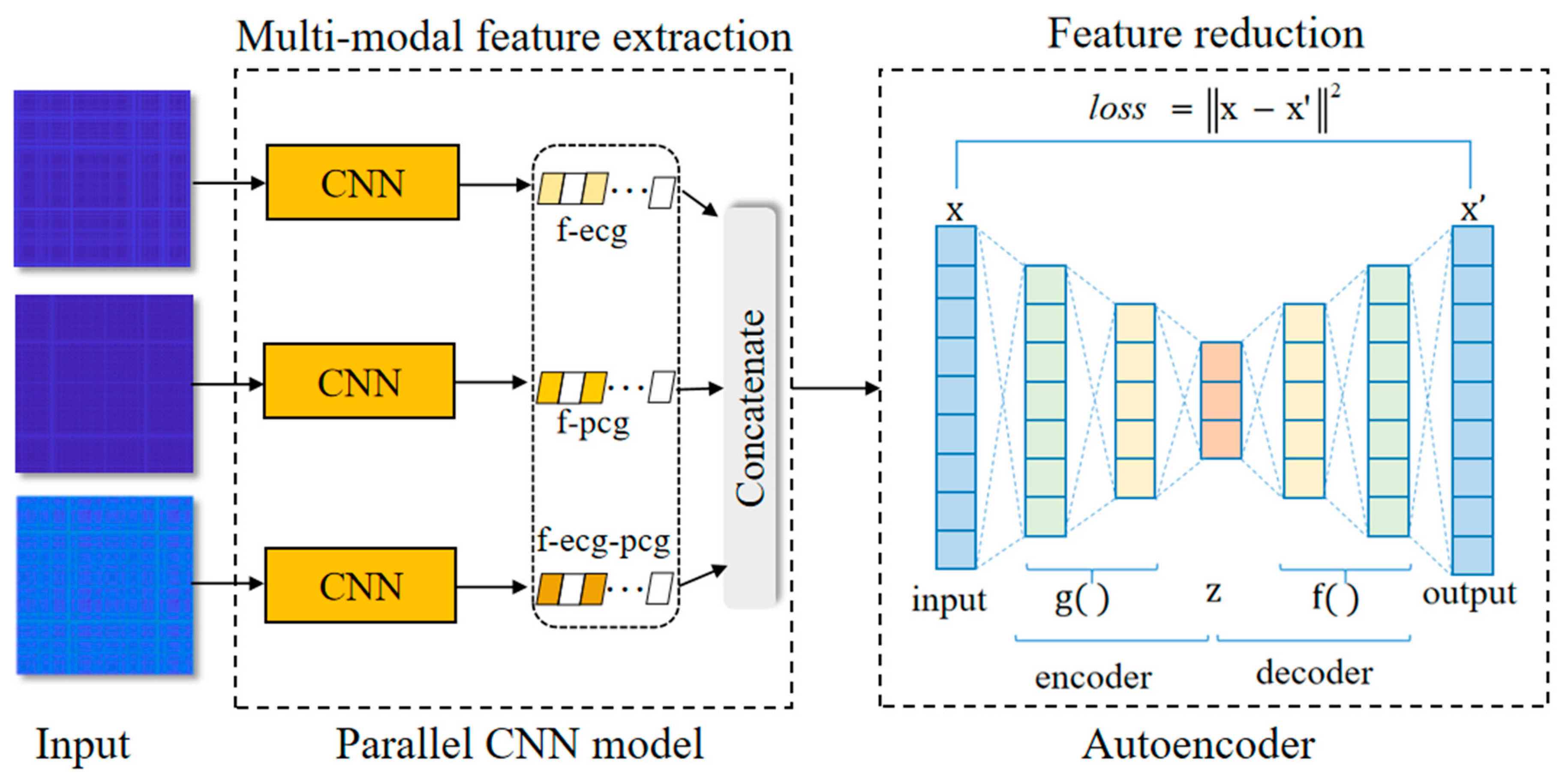
2.4. Feature Extraction Based on Integrating Deep Learning Network
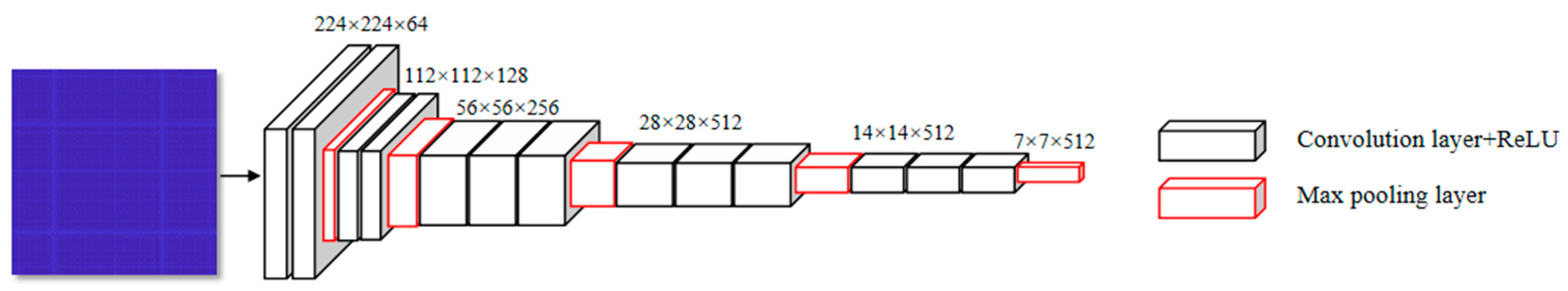
2.4.1. The Parallel CNN Network
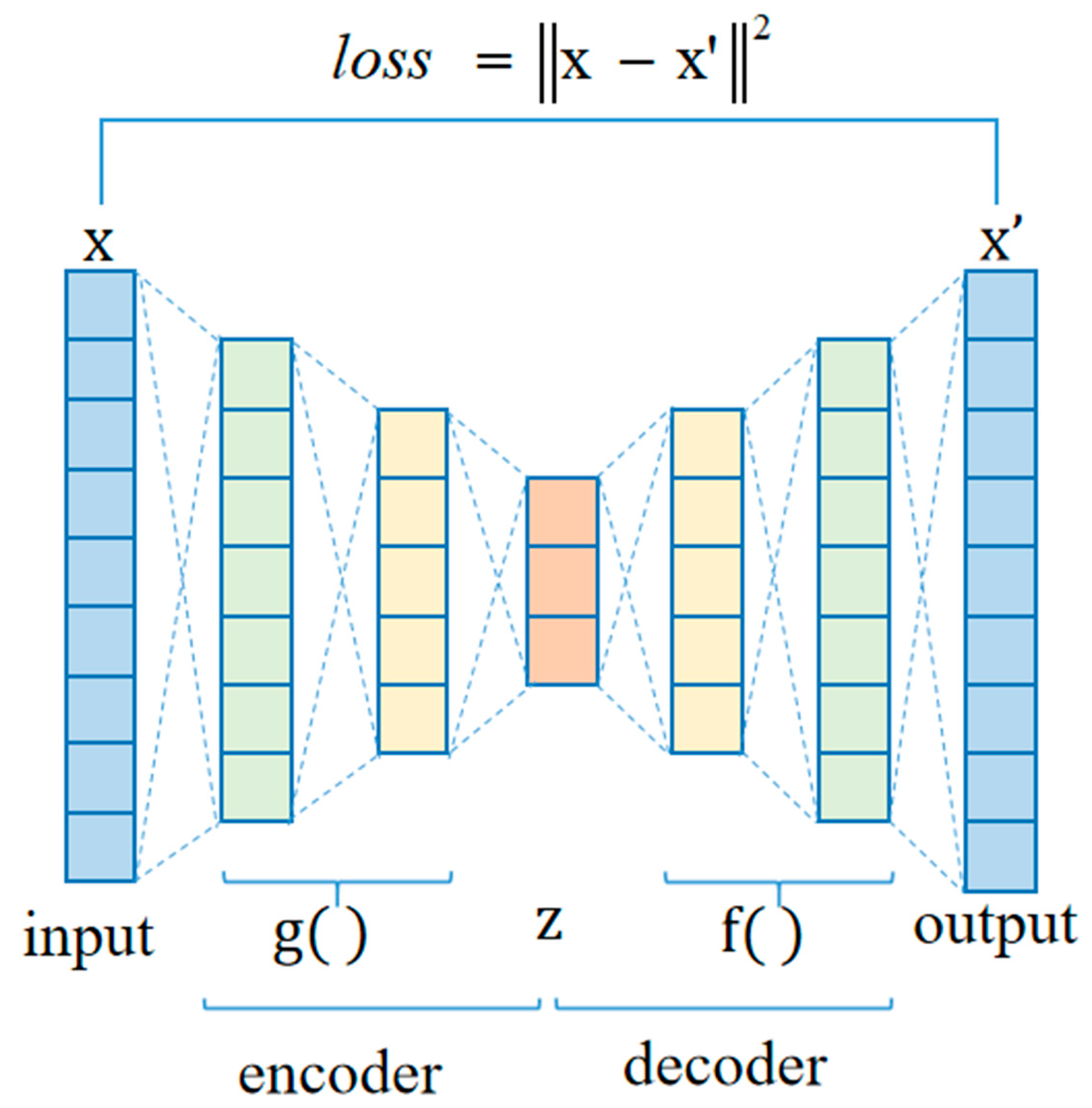
2.4.2. Autoencoder Network
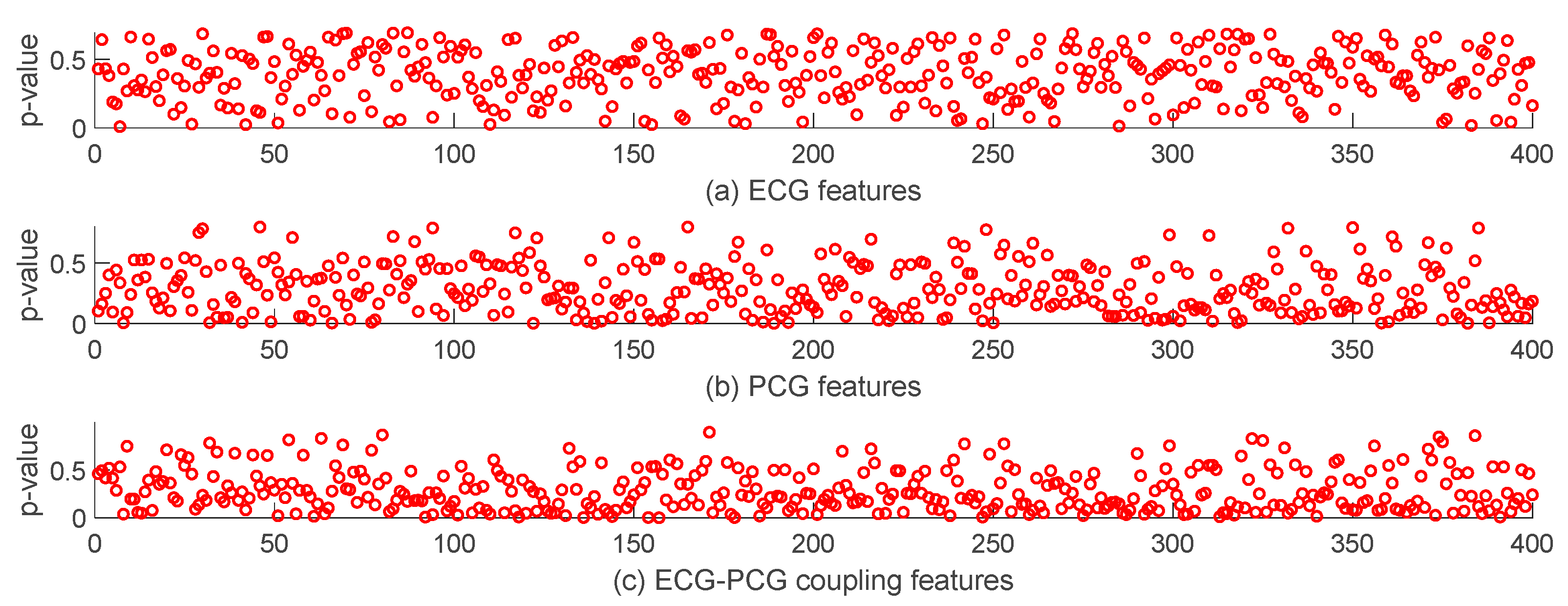
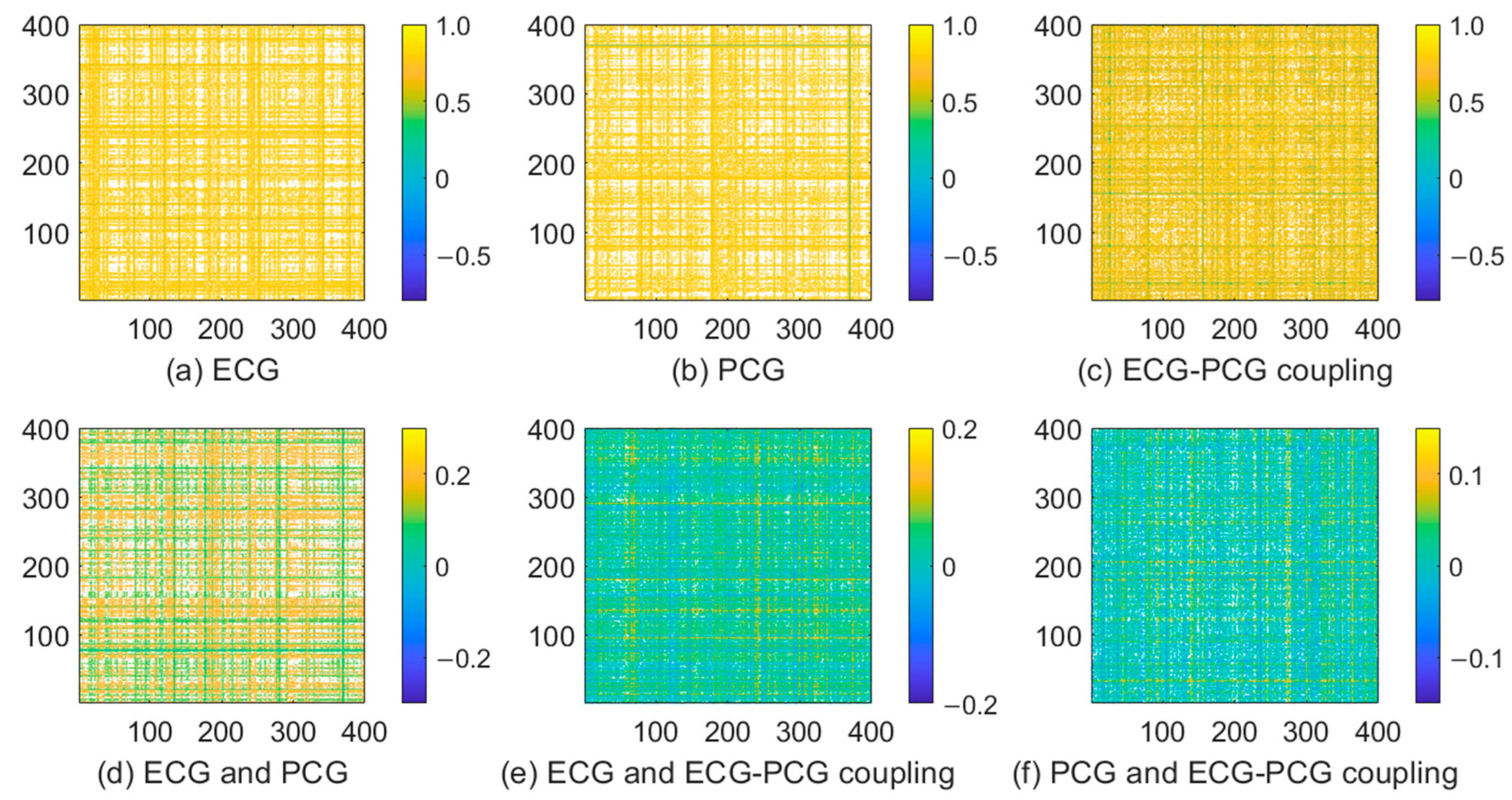
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Classification and Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Single- and Multi-Modal Data
3.2. Overall Classification Results of Multi-Modal Method
3.3. Features Analysis of Different Modal Signals
3.4. Performance Analysis of Different Models
4. Comparison and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pathak, A.; Samanta, P.; Mandana, K.; Saha, G. Detection of coronary artery atherosclerotic disease using novel features from synchrosqueezing transform of phonocardiogram. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lih, O.S.; Jahmunah, V.; San, T.R.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Yamakawa, T.; Tanabe, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Faust, O.; Acharya, U.R. Comprehensive electrocardiographic diagnosis based on deep learning. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 103, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cury, R.C.; Abbara, S.; Achenbach, S.; Agatston, A.; Berman, D.S.; Budoff, M.J.; Dill, K.E.; Jacobs, J.E.; Maroules, C.D.; Rubin, G.D.; et al. CAD-RADSTM coronary artery disease—Reporting and data system. An expert consensus document of the society of cardiovascular computed tomography (SCCT), the american college of radiology (ACR) and the north american society for cardiovascular imaging (NASCI). Endorsed by the American college of cardiology. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2016, 10, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ren, G.; Yu, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, S. Discrimination of the diastolic murmurs in coronary heart disease and in valvular disease. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 160407–160413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddens, D.P.; Mabon, R.F.; Cassanova, R.A. Measurements of disordered flows distal to subtotal vascular stenosis in the thoracic aortas of dogs. Circ. Res. 1976, 39, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, Y.M.; Akay, M.; Welkowitz, W.; Semmlow, J.L.; Kostis, J.B. Noninvasive acoustical detection of coronary artery disease: A comparative study of signal processing methods. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Hu, Y.M.; Liu, Z.P. Prediction of cardiovascular diseases by integrating multi-modal features with machine learning methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 66, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Pachori, R.B.; Acharya, U.R. Characterization of coronary artery disease using flexible analytic wavelet transform applied on ECG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.H.; Hagiwara, Y.; Pang, W.; Lim, I.; Oh, S.L.; Adam, M.; Tan, R.S.; Chen, M.; Acharya, U.R. Application of stacked convolutional and long short-term memory network for accurate identification of CAD ECG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 94, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Hagiwara, Y.; Koh, J.E.W.; Oh, S.L.; Tan, J.H.; Adam, M.; Tan, R.S. Entropies for automated detection of coronary artery disease using ECG signals: A review. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschannen, M.; Kramer, T.; Marti, G.; Heinzmann, M.; Wiatowski, T. Heart sound classification using deep structured features. In Proceedings of the 2016 Computing in Cardiology Conference, (CinC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 September 2016; pp. 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Noman, F.; Ting, C.M.; Salleh, S.H.; Ombao, H. Short-segment heart sound classification using an ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 1318–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Baydoun, M.; Safatly, L.; Ghaziri, H.; Hajj, A.E. Analysis of heart sound anomalies using ensemble learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humayun, A.I.; Ghaffarzadegan, S.; Ansari, M.I.; Feng, Z.; Hasan, T. Towards domain invariant heart sound abnormality detection using learnable filterbanks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ke, L.; Du, Q.; Chen, X.; Ding, X. Multi-modal cardiac function signals classification algorithm based on improved D-S evidence theory. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrabi, M.; Parsaei, H.; Boostani, R.; Zare, A.; Dorfeshan, Z.; Zarrabi, K.; Kojuri, J. A system for accurately predicting the risk of myocardial infarction using PCG, ECG and clinical features. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 29, 1750023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Tang, H.; Yao, L.K.; Zhang, H. Dual-input neural network integrating feature extraction and deep learning for coronary artery disease detection using electrocardiogram and phonocardiogram. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146457–146469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, K.; Zheng, D.; Li, Z.M.; Liu, C.C. Detection of coupling in short physiological series by a joint distribution entropy method. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.W.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, Y.Y.; Sun, C.F.; Jiao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, S.; Xing, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C. Non-destructive detection of CAD stenosis severity using ECG-PCG coupling analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 86, 105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zeng, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Chu, X.; Yao, L.; Wang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Karmakar, C. A fusion framework based on multi-domain features and deep learning features of phonocardiogram for coronary artery disease detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 120, 103733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, P.; Pathak, A.; Mandana, K.; Saha, G. Classification of coronary artery diseased and normal subjects using multi-channel phonocardiogram signal. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, A.; Chung, W. Automated classification of coronary atherosclerosis using single lead ECG. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Wireless Sensor (ICWISE), Kuching, Malaysia, 2–4 December 2013; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann, J.P.; Kamphorst, S.O.; Ruelle, D. Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. Europhys. Lett. 1987, 4, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathunjwa, B.M.; Lin, Y.T.; Lin, C.H.; Abbod, M.F.; Shieh, J.S. ECG arrhythmia classification by using a recurrence plot and convolutional neural network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 64, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, R.; He, Y.; Xia, L.; Liu, F. Recurrence Plot-Based Approach for Cardiac Arrhythmia Classification Using Inception-ResNet-v2. Front Physiol. 2021, 17, 648950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ke, L.; Du, Q. Classification of heart sounds based on the wavelet fractal and twin support vector machine. Entropy 2019, 21, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Yao, Q.; Cai, Y.; Miao, F.; Sun, F.; Li, Y. Multiscaled fusion of deep convolutional neural networks for screening atrial fibrillation from single lead short ECG recordings. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adam, M.; Gertych, A.; Tan, R.S. A deep convolutional neural network model to classify heartbeats. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 89, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrishami, H.; Han, C.; Zhou, X.; Campbell, M.; Czosek, R. Supervised ECG interval segmentation using LSTM neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (BIOCOMP), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9 August 2018; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmaini, S.; Tondas, A.E.; Darmawahyuni, A.; Rachmatullah, M.N.; Effendi, J.; Firdaus, F.; Tutuko, B. Electrocardiogram signal classification for automated delineation using bidirectional long short-term memory. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 22, 100507–100511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Wang, W.; Feng, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, W. Low-Dimensional Denoising Embedding Transformer for ECG Classification. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 1285–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Matias, P.; Folgado, D.; Gamboa, H.; Carreiro, A.V. Robust anomaly detection in time series through variational AutoEncoders and a local similarity score. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021), Vienna, Astria, 11–13 February 2021; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Peimankar, A.; Puthusserypady, S. DENS-ECG: A deep learning approach for ECG signal delineation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 165, 113911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Liu, C. ECG_SegNet: An ECG delineation model based on the encoder-decoder structure. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggipinto, M.; Masiero, C.; Beghi, A.; Susto, G.A. A convolutional autoencoder approach for feature extraction in virtual metrology. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 17, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.G.; Noh, K.Y.; Ryu, K.H. Mining Biosignal Data: Coronary Artery Disease Diagnosis Using Linear and Nonlinear Features of HRV. In Proceedings of the Emerging Technologies in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining: {PAKDD} 2007, International Workshops, Nanjing, China, 22–25 May 2007; pp. 218–228. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Koh, J.E.; Martis, R.J.; Tan, J.H.; Oh, S.L.; Muhammad, A.; Hagiwara, Y.; Mookiah, M.R.K.; Chua, K.P.; et al. Application of higher-order spectra for the characterization of coronary artery disease using electrocardiogram signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobillo, I.D. A tensor approach to heart sound classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 September 2016; pp. 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, M.; Majumder, S.; Halder, A.; Biswas, U. ECG-NET: A deep LSTM autoencoder for detecting anomalous ECG. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 124, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, H. Differentiable manifolds. Ann. Math. 1936, 37, 645–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennel, M.B.; Brown, R.; Abarbanel, H.D. Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Phys. Rev. A. 1992, 45, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.M.; Swinney, H.L. Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information. Phys. Rev. A. 1986, 33, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H. Multiscale Recurrence Quantification Analysis of Spatial Cardiac Vectorcardiogram Signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Huang, X.; Liang, Z.; Lin, W.; Mo, B.; Liang, D.; Ruan, S.; Chen, J. Classification of cardiac electrical signals between patients with myocardial infarction and normal subjects by using nonlinear dynamics features and different classification models. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Tao, R.; Han, W.; Zhang, P.; Yu, X.; Wu, R. A customized framework for coronary artery disease detection using phonocardiogram signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 78, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, C.C.; Li, P.; Jiao, Y. Integrating multi-domain deep features of electrocardiogram and phonocardiogram for coronary artery disease detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 138, 104914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Non-CAD | CAD |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 61 ± 10 | 62 ± 10 |
| Male/female | 30/34 | 89/46 |
| Height | 164 ± 7 | 166 ± 8 |
| Weight | 69 ± 12 | 71 ± 11 |
| Heart rate | 72 ± 12 | 75 ± 16 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 134 ± 15 | 133 ± 16 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 80 ± 11 | 82 ± 12 |
| Index | Layer | Index | Layer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | conv3_64 | 10 | max-pooling_2 |
| 2 | conv3_64 | 11 | conv3_512 |
| 3 | max-pooling_2 | 12 | conv3_512 |
| 4 | conv3_128 | 13 | conv3_512 |
| 5 | conv3_128 | 14 | max-pooling_2 |
| 6 | max-pooling_2 | 15 | conv3_512 |
| 7 | conv3_256 | 16 | conv3_512 |
| 8 | conv3_256 | 17 | conv3_512 |
| 9 | conv3_256 | 18 | max-pooling_2 |
| Indicator | Parameter | Indicator | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | 2000-1000-400-1000-2000 | Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Optimizer | SGD | Batch | 32 |
| Loss | MSE | Epoch | 1000 |
| Modal Signal | ACC (%) | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECG | 79.38 ± 4.36 | 92.59 ± 4.68 | 51.54 ± 5.76 | 61.75 ± 7.56 |
| PCG | 77.88 ± 1.92 | 91.85 ± 4.32 | 48.21 ± 11.63 | 57.54 ± 7.72 |
| ECG-PCG coupling | 84.94 ± 4.97 | 94.81 ± 6.87 | 64.10 ± 3.24 | 73.67 ± 6.12 |
| Multi-modal data | 98.49 ± 1.24 | 98.57 ± 1.75 | 98.57 ± 2.86 | 98.89 ± 0.90 |
| Number-Fold | ACC (%) | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-fold | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 2-fold | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 3-fold | 97.50 | 96.43 | 100.00 | 98.18 |
| 4-fold | 97.50 | 100.00 | 92.86 | 98.11 |
| 5-fold | 97.44 | 96.43 | 100.00 | 98.18 |
| mean ± std | 98.49 ± 1.24 | 98.57 ± 1.75 | 98.57 ± 2.86 | 98.89 ± 0.90 |
| Model | ACC (%) | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50-based model | 90.96 ± 2.89 | 94.81 ± 1.81 | 82.82 ± 5.71 | 85.45 ± 4.80 |
| Transformer-based model | 88.46 ± 3.35 | 93.33 ± 2.77 | 78.21 ± 8.81 | 81.21 ± 5.61 |
| Our model | 98.49 ± 1.24 | 98.57 ± 1.75 | 98.57 ± 2.86 | 98.89 ± 0.90 |
| Classifier | ACC (%) |
|---|---|
| Decision tree | 88.34 |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 81.65 |
| Bayse | 81.36 |
| KNN | 90.83 |
| SVM | 98.49 |
| Author | Data | Method | Result (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. [20] | Self-collected 135 CAD/60 non-CAD | PCG, multi-domain features, deep features, MLP | ACC: 90.4 SPE: 83.4 SEN: 93.7 |
| Samanta et al. [21] | Self-collected 29 CAD/37 non-CAD | PCG, time domain and frequency domain features, CNN | ACC: 82.6 SPE: 79.6 SEN: 85.6 |
| Kaveh et al. [22] | MIT-BIH 43 CAD/46 non-CAD | ECG, time domain and frequency domain features, SVM | ACC: 88.0 SPE: 92.6 SEN: 84.2 |
| Huang et al. [46] | Self-collected 348 Normal/206 CAD | PCG, MFCCs, PCG sequence, Customized model | ACC: 96.05 SPE: 96.12 SEN: 96.12 |
| Li et al. [47] | Self-collected 347 CAD/74 non-CAD | ECG and PCG, sequence, spectrum image, ST image, MFCCs image | ACC: 96.51 SPE: 90.08 SEN: 99.37 |
| This study | Self-collected 135 CAD/64 non-CAD | ECG and PPG, Multi-modal deep-coding features, SVM | ACC: 98.49 SPE: 98.57 SEN: 98.57 |
| Self-collected [39] 135 CAD/60 non-CAD | ECG and PCG, Multi-modal deep-coding features, SVM | ACC: 96.37 SPE: 90.22 SEN: 98.26 | |
| Self-collected 60 CAD/60 non-CAD | ECG and PCG, Multi-modal deep-coding features, SVM | ACC: 97.08 SPE: 96.12 SEN: 98.22 |
| Author | Classification Method | Input | Result (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Studies on ECG classification using the PhysioNet dataset | |||
| Kumar et al. [8] | SVM | Time–frequency features | ACC: 99.60 |
| Tan et al. [9] | 1-D CNN | ECG signal | ACC: 99.85 |
| Acharya et al. [10] | 1-D CNN | Entropy features | ACC: 99.27 |
| This study | SVM | MRP deep-coding features | ACC: 99.87 |
| Studies on PCG classification using the PhysioNet/CinC Challenge 2016 dataset | |||
| Tschannen et al. [11] | 1-D CNN | Time features, Frequency features | ACC: 87.00 |
| Noman et al. [12] | 2-D CNN | MFCCs image | ACC: 88.80 |
| Baydoun et al. [13] | Boosting and bagging model | Time–frequency features, Statistical features | ACC: 91.50 |
| Humayun et al. [14] | 1D-CNN | PCG signal | ACC: 97.50 |
| This study | SVM | MRP deep-coding features | ACC: 97.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S. Coronary Artery Disease Detection Based on a Novel Multi-Modal Deep-Coding Method Using ECG and PCG Signals. Sensors 2024, 24, 6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216939
Sun C, Liu C, Wang X, Liu Y, Zhao S. Coronary Artery Disease Detection Based on a Novel Multi-Modal Deep-Coding Method Using ECG and PCG Signals. Sensors. 2024; 24(21):6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216939
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chengfa, Changchun Liu, Xinpei Wang, Yuanyuan Liu, and Shilong Zhao. 2024. "Coronary Artery Disease Detection Based on a Novel Multi-Modal Deep-Coding Method Using ECG and PCG Signals" Sensors 24, no. 21: 6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216939
APA StyleSun, C., Liu, C., Wang, X., Liu, Y., & Zhao, S. (2024). Coronary Artery Disease Detection Based on a Novel Multi-Modal Deep-Coding Method Using ECG and PCG Signals. Sensors, 24(21), 6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216939






