Implantable pH Sensing System Using Vertically Stacked Silicon Nanowire Arrays and Body Channel Communication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
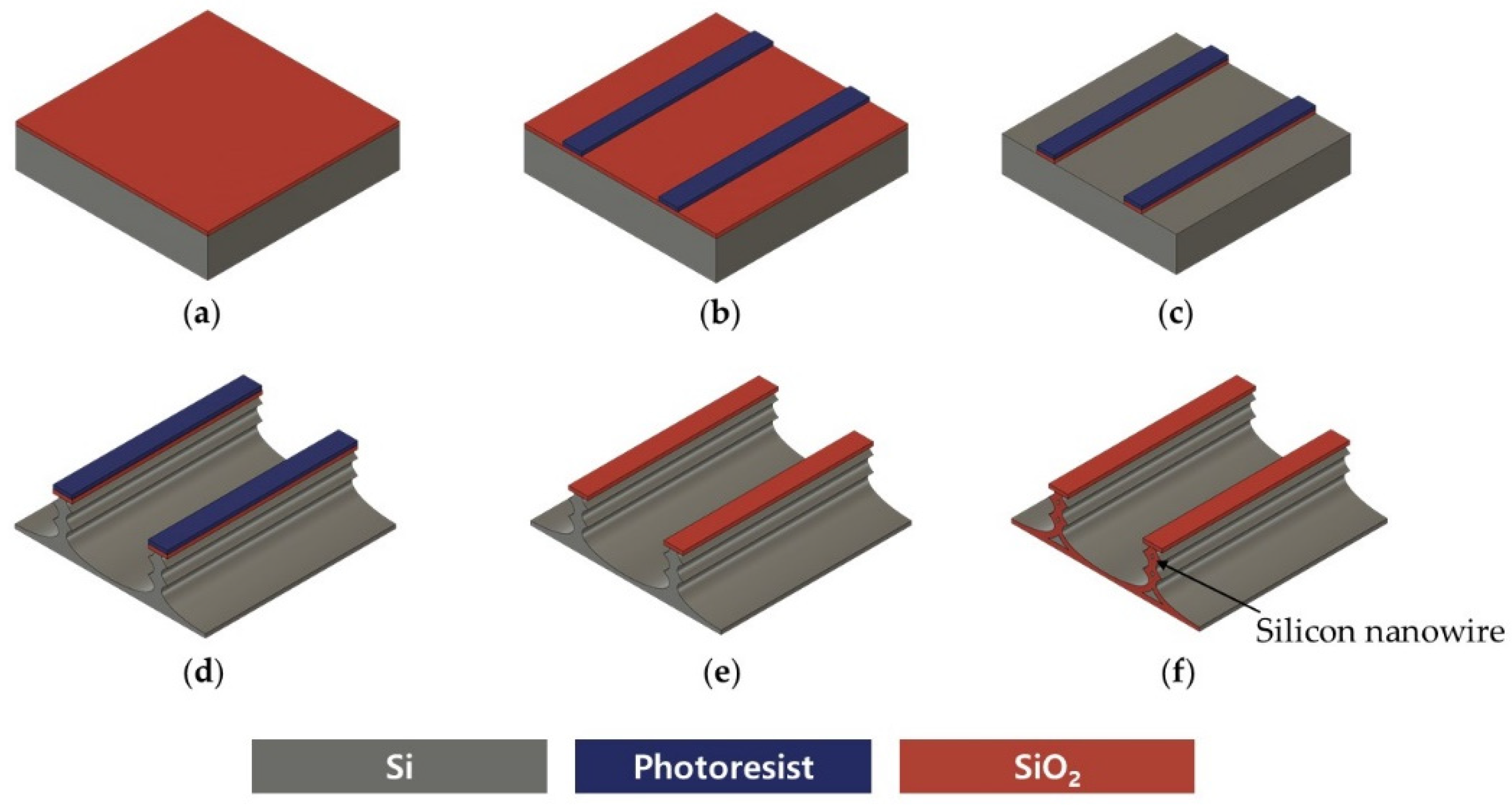
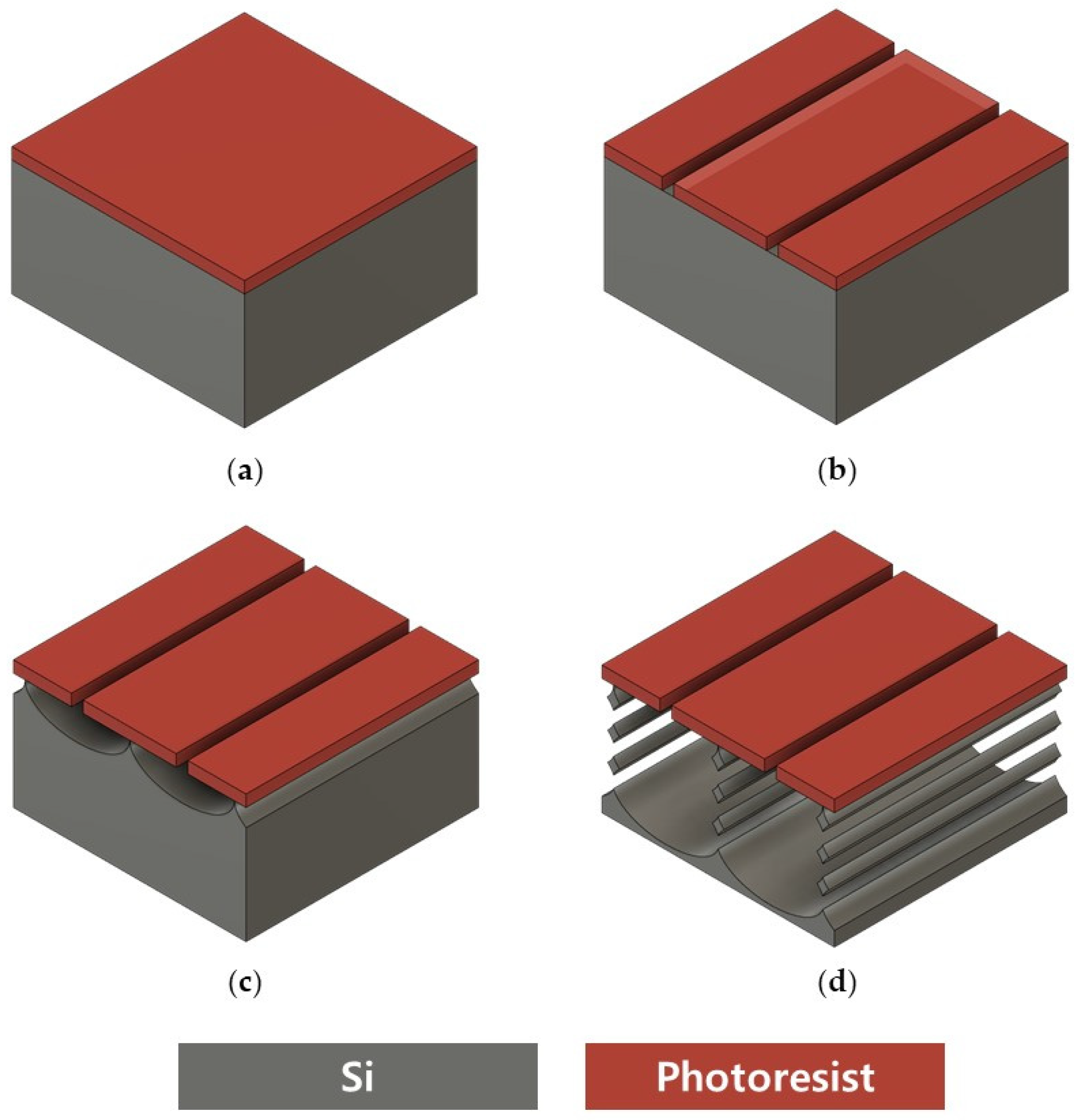
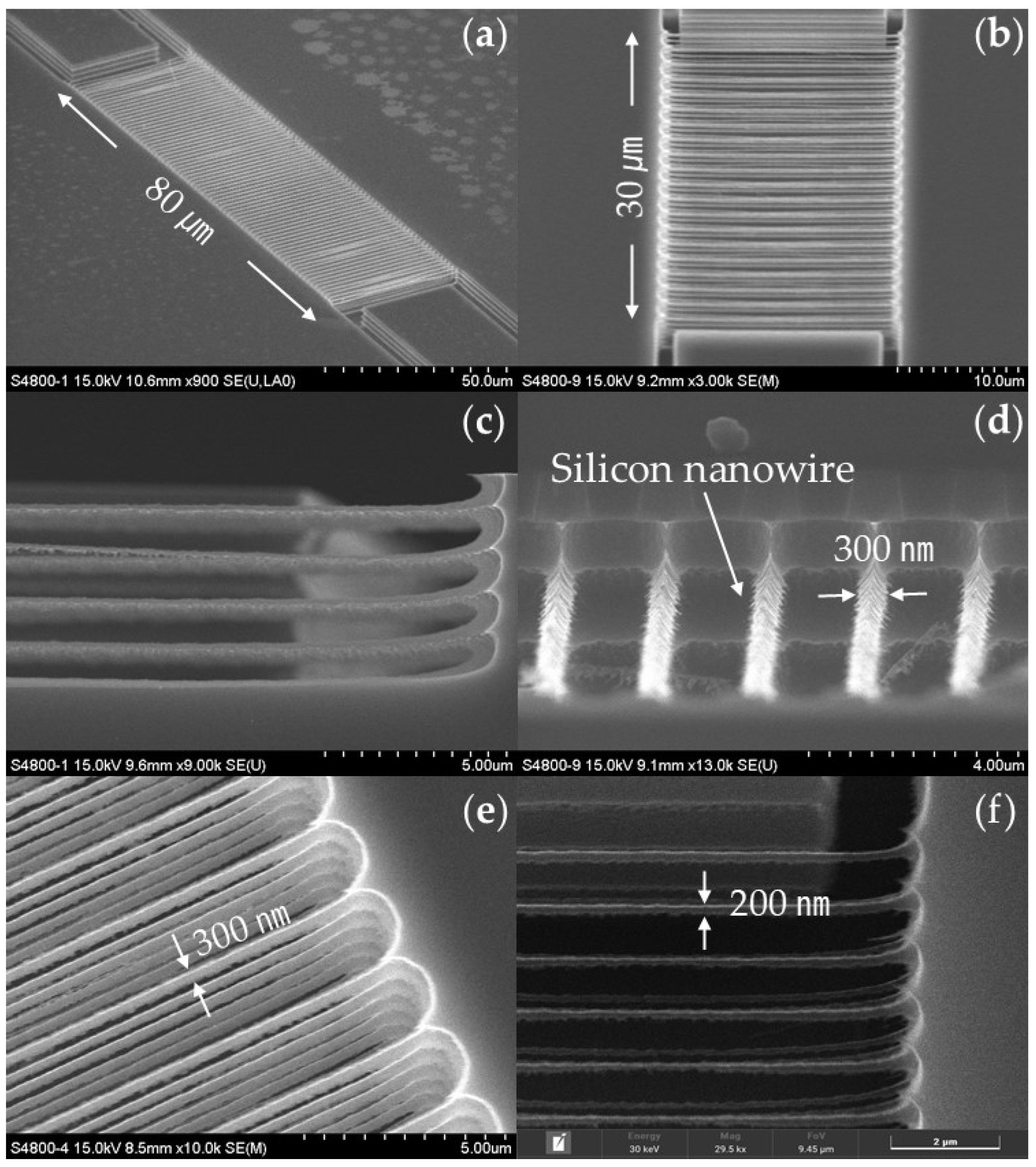
2.1. Top-Down Fabrication of Vertically Stacked Silicon Nanowires
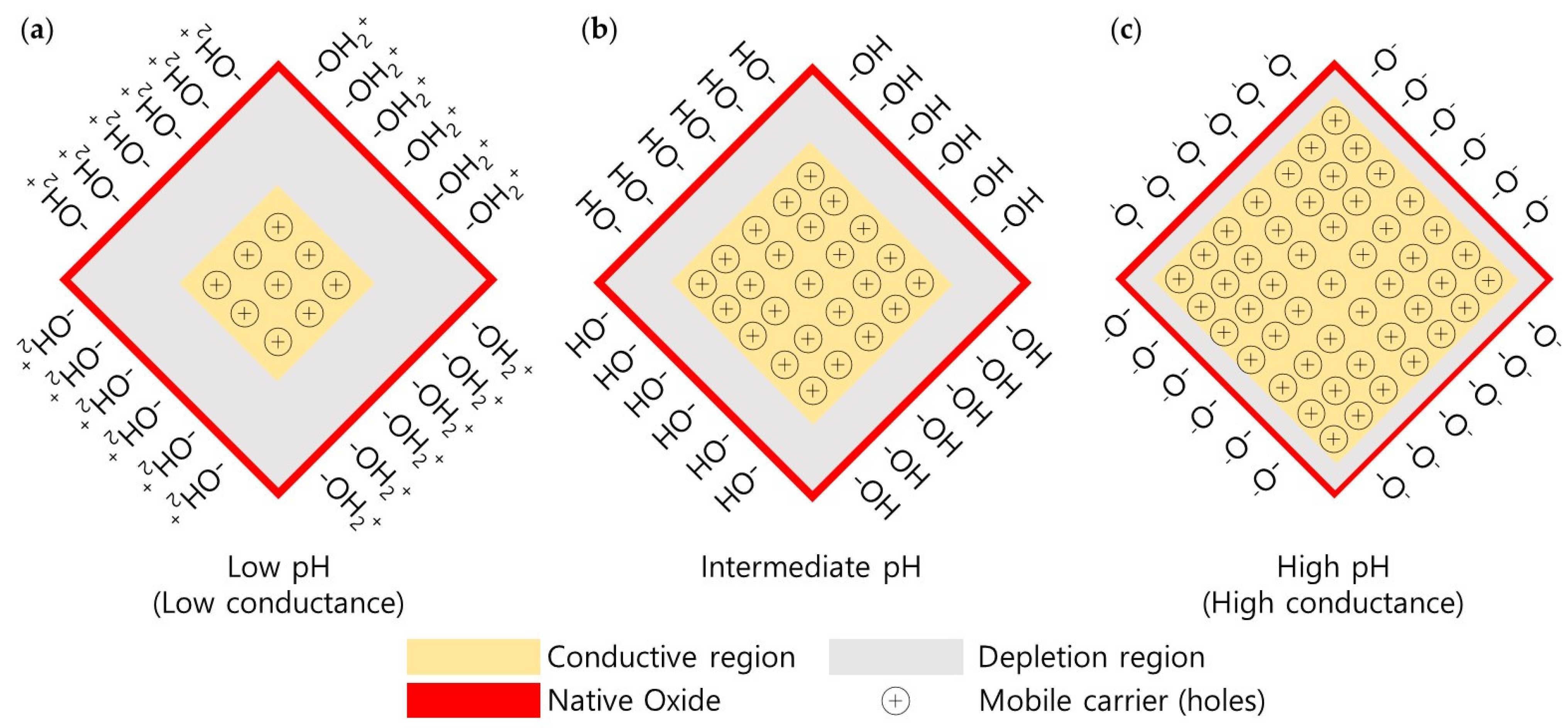
2.2. Operating Principle of Silicon Nanowire-Based pH Sensors
SiOH2+ ⇔ SiOH + H+
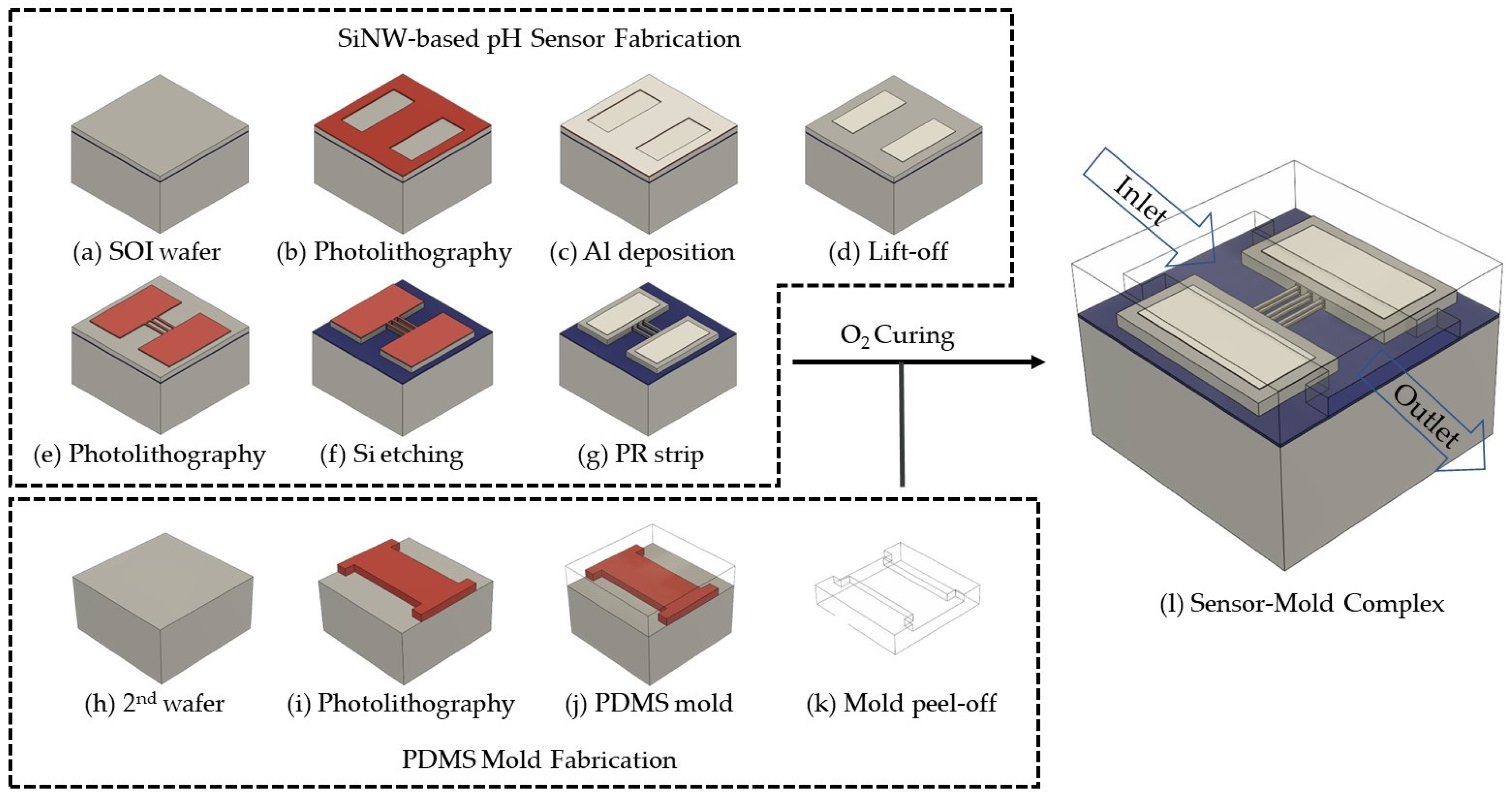
2.3. Fabrication of Silicon Nanowire-Based pH Sensor
2.4. Packaging of Silicon Nanowire pH Sensor
2.5. Measurement of pH Sensitivity of Silicon Nanowire Sensors
3. Results
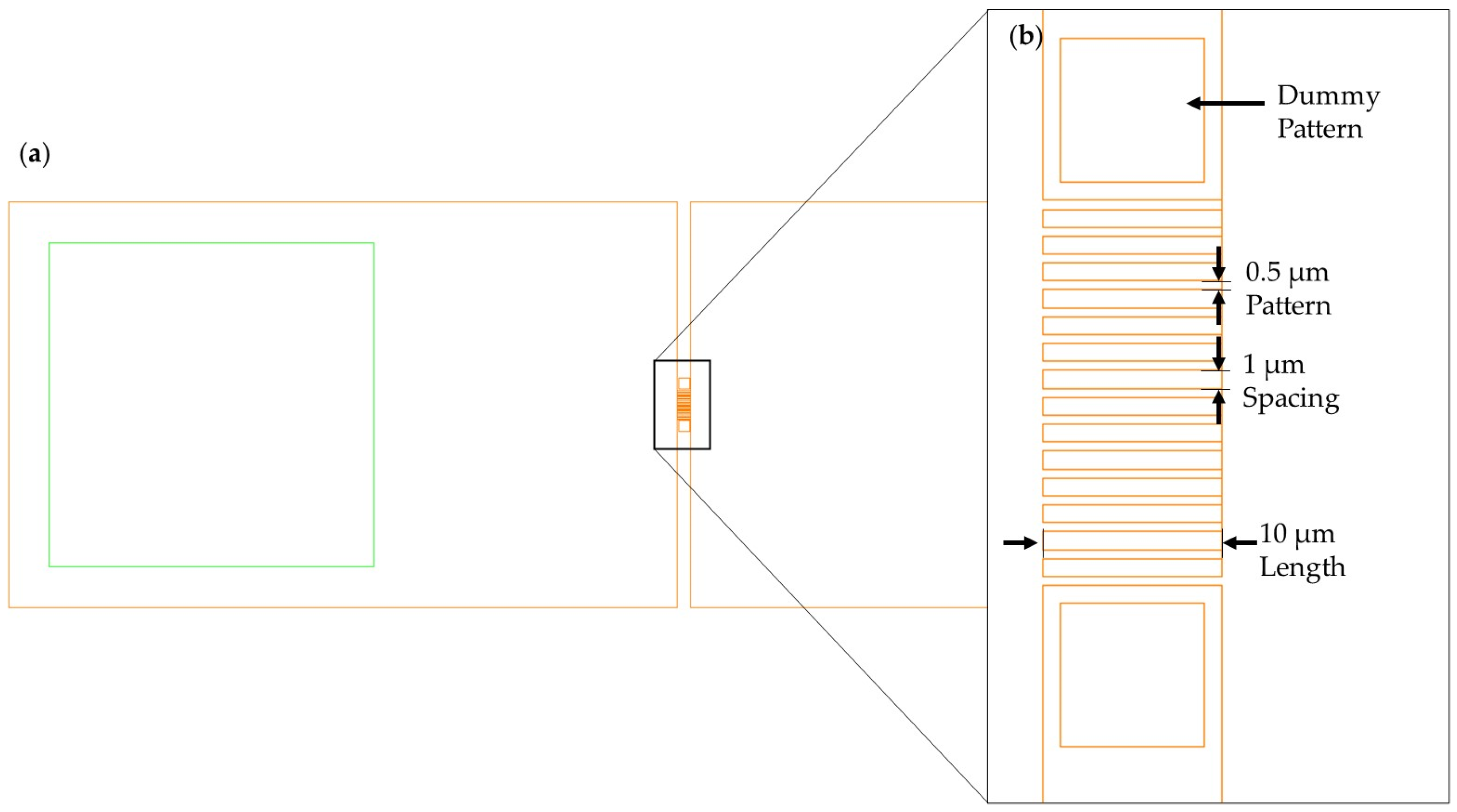
3.1. Specifications of the Fabricated Vertically Stacked Silicon Nanowire Array
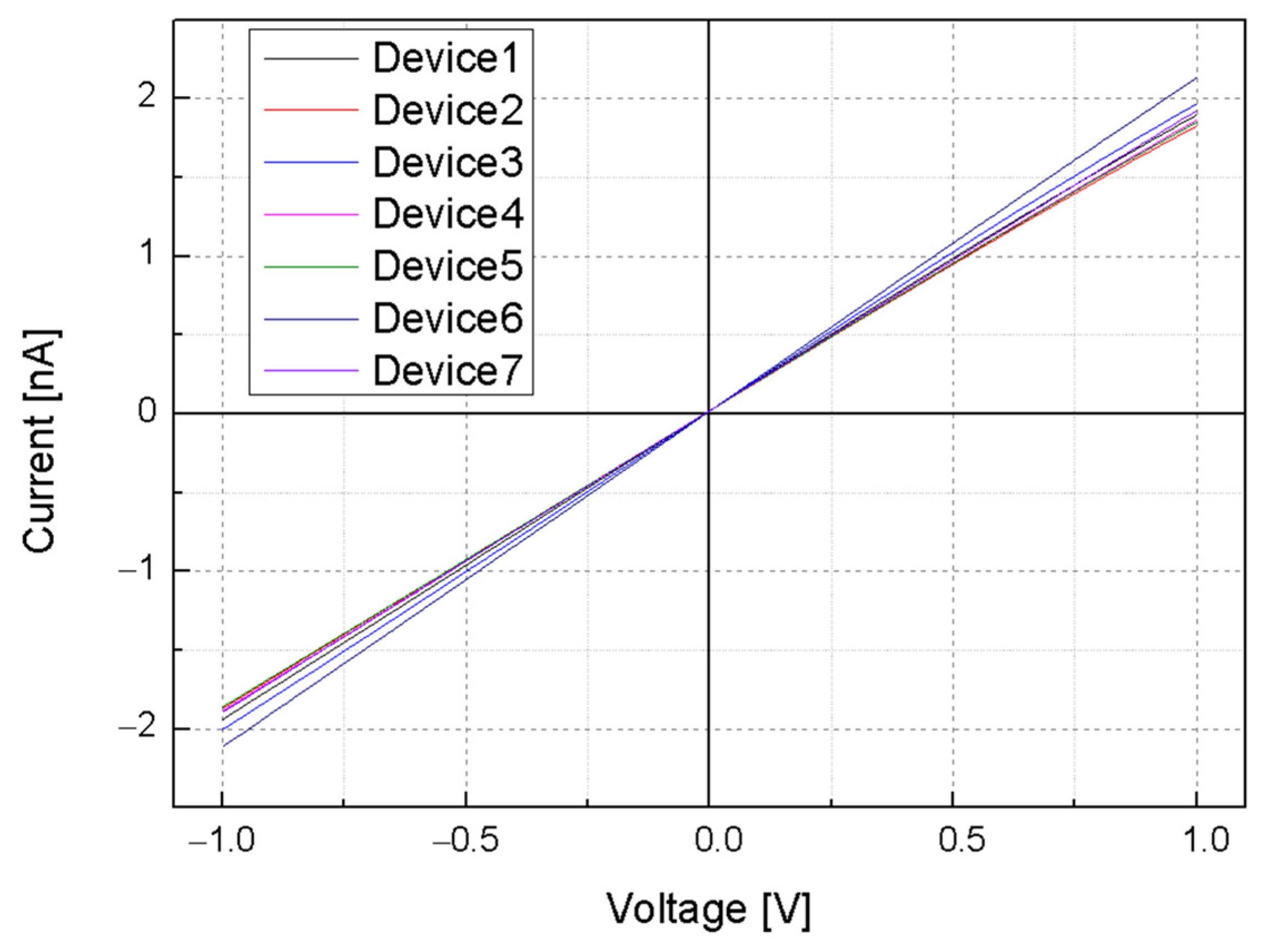
3.2. Specifications of the Fabricated pH Sensor
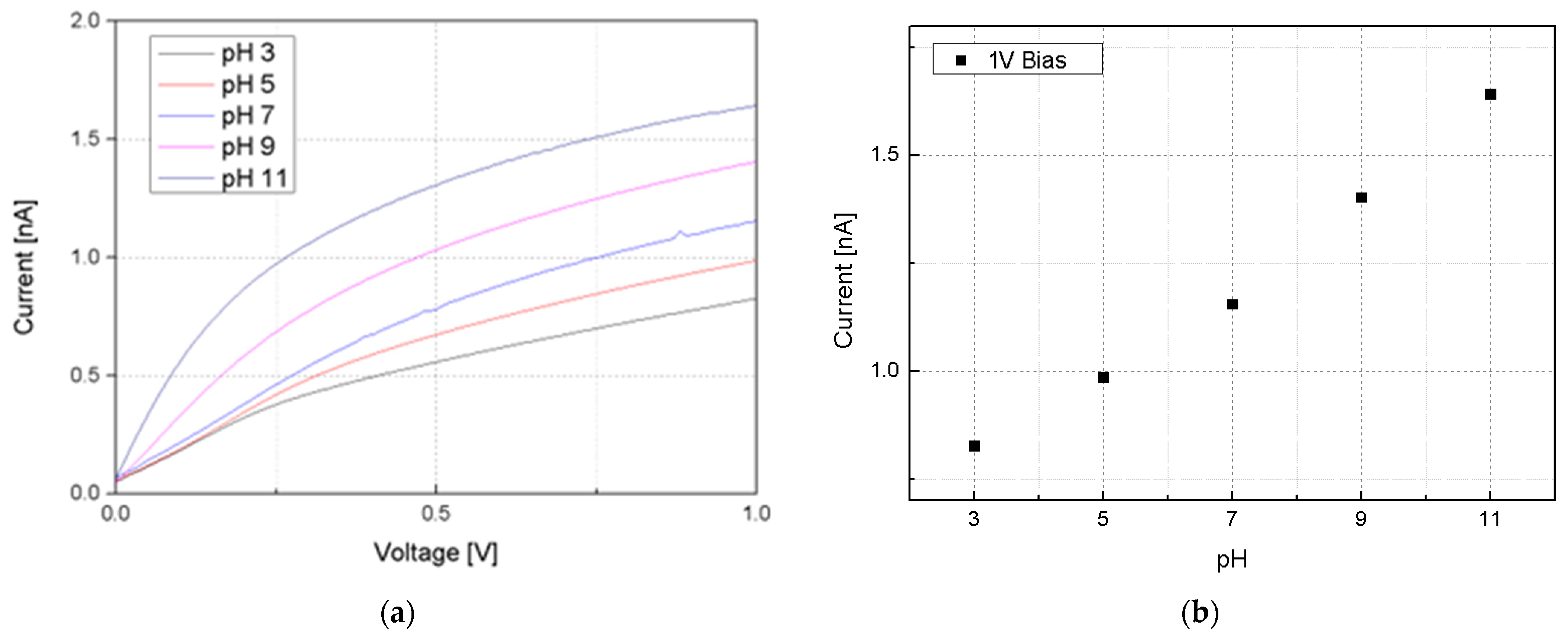
3.3. pH Sensitivity of Silicon Nanowire-Based pH Sensors
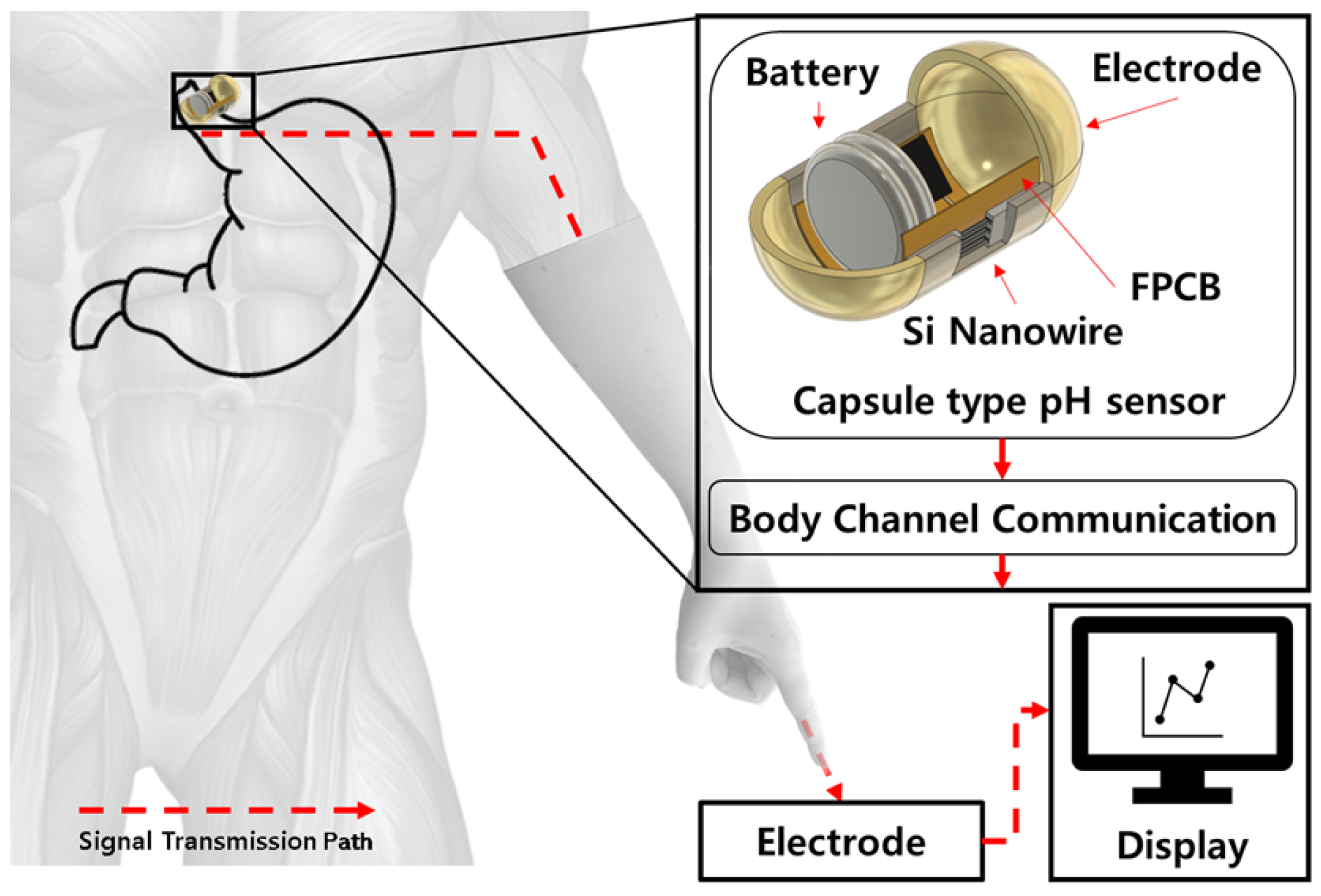
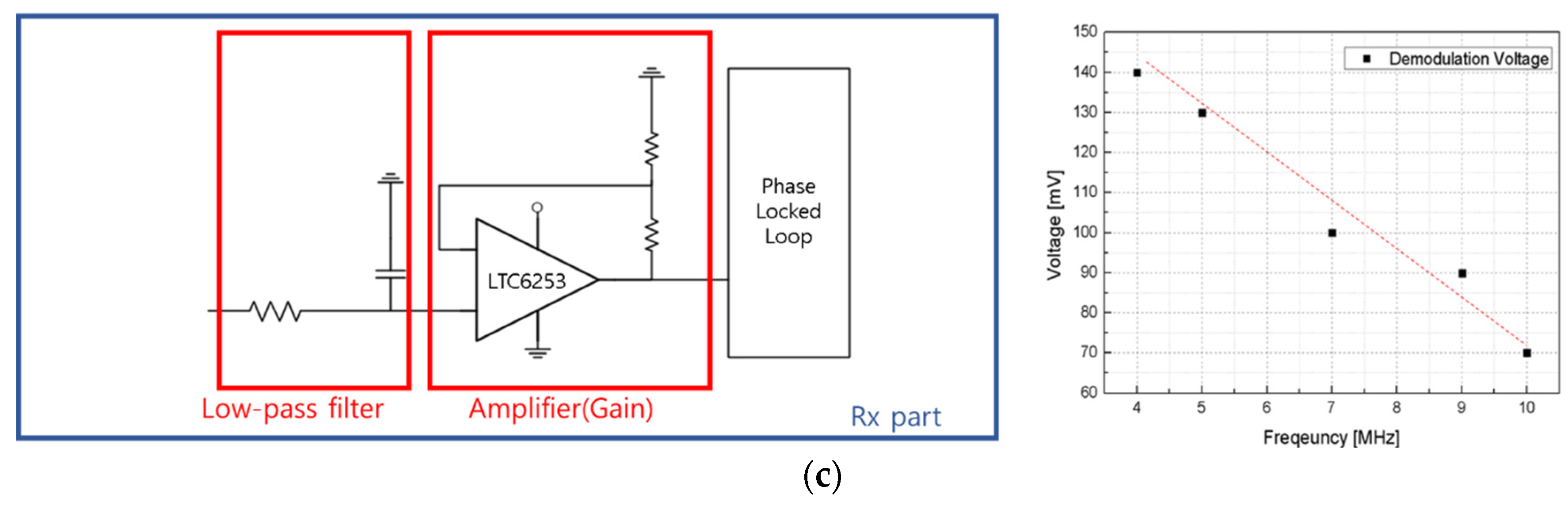
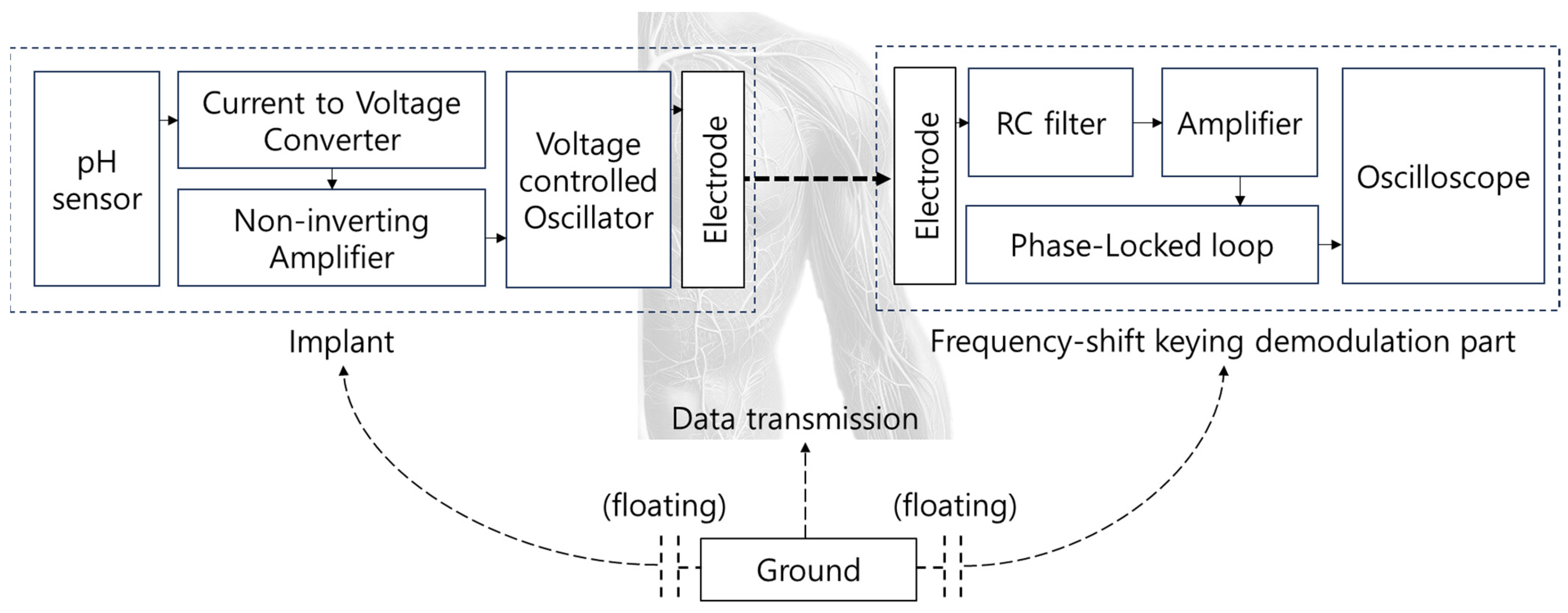
3.4. Data Lead-Out System Using Body Channel Communication
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brönstrup, G.; Jahr, N.; Leiterer, C.; Csäki, A.; Fritzsche, W.; Christiansen, S. Optical Properties of Individual Silicon Nanowires for Photonic Devices. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 7113–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonchar, K.A.; Kitaeva, V.Y.; Zharik, G.A.; Eliseev, A.A.; Osminkina, L.A. Structural and Optical Properties of Silicon Nanowire Arrays Fabricated by Metal Assisted Chemical Etching with Ammonium Fluoride. Front. Chem. 2019, 6, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramgir, N.S.; Yang, Y.; Zacharias, M. Nanowire-Based Sensors. Small 2010, 6, 1705–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Sudhölter, E.J.R.; de Smet, L.C.P.M. Silicon Nanowire-Based Devices for Gas-Phase Sensing. Sensors 2014, 14, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Borgne, B.; Pichon, L.; Salaun, A.C.; Le Bihan, B.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Martin, S.; Rogel, R.; de Sagazan, O. Bacteria Electrical Detection Using 3D Silicon Nanowires Based Resistor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1794–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wei, Q.; Park, H.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire Nanosensors for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Biological and Chemical Species. Science (1979) 2001, 293, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, E.; Klemic, J.F.; Routenberg, D.A.; Wyrembak, P.N.; Turner-Evans, D.B.; Hamilton, A.D.; LaVan, D.A.; Fahmy, T.M.; Reed, M.A. Label-Free Immunodetection with CMOS-Compatible Semiconducting Nanowires. Nature 2007, 445, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zhao, R.; Yu, X. A 3-D-Silicon Nanowire FET Biosensor Based on a Novel Hybrid Process. J. Microelectromechan. Syst. 2018, 27, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Li, Z.; Pisano, A.P.; Williams, R.S. Top-down Fabricated Silicon Nanowire Sensors for Real-Time Chemical Detection. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 015501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gao, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, T. Wafer-Level and Highly Controllable Fabricated Silicon Nanowire Transistor Arrays on (111) Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) Wafers for Highly Sensitive Detection in Liquid and Gaseous Environments. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennelli, G. Review of Nanostructured Devices for Thermoelectric Applications. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1268–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, X.; Hu, J.; Lieber, C.M. Doping and Electrical Transport in Silicon Nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 5215–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C. Silicon Nanowires Length and Numbers Dependence on Sensitivity of the Field-Effect Transistor Sensor for Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfström, N.; Juhasz, R.; Sychugov, I.; Engfeldt, T.; Karlström, A.E.; Linnros, J. Surface Charge Sensitivity of Silicon Nanowires: Size Dependence. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A.; Vollebregt, S. Effect of Temperature and Humidity on the Sensing Performance of TiO2nanowire-Based Ethanol Vapor Sensors. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 325501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyyappan, M.; Lee, J.S. Nanowire BioFETs: An Overview. In Nanowire Field Effect Transistors: Principles and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 225–240. ISBN 9781461481249. [Google Scholar]
- Tintelott, M.; Pachauri, V.; Ingebrandt, S.; Vu, X.T. Process Variability in Top-down Fabrication of Silicon Nanowire-based Biosensor Arrays. Sensors 2021, 21, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzaihan, M.; Hashim, U.; Arshad, M.K.M.; Ruslinda, A.R.; Rahman, S.F.A.; Fathil, M.F.M.; Ismail, M.H. Top-down Nanofabrication and Characterization of 20 Nm Silicon Nanowires for Biosensing Applications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Won Jung, S.; Park, S.; Ahn, J.; June Hong, S.; Jung Yoo, H.; Ho Lee, M. Fabrication and Evaluation of Silicon Nanowire Photodetectors on Flexible Substrate for Retinal Prosthetic System. Sens. Mater. 2012, 24, 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.-P.; Kozeki, T.; Dinh, T.; Fujii, T.; Qamar, A.; Zhu, Y.; Namazu, T.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Dao, D.V. Piezoresistive Effect of P-Type Silicon Nanowires Fabricated by a Top-down Process Using FIB Implantation and Wet Etching. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82121–82126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lee, S.; Koo, K.; Kim, K. Nanowire-Based Sensors for Biological and Medical Applications. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2016, 15, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrilas, P.J. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öberg, S. Esophageal PH Monitoring. In Shackelford’s Surgery of the Alimentary Tract; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Reusens, E.; Joseph, W.; Latré, B.; Braem, B.; Vermeeren, G.; Tanghe, E.; Martens, L.; Moerman, I.; Blondia, C. Characterization of On-Body Communication Channel and Energy Efficient Topology Design for Wireless Body Area Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Botero, G.A.; Hernandez-Gomez, Y.K.; Tellez, C.E.; Coronel, J.F. Human Body Communication: Channel Characterization Issues. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2019, 22, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, D. (Ed.) Autonomous Sensor Networks; Springer Series on Chemical Sensors and Biosensors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 13, ISBN 978-3-642-34647-7. [Google Scholar]
- Guvenc, I.; Gezici, S.; Sahinoglu, Z.; Kozat, U.C. (Eds.) Reliable Communications for Short-Range Wireless Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; ISBN 9780521763172. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.; Bae, J.; Yoo, H.-J. Understanding Body Channel Communication: A Review: From History to the Future Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), Austin, TX, USA, 14–17 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, J.K.; Han, S.J.; Lee, S. A Novel Top-down Fabrication Process for Vertically-Stacked Silicon-Nanowire Array. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laermer, F.; Franssila, S.; Sainiemi, L.; Kolari, K. Deep Reactive Ion Etching. In Handbook of Silicon Based MEMS Materials and Technologies, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 444–469. ISBN 9780323312233. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, J.F.; Huang, B.R.; Huang, C.S.; Chen, H.L. Silicon Nanowires as PH Sensor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 2626–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, B.; Kim, B.; Yoon, S.; Choi, S.; Bae, J. Driver Status Monitoring System with Body Channel Communication Technique Using Conductive Thread Electrodes. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2022, E105.B, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, B.; Kim, B.; Park, S.; Huh, Y.; Bae, J. An Implantable Body Channel Communication System with 3.7-PJ/b Reception and 34-PJ/b Transmission Efficiencies. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett. 2020, 3, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Jeong, H.; Han, S.; Kim, K.; Cho, J.; Kim, S.; Jung, H.; Lee, S. Multiple Biometric Signal Sensing Platform Using Body Channel Communication. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), Gangwon, Republic of Korea, 1–3 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]




| Process Step | Coil Power (W) | Platen Power (W) | Pressure (mTorr) | Gas Flow [SCCM] | Time (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4F8 | SF6 | Ar | |||||
| Polymer deposition | 825 | 1 | 22 | 100 | 0.5 | 30 | 5 |
| Polymer etching | 825 | 13 | 23 | 0.5 | 50 | 30 | 3 |
| Silicon etching | 825 | 13 | 23 | 0.5 | 10 | 30 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.; Han, S.; Kim, T.; Lee, S. Implantable pH Sensing System Using Vertically Stacked Silicon Nanowire Arrays and Body Channel Communication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030861
Kim C, Han S, Kim T, Lee S. Implantable pH Sensing System Using Vertically Stacked Silicon Nanowire Arrays and Body Channel Communication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Monitoring. Sensors. 2024; 24(3):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030861
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Changhee, Seungju Han, Taehwan Kim, and Sangmin Lee. 2024. "Implantable pH Sensing System Using Vertically Stacked Silicon Nanowire Arrays and Body Channel Communication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Monitoring" Sensors 24, no. 3: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030861
APA StyleKim, C., Han, S., Kim, T., & Lee, S. (2024). Implantable pH Sensing System Using Vertically Stacked Silicon Nanowire Arrays and Body Channel Communication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Monitoring. Sensors, 24(3), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030861







