Advancing Remote Life Sensing for Search and Rescue: A Novel Framework for Precise Vital Signs Detection via Airborne UWB Radar
Abstract
Highlights
- An airborne bio-radar system to remotely sense vital signs of survivors for post-disaster search and rescue was developed.
- Theoretical analysis of the impact of interference coming from the motion of the UAV platform and echoes from the background environment on radar detection performance.
- A signal processing framework based on blind source separation was proposed to precisely extract the respiration and heartbeat, which combines the high-order analytical tool and the feedback notch filter.
- The remote high-resolution vital signs detection approach is suitable for real-world applications such as search and rescue.
Abstract
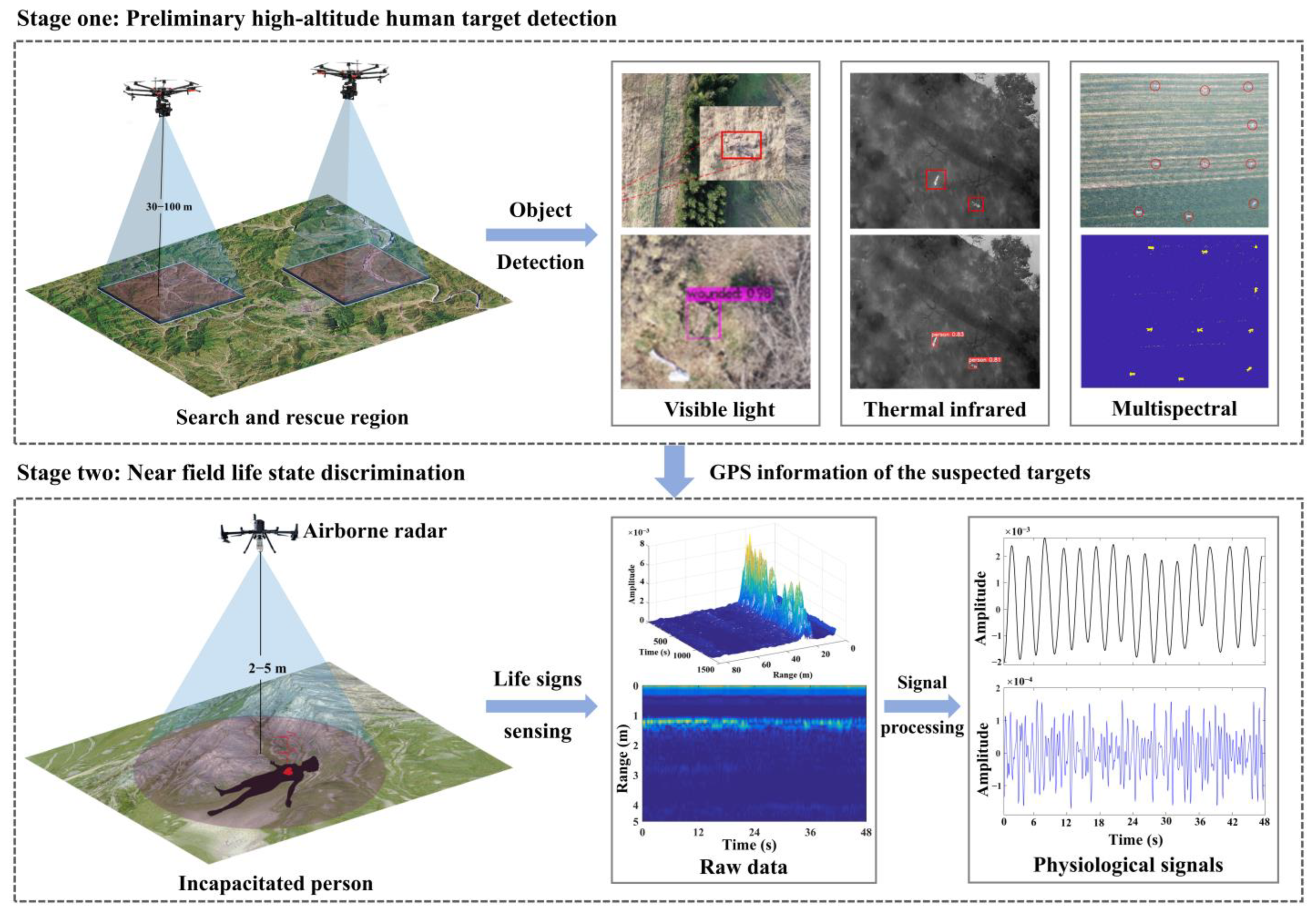
1. Introduction
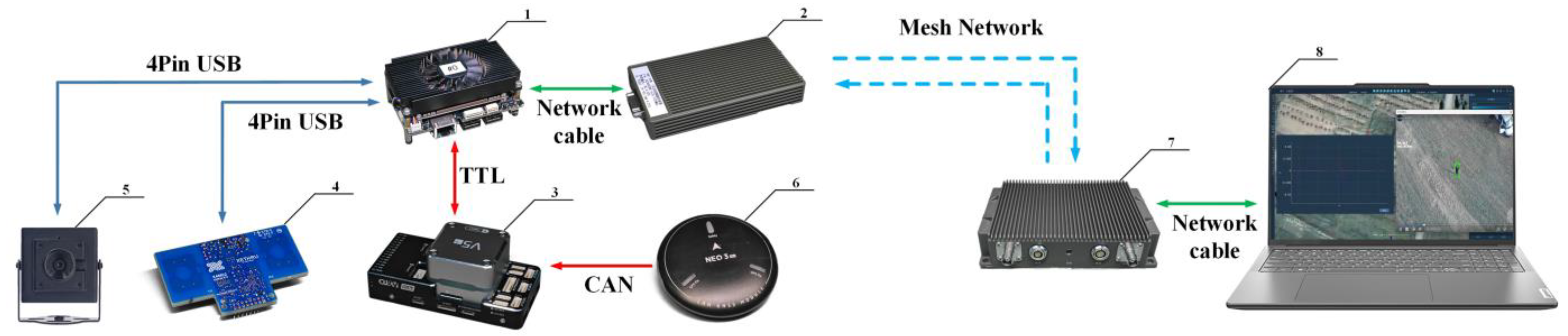
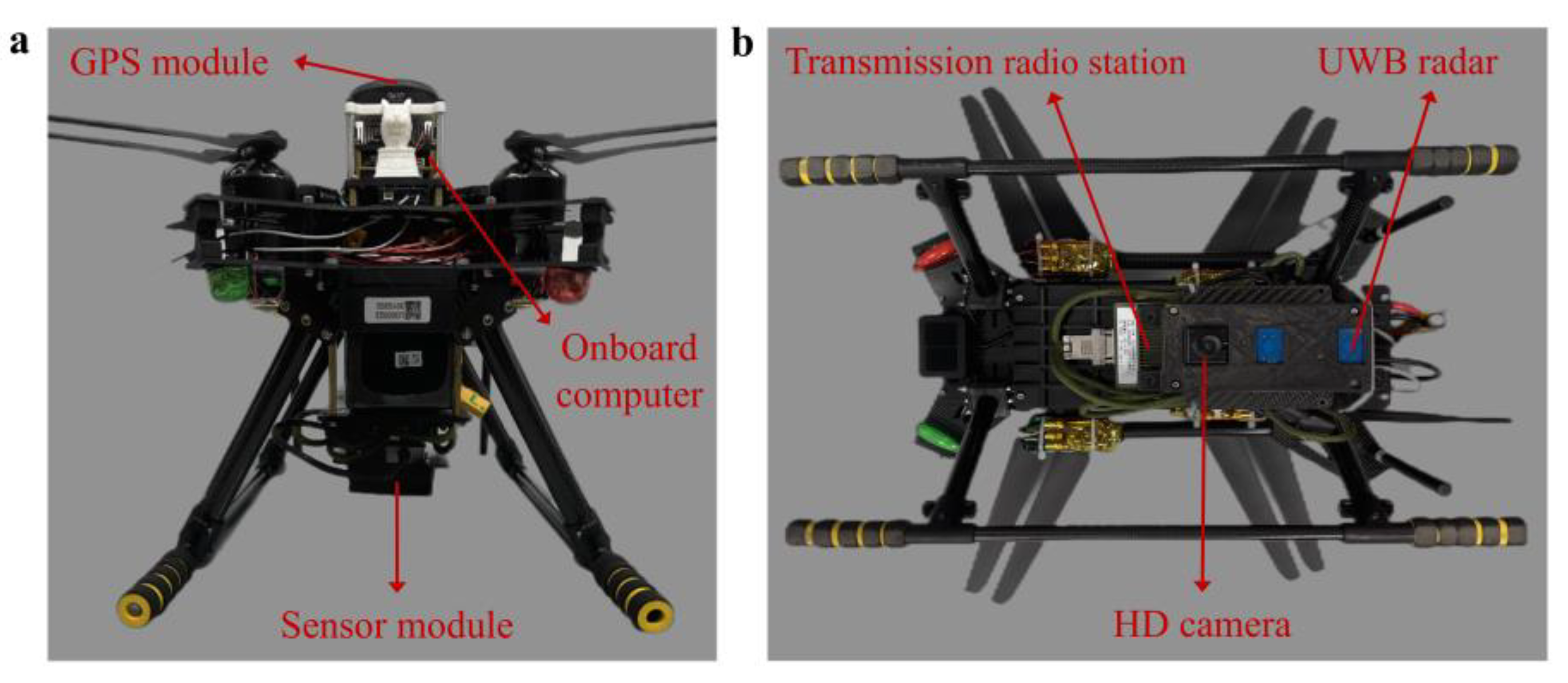
2. Airborne Bio-Radar System Design
3. Sensing Model
3.1. Principle of UWB Radar for Vital Signs Detection
3.2. Background Clutter
3.2.1. Static Background Environment
3.2.2. Dynamic Background Environment
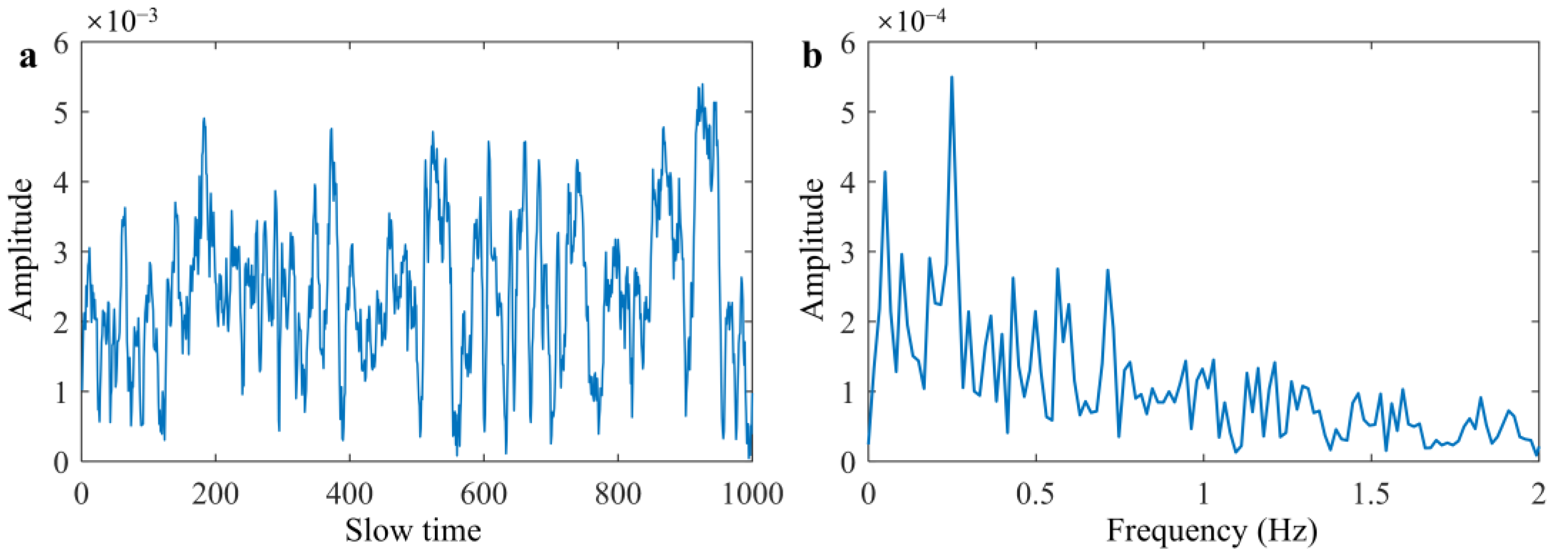
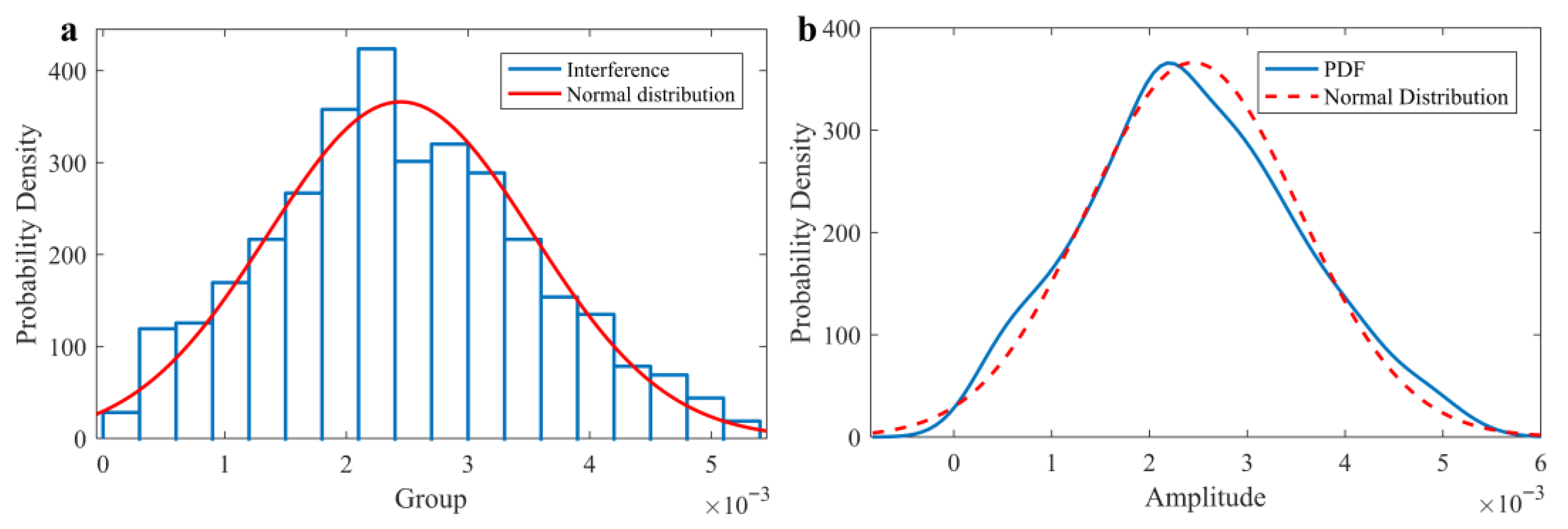
3.2.3. Statistical Characteristic Analysis of Measured Grass-Surface Clutter
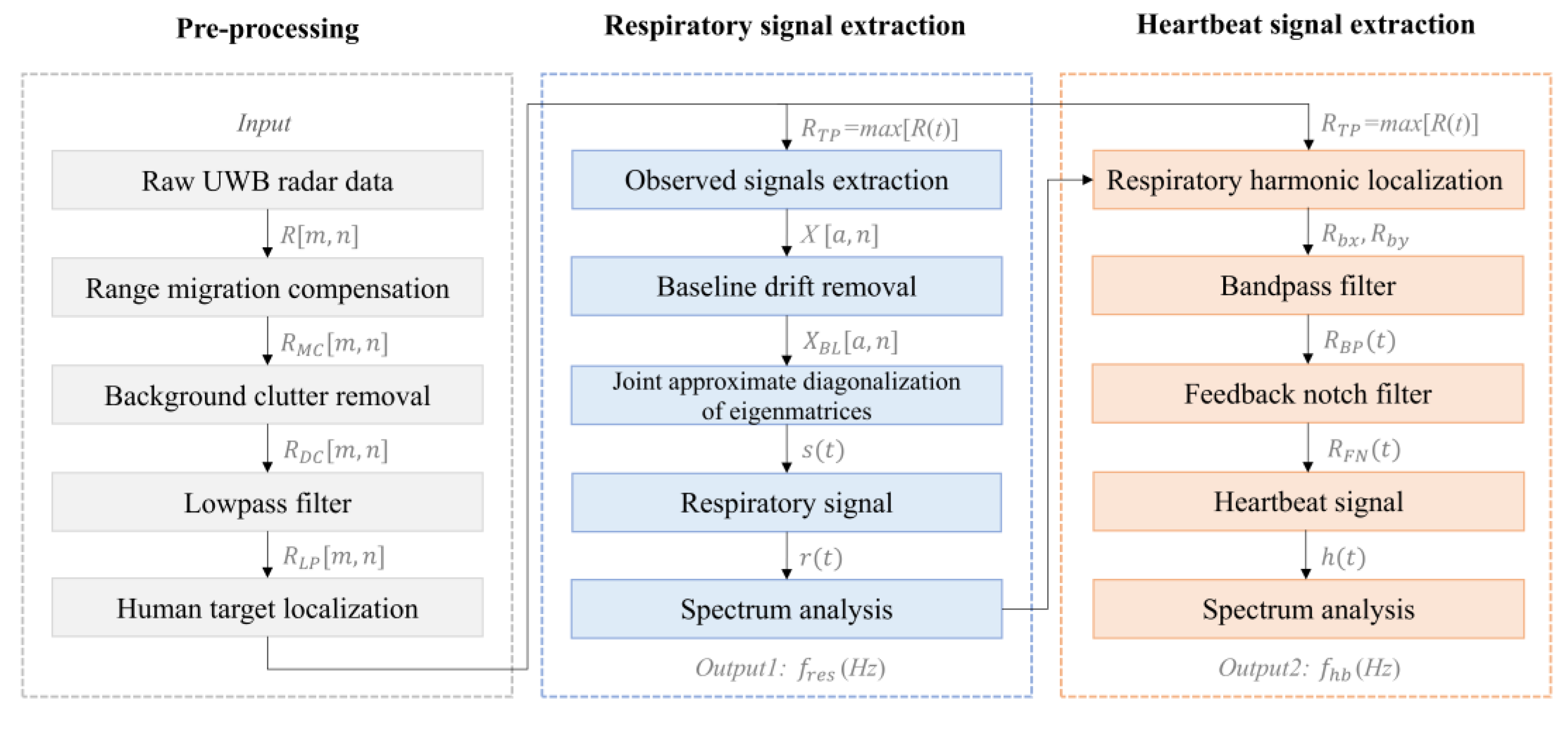
4. Proposed Vital Signals Extraction Method
4.1. Pre-Processing
4.1.1. Range Migration Compensation
4.1.2. Background Clutter Removal
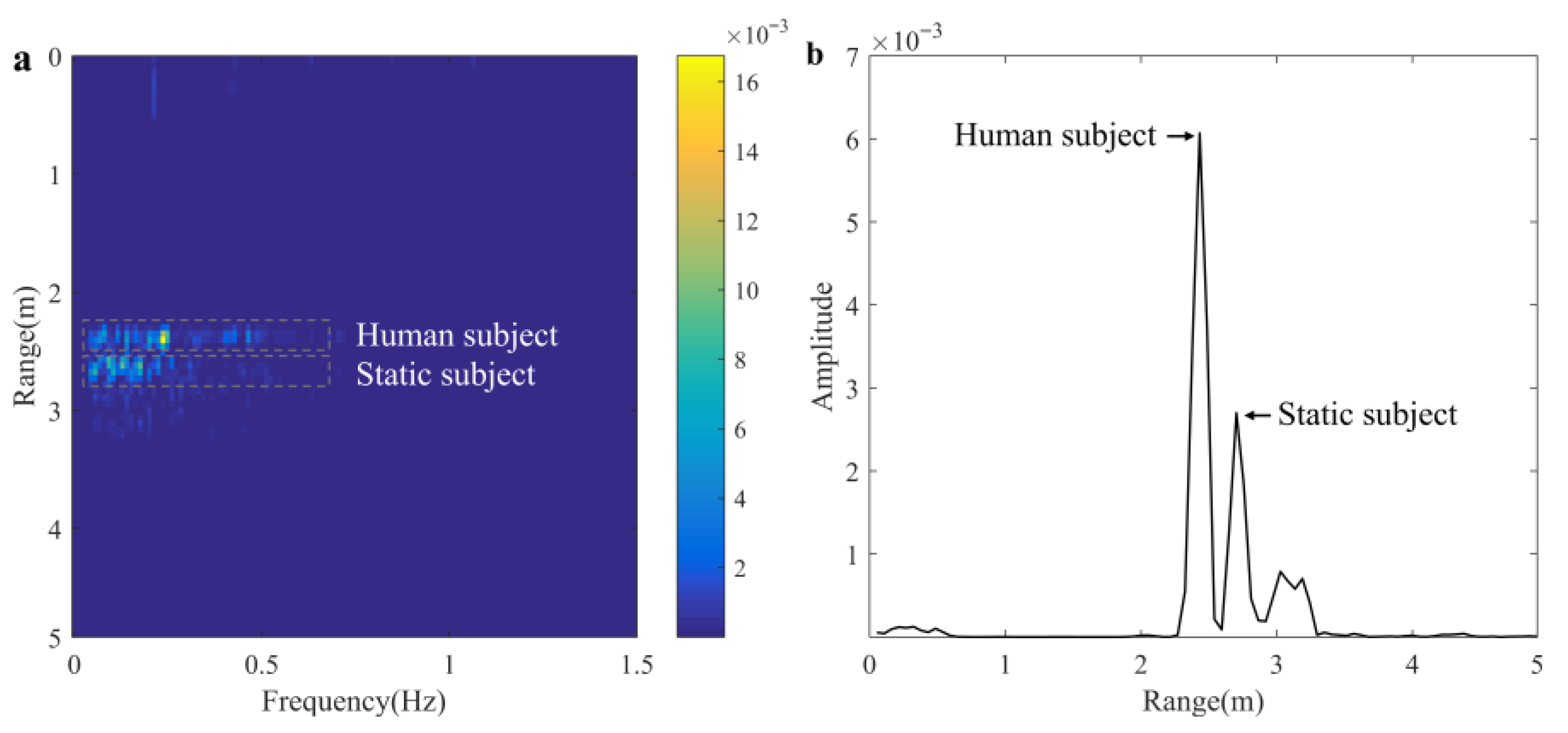
4.1.3. Human Target Localization
4.2. Respiratory Signal Extraction
4.2.1. Observed Signals Extraction
4.2.2. Joint Approximate Diagonalization of Eigenmatrices Algorithm
- (1)
- Decentralizing and whitening the observed signals matrix;
- (2)
- Constructing the high-order cumulant matrix of the whited matrix;
- (3)
- Performing joint approximate diagonalization on the matrix to obtain the estimated matrix of the unitary matrix ;
- (4)
- Estimating the source signal according to Equation (31).
4.3. Heartbeat Signal Extraction
4.3.1. Bandpass Filter
4.3.2. Respiratory Harmonic Localization
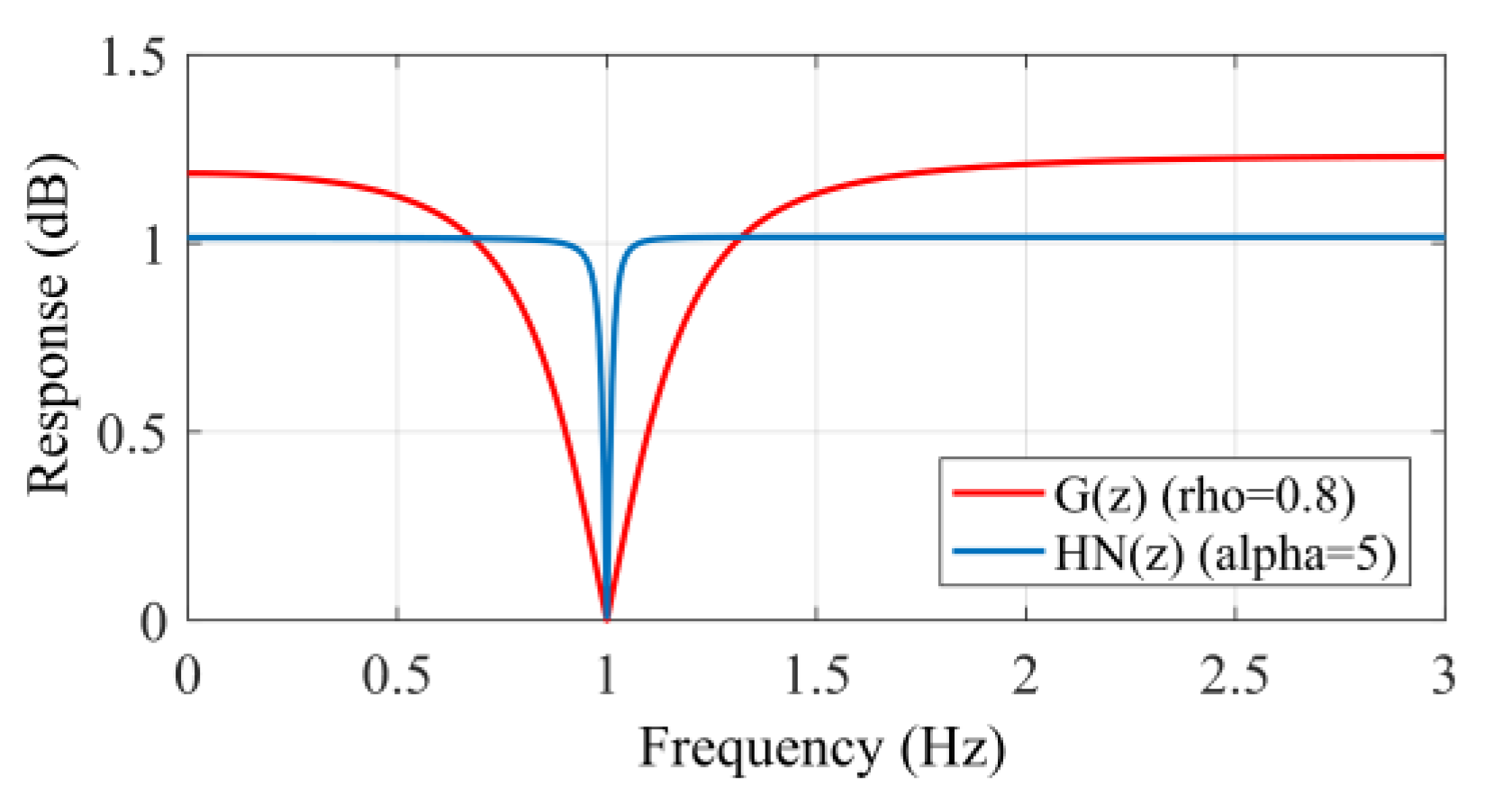
4.3.3. Feedback Notch Filter
5. Experiment and Results
5.1. Experimental Setup
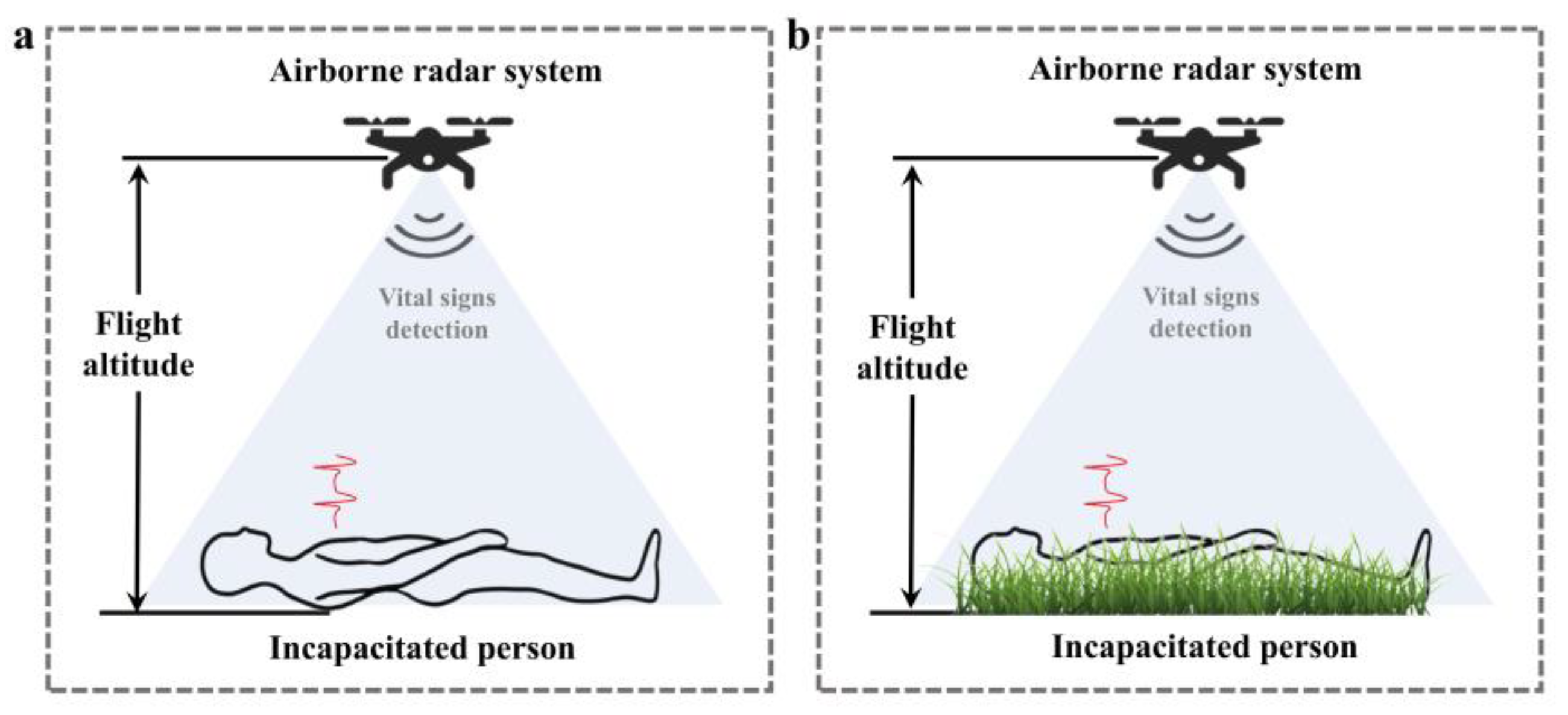
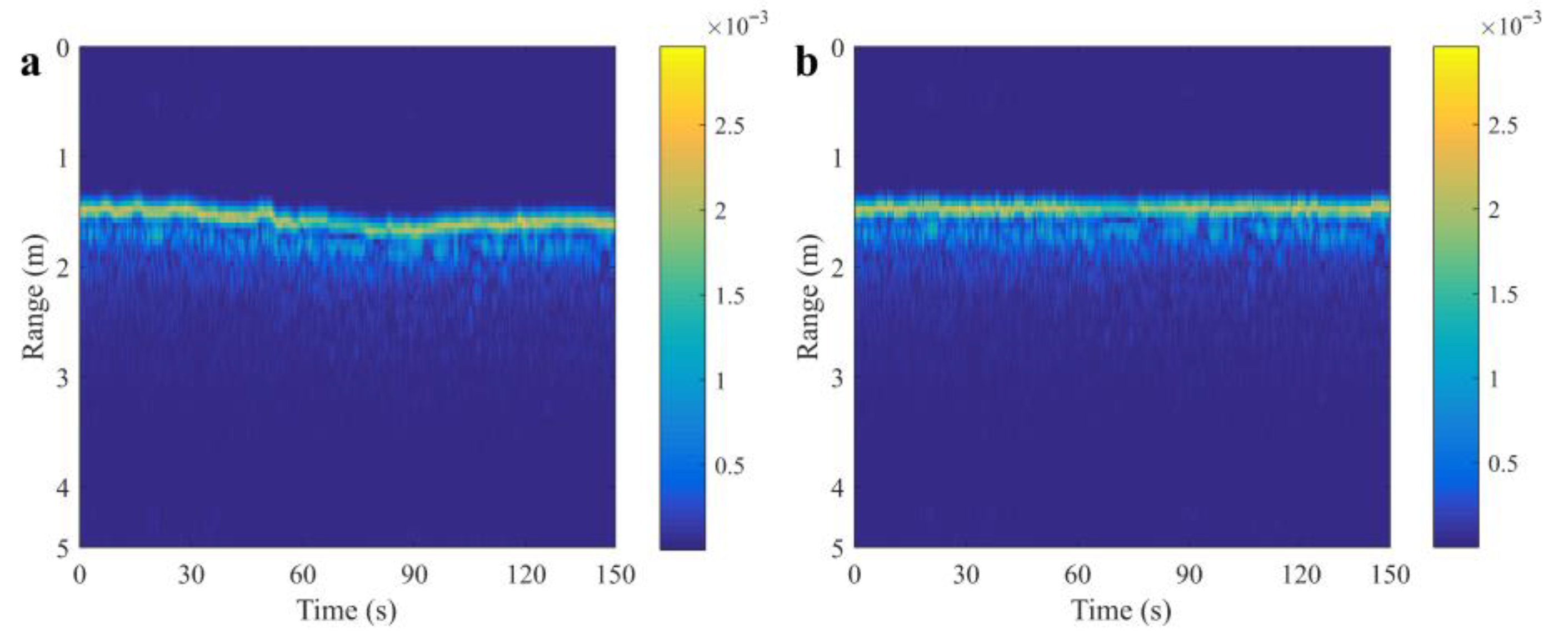
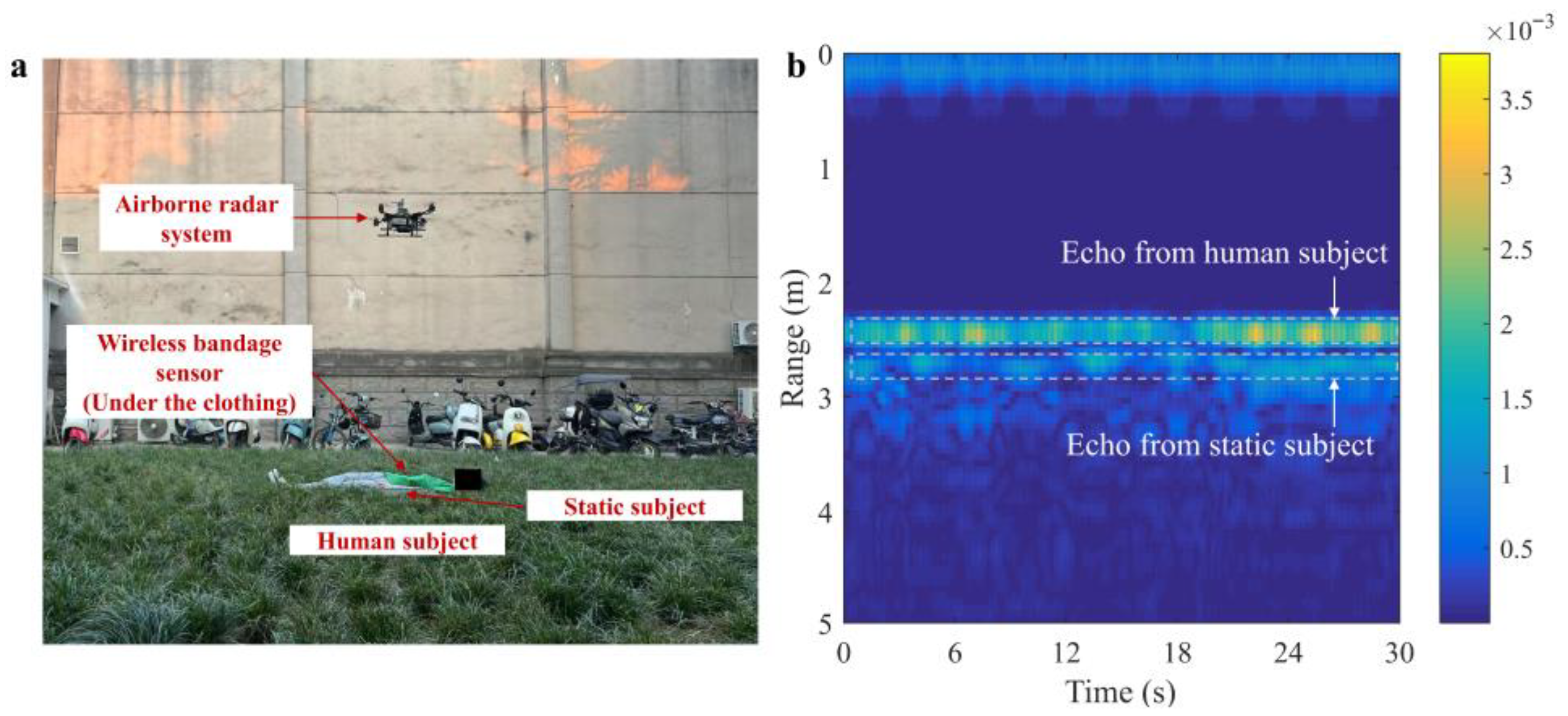
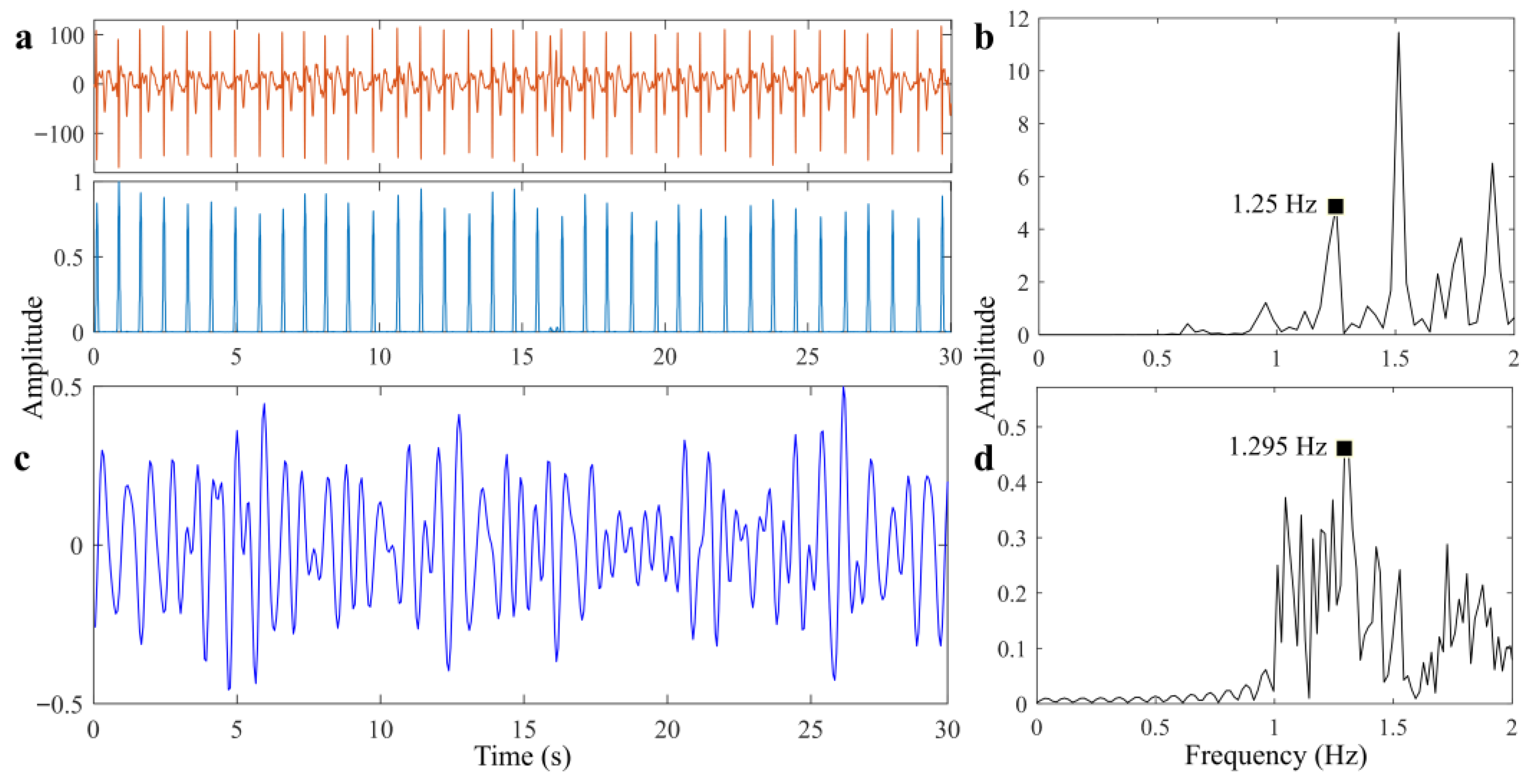
5.2. Performance in Realistic Grassland Scenario
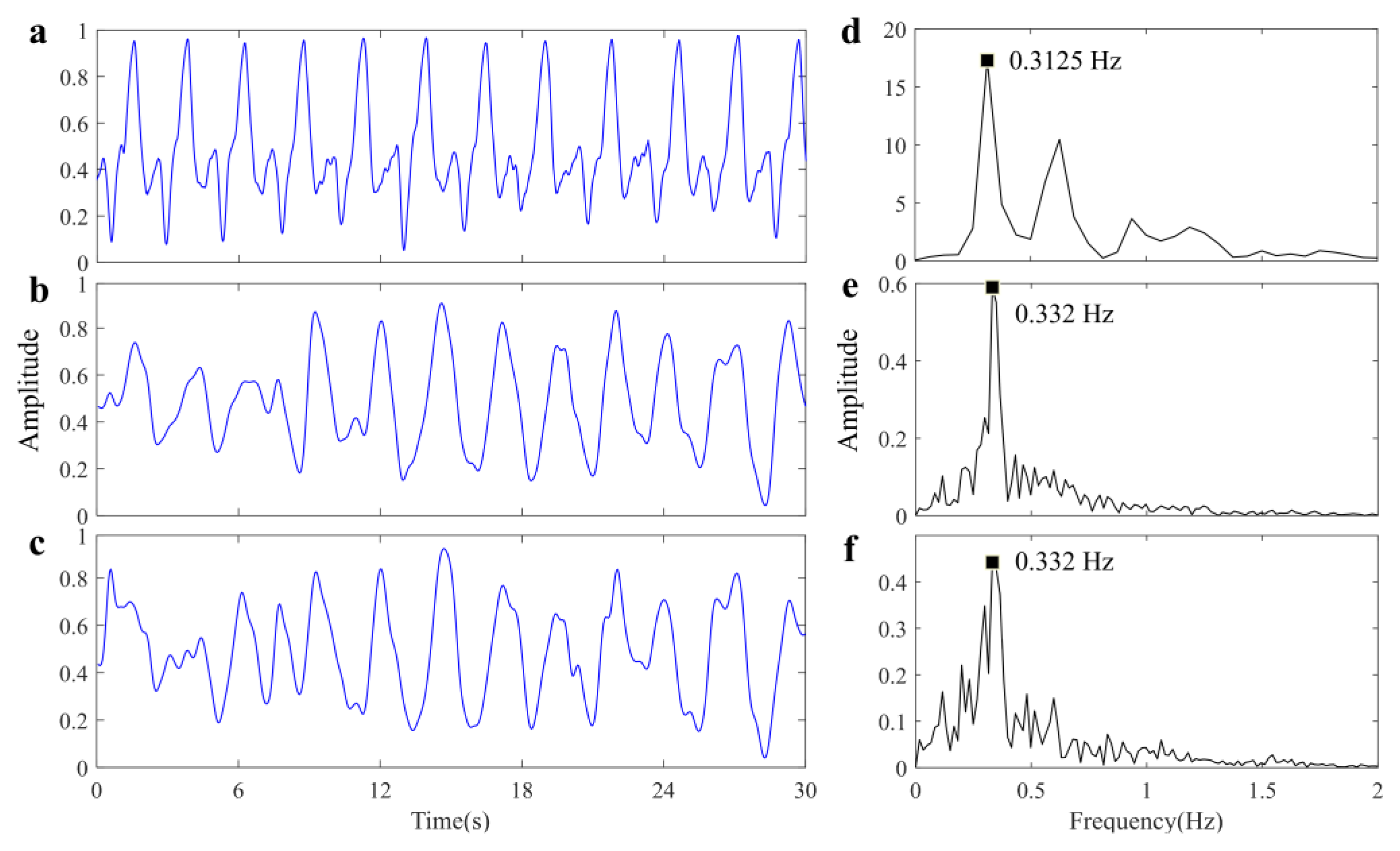
5.3. Performance in Through-the-Wall Scenario
5.4. Impact of Distance Between the System and the Victim
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wex, F.; Schryen, G.; Feuerriegel, S.; Neumann, D. Emergency Response in Natural Disaster Management: Allocation and Scheduling of Rescue Units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 235, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, M.; Tao, Y.; Lu, P. HMA-SAR: Multi-Agent Search and Rescue for Unknown Located Dynamic Targets in Completely Unknown Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 5567–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefros, C.; Kitsara, G.; Loupasakis, C. Geographical Information Systems and Remote Sensing Techniques to Reduce the Impact of Natural Disasters in Smart Cities. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Ayala, O.; González-Hernández, I.; Salazar, S.; Flores, J.; Lozano, R. Real-Time Person Detection in Wooded Areas Using Thermal Images from an Aerial Perspective. Sensors 2023, 23, 9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schedl, D.C.; Kurmi, I.; Bimber, O. Search and Rescue with Airborne Optical Sectioning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Qin, M.; Wu, W.; Kwak, K. Collaborative Human Recognition with Lightweight Models in Drone-based Search and Rescue Operations. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 73, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukayan, G.; Karacan, H. YOLO-IHD: Improved Real-Time Human Detection System for Indoor Drones. Sensors 2024, 24, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Alpiste, I.; Golcarenarenji, G.; Wang, Q.; Alcaraz-Calero, J.M. Search and Rescue Operation using UAVs: A Case Study. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 178, 114937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ren, H.; Ye, X.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H.; Nan, Y.; Sun, M.; Ren, X.; Huo, H. Object Detection from UAV Thermal Infrared Images and Videos using YOLO Models. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, W.; Shi, W. HIT-UAV: A High-altitude Infrared Thermal Dataset for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-based Object Detection. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yan, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jin, S.; Qi, F.; Li, Z.; Lei, T.; Chen, L.; Jing, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. An infrared dataset for partially occluded person detection in complex environment for search and rescue. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y. Locality Guided Cross-modal Feature Aggregation and Pixel-level Fusion for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. Inf. Fusion 2022, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Zhu, M.; Li, Z.; Lei, T.; Xia, J.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, G. Automatic Air-to-ground Recognition of Outdoor Injured Human Targets based on UAV Bimodal Information: The explore study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Xia, J.; Zhu, M.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, G. UAV Multispectral Multi-domain Feature Optimization for the Air-to-ground Recognition of Outdoor Injured Human Targets under Cross-scene Environment. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 999378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Wu, D. Accurate Multi-target Vital Signs Detection Method for FMCW Radar. Measurement 2023, 223, 113715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aflalo, K.; Zalevsky, Z. Penetrating Barriers: Noncontact Measurement of Vital Bio Signs Using Radio Frequency Technology. Sensors 2024, 24, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Qi, F.; Jing, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lei, T.; Li, Z.; Xia, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, G. Mission Chain Driven Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Swarms Cooperation for the Search and Rescue of Outdoor Injured Human Targets. Drones 2022, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, E.; Li, C.; Caddemi, A. Vital Sign Detection and Radar Self-motion Cancellation Through Clutter Identification. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Herschfelt, A.; Holtom, J.; Bliss, D.W. Cardiac and Respiratory Sensing from a Hovering UAV Radar Platform. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 11–14 July 2021; pp. 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.-B.; Zhang, D.; Song, R.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y. RF-Search: Searching Unconscious Victim in Smoke Scenes with RF-enabled Drone. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Association for Computing Machinery, Madrid, Spain, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Stockel, P.; Wallrath, P.; Herschel, R.; Pohl, N. Detection and Monitoring of People in Collapsed Buildings Using a Rotating Radar on a UAV. IEEE Trans. Radar Syst. 2024, 2, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Jia, A.L.; Liu, C. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Communication Flow Control in Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Li, X.; Xiao, B.; He, M.; Bi, X.; Li, W.; Gao, X. Learning-Refined Integral Null Space Pursuit Algorithm for Noncontact Multisubjects Vital Signs Measurements Using SFCW-UWB and IR-UWB Radar. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 8506013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antide, E.; Zarudniev, M.; Michel, O.; Pelissier, M. Comparative Study of Radar Architectures for Human Vital Signs Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cardillo, E.; Ferro, L.; Sapienza, G.; Li, C. Reliable eye-blinking detection with millimeter-wave radar glasses. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2023, 72, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Rong, Y.; Huang, H.; Duan, T. Classification Method of Uniform Circular Array Radar Ground Clutter Data Based on Chaotic Genetic Algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, L.; Duk, V. Land Clutter Statistics from an Airborne Passive Bistatic Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, E.; Li, C.; Caddemi, A. Empowering Blind People Mobility: A Millimeter-Wave Radar Cane. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT, Roma, Italy, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.; Selesnick, I.W.; Duval, L. Chromatogram baseline estimation and denoising using sparsity (BEADS). Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2014, 139, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, A.; Oja, E. Independent component analysis: Algorithms and applications. Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Pan, J.; Gao, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. Enhanced blind source separation algorithm for partial discharge signals using Joint Approximate diagonalization of Eigenmatrices. Measurement 2025, 244, 116552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Adalı, T.; Anderson, M. Joint Blind Source Separation by Generalized Joint Diagonalization of Cumulant Matrices. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 2314–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.C.; Guo, B.Y.; Lu, W.Y. Narrowband Notch Filter Using Feedback Structure Tips & Tricks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2016, 33, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Lou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, H.; Yu, X.; An, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Through-the-wall high-dimensional imaging of human vital signs by combining multiple enhancement algorithms using portable LFMCW-MIMO radar. Measurement 2022, 195, 111074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramudita, A.A.; Lin, D.B.; Hsieh, S.N.; Ali, E.; Ryanu, H.H.; Adiprabowo, T.; Purnomo, A.T. Radar System for Detecting Respiration Vital Sign of Live Victim Behind the Wall. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 14670–14685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






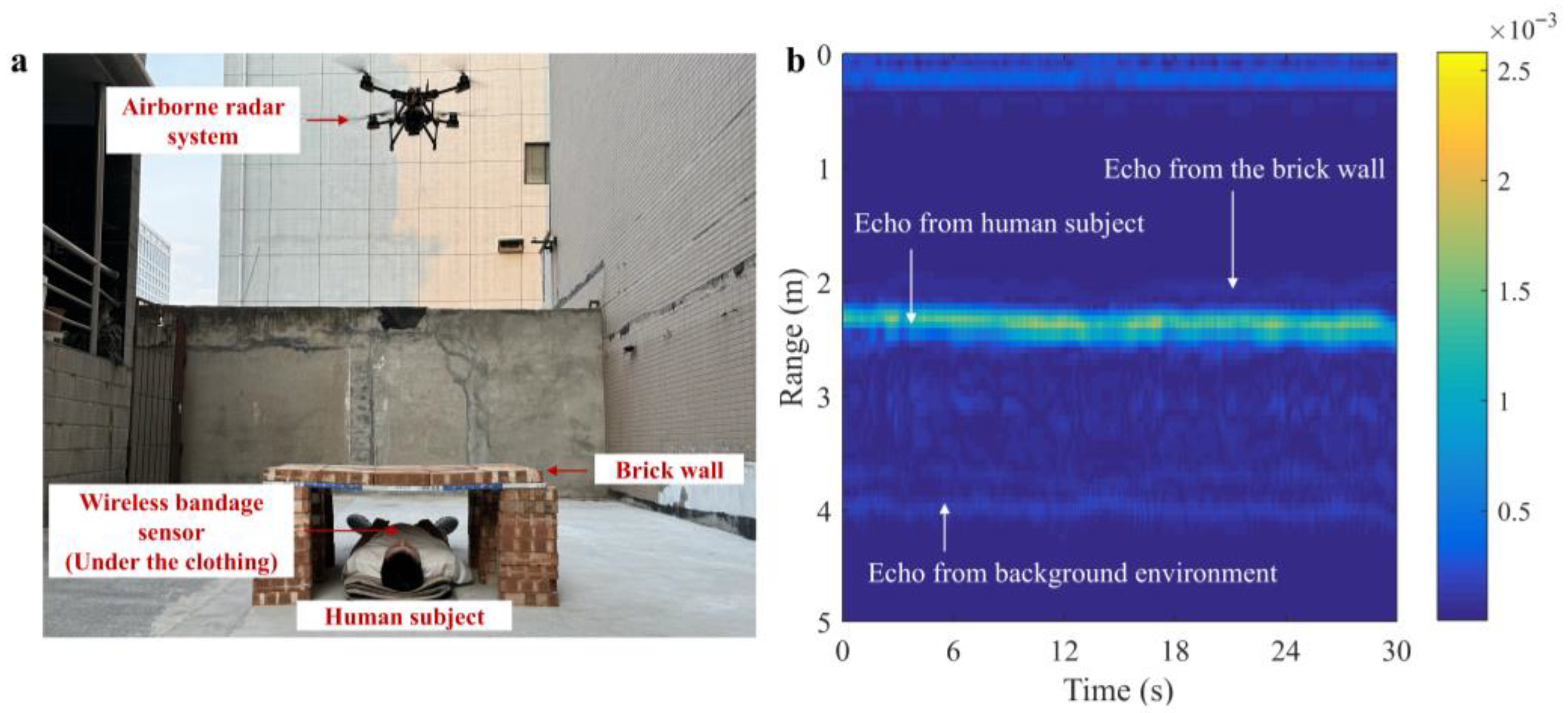
| Center Frequency | Bandwidth | Detection Zone | Range Resolution | Frame Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.29 GHz | 1.4 GHz | 0.4~5 m | 0.0514 m | 17 Hz |
| Parameter | RR (Hz) | Accuracy (%) | SNR (dB) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Proposed Method | Reference Method | Proposed Method | Reference Method | Proposed Method | Reference Method | |
| Scenario 1 | 0.3113 | 0.3154 | 0.3154 | 98.68 | 98.68 | 12.457 | 11.035 |
| Scenario 2 | 0.3125 | 0.332 | 0.332 | 93.76 | 93.76 | 9.002 | 7.983 |
| Parameter | RR (Hz) | Accuracy (%) | HR (Hz) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 m | 0.2366 | 98.50 | 1.017 | 98.44 |
| 3 m | 0.3113 | 96.48 | 1.166 | 96.25 |
| 4 m | 0.2449 | 95.74 | 1.137 | 95.99 |
| 5 m | 0.2813 | 93.15 | 1.148 | 90.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z.; Qi, F.; Lei, T.; Wang, J.; Lu, G. Advancing Remote Life Sensing for Search and Rescue: A Novel Framework for Precise Vital Signs Detection via Airborne UWB Radar. Sensors 2025, 25, 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175232
Jing Y, Yan Y, Li Z, Qi F, Lei T, Wang J, Lu G. Advancing Remote Life Sensing for Search and Rescue: A Novel Framework for Precise Vital Signs Detection via Airborne UWB Radar. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175232
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Yu, Yili Yan, Zhao Li, Fugui Qi, Tao Lei, Jianqi Wang, and Guohua Lu. 2025. "Advancing Remote Life Sensing for Search and Rescue: A Novel Framework for Precise Vital Signs Detection via Airborne UWB Radar" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175232
APA StyleJing, Y., Yan, Y., Li, Z., Qi, F., Lei, T., Wang, J., & Lu, G. (2025). Advancing Remote Life Sensing for Search and Rescue: A Novel Framework for Precise Vital Signs Detection via Airborne UWB Radar. Sensors, 25(17), 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175232








