Intelligent Operation and Maintenance of Wind Turbines Gearboxes via Digital Twin and Multi-Source Data Fusion
Abstract
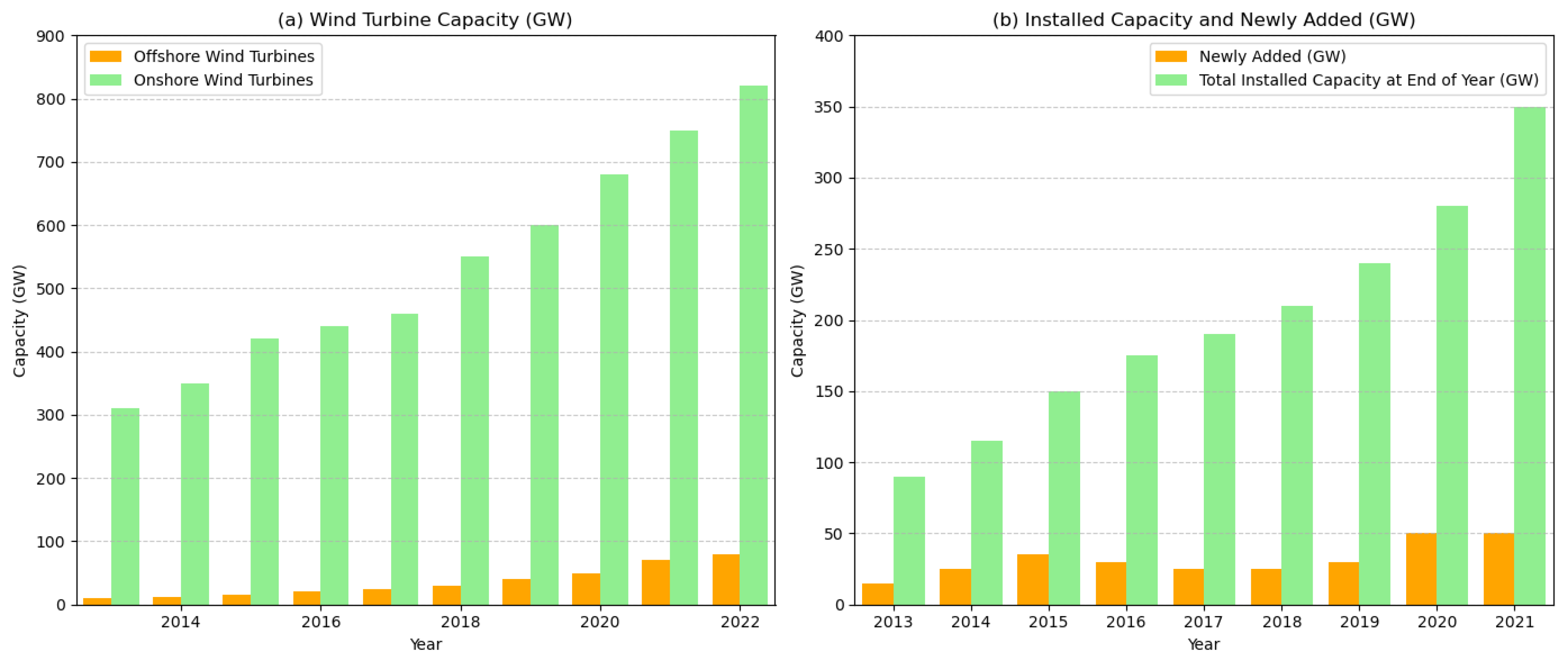
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
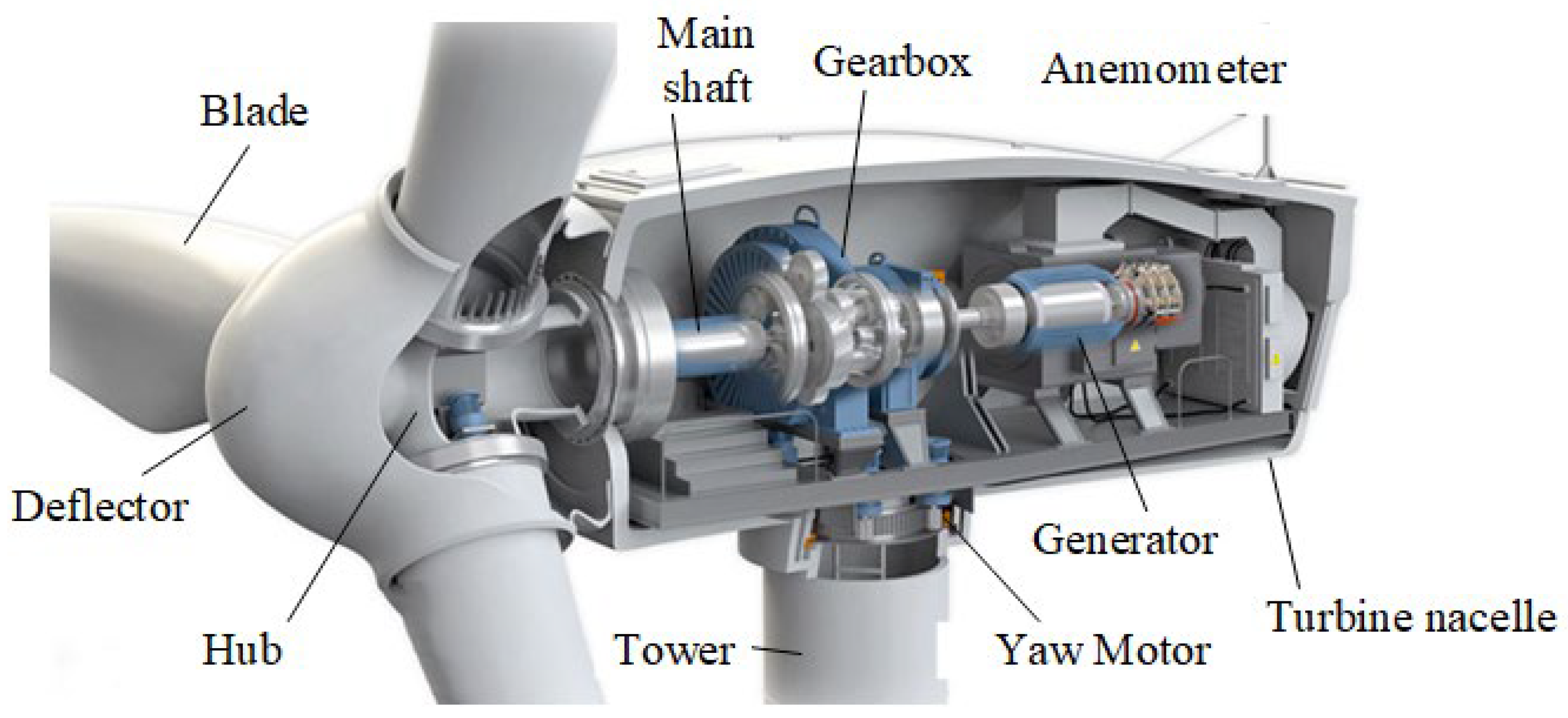
3.1. The Basic Structure of a Wind Turbine
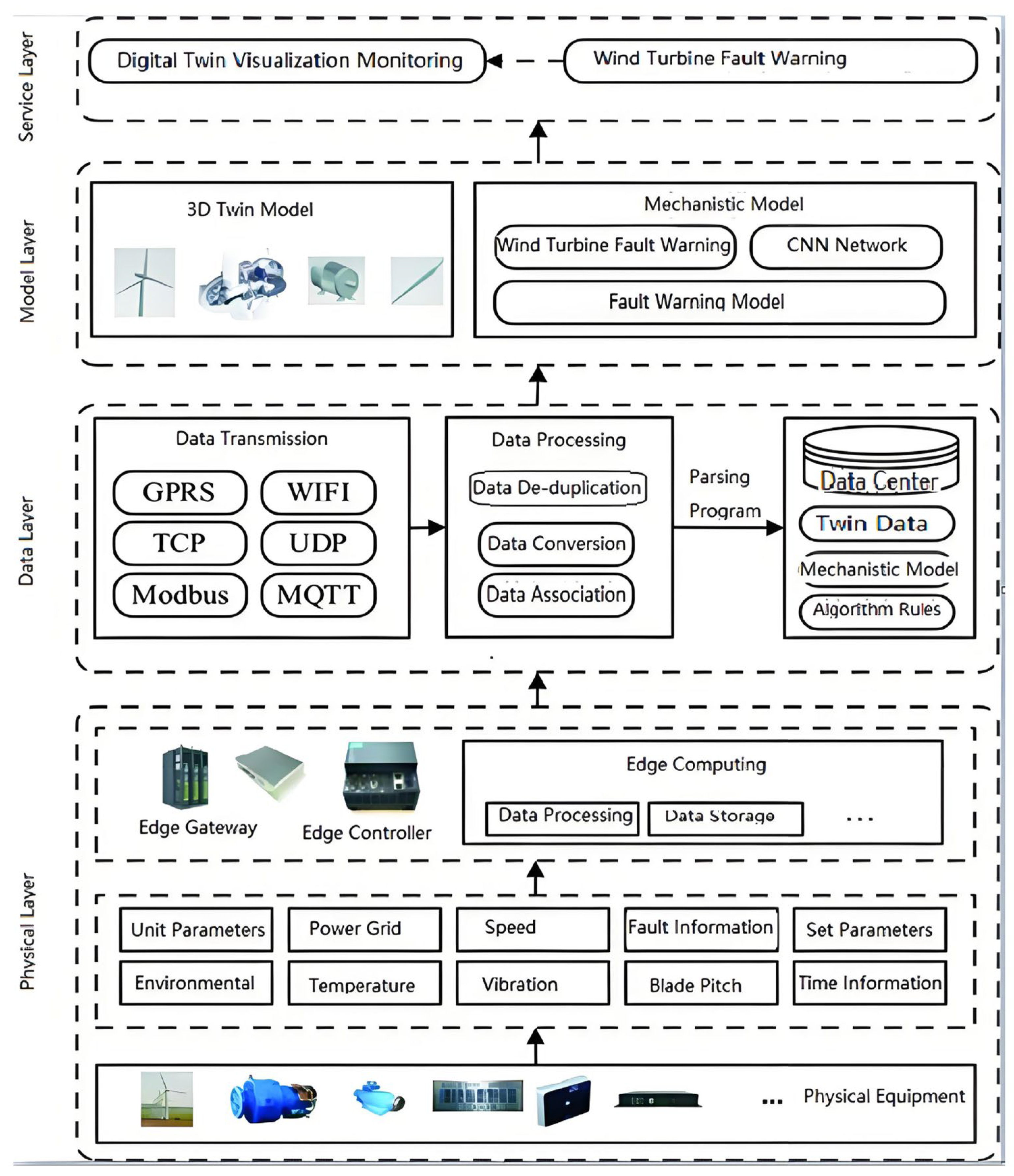
3.2. Remote Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Method for Wind Turbines Based on Digital Twin
3.2.1. Physical Layer
3.2.2. Data Layer
3.2.3. Model Layer
3.2.4. Service Layer
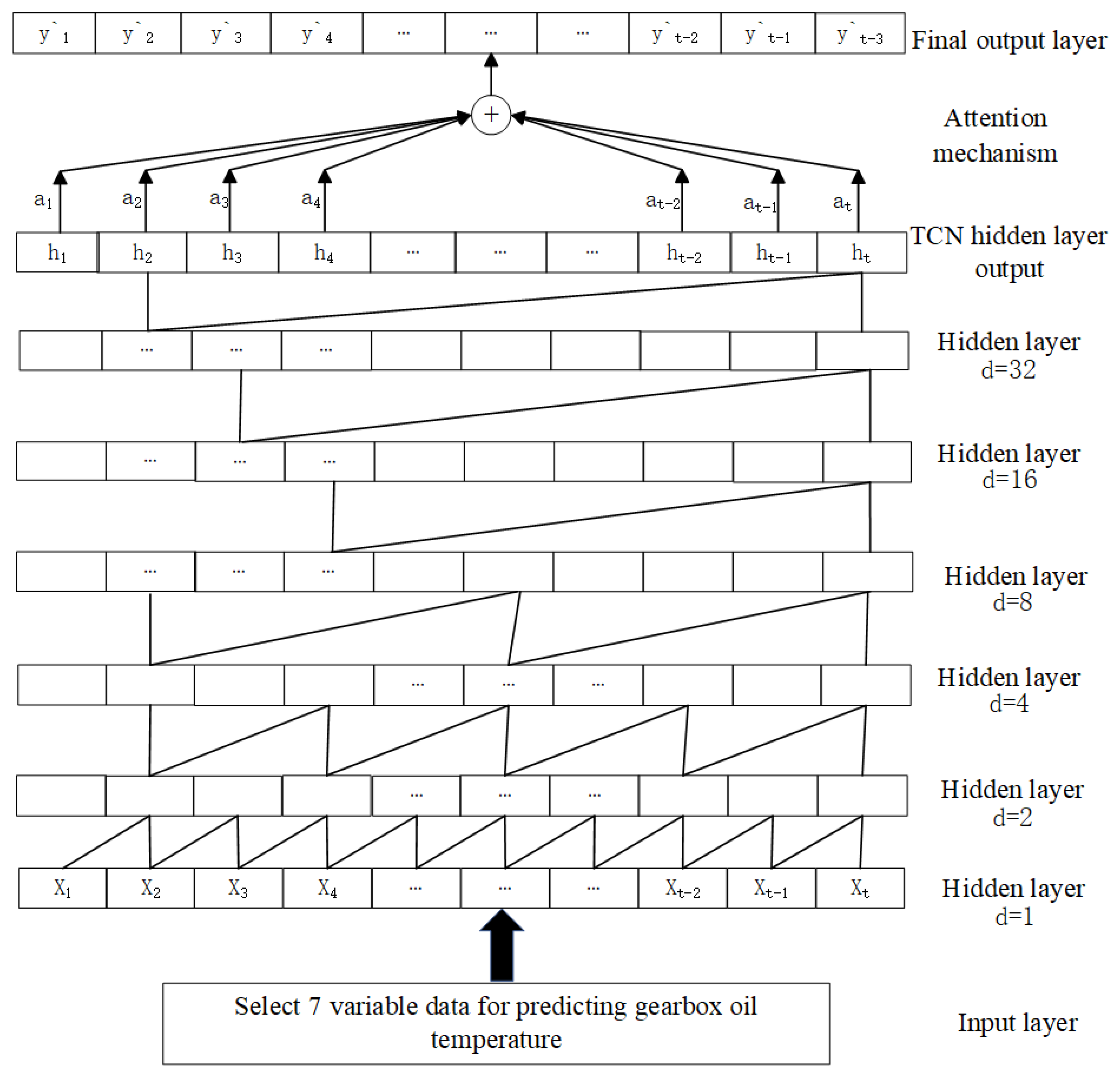
3.3. Multi-Source Data Fusion Early Warning Model for Wind Turbines Based on WOA-TCN-Attention
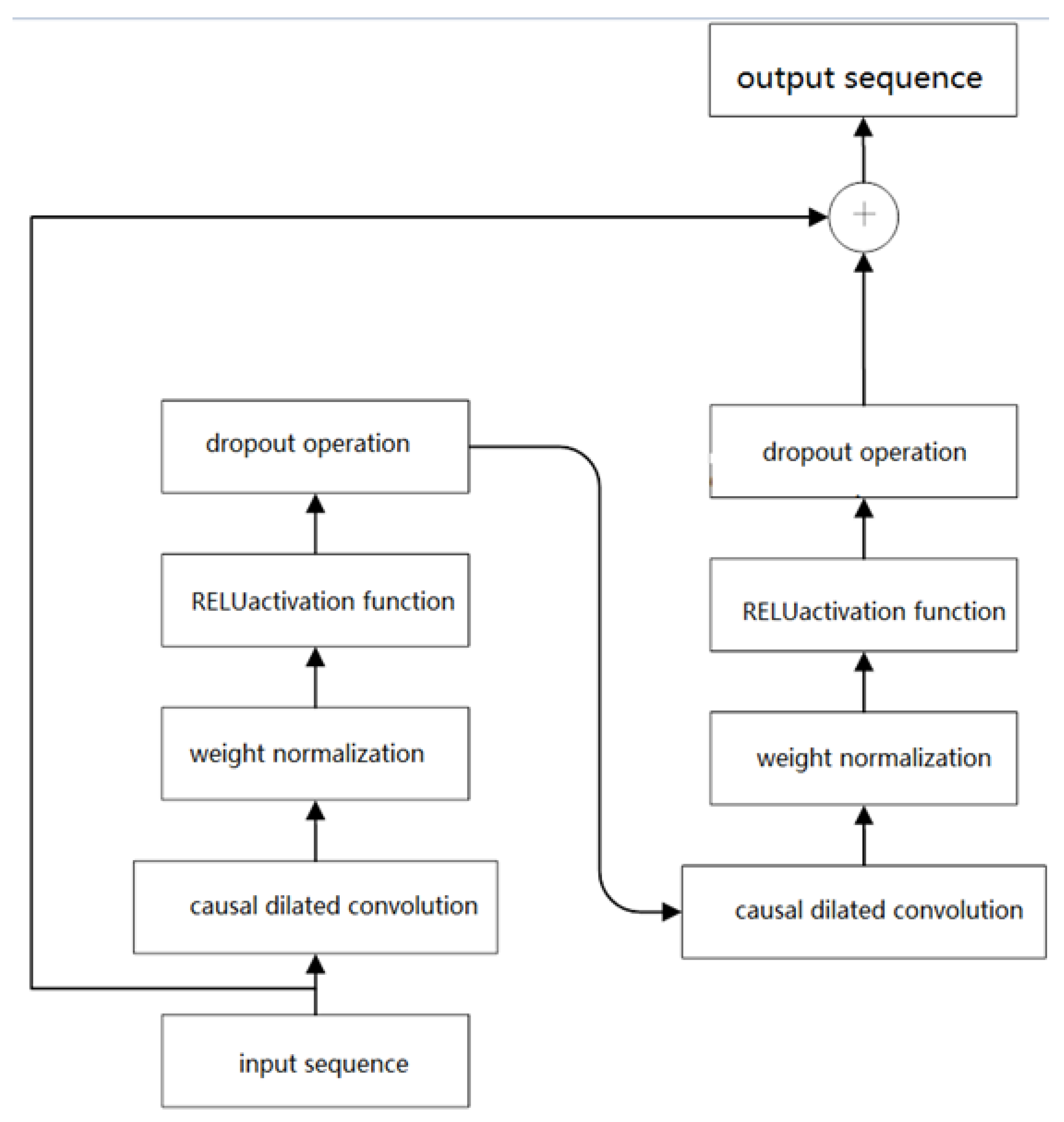
3.3.1. Time Convolutional Network (TCN)
3.3.2. Attention Mechanism
3.3.3. TCN-Attention Model
3.3.4. Parameter Optimization Based on WOA
4. Results
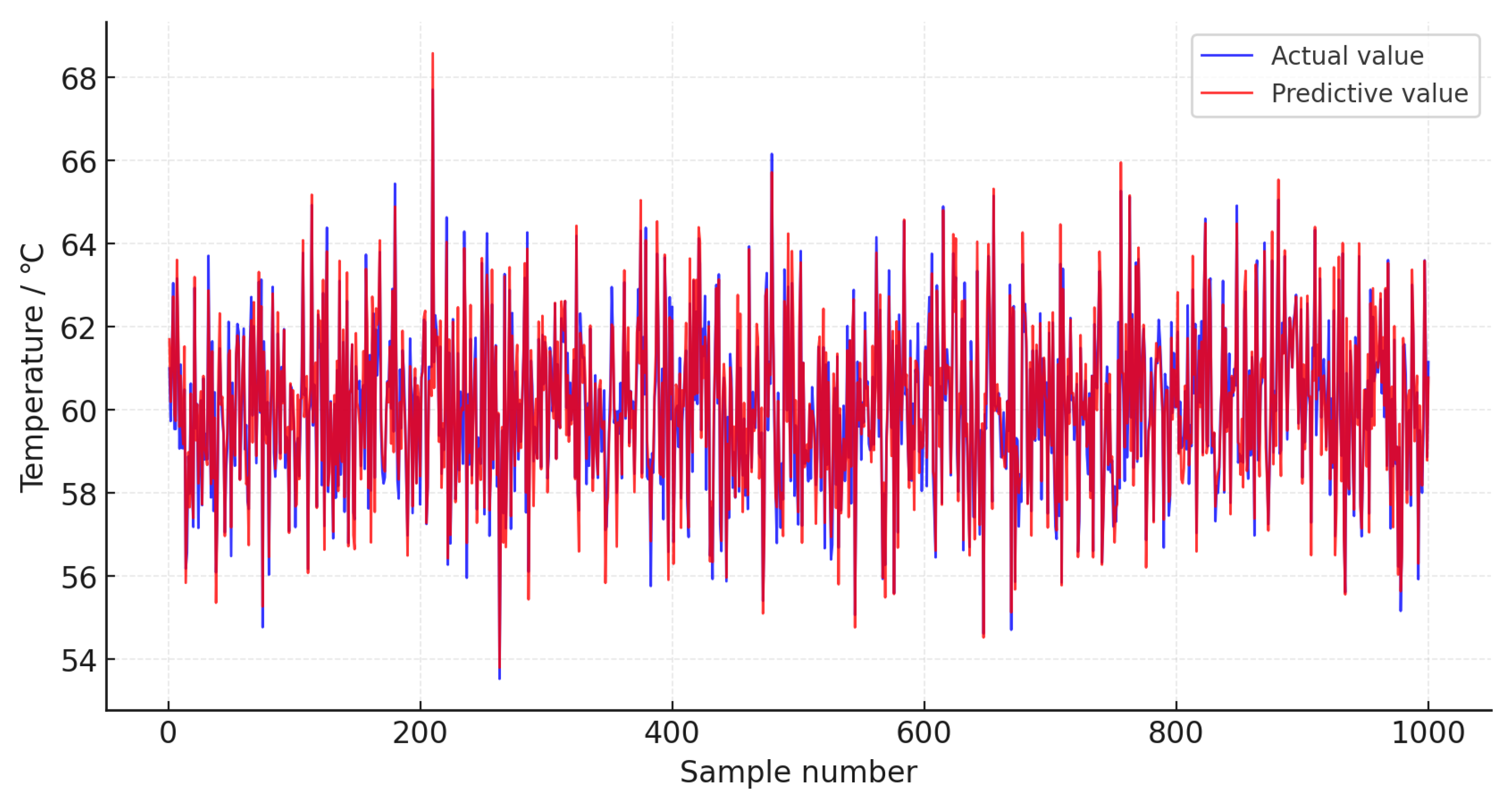
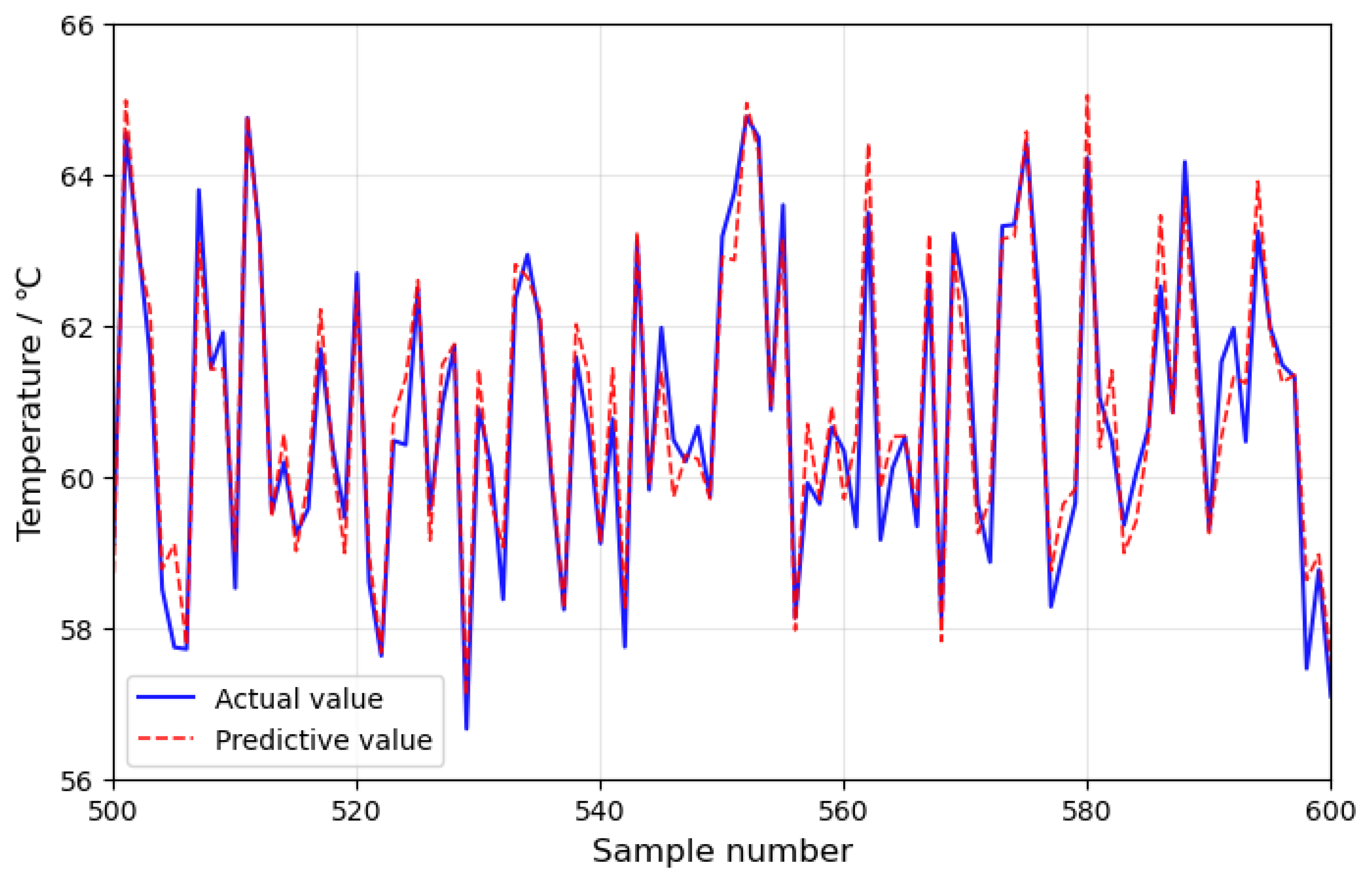
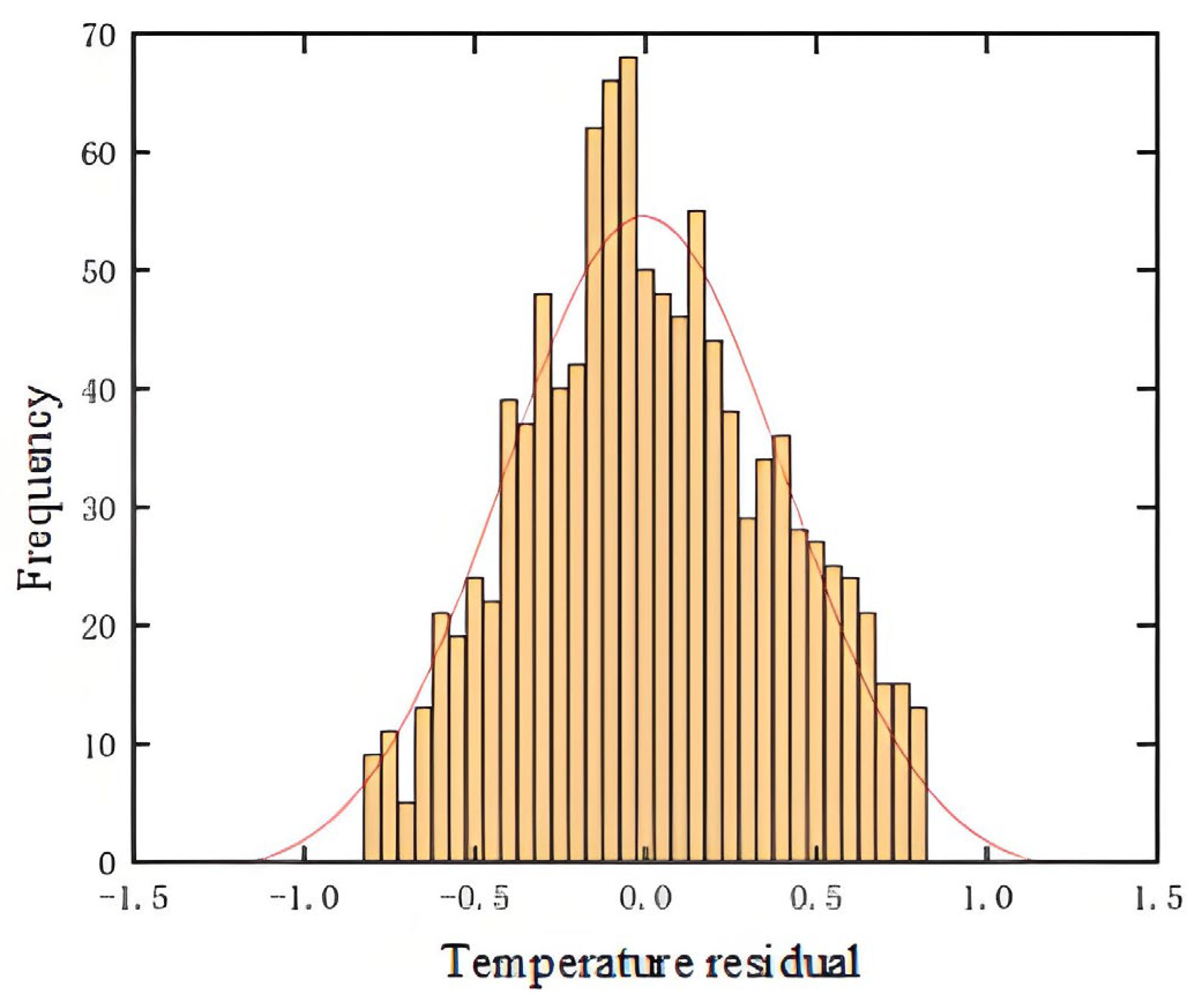
4.1. Model Training and Validation
4.2. Implementation of Intelligent Operation and Maintenance for Wind Turbines Based on Digital Twin and Multi-Source Data Fusion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yanping, H.; Juchuan, D.; Deshun, L. Research status and development trend of large wind turbine blades. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 49, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, N.; Tuohy, P.M.; Özgönenel, O.; Djurović, S. Early life failure modes and downtime analysis of onshore type-III wind turbines in Turkey. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 216, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Artigao, E.; Martín-Martínez, S.; Honrubia-Escribano, A.; Gómez-Lázaro, E. Wind turbine reliability: A comprehensive review towards effective condition monitoring development. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, P.B. On Wilcoxon rank sum test for condition monitoring and fault detection of wind turbines. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q. A Review of Fault Diagnosis, Status Prediction, and Evaluation Technology for Wind Turbines. Energies 2023, 16, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Kong, L.; Liu, G.; Dong, W.; Liu, X. Fault detection of wind turbines integrating digital twins: ASL-CatBoost method. J. Syst. Simul. 2024, 36, 873. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, S.; Wei, W.; Zhipeng, L. A review of condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of wind turbines. Shanxi Electr. Power 2023, 185, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Huan, L.; Ting, Y.; Shaohui, X. A review of data-driven condition monitoring and fault diagnosis techniques for wind turbines. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2023, 47, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xinying, T.; Zhongshan, Z.; Cheng, P. Design of real-time state monitoring system for wind turbines. Ship Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 121–123. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D. Design of Remote Integrated Monitoring System for Offshore Wind Farms Based on OPC UA; Nanjing University of Science and Technology: Jiangsu, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Z.; Yue, W.; Siyu, Z. Condition monitoring method for wind turbines based on cointegration analysis. Mech. Des. Manuf. 2023, 116, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Yanting, L.; Zhenyu, W.; Di, Z.; Jie, H. Covariance process monitoring for multi-mode and multi-unknown distributions. China Mech. Eng. 2023, 34, 2721–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Yuchen, Z. Design and Implementation of Wind Turbine State Monitoring and Analysis System; North China Electric Power University: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, X.; Xu, Z. An Adaptive Condition Monitoring Method of Wind Turbines Based on Multivariate State Estimation Technique and Continual Learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 3513009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, F.; Wu, S.; Li, D. Condition monitoring of wind turbines with the implementation of spatio-temporal graph neural network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 121, 106000. [Google Scholar]
- Dore, P.; Chakkor, S.; El Oualkadi, A.; Baghouri, M. Real-time intelligent system for wind turbine monitoring using fuzzy system. E-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2023, 3, 100096. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Xu, Z.; Qiao, W. Condition Monitoring of Wind Turbine Generators Using SCADA Data Analysis. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, X. A hybrid LSTM-KLD approach to condition monitoring of operational wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 554–566. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z. Wind Turbine Gearbox Failure Detection Based on SCADA Data: A Deep Learning-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3507911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Hu, A.; Su, H. Fault detection of wind turbine based on SCADA data analysis using CNN and LSTM with attention mechanism. Measurement 2021, 175, 109094. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, L.; Weichao, W.; Yiping, Y.; Panpan, F.; Jianxiong, G. Research on gear oil temperature trend prediction of wind turbines based on extreme learning machine. Comb. Mach. Tools Autom. Process. Technol. 2020, 11, 65–67+77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, J. Operational state assessment of wind turbine gearbox based on long short-term memory networks and fuzzy synthesis. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Bangalore, P.; Tjernberg, L.B. A fault detection framework using recurrent neural networks for condition monitoring of wind turbines. Wind Energy 2021, 24, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, W.; Fuyuan, L.; Xin, H.; Xin, H.; Xiao, L. Gearbox oil temperature early warning method for wind turbines based on multi-parameter fusion. Manuf. Autom. 2023, 45, 100–103+119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, D.; Yang, T. Anomaly detection and diagnosis for wind turbines using long short-term memory-based stacked denoising autoencoders and XGBoost. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 222, 108445. [Google Scholar]
- Yetis, Y.; Tehrani, K.; Jamshidi, M. Wind speed forecasting using machine learning approach based on meteorological data-a case study. Energy Environ. Res. 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Long, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, R. Wind turbine gearbox failure identification with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 13, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Jiang, D.; Xiang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. CDTFAFN: A novel coarse-to-fine dual-scale time-frequency attention fusion network for machinery vibro-acoustic fault diagnosis. Inf. Fusion 2024, 112, 102554. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Yan, X.; Hua, X.; Jiang, D.; Xiang, L.; Chen, N. MRCFN: A multi-sensor residual convolutional fusion network for intelligent fault diagnosis of bearings in noisy and small sample scenarios. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 259, 125214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, J. Mahalanobis semi-supervised mapping and beetle antennae search based support vector machine for wind turbine rolling bearings fault diagnosis. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, A.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Sánchez, R.V. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine gearbox based on the optimized LSTM neural network with cosine loss. Sensors 2020, 20, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Ge, F.X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J. Multisensor bearing fault diagnosis based on one-dimensional convolutional long short-term memory networks. Measurement 2020, 159, 107802. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ji, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Kan, C.; Jin, K. Multi-feature fusion for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on convolutional neural network. Comput. Commun. 2021, 173, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y. Novel three-stage feature fusion method of multimodal data for bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3514710. [Google Scholar]
- Chiachío, M.; Megía, M.; Chiachío, J.; Fernandez, J.; Jalón, M.L. Structural digital twin framework: Formulation and technology integration. Autom. Constr. 2022, 140, 104333. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, T.F.; Fang, H.R.; Chen, Y.F.; He, L.T. Research on digital twin monitoring system for large complex surface machining. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022, 35, 977–990. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, P.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, B. A digital-twin visualized architecture for Flexible Manufacturing System. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 60, 176–201. [Google Scholar]
- Kung-Jeng, W.; Ying-Hao, L.; Septianda, A. Digital twin design for real-time monitoring—A case study of die cutting machine. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 6471–6485. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Gao, C. A digital twin-based operation status monitoring system for port cranes. Sensors 2022, 22, 3216–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, K.; Beikbabaei, M.; Mehrizi-Sani, A.; Jamshidi, M. A smart multiphysics approach for wind turbines design in industry 5.0. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2024, 42, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengqiong, Q.; Lang, C.; Zhanqi, H.; Shaohan, C. Overview of research and application prospects of wind power generation systems. Mech. Des. 2021, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, W.; Lin, W.; Yun, Y.; Zhiqi, A.; Lingyun, S. Overview of the characteristics, architecture, and applications of digital twin power grids. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2022, 44, 3721–3733. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Guishan, Y.; Yang, H.; Xutao, W.; Jizhen, L. Digital twin system for wind turbines. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2022, 52, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongpeng, S. Research on Key Technologies of Digital Twin System for Operation and Maintenance of Wind Turbines; Chang’an University: Xi’An, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xuanhui, Z. Design and Development of a Digital Twin Software System for Wind Farms Based on High-Precision Models and Real-Time Simulators of Wind Turbine; Shandong University: Jinan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Dao, M.H.; Le, Q.T. Digital twining of an offshore wind turbine on a monopile using reduced-order modelling approach. Renew. Energy 2023, 206, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, O.; Adedeji, P.A.; Madushele, N.; Jen, T.C. Overview of digital twin technology in wind turbine fault diagnosis and condition monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 12th International Conference on Mechanical and Intelligent Manufacturing Technologies (ICMIMT), Cape Town, South Africa, 13–15 May 2021; pp. 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.; Semeraro, C.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Olabi, A.G. Designing and prototyping the architecture of a digital twin for wind turbine. Int. J. Thermofluids 2024, 22, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ren, S.; Jiang, H. Predictive maintenance of wind turbines based on digital twin technology. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Xu, T.; Zou, Y. Research on rapid calculation method of wind turbine blade strain for digital twin. Renew. Energy 2024, 221, 119783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Peyrano, O.G.; Gu, F.; Wang, S.; Lv, D. Research on main bearing life prediction of direct-drive wind turbine based on digital twin technology. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Hnydiuk-Stefan, A.; Feng, S.; Atilla, I.; Li, Z. Recent progress on reliability analysis of offshore wind turbine support structures considering digital twin solutions. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 232, 109168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenghui, B.; Wenlei, S.; Han, L.; Lun, J.; Bingkai, W.; Yi, W. Research on Digital Twin-Driven Remote Monitoring System for Wind Turbines. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2025, 46, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, T.; Weiran, L.; Meng, Z.; Tianliang, H.; Qinglin, Q.; He, Z.; Fangyuan, S.; Tian, W.; Hui, X.; Zuguang, H.; et al. A Five-Dimensional Model of Digital Twin and Its Applications in Ten Fields. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



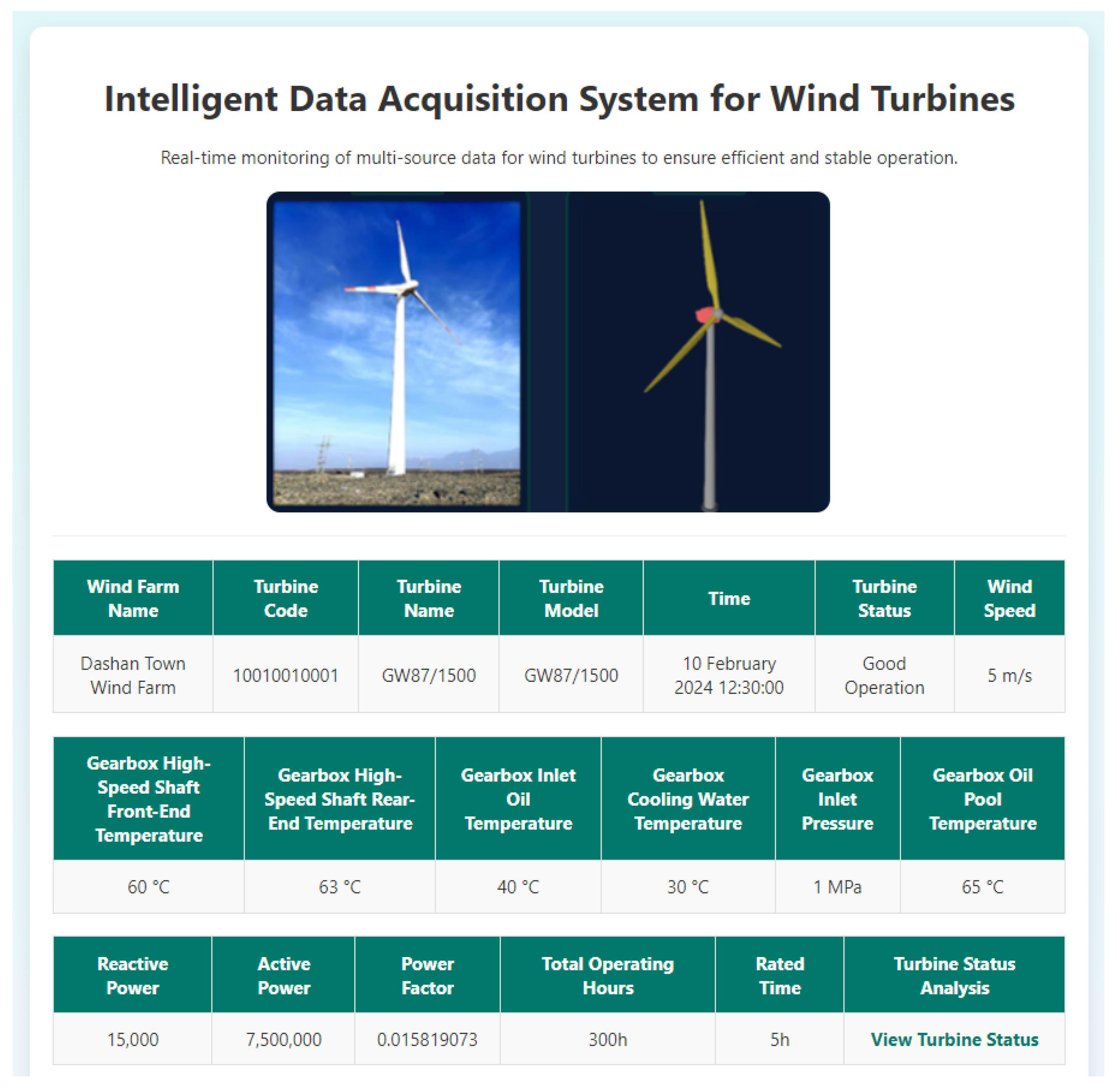
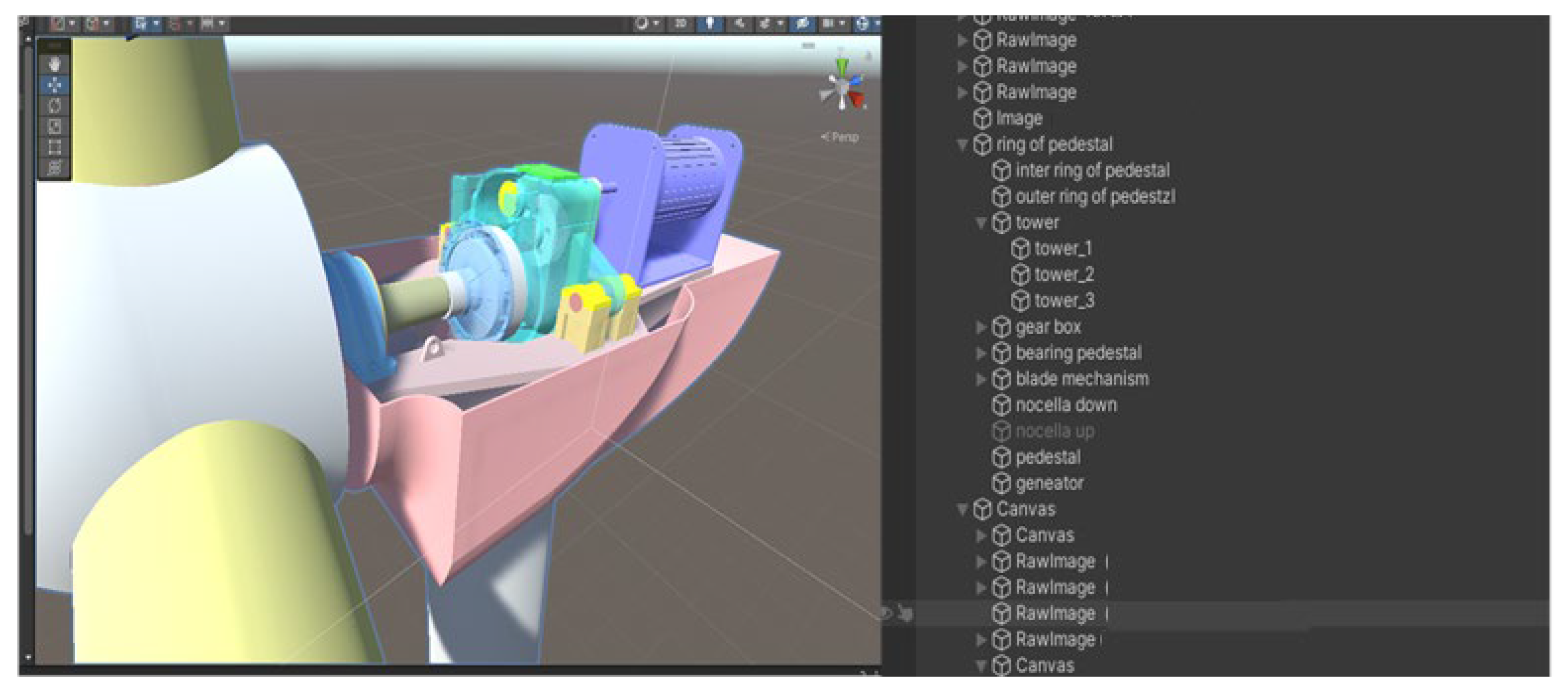


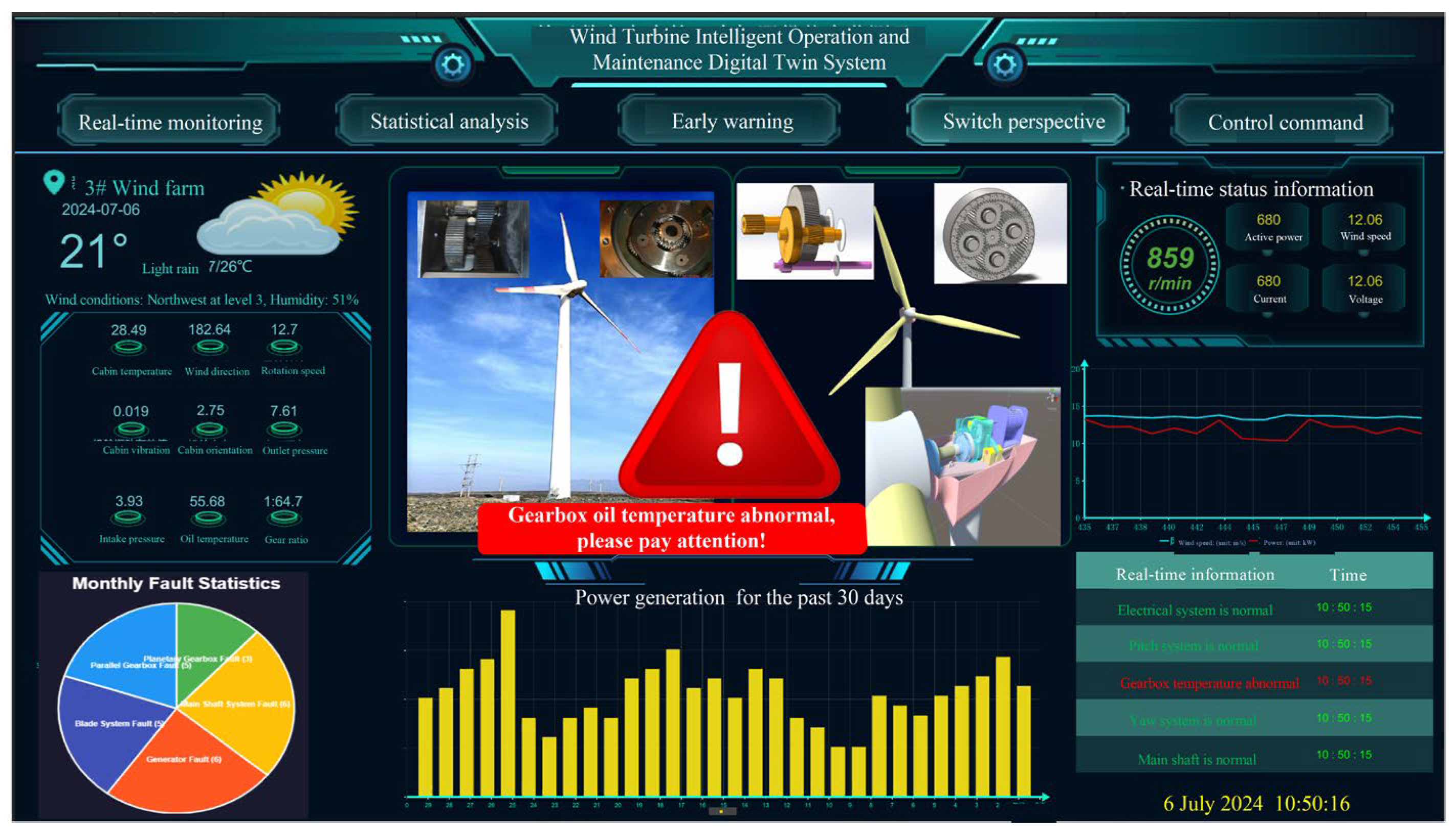
| Index | SCADA Variables | MIC Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| A0 | Front-end temperature of the gearbox high-speed shaft | 0.7855 |
| A1 | Rear-end temperature of the gearbox high-speed shaft | 0.8380 |
| A2 | Gearbox inlet oil temperature | 0.7538 |
| A3 | Active power of the generator | 0.6359 |
| A4 | Gearbox cooling water temperature | 0.7221 |
| A5 | Gearbox inlet pressure | 0.6329 |
| A6 | Gearbox oil sump temperature | 1.0000 |
| Name | Learning Rate | Filters | Convolution Kernels | Dilation List |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0.006375 | 63 | 2 | [1,2,4,8,16,32] |
| Prediction Model | EMAE | ERMSE | EMAPE | Calculation Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.3940 | 0.5728 | 0.6546 | 500 ms |
| TCN | 0.2881 | 0.4554 | 0.4969 | 100 ms |
| TCN-Attention | 0.2357 | 0.3968 | 0.3872 | 200 ms |
| WOA-TCN-Attention | 0.2188 | 0.3685 | 0.3616 | 200 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, B. Intelligent Operation and Maintenance of Wind Turbines Gearboxes via Digital Twin and Multi-Source Data Fusion. Sensors 2025, 25, 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071972
Xu T, Zhang X, Sun W, Wang B. Intelligent Operation and Maintenance of Wind Turbines Gearboxes via Digital Twin and Multi-Source Data Fusion. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071972
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tiantian, Xuedong Zhang, Wenlei Sun, and Binkai Wang. 2025. "Intelligent Operation and Maintenance of Wind Turbines Gearboxes via Digital Twin and Multi-Source Data Fusion" Sensors 25, no. 7: 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071972
APA StyleXu, T., Zhang, X., Sun, W., & Wang, B. (2025). Intelligent Operation and Maintenance of Wind Turbines Gearboxes via Digital Twin and Multi-Source Data Fusion. Sensors, 25(7), 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071972






