Water Use Efficiency Spatiotemporal Change and Its Driving Analysis on the Mongolian Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Research Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. NPP and ET Dataset
2.2.2. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) Dataset
2.2.3. Meteorological Dataset
2.2.4. WUE Dataset
2.2.5. Inversion of Vegetation Phenological Parameters
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Theil–Sen Trend Analysis and Mann–Kendall Test
2.3.2. Breaks for Additive Season and Trend (BFAST) Package
2.3.3. WUE Change Point Detection
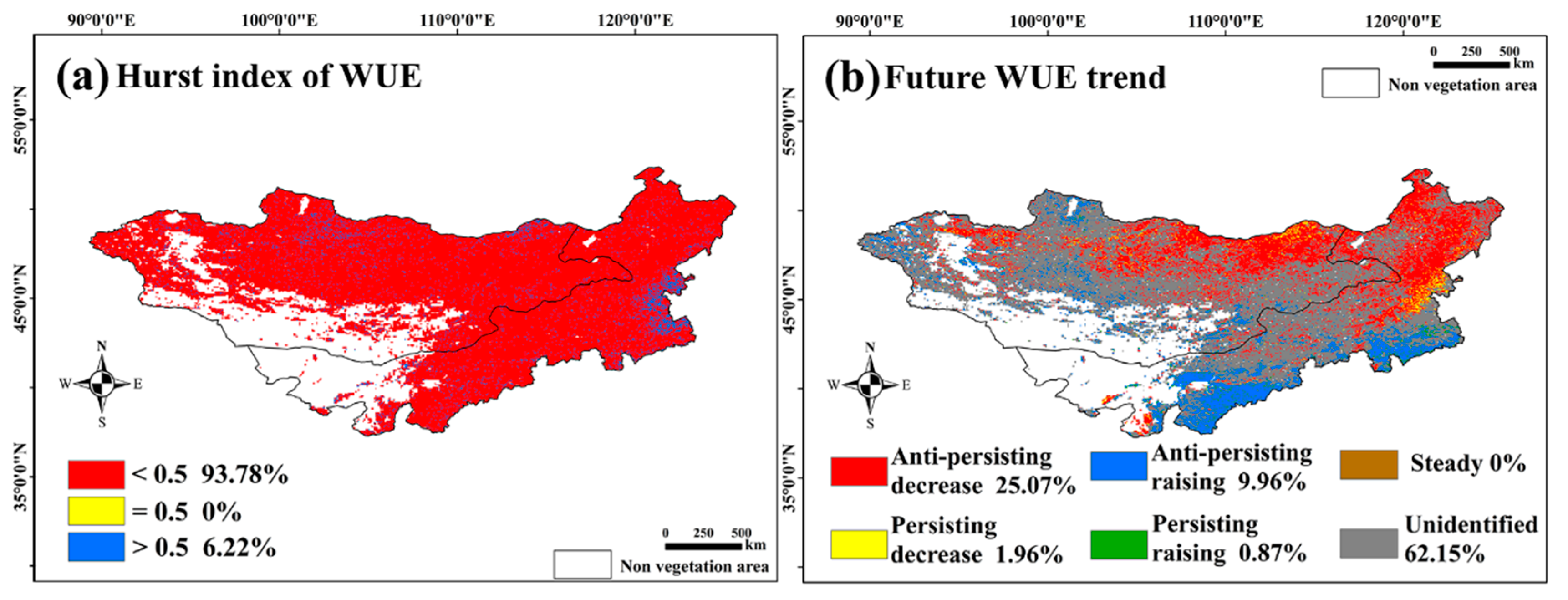
2.3.4. Hurst Index Analysis
2.3.5. Geographical Detector Model
2.3.6. Autoregressive Model
2.3.7. Residual Analysis Method
3. Results
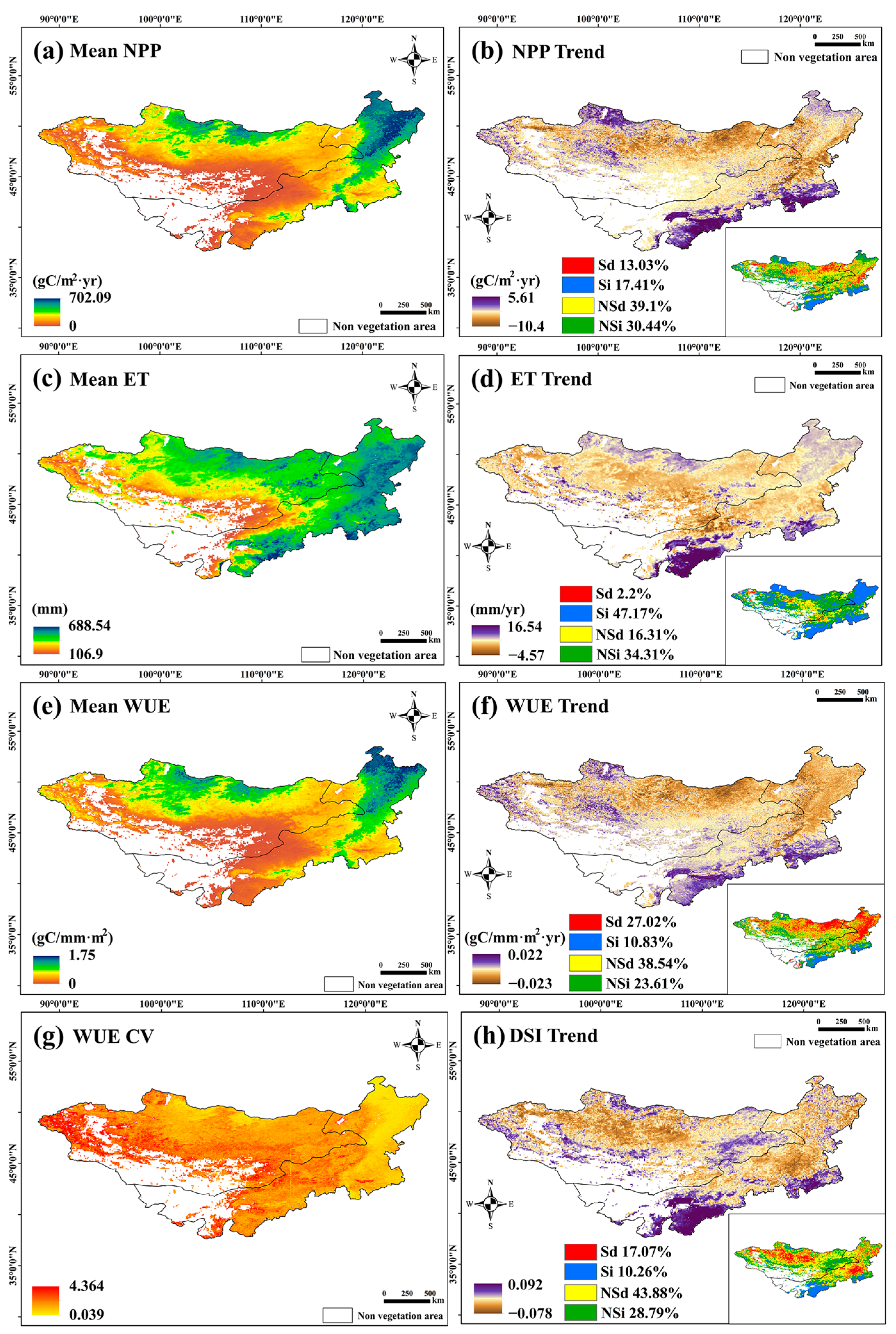
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Trend Analysis of NPP, ET, and WUE
3.1.1. Temporal Differentiation of WUE in the Mongolian Plateau
3.1.2. Spatial Distribution of WUE Dynamic Trends
3.1.3. Breakpoint Detection of WUE Time Series in the Growing Season
3.1.4. Detection of Change Points in Trends in Annual WUE
3.1.5. WUE Trends
3.2. Potential Factors Affecting WUE Changes
3.2.1. Correlations Between WUE and Meteorological Factors (PRE, TEM, SW, and DSI) on the Mongolian Plateau
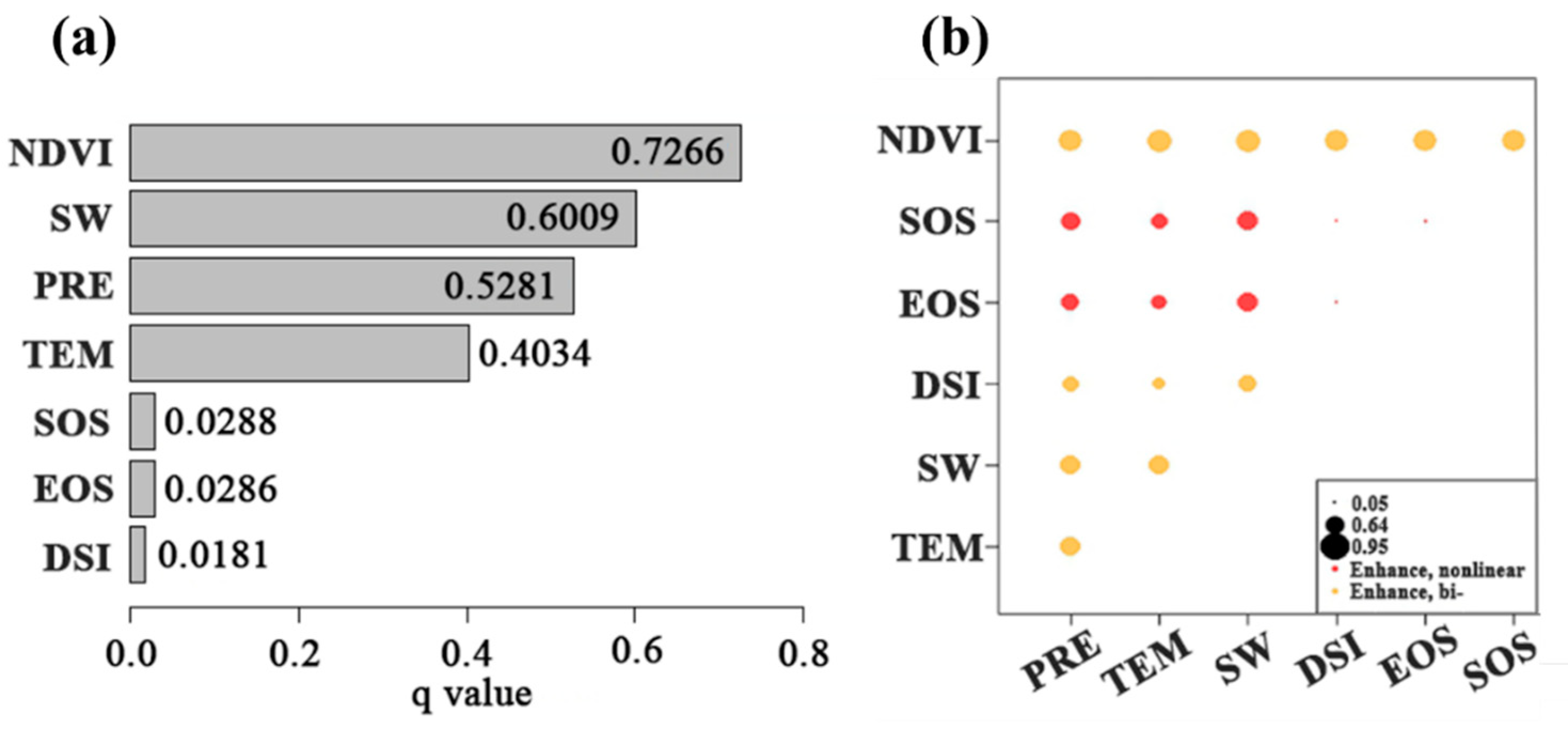
3.2.2. Geographical Detection Model for WUE Drivers
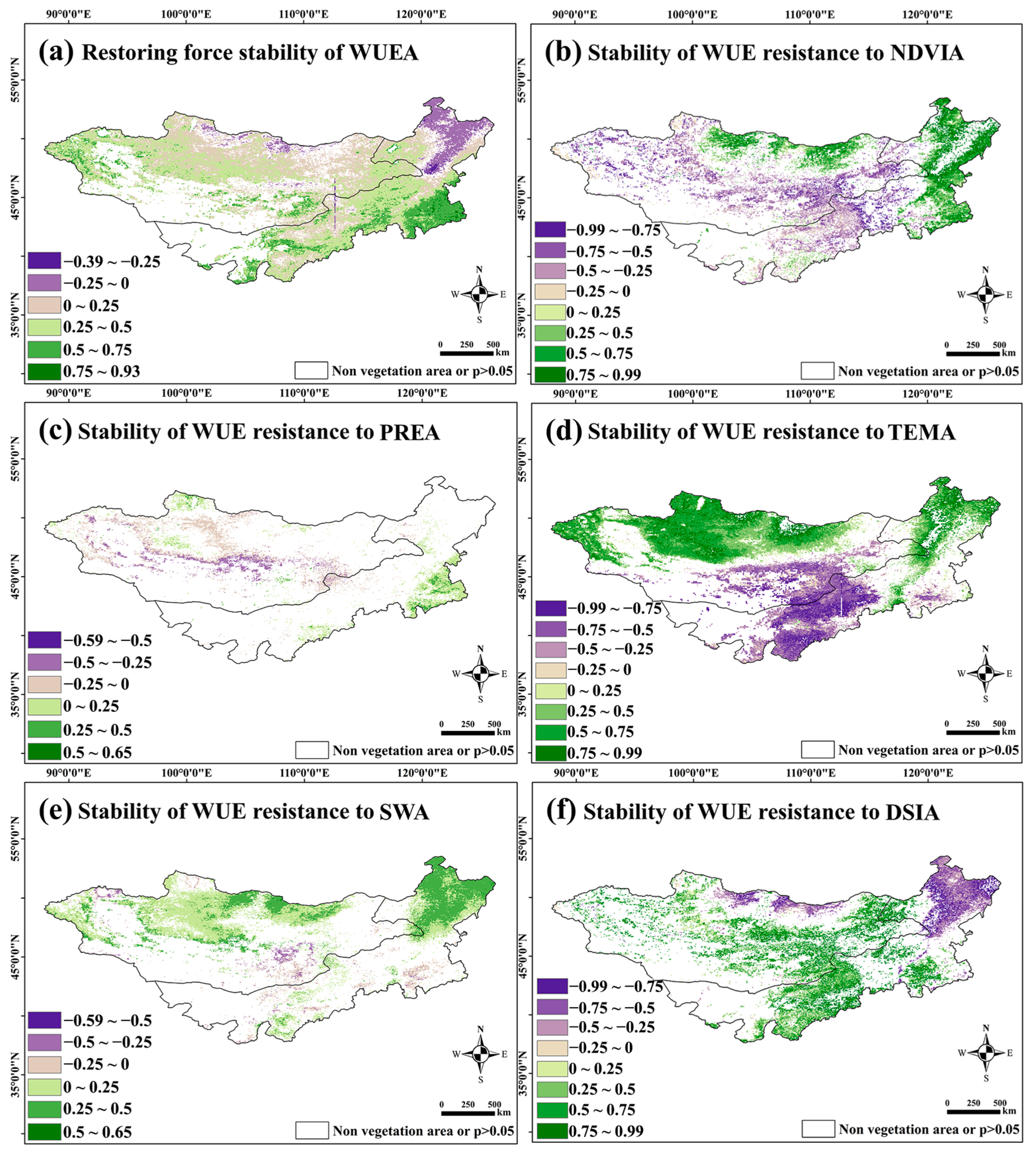
3.2.3. Spatial Distribution of WUE Anomaly Resilience and Its Resistance to Vegetation and Meteorological Factor Anomalies
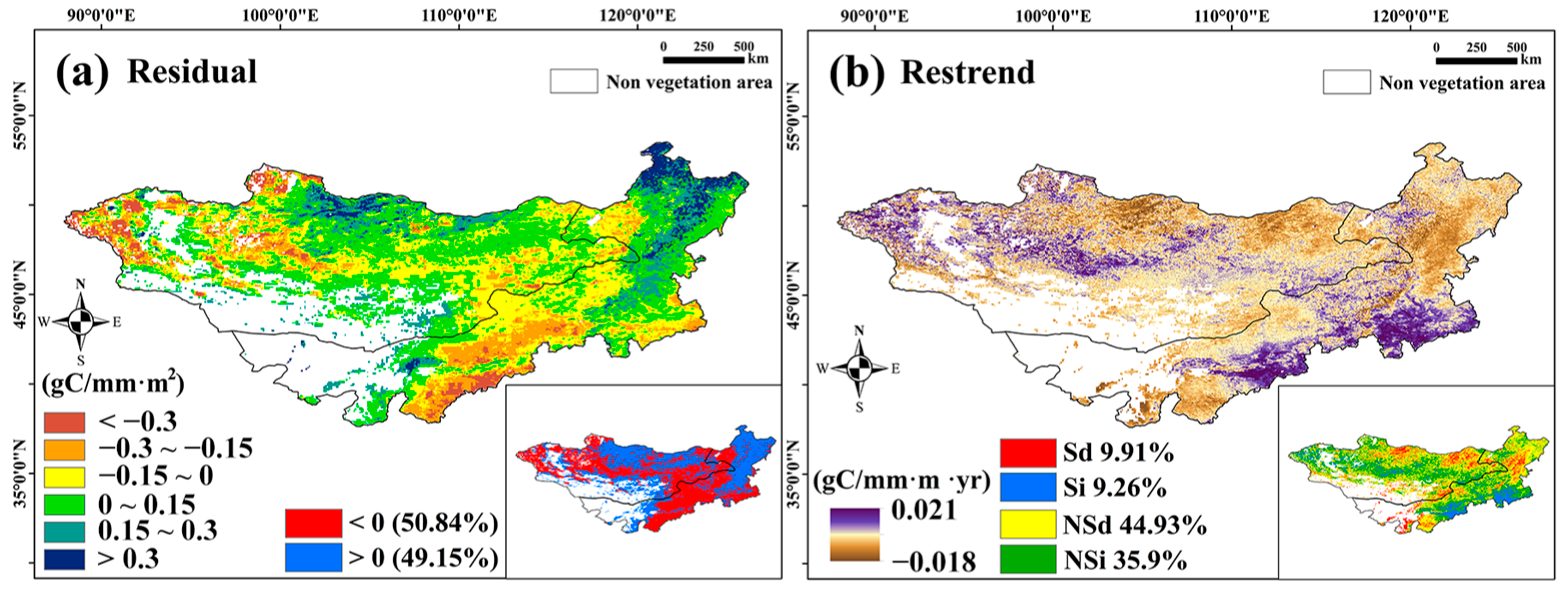
3.2.4. The Impact of Human Activities on WUE Based on Residual Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The annual average NPP and WUE were 232.75 gC/m2·year and 0.592 gC/mm·m2·year, respectively. Over 37 years, the annual WUE decreased significantly, while the annual ET increased. Significant WUE decreases were observed in Central and Eastern Mongolia and in broadleaved forests in Northeastern Inner Mongolia. Significant increases were found in Central and Southern Inner Mongolia. Two WUESeason surges were detected in 1997–1998 and 2007–2009. Some broadleaf forests in Inner Mongolia reversed their decreasing WUE trends in winter. The overall trend suggests that the WUE may shift from decreasing to increasing in the future. The Mongolian Plateau showed strong WUE resilience, except for artificial vegetation areas in Central Inner Mongolia.
- WUE was significantly affected by precipitation and soil moisture, showing resistance to anomalous water disturbances. It had a weak correlation with the temperature and limited resistance to temperature disturbances. WUE was positively correlated with the DSI, although its resistance to DSI anomalies was weak.
- Vegetation change had a stronger impact on WUE than meteorological factors. WUE showed weak resistance to anomalous NDVI disturbances. Delayed rejuvenation positively influenced WUE. Interactions between phenological parameters and meteorological factors enhanced WUE nonlinearly. Human activities significantly contributed to WUE increases in Eastern, Central, and Southern Inner Mongolia.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Zhou, G.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Dai, A.; Wang, F.; Wu, Y.; Gentine, P.; Zhang, G.; Song, Y.; Zhou, D. Rising rainfall intensity induces spatially divergent hydrological changes within a large river basin. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 823. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.J.; Sun, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wei, X. The spatiotemporal evolution and prediction of vegetation NPP in the Huangshui River Basin of Qilian Mountains. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 12, 1459669. [Google Scholar]
- Elbasiouny, H.; El-Ramady, H.; Elbehiry, F.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Mandzhieva, S. Plant nutrition under climate change and soil carbon sequestration. Sustainability 2022, 14, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. Comprehensive assessment of land degradation in the arid and semiarid area based on the optimal land degradation index model. CATENA 2024, 234, 107563. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Sun, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Luan, X.B. Status of crop water use efficiency evaluation methods: A review. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 349, 109961. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Jin, J.; Jiang, H. Strong impacts of autumn phenology on grassland ecosystem water use efficiency on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107682. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lai, Q.; Yin, S.; Bao, Y.; Qing, S.; Bayarsaikhan, S.; Bu, L.; Mei, L.; Li, Z.; Niu, J.; et al. Exploring grassland ecosystem water use efficiency using indicators of precipitation and soil moisture across the Mongolian Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109207. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Speer, J.H.; Thapa, I. Reconstructing and Mapping Annual Net Primary Productivity (NPP) Since 1940 Using Tree Rings in Southern Indiana, U.S. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2024, 129, e2023JG007929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Peng, J.; Liang, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatial–temporal patterns of water use efficiency and climate controls in China′s Loess Plateau during 2000–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, M.; Feng, S.; Cai, H. AquaCrop modeling to explore optimal irrigation of winter wheat for improving grain yield and water productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, D.L.; Abendroth, L.J.; Browning, D.M.; Saha, A.; Snyder, K.; Wagle, P.; Witthaus, L.; Baffaut, C.; Biederman, J.A.; Bosch, D.D.; et al. Indicators of water use efficiency across diverse agroecosystems and spatiotemporal scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 160992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Rehman, A.U.; Tang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Azeem, T. Recent change in ecosystem water use efficiency in China mainly dominated by vegetation greening and increased CO2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 298, 113811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Piao, S.; Sun, Y.; Ciais, P.; Cheng, L.; Mao, J.; Poulter, B.; Shi, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y. Change in terrestrial ecosystem water-use efficiency over the last three decades. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Piao, S.; Zeng, Z.; Peng, S.; Ciais, P.; Cheng, L.; Mao, J.; Poulter, B.; Shi, X.; Yao, Y. Seasonal responses of terrestrial ecosystem water-use efficiency to climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Increasing Tibetan Plateau terrestrial evapotranspiration primarily driven by precipitation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 317, 108887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zha, T.; Bourque, C.P.A.; Jia, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, P.; Yang, R.; Li, C.; Du, T.; Wu, Y. Variation in ecosystem water use efficiency along a southwest-to-northeast aridity gradient in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Still, C.; Rastogi, B.; Page, G.; Wharton, S.; Meinzer, F.; Voelker, S.; Kim, J. Trends and controls on water-use efficiency of an old-growth coniferous forest in the Pacific Northwest. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.-H.; Fei, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Sha, L.-Q.; Liu, Y.-T.; Zhou, W.-J.; Wu, C.-S.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Luo, K.; Gao, J.-B.; et al. Water use efficiency in a primary subtropical evergreen forest in Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamboll, R.D.; Nicholls, Z.R.; Smith, C.J.; Kikstra, J.S.; Byers, E.; Rogelj, J. Assessing the size and uncertainty of remaining carbon budgets. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Song, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Du, W.; Che, T.; Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Ping, B.; et al. Spatio-temporal variations in water use efficiency and its drivers in China over the last three decades. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Ju, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Performance of a two-leaf light use efficiency model for mapping gross primary productivity against remotely sensed sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, D.; Fan, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Contrasting the Performance of Eight Satellite-Based GPP Models in Water-Limited and Temperature-Limited Grassland Ecosystems. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuoku, L.; Wu, Z.; Men, B. Impacts of climate factors and human activities on NDVI change in China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Chen, S.; Su, H. Climate Dynamics of the Spatiotemporal Changes of Vegetation NDVI in Northern China from 1982 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; van Dijk, A.I.; Huete, A.; Yebra, M. Global trends in vegetation seasonality in the GIMMS NDVI3g and their robustness. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 94, 102238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zhao, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, L.; Jiang, S.; Ochirbat, B.; Chen, J.; Xin, X.; Shao, C. Non-climatic component provoked substantial spatiotemporal changes of carbon and water use efficiency on the Mongolian Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 095009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Nikoo, M.R.; Al-Maktoumi, A.; Izady, A.; Rajabi, M.M. The impact of geological heterogeneity on coupled CO2 storage and geothermal extraction in inclined reservoirs. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128950. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Dai, Q.; Li, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Yao, Y. Response of ecosystem water-use efficiency to global vegetation greening. CATENA 2024, 239, 107592. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, L.; Tong, S.; Yin, S.; Bao, Y.; Huang, X.; Alateng, T. Variation Characteristics of Ecosystem Water Use Efficiency and Its Response to Human Activity and Climate Change in Inner Mongolia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wardlow, B.D.; Xiang, D.; Hu, S.; Li, D. A review of vegetation phenological metrics extraction using time-series, multispectral satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhu, X.; Xie, Q.; Jin, J.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Monitoring nature’s calendar from space: Emerging topics in land surface phenology and associated opportunities for science applications. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 7186–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Yan, X.; Li, B.; Liu, F. Vegetation photosynthetic phenology dataset in northern terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z.; Tang, J.; Fu, Y. The advancement in spring vegetation phenology in the Northern Hemisphere will reverse after 2060 under future moderate warming scenarios. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF003788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Chen, J.M.; Shen, H.; Xie, X.; Tan, J. Comparison of big-leaf and two-leaf light use efficiency models for GPP simulation after considering a radiation scalar. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 313, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Tang, Y.; Gu, S.; Hirota, M.; Du, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. Temperature and biomass influences on interannual changes in CO2 exchange in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C.; Han, Y. Impact of seasonal global land surface temperature (LST) change on gross primary production (GPP) in the early 21st century. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 110, 105572. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, Z.; Liang, X.; Xing, J. Estimation methods of wetland carbon sink and factors influencing wetland carbon cycle: A review. Carbon Res. 2024, 3, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhao, C.; Tan, Q.; Li, Y.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.H.; Chen, F.; Li, C.J.; Ran, C.; et al. Spring photosynthetic phenology of Chinese vegetation in response to climate change and its impact on net primary productivity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 342, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Sohn, S.; Wang, Z.; Kim, Y. Nonuniform response of vegetation phenology to daytime and nighttime warming in urban areas. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, S.; Gong, Y.; Li, M.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, Y.H. A vegetation phenology dataset by integrating multiple sources using the Reliability Ensemble Averaging method. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, G. Impact of physiological and phenological change on carbon uptake on the Tibetan Plateau revealed through GPP estimation based on spaceborne solar-induced fluorescence. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, G.; Chen, J.; Chopping, M.; Bao, Y.; Bayarsaikhan, S.; Dorjsuren, A.; Tuya, A.; Jirigala, B.; Qin, Z. Dynamics of net primary productivity on the Mongolian Plateau: Joint regulations of phenology and drought. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 81, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Zhao, F.; Chen, J.; Qu, L.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Shao, C. Divergent forcing of water use efficiency from aridity in two meadows of the Mongolian Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Lutsko, N.J.; Dufour, A.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Jiang, X.; Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Miralles, D.G. High-resolution (1 km) Köppen-Geiger maps for 1901–2099 based on constrained CMIP6 projections. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 724. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Gao, Q.; Qi, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y. Wind erosion hazard assessment of the Mongolian Plateau using FCM and GIS techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 689–697. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Chen, M.; Pan, Z.; Tchebakova, N.; Sokolov, A.; Kicklighter, D.; Melillo, J.; Sirin, A.; Zhou, G. Response of evapotranspiration and water availability to changing climate and land cover on the Mongolian Plateau during the 21st century. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 108, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Bibliometric analysis of global NDVI research trends from 1985 to 2021. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Bao, Y.; Qin, Z.; Xin, X.; Bao, Y.; Bayarsaikan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chuntai, B. Modeling net primary productivity of terrestrial ecosystems in the semi-arid climate of the Mongolian Plateau using LSWI-based CASA ecosystem model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 46, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Shen, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Liang, S.; Chen, J.M.; Ju, W.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, W. Improved estimate of global gross primary production for reproducing its long-term variation, 1982–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 2725–2746. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, N.; Tian, J.; Kong, D.; Liu, C. A daily and 500 m coupled evapotranspiration and gross primary production product across China during 2000–2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 5463–5488. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Fisher, J.B.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X. Bayesian multimodel estimation of global terrestrial latent heat flux from eddy covariance, meteorological, and satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4521–4545. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Jia, K.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, B.; Fisher, J.B.; Mu, Q. A satellite-based hybrid algorithm to determine the Priestley–Taylor parameter for global terrestrial latent heat flux estimation across multiple biomes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 216–233. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Fisher, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, B. MODIS-driven estimation of terrestrial latent heat flux in China based on a modified Priestley–Taylor algorithm. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171, 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yamaguchi, Y. Characterization and evaluation of MODIS-derived Drought Severity Index (DSI) for monitoring the 2009/2010 drought over southwestern China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 74, 2129–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; HO, C.H.; GIM, H.J.; Brown, M.E. Phenology shifts at start vs. end of growing season in temperate vegetation over the Northern Hemisphere for the period 1982–2008. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 2385–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Meng, F.; Sa, C.; Duan, Y.; Bao, Y.; Liu, T.; Maeyer, P.D. Response of vegetation phenology to soil moisture dynamics in the Mongolian Plateau. CATENA. 2021, 206, 105505. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Bao, G.; Wulantuya; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Liu, C. Variations in spring phenology of different vegetation types in the Mongolian Plateau and its responses to climate change during 2001–2017. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 2490. [Google Scholar]
- Fensholt, R.; Langanke, T.; Rasmussen, K.; Reenberg, A.; Prince, S.D.; Tucker, C.; Scholes, R.J.; Le, Q.B.; Bondeau, A.; Eastman, R. Greenness in semi-arid areas across the globe 1981–2007-An Earth Observing Satellite based analysis of trends and drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetta, R.S.; Knight, J.F.; Ediriwickrema, J.; Lyon, J.G.; Worthy, L.D. Land-cover change detection using multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Verbesselt, J.; Zeileis, A.; Herold, M. Near real-time disturbance detection using satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Newnham, G.; Culvenor, D. Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, E.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; Bao, Y.; Mandula, N.; Jirigala, B.; Bao, Y.; Li, H. NDVI Indicates Long-Term Dynamics of Vegetation and Its Driving Forces from Climatic and Anthropogenic Factors in Mongolian Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersi, C.; Bayaer, T.; Bao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yong, M.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of Phenological Parameters Extracted from SIF, NDVI and NIRv Data on the Mongolian Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Ersi, C.; Bayaer, T.; Bao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yong, M.; Zhang, X. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Evapotranspiration and Its Potential Driving Factors in Mongolia over the Past 20 Years. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Zeileis, A.; Culvenor, D. Phenological change detection while accounting for abrupt and gradual trends in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2970–2980. [Google Scholar]
- Killick, R.; Fearnhead, P.; Eckley, I.A. Optimal detection of changepoints with a linear computational cost. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2012, 107, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Killick, R.; Eckley, I.A.; Pebesma, E.; Zeileis, A. changepoint: An R Package for Changepoint Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 58, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, K.J.; Prince, S.D.; Malherbe, J.; Small, J.; Frost, P.E.; VanZyl, D. Can human-induced land degradation be distinguished from the effects of rainfall variability? A case study in South Africa. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 271–297. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Li, T.X.; Cheng, S.K.; Wang, X. Spatial distribution exploration and driving factor identification for soil salinisation based on geodetector models in coastal area. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 156, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Hao, C. Analysis of the Influence of Driving Factors on Vegetation Changes Based on the Optimal-Parameter-Based Geographical Detector Model in the Yima Mining Area. Forests 2024, 15, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, A.B.; Abdallah, N.B.; Dfifaoui, Z. Wavelet decomposition and autoregressive model for time series prediction. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 199, 334–340. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, J.; Parmar, K.S.; Singh, S. Autoregressive models in environmental forecasting time series: A theoretical and application review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 19617–19641. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Shi, H.; Yu, Q.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Luo, G.; Jin, N.; Li, J. Satellite-observed vegetation stability in response to changes in climate and total water storage in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 862–871. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Yao, Y.; Tang, Q.; Liu, M.; Fisher, J.B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, K.; Li, Y.; Shang, K.; et al. Evaluation of seven satellite-based and two reanalysis global terrestrial evapotranspiration products. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130649. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Guo, E.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Mandula, N. Monitoring Vegetation Change and Its Potential Drivers in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jin, J.; Yong, B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H. Responses of water use efficiency to phenology in typical subtropical forest ecosystems—A case study in Zhejiang Province. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 145–156. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, G.; Bao, Y.; Sun, C.; Yong, M.; Gantumur, B.; Boldbayar, R.; Bao, Y. Water Use Efficiency Spatiotemporal Change and Its Driving Analysis on the Mongolian Plateau. Sensors 2025, 25, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072214
Tang G, Bao Y, Sun C, Yong M, Gantumur B, Boldbayar R, Bao Y. Water Use Efficiency Spatiotemporal Change and Its Driving Analysis on the Mongolian Plateau. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072214
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Gesi, Yulong Bao, Changqing Sun, Mei Yong, Byambakhuu Gantumur, Rentsenduger Boldbayar, and Yuhai Bao. 2025. "Water Use Efficiency Spatiotemporal Change and Its Driving Analysis on the Mongolian Plateau" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072214
APA StyleTang, G., Bao, Y., Sun, C., Yong, M., Gantumur, B., Boldbayar, R., & Bao, Y. (2025). Water Use Efficiency Spatiotemporal Change and Its Driving Analysis on the Mongolian Plateau. Sensors, 25(7), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072214







