Dynamic Deformation Analysis of Super High-Rise Buildings Based on GNSS and Accelerometer Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
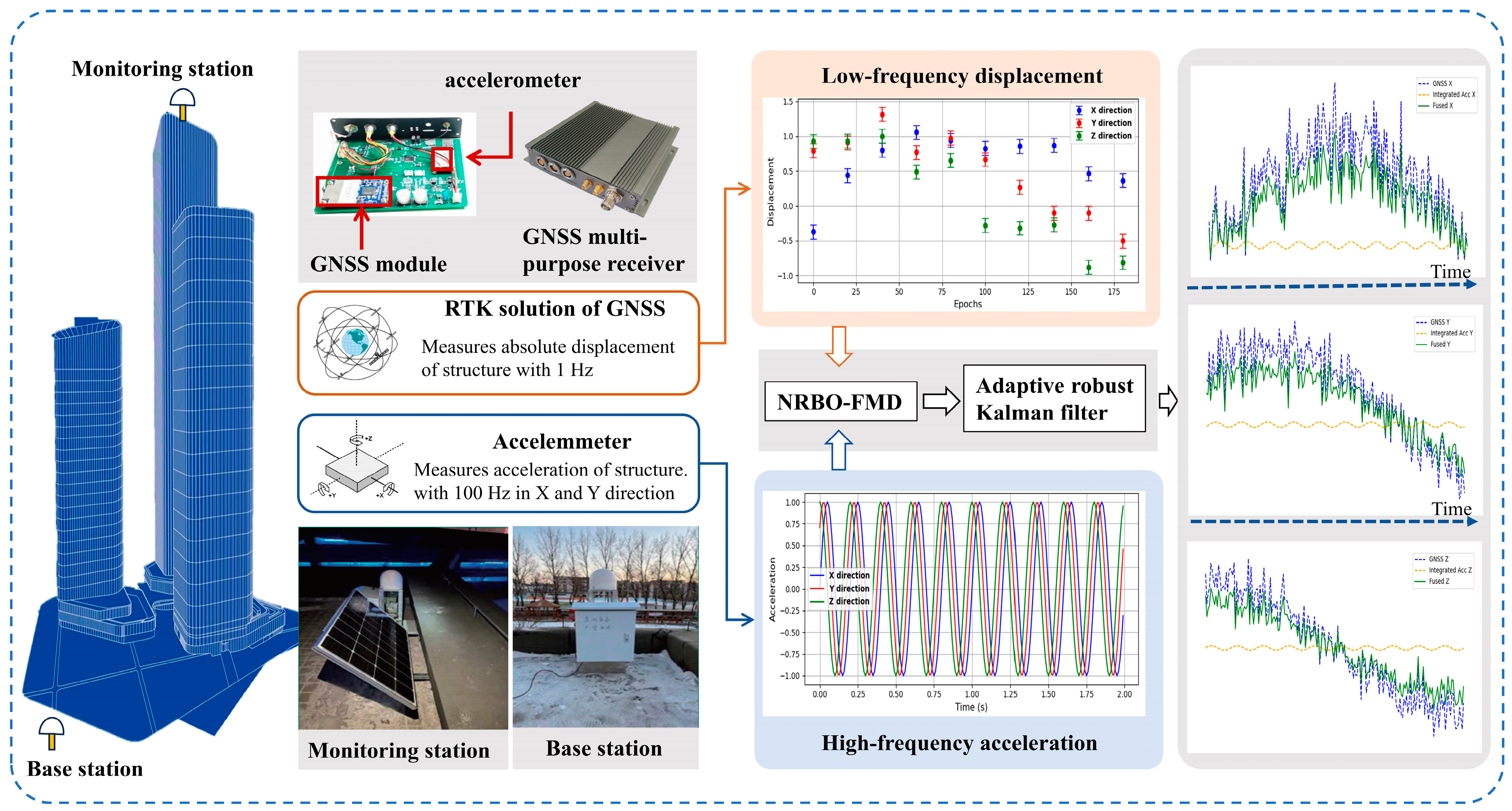
2. GNSS and Accelerometer Data Fusion Method
2.1. NRBO-FMD Optimization Workflow
2.1.1. The Feature Modal Decomposition (FMD) Algorithm
2.1.2. Newton–Raphson Optimization Algorithm (NRBO)
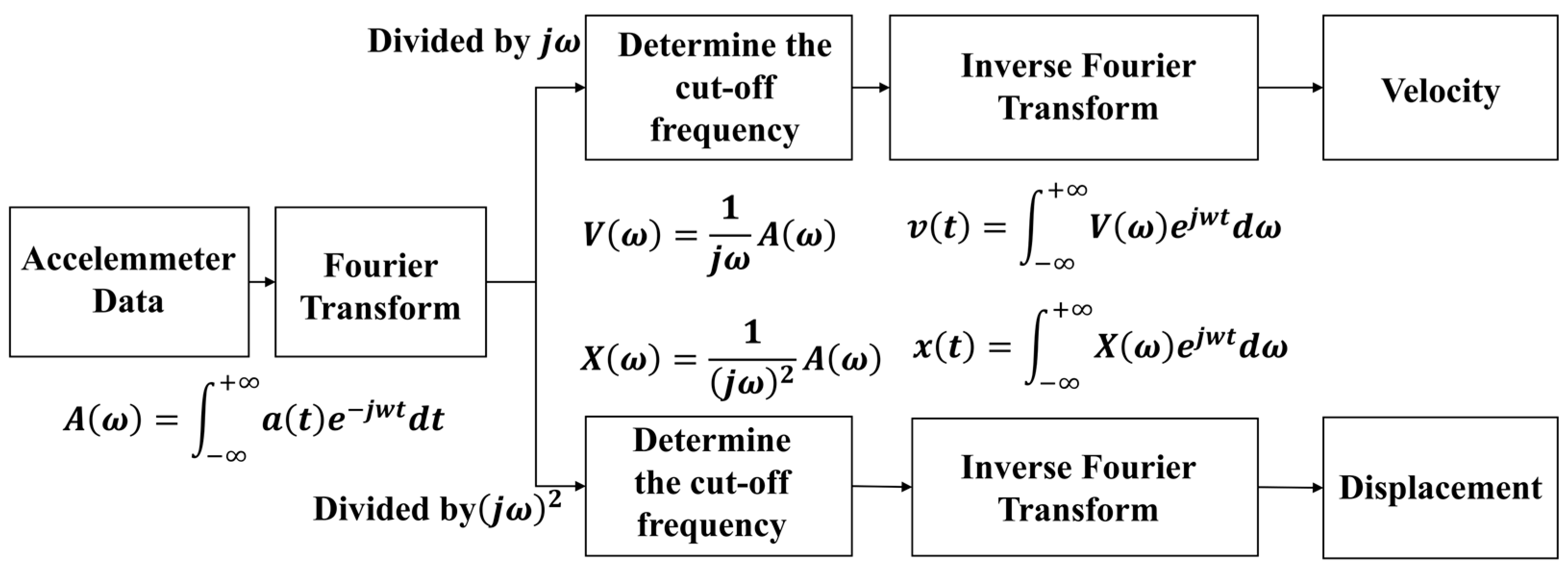
2.2. Acceleration Frequency-Domain Integral
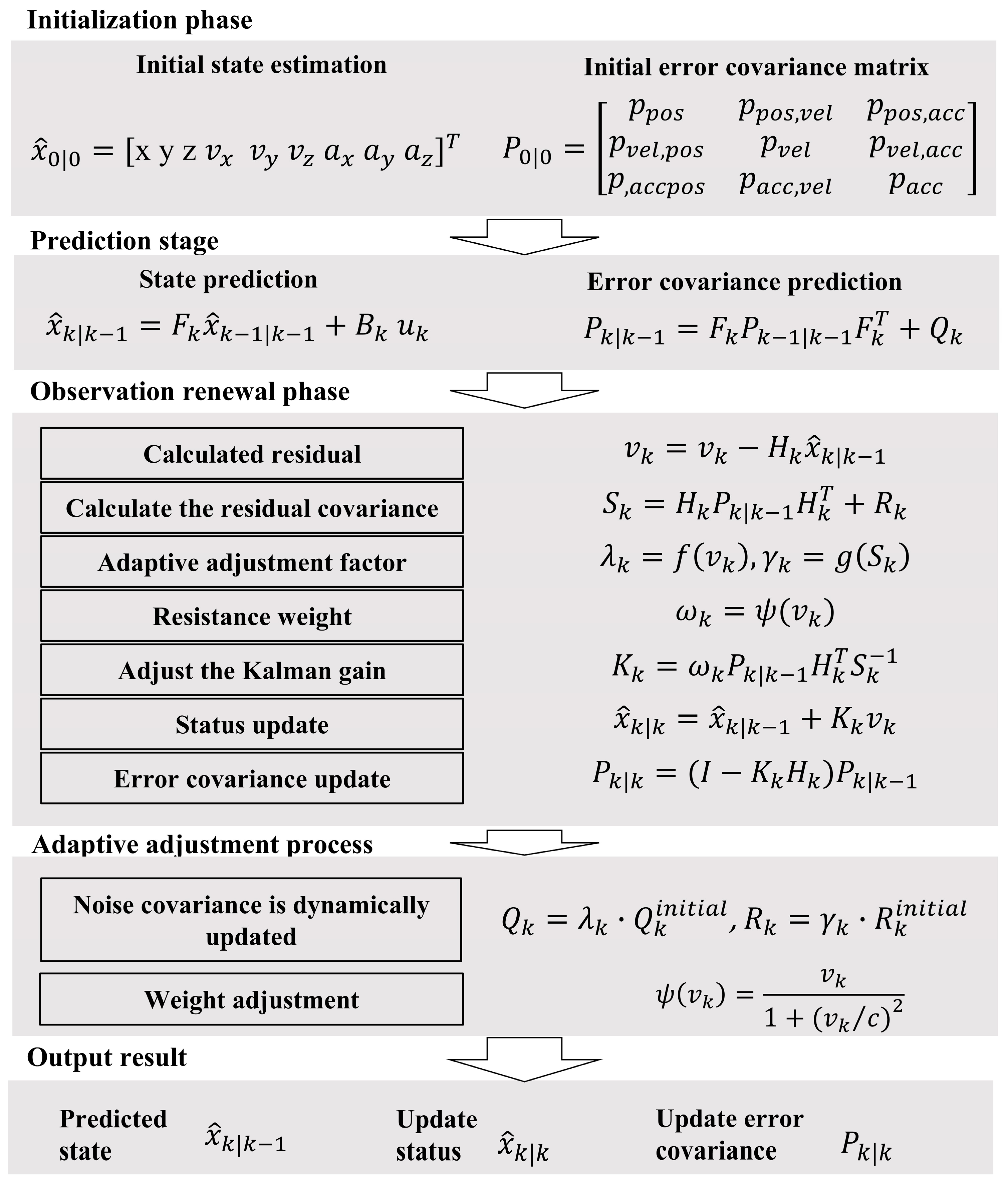
2.3. Adaptive Robust Kalman Filter (ARKF)
2.4. Overall Dynamic Displacement Reconstruction Method
3. Assessment Indicators and Numerical Simulation
3.1. Evaluation Indicators
- (1)
- Root Mean Square Error (RMSE):
- (2)
- Prior Estimation Standard Deviation (PESD):
- (3)
- Posterior Estimation Standard Deviation (POSD):
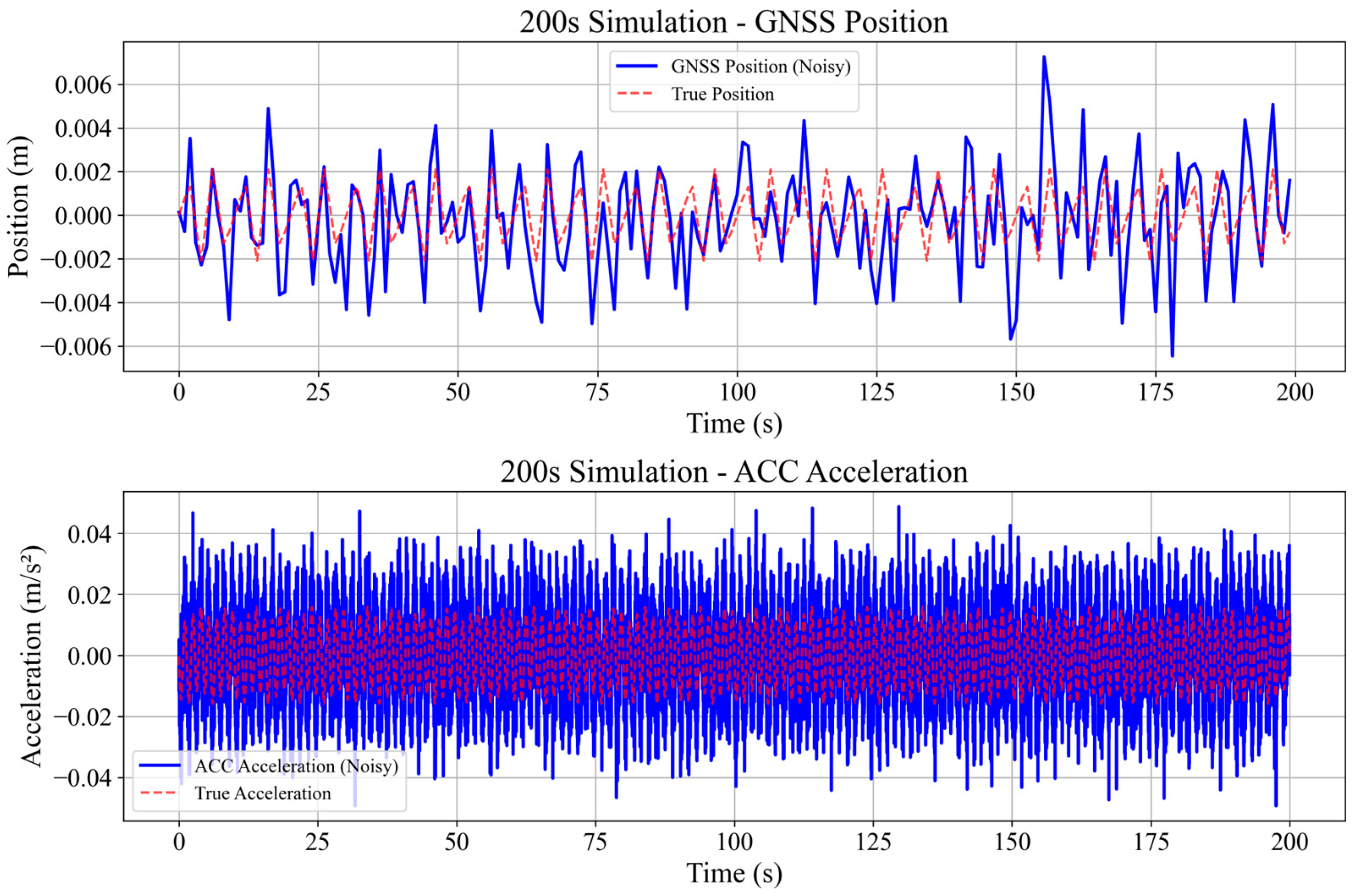
3.2. Numerical Simulation
3.3. Performance Analysis
- (1)
- Validation of the Effectiveness of the NRBO-FMD Algorithm in Mitigating GNSS Errors
- (2)
- Validation of the Effectiveness of the NRBO-FMD Algorithm in Removing High-Frequency Noise from ACC Data
- (3)
- Validation of the Effectiveness of the NRBO-FMD-ARKF Algorithm in GNSS and ACC Data Fusion
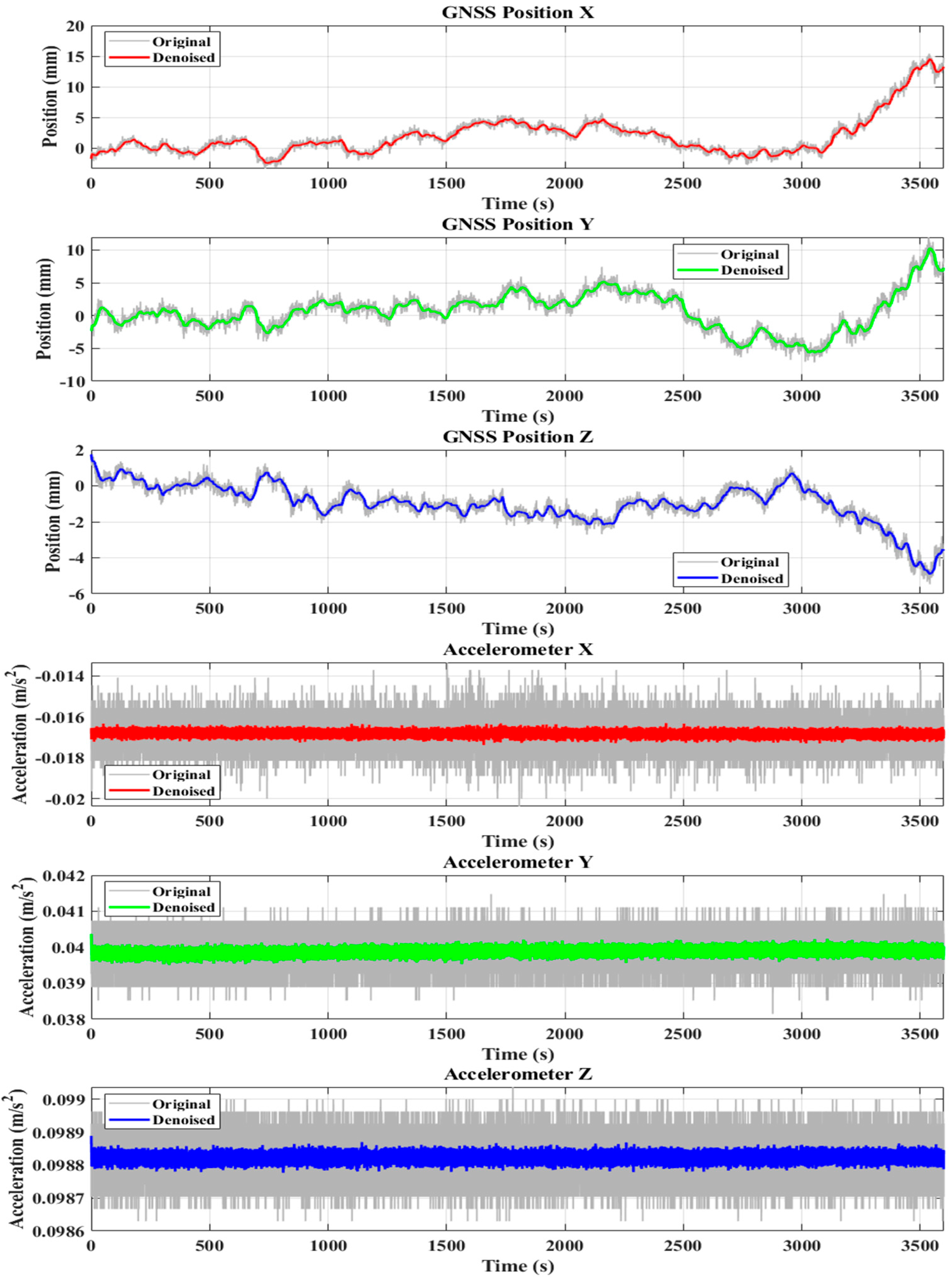
4. Experimental Analysis
5. Conclusions
- The NRBO-FMD algorithm demonstrated excellent performance in suppressing noise from both GNSS and accelerometer data. For GNSS data, the RMSE of the 100 s dataset decreased to 0.0007, and the SNR improved by 3.0186 dB. For the 200 s dataset, the RMSE reduced to 0.0010, with a 5.9980 dB improvement in SNR. For accelerometer data, the RMSE of the 100 s dataset dropped to 0.0030, and for the 200 s dataset, it decreased to 0.0062, with a 4.1488 dB increase in SNR. These results indicate that the NRBO-FMD algorithm effectively processes various types of noise while retaining critical information.
- The NRBO-FMD-ARKF fusion algorithm showed excellent performance in displacement estimation. For the 100 s dataset, the RMSE was 0.0007, with both PESD and POSD values of 0.0010. For the 200 s dataset, the RMSE, PESD, and POSD were all 0.0019. These results show that the fused data maintain high accuracy over long observation periods and effectively suppress irregular error fluctuations.
- In practical applications, the algorithm successfully fused 1 Hz GNSS data and 100 Hz accelerometer data, overcoming the limitations of a single sensor and providing more precise displacement measurements. The fusion results showed an RMSE of 0.003618 m, with PESD of 0.00257 m and POSD of 0.00476 m, demonstrating good performance in both accuracy and stability. Spectral analysis results showed that the fused displacement data more comprehensively reflected the building’s dynamic response characteristics, including multiple major frequency components ranging from 0.003 Hz to 0.314 Hz. This assists in identifying the building’s natural frequency, tracking structural stiffness changes, and detecting potential structural performance degradation early.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q. Inclination and acceleration data fusion for two-dimensional dynamic displacements and mode shapes identification of super high-rise buildings considering time delay. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 223, 111938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q. GNSS and accelerometer data fusion by variational Bayesian adaptive multi-rate Kalman filtering for dynamic displacement estimation of super high-rise buildings. Eng. Struct. 2025, 325, 119396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, Y.; Siringoringo, D.M.; Ikeda, Y.; Nagayama, T.; Mizutani, T. Research and Implementations of Structural Monitoring for Bridges and Buildings in Japan. Engineering 2019, 5, 1093–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Shahbazi, Y.; Kashavar, M.M.; Fotouhi, M.; Pedrammehr, S. Advanced Predictive Structural Health Monitoring in High-Rise Buildings Using Recurrent Neural Networks. Buildings 2014, 14, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Hao, G.; Zhu, S. Deformation Monitoring of High-Rise Building Clusters: Acquiring Deformation Coefficients by Combining Satellite Imagery and Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2024, 2024, 2326106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Qiu, F.; Xu, G.; Tianyi, S.; Kareem, A. Contribution of the second mode to wind-induced response of prismatic tall buildings. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, X.; Lu, X.; Ye, L. Influence of soil–structure interaction on seismic collapse resistance of super-tall buildings. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2014, 6, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhang, J.W.; Li, Q.S. Dynamic characteristics and wind-induced responses of a super-tall building during typhoons. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 121, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ni, Y.-Q.; Zhu, H. Deformation monitoring of a super-tall structure using real-time strain data. Eng. Struct. 2014, 67, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Dan, D.; Cheng, W.; Xia, Y. Real-time dynamic displacement monitoring with double integration of acceleration based on recursive least squares method. Measurement 2019, 141, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, T. High precision deformation monitoring with integrated GNSS and ground range observations in harsh environment. Measurement 2022, 204, 112179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Tao, T.; Wu, D.; Chen, R. A Review of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)-Based Dynamic Monitoring Technologies for Structural Health Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ren, Y.; He, S.; Gao, Z.; Li, B.; Song, J. A review of methods and applications in structural health monitoring (SHM) for bridges. Measurement 2025, 245, 116575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.S.; Xu, Y.L.; Ding, X.L.; Dai, W.J. An integrated GPS–accelerometer data processing technique for structural deformation monitoring. J. Geod. 2006, 80, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S. PLL bandwidth and noise in 100 Hz GPS measurements. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Sieradzki, R.; Rapinski, J.; Tomaszewski, D.; Stępniak, K.; Geng, J.; Li, G. Integrating low-cost GNSS and MEMS accelerometer for precise dynamic displacement monitoring. Measurement 2025, 242, 115798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajihan, S.A.V.; Chow, R.; Mechitov, K.; Fu, Y.; Hoang, T.; Spencer, B.F. Development of Synchronized High-Sensitivity Wireless Accelerometer for Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y. Displacement reconstruction from measured accelerations and accuracy control of integration based on a low-frequency attenuation algorithm. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 133, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Yang, W.; Luo, H.; Li, B. Application of Stabilized Numerical Integration Method in Acceleration Sensor Data Processing. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8194–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Choi, J.; Sohn, H. Multi-point structural displacement estimation and modal identification by combining a single-point camera and multi-point accelerometers. Measurement 2025, 244, 116578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Usman, M.; Toor, M.H.Y.; Hussaini, A.Q. Advancing structural health monitoring: A vibration-based IoT approach for remote real-time systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 365, 114863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Ge, L.; Fan, X.; Ge, C.; Ma, J. Dual straight-wing FBG accelerometer for low-frequency vibration measurement. Opt. Commun. 2024, 563, 130590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Schaufler, S.; Branzanti, M.; Chen, J. Assessing the benefits of Galileo to high-precision GNSS positioning—RTK, PPP and post-processing. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4916–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zha, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, B. Recent advances and perspectives in GNSS PPP-RTK. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Du, H.; Xue, S.; Ma, Z. Recent advances in data mining and machine learning for enhanced building energy management. Energy 2024, 307, 132636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liang, J.; Zhu, F. A comparative review on multi-modal sensors fusion based on deep learning. Signal Process. 2023, 213, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Lin, K.; Zhao, Z. Credibility-based multi-sensor fusion for non-Gaussian conversion error mitigation. Inf. Fusion 2025, 115, 102704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z. Interacting multiple model adaptive robust Kalman filter for process and measurement modeling errors simultaneously. Signal Process. 2025, 227, 109743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revach, G.; Shlezinger, N.; Ni, X.; Escoriza, L.A.; Sloun, R.J.G.; Eldar, Y.C. KalmanNet: Neural Network Aided Kalman Filtering for Partially Known Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1532–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yin, J. The Influence of Aeroelastic Effects on Wind Load and Wind-Induced Response of a Super-Tall Building: An Experimental Study. Buildings 2023, 13, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Liang, C.; Zhao, D. Dynamic-response characteristics and deformation evolution of loess slopes under seismic loads. Eng. Geol. 2020, 267, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.W.; Wu, M. Multi-rate Kalman filtering for the combination of GPS and accelerometry. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Brownjohn, J.M.W.; Hester, D.; Koo, K.Y. Long-span bridges: Enhanced data fusion of GPS displacement and deck accelerations. Eng. Struct. 2017, 147, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Ding, X.; Xu, Y.L.; Yu, W. Real-time outlier detection in integrated GNSS and accelerometer structural health monitoring systems based on a robust multi-rate Kalman filter. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Ding, X.; Xu, Y.L.; Yu, W. Correction of misalignment errors in the integrated GNSS and accelerometer system for structural displacement monitoring. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2023, 2023, 4919151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, G. GNSS/accelerometer integrated deformation monitoring algorithm based on sensors adaptive noise modeling. Measurement 2023, 218, 113179. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Choi, J.; Chung, J.; Koo, G.; Bae, I.H.; Sohn, H. Structural displacement estimation through multi-rate fusion of accelerometer and RTK-GPS displacement and velocity measurements. Measurement 2018, 130, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, R.; Premkumar, M.; Jangir, P. Newton-Raphson-based optimizer: A new population-based metaheuristic algorithm for continuous optimization problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 128, 107532. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ni, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Yang, N.; Wang, G. Neuro-enhanced fractional hysteresis modeling and identification by modified Newton-Raphson optimizer. Appl. Math. Model. 2025, 140, 115865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zou, J.; Yang, S.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y. A particle swarm algorithm based on the dual search strategy for dynamic multi-objective optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 83, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaci, S. A New Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD) Denoising Method for Seismic Signals. Energy Procedia 2016, 97, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, Z.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z. Noise-robust adaptive feature mode decomposition method for accurate feature extraction in rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 211, 111213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.F.; Tsung, F.; Unsworth, P.J. Adaptive time–frequency decomposition for transient vibration monitoring of rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2004, 18, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, Z.; Hu, X.; He, Z. High-sensitivity dual-FBG acceleration sensor for low frequency vibration measurement. J. Opt. 2024, 53, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chermite, C.; Douiri, M.R. Differential evolution algorithm featuring novel mutation combined with Newton-Raphson method for enhanced photovoltaic parameter extraction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 326, 119468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, A.; Heidarinejad, M.; Stephens, B.; Mirjalili, B. Equilibrium optimizer: A novel optimization algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 191, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezcan, J.; Marin-Artieda, C.C. Acceleration-to-displacement conversion as a single time-domain convolution operation. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2023, 185, 103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Du, Y. A novel robust adaptive Kalman filter with application to urban vehicle integrated navigation systems. Measurement 2024, 236, 114844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, B. Accelerometer-assisted computer vision data fusion framework for structural dynamic displacement reconstruction. Measurement 2025, 242, 116021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Tian, D.; Chen, C.; Xiao, X.; Wang, L.; Wen, Z.; Yang, M.; Zou, G. Residual neural network with spatiotemporal attention integrated with temporal self-attention based on long short-term memory network for air pollutant concentration prediction. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 329, 120531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, B. Unraveling nonlinear effects of environment features on green view index using multiple data sources and explainable machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, G.; Magnus, J.R.; Peracchi, F. Sampling properties of the Bayesian posterior mean with an application to WALS estimation. J. Econom. 2022, 230, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


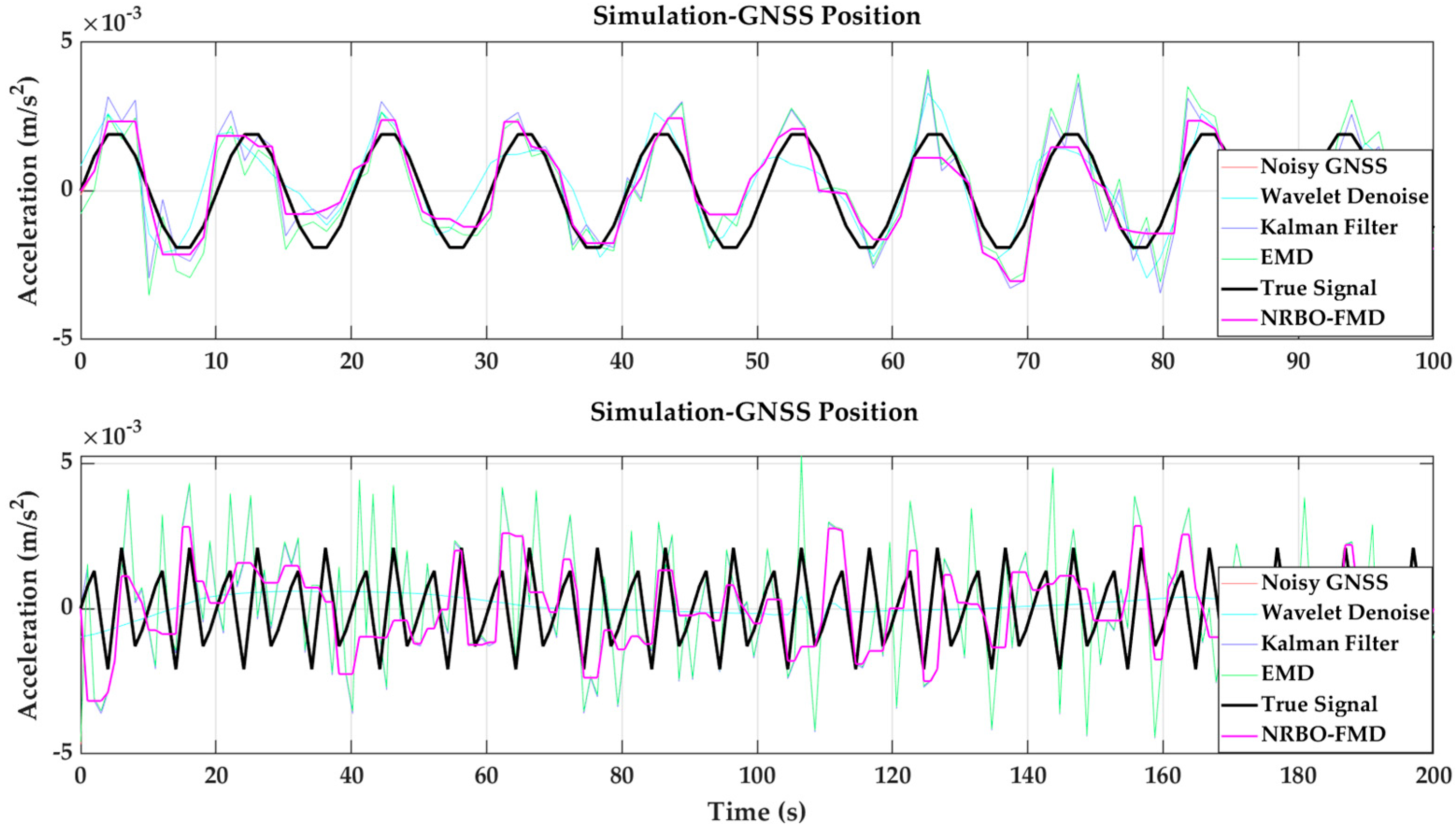
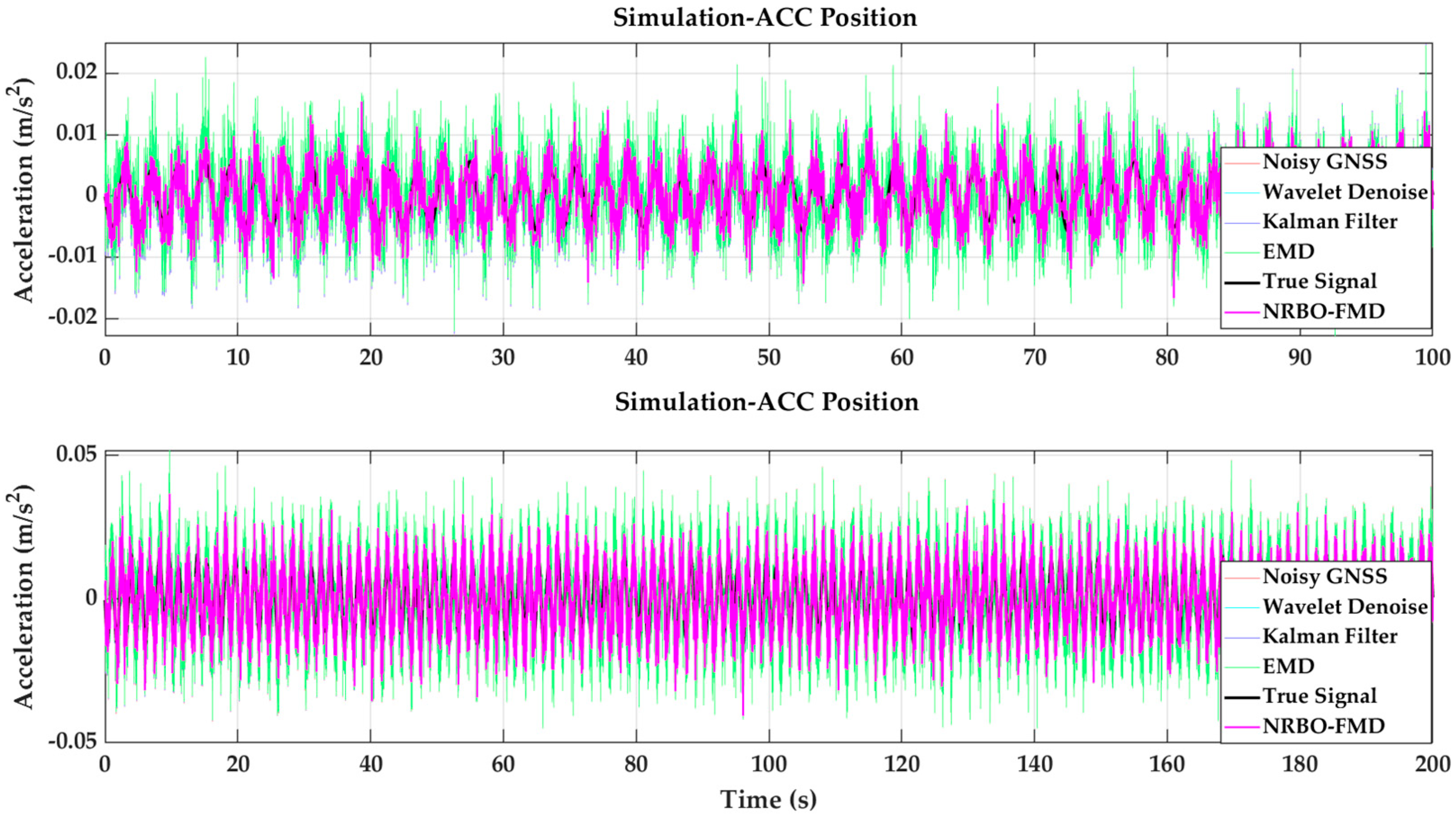
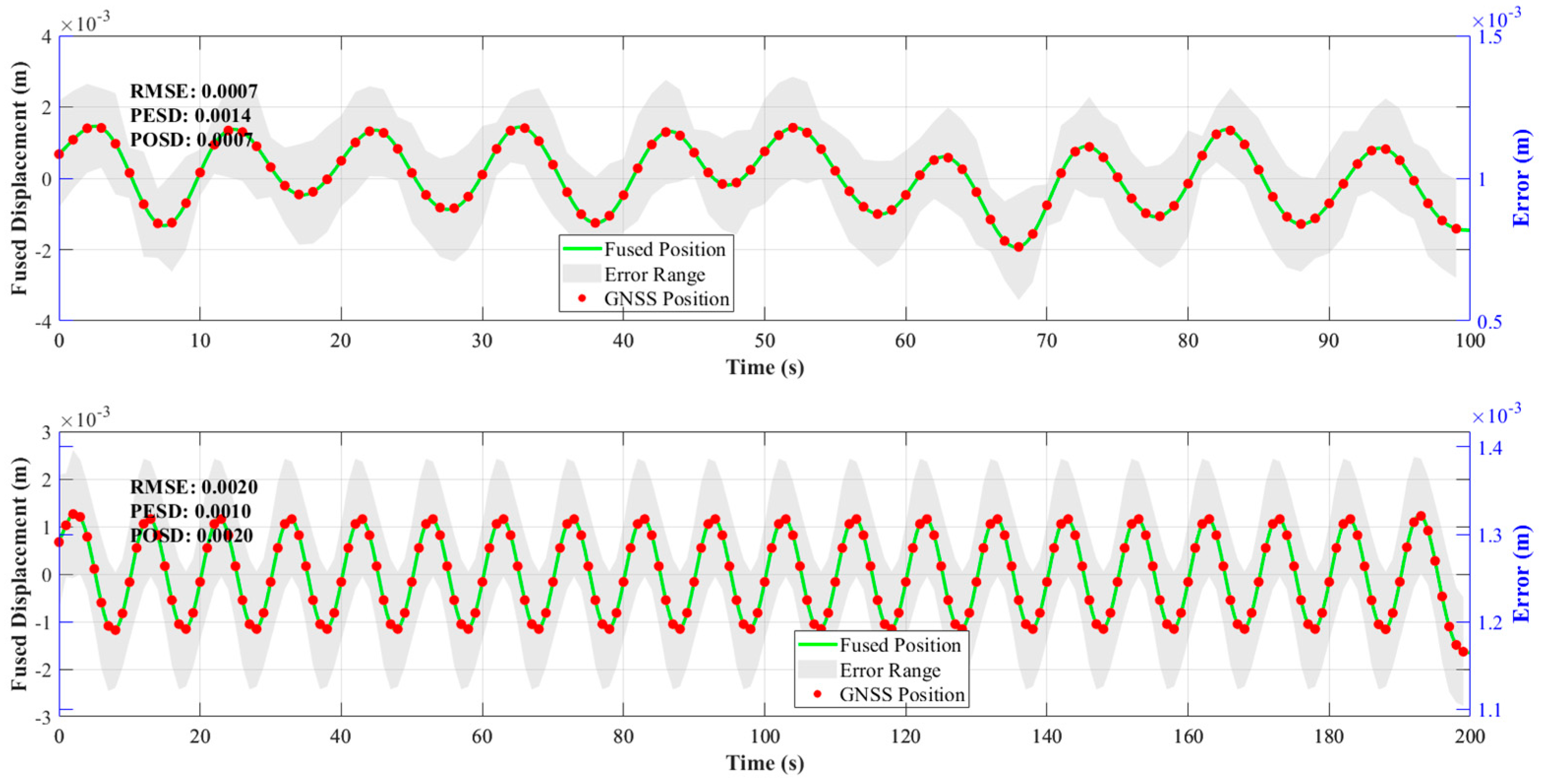
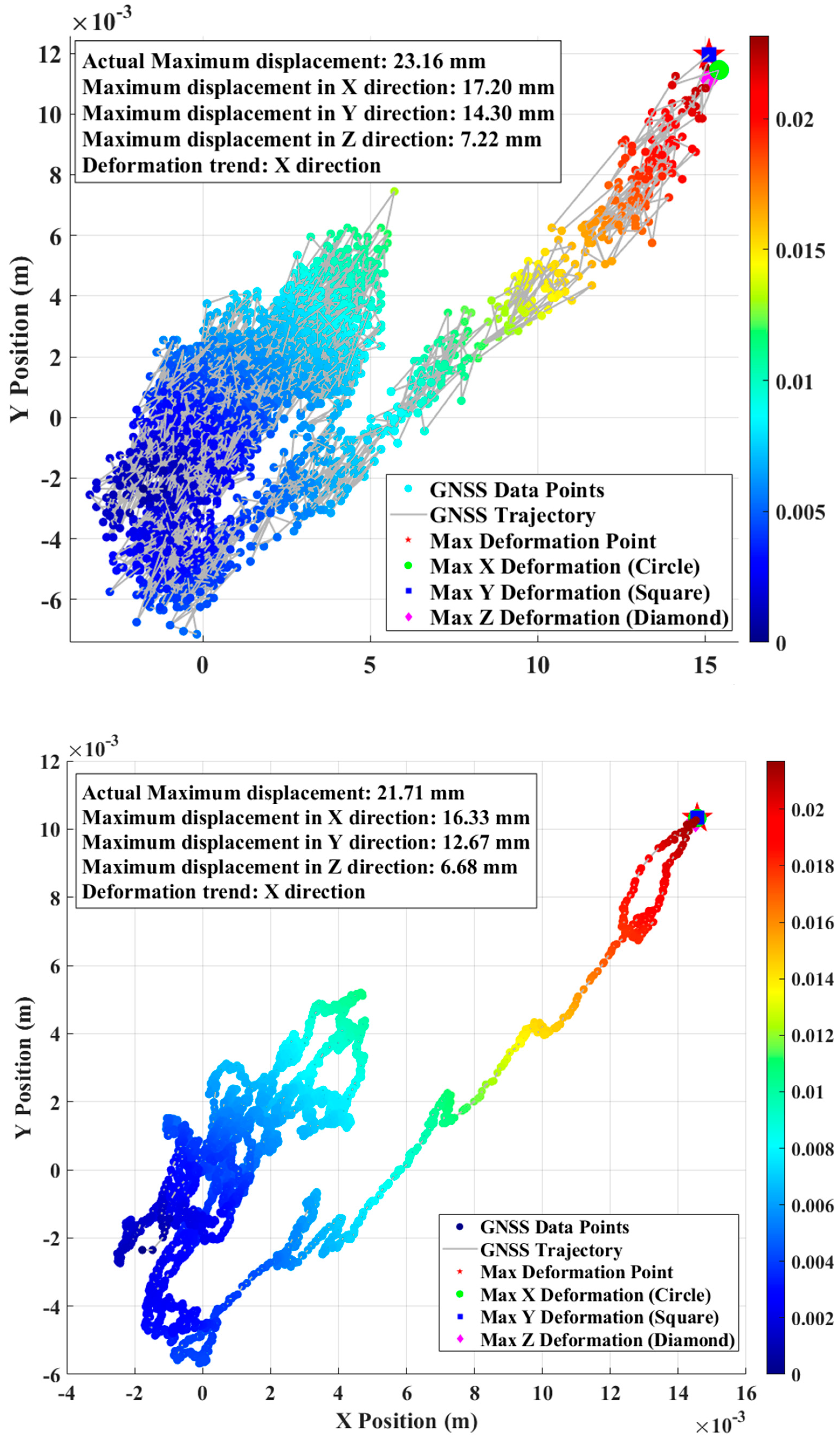
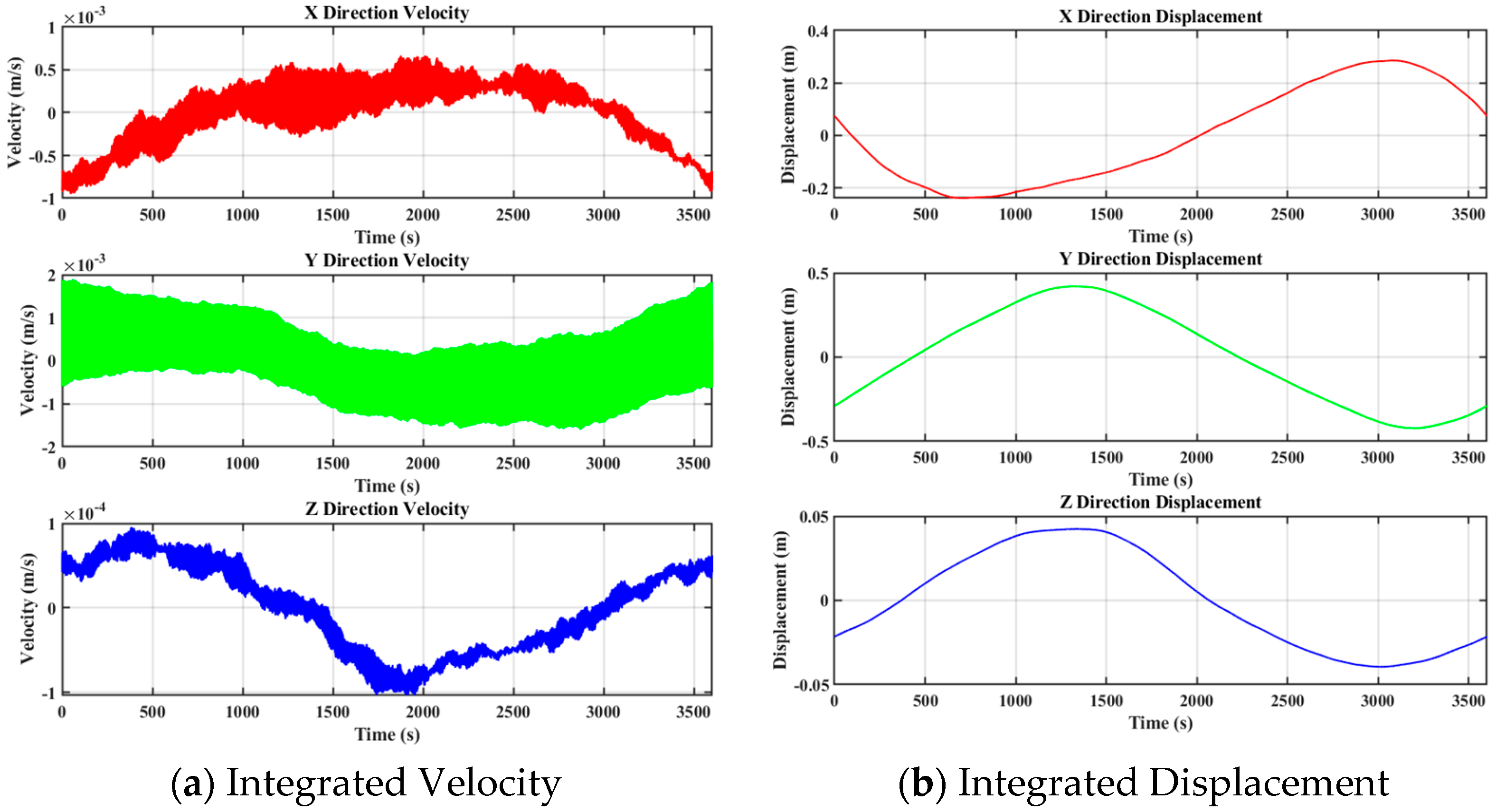

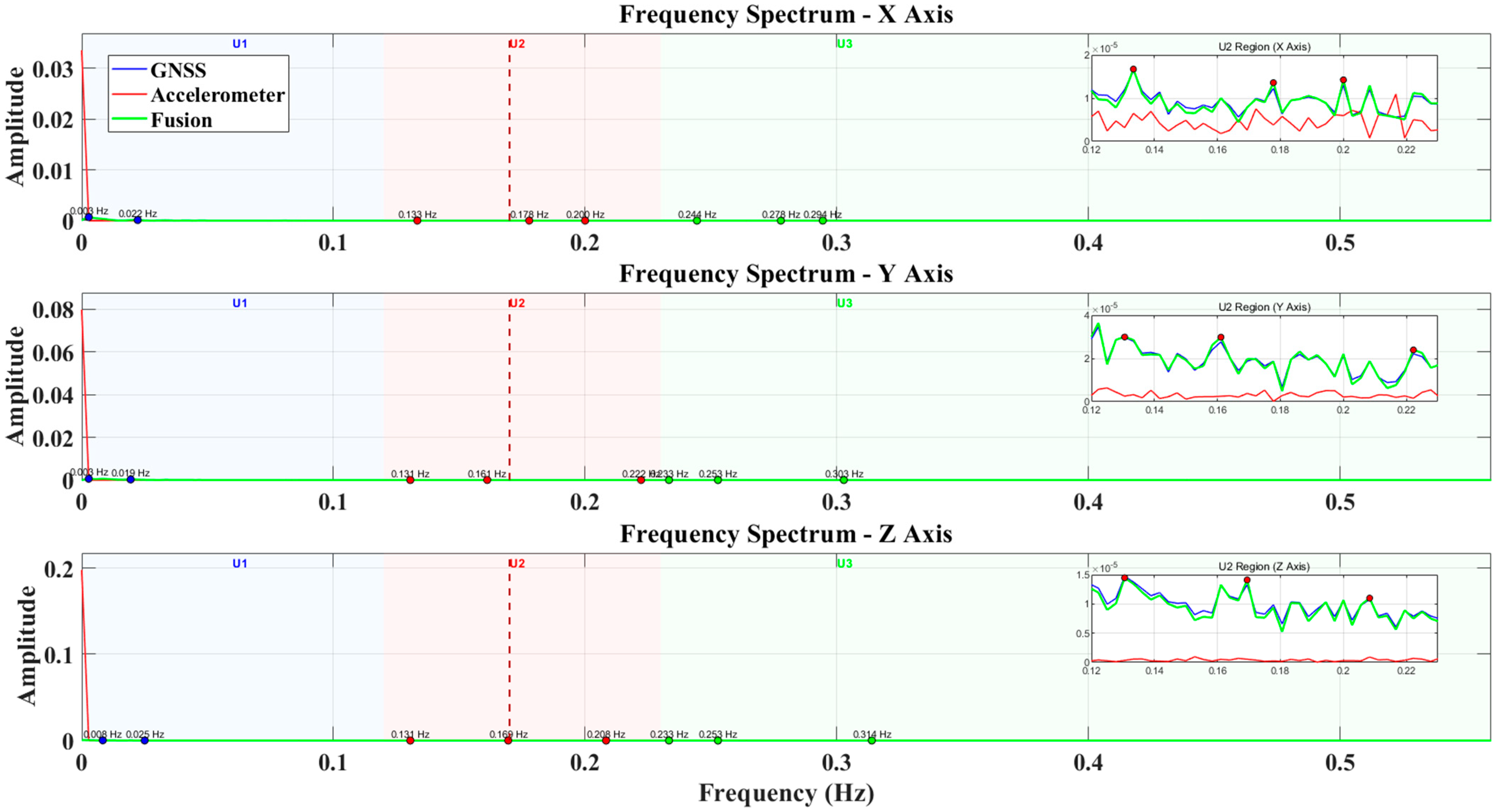
| Dataset | Amplitude (mm) | Frequency (Hz) | ) | Simulation Duration (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | b = 20, h = 5 | f1 = 0.1, f2 = 0.5 | 0.005 m/s2, 0.001 m | 100 |
| 2 | b = 15, h = 7 | f1 = 0.2, f2 = 0.07 | 0.02 m/s2, 0.01 m | 200 |
| Equipment | Performance | |
|---|---|---|
| GNSS | Signal tracking | BDS: B1/B2/B3; GPS: L1/L2/L5; GLONASS: L1/L2; GALILEO: E1/E5a/E5b; QZSS: L1/L5; |
| RTK(RMS) | Horizontal: ±8 mm + 1 ppm; Vertical: ±15 mm + 1 ppm | |
| Updating frequency | 1 Hz | |
| Accelerometer | Measurement range | 6 g |
| Noise density | 37 μg/ | |
| Offset error | 1.15 mg | |
| Linearity error | 1 mg | |
| Initial bias error (one year) | 10 mg | |
| Metric | GNSS Displacement/Accelerometer (Before) | Fused Displacement (After) |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE (m) | 0.00515 | 0.00362 |
| PESD (m) | 0.00428 | 0.00257 |
| POSD (m) | 0.00673 | 0.00476 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, X.; Han, H.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, L. Dynamic Deformation Analysis of Super High-Rise Buildings Based on GNSS and Accelerometer Fusion. Sensors 2025, 25, 2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092659
Xiao X, Han H, Wang J, Li D, Chen C, Wang L. Dynamic Deformation Analysis of Super High-Rise Buildings Based on GNSS and Accelerometer Fusion. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092659
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Xingxing, Houzeng Han, Jian Wang, Dong Li, Cai Chen, and Lei Wang. 2025. "Dynamic Deformation Analysis of Super High-Rise Buildings Based on GNSS and Accelerometer Fusion" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092659
APA StyleXiao, X., Han, H., Wang, J., Li, D., Chen, C., & Wang, L. (2025). Dynamic Deformation Analysis of Super High-Rise Buildings Based on GNSS and Accelerometer Fusion. Sensors, 25(9), 2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092659






