Characterization of a Single-Capture Bright-Field and Off-Axis Digital Holographic Microscope for Biological Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
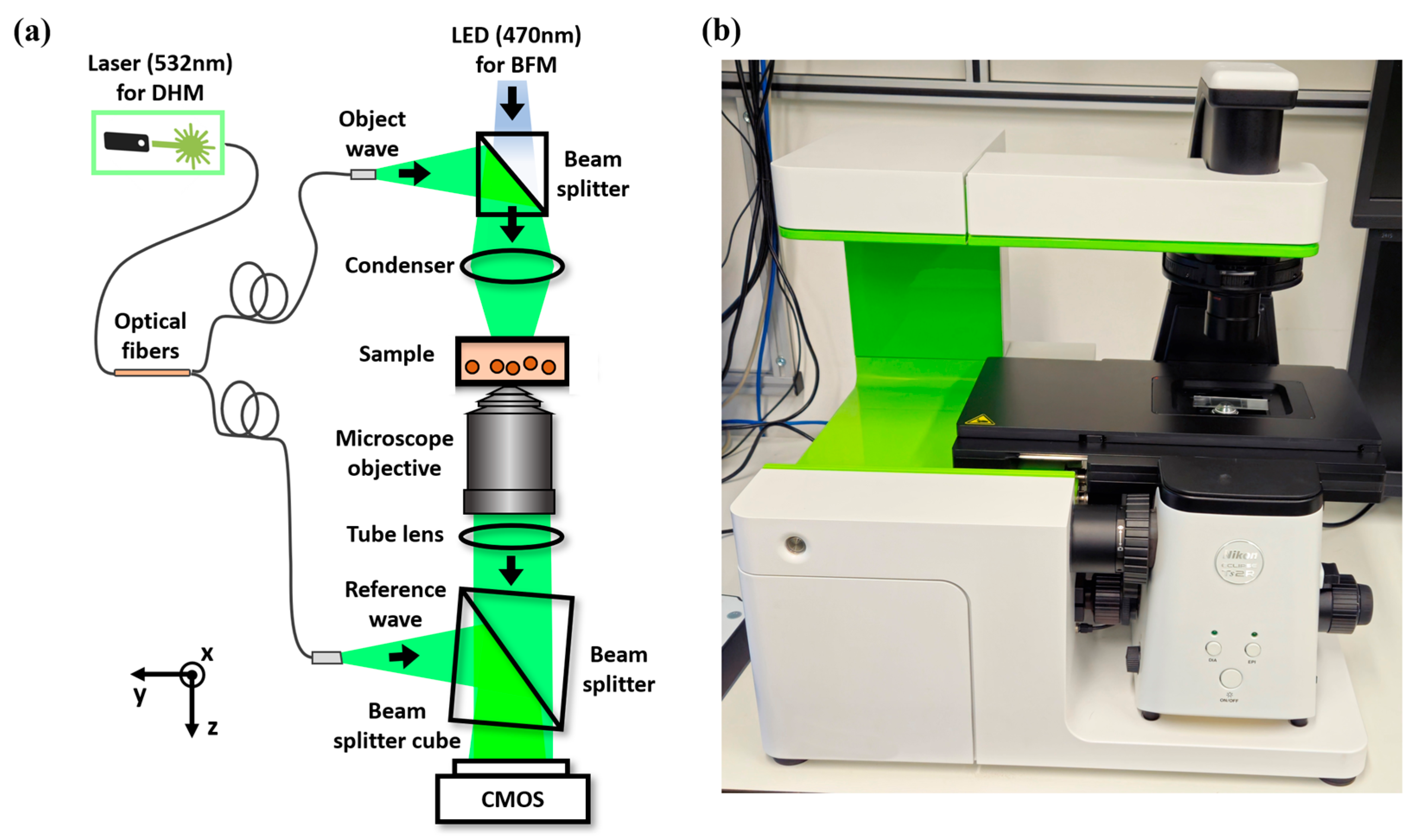
2.1. Multimodal Microscopy System
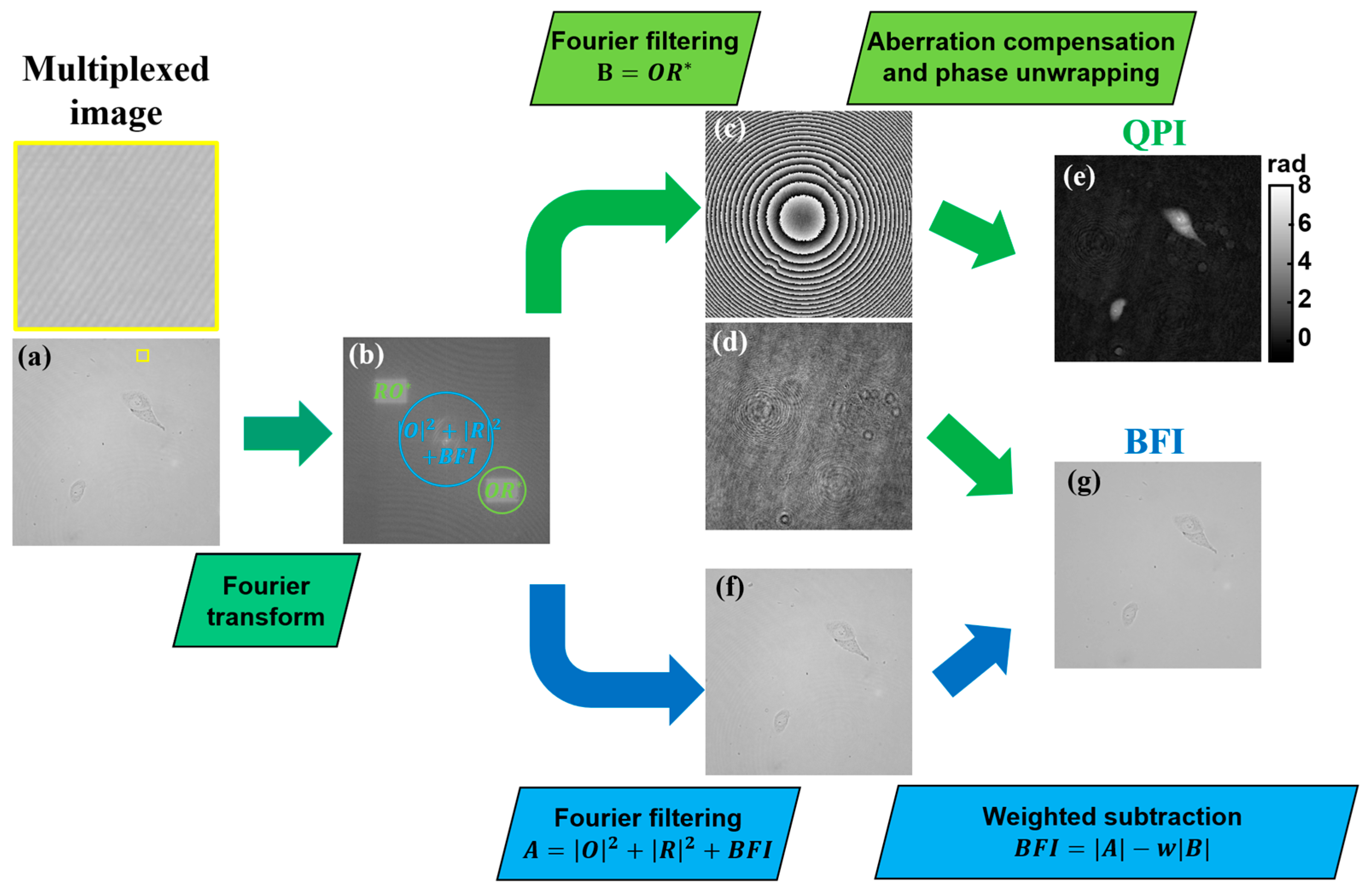
2.2. Multimodal Image Recovery
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Illumination Conditions
2.5. Microfluidic System
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Multimodal Imaging Characterization
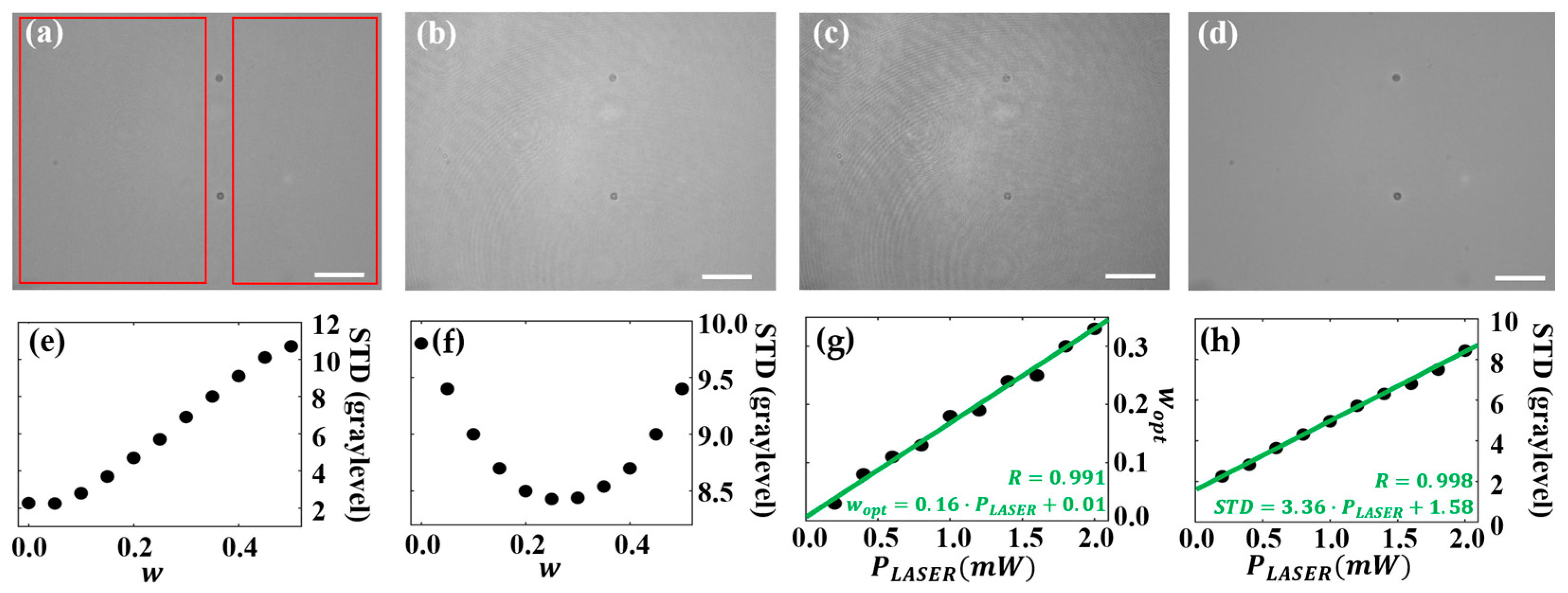
3.1.1. Influence of the Weighting Factor in the Recovered BF Image
3.1.2. Influence of Laser Light Emission Power
3.1.3. Influence of LED Light Emission Power
3.2. Multimodal Bright-Field and DHM-Based QPI of Adherent Cells
3.3. Multimodal Bright-Field and DHM-Based QPI of Cells in Flow
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stephens, D.J.; Allan, V.J. Light microscopy techniques for live cell imaging. Science 2003, 300, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zernike, F. Phase contrast, a new method for the microscopic observation of transparent objects. Physica 1942, 9, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.B.; Davidson, M.W. Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy and Modulation Contrast Microscopy. In Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 173–197. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K. Digital Holographic Microscopy. Principles, Techniques, and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.K.; Depeursinge, C.; Popescu, G. Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaz, B.; Marquet, P.; Cuche, E.; Emery, Y.; Depeursinge, C.; Magistretti, P.J. Measurement of the integral refractive index and dynamic cell morphometry of living cells with digital holographic microscopy. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 9361–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, T.; Quan, X.; Otani, R.; Takaki, Y.; Matoba, O. Digital holography and its multidimensional imaging applications: A review. Microscopy 2018, 67, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K. Principles and techniques of digital holographic microscopy. SPIE Rev. 2010, 1, 018005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquet, P.; Rappaz, B.; Magistretti, P.J.; Cuche, E.; Emery, Y.; Colomb, T.; Depeursinge, C. Digital holographic microscopy: A noninvasive contrast imaging technique allowing quantitative visualization of living cells with subwavelength axial accuracy. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, G. Quantitative Phase Imaging of Cells and Tissues; McGraw-Hill: Whitby, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Colomb, T.; Pavillon, N.; Kühn, J.; Cuche, E.; Depeursinge, C.; Emery, Y. Extended depth-of-focus by digital holographic microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 1840–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrecano, M.; Paturzo, M.; Ferraro, P. Extended focus imaging in digital holographic microscopy: A review. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 112317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hong, J.; Liu, C.; Kim, M.K. Review of digital holographic microscopy for three-dimensional profiling and tracking. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 112306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzerdjeb, N.; Garbar, C.; Camparo, P.; Sevestre, H. Digital holographic microscopy as screening tool for cervical cancer preliminary study. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016, 124, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Schich, Z.; Mölder, A.L.; Wingren, A.G. Quantitative Phase Imaging for Label-Free Analysis of Cancer Cells—Focus on Digital Holographic Microscopy. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, V.K.; Nguyen, T.C.; Chung, B.M.; Nehmetallah, G.; Raub, C.B. Quantitative assessment of cancer cell morphology and motility using telecentric digital holographic microscopy and machine learning. Cytom. Part. A 2018, 93, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vom Werth, K.L.; Kemper, B.; Kampmeier, S.; Mellmann, A. Application of Digital Holographic Microscopy to Analyze Changes in T-Cell Morphology in Response to Bacterial Challenge. Cells 2023, 12, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.; Anand, A.; Andemariam, B.; Javidi, B. Deep learning-based cell identification and disease diagnosis using spatio-temporal cellular dynamics in compact digital holographic microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 4491–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimovich, A.; Witte, R.; Andriasyan, V.; Georgi, F.; Greber, U.F. Label-Free Digital Holo-tomographic Microscopy Reveals Virus-Induced Cytopathic Effects in Live Cells. mSphere 2018, 3, e00599-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, J.; Shaffer, E.; Mena, J.; Breton, B.; Parent, J.; Rappaz, B.; Chambon, M.; Emery, Y.; Magistretti, P.; Depeursinge, C.; et al. Label-Free Cytotoxicity Screening Assay by Digital Holographic Microscopy. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2013, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, K.M.; Marzi, A.; Barroso, Á.; Ketelhut, S.; Kemper, B.; Schnekenburger, J. Label-Free Digital Holographic Microscopy for In Vitro Cytotoxic Effect Quantification of Organic Nanoparticles. Cells 2022, 11, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnano, M.; Memmolo, P.; Miccio, L.; Grilli, S.; Merola, F.; Calabuig, A.; Bramanti, A.; Mazzon, E.; Ferraro, P. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of cadmium by label-free holographic microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201800099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquet, P.; Depeursinge, C.; Magistretti, P.J. Review of quantitative phase-digital holographic microscopy: Promising novel imaging technique to resolve neuronal network activity and identify cellular biomarkers of psychiatric disorders. Neurophotonics 2014, 1, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, B.; Bauwens, A.; Bettenworth, D.; Götte, M.; Greve, B.; Kastl, L.; Ketelhut, S.; Lenz, P.; Mues, S.; Schnekenburger, J.; et al. Label-Free Quantitative In Vitro Live Cell Imaging with Digital Holographic Microscopy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Pradeep, S.; Judson-Torres, R.L.; Reed, J.; Teitell, M.A.; Zangle, T.A. Quantitative Phase Imaging: Recent Advances and Expanding Potential in Biomedicine. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11516–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacace, T.; Bianco, V.; Ferraro, P. Quantitative phase imaging trends in biomedical applications. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 135, 106188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, H.; Sridharan, S.; Mir, M.; Ma, L.; Min, E.; Jung, W.; Popescu, G. Quantitative phase imaging for medical diagnosis. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 177–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Cao, L. Quantitative phase imaging based on holography: Trends and new perspectives. Light. Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavillon, N.; Benke, A.; Boss, D.; Moratal, C.; Kühn, J.; Jourdain, P.; Depeursinge, C.; Magistretti, P.J.; Marquet, P. Cell morphology and intracellular ionic homeostasis explored with a multimodal approach combining epifluorescence and digital holographic microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2010, 3, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.K.; Popescu, G.; Badizadegan, K.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S.; Park, Y.K.; Badizadegan, K.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Diffraction phase and fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 8263–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Eldridge, W.J.; Wax, A.; Izatt, J.A. Spatial frequency-domain multiplexed microscopy for simultaneous, single-camera, one-shot, fluorescent, and quantitative-phase imaging. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 4839–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygate, Y.N.; Singh, G.; Barnea, I.; Shaked, N.T. Simultaneous off-axis multiplexed holography and regular fluorescence microscopy of biological cells. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavillon, N.; Hobro, A.J.; Akira, S.; Smith, N.I. Noninvasive detection of macrophage activation with single-cell resolution through machine learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 201711872-E2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Eldridge, W.J.; Wax, A.; Izatt, J.A. Structured illumination multimodal 3D-resolved quantitative phase and fluorescence sub-diffraction microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2496–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea, I.; Luria, L.; Girsault, A.; Dabah, O.; Dudaie, M.; Mirsky, S.K.; Merkel, D.; Shaked, N.T. Analyzing Blood Cells of High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome Patients Using Interferometric Phase Microscopy and Fluorescent Flow Cytometry. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McReynolds, N.; Cooke, F.G.M.; Chen, M.; Powis, S.J.; Dholakia, K. Multimodal discrimination of immune cells using a combination of Raman spectroscopy and digital holographic microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Managò, S.; Ferrara, M.A.; Napolitano, M.; Coppola, G.; De Luca, A.C. Combined Raman Spectroscopy and Digital Holographic Microscopy for Sperm Cell Quality Analysis. J. Spectrosc. 2017, 2017, 9876063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Nitta, K.; Matoba, O.; Xia, P.; Awatsuji, Y. Phase and fluorescence imaging by combination of digital holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Rev. 2015, 22, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Kumar, M.; Rajput, S.K.; Tamada, Y.; Awatsuji, Y.; Matoba, O. Multimodal Microscopy: Fast Acquisition of Quantitative Phase and Fluorescence Imaging in 3D Space. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2021, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Quan, X.; Awatsuji, Y.; Tamada, Y.; Matoba, O. Digital Holographic Multimodal Cross-Sectional Fluorescence and Quantitative Phase Imaging System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, C.E.; Dierker, C.; Schmidt, L.; Przibilla, S.; von Bally, G.; Kemper, B.; Schnekenburger, J. Contrast-enhanced digital holographic imaging of cellular structures by manipulating the intracellular refractive index. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 041509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettenworth, D.; Lenz, P.; Krausewitz, P.; Brückner, M.; Ketelhut, S.; Domagk, D.; Kemper, B. Quantitative Stain-Free and Continuous Multimodal Monitoring of Wound Healing In Vitro with Digital Holographic Microscopy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo-Bueno, J.Á.; Barroso, Á.; Ketelhut, S.; Schnekenburger, J.; Mico, V.; Kemper, B. Single capture bright field and off-axis digital holographic microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picart, P. New Techniques in Digital Holography; ISTE Press: London, UK; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Picazo-Bueno, J.Á.; Cojoc, D.; Iseppon, F.; Torre, V.; Mico, V. Single-shot, dual-mode, water-immersion microscopy platform for biological applications. Appl. Opt. 2017, 57, A242–A249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.; Dardikman, G.; Mirsky, S.K.; Turko, N.A.; Shaked, N.T. Six-pack off-axis holography. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4611–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsky, S.K.; Barnea, I.; Shaked, N.T. Dynamic Tomographic Phase Microscopy by Double Six-Pack Holography. ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, B.; Carl, D.; Höink, A.; von Bally, G.; Bredebusch, I.; Schnekenburger, J. Modular digital holographic microscopy system for marker free quantitative phase contrast imaging of living cells. In Proceedings of the SPIE Photonics Europe, Strasbourg, France, 3–7 April 2006; Volume 6191, pp. 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Min, J.; Yao, B.; Ketelhut, S.; Engwer, C.; Greve, B.; Kemper, B. Simple and fast spectral domain algorithm for quantitative phase imaging of living cells with digital holographic microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Microparticles and Nanoparticles (Beads): PolyAn. Available online: https://www.poly-an.de/micro-nanoparticles (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zanini, L.; Zaltron, A.; Turato, E.; Zamboni, R.; Sada, C. Opto-Microfluidic Integration of the Bradford Protein Assay in Lithium Niobate Lab-on-a-Chip. Sensors 2022, 22, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamboni, R.; Gauthier-Manuel, L.; Zaltron, A.; Lucchetti, L.; Chauvet, M.; Sada, C. Opto-microfluidic coupling between optical waveguides and tilted microchannels in lithium niobate. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 28423–28436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics, 7th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Elsässer, H.P.; Lehr, U.; Agricola, B.; Kern, H.F. Establishment and characterisation of two cell lines with different grade of differentiation derived from one primary human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Virchows Arch. B 1992, 61, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, B.; Carl, D.; Schnekenburger, J.; Bredebusch, I.; Schäfer, M.; Domschke, W.; von Bally, G. Investigation of living pancreas tumor cells by digital holographic microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 034005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Chhaniwal, V.; Javidi, B. Tutorial: Common path self-referencing digital holographic microscopy. APL Photonics 2018, 3, 071101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmersmann, C.; Stürwald, S.; Kemper, B.; Langehanenberg, P.; Von Bally, G. Phase noise optimization in temporal phase-shifting digital holography with partial coherence light sources and its application in quantitative cell imaging. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, A.; Eder, K.M.; Barroso, Á.; Kemper, B.; Schnekenburger, J. Quantitative Phase Imaging as Sensitive Screening Method for Nanoparticle-Induced Cytotoxicity Assessment. Cells 2024, 13, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo-Bueno, J.Á.; Barroso, Á.; Ketelhut, S.; Micó, V.; Schenekenburger, J.; Kemper, B. Multimodal imaging flow cytometry based on single capture bright field and digital holographic microscopy for the analysis of living cells. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optical Metrology, Munich, Germany, 26–29 June 2023; Volume 12622. [Google Scholar]
- Dardikman-Yoffe, G.; Mirsky, S.K.; Barnea, I.; Shaked, N.T. High-resolution 4-D acquisition of freely swimming human sperm cells without staining. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugonnet, H.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, M.; Shin, S.; Hruban, R.H.; Hong, S.-M.; Park, Y. Multiscale label-free volumetric holographic histopathology of thick-tissue slides with subcellular resolution. Adv. Photonics 2021, 3, 026004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemczonok, M.; Kuś, A.; Wasylczyk, P.; Kujawińska, M. 3D-printed biological cell phantom for testing 3D quantitative phase imaging systems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Barroso, Á.; Ketelhut, S.; Schnekenburger, J.; Kemper, B.; Picazo-Bueno, J.Á. Characterization of a Single-Capture Bright-Field and Off-Axis Digital Holographic Microscope for Biological Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092675
Kim J, Barroso Á, Ketelhut S, Schnekenburger J, Kemper B, Picazo-Bueno JÁ. Characterization of a Single-Capture Bright-Field and Off-Axis Digital Holographic Microscope for Biological Applications. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092675
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jian, Álvaro Barroso, Steffi Ketelhut, Jürgen Schnekenburger, Björn Kemper, and José Ángel Picazo-Bueno. 2025. "Characterization of a Single-Capture Bright-Field and Off-Axis Digital Holographic Microscope for Biological Applications" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092675
APA StyleKim, J., Barroso, Á., Ketelhut, S., Schnekenburger, J., Kemper, B., & Picazo-Bueno, J. Á. (2025). Characterization of a Single-Capture Bright-Field and Off-Axis Digital Holographic Microscope for Biological Applications. Sensors, 25(9), 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092675






