3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
The melting point values of the prepared compounds were recorded on a Thermocouple digital melting point apparatus and are uncorrected. Their IR spectra were recorded as powders on a Bruker VERTEX 70 FT-IR Spectrometer (Bruker Optics, Billerica, MA, USA) with a diamond ATR (attenuated total reflectance) accessory by using the thin-film method. Merck kieselgel 60 (0.063–0.200 mm) (Merck KGaA, Frankfurt, Germany) was used as stationary phase for column chromatography. The
1H-NMR and
13C-NMR spectra were obtained as DMSO-
d6 solutions using Agilent 300 MHz NMR (Agilent Technologies, Oxford, UK) spectrometer and the chemical shifts are quoted relative to the TMS peak. The high-resolution mass spectra were recorded at an ionization potential of 70 eV using Waters Synapt G2 Quadrupole Time-of-flight mass spectrometer (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA) at the University of Stellenbosch Central Analytical Facility (CAF). The synthesis and analytical data of compounds
1a–
d have been described before [
14].
3.2. Typical Procedure for the PdCl2-Mediated Heteroannulation of 1a–d
A stirred mixture of 1 (1 equiv.) and PdCl2 (0.2 equiv.) in acetonitrile (15 mL/mmol of 1) was heated at 80 °C under an argon atmosphere for 3 h. The mixture was evaporated to dryness on a rotary evaporator and the residue was dissolved in chloroform. The organic solvent was washed with brine and then dried over anhydrous MgSO4. The salt was filtered off and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by column chromatography on a silica gel using 10% EtOAc-hexane as eluent to afford 2 as a solid. Compounds 2a–d were prepared in this fashion.
1-(5-Bromo-2-phenyl-1H-indol-7-yl)ethanone (2a). A mixture of 1a (1.00 g, 3.18 mmol) and PdCl2 (0.11 g, 0.64 mmol) in acetonitrile (50 mL) afforded 2a as a solid (0.92 g, 92%), Rf 0.36, mp. 139–142 °C; νmax (ATR) 550, 596, 671, 750, 849, 961, 1043, 1163, 1230, 1251, 1322, 1360, 1448, 1490, 1516, 1595, 1650, 3436 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.71 (3H, s, CH3), 6.98 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.38 (1H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, 4′-H), 7.47 (2H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.89 (2H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 7.94 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.05 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 11.14 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.6, 99.5, 111.7, 122.1, 126.4, 127.4, 128.6, 128.9, 129.4, 131.3, 132.6, 134.0, 141.3, 199.2; HRMS (ES): found 314.0191. C16H13NO79Br+ requires 314.0181. Anal calcd for C16H12NOBr: C, 61.17; H, 3.85; N, 4.46. Found: C, 61.02; H, 3.79; N, 4.52.
1-[5-Bromo-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl]ethanone (2b). A mixture of 1b (1.00 g, 3.01 mmol) and PdCl2 (0.11 g, 0.60 mmol) in acetonitrile (50 mL) afforded 2b as a solid (0.84 g, 84%), Rf 0.35, mp. 171–173 °C; νmax (ATR) 549, 749, 786, 835, 925, 1006, 1043, 1162, 1231, 1251, 1321, 1360, 1449, 1491, 1578, 1595, 1650, 3436 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.69 (3H, s, CH3), 6.91 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.29 (2H, t, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.91–7.95 (3H, m, 4-H and 2′,6′-H), 8.01 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 11.19 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.6, 99.4, 111.7, 116.2 (d, 2JCF = 21.8 Hz), 122.2, 127.3, 128.0 (d, 4JCF = 3.5 Hz), 128.5, 128.8 (d, 3JCF = 8.0 Hz), 132.5, 134.0, 140.5, 162.2 (d, 1JCF = 243.9 Hz), 199.1; HRMS (ES) found 332.0090. C16H12NO79FBr+ requires 332.0086. Anal calcd for C16H11NOFBr: C, 57.85; H, 3.34; N, 4.22. Found: C, 57.79; H, 3.30; N, 4.12.
1-[5-Bromo-2-(3-chlorophenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl]ethanone (2c). A mixture of 1c (1.00 g, 2.87 mmol) and PdCl2 (0.10 g, 0.57 mmol) in acetonitrile (50 mL) afforded 2c as a solid (0.77 g, 77%), Rf 0.34, mp. 140–143 °C; νmax (ATR) 452, 542, 572, 673, 751, 785, 852, 878, 969, 1052, 1082, 1164, 1252, 1323, 1357, 1452, 1590, 1653, 3424 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.69 (3H, s, CH3), 7.04 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.38–7.49 (2H, m, 4′,5′-H), 7.82–7.86 (1H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 6′-H), 7.93 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.03–8.04 (2H, m, 2′-H and 6-H), 11.33 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.6, 100.7, 111.8, 122.4, 125.2, 126.2, 127.8, 128.4, 128.7, 131.0, 132.3, 133.4, 134.0, 134.1, 139.8, 198.9; HRMS (ES): found 347.9779. C16H12NO35Cl79Br+ requires 347.9791. Anal calcd for C16H11NOClBr: C, 55.12; H, 3.18; N, 4.02. Found: C, 55.10; H, 3.33; N, 3.89.
1-[5-Bromo-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl]ethanone (2d). A mixture of 1d (1.00 g, 2.91 mmol) and PdCl2 (0.10 g, 0.58 mmol) in acetonitrile (50 mL) afforded 2d as a solid (0.85 g, 85%), Rf = 0.27, mp. 140–142 °C; νmax (ATR) 550, 589, 749, 825, 925, 1028, 1162, 1181, 1253, 1290, 1321, 1361, 1451, 1497, 1578, 1654, 3433 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.69 (3H, s, CH3), 3.80 (3H, s, OCH3), 6.86 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.03 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.84 (2H, d, J 8.7 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.01 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 11.06 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.6, 55.7, 98.2, 111.6, 114.8, 121.9, 123.8, 126.8, 127.9, 128.2, 132.8, 133.9, 141.5, 160.0, 199.3; HRMS (ES) found 344.0289. C17H15NO279Br+ requires 344.0286. Anal calcd for C17H14NO2Br: C, 59.32; H, 4.10; N, 4.07. Found: C, 59.32; H, 3.87; N, 4.10.
3.3. Typical Procedure for the Synthesis of Oxime Derivatives 3a–d from 2a–d
A stirred mixture of 2 (1 equivalent), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (1.5 equivalent) and pyridine (1.5 equivalent) in ethanol (20 mL/mmol of 2) was heated at 80 °C for 5 h. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, quenched with an ice-cold water and then extracted with chloroform. The combined organic phases were washed with water and dried over anhydrous MgSO4. The salt was filtered off and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using 20% EtOAc-hexane as an eluent to afford the oxime derivative 3 as a solid. Products 3a–d were prepared in this fashion:
1-(5-Bromo-2-phenyl-1H-indol-7-yl)ethanone oxime (3a). A mixture of 2a (0.30 g, 0.95 mmol), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (0.10 g, 1.43 mmol) and pyridine (0.11 g, 1.43 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL) afforded 3a as a solid (0.28 g, 90%), Rf = 0.69, mp. 198–200 °C; νmax (ATR) 524, 542, 634, 679, 734, 763, 839, 989, 1093, 1172, 1261, 1298, 1331, 1368, 1448, 3269, 3438 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.30 (3H, s, CH3), 6.96 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.37 (1H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, 4′-H), 746–7.52 (3H, m, 6-H and 3′,5′-H), 7.78–7.81 (3H, m, 4-H and 2′,6′-H), 10.94 (1H, s, NH), 11.56 (1H, s, OH); 13C-NMR: 11.2, 99.3, 112.4, 121.7, 123.4, 123.8, 125.5, 128.7, 129.6, 131.3, 131.5, 132.5, 139.2, 154.1; HRMS (ES): found 329.0276. C16H14N2O79Br+ requires 329.0290.
1-(5-Bromo-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl)ethanone oxime (3b). A mixture of 2b (0.30 g, 0.90 mmol), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (0.09 g, 1.35 mmol) and pyridine (0.11 g, 1.35 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL) afforded 3b as a solid (0.27 g, 87%), Rf = 0.64, mp. 213–216 °C; νmax (ATR) 530, 595, 651, 680, 744, 764, 828, 846, 912, 984, 1091, 1159, 1230, 1332, 1366, 1428, 1464, 1501, 3258, 3432 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.30 (3H, s, CH3), 6.93 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.34 (2H, t, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.45 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 7.84–7.87 (2H, dd, J = 5.4 and 8.7 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 10.92 (1H, s, NH), 11.56 (1H, s, OH); 13C-NMR: 11.3, 99.3, 112.5, 116.5 (d, 2JCF = 21.8 Hz), 121.8, 123.4, 123.7, 127.7 (d, 3JCF = 9.1 Hz), 128.3 (d, 4JCF = 3.5 Hz), 131.3, 132.5, 138.4, 154.0, 162.4 (d, 1JCF = 243.9 Hz); HRMS (ES): found 347.0179. C16H13N2OF79Br+ requires 347.0195.
1-(5-Bromo-2-(3-chlorophenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl)ethanone oxime (3c). A mixture of 2c (0.30 g, 0.86 mmol), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (0.09 g, 1.29 mmol) and pyridine (0.10 g, 1.29 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL) afforded 3c as a solid (0.26 g, 82%), Rf = 0.63, mp. 204–206 °C; νmax (ATR) 454, 532, 631, 673, 742, 784, 847, 876, 947, 985, 1094. 1167, 1268, 1268, 1296, 1334, 1368, 1421, 1463, 3203, 3392 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.32 (3H, s, CH3), 7.09 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.44–7.55 (3H, m, 6-H and 4′,5′-H), 7.78–7.81 (2H, m, 4-H and 6′-H), 7.92 (1H, s Hz, 2′-H), 11.02 (1H, s, NH), 11.60 (1H, s, OH); 13C-NMR: 11.5, 100.5, 112.6, 122.1, 123.8, 123.9, 124.2, 125.1, 128.3, 131.1, 131.4, 132.7, 133.4, 134.4, 137.7, 153.8; HRMS (ES): found 362.9893. C16H13N2O35Cl79Br+ requires 362.9900.
1-(5-Bromo-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl)ethanone oxime (3d). A mixture of 2d (0.30 g, 0.87 mmol), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (0.09 g, 1.31 mmol) and pyridine (0.10 g, 1.31 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL) afforded 3d as a solid (0.25 g, 80%), Rf = 0.45, mp. 202–204 °C; νmax (ATR) 521, 585, 612, 653, 671, 755, 796, 826, 984, 1017, 1172, 1185, 1246, 1323, 1372, 1439, 1460, 1497, 3372, 3518 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.30 (3H, s, CH3), 3.80 (3H, s, OCH3), 6.80 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.04 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.42 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 7.70 (3H, m, 4-H and 2′,6′-H), 10.84 (1H, s, NH), 11.57 (1H, s, OH); 13C-NMR: 11.3, 55.7, 98.0, 112.3, 115.0, 121.4, 122.9, 123.4, 124.2, 126.9, 131.6, 132.2, 139.4, 154.2, 159.8; HRMS (ES): found 359.0293. C17H16N2O279Br+ requires 359.0395.
3.4. Typical Procedure for the Beckmann Rearrangement of 3a–d
A stirred mixture of 3 (1 equiv.) and TFA (1.2 equiv.) in acetonitrile (10 mL/mmol of 3) was heated at 80 °C for 2 h. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, quenched with ice-cold water and the product was extracted with chloroform (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4 and the salt was filtered off. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator and the residue was purified by column chromatography on a silica gel using 60% EtOAc-hexane as an eluent to afford 4. The following compounds were prepared in this fashion:
N-(5-Bromo-2-phenyl-1H-indol-7-yl)acetamide (4a). A mixture of 3a (0.20 g, 0.61 mmol) and TFA (0.08 g, 0.73 mmol) in acetonitrile (15 mL) afforded 4a as solid (0.16 g, 81%), Rf = 0.56, mp. 243–244 °C; νmax (ATR) 518, 562, 600, 688, 740, 760, 842, 998, 1184, 1273, 1315, 1404, 1425, 1455, 1530, 1623, 1651, 3267, 3319 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.19 (3H, s, CH3), 6.88 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.38 (1H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, 4′-H), 7.46–7.52 (3H, m, 4-H and 3′,5′-H), 7.82 (2H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 9.76 (1H, s, NH), 11.28 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.5, 99.5, 112.1, 115.5, 118.2, 125.5, 125.7, 127.3, 128.5, 129.5, 131.6, 131.9, 139.0, 169.1; HRMS (ES): found 329.0265. C16H14N2O79Br+ requires 329.0289. Anal calcd for C16H13N2OBr: C, 58.38; H, 3.98; N, 8.51. Found: C, 58.24; H, 3.93; N, 8.47.
N-[5-Bromo-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl]acetamide (4b). A mixture of 3b (0.20 g, 0.58 mmol) and TFA (0.08 g, 0.69 mmol) in acetonitrile (15 mL) afforded 4b as solid (0.14 g, 76%); Rf = 0.53, mp. 263–265 °C; νmax (ATR) 519, 576, 695, 744, 780, 837, 1000, 1163, 1231, 1274, 1318, 1438, 1474, 1502, 1542, 1624, 1654, 3267, 3355 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.17 (3H, s, CH3), 6.84 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.34 (2H, t, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.44 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 7.82–7.86 (3H, m, 6-H and 2′,6′-H), 9.71 (1H, s, NH), 11.23 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.5, 99.4, 112.2, 115.7, 116.5 (d, 2JCF = 21.8 Hz), 118.3, 125.4, 127.5, 127.8 (d, 3JCF = 8.0 Hz), 128.6 (d, 4JCF = 3.4 Hz), 131.5, 138.1, 162.3 (d, 1JCF = 243.9 Hz), 169.1; HRMS (ES): found 347.0168. C16H13N2OF79Br+ requires 347.0195. Anal calcd for C16H12N2OFBr: C, 55.35; H, 3.48; N, 8.07. Found: C, 55.22; H, 3.39; N, 7.89.
N-(5-Bromo-2-(3-chlorophenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl)acetamide (4c). A mixture of 3c (0.30 g, 0.55 mmol) and TFA (0.08 g, 0.66 mmol) in acetonitrile (15 mL) afforded 4c as solid (0.15 g, 73%), Rf = 0.54, mp. 261–263 °C; νmax (ATR) 562, 598, 668, 680, 751, 775, 846, 1010, 1095, 1277, 1317, 1445, 1462, 1538, 1573, 1622, 1650, 3268, 3397 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.18 (3H, s, CH3), 6.97 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.38–7.53 (3H, m, 4-H and 4′,5′-H), 7.77 (1H, d. J = 8.7 Hz, 6′-H), 7.87–7.90 (2H, m, 6-H and 2′-H), 9.70 (1H, s, NH), 11.28 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.6, 100.6, 112.3, 116.2, 118.5, 124.4, 125.0, 125.5, 127.8, 128.1, 131.3, 131.4, 134.0, 134.4, 137.3, 169.1; HRMS (ES): found 362.9890. C16H13N2O35Cl79Br+ requires 362.9900. Anal calcd for C16H12N2OClBr: C, 52.85; H, 3.33; N, 7.70. Found: C, 52.78; H, 3.41; N, 7.59.
N-[5-Bromo-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl]acetamide (4d). A mixture of 3d (0.30 g, 0.56 mmol) and TFA (0.08 g, 0.67 mmol) in acetonitrile (15 mL) afforded 4d as solid (0.16 g, 76%), Rf = 0.36, mp. 226–228 °C; νmax (ATR) 559, 584, 694 786, 834, 1021, 1179, 1244, 1320, 1398, 1439, 1500, 1612, 1658, 3300, 3403 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.18 (3H, s, CH3), 3.80 (3H, s, OCH3), 6.74 (1H, s, 3-H), 7.06 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.41 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 7.74 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 7.83 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 9.71 (1H, s, NH), 11.14 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.6, 55.7, 98.2, 112.0, 114.9 (2C), 115.1, 117.9, 124.5, 125.2, 127.1, 131.8, 139.1, 159.7, 169.1; HRMS (ES): found 359.0393. C17H16N2O279Br+ requires 359.0395. Anal calcd for C17H15N2O2Br: C, 56.84; H, 4.21; N, 7.80. Found: C, 56.79; H, 4.13; N, 7.56.
3.5. Typical Procedure for the Trifluoroacetylation of 2a–d and 4a–d
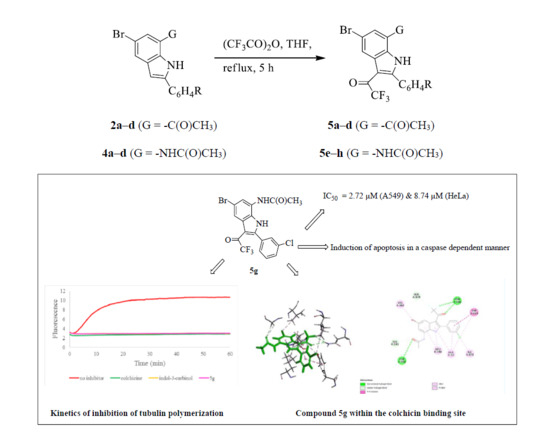
A mixture of 2/4 (1 equivalent) and TFAA (1.5 equivalent) in THF (15 mL/mmol of 1/4) was heated at 60 °C for 5 h. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and quenched with saturated sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. The mixture was extracted with chloroform (3 × 20 mL) and the combined organic layers were dried with anhydrous MgSO4. The salt was filtered off and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by column chromatography on a silica gel using 20% or 60% EtOAc-hexane as eluent to afford 5a−d or 5e−h as solids, respectively. Compounds 5a–h were prepared in this fashion.
1-(7-Acetyl-5-bromo-2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethanone (4a). A mixture of 2a (0.30 g, 0.95 mmol) and TFAA (0.30 g, 1.43 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5a as solid (0.30 g, 78%); Rf 0.86, mp. 175–176 °C; νmax (ATR) 515, 647, 671, 697, 746, 767, 861, 911, 994, 1083, 1143, 1203, 1275, 1358, 1433, 1450, 1660, 3401 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.70 (3H, s, CH3), 7.47–7.55 (5H, m, Ph), 8.14 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.42 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 12.52 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.8, 107.3, 115.6, 116.2 (q, 1JCF 288.5 Hz), 123.7, 128.1, 128.3, 129.3, 130.4, 130.5 (2C), 130.7, 132.3, 151.6, 176.6 (q, 2JCF 35.6 Hz), 198.3; HRMS (ES): found 410.0015. C18H12NO2F379Br+ requires 410.0003. Anal calcd for C18H11NO2F3Br: C, 52.71; H, 2.70; N, 3.41. Found: C, 52.62; H, 2.35; N, 3.39.
1-[7-Acetyl-5-bromo-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-2,2,2-trifluoroethanone (5b). A mixture of 2b (0.30 g, 0.90 mmol) and TFAA (0.28 g, 1.35 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5b as solid (0.26 g, 69%); Rf 0.86, mp. 168–171 °C; νmax (ATR) 518, 587, 645, 667, 706, 746, 842, 911, 999, 1082, 1142, 1205, 1244, 1274, 1435, 1489, 1606, 1662, 3401 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.70 (3H, s, CH3), 7.33 (2H, t, J 8.5 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.62 (2H, t, J = 6.9 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 8.14 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.42 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 12.61 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.8, 107.4, 115.1 (d, 2JCF = 21.8 Hz), 115.7, 116.3 (q, 1JCF = 288.6 Hz), 123.6, 127.1 (d, 4JCF = 3.5 Hz), 128.4, 129.4, 130.3, 132.2, 133.2 (d, 3JCF = 8.0 Hz), 150.7, 163.6 (d, 1JCF = 246.2 Hz), 176.3 (q, 2JCF = 35.5 Hz), 198.3; HRMS (ES): found 427.9721. C18H11NO2F479Br+ requires 427.9909. Anal calcd for C18H10NO2F4Br: C, 50.49; H, 2.35; N, 3.27. Found: C, 50.44; H, 2.31; N, 3.30.
1-[7-Acetyl-5-bromo-2-(3-chlorophenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-2,2,2-trifluoroethanone (5c). A mixture of 2c (0.30 g, 0.86 mmol) and TFAA (0.27 g, 1.29 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5c as solid (0.21 g, 56%); Rf 0.86, mp. 138–141 °C; νmax (ATR) 581, 661, 702, 728, 769, 795, 870, 903, 913, 946, 997, 1074, 1147, 1209, 1281, 1316, 1433, 1462, 1651, 3257 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.70 (3H, s, CH3), 7.51–7.52 (2H, m, 4′,5′-H), 7.60–7.62 (1H, m, 6′-H), 7.67 (1H, s, 2′-H), 8.15 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.42 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 12.72 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.9, 107.5, 115.7, 116.3 (q, 1JCF 288.6 Hz), 123.7, 128.4, 129.6, 129.7, 129.9, 130.1, 130.2, 130.5, 132.2, 132.6, 132.7, 149.9, 176.2 (q, 2JCF 35.5 Hz), 198.3; HRMS (ES): found 443.9623. C18H11NO2F335Cl79Br+ requires 443.9614. Anal calcd for C18H10NO2F3ClBr: C, 48.62; H, 2.27; N, 3.15. Found: C, 48.47; H, 2.26; N, 2.98.
1-[7-Acetyl-5-bromo-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-2,2,2-trifluoroethanone (5d). A mixture of 2d (0.30 g, 0.87 mmol) and TFAA (0.27 g, 1.31 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5d as solid (0.29 g, 75%); Rf 0.70, mp. 170–173 °C; νmax (ATR) 615, 642, 660, 746, 836, 910, 1028, 1082, 1140, 1173, 1202, 1262, 1437, 1489, 1607, 1657, 3392 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.70 (3H, s, CH3), 3.83 (3H, s, OCH3), 7.05 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.52 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 8.11 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.38 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 12.32 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 27.9, 107.0, 113.7, 115.5, 116.3 (q, 1JCF = 289.7 Hz), 122.8, 123.0, 123.5, 128.2, 129.2, 130.5, 132.2, 132.4, 151.8, 161.2, 176.7 (q, 2JCF = 35.6 Hz), 198.5; HRMS (ES): found 440.0110. C19H14NO3F379Br+ requires 440.0109. Anal calcd for C19H13NO3F3Br: C, 51.84; H, 2.98; N, 3.18. Found: C, 51.78; H, 2.93; N, 3.14.
N-[5-Bromo-2-phenyl-3-trifluoroacetyl-1H-indol-7-yl]acetamide (5e). A mixture of 4a (0.30 g, 0.91 mmol) and TFAA (0.29 g, 1.37 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5e as solid (0.32 g, 84%); Rf 0.49, mp. 141–144 °C; νmax (ATR) 502, 582, 659, 699, 738, 773, 863, 882, 922, 1010, 1143, 1199, 1269, 1334, 1389, 1434, 1449, 1546, 1627, 1655, 3210, 3329 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.11 (3H, s, CH3), 7.53–7.63 (5H, m, Ar), 7.94 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 7.96 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 9.74 (1H, s, NH), 12.53 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.3, 107.2, 116.2, 116.6 (q, 1JCF = 295.5 Hz), 118.8, 126.2, 126.3, 126.8, 128.6, 129.5, 130.3, 130.6, 131.3, 149.2, 169.3, 175.9 (q, 2JCF = 35.6 Hz); HRMS (ES): found 425.0107. C18H13N2O2F379Br+ requires 425.0112. Anal calcd for C18H12N2O2F3Br: C, 50.85; H, 2.84; N, 6.99. Found: C, 50.52; H, 2.87; N, 6.94.
N-[5-Bromo-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-trifluoroacetyl-1H-indol-7-yl]acetamide (5f). A mixture of 4b (0.30 g, 0.86 mmol) and TFAA (0.27 g, 1.30 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5f as solid (0.29 g, 78%); Rf 0.50, mp. 195–197 °C; νmax (ATR) 515, 611, 732, 844, 884, 924, 1011, 1044, 1146, 1198, 1224, 1271, 1330, 1447, 1497, 1631, 1659, 3196, 3286 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.12 (3H, s, CH3), 7.41 (2H, t, J = 9.0 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.69 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 7.93 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 7.94 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 9.77 (1H, s, NH), 12.54 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.2, 107.4, 115.7 (d, 2JCF 21.8 Hz), 116.1, 116.5 (q, 1JCF 288.6 Hz), 118.7, 118.8, 126.2, 126.9, 127.6 (d, 4JCF = 3.5 Hz), 129.4, 133.8 (d, 3JCF = 9.1 Hz), 148.2, 163.6 (d, 1JCF = 246.2 Hz), 169.3, 176.6 (q, 2JCF = 35.5 Hz); HRMS (ES): found 443.0020. C18H13N2O2F479Br+ requires 443.0020. Anal calcd for C18H12N2O2F4Br: C, 48.78; H, 2.50; N, 6.32. Found: C, 48.59; H, 2.39; N, 6.30.
N-[5-Bromo-2-(3-chlorophenyl)-3-trifluoroacetyl-1H-indol-7-yl]acetamide (5g). A mixture of 4c (0.30 g, 0.83 mmol) and TFAA (0.26 g, 1.23 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5g as solid (0.19 g, 52%); Rf 0.50, mp. 172–174 °C; νmax (ATR) 541, 570, 685, 746, 794, 851, 913, 1010, 1039, 1083, 1143, 1198, 1260, 1369, 1441, 1542, 1630, 1660, 3217, 3356 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.12 (3H, s, CH3), 7.60–7.66 (3H, m, Ar), 7.75 (1H, s, 2′-H), 8.28 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 8.29 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 9.77 (1H, s, NH), 12.61 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.3, 107.4, 116.2, 116.5 (q, 1JCF = 289.7 Hz), 118.9, 126.3, 127.2, 129.3, 129.9, 130.5, 133.2, 133.4, 147.3, 169.3, 175.6 (q, 2JCF = 34.4 Hz); HRMS (ES): found 458.9731. C18H12F3N2O235Cl79Br+ requires 458.9723. Anal calcd for C18H11F3N2O2ClBr: C, 47.03; H, 2.41; N, 6.09. Found: C, 47.10; H, 2.36; N, 6.05.
N-[5-Bromo-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-trifluoroacetyl-1H-indol-7-yl]acetamide (5h). A mixture of 4d (0.30 g, 0.83 mmol) and TFAA (0.26 g, 1.25 mmol) in THF (15 mL) afforded 5h as solid (0.30 g, 80%); Rf 0.23, mp. 179–182 °C; νmax (ATR) 520, 573, 643, 751, 838, 884, 922, 1009, 1031, 1154, 1191, 1250, 1415, 1448, 1499, 1538, 1629, 1645, 3211, 3369 cm−1; 1H-NMR: 2.08 (3H, s, CH3), 3.80 (3H, s, OCH3), 7.07 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 3′,5′-H), 7.52 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2′,6′-H), 7.86 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 4-H), 9.91 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, 6-H), 9.74 (1H, s, NH), 12.39 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR: 24.2, 55.8, 107.0, 114.1, 116.0, 116.6 (q, 1JCF = 289.7 Hz),118.4, 118.6, 123.2, 126.3, 126.8, 129.6, 131.9, 149.5, 161.2, 169.2, 176.9 (q, 2JCF = 35.5 Hz); HRMS (ES): found 455.0195. C19H15N2O3F379Br+ requires 455.0219. Anal calcd for C19H14N2O3F3Br: C, 50.13; H, 3.10; N, 6.15. Found: C, 49.95; H, 3.20; N, 6.00.
3.6. Evaluation for Cytotoxicity
3.6.1. Screening Protocol
The human cervical cancer cell line, HeLa, and lung cancer cell line, A549 were used for the screening assay. HeLa cells were grown and maintained in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and A549 cells were grown and maintained in EMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 10% non-essential amino acids. In the case of screening experiments, the cells were seeded into 96 well microtiter plates at a density of 6000 cells/well to a total volume of 200 μL per well. The microtiter plates were incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 100% relative humidity for 24 h to allow for cell attachment. Each of the test compounds was first reconstituted in DMSO at a concentration of 40 mM and then stored at 4 °C prior to use and final dilution to working concentrations with culture complete medium on the day of treatment. Two hundred microliters aliquots of the diluted compound in fresh medium was used to treat cells after aspiration of seeding medium. Each of the cell lines was incubated for 48 h at 37 °C in a humidified incubator under 5% CO2 atmosphere. Treatment medium was aspirated from all wells and replaced with 100 μL of Hoechst 33342 nuclear dye (5 μg/mL) and incubated for 10 min at room temperature. Thereafter, cells were stained with propidium iodide (PI) at 100 μg/mL in order to enumerate the proportion of dead cells within the population. Cells were imaged immediately after addition of PI using the ImageXpress Micro XLS Widefield Microscope (Separations, Randburg, South Africa).
3.6.2. Dose Response Analysis and Determination of IC50 Values
Cells were seeded as described in above. The compounds were tested at a concentration range of 0–100 μM to determine their respective IC50 values on lung cancer (A549) cells and cervical cancer (HeLa) cells. The medium was aspirated and replaced with 200 μL fresh medium containing the dilution of the respective test compound. The test sample were added to each well and the plates were incubated for a further 48 h at 37 °C under 5% CO2 atmosphere in a humidified incubator. After this incubation period, the medium was removed and then replaced with 100 μL fresh culture medium containing MTT at a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. The 96-well plates were returned to the incubator and incubated for an additional 3 h. The medium was removed and the MTT crystals were solubilized in 100 μL DMSO and the absorbance was measured at 560 nm using a Labsystems Multiwell Scanning spectrophotometer (Thermo Fischer Scientific, Edenvale, South Africa).
3.6.3. Data Analysis
Quantification of live and dead cells for the screening assay was performed using the ImageXpress Micro XLS Widefield Microscope and acquired images analysed using the MetaXpress software and Multi-Wavelength Cell Scoring Application Module. Acquired data was transferred to an EXCEL spreadsheet and relative cell viability was determined using quadruplicate wells for each concentration. Untreated cells were considered to have 100% cell viability (i.e., the mean OD of the untreated wells = 100% viability). Cell viabilities in other test wells were calculated relative to the untreated control and expressed as a percentage. Dose response analysis was performed using the statistical software GraphPad Prism and IC50 values calculated from the concentration-response data using a mathematical Hill function. If the concentration range selected did not produce 100% inhibition, a lower concentration equal to zero was included to allow IC50 determination.
3.7. Evaluation of Mode of Cell Death
3.7.1. Caspace Activation
Compounds 4c and 5g were selected for mechanism studies and these test compounds were reconstituted in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) to give a final concentration of 40 mM. Samples were stored at 4 °C until required. Cells were seeded and treated as described in 3.6.1 Cells were first fixed and permeabilized using the IntraPrep kit as per manufacturer’s instructions (Beckman Coulter). This kit allows for the immunological detection of intracellular antigens by creating apertures in the cell membrane without affecting the morphology of the cell. Cleaved caspase-8 (Asp 391) and cleaved caspase-3 (Asp 175) monoclonal antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) were used to determine the presence of activated caspase-8 and caspase-3, respectively. Cells were first blocked using PBS containing 0.5% BSA and thereafter incubated with the antibodies separately (1:200 for caspase-8 and 1:100 for caspase-3) for 1 h at 37 °C. The cells were washed and incubated with the Alexa 647 conjugated secondary antibody (1:1000) for 30 min at 37 °C in the dark. Both cell lines were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2 and then treated with the IC50 values of each compound for 24 h. 200 µL Aliquots of the diluted compound in fresh medium was used to treat cells after aspiration of seeding medium. Treatment medium was aspirated from all wells and replaced with 100 μL of Hoechst 33342 nuclear dye (5 μg/mL) and incubated for 10 min at RT.
3.7.2. Data Quantification
Quantification of live and dead cells for the assay was performed using the ImageXpress Micro XLS Widefield Microscope and acquired images analysed using the MetaXpress software and Multi-Wavelength Cell Scoring Application Module and the Cell Cycle Module. Acquired data was transferred to an EXCEL spreadsheet and data was analysed and processed.
3.8. Tubulin Polymerization Assay
Tubulin polymerization assays were conducted using the tubulin polymerization assay kit following the manufacturer’s instructions (Cytoskeleton, Inc., Denver, CA, USA). Briefly, 50 μL of 1.3 mg/mL tubulin (>99% pure) proteins in G-PEM buffer (consisting of 80 mmol/L PIPES 2 mmol/L MgCl2, 0.5 mmol/L EGTA, 1 mmol/L GTP, and 15% glycerol at pH 6.9,) was placed in a quartz cuvette in the presence of the test agent (concentration: 0.25 µM). Polymerization was measured at every 3 s for 1 h using an Applied Photophysics Chirascan spectroflourimeter (excitation at 360 nm and emission at 420 nm) at 37 °C.
3.9. Methodology for Docking Studies
Docking of the compounds
2a,
4a and
5e–
h was performed to the crystal structure of a tubulin heterodimer (PDB code:1TUB) [
29]. using the CDOCKER protocol [
30] in Discovery Studio 2017. Prior to performing the docking, compounds were drawn using Discovery Studio and prepared using the ‘Prepare Ligand’ protocol. The protein structure was obtained from the Protein Data Bank, prepared using the ‘Prepare Protein’ protocol in Discovery Studio which included: removing any existing ligands bound to the model and binding sites defined from receptor cavities as well as all water molecules, protonate the protein at pH 7.5, The receptor cavity in this tubulin structure is present between the two monomers of the tubulin dimer structure. Docking was performed using CHARMm force field and the best conformation of the ligand selected and evaluated.