Physical Stability and Viscoelastic Properties of Co-Amorphous Ezetimibe/Simvastatin System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Thermal Properties of Ezetimibe, Simvastatin And Its Binary System
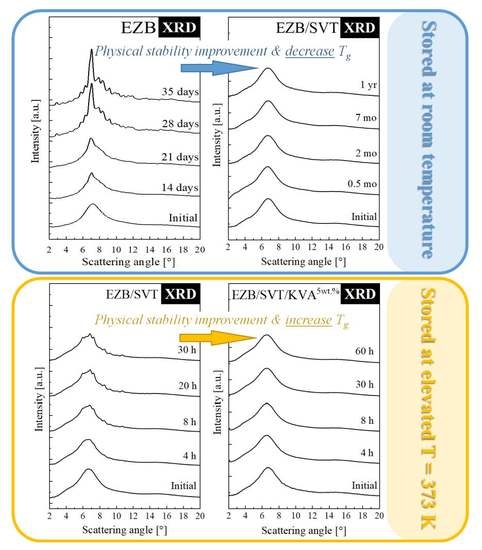
2.2. Physical Stability Studies of the Amorphous Ezb/Svt System Stored at Both Supercooled Liquid and Glassy State
2.3. Impact of KVA 64 Polymer on the Thermal Properties as Well as Physical Stability of the EZB/SVT System
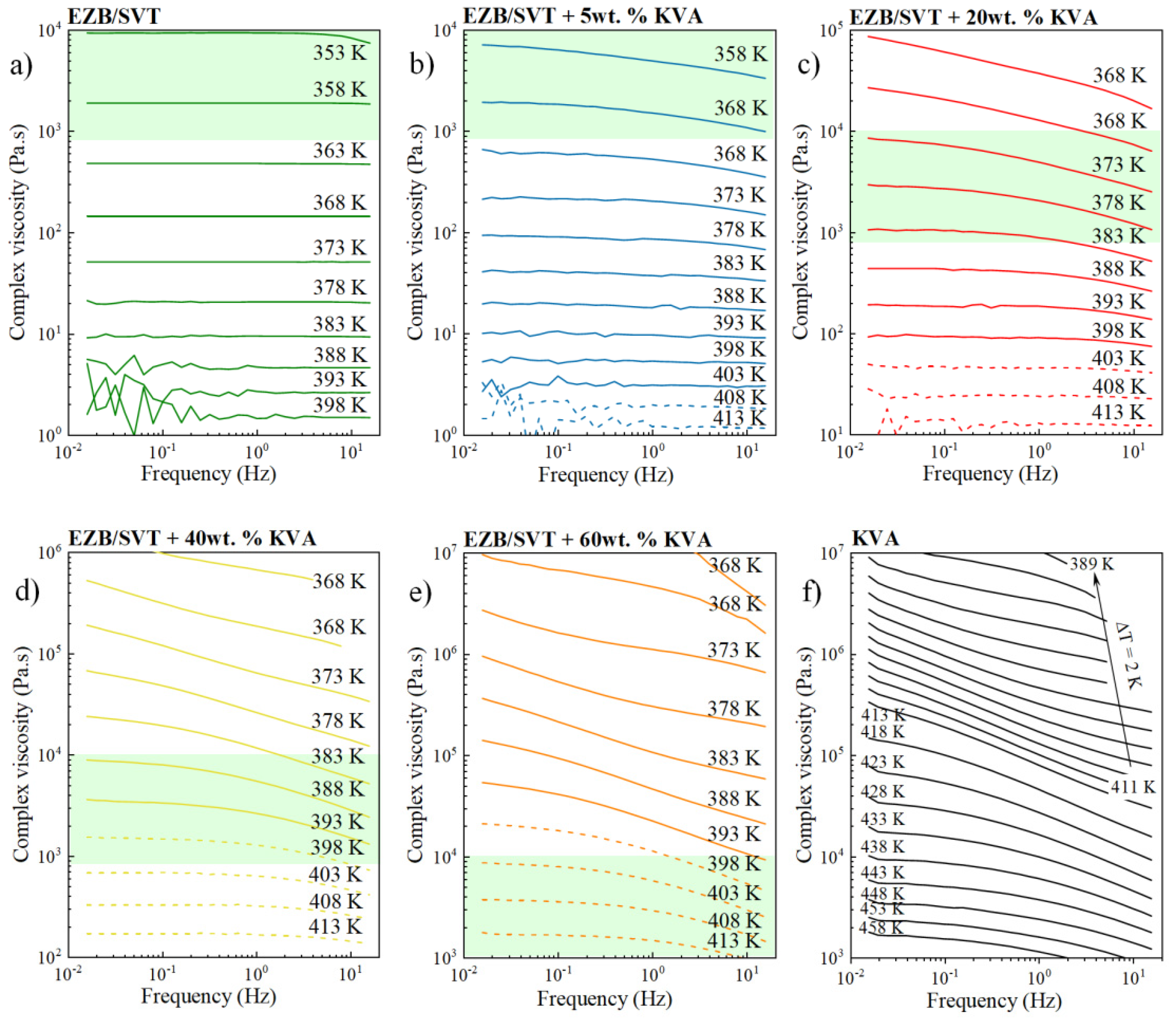
2.4. The Impact of KVA on the Complex Viscosity of the EZB/SVT System
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Binary and Ternary Systems
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.5. Rheological Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bangalore, S.; Kamalakkannan, G.; Parkar, S.; Messerli, F.H. Fixed-Dose Combinations Improve Medication Compliance: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaragoza, C.; Gomez-Guerrero, C.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; Blanco-Colio, L.; Tarin, C.; Mas, S.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J. Animal Models of Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 497841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelein, J.J.P.; Akdim, F.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Bots, M.L.; Stalenhoef, A.F.H.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Sijbrands, E.J.G.; Trip, M.D.; Stein, E.A.; et al. Simvastatin with or without Ezetimibe in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPiro, J.T.; Talbert, R.L.; Yee, G.C.; Matzke, G.R.; Wells, B.G.; Posey, L.M. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 7th ed.; The McGraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 0071643257. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Husein, B.A.A. Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Simvastatin-Mediated Inhibition of Prostate Cancer Cellular Functions In Vitro AND Tumor Growth In Vivo. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, A.; Pineda, M.; Venkata, K. Comprehension of Top 200 Prescribed Drugs in the US as a Resource for Pharmacy Teaching, Training and Practice. Pharmacy 2018, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.H.; McGarry, T.; Bettis, R.; Melani, L.; Lipka, L.J.; LeBeaut, A.P.; Suresh, R.; Sun, S.; Veltri, E.P. Ezetimibe coadministered with simvastatin in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, C.M.; Abate, N.; Yuan, Z.; King, T.R.; Palmisano, J. Dose-comparison study of the combination of ezetimibe and simvastatin (Vytorin) versus atorvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia: The Vytorin Versus Atorvastatin (VYVA) Study. Am. Heart J. 2005, 149, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigent, C.; Landray, M.J.; Reith, C.; Emberson, J.; Wheeler, D.C.; Tomson, C.; Wanner, C.; Krane, V.; Cass, A.; Craig, J.; et al. The eff ects of lowering LDL cholesterol with simvastatin plus ezetimibe in patients with chronic kidney disease (Study of Heart and Renal Protection): A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari Nanam, P.; Thadkala, K.; Sailu, C.; Aukunuru, J. Investigation of various practical techniques to enhance dissolution of ezetimibe from oral tablets: A comparative study. J. Young Pharm. 2014, 6, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B. Optimized self nano-emulsifying systems of ezetimibe with enhanced bioavailability potential using long chain and medium chain triglycerides. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 100, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Mandage, Y.; Thanki, K.; Bhise, S. Dissolution improvement of simvastatin by surface solid dispersion technology. Dissolut. Technol. 2010, 17, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, K.; Adrjanowicz, K.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Hawelek, L.; Paluch, M.; Zakowiecki, D.; Mazgalski, J. Molecular Dynamics of the Cryomilled Base and Hydrochloride Ziprasidones by Means of Dielectric Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2642–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Teng, J.; Selbo, J.; Cao, Y.; Teng, J.; Selbo, J. Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Epigallocatechin Gallate for Enhanced Physical Stability and Controlled Release. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Parks, M. What is the True Solubility Advantage for Amorphous Pharmaceuticals? Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, D.Q.; Royall, P.G.; Kett, V.L.; Hopton, M.L. The relevance of the amorphous state to pharmaceutical dosage forms: Glassy drugs and freeze dried systems. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 179, 179–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Adrjanowicz, K.; Kaminski, K.; Paluch, M.; Hawelek, L.; Wrzalik, R.; Dulski, M.; Sawicki, W.; Mazgalski, J.; et al. Study of the amorphous glibenclamide drug: Analysis of the molecular dynamics of quenched and cryomilled material. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1692–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrjanowicz, K.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Wlodarczyk, P.; Kaminski, K.; Paluch, M.; Mazgalski, J. Molecular mobility in liquid and glassy states of Telmisartan (TEL) studied by Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowska, K.; Paluch, M.; Grzybowski, A.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Hawelek, L.; Kolodziejczyk, K.; Ngai, K.L. Molecular dynamics and physical stability of amorphous anti-inflammatory drug: Celecoxib. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 12792–12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, A.; Hempenstall, J.; Rades, T. Characterization of glass solutions of poorly water-soluble drugs produced by melt extrusion with hydrophilic amorphous polymers. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in Vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, T.N.; Muzeeb, Y.I.; Rani, P.S.; Pradesh, A. Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Drug Ezetimibe By Solid Dispersion Technique. J. Adv. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2013, 4, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Murdande, S.B.; Pikal, M.J.; Shanker, R.M.; Bogner, R.H. Solubility advantage of amorphous pharmaceuticals: I. A thermodynamic analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.; Trevaskis, N.; Charman, S.; Shanker, R.; Charman, W.; Pouton, C.; Porter, C. Strategies to address low drug solubility in discovery and development. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 315–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descamps, M.; Willart, J.-F. Scaling laws and size effects for amorphous crystallization kinetics: Constraints imposed by nucleation and growth specificities. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 542, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descamps, M.; Dudognon, E. Crystallization from the Amorphous State: Nucleation-Growth Decoupling, Polymorphism Interplay, and the Role of Interfaces. Pharm. Assoc. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2615–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Rams-Baron, M.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Ngai, K.L.; Paluch, M. Atorvastatin as a promising crystallization inhibitor of amorphous probucol. Dielectric studies at ambient and elevated pressure. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2670–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmiel, K.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Sawicki, W.; Jachowicz, R.; Paluch, M. A New Method To Identify Physically Stable Concentration of Amorphous Solid Dispersions (I): Case of Flutamide + Kollidon VA64. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3370–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Grohganz, H.; Gordon, K.C.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T. Coamorphous drug systems: Enhanced physical stability and dissolution rate of indomethacin and naproxen. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Moinuddin, S.M.; Cai, T. Advances in coamorphous drug delivery systems. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik, J.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Stankiewicz, A.; Paluch, M. Stabilization of the Amorphous Ezetimibe Drug by Confining Its Dimension. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapik, J.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Tajber, L.; Paluch, M. Molecular dynamics and physical stability of coamorphous ezetimib and indapamide mixtures. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3610–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafraniec, J.; Antosik, A.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Kurek, M.; Syrek, K.; Chmiel, K.; Paluch, M.; Jachowicz, R. Planetary ball milling and supercritical fluid technology as a way to enhance dissolution of bicalutamide. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 30, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yin, Q.; Jiang, C.; Gong, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Hou, B.; Hao, H. Solution thermodynamics of simvastatin in pure solvents and binary solvent mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2015, 406, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik, J.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Hawelek, L.; Sawicki, W.; Wlodarski, K.; Markowski, J.; Paluch, M. Physical stability of the amorphous anticholesterol agent (Ezetimibe): The role of molecular mobility. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4280–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Jiménez, C.; Cruz-Angeles, J.; Videa, M.; Martínez, L.; Martínez-Jiménez, C.; Cruz-Angeles, J.; Videa, M.; Martínez, L.M. Co-Amorphous Simvastatin-Nifedipine with Enhanced Solubility for Possible Use in Combination Therapy of Hypertension and Hypercholesterolemia. Molecules 2018, 23, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Tu, W.; Chmiel, K.; Rams-Baron, M.; Paluch, M. Co-Stabilization of Amorphous Pharmaceuticals - The Case of Nifedipine and Nimodipine. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Sandhu, H.; Choi, D.S.; Chokshi, H.; Malick, A.W. Amorphous Solid Dispersions Theory and Practice; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9781493915989. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H.; Atef, E. Amorphous stabilization and dissolution enhancement of amorphous ternary solid dispersions: Combination of polymers showing drug-polymer interaction for synergistic effects. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3511–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zografi, G. Phase behaviour of binary and ternary amourphous mixtures containing indomethacin, citric acid and PVP. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, S.; Nagels, S.; Armas, H.N. de; D’Autry, W.; Van Schepdael, A.; Van den Mooter, G. Formulation and characterization of ternary solid dispersions made up of Itraconazole and two excipients, TPGS 1000 and PVPVA 64, that were selected based on a supersaturation screening study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couchman, P.R. Compositional Variation of Glass-Transition Temperatures. 2. Application of the Thermodynamic Theory to Compatible Polymer Blends. Macromolecules 1978, 11, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couchman, P.R.; Karasz, F.E. A Classical Thermodynamic Discussion of the Effect of Composition on Glass-Transition Temperatures. Macromolecules 1978, 11, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repka, M.A.; Battu, S.K.; Upadhye, S.B.; Thumma, S.; Crowley, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Martin, C.; McGinity, J.W. Pharmaceutical applications of hot-melt extrusion: Part II. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarode, A.L.; Sandhu, H.; Shah, N.; Malick, W.; Zia, H. Hot melt extrusion (HME) for amorphous solid dispersions: Predictive tools for processing and impact of drug-polymer interactions on supersaturation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.S.; Solanki, N.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Investigation of Thermal and Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers Relevant to Hot Melt Extrusion, IV: AffinisolTM HPMC HME Polymers. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochmann, E.S.; Üstüner, E.E.; Gryczke, A.; Wagner, K.G. Predicting melt rheology for hot-melt extrusion by means of a simple Tg-measurement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 119, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochmann, E.S.; Steffens, K.E.; Gryczke, A.; Wagner, K.G. Numerical simulation of hot-melt extrusion processes for amorphous solid dispersions using model-based melt viscosity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 124, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, N.; Gupta, S.S.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Rheological analysis of itraconazole-polymer mixtures to determine optimal melt extrusion temperature for development of amorphous solid dispersion. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, J.; Edinger, M.; Botker, J.; Baldursdottir, S.; Rantanen, J. Oscillatory Shear Rheology in Examining the Drug-Polymer Interactions Relevant in Hot Melt Extrusion. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H. Das Temperaturabhangigkeitgesetz der Viskosität von Flüssigkeiten. J. Phys. Z. 1921, 22, 645–646. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher, G.S. Analysis of Recent Measurements of the Viscosity of Glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1925, 8, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G.; Hesse, W. Die Abhängigkeit der Viscosität von der Temperatur bie unterkühlten Flüssigkeiten. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1926, 156, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| System | Te [K] | Tl [K] | Tg exp [K] | Tg pred [K] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EZB/SVT | 391 | 406 | 323 | 323 |
| EZB/SVT + 5wt.% KVA | 390 | 406 | 324 | 324 |
| EZB/SVT + 20wt.% KVA | 389 | 401 | 332 | 332 |
| EZB/SVT + 40wt.% KVA | 388 | - | 345 | 342 |
| EZB/SVT + 60wt.% KVA | 388 | - | 355 | 353 |
| KVA | - | - | 378 | - |
| System | Log10η∞ | B = DT0 | T0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EZB/SVT | 4.67 ± 0.17 | 1148.34 ± 60.19 | 295.12 ± 1.86 |
| EZB/SVT + 5wt.% KVA | −4.55 ± 0.09 | 1303.53 ± 37.27 | 290.77 ± 1.22 |
| EZB/SVT + 20wt.% KVA | −6.19 ± 2.67 | 2411.64 ± 148.98 | 269.49 ± 3.66 |
| EZB/SVT + 40wt.% KVA | −5.59 ± 0.22 | 2515.29 ± 126.57 | 273.42 ± 3.04 |
| EZB/SVT + 60wt.% KVA | −7.15 ± 0.4 | 3816.61 ± 278.45 | 253.35 ± 5.37 |
| KVA | −4.13 ± 0.83 | 2981.70 ± 565.27 | 278.26 ± 13.87 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Chmiel, K.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Correia, N.T.; Sawicki, W.; Paluch, M. Physical Stability and Viscoelastic Properties of Co-Amorphous Ezetimibe/Simvastatin System. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12010040
Knapik-Kowalczuk J, Chmiel K, Jurkiewicz K, Correia NT, Sawicki W, Paluch M. Physical Stability and Viscoelastic Properties of Co-Amorphous Ezetimibe/Simvastatin System. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnapik-Kowalczuk, Justyna, Krzysztof Chmiel, Karolina Jurkiewicz, Natália T. Correia, Wiesław Sawicki, and Marian Paluch. 2019. "Physical Stability and Viscoelastic Properties of Co-Amorphous Ezetimibe/Simvastatin System" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12010040
APA StyleKnapik-Kowalczuk, J., Chmiel, K., Jurkiewicz, K., Correia, N. T., Sawicki, W., & Paluch, M. (2019). Physical Stability and Viscoelastic Properties of Co-Amorphous Ezetimibe/Simvastatin System. Pharmaceuticals, 12(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12010040