Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Study of the Boron-Containing Prodrug of Belinostat (ZL277), a Pan HDAC Inhibitor with Enhanced Bioavailability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. In Vitro Metabolism of ZL277 in Liver S9 Fraction
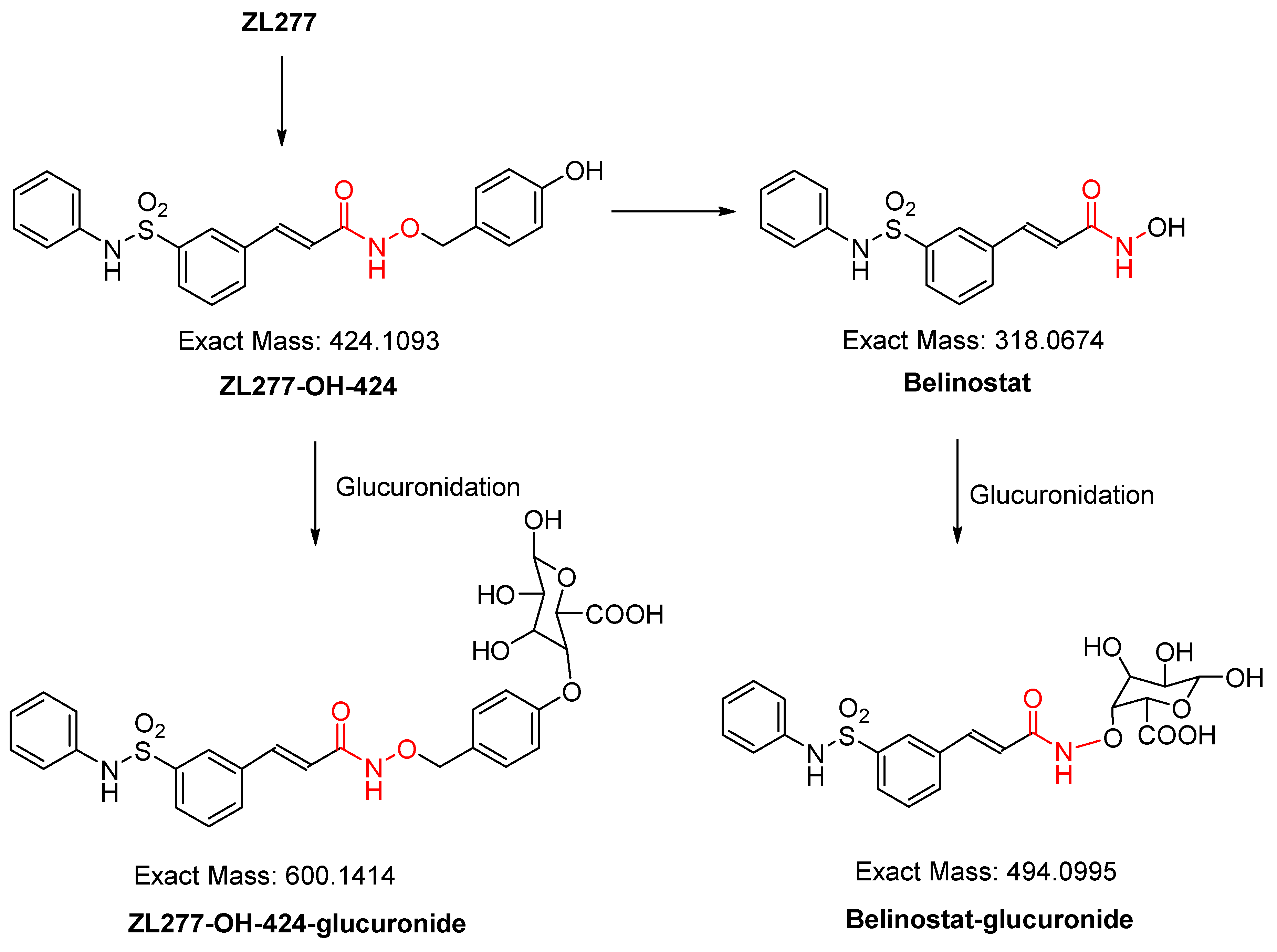
2.2. In Vitro Glucuronidation of ZL277
2.3. In Vitro Sulfate Conjugate Formation of ZL277
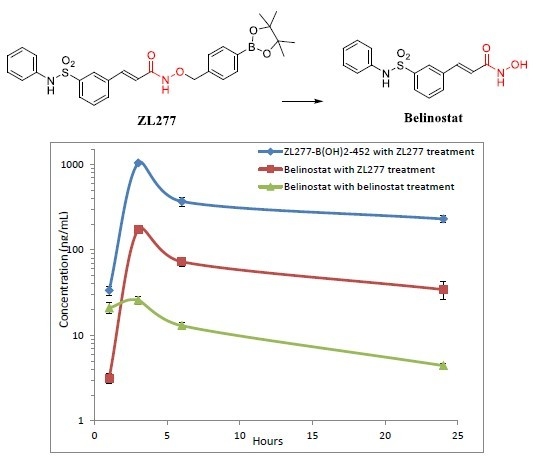
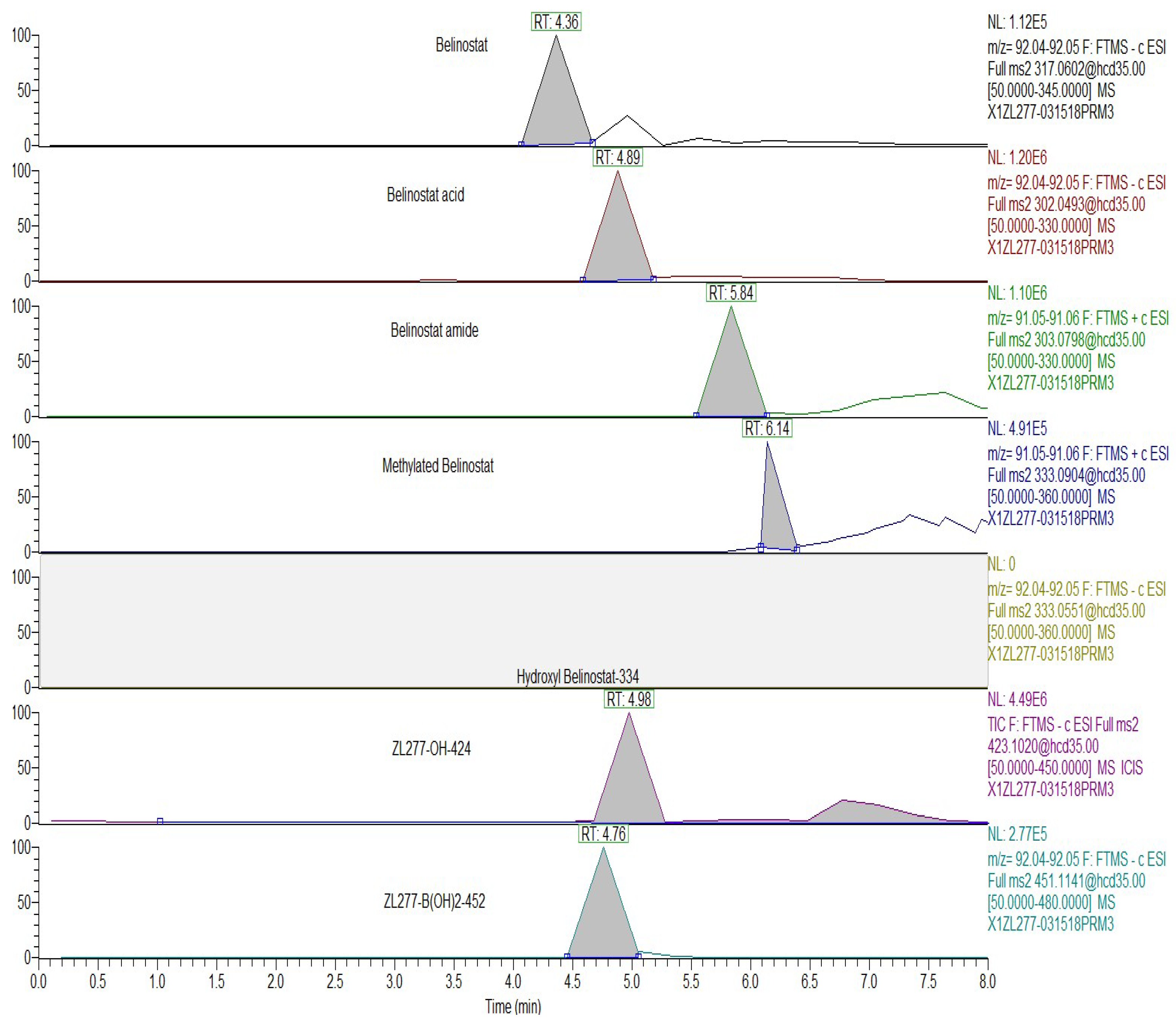
2.4. Pharmacokinetics and in Vivo Metabolites of ZL277 in Mice Plasma
2.5. Metabolites of ZL277 in Tumor Tissues
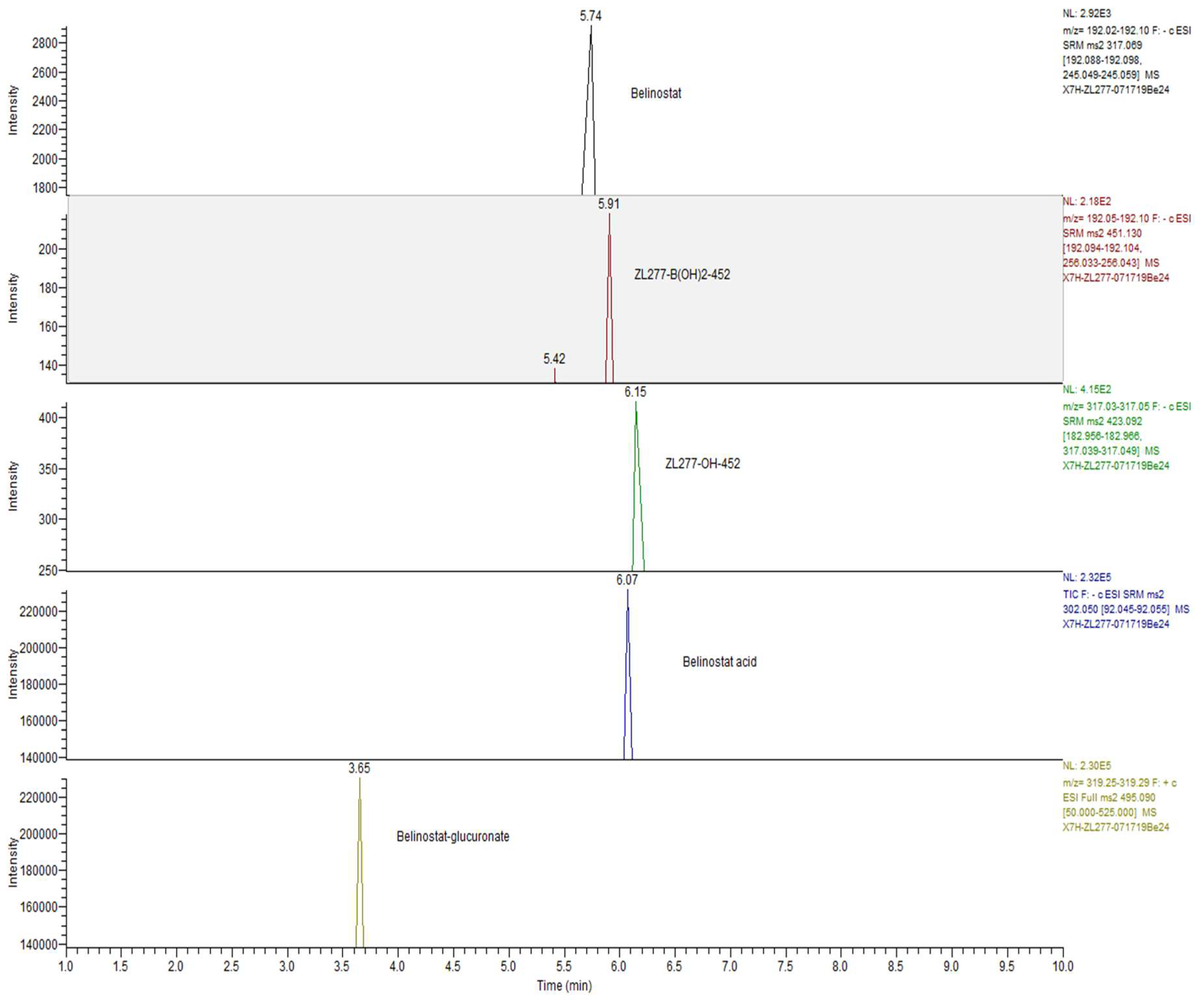
2.6. The Metabolites of ZL277 in Urine Samples from Mice Treated with ZL277
2.7. The Metabolites of ZL277 in Fecal Samples from Mice Treated with ZL277
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Liver S9 Fraction Metabolism of ZL277
3.3. Glucuronidation of ZL277 in Liver Microsomes
3.4. Sulfation of ZL277 in Liver Cytosols
3.5. Sample Collection of Plasma, Urine, and Feces in Metabolite Study and Pharmacokinetics Study
3.6. Sample Collection of Breast Tumors in Nude Mice Model
3.7. Analysis of Metabolites on HR Mass Spectrometer
3.8. Analysis of Metabolites on TSQ Mass Spectrometer
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, T.; Ahmad, D.; Cui, G. Research advances in the use of histone deacetylase inhibitors for epigenetic targeting of cancer. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottamal, M.; Zheng, S.; Huang, T.L.; Wang, G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical studies as templates for new anticancer agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3898–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziemka-Nalecz, M.; Jaworska, J.; Sypecka, J.; Zalewska, T. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: A Therapeutic Key in Neurological Disorders? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maria, A.H.; Melanie, R.A.; Matthew, J.S.; David, P.F. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors In Inflammatory Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Eom, G.H. HDAC and HDAC Inhibitor: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Diseases. Chonnam Med. J. 2016, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poole, R.M. Belinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Yan, C.; Watson, C.C.; Massengill, M.; Xie, M.; Massengill, C.; Noyes, D.R.; Martinez, G.V.; Afzal, R. HDAC inhibitors enhance T-cell chemokine expression and augment response to PD-1 immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4119–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woods, D.M.; Sodré, A.L.; Villagra, A.; Sarnaik, A.; Sotomayor, E.M.; Weber, J. HDAC Inhibition Upregulates PD-1 Ligands in Melanoma and Augments Immunotherapy with PD-1 Blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banik, D.; Moufarrij, S.; Villagra, A. Immunoepigenetics Combination Therapies: An Overview of the Role of HDACs in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, S.; Guo, S.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G. Biocompatible Boron-Containing Prodrugs of Belinostat for the Potential Treatment of Solid Tumors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Rahn, J.; Lichtenfels, R.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Seliger, B. Hydrogen peroxide - production, fate and role in redox signaling of tumor cells. Cell Commun. Signal 2015, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szatrowski, T.P.; Nathan, C.F. Production of Large Amounts of Hydrogen Peroxide by Human Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kiesel, B.F.; Parise, R.A.; Tjørnelund, J.; Christensen, M.K.; Loza, E.; Tawbi, H.; Chu, E.; Kummar, S.; Beumer, J.H. LC–MS/MS assay for the quantitation of the HDAC inhibitor belinostat and five major metabolites in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 81–82, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calvo, E.; Reddy, G.; Boni, V.; García-Cañamaque, L.; Song, T.; Tjornelund, J.; Choi, M.R.; Allen, L.F. Pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and excretion of 14C-labeled belinostat in patients with recurrent or progressive malignancies. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, H.; McPherson, J.P.; Bailey, E.B.; Werner, T.L.; Gupta, S.; Batten, J.; Reddy, G.; Bhat, G.; Sharma, S.; Agarwal, N. A phase I study to determine the pharmacokinetics and urinary excretion of belinostat and metabolites in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2016, 78, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, N.L.; Plumb, J.A.; Vidal, L.; Tjørnelund, J.; Knoblauch, P.; Rasmussen, A.; Ooi, C.E.; Buhl-Jensen, P.; Brown, R.; Evans, T.R.J.; et al. A Phase 1 Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Belinostat in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steele, N.L.; Plumb, J.A.; Vidal, L.; Tjørnelund, J.; Knoblauch, P.; Buhl-Jensen, P.; Molife, R.; Brown, R.; de Bono, J.S.; Evans, T.R.J. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of an oral formulation of the histone deacetylase inhibitor Belinostat (PXD101). Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2011, 67, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-Z.; Ramírez, J.; Yeo, W.; Chan, M.-Y.M.; Thuya, W.-L.; Lau, J.-Y.A.; Wan, S.-C.; Wong, A.L.-A.; Zee, Y.-K.; Lim, R.; et al. Glucuronidation by UGT1A1 Is the Dominant Pathway of the Metabolic Disposition of Belinostat in Liver Cancer Patients. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e54522. [Google Scholar]
- Mazerska, Z.; Mróz, A.; Pawłowska, M.; Augustin, E. The role of glucuronidation in drug resistance. Pharm. Therap. 2016, 159, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilissen, R.A.H.J.; Ringer, D.P.; Stavenuiter, H.J.F.C.; Mulder, G.J.; Meerman, J.H.N. Sulfation of hydroxylamines and hydroxamic acids in liver cytosol from male and female rats and purified aryl sulfotransferase IV. Carcinogenesis 1992, 13, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, G.J.; Meerman, J.H. Sulfation and glucuronidation as competing pathways in the metabolism of hydroxamic acids: the role of N,O-sulfonation in chemical carcinogenesis of aromatic amines. Environ. Health Perspect. 1983, 49, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-Z.; Chan, D.; Yeo, W.; Wan, S.-C.; Chan, S.; Chan, A.; Lee, S.-C.; Lee, H.-S.; Goh, B.-C. A sensitive and specific liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric method for determination of belinostat in plasma from liver cancer patients. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 2409–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, S.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G. Metabolism, pharmacokinetics, and bioavailability of ZB716, a Steroidal Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulator (SERD). Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103874–103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Time Point (h) | ZL277 (Molecular Weight (MW) = 534.1) | Belinostat (MW = 318.1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belinostat (ng/mL) | ZL277-B(OH)2-452 (ng/mL) | Belinostat (ng/mL) | |
| 1 | 3.16 ± 0.22 | 36.75 ± 3.85 | 20.94 ± 2.99 |
| 3 | 172.67 ± 5.63 | 930.77 ± 50.07 | 25.78 ± 2.80 |
| 6 | 72.54 ± 5.11 | 367.62 ± 44.71 | 14.28 ± 1.29 |
| 24 | 34.31 ± 4.54 | 229.35 ± 20.23 | 5.32 ± 0.28 |
| IP Drug | Belinostat (MW = 318.1) | ZL277 (MW = 534.1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belinostat | Belinostat | ZL277-B(OH)2-452 | |
| t1/2 (h) | 10.18 | 10.72 | 13.18 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 25.8 | 172.7 | 930.8 |
| AUC (µg/mL∙h) | 0.29 | 1.51 | 8.31 |
| Plasma | Tumor | Feces | Urine | RT (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZL277 | − | − | − | − | |
| ZL277-B(OH)2-452 | + | + | + | + | 5.90 |
| ZL277-OH-424 | + | + | + | + | 6.05 |
| Belinostat | + | + | + | + | 5.70 |
| Belinostat amide | + | + | + | + | 5.17 |
| Belinostat acid | + | + | + | + | 6.09 |
| Methylated belinostat | + | + | + | + | 6.55 |
| ZL277-OH-424-sufate | − | − | − | − | |
| Belinostat–sulfate | − | − | − | − | |
| ZL277-OH-424-glucuronide | − | − | − | − | |
| Belinostat–glucuronide | + | − | + | + | 3.75 |
| ZL277 | Belinostat | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Belinostat (ng/g) | ZL277-OH-424 (ng/g) | ZL277-B(OH)2-452 (ng/g) | Belinostat (ng/g) |
| 223.1± 29.2 | 166.2 ± 45.3 | 2706.1 ± 152.5 | 172.1 ± 28.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Guo, S.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Hossain, A.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G. Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Study of the Boron-Containing Prodrug of Belinostat (ZL277), a Pan HDAC Inhibitor with Enhanced Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040180
Zhang C, Guo S, Zhong Q, Zhang Q, Hossain A, Zheng S, Wang G. Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Study of the Boron-Containing Prodrug of Belinostat (ZL277), a Pan HDAC Inhibitor with Enhanced Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040180
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Changde, Shanchun Guo, Qiu Zhong, Qiang Zhang, Ahamed Hossain, Shilong Zheng, and Guangdi Wang. 2019. "Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Study of the Boron-Containing Prodrug of Belinostat (ZL277), a Pan HDAC Inhibitor with Enhanced Bioavailability" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 4: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040180
APA StyleZhang, C., Guo, S., Zhong, Q., Zhang, Q., Hossain, A., Zheng, S., & Wang, G. (2019). Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Study of the Boron-Containing Prodrug of Belinostat (ZL277), a Pan HDAC Inhibitor with Enhanced Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals, 12(4), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040180