A Novel Integrated Active Herbal Formulation Ameliorates Dry Eye Syndrome by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Enhancing Glycosylated Phosphoproteins in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
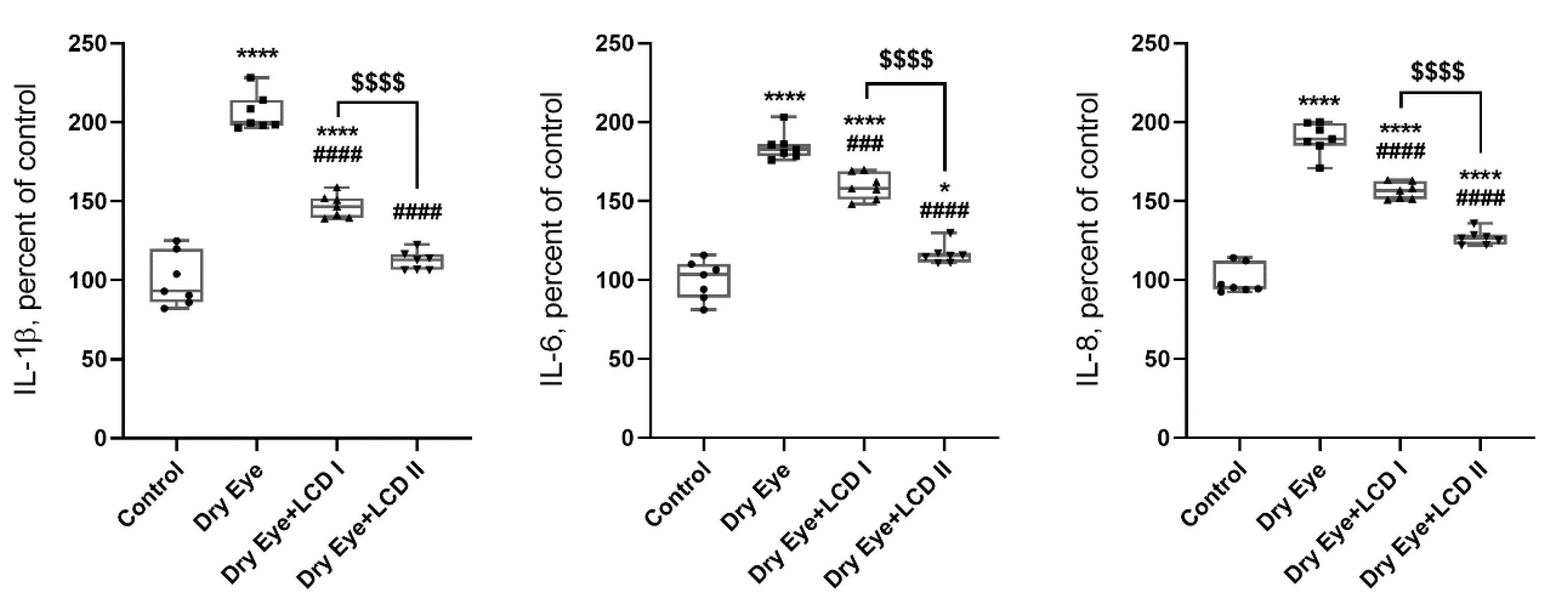
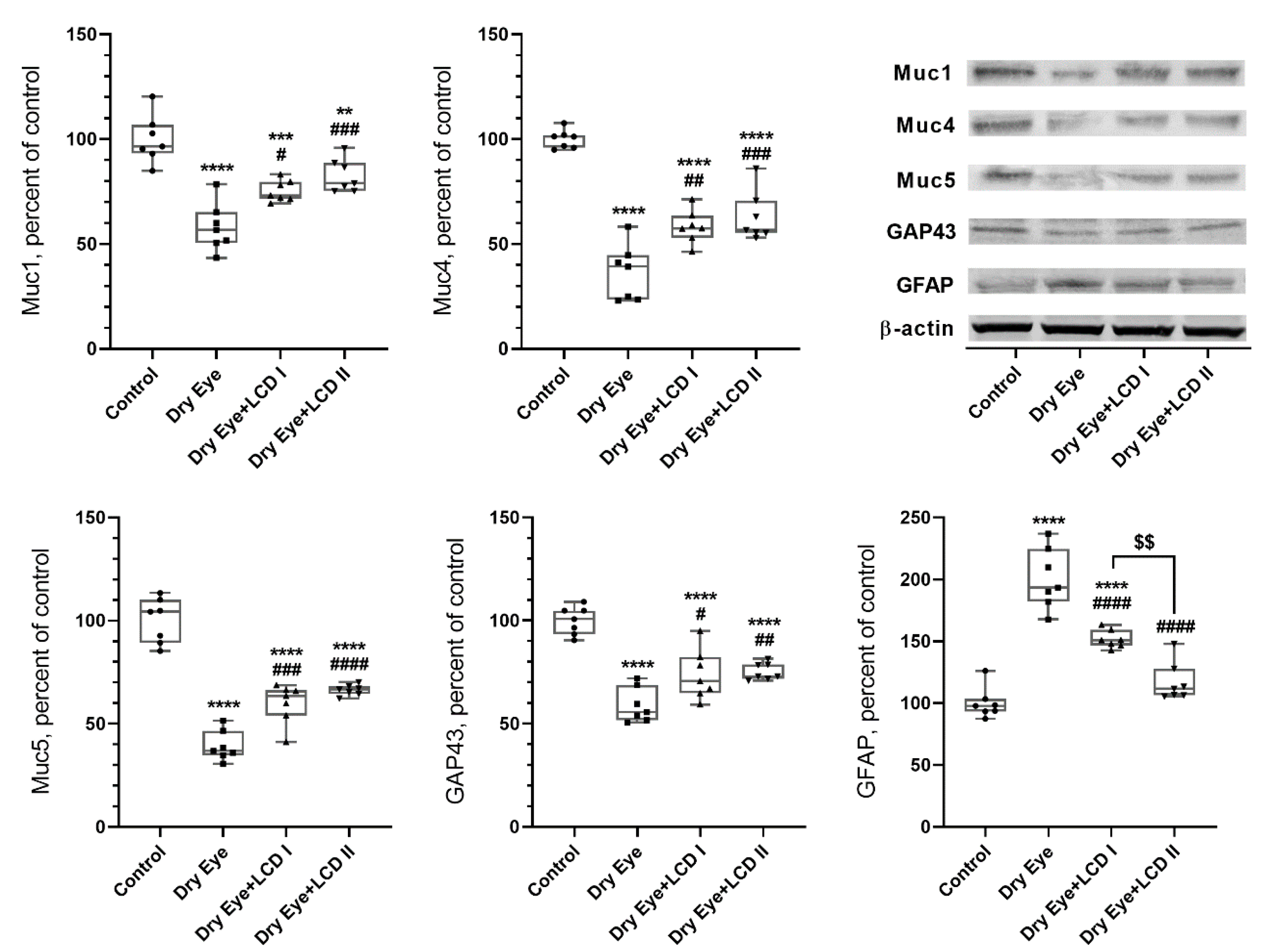
2. Results
2.1. LCD Formulation
2.2. Serum Biochemical Profile
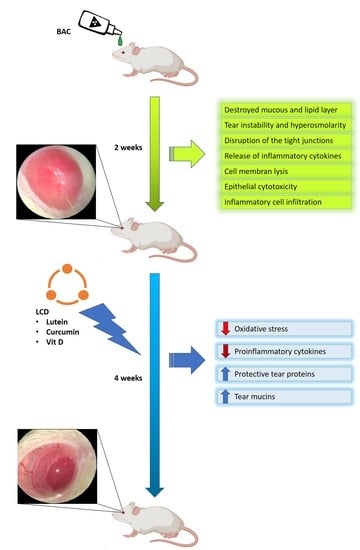
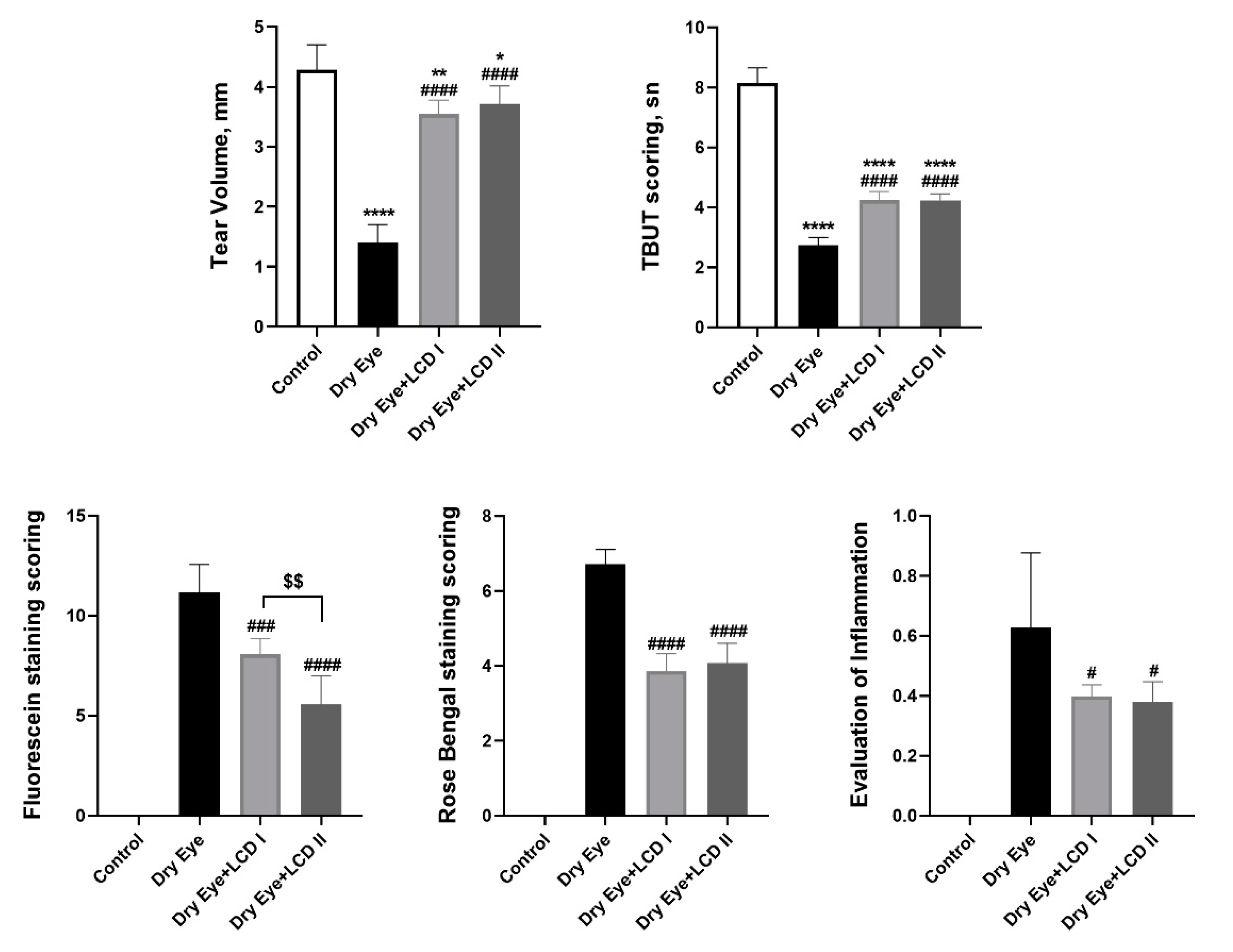
2.3. Changes in Ophthalmologic Findings
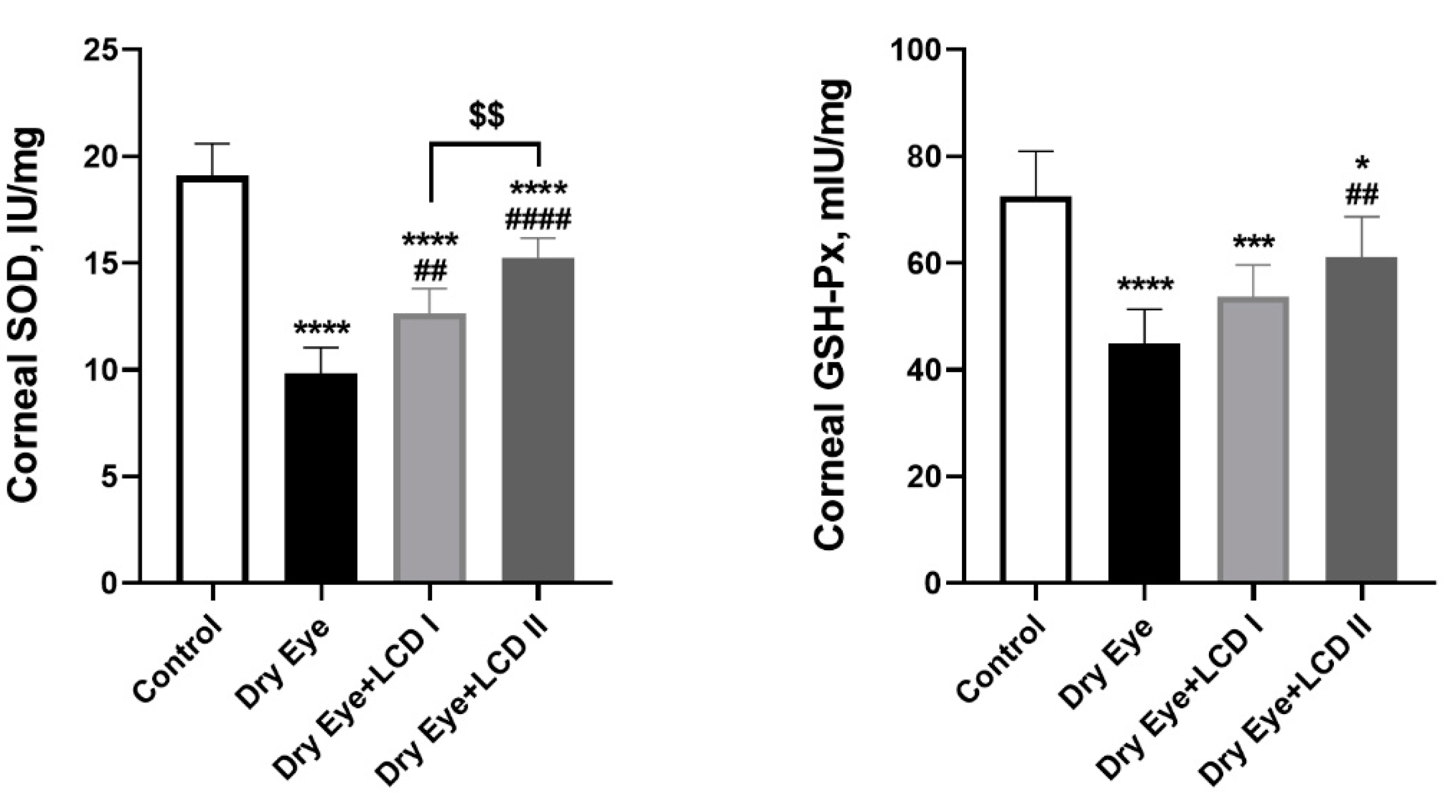
2.4. Changes in Oxidative Status
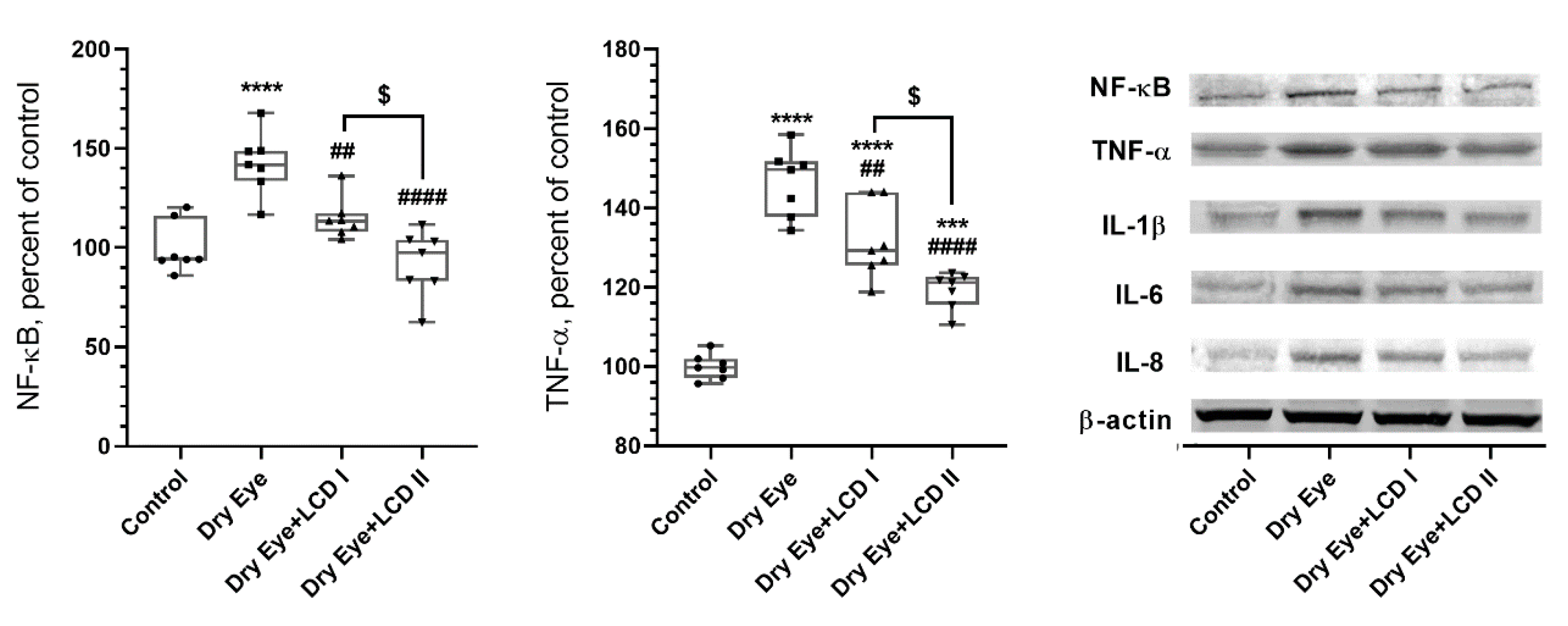
2.5. Changes in Protein Levels
2.6. Changes in Histopathologic Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of LCD Formulation
4.2. Particle Size Determination
4.3. HPLC Assay for Active Ingredients
4.4. Animals and Experimental Design
4.5. Tear Volume Measurement
4.6. TBUT Scoring
4.7. Fluorescein Staining Scoring
4.8. Rose Bengal Staining Scoring
4.9. Evaluation of Inflammation
4.10. Biochemical Analyses
4.11. Histological Analyses
4.12. Western Blot Analyses
4.13. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, J.P.; Nichols, K.K.; Akpek, E.K.; Caffery, B.; Dua, H.S.; Joo, C.K.; Liu, Z.; Nelson, J.D.; Nichols, J.J.; Tsubota, K.; et al. TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report. Ocul Surf. 2017, 15, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, F.; Alves, M.; Bunya, V.Y.; Jalbert, I.; Lekhanont, K.; Malet, F.; Na, K.S.; Schaumberg, D.; Uchino, M.; Vehof, J.; et al. TFOS DEWS II epidemiology report. Ocul Surf. 2017, 15, 334–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Asche, C.V.; Fairchild, C.J. The economic burden of dry eye disease in the United States: A decision tree analysis. Cornea 2011, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkar, M.M.; Shihadeh, W.A.; Haddad, M.F.; Khader, Y.S. Epidemiology of symptoms of dry eye disease (DED) in jordan. A cross-sectional non-clinical population-based study. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2016, 39, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergqvist, U. Possible health effects of working with VDUs. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1989, 46, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Knave, B.G.; Wibom, R.I.; Voss, M.; Hedström, L.D.; Bergqvist, U.O. Work with video display terminals among office employees. I. Subjective symptoms and discomfort. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1985, 11, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Messmer, E.M.; Aragona, P.; Geerling, G.; Akova, Y.A.; Benítez-del-Castillo, J.; Boboridis, K.G.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Rolando, M.; Labetoulle, M. Revisiting the vicious circle of dry eye disease: A focus on the pathophysiology of meibomian gland dysfunction. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, A.J.; de Paiva, C.S.; Chauhan, S.K.; Bonini, S.; Gabison, E.E.; Jain, S.; Knop, E.; Markoulli, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Perez, V.; et al. TFOS DEWS II pathophysiology report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 438–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonge, M.; Enriquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Diebold, Y.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.J.; Reinoso, R.; Herreras, J.M.; Corell, A. Dry eye disease as an inflammatory disorder. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2010, 18, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paiva, C.S.; Corrales, R.M.; Villarreal, A.L.; Farley, W.J.; Li, D.Q.; Stern, M.E.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Corticosteroid and doxycycline suppress MMP-9 and inflammatory cytokine expression, MAPK activation in the corneal epithelium in experimental dry eye. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Q.; Chen, Z.; Song, X.J.; Luo, L.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Stimulation of matrix metalloproteinases by hyperosmolarity via a JNK pathway in human corneal epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4302–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogru, M.; Kojima, T.; Simsek, C.; Tsubota, K. Potential role of oxidative stress in ocular surface inflammation and dry eye disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, DES163–DES168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Q.; Sun, W.; Gu, Y.S. A clinical study of the efficacy of topical corticosteroids on dry eye. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2006, 7, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbell, P.A.; Maguire, M.G.; Pistilli, M.; Ying, G.S.; Szczotka-Flynn, L.B.; Hardten, D.R.; Lin, M.C.; Shtein, R.M. n-3 fatty acid supplementation for the treatment of dry eye disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deinema, L.; Vingrys, A.J.; Wong, C.Y.; Jackson, D.C.; Chinnery, H.R.; Downie, L.E. A randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled clinical trial of two forms of omega-3 supplements for treating dry eye disease. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.C.; Nien, C.W.; Iacob, C.; Hu, D.N.; Huang, S.C.; Lin, H.Y. Effects of lutein on hyperosmoticity-induced upregulation of il-6 in cultured corneal epithelial cells and its relevant signal pathways. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 8341439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.C.; Vagaggini, T.; Nien, C.W.; Huang, S.C.; Lin, H.Y. Effects of lutein and zeaxanthin on lps-induced secretion of il-8 by uveal melanocytes and relevant signal pathways. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 152854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reins, R.Y.; Baidouri, H.; McDermott, A.M. Vitamin D activation and function in human corneal epithelial cells during TLR-induced inflammation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 7715–7727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.L.; Zhu, H.; Thakur, A.; Willcox, M. 1 alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in human corneal epithelial cells colonized with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Wu, D.; Xu, J. Calcitriol, the active metabolite of vitamin D3, inhibits dry eye related corneal inflammation in vivo and in vitro. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2019, 27, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.Y.; Bae, S.H.; Shin, Y.J.; Park, S.G.; Hwang, S.H.; Hyon, J.Y.; Wee, W.R. Low serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D levels are associated with dry eye syndrome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Inoue, S.; Inagaki, E.; Suzuki, A.; Ooe, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Tsubota, K. Bilberry extract supplementation for preventing eye fatigue in video display terminal workers. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, P.S.; Li, B.; Vachali, P.P.; Gorusupudi, A.; Shyam, R.; Henriksen, B.S.; Nolan, J.M. Lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin: The basic and clinical science underlying carotenoid-based nutritional interventions against ocular disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 50, 34–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.E.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; Danis, R.; Ferris, F.L.; Elman, M.; Fish, G. Lutein + zeaxanthin and omega-3 fatty acids for age-related macular degeneration: The age-related eye disease study 2 (AREDS2) randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Hao, J.L.; Xie, T.; Mukhtar, N.J.; Zhang, W.; Malik, T.H.; Lu, C.W.; Zhou, D.D. Curcumin, a potential therapeutic candidate for anterior segment eye diseases: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, J.A.; Chuck, R.S.; Joo, C.K. Curcumin suppresses ovalbumin-induced allergic conjunctivitis. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Hu, D.N.; Pan, Z.; Lu, C.W.; Xue, C.Y.; Aass, I. Curcumin protects against hyperosmoticity-induced IL-1beta elevation in human corneal epithelial cell via MAPK pathways. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, I.; Pawliczak, R. the active metabolite of vitamin D3 as a potential immunomodulator. Scand. J. Immunol. 2016, 83, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Christakos, S. Mechanisms underlying the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by Vitamin D. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8251–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalem, J.A.; Patel, D.; Susarla, R.; Coca-Prados, M.; Bland, R.; Walker, E.A.; Rauz, S.; Wallace, G.R. Characterization of vitamin D production by human ocular barrier cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Pintea, V.; Lin, Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Watsky, M.A. Vitamin D enhances corneal epithelial barrier function. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7359–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, K.W.; Ro, J.W.; Shin, Y.J.; Hyon, J.Y.; Wee, W.R.; Park, S.G. Correlation of vitamin D levels with tear film stability and secretion in patients with dry eye syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, e230–e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaumeil, J.C. Micronization: A method of improving the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 20, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, D.-M.; Curl, R.L.; Yong, C.-S.; Amidon, G.L. Effect of micronization on the extent of drug absorption from suspensions in humans. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1995, 18, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidhi, B.; Mamatha, B.S.; Baskaran, V. Olive oil improves the intestinal absorption and bioavailability of lutein in lutein-deficient mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugasini, D.; Lokesh, B.R. Curcumin and linseed oil co-delivered in phospholipid nanoemulsions enhances the levels of docosahexaenoic acid in serum and tissue lipids of rats. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2017, 119, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Okadome, H.; Sotome, I.; Itoh, T.; Isobe, S. Effective extraction of curcuminoids by grinding turmeric (Curcuma longa) with medium-chain triacylglycerols. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 19, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.; Sabbione, F.; Gabelloni, M.L.; Vanzulli, S.; Trevani, A.S.; Giordano, M.N.; Galletti, J.G. Restoring conjunctival tolerance by topical nuclear factor-κB inhibitors reduces preservative-facilitated allergic conjunctivitis in mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6116–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; He, H.; Liu, Z. A mouse dry eye model induced by topical administration of benzalkonium chloride. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, C.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, X.; Ma, P.; Ye, C.; Ge, J.; et al. A rabbit dry eye model induced by topical medication of a preservative benzalkonium chloride. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Labbe, A.; Liang, H.; Pauly, A.; Brignole-Baudouin, F. Preservatives in eyedrops: The good, the bad and the ugly. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2010, 29, 312–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.A.P.; Azar, D.T.; Baudouin, C.; Efron, N.; Hirayama, M.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Kim, T.; Mehta, J.S.; Messmer, E.M.; Pepose, J.S.; et al. TFOS DEWS II iatrogenic report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 511–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Balne, P.K.; Veerappan, A.; Au, V.B.; Lee, B.; Loo, E.; Ghosh, A.; Tong, L.; Teoh, S.C.; Connolly, J.; et al. A distinct cytokines profile in tear film of dry eye disease (DED) patients with HIV infection. Cytokine 2016, 88, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, K.; Redfern, R.L.; Nichols, J.J.; Nichols, K.K. Analysis of tear inflammatory mediators: A comparison between the microarray and Luminex methods. Mol. Vis 2016, 22, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mrugacz, M.; Ostrowska, L.; Bryl, A.; Szulc, A.; Zelazowska-Rutkowska, B.; Mrugacz, G. Pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with clinical severity of dry eye disease of patients with depression. Adv. Med. Sci. 2017, 62, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheng, Y. Level of tear cytokines in population-level participants and correlation with clinical features. Cytokine 2018, 110, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDerMeid, K.R.; Su, S.P.; Ward, K.W.; Zhang, J.Z. Correlation of tear inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases with four dry eye diagnostic tests. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C. The pathology of dry eye. Surv Ophthalmol. 2001, 45 (Suppl. 2), 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, D.Q.; Doshi, A.; Farley, W.; Corrales, R.M.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Experimental dry eye stimulates production of inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 and activates MAPK signaling pathways on the ocular surface. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Ahsan, H. Biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in ophthalmic disorders. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2020, 41, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejkova, J.; Ardan, T.; Jirsova, K.; Jechova, G.; Malec, J.; Simonova, Z.; Cejka, C.; Filipec, M.; Dotrelova, D.; Brunova, B. The role of conjunctival epithelial cell xanthine oxidoreductase/xanthine oxidase in oxidative reactions on the ocular surface of dry eye patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Histol. Histopathol. 2007, 22, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cejkova, J.; Ardan, T.; Simonova, Z.; Cejka, C.; Malec, J.; Dotrelova, D.; Brunova, B. Decreased expression of antioxidant enzymes in the conjunctival epithelium of dry eye (Sjogren’s syndrome) and its possible contribution to the development of ocular surface oxidative injuries. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Lian, C.; Ying, L.; Kim, G.E.; You, I.C.; Park, S.H.; Yoon, K.C. Expression of lipid peroxidation markers in the tear film and ocular surface of patients with Non-Sjogren syndrome: Potential biomarkers for dry eye disease. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benowitz, L.I.; Routtenberg, A. GAP-43: An intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Namavari, A.; Yco, L.; Chang, J.H.; Sonawane, S.; Khanolkar, V.; Sarkar, J.; Jain, S. Neurotrophins and nerve regeneration-associated genes are expressed in the cornea after lamellar flap surgery. Cornea 2012, 31, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.E.; Bazan, N.G. Growth-associated protein GAP-43 and nerve cell adhesion molecule in sensory nerves of cornea. Exp. Eye Res. 1992, 55, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Yokoo, S.; Yanagi, Y.; Usui, T.; Yokota, C.; Mimura, T.; Araie, M.; Yamagami, S.; Amano, S. Sphere formation and expression of neural proteins by human corneal stromal cells in vitro. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Chen, H.; Song, Z.; Yin, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M. Glial fibrillary acidic protein expression during HSV-1 infection in mouse cornea. Apmis. 2014, 122, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argueso, P.; Gipson, I.K. Epithelial mucins of the ocular surface: Structure, biosynthesis and function. Exp. Eye Res. 2001, 73, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, S.; Zhang, L.; Finn, O.J. MUC1 protein expression in tumor cells regulates transcription of proinflammatory cytokines by forming a complex with nuclear factor-kappaB p65 and binding to cytokine promoters: Importance of extracellular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42248–42256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Hollingsworth, M.A. Cell surface-associated mucins in signal transduction. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumblatt, M.M.; McKenzie, R.W.; Steele, P.S.; Emberts, C.G.; Jumblatt, J.E. MUC7 expression in the human lacrimal gland and conjunctiva. Cornea 2003, 22, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, F.; Langer, G.; Hoffmann, W.; Berry, M. Human lacrimal gland mucins. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 316, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardon, R.; Price, R.E.; Julian, J.; Lagow, E.; Tseng, S.C.; Gendler, S.J.; Carson, D.D. Bacterial conjunctivitis in Muc1 null mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Danjo, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Tisdale, A.; George, M.; Tsumura, T.; Abelson, M.B.; Gipson, I.K. Alteration of mucin in human conjunctival epithelia in dry eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar]
- Argueso, P.; Balaram, M.; Spurr-Michaud, S.; Keutmann, H.T.; Dana, M.R.; Gipson, I.K. Decreased levels of the goblet cell mucin MUC5AC in tears of patients with Sjogren syndrome. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Yu, L.; Wang, M. Expression patterns of conjunctival mucin 5AC and aquaporin 5 in response to acute dry eye stress. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, Y.; Shoji, J.; Harada, N.; Inada, N. Two patients with dry eye disease followed up using an expression assay of ocular surface mucin. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. 2016, 7, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.; Kang, H.G.; Yeo, A.; Noh, H.; Kim, H.C.; Song, J.S.; Ji, Y.W.; Lee, H.K. Comparison of ocular surface mucin expression after topical ophthalmic drug administration in dry eye-induced mouse model. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 34, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bijsterveld, O.P. Diagnostic tests in the sicca syndrome. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1969, 82, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G* Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| PSD(D90), in Microns | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Turmeric Extract | Marigold Extract | LCD Oil Suspension | |
| Before micronization | 18.3 ± 1.9 | 17.5 ± 1.4 | 30.3 ± 2.5 |
| After micronization | 3.71 ± 0.4 | 2.12 ± 0.2 | 3.9 ± 0.3 |
| Items | Groups | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Dry Eye | Dry Eye + LCD I | Dry Eye + LCD II | ||
| Glucose, mg/dL | 120.43 ± 11.97 | 123.57 ± 7.32 | 122.86 ± 11.14 | 119.29 ± 7.72 | 0.826 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.39 ± 0.11 | 0.38 ± 0.09 | 0.40 ± 0.12 | 0.38 ± 0.08 | 0.974 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 23.24 ± 2.14 | 22.93 ± 0.91 | 22.54 ± 1.71 | 21.24 ± 2.82 | 0.289 |
| TP, g/dL | 7.03 ± 0.57 | 6.90 ± 0.50 | 6.60 ± 0.37 | 6.93 ± 0.34 | 0.352 |
| ALB, g/dL | 3.84 ± 0.39 | 3.66 ± 0.16 | 3.61 ± 0.21 | 3.73 ± 0.24 | 0.410 |
| GLOB, g/dL | 3.76 ± 0.35 a | 3.49 ± 0.22 ab | 3.19 ± 0.26 b | 3.36 ± 0.35 ab | 0.012 |
| ALT, U/L | 86.71 ± 7.54 | 83.00 ± 6.35 | 87.29 ± 10.06 | 84.29 ± 9.89 | 0.764 |
| AST, U/L | 121.00 ± 16.21 | 117.29 ± 13.31 | 122 ± 20.67 | 119.57 ± 12.03 | 0.950 |
| TBIL, mg/dL | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.162 |
| Curcuminoids | Lutein and Zeaxanthin | Vitamin D3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Column | Agilent Eclipse plus C18 (100 × 4.6) mm, 3.5 µm | Kromasil silica column (4 × 250) mm, 5 µm | Inertsil ODS C18 (250 × 4.6) mm, 5 μm |
| Wavelength | 420 nm | 446 nm | 265 nm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 mL per minute | 1 mL/minute | 1 mL/min |
| Column oven Temp. | 30 °C | 25 °C | 40 ± 2 °C |
| Sample oven temperature | 25 °C | 15 °C | 20 °C |
| Injection volume | 20 µL | 20 µL | 50 µL |
| Run time | 15 min | 20 min | 20 min |
| Mobile phase | MP-A (Buffer): MP-B (THF) 600:400 ratio | hexane: ethyl acetate (500:500) v/v | 600:400 (acetonitrile: methanol) |
| Diluent | Use the mobile phase | Mobile phase | Use the mobile phase |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muz, O.E.; Orhan, C.; Erten, F.; Tuzcu, M.; Ozercan, I.H.; Singh, P.; Morde, A.; Padigaru, M.; Rai, D.; Sahin, K. A Novel Integrated Active Herbal Formulation Ameliorates Dry Eye Syndrome by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Enhancing Glycosylated Phosphoproteins in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100295
Muz OE, Orhan C, Erten F, Tuzcu M, Ozercan IH, Singh P, Morde A, Padigaru M, Rai D, Sahin K. A Novel Integrated Active Herbal Formulation Ameliorates Dry Eye Syndrome by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Enhancing Glycosylated Phosphoproteins in Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(10):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100295
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuz, Omer Ersin, Cemal Orhan, Fusun Erten, Mehmet Tuzcu, Ibrahim Hanifi Ozercan, Prafull Singh, Abhijeet Morde, Muralidhara Padigaru, Deshanie Rai, and Kazim Sahin. 2020. "A Novel Integrated Active Herbal Formulation Ameliorates Dry Eye Syndrome by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Enhancing Glycosylated Phosphoproteins in Rats" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 10: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100295
APA StyleMuz, O. E., Orhan, C., Erten, F., Tuzcu, M., Ozercan, I. H., Singh, P., Morde, A., Padigaru, M., Rai, D., & Sahin, K. (2020). A Novel Integrated Active Herbal Formulation Ameliorates Dry Eye Syndrome by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Enhancing Glycosylated Phosphoproteins in Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 13(10), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100295