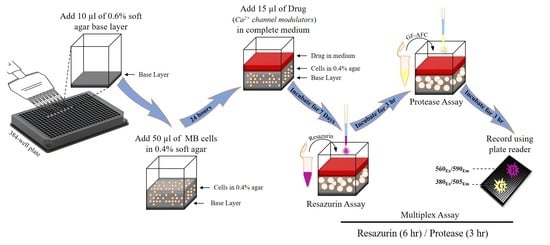
Development of a High-throughput Agar Colony Formation Assay to Identify Drug Candidates against Medulloblastoma
Abstract
Share and Cite
Sedeeq, M.; Maklad, A.; Gueven, N.; Azimi, I. Development of a High-throughput Agar Colony Formation Assay to Identify Drug Candidates against Medulloblastoma. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110368
Sedeeq M, Maklad A, Gueven N, Azimi I. Development of a High-throughput Agar Colony Formation Assay to Identify Drug Candidates against Medulloblastoma. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(11):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110368
Chicago/Turabian StyleSedeeq, Mohammed, Ahmed Maklad, Nuri Gueven, and Iman Azimi. 2020. "Development of a High-throughput Agar Colony Formation Assay to Identify Drug Candidates against Medulloblastoma" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 11: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110368
APA StyleSedeeq, M., Maklad, A., Gueven, N., & Azimi, I. (2020). Development of a High-throughput Agar Colony Formation Assay to Identify Drug Candidates against Medulloblastoma. Pharmaceuticals, 13(11), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110368