Opioid Preconditioning Modulates Repair Responses to Prevent Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Opioid Preconditioning Reduced Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
2.2. Opioids Stimulated HIF-1α Expression in the Kidney
2.3. Intrarenal Expression of VEGF and VEGF-R2 Was Modified by Opioid Preconditioning
2.4. Opioids Promoted the Expression of Molecules Associated with Vessel Formation
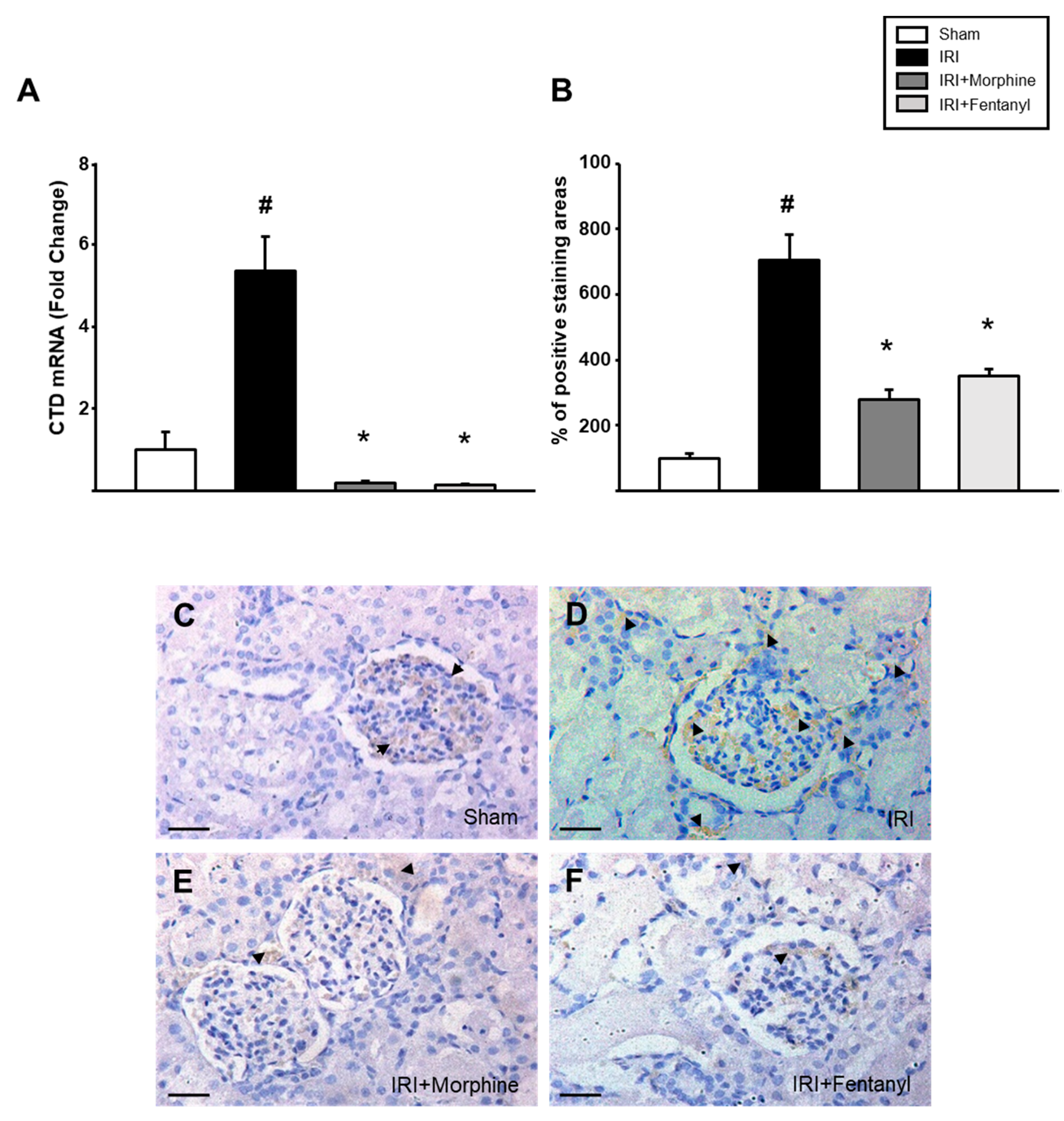
2.5. Opioid Preconditioning Prevented the Increase in IRI-Induced Cathepsin D Expression
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
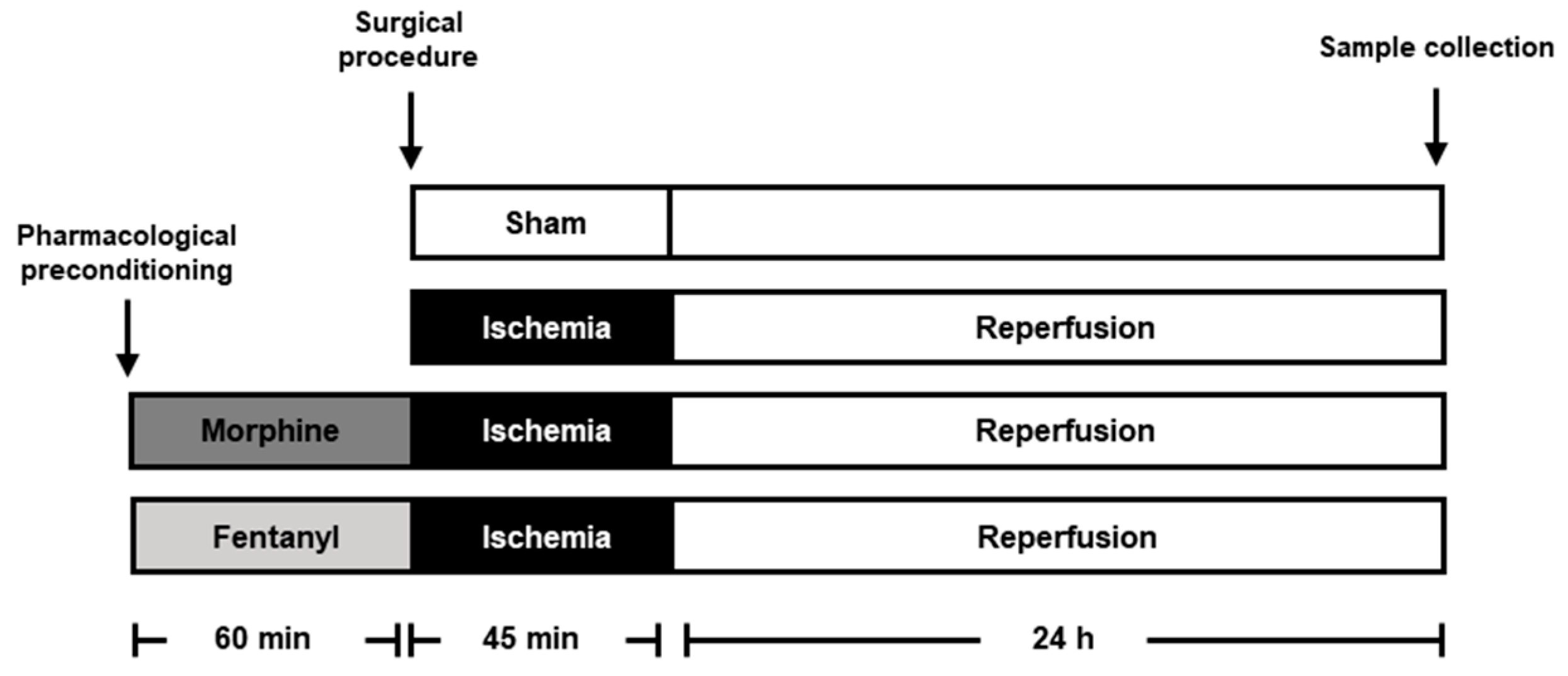
4.2. Study Design
4.3. Experimental Procedures
4.4. Real-Time PCR
4.5. Luminex
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieuwenhuijs-Moeke, G.J.; Pischke, S.; Berger, S.P.; Sanders, J.-S.; Pol, R.A.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Ploeg, R.J.; Leuvenink, H. Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation: Relevant Mechanisms in Injury and Repair. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowle, J.R. Sepsis-Associated AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, M.; Nematbakhsh, M. Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury; from pathophysiology to treatment. J. Ren. Inj. Prev. 2015, 4, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Situmorang, G.R.; Sheerin, N. Ischaemia reperfusion injury: mechanisms of progression to chronic graft dysfunction. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 34, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.P.; Anderson, M.D.; Sutton, T.A. Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injury. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1303–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.P. The transforming growth factor beta system in kidney disease and repair: Recent progress and future directions. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1999, 8, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.P. The case for capillary rarefaction in the AKI to CKD progression: Insights from multiple injury models. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2019, 317, F1253–F1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Anand, V.; Roy, S. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling in Hypoxia and Inflammation. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinand, C.S.; Raju, R.; Soumya, S.J.; Arya, P.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R. VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling network in endothelial cells relevant to angiogenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 10, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziello, J.E.; Jovin, I.S.; Huang, Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 Regulatory Pathway and its Potential for Therapeutic Intervention in Malignancy and Ischemia. Yale J. Boil. Med. 2007, 80, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.-J.; Hong, S.-H.; Park, R.-K.; Shin, T.; An, N.-H.; Kim, H.-M. Hypoxia-induced IL-6 production is associated with activation of MAP kinase, HIF-1, and NF-κB on HEI-OC1 cells. Hear. Res. 2005, 207, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Tang, C.; Dong, Z. Hypoxia and Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Kidney Injury and Repair. Cells 2019, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Lei, C.-T.; Zhang, C. Interleukin-6 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Kidney Disease: An Update. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, J.; Monkawa, T.; Tsuji, M.; Hayashi, M.; Saruta, T. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Is Involved in Tubular Regeneration after Experimental Acute Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 3090–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Ye, J.; Shen, F.; Zhu, Y.; Yeghiazarians, Y.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Y.; Lawton, M.T.; Young, W.L.; Yang, G.-Y. Interleukin-6 Stimulates Circulating Blood-Derived Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 28, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, J.; Echavarria, R.; Franco-Acevedo, A.; Moreno-Carranza, B.; Melo, Z. Opioids Preconditioning Upon Renal Function and Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2019, 55, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscusi, E.; Reynolds, L.; Chung, F.; Atkinson, L.E.; Khanna, S. Patient-Controlled Transdermal Fentanyl Hydrochloride vs Intravenous Morphine Pump for Postoperative Pain. JAMA 2004, 291, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminian, A.; Javadi, S.; Rahimian, R.; Dehpour, A.R.; Amoli, F.A.; Moghaddas, P.; Mehr, S.E. Enhancement of Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity by Morphine and Its Attenuation by the Opioid Antagonist Naltrexone. Acta Med. Iran. 2016, 54, 422–429. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-J.; Yu, J.-J.; Xu, X.-L. Kappa-opioid receptor agonist U50448H protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallappallil, M.; Sabu, J.; Friedman, E.A.; Salifu, M. What Do We Know about Opioids and the Kidney? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Milner, Q.J.W. Postoperative analgesia following renal transplantation—Current practice in the UK. Anaesthesia 2003, 58, 712–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondrovics, M.; Hoelbl-Kovacic, A.; Fux, D.A. Opioids: Modulators of angiogenesis in woundhealing and cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25783–25796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Poonawala, T.; Farooqui, M.; Ericson, M.; Gupta, K. Topical fentanyl stimulates healing of ischemic wounds in diabetic rats. J. Diabetes 2015, 7, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimonte, S.; Barbieri, A.; Rea, D.; Palma, G.; Luciano, A.; Cuomo, A.; Arra, C.; Izzo, F. Morphine Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis and Increases Breast Cancer Progression. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoos, A.; Gabriel, C.; Knab, V.M.; Fux, D.A. Activation of HIF-1alpha by delta-Opioid Receptors Induces COX-2 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells and Leads to Paracrine Activation of Vascular Endothelial Cells. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Chen, C.; Lutty, G.A.; Hebbel, R.P. Morphine promotes neovascularizing retinopathy in sickle transgeneic mice. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ramírez, V.; Ichimura, T.; Bobadilla, N.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1: A sensitive quantitative biomarker for early detection of kidney tubular injury. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2006, 290, F517–F529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogare, A.L.; Veronese, F.V.; Carpio, V.N.; Montenegro, R.M.; Pedroso, J.A.; Pegas, K.L.; Gonçalves, L.F.; Manfro, R.C. Kidney injury molecule-1 expression in human kidney transplants with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echavarría, R.; Garcia, D.; Figueroa, F.; Franco, A.; Palomino, J.; De Buen, E.P.; Monraz, M.D.L.P.G.; Moreno-Carranza, B.; Melo, Z. Anesthetic preconditioning increases sirtuin 2 gene expression in a renal ischemia reperfusion injury model. Minerva Urol. Nefrol 2020, 72, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Choi, D.-K. Hypoxia Inducible Factor Pathway and Physiological Adaptation: A Cell Survival Pathway? Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchiaro, P.; De Pasquale, V.; Della Morte, R.; Tafuri, S.; Avallone, L.; Pizard, A.; Moles, A.; Pavone, L.M. The Multifaceted Role of the Lysosomal Protease Cathepsins in Kidney Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, M.A.; Weinberg, J.M.; Kriz, W.; Bidani, A.K. Failed Tubule Recovery, AKI-CKD Transition, and Kidney Disease Progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Li, H.; Irwin, M.G. Myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury: The challenge of translating ischaemic and anaesthetic protection from animal models to humans. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117, ii44–ii62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; He, X.; Yang, Y.; Chao, D.; Lazarus, L.H.; Xia, Y. Current Research on Opioid Receptor Function. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abecassis, M.; Bartlett, S.T.; Collins, A.J.; Davis, C.L.; Delmonico, F.L.; Friedewald, J.J.; Hays, R.; Howard, A.; Jones, E.; Leichtman, A.B.; et al. Kidney Transplantation as Primary Therapy for End-Stage Renal Disease: A National Kidney Foundation/Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF/KDOQI™) Conference. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezdorn, N.; Tasigiorgos, S.; Wo, L.; Turk, M.; Lopdrup, R.; Kiwanuka, H.; Win, T.-S.; Bueno, E.; Pomahac, B. Tissue conservation for transplantation. Innov. Surg. Sci. 2017, 2, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenbach, D.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Mechanisms of maladaptive repair after AKI leading to accelerated kidney ageing and CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, O.C.; McGowan, J.W.D.; George, E.M.; Bidwell, G.L. Therapeutic angiogenesis by vascular endothelial growth factor supplementation for treatment of renal disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, L.O.; Chade, A.R. Angiogenesis in the kidney: A new therapeutic target? Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, C.; Mandriota, S.; Jürgensen, J.S.; Wiesener, M.S.; Hörstrup, J.H.; Frei, U.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Maxwell, P.H.; Bachmann, S.; Eckardt, K.-U. Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 and -2 in Hypoxic and Ischemic Rat Kidneys. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Song, N.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, X.; Hu, J.; Liang, M.; Teng, J.; Ding, X. Renal Protection Mediated by Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Depends on Proangiogenesis Function of miR-21 by Targeting Thrombospondin. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.-M.; You, S.J.; Lee, Y.-M.; Oh, S.-W.; Ahn, S.-Y.; Kim, S.; Chin, H.J.; Chae, N.-W.; Na, K.Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Activation Protects the Kidney from Gentamicin-Induced Acute Injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Jiang, D.; Xiao, J.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, X. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced kidney injury by activating autophagy via the SGK1 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, P.; Shukla, D.; Tran, M.G.B.; Aragones, J.; Cook, H.T.; Carmeliet, P.; Maxwell, P.H. Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor hydroxylases protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, W.M.; Câmpean, V.; Kany, S.; Jürgensen, J.-S.; Weidemann, A.; Warnecke, C.; Arend, M.; Klaus, S.; Günzler, V.; Amann, K.; et al. Preconditional Activation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Ameliorates Ischemic Acute Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Li, P.-L.; Dhaduk, R.; Zhang, F.; Gehr, T.W.; Li, N. Silencing of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α gene attenuates chronic ischemic renal injury in two-kidney, one-clip rats. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2014, 306, F1236–F1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.F.; Kimura, K.; Iwano, M.; Haase, V.H. Hypoxia-inducible factor signaling in the development of tissue fibrosis. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolyada, A.Y.; Tighiouart, H.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Liangos, O.; Madias, N.E.; Jaber, B.L. A genetic variant of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is associated with adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.-S.; Rohan, R.; Sunday, M.E.; Demello, D.E.; D’Amore, P.A. Differential expression of VEGF isoforms in mouse during development and in the adult. Dev. Dyn. 2001, 220, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.P.; Fredrich, K.; Chelladurai, B.; Leonard, E.C.; Parrish, A.R. Renal ischemia reperfusion inhibits VEGF expression and induces ADAMTS-1, a novel VEGF inhibitor. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2008, 294, F928–F936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, T.W.; Engel, J.E.; Chade, A.R. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Podocyte Protection in Chronic Hypoxia: Effects of Endothelin-A Receptor Antagonism. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 43, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, C.C.; Maldonado, A.; Mallipattu, S.K. Therapeutic Inhibition of VEGF Signaling and Associated Nephrotoxicities. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, V.; Jefferson, J.A.; Kowalewska, J.; Hochster, H.; Haas, M.; Weisstuch, J.; Richardson, C.; Kopp, J.B.; Kabir, M.G.; Backx, P.H.; et al. VEGF Inhibition and Renal Thrombotic Microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.E.; Williams, E.; Williams, M.L.; Bidwell, G.L.; Chade, A.R. Targeted VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) Therapy Induces Long-Term Renal Recovery in Chronic Kidney Disease via Macrophage Polarization. Hypertension 2019, 74, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, E.C.; Friedrich, J.L.; Basile, D.P. VEGF-121 preserves renal microvessel structure and ameliorates secondary renal disease following acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2008, 295, F1648–F1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac Gabhann, F.; Popel, A.S.; Gabhann, F.M. Differential binding of VEGF isoforms to VEGF receptor 2 in the presence of neuropilin-1: A computational model. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H2851–H2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchiaro, P.; Fox, C.; Tregidgo, N.W.; Howarth, R.; Wood, K.M.; Situmorang, G.R.; Pavone, L.M.; Sheerin, N.S.; Moles, A. Lysosomal protease cathepsin D; a new driver of apoptosis during acute kidney injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.; Cocchiaro, P.; Oakley, F.; Howarth, R.; Callaghan, K.; Leslie, J.; Luli, S.; Wood, K.M.; Genovese, F.; Sheerin, N.S.; et al. Inhibition of lysosomal protease cathepsin D reduces renal fibrosis in murine chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthi, I.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 41, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Kersten, J.R.; Riess, M.M.L. Opioid-induced Cardioprotection. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 5696–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahsili-Fahadan, P.; Yahyavi-Firouz-Abadi, N.; Khoshnoodi, M.A.; Motiei-Langroudi, R.; Tahaei, S.A.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Dehpour, A.R. Agmatine Potentiates Morphine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Mice: Modulation by Alpha(2)-Adrenoceptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 31, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Melo, Z.; Cruz-Rangel, S.; Bautista, R.; Vázquez, N.; Castañeda-Bueno, M.; Mount, D.B.; Pasantes-Morales, H.; Mercado, A.; Gamba, G. Molecular evidence for a role for K+-Cl− cotransporters in the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2013, 305, F1402–F1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Target Gene | Sequences (5′-3′) | Annealing Temp. (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| KIM-1 | F-TCCTGTGGGATTCATGCAGT | R-GCAGGAGGCCTGAAATGAAG | 53 |
| IL-6 | F-TGAGAAAAGAGTTGTGCAATGG | R-GCATCATCGCTGTTCATACAAT | 51 |
| CD31 | F-TTGTGACCAGTCTCCGAAGC | R-TGGCTGTTGGTTTCCACACT | 54 |
| HIF-1α | F-GCAACTGCCACCACTGATGA | R-GCTGCTTGAAAAAGGGAGCC | 54 |
| VEGF | F-GGCCTCTGAAACCATGAACT | R-TGCTCCCCTTCTGTCGTG | 53 |
| VEGF-R2 | F-TTTTGGCAAATACAACCCTTC | R-AGATTACTTGCAGGGGACAGA | 53 |
| CTD | F-CCGTCGGACTATGACGGAAG | R-ACAGCTCCCCGTGGTAGTAT | 60.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco-Acevedo, A.; Echavarria, R.; Moreno-Carranza, B.; Ortiz, C.-I.; Garcia, D.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, R.; Bitzer-Quintero, O.-K.; Portilla-De Buen, E.; Melo, Z. Opioid Preconditioning Modulates Repair Responses to Prevent Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110387
Franco-Acevedo A, Echavarria R, Moreno-Carranza B, Ortiz C-I, Garcia D, Gonzalez-Gonzalez R, Bitzer-Quintero O-K, Portilla-De Buen E, Melo Z. Opioid Preconditioning Modulates Repair Responses to Prevent Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(11):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110387
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco-Acevedo, Adriana, Raquel Echavarria, Bibiana Moreno-Carranza, Cesar-Ivan Ortiz, David Garcia, Ricardo Gonzalez-Gonzalez, Oscar-Kurt Bitzer-Quintero, Eliseo Portilla-De Buen, and Zesergio Melo. 2020. "Opioid Preconditioning Modulates Repair Responses to Prevent Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 11: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110387
APA StyleFranco-Acevedo, A., Echavarria, R., Moreno-Carranza, B., Ortiz, C.-I., Garcia, D., Gonzalez-Gonzalez, R., Bitzer-Quintero, O.-K., Portilla-De Buen, E., & Melo, Z. (2020). Opioid Preconditioning Modulates Repair Responses to Prevent Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Pharmaceuticals, 13(11), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110387






