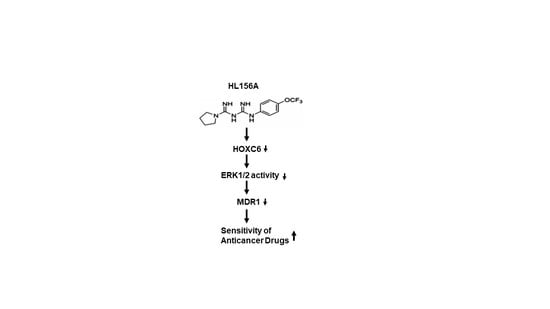
Metformin Derivative HL156A Reverses Multidrug Resistance by Inhibiting HOXC6/ERK1/2 Signaling in Multidrug-Resistant Human Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
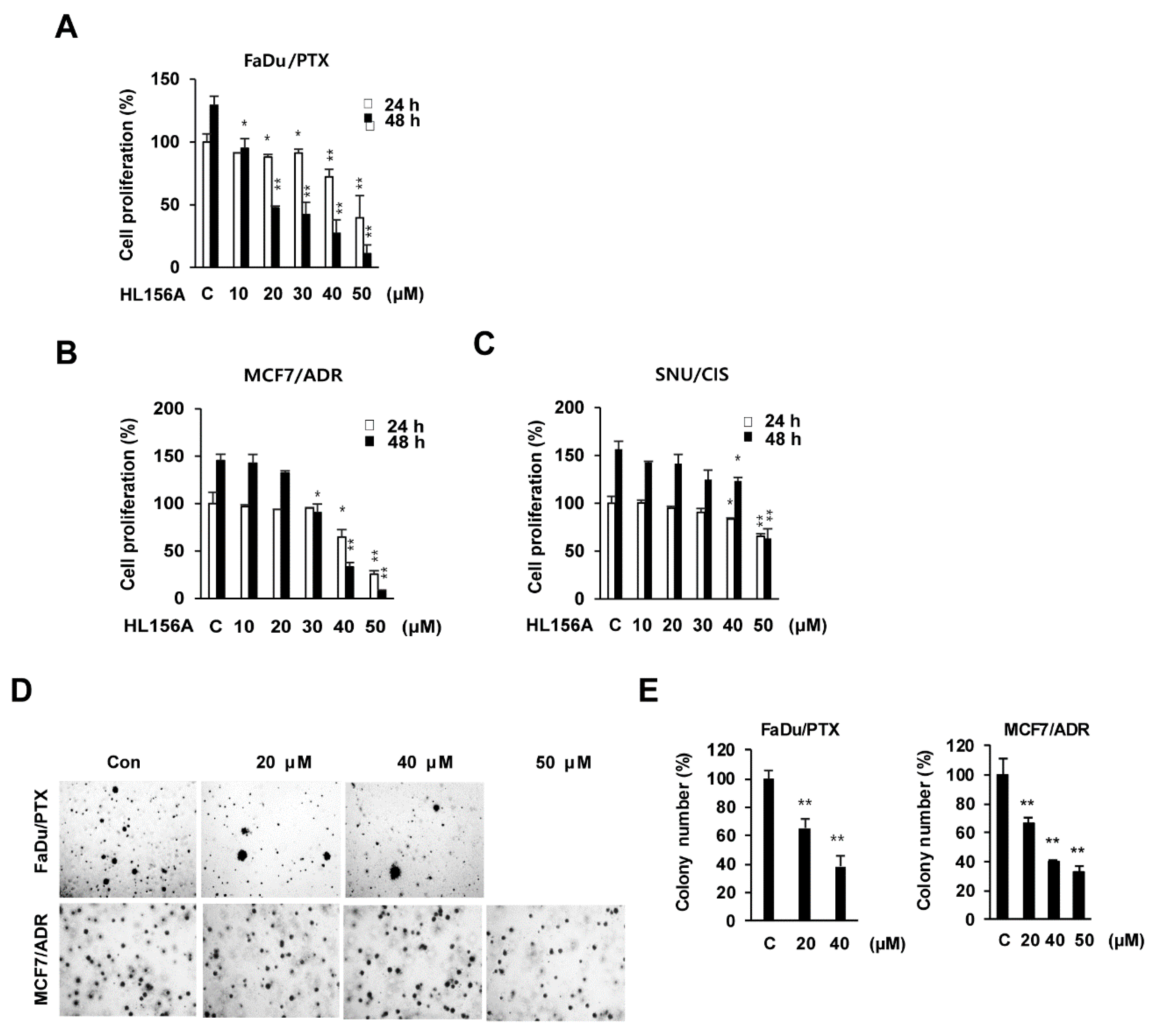
2.1. Effects of HL156A on MDR Cell Proliferation
2.2. HL156A Induces G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
2.3. HL156A Inhibits the Migration and Invasion Ability of MDR Cells
2.4. HL156A Suppresses MDR1 through the HOXC6-ERK1/2 Pathway
2.5. siHOXC6 Regulates MDR1 Expression by Suppressing ERK1/2 Activity
2.6. HL156A Enhances Drug Accumulation and Sensitivity in MDR Cells
2.7. HL156A Prevents Angiogenesis of Xenografted MDR Cells in the CAM Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.3. Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay
4.4. Wound Healing Motility Assay
4.5. Cell Migration Assay
4.6. Cell Aycle Analysis and Annexin V-FITC/PI Double Staining
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.9. siRNA Interference Assay
4.10. Rhodamine Accumulation Assay
4.11. Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottesman, M.M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, M.F. Cancer multidrug resistance (MDR): A major impediment to effective chemotherapy. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2008, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clynes, M. Cellular models for multiple drug resistance in cancer. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 1993, 29, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambudkar, S.V.; Dey, S.; Hrycyna, C.A.; Ramachandra, M.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 361–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.W.; Goldenberg, S.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Decreased accumulation of [14C] carboplatin in human cisplatin-resistant cells results from reduced energy-dependent uptake. J. Cell Physiol. 2000, 183, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synold, T.W.; Dussault, I.; Forman, B.M. The orphan nuclear receptor SXR coordinately regulates drug metabolism and efflux. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Davudian, S.; Shirjang, S.; Baradaran, B. The Different Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance: A Brief Review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, R.; Luk, F.; Bebawy, M. Inhibition of the Multidrug Resistance P-Glycoprotein: Time for a Change of Strategy? Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, G.D.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. The role of ABC transporters in clinical practice. Oncologist 2003, 8, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, L.M.; Markova, S.M.; Chinn, L.W.; Gow, J.M.; Kroetz, D.L.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Very important pharmacogene summary: ABCB1 (MDR1,P-glycoprotein). Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Bian, Y.; Zeng, S. Involvement of AP-1 and NF-κB in the up-regulation of P-gp in vinblastine resistant Caco-2 cells. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2014, 29, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y. The cytotoxic effect of the benzene metabolite hydroquinone is mediated by the modulation of MDR1 expression via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldonza, M.B.; Hong, J.Y.; Bae, S.Y.; Song, J.; Kim, W.K.; Oh, J.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.K. Suppression of MAPK signaling and reversal of mTOR-dependent MDR1-associated multidrug resistance by 21α-methylmelianodiol in lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133922. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, K.; Noguchi, K.; Sugimoto, Y. Regulations of P-glycoprotein/ABCB1/MDR1 in human cancer cells. New J. Sci. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.J.; Hellberg, K.; Turner, M.; Talbott, G.; Kolar, M.J.; Ross, D.S.; Hoxhaj, G.; Saghatelian, A.; Shaw, R.J.; Manning, B.D. Metformin inhibits hepatic mTORC1 signaling via dose-dependent mechanisms involving AMPK and the TSC complex. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Barco, S.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Cufí, S.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Joven, J.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin: Multi-faceted protection against cancer. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 896–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinello, P.C.; Panis, C.; Silva, T.N.X.; Binato, R.; Abdelhay, E.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Mencalha, A.L.; Lopes, N.M.D.; Luiz, R.C.; Cecchini, R.; et al. Metformin prevention of doxorubicin resistance in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 involves oxidative stress generation and modulation of cell adaptation genes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5864–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.; Lobanova, L.; Dawicki, W.; Groot, G.; Gordon, J.R.; Bowen, M.; Harkness, T.; Arnason, T. Metformin inhibits the development, and promotes the resensitization, of treatment-resistant breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jia, K.; Feng, T.; Sun, D.; Gao, Z.; Xu, F.; Hou, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Metformin reverses multidrug resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma Bel 7402/5 fluorouracil cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 2891–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.A.; Quirantes-Pine, R.; Rodriguez-Gallego, E.; Cufi, S.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Cuyas, E.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Joven, J. Oncobiguanides: Paracelsus’ law and nonconventional routes for administering diabetobiguanides for cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, K.D.; Kim, H.J.; Tsogbadrakh, B.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.; Cho, E.J.; Hwang, Y.H.; Kim, K.; Yang, J.; Ahn, C.; et al. HL156A, a novel AMP-activated protein kinase activator, is protective against peritoneal fibrosis in an in vivo and in vitro model of peritoneal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2016, 310, F342–F350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, I.; Shim, J.K.; Park, J.; Jeon, J.Y.; Yun, M.; Kim, S.H.; Yook, J.I.; Kim, E.H.; et al. Inhibiting stemness and invasive properties of glioblastoma tumorsphere by combined treatment with temozolomide and a newly designed biguanide (HL156A). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65643–65659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Shin, H.S.; Choi, J.; Bae, S.J.; Wee, H.J.; Son, T.; Seo, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, K.W. AMP-activated protein kinase activator, HL156A reduces thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice and inhibits the activation of cultured hepatic stellate cells and macrophages. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsogbadrakh, B.; Ju, K.D.; Lee, J.; Han, M.; Koh, J.; Yu, Y.; Lee, H.; Yu, K.S.; Oh, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; et al. HL156A, a novel pharmacological agent with potent adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator activity ameliorates renal fibrosis in a rat unilateral ureteral obstruction model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.G.; Jeong, Y.S.; Kim, S.A.; Ahn, S.G. New metformin derivative HL 156A prevents oral insulin—Like growth factor/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathways. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.; Lam, T.G.; Yook, J.I.; Ahn, S.G. Antioxidant modifications induced by the new metformin derivative HL156A regulate metabolic reprogramming in SAMP1/kl(-/-) mice. Aging (Albany NY) 2018, 10, 2338–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Moon, S.M.; Kim, S.A.; Kang, K.W.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.G. Transcriptional regulation of MDR-1 by HOXC6 in multidrug-resistant cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jacob, L.; Kostev, K.; Rathmann, W.; Kalder, M. Impact of metformin on metastases in patients with breast cancer and type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, A.; Vacheron, A.; Zuber, J.; Solomon, S.S. Metformin associated with increased survival in type 2 diabetes patients with pancreatic cancer and lymphoma. Am. J. Med. Sci 2019, 358, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei-Irannejad, V.; Samadi, N.; Yousefi, B.; Salehi, R.; Velaei, K.; Zarghami, N. Metformin enhances doxorubicin sensitivity via inhibition of doxorubicin efflux in P-gp-overexpressing MCF-7 cells. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Yang, J.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, H.; Yao, M.; Wang, L.; Gu, J.J.; Cai, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yao, D.F. Reversal of multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by metformin through inhibiting NF-κB gene transcription. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; He, Z. Metformin reverses multidrug resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 386, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gekeler, V.; Beck, J.; Noller, A.; Wilisch, A.; Frese, G.; Neumann, M.; Handgretinger, R.; Ehninger, G.; Probst, H.; Niethammer, D. Drug-induced changes in the expression of MDR-associated genes: Investigations on cultured cell lines and chemotherapeutically treated leukemias. Ann. Hematol. 1994, 69, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Sinz, M.; Zoeckler, M.; Staudinger, J.; Redinbo, M.R.; Teotico, D.G.; Locker, J.; Kalpana, G.V.; Mani, S. Inhibition of drug metabolism by blocking the activation of nuclear receptors by ketoconazole. Oncogene 2007, 26, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, I.S.; Jones, K.; Coleman, T.; Simmons, N.L. Rifampin and digoxin induction of MDR1 expression and function in human intestinal (T84) epithelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, R.; Iwasaki, T.; Rokutanda, N.; Takeshita, A.; Koibuchi, Y.; Horiguchi, J.; Shimokawa, N.; Iino, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Koibuchi, N. Tamoxifen activates CYP3A4 and MDR1 genes through steroid and xenobiotic receptor in breast cancer cells. Endocr 2006, 30, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Lin-Lee, Y.C.; Claret, F.X.; Kuo, M.T. 2-acetylaminofluorene up-regulates rat mdr1b expression through generating reactive oxygen species that activate NF-kappa B pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.T.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lin-Lee, Y.C.; Tatebe, S.; Mills, G.B.; Unate, H. Induction of human MDR1 gene expression by 2-acetylaminofluorene is mediated by effectors of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway that activate NF-κB signaling. Oncogene 2002, 21, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantappiè, O.; Masini, E.; Sardi, I.; Raimondi, L.; Bani, D.; Solazzo, M.; Vannacci, A.; Mazzanti, R. The MDR phenotype is associated with the expression of COX-2 and iNOS in a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Hepatology 2002, 35, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Ghatak, S.; Toole, B.P. Regulation of MDR1 expression and drug resistance by a positive feedback loop involving hyaluronan, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and ErbB2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20310–20315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, K.; Yoshioka, S.; Tsukahara, S.; Mitsuhashi, J.; Sugimoto, Y. Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway results in the down-regulation of P-glycoprotein. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2092–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Yuan, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Li, D.; Li, D. PD-1/PD-L1 interaction up-regulates MDR1/P-gp expression in breast cancer cells via PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99901–99912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Gene | Sense | Antisense |
|---|---|---|
| HOXC6 | CACCGCCTATGATCCAGTGAGGCA | GCTGGAACTGAACACGACATTCTC |
| MDR1 | GACTGTCAGCTGCTGTCTGGGCAA | GCCAAGACCTCTTCAGCTACTGC |
| GAPDH | AGCCAAAAGGGTCATCATCTCTGC | GCATTGGGATGATCTTGAGGCTG |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, Y.S.; Lam, T.G.; Jeong, S.; Ahn, S.-G. Metformin Derivative HL156A Reverses Multidrug Resistance by Inhibiting HOXC6/ERK1/2 Signaling in Multidrug-Resistant Human Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090218
Jeong YS, Lam TG, Jeong S, Ahn S-G. Metformin Derivative HL156A Reverses Multidrug Resistance by Inhibiting HOXC6/ERK1/2 Signaling in Multidrug-Resistant Human Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(9):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090218
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Yun Soo, Thuy Giang Lam, Seho Jeong, and Sang-Gun Ahn. 2020. "Metformin Derivative HL156A Reverses Multidrug Resistance by Inhibiting HOXC6/ERK1/2 Signaling in Multidrug-Resistant Human Cancer Cells" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 9: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090218
APA StyleJeong, Y. S., Lam, T. G., Jeong, S., & Ahn, S.-G. (2020). Metformin Derivative HL156A Reverses Multidrug Resistance by Inhibiting HOXC6/ERK1/2 Signaling in Multidrug-Resistant Human Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 13(9), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090218