Pharmacokinetics of Mephedrone Enantiomers in Whole Blood after a Controlled Intranasal Administration to Healthy Human Volunteers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation
2.2. Determination of the Elution Order
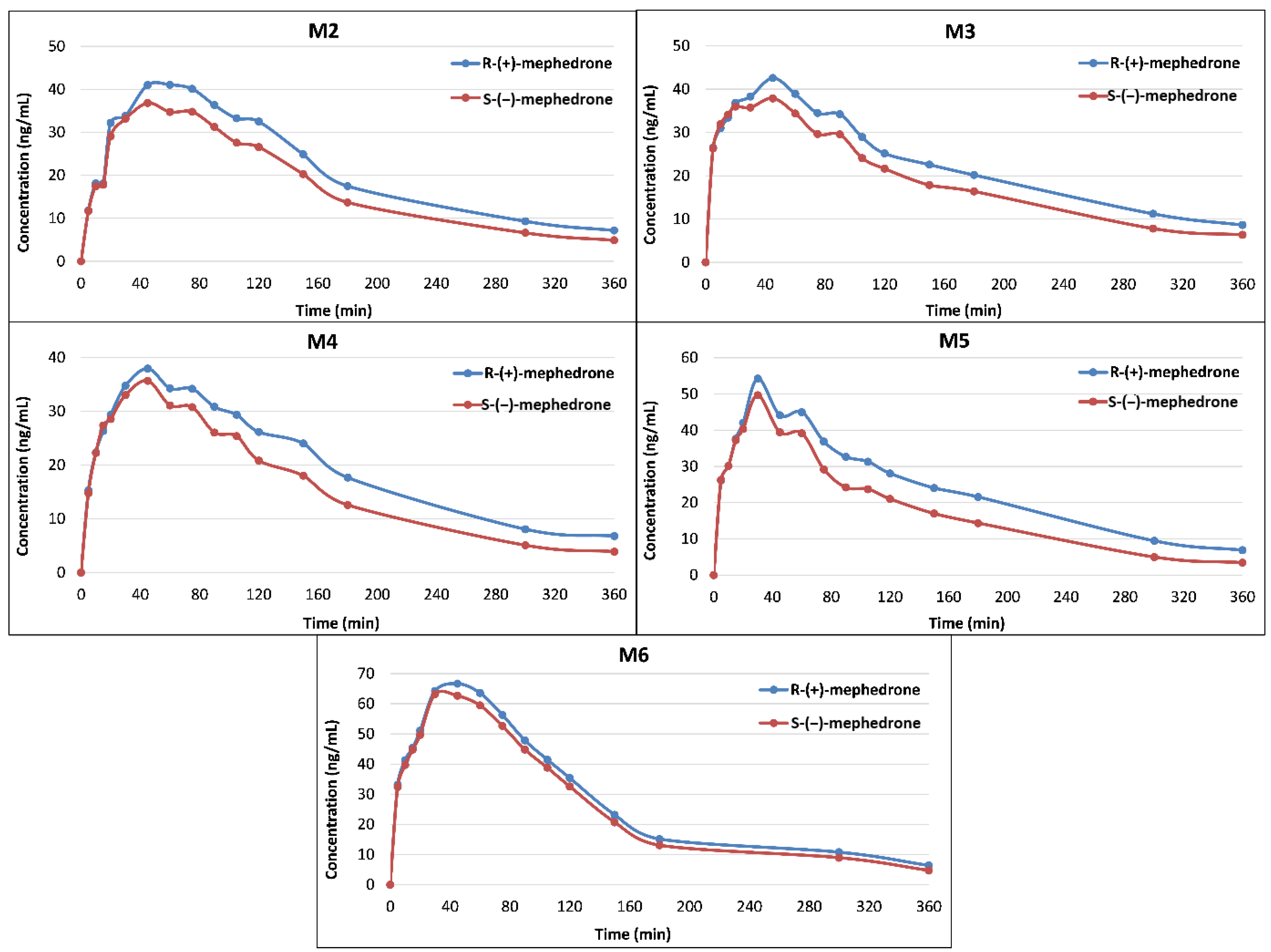
2.3. Concentrations of Mephedrone Enantiomers in Whole Blood
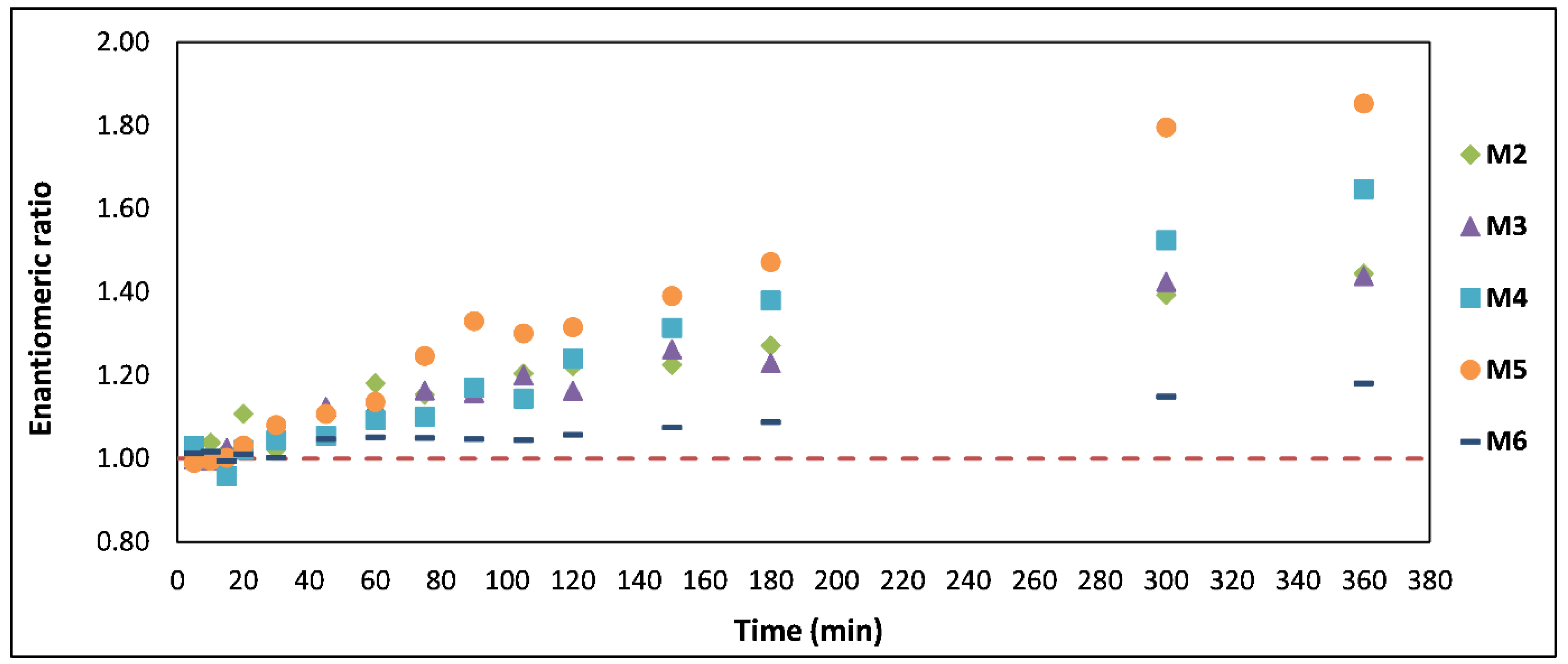
2.4. Enantiomeric Ratio (ER)
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Blank Matrix
4.3. Volunteer Administration Study and Sample Collection
4.4. Working Solutions
4.5. Calibration Standards and Quality Control Samples
4.6. Sample Preparation
4.7. Instrumentation
4.8. Determination of the Elution Order
4.9. Pharmacokinetic Calculations
4.10. Statistical Analysis
4.11. Validation Procedure
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood, D.M.; Dargan, P.I. Mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone): What is new in our understanding of its use and toxicity. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 39, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrignanò, E.; Mardal, M.; Rydevik, A.; Miserez, B.; Ramsey, J.; Shine, T.; Panto, G.D.; Meyer, M.R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A new approach towards biomarker selection in estimation of human exposure to chiral chemicals: A case study of mephedrone. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargan, P.I.; Sedefov, R.; Gallegos, A.; Wood, D.M. The pharmacology and toxicology of the synthetic cathinone mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone). Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, A.; Johnston, M.R.; Brennan, M.; Davis, S.; Caldicott, D.G.E. Chemical analysis of four capsules containing the controlled substance analogues 4-methylmethcathinone, 2-fluoromethamphetamine, alpha-phthalimidopropiophenone and N-ethylcathinone. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 197, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Olivares, M.; Rezende, M.C.; Sepúlveda-Boza, S.; Cassels, B.K.; Baggio, R.F.; Muñoz-Acevedo, J.C. A two-step method for the preparation of homochiral cathinones. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2003, 14, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, S.; Zloh, M. An analysis of the “legal high” mephedrone. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4135–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Chiral drugs: An overview. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 2, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gregg, R.A.; Baumann, M.H.; Partilla, J.S.; Bonano, J.S.; Vouga, A.; Tallarida, C.S.; Velvadapu, V.; Smith, G.R.; Peet, M.M.; Reitz, A.B.; et al. Stereochemistry of mephedrone neuropharmacology: Enantiomer-specific behavioural and neurochemical effects in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castrignanò, E.; Lubben, A.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Enantiomeric profiling of chiral drug biomarkers in wastewater with the usage of chiral liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1438, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, F.P.; Cintulova, D.; Pittrich, D.A.; Wimmer, L.; Luethi, D.; Holy, M.; Jaentsch, K.; Tischberger, S.; Gmeiner, G.; Hoener, M.C.; et al. Stereochemistry of phase-1 metabolites of mephedrone determines their effectiveness as releasers at the serotonin transporter. Neuropharmacology 2019, 148, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czerwinska, J.; Parkin, M.C.; George, C.; Kicman, A.T.; Dargan, P.I.; Abbate, V. Pharmacokinetics of mephedrone and its metabolites in whole blood and plasma after a controlled intranasal administration to healthy human volunteers. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2020. Accepted for Publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Geus, H.-J.; Wester, P.G.; de Boer, J.; Brinkman, U.A.T. Enantiomer fractions instead of enantiomer ratios. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawley, R.E. Do the terms “% ee” and “% de” make sense as expressions of stereoisomer composition or stereoselectivity? J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 2411–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brocks, D.R. Drug disposition in three dimensions: An update on stereoselectivity in pharmacokinetics. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2006, 27, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambuchen, M.D.; Hendrickson, H.P.; Gunnell, M.G.; McClenahan, S.J.; Ewing, L.E.; Gibson, D.M.; Berquist, M.D.; Owens, S.M. The pharmacokinetics of racemic MDPV and its (R) and (S) enantiomers in female and male rats. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2017, 179, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, M.D. Human Drug Metabolism: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Olesti, E.; Farré, M.; Carbó, M.; Papaseit, E.; Perez-Mañá, C.; Torrens, M.; Yubero-Lahoz, S.; Pujadas, M.; Pozo, Ó.J.; Torre, R. Dose-Response Pharmacological Study of Mephedrone and Its Metabolites: Pharmacokinetics, Serotoninergic Effects, and Impact of CYP2D6 Genetic Variation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 106, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaninger, A.E.; Meyer, M.R.; Barnes, A.J.; Kolbrich-Spargo, E.A.; Gorelick, D.A.; Goodwin, R.S.; Huestis, M.A.; Maurer, H.H. Stereoselective urinary MDMA (ecstasy) and metabolites excretion kinetics following controlled MDMA administration to humans. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czerwinska, J.; Parkin, M.C.; Dargan, P.I.; George, C.; Kicman, A.T.; Abbate, V. Stability of mephedrone and five of its phase I metabolites in human whole blood. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 11, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cilibrizzi, A.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Bartolucci, G.; Crocetti, L.; Dal Piaz, V.; Giovannoni, M.P.; Graziano, A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Quinn, M.T.; Vergelli, C. Synthesis, enantioresolution, and activity profile of chiral 6-methyl-2,4-disubstituted pyridazin-3(2H)-ones as potent N-formyl peptide receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3781–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Yang, B.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, K.; He, Z. A novel potential primary method for quantification of enantiomers by high performance liquid chromatography-circular dichroism. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018.
- Peters, F.T.; Drummer, O.H.; Musshoff, F. Validation of new methods. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 165, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| R-MEPH | |||||||
| Cmax | Tmax | kel | t1/2 | AUC | CL | Vd | |
| (ng/mL) | (min) | (min−1) | (h) | (ng mL−1 h) | (mL min−1 kg−1) | (L kg−1) | |
| M2 | 41.1 | 60 | 0.006 | 1.87 | 192 | 114 | 18.5 |
| M3 | 42.5 | 45 | 0.005 | 2.3 | 209 | 122 | 24.4 |
| M4 | 38 | 45 | 0.006 | 2 | 179 | 157 | 27.2 |
| M5 | 54.2 | 30 | 0.006 | 1.89 | 201 | 100 | 16.5 |
| M6 | 66.7 | 45 | 0.007 | 1.56 | 219 | 137 | 18.6 |
| Mean ± SD | 48.5 ± 11.9 | 45 ± 11 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 1.92 ± 0.27 | 200 ± 16 | 126 ± 22 | 21.0 ± 4.5 |
| S-MEPH | |||||||
| Cmax | Tmax | kel | t1/2 | AUC | CL | Vd | |
| (ng/mL) | (min) | (min−1) | (h) | (ng mL−1 h) | (mL min−1 kg−1) | (L kg−1) | |
| M2 | 36.8 | 45 | 0.007 | 1.69 | 150 | 146 | 21.4 |
| M3 | 37.9 | 45 | 0.006 | 2.01 | 168 | 153 | 26.6 |
| M4 | 35.7 | 45 | 0.007 | 1.57 | 130 | 216 | 29.4 |
| M5 | 49.7 | 30 | 0.008 | 1.45 | 136 | 148 | 18.6 |
| M6 | 63.2 | 30 | 0.008 | 1.44 | 191 | 158 | 19.7 |
| Mean ± SD | 44.6 ± 11.8 | 39 ± 8 | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 1.63 ± 0.23 | 155 ± 25 | 164 ± 29 | 23.1 ± 4.6 |
| Analyte | Retention Time (min) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | Internal Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-MEPH | 5.9 | 160.4 ** | 145.1 * | 15 | S-MEPH-d3 |
| 144.1 | 33 | ||||
| 91.1 | 28 | ||||
| R-MEPH | 4.9 | 160.4 ** | 145.1 * | 15 | R-MEPH-d3 |
| 144.1 | 33 | ||||
| 91.1 | 28 | ||||
| S-MEPH-d3 | 5.9 | 163.4 ** | 148.4 | 19 | |
| R-MEPH-d3 | 4.9 | 163.4 ** | 148.4 | 19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czerwinska, J.; Parkin, M.C.; Cilibrizzi, A.; George, C.; Kicman, A.T.; Dargan, P.I.; Abbate, V. Pharmacokinetics of Mephedrone Enantiomers in Whole Blood after a Controlled Intranasal Administration to Healthy Human Volunteers. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010005
Czerwinska J, Parkin MC, Cilibrizzi A, George C, Kicman AT, Dargan PI, Abbate V. Pharmacokinetics of Mephedrone Enantiomers in Whole Blood after a Controlled Intranasal Administration to Healthy Human Volunteers. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzerwinska, Joanna, Mark C. Parkin, Agostino Cilibrizzi, Claire George, Andrew T. Kicman, Paul I. Dargan, and Vincenzo Abbate. 2021. "Pharmacokinetics of Mephedrone Enantiomers in Whole Blood after a Controlled Intranasal Administration to Healthy Human Volunteers" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010005
APA StyleCzerwinska, J., Parkin, M. C., Cilibrizzi, A., George, C., Kicman, A. T., Dargan, P. I., & Abbate, V. (2021). Pharmacokinetics of Mephedrone Enantiomers in Whole Blood after a Controlled Intranasal Administration to Healthy Human Volunteers. Pharmaceuticals, 14(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010005





