Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors That Prevent the Neuroparalysis of Tetanus Neurotoxin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inhibitors of the Thioredoxin Reductase–Thioredoxin Redox System Prevent the TeNT-Induced Cleavage of VAMP-2 in Cultured Neurons
2.2. EGA Prevents TeNT-Induced Cleavage of VAMP-2 in Cultured Neurons
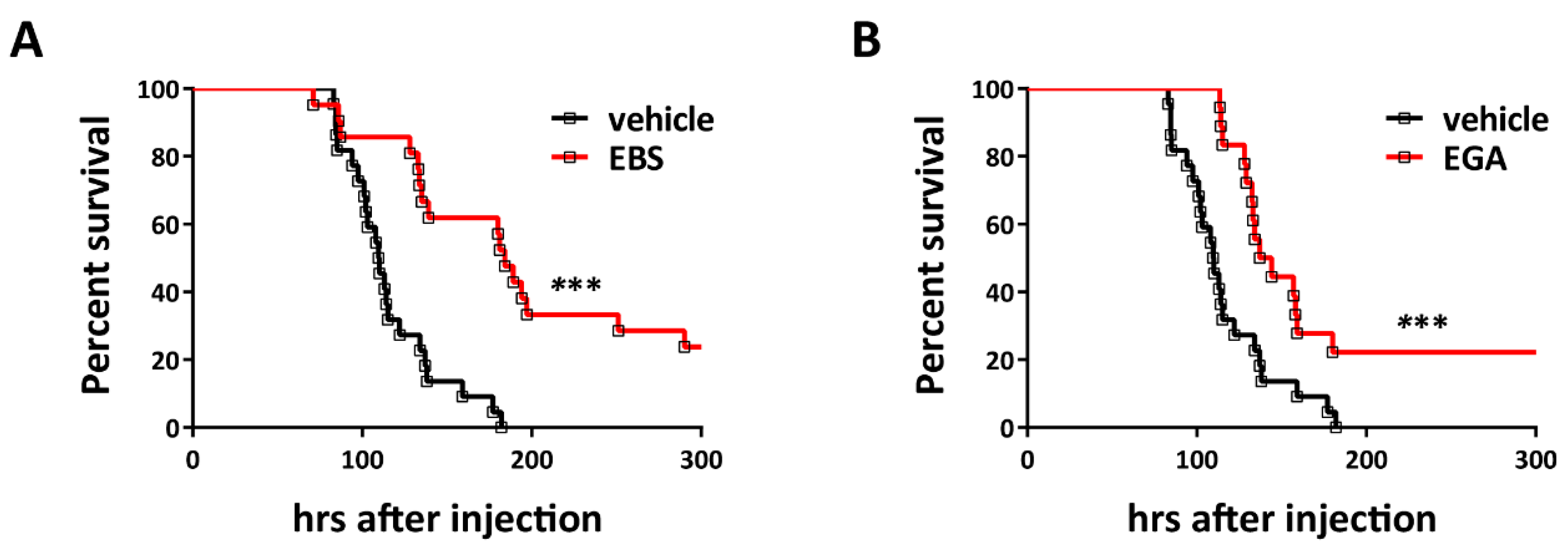
2.3. Ebselen and EGA Attenuate Generalized Tetanus In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Neuronal Cultures and Intoxication Assay
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.5. Mouse Bioassay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peck, M.W.; Smith, T.J.; Anniballi, F.; Austin, J.W.; Bano, L.; Bradshaw, M.; Cuervo, P.; Cheng, L.W.; Derman, Y.; Dorner, B.G.; et al. Historical Perspectives and Guidelines for Botulinum Neurotoxin Subtype Nomenclature. Toxins 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehran, D.A.; Pirazzini, M. Novel Botulinum Neurotoxins: Exploring Underneath the Iceberg Tip. Toxins 2018, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, M.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Tables of Toxicity of Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binz, T.; Rummel, A. Cell entry strategy of clostridial neurotoxins. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, A. Two Feet on the Membrane: Uptake of Clostridial Neurotoxins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 406, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colasante, C.; Rossetto, O.; Morbiato, L.; Pirazzini, M.; Molgó, J.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A is Internalized and Translocated from Small Synaptic Vesicles at the Neuromuscular Junction. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.B.; Papadopulos, A.; Martin, S.; Matthews, D.R.; Morgan, G.P.; Nguyen, T.H.; Wang, T.; Nair, D.; Choquet, D.; Meunier, F.A. Botulinum neurotoxin type-A enters a non-recycling pool of synaptic vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surana, S.; Tosolini, A.P.; Meyer, I.F.; Fellows, A.D.; Novoselov, S.; Schiavo, G. The travel diaries of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2018, 147, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercsenyi, K.; Schmieg, N.; Bryson, J.B.; Wallace, M.; Caccin, P.; Golding, M.; Zanotti, G.; Greensmith, L.; Nischt, R.; Schiavo, G. Tetanus toxin entry. Nidogens are therapeutic targets for the prevention of tetanus. Science 2014, 346, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megighian, A.; Pirazzini, M.; Fabris, F.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and tetanus neurotoxin: From peripheral uptake to central nervous tissue targets. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteoli, M.; Verderio, C.; Rossetto, O.; Iezzi, N.; Coco, S.; Schiavo, G.; Montecucco, C. Synaptic vesicle endocytosis mediates the entry of tetanus neurotoxin into hippocampal neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13310–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harper, C.B.; Martin, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Daniels, S.J.; Lavidis, N.A.; Popoff, M.R.; Hadzic, G.; Mariana, A.; Chau, N.; McCluskey, A.; et al. Dynamin Inhibition Blocks Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Endocytosis in Neurons and Delays Botulism. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35966–35976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montal, M. Botulinum Neurotoxin: A Marvel of Protein Design. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 591–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pirazzini, M.; Tehran, D.A.; Leka, O.; Zanetti, G.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. On the translocation of botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins across the membrane of acidic intracellular compartments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Papini, E.; Genna, G.; Montecucco, C. An intact interchain disulfide bond is required for the neurotoxicity of tetanus toxin. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 4136–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kistner, A.; Habermann, E. Evidence for two redox isomers of tetanus toxin. Reductive cleavage of tetanus toxin and botulinum neurotoxin A by the thioredoxin system from brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1992, 345, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Bordin, F.; Rossetto, O.; Shone, C.C.; Binz, T.; Montecucco, C. The thioredoxin reductase-thioredoxin system is involved in the entry of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins in the cytosol of nerve terminals. FEBS Lett. 2012, 587, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Tehran, D.A.; Zanetti, G.; Megighian, A.; Scorzeto, M.; Fillo, S.; Shone, C.C.; Binz, T.; Rossetto, O.; Lista, F.; et al. Thioredoxin and Its Reductase Are Present on Synaptic Vesicles, and Their Inhibition Prevents the Paralysis Induced by Botulinum Neurotoxins. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, G.; Tehran, D.A.; Pirazzini, M.; Binz, T.; Shone, C.C.; Fillo, S.; Lista, F.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Inhibition of botulinum neurotoxins interchain disulfide bond reduction prevents the peripheral neuroparalysis of botulism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirazzini, M.; Tehran, D.A.; Zanetti, G.; Lista, F.; Binz, T.; Shone, C.C.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. The thioredoxin reductase—Thioredoxin redox system cleaves the interchain disulphide bond of botulinum neurotoxins on the cytosolic surface of synaptic vesicles. Toxicon 2015, 107, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Montal, M. Crucial Role of the Disulfide Bridge between Botulinum Neurotoxin Light and Heavy Chains in Protease Translocation across Membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29604–29611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Lista, F.; Montecucco, C. The role of the single interchains disulfide bond in tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins and the development of antitetanus and antibotulism drugs. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; De Laureto, P.P.; Dasgupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantano, S.; Montecucco, C. The blockade of the neurotransmitter release apparatus by botulinum neurotoxins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 71, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Südhof, T.C.; Rizo, J. Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, V.B.; Curtis, D.R.; Eccles, J.C. Mode of Action of Tetanus Toxin. Nature 1955, 175, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, V.B.; Curtis, D.R.; Eccles, J.C. The action of tetanus toxin on the inhibition of motoneurones. J. Physiol. 1957, 135, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popoff, M.R. Tetanus in animals. J. Veter. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, L.M.; Thwaites, C.L. Tetanus. Lancet 2019, 393, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfery, D.D.; Rauscher, L.A. Tetanus. Crit. Care Med. 1979, 7, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenck, T.P. Clinical aspects of tetanus. In Botulinum Neurotoxins and Tetanus Toxin; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhuang, C. Clinical features and outcomes of tetanus: A retrospective study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thwaites, C.L.; Loan, H.T. Eradication of tetanus. Br. Med. Bull. 2015, 116, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pirazzini, M.; Grinzato, A.; Corti, D.; Barbieri, S.; Leka, O.; Vallese, F.; Tonellato, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Piccoli, L.; Kandiah, E.; et al. Exceptionally potent human monoclonal antibodies are effective for prophylaxis and therapy of tetanus in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Yu, R.; Chi, X.; Chen, Z.; Hao, M.; Du, P.; Fan, P.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fang, T.; et al. Tetanus vaccine-induced human neutralizing antibodies provide full protection against neurotoxin challenge in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 91, 107297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Lin, S.; Liu, T.; Zan, L.; Li, N.; Hong, P.; Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; et al. Structural basis of tetanus toxin neutralization by native human monoclonal antibodies. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotloo, S.; Amiri, M.M.; Khoshnoodi, J.; Abbasi, E.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; Golsaz-Shirazi, F.; Shokri, F. Contribution of Fc fragment of monoclonal antibodies to tetanus toxin neutralization. Neurotox. Res. 2019, 37, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelfrene, E.; Mura, M.; Sanches, A.C.; Cavaleri, M. Monoclonal antibodies as anti-infective products: A promising future? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 25, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliprandini, E.; Takata, D.Y.; Lepique, A.; Kalil, J.; Boscardin, S.B.; Moro, A.M. An oligoclonal combination of human monoclonal antibodies able to neutralize tetanus toxin in vivo. Toxicon X 2019, 2, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazka, A.; Gasse, F. The Present Status of Tetanus and Tetanus Vaccination. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 1995, 195, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Tetanus vaccines: WHO position paper—February 2017. Wkly Epidemiol. Rec. 2017, 92, 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Moynan, D.; O’Riordan, R.; O’Connor, R.; Merry, C. Tetanus—A Rare But Real Threat. IDCases 2018, 12, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirazzini, M.; Rossetto, O. Challenges in searching for therapeutics against Botulinum Neurotoxins. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirazzini, M.; Azarnia Tehran, D.; Zanetti, G.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Hsp90 and Thioredoxin-Thioredoxin Reductase enable the catalytic activity of Clostridial neurotoxins inside nerve terminals. Toxicon 2018, 147, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehran, D.A.; Zanetti, G.; Leka, O.; Lista, F.; Fillo, S.; Binz, T.; Shone, C.C.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C.; Paradisi, C.; et al. A Novel Inhibitor Prevents the Peripheral Neuroparalysis of Botulinum Neurotoxins. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tehran, D.A.; Pirazzini, M. Preparation of Cerebellum Granule Neurons from Mouse or Rat Pups and Evaluation of Clostridial Neurotoxin Activity and Their Inhibitors by Western Blot and Immunohistochemistry. Bio-Protocol 2018, 8, e2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, E.J.; Ho, C.-L.C.; Balaji, K.; Clemens, D.L.; Deng, G.; Wang, Y.E.; Elsaesser, H.J.; Tamilselvam, B.; Gargi, A.; Dixon, S.D.; et al. Selective inhibitor of endosomal trafficking pathways exploited by multiple toxins and viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4904–E4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnell, L.; Mittler, A.-K.; Sadi, M.; Popoff, M.R.; Schwan, C.; Aktories, K.; Mattarei, A.; Tehran, D.A.; Montecucco, C.; Barth, H. EGA Protects Mammalian Cells from Clostridium difficile CDT, Clostridium perfringens Iota Toxin and Clostridium botulinum C2 Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnell, L.; Mittler, A.-K.; Mattarei, A.; Tehran, D.A.; Montecucco, C.; Barth, H. Semicarbazone EGA Inhibits Uptake of Diphtheria Toxin into Human Cells and Protects Cells from Intoxication. Toxins 2016, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montecucco, C.; Rasotto, M.B. On Botulinum Neurotoxin Variability. mBio 2015, 6, e02131-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, A.P.; De Freitas, B.A.C.; Rodrigues, D.C.; Da Silveira, G.L.; Tavares, W.; Siqueira-Batista, R. Clostridium tetani infections in newborn infants: A tetanus neonatorum review. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2011, 23, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roper, M.; Vandelaer, J.H.; Gasse, F.L. Maternal and neonatal tetanus. Lancet 2007, 370, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, E.; Laberge, C.; Guay, M.; Bramadat, P.; Roy, R.; Bettinger, J.A. Vaccine hesitancy: An overview. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabura, L.; Ilibagiza, D.; Menten, J.; Ende, J.V.D. Intrathecal vs. intramuscular administration of human antitetanus immunoglobulin or equine tetanus antitoxin in the treatment of tetanus: A meta-analysis. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2006, 11, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, D.D.B.; Ximenes, R.A.D.A.; Barone, A.A.; Vaz, V.L.; Vieira, A.G.; Albuquerque, V.M.G. Randomised controlled trial of tetanus treatment with antitetanus immunoglobulin by the intrathecal or intramuscular route. BMJ 2004, 328, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiavo, G.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulism neurotoxins: Isolation and assay. Methods Enzym. 1995, 248, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanetti, G.; Mattarei, A.; Lista, F.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C.; Pirazzini, M. Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors That Prevent the Neuroparalysis of Tetanus Neurotoxin. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111134
Zanetti G, Mattarei A, Lista F, Rossetto O, Montecucco C, Pirazzini M. Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors That Prevent the Neuroparalysis of Tetanus Neurotoxin. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(11):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111134
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanetti, Giulia, Andrea Mattarei, Florigio Lista, Ornella Rossetto, Cesare Montecucco, and Marco Pirazzini. 2021. "Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors That Prevent the Neuroparalysis of Tetanus Neurotoxin" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 11: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111134
APA StyleZanetti, G., Mattarei, A., Lista, F., Rossetto, O., Montecucco, C., & Pirazzini, M. (2021). Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors That Prevent the Neuroparalysis of Tetanus Neurotoxin. Pharmaceuticals, 14(11), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111134








