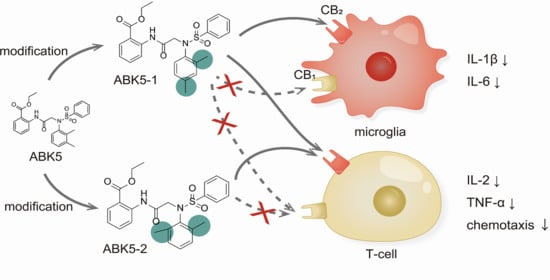
Characterization of Subtype Selective Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
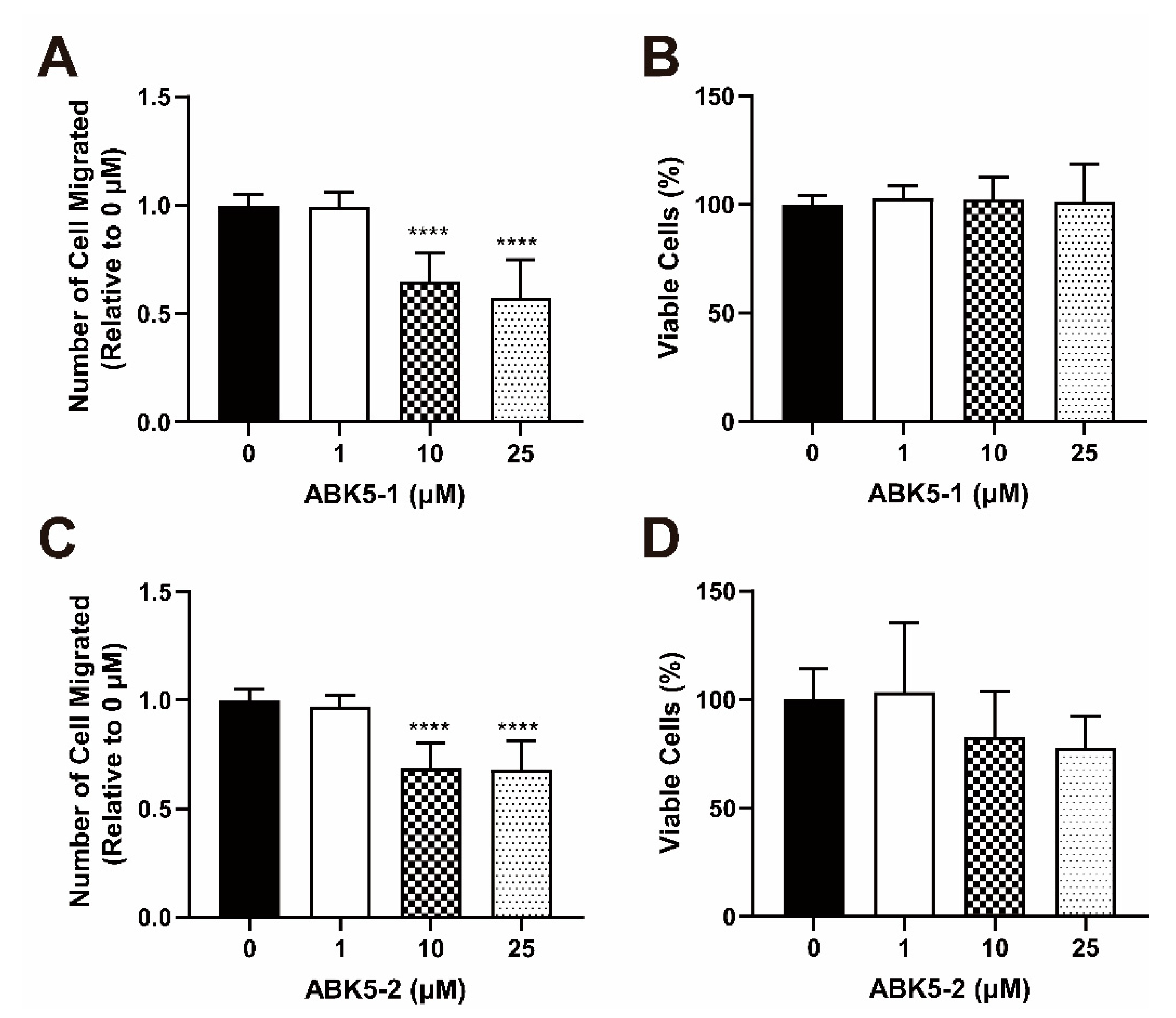
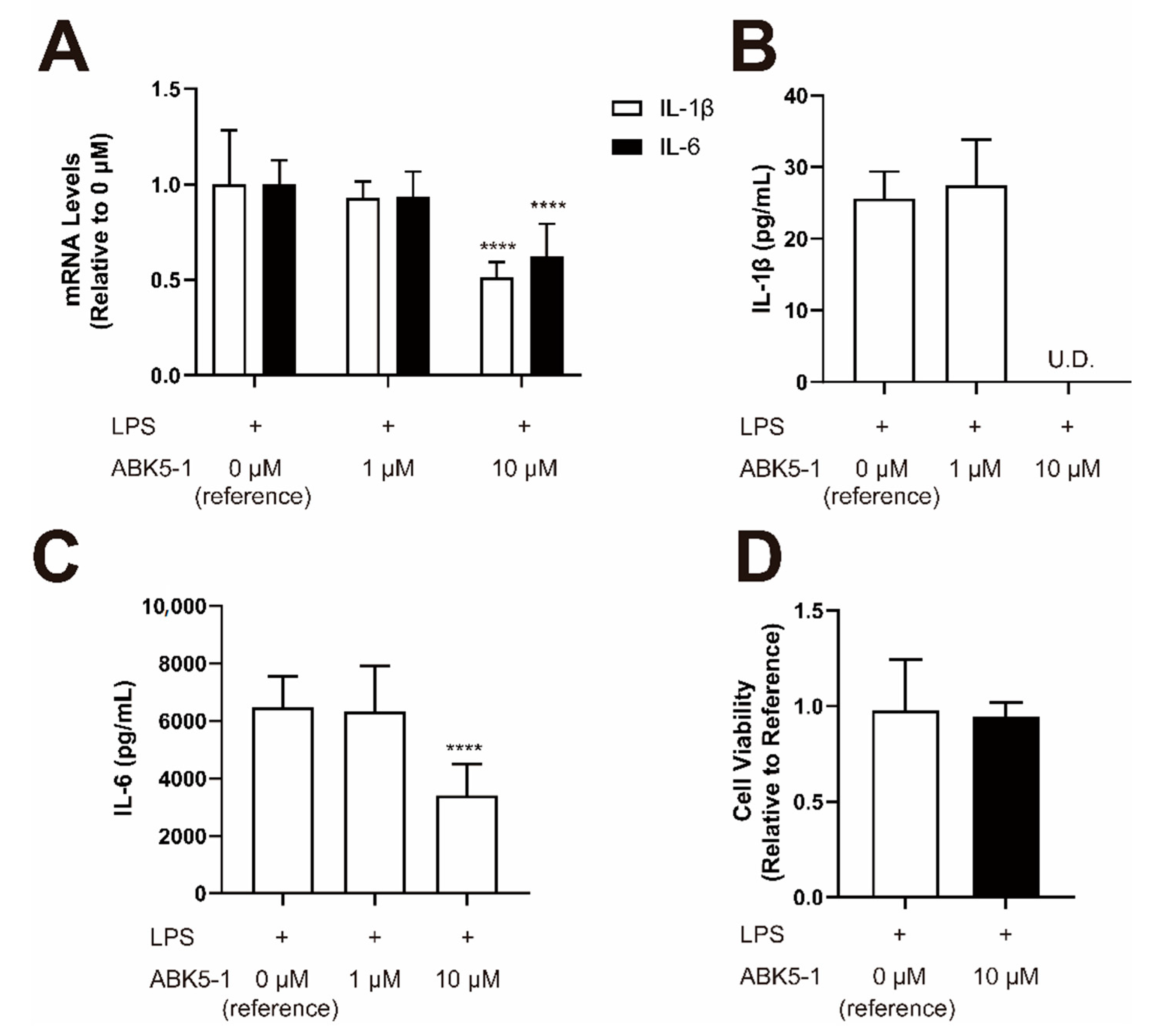
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cannabinoid Receptor Expression and Membrane Preparation
4.4. Ligand Binding
4.5. GTPγS Binding
4.6. Compound Treatment for Cytokine Analysis
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. Migration Assay
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nat. Cell Biol. 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busquets-Garcia, A.; Bains, J.; Marsicano, G. CB1 Receptor Signaling in the Brain: Extracting Specificity from Ubiquity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiegue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carriere, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Expression of Central and Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptors in Human Immune Tissues and Leukocyte Subpopulations. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 232, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nat. Cell Biol. 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Guindon, J.; Cornett, B.L.; Makriyannis, A.; Mackie, K.; Hohmann, A.G. Chronic Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Activation Reverses Paclitaxel Neuropathy Without Tolerance or Cannabinoid Receptor 1–Dependent Withdrawal. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malan, T.P., Jr.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Deng, H.; Liu, Q.; Mata, H.P.; Vanderah, T.W.; Porreca, F.; Makriyannis, A. CB2 cannabinoid receptor-mediated peripheral antinociception. Pain 2001, 93, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan, T.P.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Lai, J.; Vanderah, T.W.; Makriyannis, A.; Porreca, F. CB cannabinoid receptor agonists: Pain relief without psychoactive effects? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-J.; Gao, M.; Gao, F.-F.; Su, Q.-X.; Wu, J. Brain cannabinoid receptor 2: Expression, function and modulation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, B.; Urban, L. Mechanisms of inflammatory pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2001, 87, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, G.G.; Delay, L.; Yaksh, T.L.; Corr, M. Neuraxial Cytokines in Pain States. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahlhamer, J.; Lucas, J.; Zelaya, C.; Nahin, R.; Mackey, S.; DeBar, L.; Kerns, R.; Von Korff, M.; Porter, L.; Helmick, C. Prevalence of Chronic Pain and High-Impact Chronic Pain Among Adults—United States, 2016. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baral, P.; Udit, S.; Chiu, I.M. Pain and immunity: Implications for host defence. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencioni, M.T.; Chiurchiù, V.; Catanzaro, G.; Borsellino, G.; Bernardi, G.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. Anandamide Suppresses Proliferation and Cytokine Release from Primary Human T-Lymphocytes Mainly via CB2 Receptors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börner, C.; Smida, M.; Höllt, V.; Schraven, B.; Kraus, J. Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1- and 2-mediated Increase in Cyclic AMP Inhibits T Cell Receptor-triggered Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35450–35460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berdyshev, E.V.; Boichot, E.; Germain, N.; Allain, N.; Anger, J.-P.; Lagente, V. Influence of fatty acid ethanolamides and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cytokine and arachidonate release by mononuclear cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 330, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljaschewitsch, E.; Witting, A.; Mawrin, C.; Lee, T.; Schmidt, P.M.; Wolf, S.; Hoertnagl, H.; Raine, C.S.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Nitsch, R.; et al. The Endocannabinoid Anandamide Protects Neurons during CNS Inflammation by Induction of MKP-1 in Microglial Cells. Neuron 2006, 49, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, R.A.; Brockie, H.C.; Pertwee, R.G. Inhibition of nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 macrophages by cannabinoids and palmitoylethanolamide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 401, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Kiertscher, S.M.; Cheng, Q.; Zoumalan, R.; Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol regulates Th1/Th2 cytokine balance in activated human T cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 133, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sandoval, E.A.; Horvath, R.; Landry, R.P.; De Leo, J.A. CANnabinoid Receptor Type 2 Activation Induces a Microglial Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype and Reduces Migration via MKP Induction and ERK Dephosphorylation. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Preet, A.; Groopman, J.; Ganju, R. Cannabinoid receptor CB2 modulates the CXCL12/CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis of T lymphocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raborn, E.S.; Marciano-Cabral, F.; Buckley, N.E.; Martin, B.R.; Cabral, G.A. The Cannabinoid Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol Mediates Inhibition of Macrophage Chemotaxis to RANTES/CCL5: Linkage to the CB2 Receptor. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coopman, K.; Smith, L.D.; Wright, K.L.; Ward, S.G. Temporal variation in CB2R levels following T lymphocyte activation: Evidence that cannabinoids modulate CXCL12-induced chemotaxis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.E.; Tang, Y.; Alt, A.; Burford, N.T.; Gerritz, S.W.; Ogawa, L.M.; Zhang, L.; Kendall, D.A. Identification and biochemical analyses of selective CB2 agonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 854, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wolk, B.; Britch, S.C.; Craft, R.M.; Kendall, D.A. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of the selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist ABK5. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 145, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, L.M.; Burford, N.T.; Liao, Y.-H.; Scott, C.E.; Hine, A.M.; Dowling, C.; Chin, J.; Power, M.; Hunnicutt, E.J.; Emerick, V.L.; et al. Discovery of Selective Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists by High-Throughput Screening. SLAS Discov. Adv. Life Sci. R&D 2017, 23, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, J.; Niggemann, B.; Zaenker, K.S.; Entschladen, F. Anandamide is an endogenous inhibitor for the migration of tumor cells and T lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2004, 53, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, M.N. Mediators of Pain and Pain Processing. In Deer’s Treatment of Pain: An Illustrated Guide for Practitioners; Deer, T.R., Pope, J.E., Lamer, T.J., Provenzano, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Elmes, S.J.; Winyard, L.A.; Medhurst, S.J.; Clayton, N.M.; Wilson, A.W.; Kendall, D.A.; Chapman, V. Activation of CB1 and CB2 receptors attenuates the induction and maintenance of inflammatory pain in the rat. Pain 2005, 118, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartilho, A.; Mata, H.P.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Vanderah, T.W.; Porreca, F.; Makriyannis, A.; Malan, T.P., Jr. Inhibition of Inflammatory Hyperalgesia by Activation of Peripheral CB2Cannabinoid Receptors. Anesthesiology 2003, 99, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-E.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Qiu, Z.-L.; Sun, X.-B.; Yang, J.-J.; Chen, S.; Yi, C.; Chai, X.; et al. From a Designer Drug to the Discovery of Selective Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor Agonists with Favorable Pharmacokinetic Profiles for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, A.; Mattei, V.; Martellucci, S.; Manganelli, V.; Saccomanni, G.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; Manera, C.; Misasi, R. Anti-Proliferative Properties and Proapoptotic Function of New CB2 Selective Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist in Jurkat Leukemia Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louvet, A.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Chobert, M.-N.; Deveaux, V.; Pavoine, C.; Zimmer, A.; Pecker, F.; Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors protect against alcoholic liver disease by regulating Kupffer cell polarization in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhart, J.; Obregon, D.; Mori, T.; Hou, H.; Sun, N.; Bai, Y.; Klein, T.; Fernandez, F.; Tan, J.; Shytle, R.D. Stimulation of cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) suppresses microglial activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2005, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Jia, J.; Liu, X.; Bai, F.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, L. Activation of murine microglial N9 cells is attenuated through cannabinoid receptor CB2 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, A.; Gironella, M.; Lorente, M.; Garcia, S.; Guzmán, M.; Velasco, G.; Iovanna, J.L. Cannabinoids Induce Apoptosis of Pancreatic Tumor Cells via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress–Related Genes. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6748–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarfaraz, S.; Afaq, F.; Adhami, V.M.; Malik, A.; Mukhtar, H. Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist-induced Apoptosis of Human Prostate Cancer Cells LNCaP Proceeds through Sustained Activation of ERK1/2 Leading to G1 Cell Cycle Arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39480–39491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Qadri, Y.J.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.-R. Microglia in Pain: Detrimental and Protective Roles in Pathogenesis and Resolution of Pain. Neuron 2018, 100, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.-R.; Chamessian, A.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science 2016, 354, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashton, J.C.; Glass, J.C.A.A.M. The Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor as a Target for Inflammation-Dependent Neurodegeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2007, 5, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maresz, K.; Carrier, E.J.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Hillard, C.J.; Dittel, B.N. Modulation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in microglial cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concannon, R.M.; Okine, B.N.; Finn, D.P.; Dowd, E. Differential upregulation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in neurotoxic and inflammation-driven rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 269, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Mika, J.; Przewlocka, B.; Starowicz, K. Anandamide, Acting viaCB2Receptors, Alleviates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation in Rat Primary Microglial Cultures. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernangómez, M.; Mestre, L.; Correa, F.G.; Loría, F.; Mecha, M.; Iñigo, P.M.; Docagne, F.; Williams, R.O.; Borrell, J.; Guaza, C. CD200-CD200R1 interaction contributes to neuroprotective effects of anandamide on experimentally induced inflammation. Glia 2012, 60, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Sackett, S.; Zhang, Y. Endocannabinoid Modulation of Microglial Phenotypes in Neuropathology. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, F.; Hernangómez, M.; Mestre, L.; Loría, F.; Spagnolo, A.; Docagne, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Guaza, C.; Di Marzo, V. Anandamide enhances IL-10 production in activated microglia by targeting CB2receptors: Roles of ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-κB. Glia 2009, 58, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, M.; Khan, Z.T.; Khan, M.B.; Kumar, M.; Ward, A.; Achyut, B.R.; Arbab, A.S.; Hess, D.C.; Hoda, N.; Baban, B.; et al. Selective activation of cannabinoid receptor-2 reduces neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury via alternative macrophage polarization. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 68, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhong, X.; Wang, G. Low-dose cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist induces microglial activation in a cancer pain-morphine tolerance rat model. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung-Chi, C.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (KI) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| CP55,940 | GTPγS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ki (nM) a | EC50 (nM) b | ||
| Compound | CB2 | CB1 | CB2 |
| ABK5-1 | 28 ± 5 | N.B. c | 11 ± 14 |
| ABK5-2 | 69 ± 19 | N.B. c | 24 ± 25 |
| ABK5-5 | N.D. d | N.D. d | N.D. d |
| ABK5-6 | 14 ± 2 | >1000 | 10 ± 5 |
| ABK5 e | 16 ± 14 | N.B. c | 4 ± 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Wolk, B.; Nolan, R.; Scott, C.E.; Kendall, D.A. Characterization of Subtype Selective Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040378
Tang Y, Wolk B, Nolan R, Scott CE, Kendall DA. Characterization of Subtype Selective Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(4):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040378
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yaliang, Barbara Wolk, Ryan Nolan, Caitlin E. Scott, and Debra A. Kendall. 2021. "Characterization of Subtype Selective Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 4: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040378
APA StyleTang, Y., Wolk, B., Nolan, R., Scott, C. E., & Kendall, D. A. (2021). Characterization of Subtype Selective Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Pharmaceuticals, 14(4), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040378