Recent Advances in Hepatitis B Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HBV Replication Cycle
2.1. Virion Structure and Genome
2.2. Viral Entry
2.3. cccDNA Formation/Maintenance
2.4. Transcription-Translation-Reverse Transcription-Nucleocapsid Assembly
3. Current Therapies
4. Novel Therapeutic Strategies
4.1. HBV Entry Inhibitors
4.2. Directly Targeting cccDNA
4.3. Immune Therapy
4.3.1. Targeting Innate Immunity
4.3.2. Targeting Adaptive Immunity
4.4. RNA Interference—Post-Transcriptional Control
4.5. Ribonuclease H Inhibitors
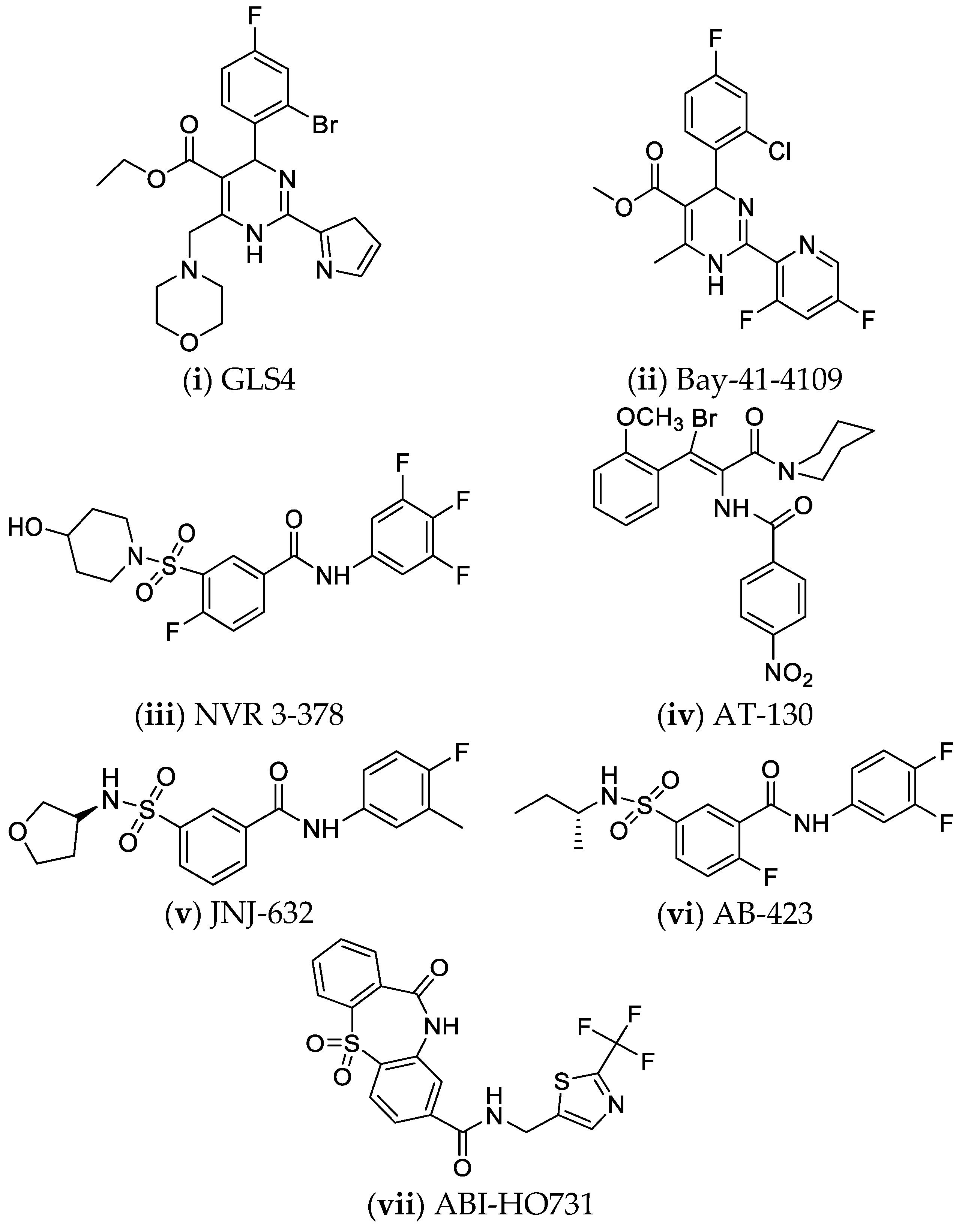
4.6. Nucleocapsid Assembly Inhibitors or Modulators
5. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, C.-L.; Kao, J.-H. Natural History of Acute and Chronic Hepatitis B: The Role of HBV Genotypes and Mutants. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trépo, C.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Lok, A. Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Lancet 2014, 384, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Hepatitis B-Key Facts. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, D.-S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.-L. Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk-Fong Lok, A. Hepatitis B: 50 Years after the Discovery of Australia Antigen. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepo, C. A Brief History of Hepatitis Milestones. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Zoulim, F.; Dusheiko, G.; Ghany, M.G. Hepatitis B Cure: From Discovery to Regulatory Approval. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hadziyannis, E.; Laras, A. Viral Biomarkers in Chronic HBeAg Negative HBV Infection. Genes 2018, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. Novel Biomarkers for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudi, I.; Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Clinical Significance of HBcrAg and M2BPGi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, C.; Michler, T.; Protzer, U. Novel Viral and Host Targets to Cure Hepatitis B. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 24, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lampertico, P. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.-M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 Hepatitis B Guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Lau, G.K.; Abbas, Z.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chien, R.N.; et al. Asian-Pacific Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Hepatitis B: A 2015 Update. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayiannis, P. Hepatitis B Virus: Virology, Molecular Biology, Life Cycle and Intrahepatic Spread. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, K.A.; Wieland, S.F.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Gerin, J.L.; Chisari, F.V.; Yeager, M. Native Hepatitis B Virions and Capsids Visualized by Electron Cryomicroscopy. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K. Hepatitis B Virus Biology and Life Cycle. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipery, A.; Gehring, A.J.; Isogawa, M. Mechanisms of HBV Immune Evasion. Antivir. Res. 2020, 179, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H. (Ed.) Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Molecular Virology to Antiviral Drugs; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1179, ISBN 9789811391507. [Google Scholar]
- Glebe, D.; Bremer, C. The Molecular Virology of Hepatitis B Virus. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, R.J.; Bagga, S.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis. Hepatoma Res. 2016, 2, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, A.L.; D’Arienzo, V.; Ansari, M.A.; Lumley, S.F.; Littlejohn, M.; Revill, P.; McKeating, J.A.; Matthews, P.C. Insights From Deep Sequencing of the HBV Genome—Unique, Tiny, and Misunderstood. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locarnini, S.; Zoulim, F. Molecular Genetics of HBV Infection. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavesi, A. Different Patterns of Codon Usage in the Overlapping Polymerase and Surface Genes of Hepatitis B Virus Suggest a de Novo Origin by Modular Evolution. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3577–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Is a Functional Receptor for Human Hepatitis B and D Virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Saso, W.; Nishioka, K.; Ohashi, H.; Sugiyama, R.; Ryo, A.; Ohki, M.; Yun, J.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Ohshima, T.; et al. The Machinery for Endocytosis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Coordinates the Transport of Incoming Hepatitis B Virus to the Endosomal Network. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrscher, C.; Pastor, F.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; Dumans, A.; Seigneuret, F.; Moreau, A.; Patient, R.; Eymieux, S.; Rocquigny, H.; Hourioux, C.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Entry into HepG2-NTCP Cells Requires Clathrin-mediated Endocytosis. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinazi, R.F.; Ehteshami, M.; Bassit, L.; Asselah, T. Towards HBV Curative Therapies. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; McAllister, R.; Boregowda, R.; Sohn, J.A.; Ledesma, F.C.; Caldecott, K.W.; Seeger, C.; Hu, J. Does Tyrosyl DNA Phosphodiesterase-2 Play a Role in Hepatitis B Virus Genome Repair? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Königer, C.; Wingert, I.; Marsmann, M.; Rösler, C.; Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Involvement of the Host DNA-Repair Enzyme TDP2 in Formation of the Covalently Closed Circular DNA Persistence Reservoir of Hepatitis B Viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4244–E4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA Is Formed through Distinct Repair Processes of Each Strand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.C.K.; Joshi, S.S.; Mahoney, D.J.; Mason, A.L.; van Marle, G.; Osiowy, C.; Coffin, C.S. Differences in HBV Replication, APOBEC3 Family Expression, and Inflammatory Cytokine Levels Between Wild-Type HBV and Pre-Core (G1896A) or Basal Core Promoter (A1762T/G1764A) Mutants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tu, Z.; Hu, J.; Tavis, J.E.; Huang, A.; Hu, Y. Association of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA and Human APOBEC3B in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle–Lapostolle, B.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S.; Wursthorn, K.; Petersen, J.; Lau, G.; Trepo, C.; Marcellin, P.; Goodman, Z.; Delaney IV, W.E. Persistence of CccDNA during the Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B and Decline during Adefovir Dipivoxil Therapy1. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Guo, H. Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA: Formation, Regulation and Therapeutic Potential. Antivir. Res. 2020, 180, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Cai, D.; Zong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mercier, A.; Guo, H.; Hou, J.; Colonno, R.; et al. Rapid Turnover of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Indicated by Monitoring Emergence and Reversion of Signature-Mutation in Treated Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Hepatology 2021, 73, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. Molecular Biology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Virology 2015, 479–480, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, J.-H.; Chen, D.-S. (Eds.) Hepatitis B Virus and Liver Disease; Springer: Singapore, 2018; ISBN 978-981-10-4842-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Kottilil, S.; Wilson, E. Strategies to Eliminate HBV Infection: An Update. Future Virol. 2020, 15, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolla, N.; Kew, M.; Arbuthnot, P. Regulatory Elements of Hepatitis B Virus Transcription. J. Viral Hepat. 2002, 9, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.-H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Chen, W.-X.; Cai, X.-F.; Chen, K.; Ko, B.C.B.; Song, C.-L.; Ran, L.-K.; Li, W.-Y.; et al. Sirtuin 1 Regulates Hepatitis B Virus Transcription and Replication by Targeting Transcription Factor AP-1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Arienzo, V.; Ferguson, J.; Giraud, G.; Chapus, F.; Harris, J.M.; Wing, P.A.C.; Claydon, A.; Begum, S.; Zhuang, X.; Balfe, P.; et al. The CCCTC-binding Factor CTCF Represses Hepatitis B Virus Enhancer I and Regulates Viral Transcription. Cell. Microbiol. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quasdorff, M.; Protzer, U. Control of Hepatitis B Virus at the Level of Transcription: Control of Hepatitis B Virus. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorsière, A.; Mueller, H.; van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Identifies the Smc5/6 Complex as a Host Restriction Factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, B.; Guo, H. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Crosses out Smc5/6 Complex to Maintain Covalently Closed Circular DNA Transcription. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2246–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Nio, K.; Reszka-Blanco, N.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Su, L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Promotes Degradation of SMC5/6 to Enhance HBV Replication. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livingston, C.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Strubin, M.; Fletcher, S.; Beran, R. Identifying and Characterizing Interplay between Hepatitis B Virus X Protein and Smc5/6. Viruses 2017, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Arzberger, S.; Durantel, D.; Belloni, L.; Strubin, M.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Is Essential to Initiate and Maintain Virus Replication after Infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, M.A.; Bonamassa, B.; Arzumanyan, A. The Roles of Hepatitis B Virus-Encoded X Protein in Virus Replication and the Pathogenesis of Chronic Liver Disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagle, B.L.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B Virus X and Regulation of Viral Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a021402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, D.N.; Hu, J. Unveiling the Roles of HBV Polymerase for New Antiviral Strategies. Future Virol. 2015, 10, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, D.N.; Hu, J. Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase—Target of Current Antiviral Therapy and Future Drug Development. Antivir. Res. 2015, 123, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J. Studying DHBV Polymerase by In Vitro Transcription and Translation. In Hepatitis B and D Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 259–270. ISBN 978-1-59259-669-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Boyer, M. Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase and ε RNA Sequences Required for Specific Interaction In Vitro. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.A.; Clark, D.N.; Cao, F.; Tavis, J.E.; Hu, J. Comparative Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase Sequences Required for Viral RNA Binding, RNA Packaging, and Protein Priming. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, F.; Jones, S.; Li, W.; Cheng, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Tavis, J.E. Sequences in the Terminal Protein and Reverse Transcriptase Domains of the Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase Contribute to RNA Binding and Encapsidation. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buhlig, T.S.; Bowersox, A.F.; Braun, D.L.; Owsley, D.N.; James, K.D.; Aranda, A.J.; Kendrick, C.D.; Skalka, N.A.; Clark, D.N. Molecular, Evolutionary, and Structural Analysis of the Terminal Protein Domain of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase, a Potential Drug Target. Viruses 2020, 12, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Hu, J. Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase: Diverse Functions as Classical and Emerging Targets for Antiviral Intervention. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badtke, M.P.; Khan, I.; Cao, F.; Hu, J.; Tavis, J.E. An Interdomain RNA Binding Site on the Hepadnaviral Polymerase That Is Essential for Reverse Transcription. Virology 2009, 390, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datta, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Veer, V.; Chakravarty, R. Molecular Biology of the Hepatitis B Virus for Clinicians. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2012, 2, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villa, J.A.; Pike, D.P.; Patel, K.B.; Lomonosova, E.; Lu, G.; Abdulqader, R.; Tavis, J.E. Purification and Enzymatic Characterization of the Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H, a New Target for Antiviral Inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2016, 132, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavis, J.E.; Lomonosova, E. The Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H as a Drug Target. Antivir. Res. 2015, 118, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Liu, K. Complete and Incomplete Hepatitis B Virus Particles: Formation, Function, and Application. Viruses 2017, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration Occurs Early in the Viral Life Cycle in an In Vitro Infection Model via Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide-Dependent Uptake of Enveloped Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02007-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hepatitis B Foundation: Approved Drugs for Adults. Available online: https://www.hepb.org/treatment-and-management/treatment/approved-drugs-for-adults/ (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Woo, A.S.J.; Kwok, R.; Ahmed, T. Alpha-Interferon Treatment in Hepatitis B. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, H.; Lok, A.S. Hepatitis B Therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. IFN-α Inhibits HBV Transcription and Replication in Cell Culture and in Humanized Mice by Targeting the Epigenetic Regulation of the Nuclear CccDNA Minichromosome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucifora, J.; Xia, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Zhang, K.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Koppensteiner, H.; Makowska, Z.; Volz, T.; et al. Specific and Nonhepatotoxic Degradation of Nuclear Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA. Science 2014, 343, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yang, G.; Yun, H.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Geng, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; et al. IFN-α Confers Epigenetic Regulation of HBV CccDNA Minichromosome by Modulating GCN5-Mediated Succinylation of Histone H3K79 to Clear HBV CccDNA. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; van Zonneveld, M.; Senturk, H.; Zeuzem, S.; Akarca, U.S.; Cakaloglu, Y.; Simon, C.; So, T.M.K.; Gerken, G.; de Man, R.A.; et al. Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2b Alone or in Combination with Lamivudine for HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B: A Randomised Trial. Lancet 2005, 365, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Lebossé, F.; Levrero, M. Current Treatments for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 18, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierra Rouviere, C.; Dousson, C.B.; Tavis, J.E. HBV Replication Inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2020, 179, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, J.; Yuen, L.; Rosenberg, G.; Wong, D.; Littlejohn, M.; Jackson, K.; Gaggar, A.; Kitrinos, K.M.; Subramanian, G.M.; Marcellin, P.; et al. Deep Sequencing Shows That HBV Basal Core Promoter and Precore Variants Reduce the Likelihood of HBsAg Loss Following Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Therapy in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B. Gut 2017, 66, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El Aziz, M.A.; Sacco, R.; Facciorusso, A. Nucleos(t)Ide Analogues and Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Literature Review. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2020, 28, 204020662092133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.-H. Long-Term Lamivudine for Chronic Hepatitis B and Cirrhosis: A Real-Life Cohort Study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Jang, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, C.-H.; Yoo, S.H.; Bae, S.H.; Yoon, S.K. Should Lamivudine Monotherapy Be Stopped or Continued in Patients Infected with Hepatitis B with Favorable Responses after More than 5 Years of Treatment? J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, J.R.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, T.N.; Lee, K.S. Risk Assessment for the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: According to on-Treatment Viral Response during Long-Term Lamivudine Therapy in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Jiang, X.; Ren, H. Lamivudine plus Tenofovir Combination Therapy versus Lamivudine Monotherapy for HBV/HIV Coinfection: A Meta-Analysis. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-L.; Zhao, W.; Lee, C.; Hann, H.-W.; Peng, C.-Y.; Tanwandee, T.; Morozov, V.; Klinker, H.; Sollano, J.D.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; et al. Outcomes of Long-Term Treatment of Chronic HBV Infection With Entecavir or Other Agents From a Randomized Trial in 24 Countries. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 457–467.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liaw, Y.; Gane, E.; Leung, N.; Zeuzem, S.; Wang, Y.; Lai, C.L.; Heathcote, E.J.; Manns, M.; Bzowej, N.; Niu, J.; et al. 2-Year GLOBE Trial Results: Telbivudine Is Superior to Lamivudine in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Yin, Y.-K.; Xu, D.; Tan, D.; Niu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, Y.; Ren, H.; et al. Telbivudine versus Lamivudine in Chinese Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: Results at 1 Year of a Randomized, Double-Blind Trial. Hepatology 2007, 47, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-L.; Hsu, C.-W.; Chen, Y.; Bzowej, N.; Bisceglie, A.M.D.; Moon, Y.M.; Chao, G.; Brown, N.A. Telbivudine versus Lamivudine in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2576–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Lee, C.-M.; Chiu, K.-W.; Wang, J.-H.; Lu, S.-N.; Tseng, P.-L.; Chang, K.-C.; Yen, Y.-H.; et al. A Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of 2-Year Telbivudine and Entecavir Treatment in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Match–Control Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O90–O100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, G.L.-H.; Seto, W.-K.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Yuen, M.-F.; Chan, H.L.-Y. Review Article: Long-Term Safety of Oral Anti-Viral Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Cai, S.; Li, Z.; Zheng, C.; Xue, X.; Zeng, J.; Peng, J. Potential Effects of Telbivudine and Entecavir on Renal Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Corsa, A.C.; Buti, M.; Cathcart, A.L.; Flaherty, J.F.; Miller, M.D.; Kitrinos, K.M.; Marcellin, P.; Gane, E.J. No Detectable Resistance to Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in HBeAg+ and HBeAg− Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B after 8 Years of Treatment. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, K.; Huang, Y. The Effectiveness of TDF versus ETV on Incidence of HCC in CHB Patients: A Meta Analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, W.-M.; Choi, J.; Lim, Y.-S. Effects of Tenofovir vs Entecavir on Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Chronic HBV Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 246–258.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lv, T.; Wu, S.; Wei, W.; Wu, X.; Ou, X.; Ma, H.; Chow, S.-C.; Kong, Y.; You, H.; et al. Tenofovir versus Entecavir in Lowering the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Critical Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Yoon, E.L.; Jun, D.W.; Ahn, S.B.; Lee, H.-Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, S.E.; Shim, J.-J.; et al. No Difference in Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Treated With Entecavir vs Tenofovir. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2793–2802.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Peng, C.-Y.; Yeh, M.-L.; Cheung, K.-S.; Toyoda, H.; Huang, C.-F.; Trinh, H.; Xie, Q.; et al. Tenofovir Versus Entecavir for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention in an International Consortium of Chronic Hepatitis B. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatin, U. Drugs in the Pipeline for HBV. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 535–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijckborst, V.; Sonneveld, M.J.; Janssen, H.L.A. Review Article: Chronic Hepatitis B—Anti-Viral or Immunomodulatory Therapy?: Review: Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revill, P.; Testoni, B.; Locarnini, S.; Zoulim, F. Global Strategies Are Required to Cure and Eliminate HBV Infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukano, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T. Concept of Viral Inhibitors via NTCP. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 078–085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.A.; Lan, T.; Rao, A. Bile Acid Transporters. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 2340–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gripon, P.; Cannie, I.; Urban, S. Efficient Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Infection by Acylated Peptides Derived from the Large Viral Surface Protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glebe, D.; Urban, S.; Knoop, E.V.; Çaǧ, N.; Krass, P.; Grün, S.; Bulavaite, A.; Sasnauskas, K.; Gerlich, W.H. Mapping of the Hepatitis B Virus Attachment Site by Use of Infection-Inhibiting PreS1 Lipopeptides and Tupaia Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Mier, W.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Volz, T.; von Weizsäcker, F.; Haberkorn, U.; Fischer, L.; Pollok, J.-M.; Erbes, B.; et al. Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Vivo by Entry Inhibitors Derived from the Large Envelope Protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passioura, T.; Watashi, K.; Fukano, K.; Shimura, S.; Saso, W.; Morishita, R.; Ogasawara, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizokami, M.; Sureau, C.; et al. De Novo Macrocyclic Peptide Inhibitors of Hepatitis B Virus Cellular Entry. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 906–915.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Zhou, M.; He, Y.; Wan, Y.; Bai, W.; Tao, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Efficient Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Infection by a PreS1-Binding Peptide. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Schieck, A.; Ni, Y.; Mier, W.; Urban, S. Fine Mapping of Pre-S Sequence Requirements for Hepatitis B Virus Large Envelope Protein-Mediated Receptor Interaction. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; MBarek, M.B.; Warlich, M.; Lohse, A.W.; Pollok, J.M.; Alexandrov, A.; Urban, S.; Petersen, J.; Lütgehetmann, M.; et al. The Entry Inhibitor Myrcludex-B Efficiently Blocks Intrahepatic Virus Spreading in Humanized Mice Previously Infected with Hepatitis B Virus. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, R.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; et al. Upregulation of HBV Transcription by Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide at the Postentry Step Is Inhibited by the Entry Inhibitor Myrcludex B. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkongolo, S.; Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Kaufman, C.; Lindner, T.; Esser-Nobis, K.; Lohmann, V.; Mier, W.; Mehrle, S.; Urban, S. Cyclosporin A Inhibits Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D Virus Entry by Cyclophilin-Independent Interference with the NTCP Receptor. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, A.; Markert, C.; Hohmann, N.; Carls, A.; Mikus, G.; Lehr, T.; Alexandrov, A.; Haag, M.; Schwab, M.; Urban, S.; et al. First-in-Human Application of the Novel Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D Virus Entry Inhibitor Myrcludex B. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Syed, Y.Y. Bulevirtide: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, P.; Helm, F.; Hofhaus, G.; Brings, S.; Kaufman, C.; Leotta, K.; Urban, S.; Haberkorn, U.; Mier, W.; Fricker, G. A Liposomal Formulation for the Oral Application of the Investigational Hepatitis B Drug Myrcludex B. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, A.; Meier, K.; Urban, S.; Haefeli, W.E.; Weiss, J. Drug–Drug Interaction Potential of the Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D Virus Entry Inhibitor Myrcludex B Assessed in Vitro. Antivir. Ther. 2017, 23, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watashi, K.; Sluder, A.; Daito, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Ryo, A.; Nagamori, S.; Iwamoto, M.; Nakajima, S.; Tsukuda, S.; Borroto-Esoda, K.; et al. Cyclosporin A and Its Analogs Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus Entry into Cultured Hepatocytes through Targeting a Membrane Transporter, Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide (NTCP). Hepatology 2014, 59, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, S.; Watashi, K.; Fukano, K.; Peel, M.; Sluder, A.; Kawai, F.; Iwamoto, M.; Tsukuda, S.; Takeuchi, J.S.; Miyake, T.; et al. Cyclosporin Derivatives Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus Entry without Interfering with NTCP Transporter Activity. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Esser, K.; Protzer, U. Ezetimibe Blocks Hepatitis B Virus Infection after Virus Uptake into Hepatocytes. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, T.; Mao, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, S. Irbesartan, an FDA Approved Drug for Hypertension and Diabetic Nephropathy, Is a Potent Inhibitor for Hepatitis B Virus Entry by Disturbing Na+-Dependent Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Activity. Antivir. Res. 2015, 120, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saso, W.; Tsukuda, S.; Ohashi, H.; Fukano, K.; Morishita, R.; Matsunaga, S.; Ohki, M.; Ryo, A.; Park, S.-Y.; Suzuki, R.; et al. A New Strategy to Identify Hepatitis B Virus Entry Inhibitors by AlphaScreen Technology Targeting the Envelope-Receptor Interaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukano, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Oshima, M.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ohki, M.; Park, S.-Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Wakita, T.; Sureau, C.; et al. Troglitazone Impedes the Oligomerization of Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide and Entry of Hepatitis B Virus Into Hepatocytes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkers, J.M.; Zehnder, B.; van Westen, G.J.P.; Kwakkenbos, M.J.; IJzerman, A.P.; Oude Elferink, R.P.J.; Beuers, U.; Urban, S.; van de Graaf, S.F.J. Reduced Hepatitis B and D Viral Entry Using Clinically Applied Drugs as Novel Inhibitors of the Bile Acid Transporter NTCP. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwamoto, M.; Watashi, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Aly, H.H.; Fukasawa, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ito, T.; Koiwai, O.; et al. Evaluation and Identification of Hepatitis B Virus Entry Inhibitors Using HepG2 Cells Overexpressing a Membrane Transporter NTCP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.-C.; Tao, M.-H.; Hung, T.-M.; Chen, J.-C.; Lin, Z.-J.; Huang, C. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Entry of Hepatitis B Virus into Hepatocytes. Antivir. Res. 2014, 111, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, H.; Kamisuki, S.; Kaneko, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Watashi, K.; Sugawara, F. Isolation and Structure of Vanitaracin A, a Novel Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Compound from Talaromyces sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4325–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, M.; Watashi, K.; Kamisuki, S.; Matsunaga, H.; Iwamoto, M.; Kawai, F.; Ohashi, H.; Tsukuda, S.; Shimura, S.; Suzuki, R.; et al. A Novel Tricyclic Polyketide, Vanitaracin A, Specifically Inhibits the Entry of Hepatitis B and D Viruses by Targeting Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11945–11953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K.; Hojima, T.; Isogawa, M.; Iwamoto, M.; Omagari, K.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Kojima, S.; Sugiyama, M.; et al. A New Class of Hepatitis B and D Virus Entry Inhibitors, Proanthocyanidin and Its Analogs, That Directly Act on the Viral Large Surface Proteins. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirstgen, M.; Lowjaga, K.A.A.T.; Müller, S.F.; Goldmann, N.; Lehmann, F.; Alakurtti, S.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Glebe, D.; Geyer, J. Selective Hepatitis B and D Virus Entry Inhibitors from the Group of Pentacyclic Lupane-Type Betulin-Derived Triterpenoids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Pan, D.; Liu, B.; Ouyang, L. Discovery of a Novel Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide (NTCP) Inhibitor: Design, Synthesis, and Anti-Proliferative Activities. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, J.; Jeong, M.S.; Hong, H.J. Construction and Characterization of an Anti-Hepatitis B Virus PreS1 Humanized Antibody That Binds to the Essential Receptor Binding Site. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, H.J.; Ryu, C.J.; Hur, H.; Kim, S.; Oh, H.K.; Oh, M.S.; Park, S.Y. In Vivo Neutralization of Hepatitis B Virus Infection by an Anti-PreS1 Humanized Antibody in Chimpanzees. Virology 2004, 318, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.-Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Yuan, L.-Z.; Lan, Y.; Lo, Y.-C.; Sun, C.-P.; Wu, C.-R.; Zhang, J.-F.; et al. Prolonged Suppression of HBV in Mice by a Novel Antibody That Targets a Unique Epitope on Hepatitis B Surface Antigen. Gut 2016, 65, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, S.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Mao, F.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Pan, L.; et al. A Potent Human Neutralizing Antibody Fc-Dependently Reduces Established HBV Infections. eLife 2017, 6, e26738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, A.U.; Phillips, S.; Levine, I.; Ijaz, S.; Dahari, H.; Eren, R.; Dagan, S.; Naoumov, N.V. Novel Mechanism of Antibodies to Hepatitis B Virus in Blocking Viral Particle Release from Cells. Hepatology 2010, 52, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galun, E.; Eren, R.; Safadi, R.; Ashour, Y.; Terrault, N.; Keeffe, E.B.; Matot, E.; Mizrachi, S.; Terkieltaub, D.; Zohar, M.; et al. Clinical Evaluation (Phase I) of a Combination of Two Human Monoclonal Antibodies to HBV: Safety and Antiviral Properties. Hepatology 2002, 35, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J. Have the Starting Lineup of Five for Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Synthesis Been Identified? Hepatology 2020, 72, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revill, P.A.; Chisari, F.V.; Block, J.M.; Dandri, M.; Gehring, A.J.; Guo, H.; Hu, J.; Kramvis, A.; Lampertico, P.; Janssen, H.L.A.; et al. A Global Scientific Strategy to Cure Hepatitis B. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic Strategies for Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Towards a Cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockmann, J.-H.; Stadler, D.; Xia, Y.; Ko, C.; Wettengel, J.M.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Dandri, M.; Protzer, U. Comparative Analysis of the Antiviral Effects Mediated by Type I and III Interferons in Hepatitis B Virus–Infected Hepatocytes. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeger, C.; Sohn, J.A. Complete Spectrum of CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Mutations on HBV CccDNA. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyushev, D.; Brezgin, S.; Kostyusheva, A.; Zarifyan, D.; Goptar, I.; Chulanov, V. Orthologous CRISPR/Cas9 Systems for Specific and Efficient Degradation of Covalently Closed Circular DNA of Hepatitis B Virus. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1779–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, F.; Rudin, C.M.; Sen, T. CRISPR Gene Therapy: Applications, Limitations, and Implications for the Future. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd-Ismail; Lim; Gunaratne; Tan Mapping the Interactions of HBV CccDNA with Host Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4276. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cradick, T.J.; Keck, K.; Bradshaw, S.; Jamieson, A.C.; McCaffrey, A.P. Zinc-Finger Nucleases as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Targeting Hepatitis B Virus DNAs. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ely, A.; Moyo, B.; Arbuthnot, P. Progress With Developing Use of Gene Editing To Cure Chronic Infection With Hepatitis B Virus. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.; Wang, F.; Levin, A.; Le, C.; Eltayebi, Y.; Houghton, M.; Tyrrell, L.; Barakat, K. Targeting the Achilles Heel of the Hepatitis B Virus: A Review of Current Treatments against Covalently Closed Circular DNA. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, M.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, Z. An Efficient Antiviral Strategy for Targeting Hepatitis B Virus Genome Using Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeger, C. Control of Viral Transcripts as a Concept for Future HBV Therapies. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 30, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Mills, C.; Yu, W.; Yan, R.; Aldrich, C.E.; Saputelli, J.R.; Mason, W.S.; Xu, X.; Guo, J.-T.; Block, T.M.; et al. Identification of Disubstituted Sulfonamide Compounds as Specific Inhibitors of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4277–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morikawa, K.; Suda, G.; Sakamoto, N. Viral Life Cycle of Hepatitis B Virus: Host Factors and Druggable Targets: HBV Antivirals and Viral Life Cycle. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Gehring, A.J. The Immune Response during Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen Recognition and Innate Immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, K.; Liu, J.; Broering, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Dittmer, U.; Lu, M. Recent Advances in the Discovery and Development of TLR Ligands as Novel Therapeutics for Chronic HBV and HIV Infections. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslov, A.; Wieland, S.; Menne, S. Modulators of Innate Immunity as Novel Therapeutics for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 30, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lu, M. Advances in Targeting the Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems to Cure Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehring, A.J.; Protzer, U. Targeting Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to Cure Chronic HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Cao, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, E.; Lu, M. Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus and Toll-Like Receptors: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Use for Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucifora, J.; Bonnin, M.; Aillot, L.; Fusil, F.; Maadadi, S.; Dimier, L.; Michelet, M.; Floriot, O.; Ollivier, A.; Rivoire, M.; et al. Direct Antiviral Properties of TLR Ligands against HBV Replication in Immune-Competent Hepatocytes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gane, E.; Pastagia, M. Pharmacodynamics of Oral JNJ-64794964, a Toll-like Receptor-7 Agonist, in Healthy Adults. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Brunetto, M.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Ferrari, C.; Massetto, B.; Nguyen, A.-H.; Joshi, A.; Woo, J.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Safety, Efficacy and Pharmacodynamics of Vesatolimod (GS-9620) in Virally Suppressed Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Ahn, S.H.; Elkhashab, M.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; Bulusu, A.; Tian, X.; Cathcart, A.L.; Woo, J.; Subramanian, G.M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Vesatolimod (GS-9620) in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Who Are Not Currently on Antiviral Treatment. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, D.; Herschke, F.; Pauwels, F.; Stoops, B.; Last, S.; Pieters, S.; Scholliers, A.; Thoné, T.; Van Schoubroeck, B.; De Pooter, D.; et al. Novel Pyrimidine Toll-like Receptor 7 and 8 Dual Agonists to Treat Hepatitis B Virus. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7936–7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embrechts, W.; Herschke, F.; Pauwels, F.; Stoops, B.; Last, S.; Pieters, S.; Pande, V.; Pille, G.; Amssoms, K.; Smyej, I.; et al. 2,4-Diaminoquinazolines as Dual Toll-like Receptor (TLR) 7/8 Modulators for the Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6236–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, R.L.; Mish, M.; Chin, G.; Perry, J.K.; Appleby, T.; Aktoudianakis, V.; Metobo, S.; Pyun, P.; Niu, C.; Daffis, S.; et al. Discovery of GS-9688 (Selgantolimod) as a Potent and Selective Oral Toll-Like Receptor 8 Agonist for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 10188–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolowicz, K.E.; Iyer, R.P.; Czerwinski, S.; Suresh, M.; Yang, J.; Padmanabhan, S.; Sheri, A.; Pandey, R.K.; Skell, J.; Marquis, J.K.; et al. Antiviral Efficacy and Host Innate Immunity Associated with SB 9200 Treatment in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, M.; Korolowicz, K.E.; Balarezo, M.; Iyer, R.P.; Padmanabhan, S.; Cleary, D.; Gimi, R.; Sheri, A.; Yon, C.; Kallakury, B.V.; et al. Antiviral Efficacy and Host Immune Response Induction during Sequential Treatment with SB 9200 Followed by Entecavir in Woodchucks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Locarnini, S.; Wong, D.; Jackson, K.; Walsh, R.; Edwards, R.; Hammond, R.; Macfarlane, C.; Iyer, R.P.; Afdhal, N.; Yuen, M.-F. Novel Anti-Viral Activity of SB 9200, a RIG-I Agonist; Results from Cohort 1 of the Achieve Trial. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1269–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Roethle, P.A.; McFadden, R.M.; Yang, H.; Hrvatin, P.; Hui, H.; Graupe, M.; Gallagher, B.; Chao, J.; Hesselgesser, J.; Duatschek, P.; et al. Identification and Optimization of Pteridinone Toll-like Receptor 7 (TLR7) Agonists for the Oral Treatment of Viral Hepatitis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7324–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, A.R.; Pallett, L.J.; McCoy, L.E.; Suveizdyte, K.; Amin, O.E.; Swadling, L.; Alberts, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Circulating and Intrahepatic Antiviral B Cells Are Defective in Hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4588–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Massari, M.; Loggi, E.; Biasini, E.; Sacchelli, L.; Cavallo, M.C.; Silini, E.M.; Andreone, P.; Missale, G.; et al. Antiviral Intrahepatic T-Cell Responses Can Be Restored by Blocking Programmed Death-1 Pathway in Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 682–693.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, E.; Ma, Z.; Wu, W.; Kosinska, A.; Zhang, X.; Möller, I.; Seiz, P.; Glebe, D.; Wang, B.; et al. Enhancing Virus-Specific Immunity In Vivo by Combining Therapeutic Vaccination and PD-L1 Blockade in Chronic Hepadnaviral Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezzikouri, S.; Hoque Kayesh, M.E.; Benjelloun, S.; Kohara, M.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K. Targeting Host Innate and Adaptive Immunity to Achieve the Functional Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B. Vaccines 2020, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Tian, Y.; Kosinska, A.D.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Dittmer, U.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. The Expression of PD-1 Ligands and Their Involvement in Regulation of T Cell Functions in Acute and Chronic Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salimzadeh, L.; Le Bert, N.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Gill, U.S.; Newell, E.W.; Frey, C.; Hung, M.; Novikov, N.; Fletcher, S.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; et al. PD-1 Blockade Partially Recovers Dysfunctional Virus–Specific B Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4573–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; Flies, D.B.; van Deursen, J.M.A.; Chen, L. B7-H1 Determines Accumulation and Deletion of Intrahepatic CD8+ T Lymphocytes. Immunity 2004, 20, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An Open-Label, Non-Comparative, Phase 1/2 Dose Escalation and Expansion Trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiner, B.; Kirstein, M.M.; Hucke, F.; Finkelmeier, F.; Schulze, K.; Hinrichs, J.B.; Waneck, F.; Waidmann, O.; Reiberger, T.; Müller, C.; et al. Programmed Cell Death Protein-1 (PD-1)-targeted Immunotherapy in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Efficacy and Safety Data from an International Multicentre Real-world Cohort. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gish, R.G.; Yuen, M.-F.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Given, B.D.; Lai, C.-L.; Locarnini, S.A.; Lau, J.Y.N.; Wooddell, C.I.; Schluep, T.; Lewis, D.L. Synthetic RNAi Triggers and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Therapies with Curative Intent. Antivir. Res. 2015, 121, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grimm, D.; Thimme, R.; Blum, H.E. HBV Life Cycle and Novel Drug Targets. Hepatol. Int. 2011, 5, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriano, V.; Barreiro, P.; Cachay, E.; Kottilil, S.; Fernandez-Montero, J.V.; de Mendoza, C. Advances in Hepatitis B Therapeutics. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 204993612096502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liang, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Discovery of RG7834: The First-in-Class Selective and Orally Available Small Molecule Hepatitis B Virus Expression Inhibitor with Novel Mechanism of Action. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10619–10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Gatti, P.; Papoian, T. Safety of Antisense Oligonucleotide and SiRNA-Based Therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billioud, G.; Kruse, R.L.; Carrillo, M.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Gao, D.; Kim, A.; Chen, L.; McCaleb, M.L.; Crosby, J.R.; Hamatake, R.; et al. In Vivo Reduction of Hepatitis B Virus Antigenemia and Viremia by Antisense Oligonucleotides. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausen, P.; Stein, H. Ribonuclease H. An Enzyme Degrading the RNA Moiety of DNA-RNA Hybrids. Eur. J. Biochem. 1970, 14, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, W.; Crouch, R. Degradation of DNA RNA Hybrids by Ribonuclease H and DNA Polymerases of Cellular and Viral Origin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 3360–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edwards, T.C.; Ponzar, N.L.; Tavis, J.E. Shedding Light on RNaseH: A Promising Target for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV). Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerelsaikhan, T.; Tavis, J.E.; Bruss, V. Hepatitis B Virus Nucleocapsid Envelopment Does Not Occur without Genomic DNA Synthesis. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4269–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowotny, M.; Gaidamakov, S.A.; Crouch, R.J.; Yang, W. Crystal Structures of RNase H Bound to an RNA/DNA Hybrid: Substrate Specificity and Metal-Dependent Catalysis. Cell 2005, 121, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowotny, M.; Yang, W. Stepwise Analyses of Metal Ions in RNase H Catalysis from Substrate Destabilization to Product Release. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavis, J.E.; Zoidis, G.; Meyers, M.J.; Murelli, R.P. Chemical Approaches to Inhibiting the Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, E.; Corona, A.; Menéndez-Arias, L. Ribonuclease H, an Unexploited Target for Antiviral Intervention against HIV and Hepatitis B Virus. Antivir. Res. 2019, 171, 104613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.C.; Mani, N.; Dorsey, B.; Kakarla, R.; Rijnbrand, R.; Sofia, M.J.; Tavis, J.E. Inhibition of HBV Replication by N-Hydroxyisoquinolinedione and N-Hydroxypyridinedione Ribonuclease H Inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, T.C.; Lomonosova, E.; Patel, J.A.; Li, Q.; Villa, J.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Morrison, L.A.; Bailly, F.; Cotelle, P.; Giannakopoulou, E.; et al. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Replication by N -Hydroxyisoquinolinediones and Related Polyoxygenated Heterocycles. Antivir. Res. 2017, 143, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Cao, F.; Huang, A.; Tavis, J.E. β-Thujaplicinol Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Blocking the Viral Ribonuclease H Activity. Antivir. Res. 2013, 99, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Lomonosova, E.; Cheng, X.; Moran, E.A.; Meyers, M.J.; Le Grice, S.F.J.; Thomas, C.J.; Jiang, J.; Meck, C.; Hirsch, D.R.; et al. Hydroxylated Tropolones Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Blocking Viral Ribonuclease H Activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomonosova, E.; Daw, J.; Garimallaprabhakaran, A.K.; Agyemang, N.B.; Ashani, Y.; Murelli, R.P.; Tavis, J.E. Efficacy and Cytotoxicity in Cell Culture of Novel α-Hydroxytropolone Inhibitors of Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H. Antivir. Res. 2017, 144, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.R.; Lomonosova, E.; Li, Q.; Ponzar, N.L.; Villa, J.A.; Touchette, E.; Rapp, S.; Liley, R.M.; Murelli, R.P.; Grigoryan, A.; et al. Efficacy of Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H Inhibitors, a New Class of Replication Antagonists, in FRG Human Liver Chimeric Mice. Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyemang, N.B.; Kukla, C.R.; Edwards, T.C.; Li, Q.; Langen, M.K.; Schaal, A.; Franson, A.D.; Casals, A.G.; Donald, K.A.; Yu, A.J.; et al. Divergent Synthesis of a Thiolate-Based α-Hydroxytropolone Library with a Dynamic Bioactivity Profile. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 34227–34234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, A.J.; Abdelmessih, R.G.; Murelli, R.P. Amidation Strategy for Final-Step α-Hydroxytropolone Diversification. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 3026–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lomonosova, E.; Donlin, M.J.; Cao, F.; O’Dea, A.; Milleson, B.; Berkowitz, A.J.; Baucom, J.-C.; Stasiak, J.P.; Schiavone, D.V.; et al. Amide-Containing α-Hydroxytropolones as Inhibitors of Hepatitis B Virus Replication. Antivir. Res. 2020, 177, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, E.; Miller, J.T.; Noronha, A.; Tavis, J.; Gallicchio, E.; Murelli, R.P.; Le Grice, S.F.J. 3,7-Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus Minus-Strand DNA Synthesis. Molecules 2020, 25, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.W.; Lomonosova, E.; Moran, E.A.; Cheng, X.; Patel, K.B.; Bailly, F.; Cotelle, P.; Meyers, M.J.; Tavis, J.E. Hepatitis B Virus Replication Is Blocked by a 2-Hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-Dione (HID) Inhibitor of the Viral Ribonuclease H Activity. Antivir. Res. 2014, 108, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavis, J.E.; Cheng, X.; Hu, Y.; Totten, M.; Cao, F.; Michailidis, E.; Aurora, R.; Meyers, M.J.; Jacobsen, E.J.; Parniak, M.A.; et al. The Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H Is Sensitive to Inhibitors of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Ribonuclease H and Integrase Enzymes. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Villa, J.A.; Donlin, M.J.; Edwards, T.C.; Cheng, X.; Heier, R.F.; Meyers, M.J.; Tavis, J.E. Hepatitis B Virus Genetic Diversity Has Minimal Impact on Sensitivity of the Viral Ribonuclease H to Inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2016, 135, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomonosova, E.; Zlotnick, A.; Tavis, J.E. Synergistic Interactions between Hepatitis B Virus RNase H Antagonists and Other Inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02441-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Liu, F.; Tong, X.; Hoffmann, D.; Zuo, J.; Lu, M. Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Using Small Molecule Modulators of Nucleocapsid Assembly: Recent Advances and Perspectives. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, S.F.; Liu, G. Past, Current, and Future Developments of Therapeutic Agents for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 6461–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.J.; Burger, D.M.; Feld, J.J.; Kiser, J.J. Review Article: Clinical Pharmacology of Current and Investigational Hepatitis B Virus Therapies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoulim, F.; Lenz, O.; Vandenbossche, J.J.; Talloen, W.; Verbinnen, T.; Moscalu, I.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Bourgeois, S.; Buti, M.; Crespo, J.; et al. JNJ-56136379, an HBV Capsid Assembly Modulator, Is Well-Tolerated and Has Antiviral Activity in a Phase 1 Study of Patients With Chronic Infection. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 521–533.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Cai, D.; Yan, R.; Li, L.; Zong, Y.; Guo, L.; Mercier, A.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, A.; Henne, K.; et al. Preclinical Profile and Characterization of the Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein Inhibitor ABI-H0731. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01463-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, N.; Cole, A.G.; Phelps, J.R.; Ardzinski, A.; Cobarrubias, K.D.; Cuconati, A.; Dorsey, B.D.; Evangelista, E.; Fan, K.; Guo, F.; et al. Preclinical Profile of AB-423, an Inhibitor of Hepatitis B Virus Pregenomic RNA Encapsidation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00082-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Arzumanyan, A.; Clayton, M.M.; Schinazi, R.F.; Wang, Z.; Goldmann, S.; Ren, Q.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of GLS4, an Inhibitor of Hepatitis B Virus Core Particle Assembly. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5344–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berke, J.M.; Dehertogh, P.; Vergauwen, K.; Van Damme, E.; Mostmans, W.; Vandyck, K.; Pauwels, F. Capsid Assembly Modulators Have a Dual Mechanism of Action in Primary Human Hepatocytes Infected with Hepatitis B Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00560-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razavi-Shearer, D.; Gamkrelidze, I.; Nguyen, M.H.; Chen, D.-S.; Van Damme, P.; Abbas, Z.; Abdulla, M.; Abou Rached, A.; Adda, D.; Aho, I.; et al. Global Prevalence, Treatment, and Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in 2016: A Modelling Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, H.; Block, T.; Brown, N.; Brownstein, A.; Brosgart, C.; Chang, K.-M.; Chen, P.-J.; Chisari, F.V.; Cohen, C.; El-Serag, H.; et al. A Research Agenda for Curing Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Name | Structure | Class | IC50 1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ezetimibe |  | Cholesterol absorption inhibitor | 18 μΜ 2 | [113] |
| (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate |  | Flavonoid in green tea extract | ≈10 μM | [119] |
| Proanthocyanidin |  | Oligomeric flavonoid, derived from extract of grape seed | 7.8 μM | [122] |
| Oolonghomobisflavan C |  | Proanthocyanidin analogue | 4.3 μM | [122] |
| Temsirolimus |  | Rapamycin derivative and prodrug | 7.86 μM | [115] |
| Compound 2 |  | Betulin derivative | 4 μM | [123] |
| Cyclosporin A |  | Immunosuppressant | 1.17 μM | [111] |
| Rosiglitazone |  | Thiazolidinedione (PPAR-γ agonist) | 5.1 μM | [117] |
| Ciglitazone |  | Thiazolidinedione (PPAR-γ agonist) | 4.7 μM | [116] |
| Irbesartan |  | Angiotensin II receptor antagonist | 3.3 μM | [114] |
| Zafirlukast |  | Leukotriene receptor antagonist | 6.5 μM | [117] |
| TRIAC |  | Thyroid hormone analogue | 6.9 μM | [117] |
| B7 |  | Novel synthetic compound | 7.36 μM | [124] |
| Vanitaracin A |  | Isolated from Talaromyces sp. | 0.61 μM | [121] |
| α-hydroxytropolones | |||||
 α-hydroxytropolones |  46 [190] EC50 = 1.0 μM CC50 = 25 μM TI = 25 |  110 [190] EC50 = 0.34 μM CC50 = 32 μM TI = 94 |  280 [191] EC50 = 0.5 μM CC50 = >77 M TI = >154 | ||
| N-hydroxyimides | |||||
 86 [188] HID EC50 = 1.4 μM CC50 = 99 μM TI = 71 |  12 [185] HNO EC50 = 3.4 μM CC50 = 7.1 μM TI = 2 |  17 [185] N-hydroxypyrimidinedione EC50 = 5.5 μM CC50 = >100 μM TI = >18 | |||
 A23 [187] HPD EC50 = 0.11 μM CC50 = 33 μM TI = 300 |  A24 [187] HPD EC50 = 0.29 μM CC50 = 102 μM TI = 352 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prifti, G.-M.; Moianos, D.; Giannakopoulou, E.; Pardali, V.; Tavis, J.E.; Zoidis, G. Recent Advances in Hepatitis B Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050417
Prifti G-M, Moianos D, Giannakopoulou E, Pardali V, Tavis JE, Zoidis G. Recent Advances in Hepatitis B Treatment. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050417
Chicago/Turabian StylePrifti, Georgia-Myrto, Dimitrios Moianos, Erofili Giannakopoulou, Vasiliki Pardali, John E. Tavis, and Grigoris Zoidis. 2021. "Recent Advances in Hepatitis B Treatment" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050417
APA StylePrifti, G.-M., Moianos, D., Giannakopoulou, E., Pardali, V., Tavis, J. E., & Zoidis, G. (2021). Recent Advances in Hepatitis B Treatment. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050417