Rational Design of Novel Inhibitors of α-Glucosidase: An Application of Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship and Structure-Based Virtual Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
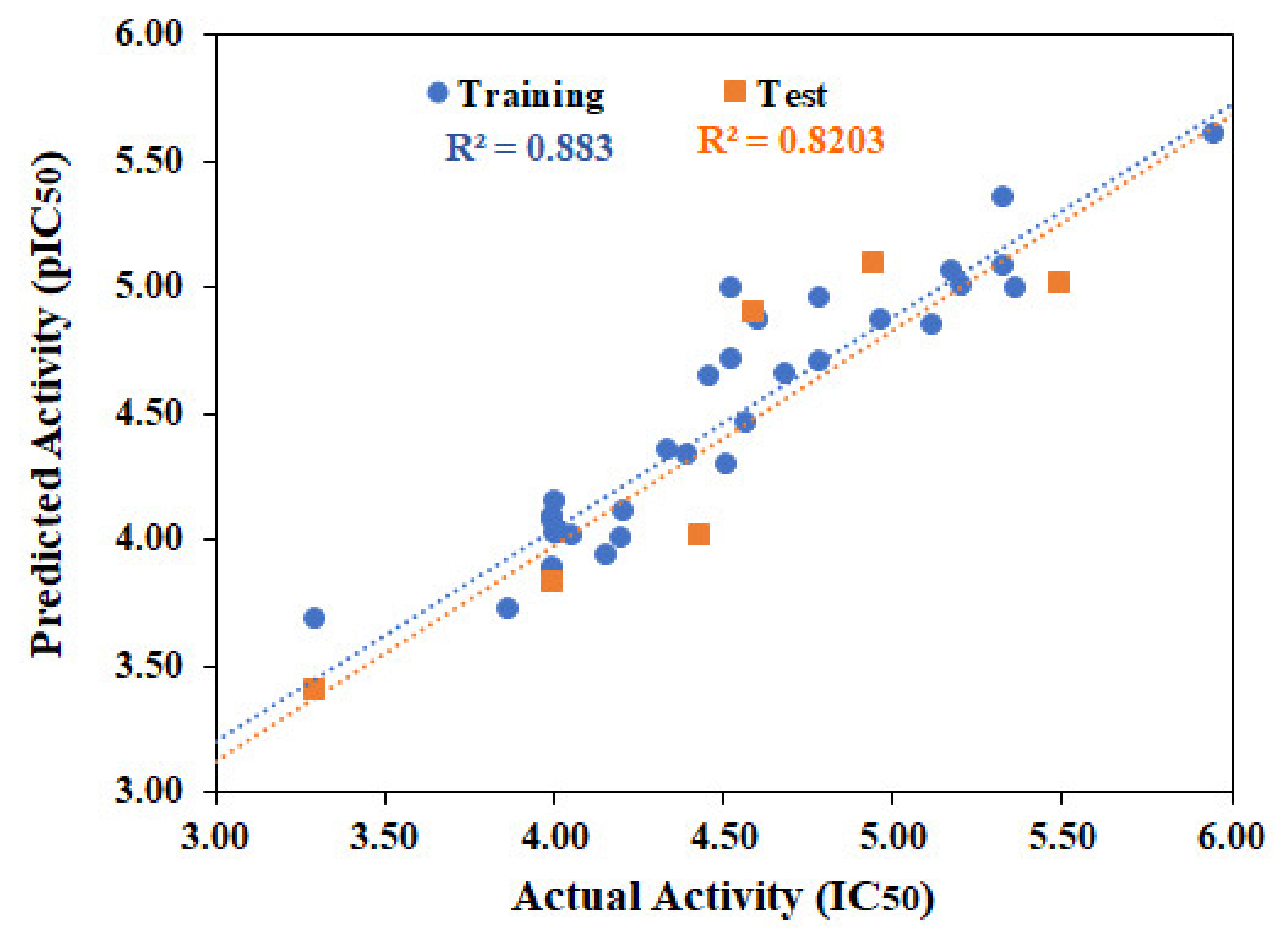
2.1. QSAR Modeling
2.2. Structure-Based Screening of Filtered Compounds against α-Glucosidase
2.3. ADMET Analysis of Selected Hits
2.4. Protein-Ligand Interaction Analysis of 142 Compounds
2.5. The Binding Potential of High Active Hits
2.6. Prediction of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities of Compounds (20, 28, 48, 63, 94, 112, 135 and 140) by QSAR Model
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Selection of Data Set for QSAR Analysis
The Generation and Validation of QSAR Model
3.2. Filtration of ZINC Database for Virtual Screening
3.3. Docking Based Screening
3.4. Pharmacokinetic (ADMET) Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Roglic, G. WHO Global report on diabetes: A summary. Int. J. Noncommun. Dis. 2016, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, M.E.; Karantas, I.D.; Siafaka, P.I. Diabetes mellitus: A review on pathophysiology, current status of oral medica-tions and future perspectives. Acta Pharm. Sci. 2017, 55, 61–82. [Google Scholar]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Yardley, J.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Dunstan, D.W.; Dempsey, P.C.; Horton, E.S.; Castorino, K.; Tate, D.F. Physical activity/exercise and diabetes: A position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moelands, S.V.; Lucassen, P.L.; Akkermans, R.P.; De Grauw, W.J.; Van de Laar, F.A. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors for pre-vention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk of develop-ing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, CD005061. [Google Scholar]
- Damsud, T.; Chanwun, T.; Kaewpiboon, C. Antidiabetic agents with α-glucosidase inhibition and antioxidant capacity from the shoots of Clausena cambodiana Guill. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2017, 13, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Saltos, M.B.V.; Puente, B.F.N.; Faraone, I.; Milella, L.; De Tommasi, N.; Braca, A. Inhibitors of α-amylase and α-glucosidase from Andromachia igniaria Humb. & Bonpl. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 14, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.S. Cerebrovascular Complications of Diabetes: Alpha Glucosidase Inhibitor as Potential Therapy. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, A.; Duvoor, C.; Dendi, V.S.R.; Kraleti, S.; Chada, A.; Ravilla, R.; Marco, A.; Shekhawat, N.S.; Montales, M.T.; Kuriakose, K.; et al. Clinical Review of Antidiabetic Drugs: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, S.A.; Lamos, E.M.; Davis, S.N. A review of the efficacy and safety of oral antidiabetic drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2013, 12, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proença, C.; Freitas, M.; Ribeiro, D.; Oliveira, E.F.T.; Sousa, J.L.C.; Tomé, S.M.; Ramos, M.J.; Silva, A.M.S.; Fernandes, P.A.; Fernandes, E. α-Glucosidase inhibition by flavonoids: An in vitro and in silico structure–activity relationship study. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Yuan, G.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Network Pharmacology Studies on the Bioactive Compounds and Action Mechanisms of Natural Products for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, P.-P.; Zhang, B.-J.; Cui, X.-P.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Zhong, Y.-Y.; Mai, Y.-Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Chen, H.-S.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel ursolic acid analogues as potential α-glucosidase inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan Baig, M.; Ahmad, K.; Roy, S.; Mohammad Ashraf, J.; Adil, M.; Haris Siddiqui, M.; Khan, S.; Amjad Kamal, M.; Provazník, I.; Choi, I. Computer aided drug design: Success and limitations. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada-Gracia, D.; Huerta-Yépez, S.; Moreno-Vargas, L.M. Application of computational methods for anticancer drug discovery, design, and optimization. Bol. Med. Hosp. Infant. México 2016, 73, 411–423. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Luo, C. Computer-Aided Drug Design in Epigenetics. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avula, S.K.; Khan, A.; Halim, S.A.; Al-Abri, Z.; Anwar, M.U.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Csuk, R.; Al-Harrasi, A. Synthesis of novel (R)-4-fluorophenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazoles: A new class of α-glucosidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, T.; Hussain, I.; Ali, L.; Mabood, F.; Khan, A.; Shujah, S.; Rehman, N.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Hussain, J.; Khan, A.; et al. New gorgonane sesquiterpenoid from Teucrium mascatense Boiss, as α-glucosidase inhibitor. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, N.; Rafiq, K.; Khan, A.; Ahsan Halim, S.; Ali, L.; Al-Saady, N.; Hilal Al-Balushi, A.; Al-Busaidi, H.K.; Al-Harrasi, A. α-Glucosidase Inhibition and Molecular Docking Studies of Natural Bromin-ated Metabolites from Marine Macro Brown Alga Dictyopteris hoytii. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U.; Eisenberg, D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 1992, 356, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, K.; Miyake, H.; Kusunoki, M.; Osaki, S. Steric hindrance by 2 amino acid residues determines the substrate specificity of isomaltase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M. Zanamivir: From drug design to the clinic. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cushman, D.W.; Ondetti, M.A. Design of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Gui, C.; Luo, X.; Yang, Q.; Günther, S.; Scandella, E.; Drosten, C.; Bai, D.; He, X.; Ludewig, B.; et al. Cinanserin Is an Inhibitor of the 3C-Like Proteinase of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus and Strongly Reduces Virus Replication In Vitro. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7095–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graves, B.J.; Hatada, M.H.; Miller, J.K.; Graves, M.C.; Roy, S.; Cook, M.C.; Krohn, A.; Martin, J.A.; Roberts, N.A. The Three-Dimensional X-Ray Crystal Structure of HIV-1 Protease Complexed with a Hydroxyethylene Inhibitor. In Structure and Function of the Aspartic Proteinases; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991; pp. 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Pollack, V.A.; Savage, D.M.; Baker, D.A.; Tsaparikos, K.E.; Sloan, D.E.; Moyer, J.D.; Barbacci, E.G.; Pustilnik, L.R.; Smolarek, T.A.; Davis, J.A.; et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-associated tyrosine phos-phorylation in human carcinomas with CP-358,774: Dynamics of receptor inhibition in situ and antitumor effects in athymic mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 291, 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, S.S.; Tsao, M.-S.; Nicklee, T.; Hedley, D.W. Effects of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor OSI-774, Tarceva, on downstream signaling pathways and apoptosis in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma 1 supported by the Na-tional Cancer Institute of Canada and the Pat Myhal Fund for Pancreatic Cancer Research. 1. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bulgaru, A.M.; Mani, S.; Goel, S.; Perez-Soler, R. Erlotinib (Tarceva®): A promising drug targeting epidermal growth fac-tor receptor tyrosine kinase. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2003, 3, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, M.; Sharifi, M.; Hilger, R.; Scheulen, M.; Seeber, S.; Strumberg, D. Antitumor effect and potentiation or reduction in cytotoxic drug activity in human colon carcinoma cells by the Raf kinase inhibitor (RKI) BAY 43-9006. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 41, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Eisen, T. Kinase Inhibition with BAY 43–9006 in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6388S–6392S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Carter, C.; Tang, L.; Wilkie, D.; McNabola, A.; Rong, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Vincent, P.; McHugh, M.; et al. BAY 43-9006 Exhibits Broad Spectrum Oral Antitumor Activity and Targets the RAF/MEK/ERK Pathway and Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Involved in Tumor Progression and Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7099–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Liu, L.-H.; Ho, P.; Spector, N.L. Truncated ErbB2 receptor (p95 ErbB2) is regulated by heregulin through hetero-dimer formation with ErbB3 yet remains sensitive to the dual EGFR/ErbB2 kinase inhibitor GW572016. Oncogene 2004, 23, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, E.R.; Truesdale, A.T.; McDonald, O.B.; Yuan, D.; Hassell, A.; Dickerson, S.H.; Ellis, B.; Pennisi, C.; Horne, E.; Lackey, K.; et al. A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): Relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6652–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarman, M.; Barrie, S.E.; Llera, J.M. The 16, 17-double bond is needed for irreversible inhibition of human cytochrome P45017α by abiraterone (17-(3-Pyridyl) androsta-5, 16-dien-3β-ol) and related steroidal inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 5375–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnel, A.; Judson, I.; Dowsett, M.; Raynaud, F.; Dearnaley, D.; Mason, M.; Harland, S.; Robbins, A.; Halbert, G.; Nutley, B.; et al. Hormonal impact of the 17alpha-hydroxylase/C (17, 20)-lyase inhibitor abi-raterone acetate (CB7630) in patients with prostatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagusch, C.; Negri, M.; Hille, U.E.; Hu, Q.; Bartels, M.; Jahn-Hoffmann, K.; Mendieta, M.A.; Rodenwaldt, B.; Müller-Vieira, U.; Schmidt, D.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling studies of methylene-imidazole substituted biaryls as inhibitors of human 17α-hydroxylase-17, 20-lyase (CYP17). Part I: Heterocyclic modifications of the core structure. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 1992–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrynski, J.E.; D’Adamo, D.R.; Hornick, J.L.; Cin, P.D.; Antonescu, C.R.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Ladanyi, M.; Capelletti, M.; Rodig, S.J.; Ramaiya, N.; et al. Crizotinib inALK-Rearranged Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodig, S.J.; Shapiro, G.I. Crizotinib, a small-molecule dual inhibitor of the c-Met and ALK receptor tyrosine kinases. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 11, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, B.J.; Braga, R.C.; Melo-Filho, C.C.; Moreira-Filho, J.T.; Muratov, E.N.; Andrade, C.H. QSAR-based virtual screening: Advances and applications in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, S.; Bae, H.; Jo, J.; Yoon, S. Comprehensive ensemble in QSAR prediction for drug discovery. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Afifi, M.; Imran, S.; Sultan, S.; Rahim, F.; Khan, K.M. Synthesis, α-glucosidase inhibition and molecular docking study of coumarin based derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, Z.; Deng, B.; Chen, S.; Li, W. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies of chromone hydra-zone derivatives as α-glucosidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2957–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassan, A.M.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Latip, J.; Shah, S.A.A. A new sulphated flavone and other phytoconstituents from the leaves of Tetracera indica Merr. and their alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Peng, Y.; Qiu, J.; Cao, A.; Wang, G.; Peng, Z. Synthesis, In Vitro α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity and Molecular Docking Studies of Novel Benzothiazole-Triazole Derivatives. Molecules 2017, 22, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MOE. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2013.08; Chemical Computing Group: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. ZINC—A Free Database of Commercially Available Compounds for Virtual Screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| αGIs | R1 | R2 | IC50 (µM) | pIC50 | Predicted | Residual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||
| αGI1 | H |  | 26.7 | 4.57 | 4.46 | 0.11 |
| αGI2 | H |  | 39.8 | 4.40 | 4.33 | 0.07 |
| αGI3 | H |  | 96.9 | 4.01 | 4.02 | −0.01 |
| αGI4 | H |  | 20.1 | 4.69 | 4.65 | 0.04 |
| αGI5 * | H |  | 100 | 4.00 | 3.83 | 0.17 |
| αGI6 | H |  | 100 | 4.00 | 3.88 | 0.12 |
| αGI7 | H |  | 100 | 4.00 | 4.07 | −0.07 |
| αGI8 | H |  | 100 | 4.00 | 3.89 | 0.11 |
| αGI9 | OH |  | 60.8 | 4.21 | 4.11 | 0.10 |
| αGI10 | H |  | 45.7 | 4.34 | 4.35 | −0.01 |
| αGI11 | OH |  | 96.7 | 4.01 | 4.15 | −0.14 |
| αGI12 | OH |  | 100 | 4.00 | 4.09 | −0.09 |
| αGI13 | OH |  | 95.4 | 4.02 | 4.02 | 0.00 |
| αGI14 | OH |  | 86.3 | 4.06 | 4.01 | 0.05 |
| αGI15 | H |  | 30.8 | 4.51 | 4.29 | 0.22 |
| αGI16 * | OH |  | 25.2 | 4.59 | 4.90 | −0.31 |
 | ||||||
| αGIs | R | IC50 (µM) | pIC50 | Predicted | Residual | |
| αGI17 |  | 29.14 | 4.53 | 4.99 | −0.46 | |
| αGI18 |  | 7.58 | 5.12 | 4.85 | 0.27 | |
| αGI19 |  | 1.1 | 5.95 | 5.60 | 0.35 | |
| αGI20 |  | 4.26 | 5.37 | 4.99 | 0.38 | |
| αGI21 * |  | 3.15 | 5.50 | 5.01 | 0.49 | |
| αGI22 |  | 6.1 | 5.21 | 5.00 | 0.21 | |
| αGI23 |  | 4.58 | 5.33 | 5.35 | −0.02 | |
| αGI24 |  | 16.1 | 4.79 | 4.95 | −0.16 | |
| αGI25 * |  | 36.46 | 4.43 | 4.01 | 0.42 | |
| αGI26 |  | 24.14 | 4.61 | 4.87 | −0.26 | |
| αGI27 |  | 29.14 | 4.53 | 4.71 | −0.18 | |
| αGI28 |  | 4.58 | 5.33 | 5.08 | 0.25 | |
| αGI29 |  | 16.1 | 4.79 | 4.70 | 0.09 | |
| αGI30 |  | 6.46 | 5.18 | 5.06 | 0.12 | |
| αGI31 |  | 34.14 | 4.46 | 4.64 | −0.18 | |
| αGI32 * |  | 11.14 | 4.95 | 5.09 | −0.14 | |
| αGI33 |  | 10.58 | 4.97 | 4.87 | 0.10 | |
| αGIs 34–38 | ||||||
| αGI34 |  | 133.57 | 3.87 | 3.72 | 0.15 | |
| αGI35 * |  | 500 | 3.30 | 3.40 | −0.10 | |
| αGI36 |  | 500 | 3.30 | 3.68 | −0.38 | |
| αGI37 |  | 68.46 | 4.16 | 3.93 | 0.23 | |
| αGI38 |  | 61.86 | 4.20 | 4.00 | 0.20 | |
| Comp | Chemical Formula | Chemical Structure | Interactions with Active Site Residues | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB | II | WB | |||
| 20 | C25H31N5O2 |  | ASP214, GLU276, THR215 | ASP68, ASP214, GLU276 | HOH1174 |
| 28 | C23H23ClN5O4 |  | ASP349, ASP214, ARG212 | ASP349 | none |
| 48 | C19H21BrN3O2S |  | ASP214, ARG439 | ASP214 | HOH1026 |
| 63 | C18H20F2N2O4S |  | ASP214, THR215 | none | none |
| 94 | C17H14BrN3O3S |  | ASP68, ASP214, THR215, HIS111, | none | HOH1102, HOH1174 |
| 112 | C24H27FN5O4 |  | GLU276, ARG212 | ASP349 | none |
| 135 | C20H19BrFN5 |  | GLU276, ASP68, HIS348 | GLU276, ASP68 | HOH1026, HOH1228 |
| 140 | C21H20ClF3N2O5 |  | ASP349, ASP214, ARG212, HIS348 | none | none |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halim, S.A.; Jabeen, S.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Rational Design of Novel Inhibitors of α-Glucosidase: An Application of Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship and Structure-Based Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050482
Halim SA, Jabeen S, Khan A, Al-Harrasi A. Rational Design of Novel Inhibitors of α-Glucosidase: An Application of Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship and Structure-Based Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050482
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalim, Sobia Ahsan, Sumaira Jabeen, Ajmal Khan, and Ahmed Al-Harrasi. 2021. "Rational Design of Novel Inhibitors of α-Glucosidase: An Application of Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship and Structure-Based Virtual Screening" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050482
APA StyleHalim, S. A., Jabeen, S., Khan, A., & Al-Harrasi, A. (2021). Rational Design of Novel Inhibitors of α-Glucosidase: An Application of Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship and Structure-Based Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050482









