Neuropeptide S Receptor Stimulation Excites Principal Neurons in Murine Basolateral Amygdala through a Calcium-Dependent Decrease in Membrane Potassium Conductance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
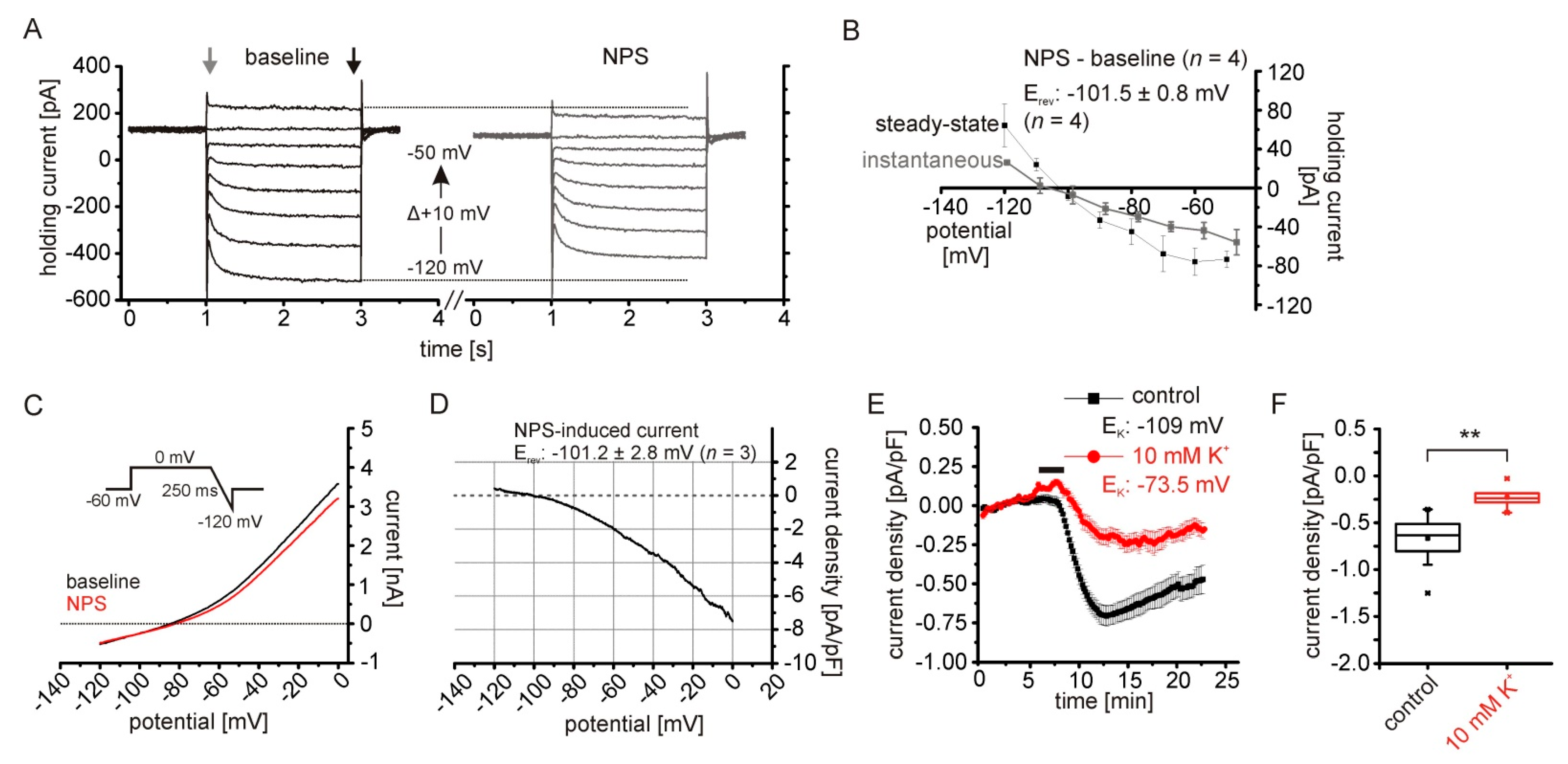
2.1. NPS-Induced Inward Currents in NPSR1-Expressing aBA Principal Neurons
2.2. The NPSR1-Dependent Current Results from Reduced Potassium Conductances
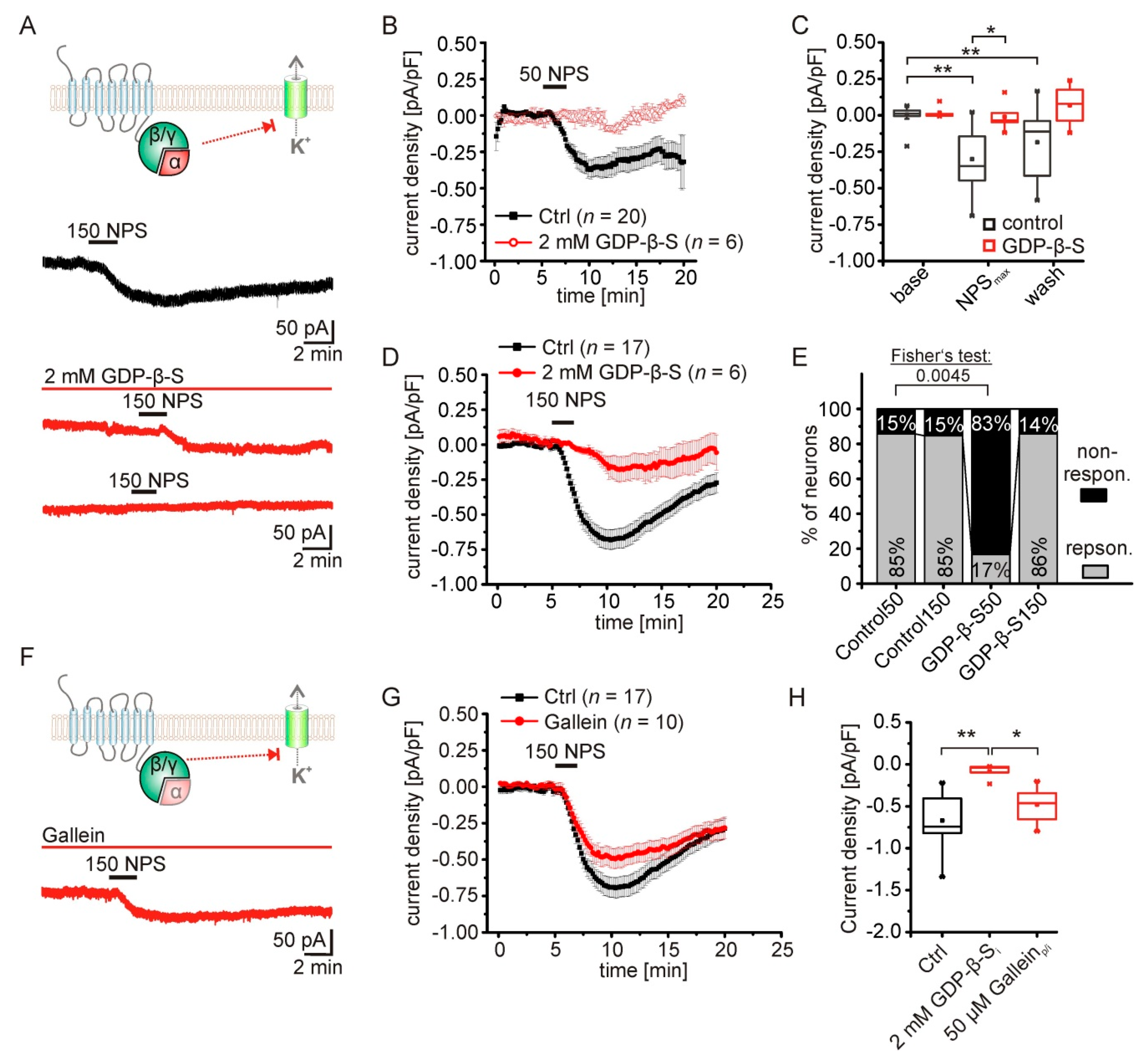
2.3. The NPS-Induced Current Is Dependent on NPSR1-Gα-Signaling
2.4. The NPSR1-Mediated Current Depends on Rise of Intracellular Calcium Concentrations
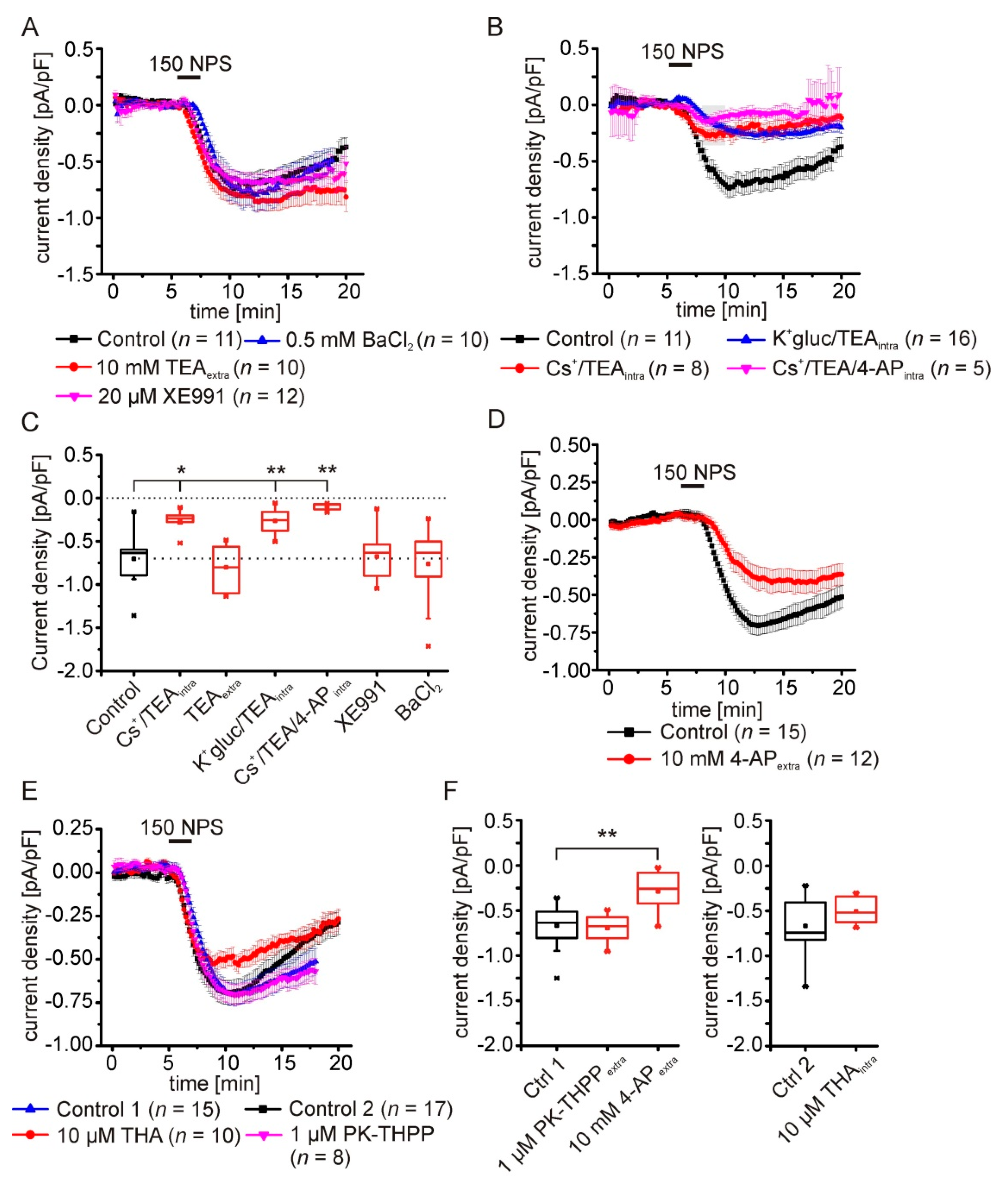
2.5. Pharmacological Characterization of the NPSR1-Modulated K+ Conductance
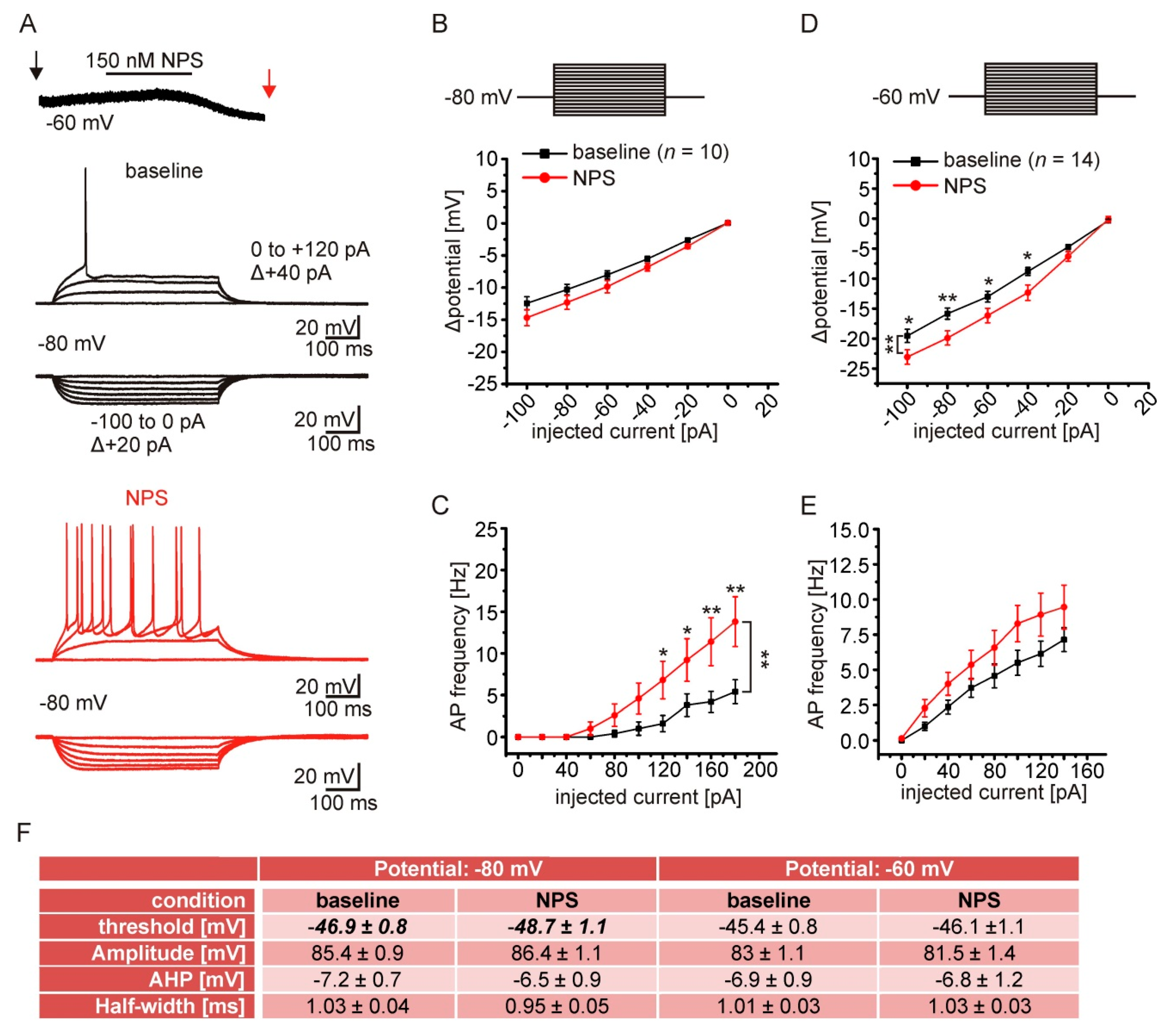
2.6. NPSR1 Activation Enhances Action Potential Generation in aBA PNs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Electrophysiology
4.3. RNAScope
4.4. Analysis and Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.-L.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Huitron-Resendiz, S.; Clark, S.D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.H.; Brucher, F.A.; Zeng, J.; Ly, N.K.; Henriksen, S.J.; et al. Neuropeptide S: A neuropeptide promoting arousal and anxiolytic-like effects. Neuron 2004, 43, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adori, C.; Barde, S.; Bogdanovic, N.; Uhlén, M.; Reinscheid, R.R.; Kovacs, G.G.; Hökfelt, T. Neuropeptide S- and Neuropeptide S receptor-expressing neuron populations in the human pons. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.D.; Duangdao, D.M.; Schulz, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.-L.; Reinscheid, R.K. Anatomical characterization of the neuropeptide S system in the mouse brain by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1867–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, A.; Theodorsson, E.; Fahrenkrug, J.; Reinscheid, R.K. Molecular fingerprint of neuropeptide s-producing neurons in the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1847–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Si, W.; Garau, C.; Jüngling, K.; Pape, H.C.; Schulz, S.; Reinscheid, R.K. Neuropeptide S precursor knockout mice display memory and arousal deficits. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, N.; Garau, C.; Duangdao, D.M.; Clark, S.D.; Jüngling, K.; Pape, H.C.; Reinscheid, R.K. Neuropeptide S enhances memory during the consolidation phase and interacts with noradrenergic systems in the brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüngling, K.; Lange, M.D.; Szkudlarek, H.J.; Lesting, J.; Erdmann, F.S.; Doengi, M.; Kügler, S.; Pape, H.-C. Increased GABAergic Efficacy of Central Amygdala Projections to Neuropeptide S Neurons in the Brainstem During Fear Memory Retrieval. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüngling, K.; Seidenbecher, T.; Sosulina, L.; Lesting, J.; Sangha, S.; Clark, S.D.; Okamura, N.; Duangdao, D.M.; Xu, Y.L.; Reinscheid, R.K.; et al. Neuropeptide S-Mediated Control of Fear Expression and Extinction: Role of Intercalated GABAergic Neurons in the Amygdala. Neuron 2008, 59, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendt, M.; Imobersteg, S.; Bürki, H.; McAllister, K.H.; Sailer, A.W. Intra-amygdala injections of neuropeptide S block fear-potentiated startle. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 474, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germer, J.; Kahl, E.; Fendt, M. Memory generalization after one-trial contextual fear conditioning: Effects of sex and neuropeptide S receptor deficiency. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 361, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grund, T.; Neumann, I.D. Brain neuropeptide S: Via GPCR activation to a powerful neuromodulator of socio-emotional behaviors. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 375, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, B.; Braconi, S.; Cannella, N.; Kallupi, M.; Soverchia, L.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Ubaldi, M. Neuropeptide S receptor gene expression in alcohol withdrawal and protracted abstinence in postdependent rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallupi, M.; Cannella, N.; Economidou, D.; Ubaldi, M.; Ruggeri, B.; Weiss, F.; Massi, M.; Marugan, J.; Heilig, M.; Bonnavion, P.; et al. Neuropeptide S facilitates cue-induced relapse to cocaine seeking through activation of the hypothalamic hypocretin system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisyunov, A.I. Molecular mechanisms of G protein-independent signaling mediated by 7-transmembrane receptors. Neurophysiology 2012, 44, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, D.; Masureel, M.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, A.L.; Marzola, E.; Rizzi, A.; Arduin, M.; Trapella, C.; Corti, C.; Vergura, R.; Martinelli, P.; Salvadori, S.; Regoli, D.; et al. Structure-activity studies on neuropeptide S: Identification of the amino acid residues crucial for receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinscheid, R.K.; Xu, Y.-L.; Okamura, N.; Zeng, J.; Chung, S.; Pai, R.; Wang, Z.; Civelli, O. Pharmacological Characterization of Human and Murine Neuropeptide S Receptor Variants. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Lu, B.; Ma, Q.; Wu, G.; Lai, X.; Zang, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, D.; Han, F.; Zhou, N. Human Neuropeptide S Receptor Is Activated via a Gαq Protein-biased Signaling Cascade by a Human Neuropeptide S Analog Lacking the C-terminal 10 Residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7505–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, F.; Kügler, S.; Blaesse, P.; Lange, M.D.; Skryabin, B.V.; Pape, H.C.; Jüngling, K. Neuronal expression of the human neuropeptideS receptor NPSR1 identifies NPS-induced calcium signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grund, T.; Goyon, S.; Li, Y.; Eliava, M.; Liu, H.; Charlet, A.; Grinevich, V.; Neumann, I.D. Neuropeptide S Activates Paraventricular Oxytocin Neurons to Induce Anxiolysis. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 12214–12225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncacè, V.; Polli, F.S.; Zojicic, M.; Kohlmeier, K.A. Neuropeptide S (NPS) is a neuropeptide with cellular actions in arousal and anxiety-related nuclei: Functional implications for effects of NPS on wakefulness and mood. Neuropharmacology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, S.; Bergado-Acosta, J.R.; Yanagawa, Y.; Obata, K.; Stork, O.; Munsch, T. Identification of a Neuropeptide S Responsive Circuitry Shaping Amygdala Activity via the Endopiriform Nucleus. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meis, S.; Munsch, T.; Sosulina, L.; Pape, H.C. Postsynaptic mechanisms underlying responsiveness of amygdaloid neurons to cholecystokinin are mediated by a transient receptor potential-like current. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 35, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoetxea, X.; Goedecke, L.; Remmes, J.; Blaesse, P.; Grosch, T.; Lesting, J.; Pape, H.C.; Jüngling, K. Human-specific neuropeptide S receptor variants regulate fear extinction in the basal amygdala of male and female mice depending on threat salience. Biol. Psychiatry 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, N.; Habay, S.A.; Zeng, J.; Chamberlin, A.R.; Reinscheid, R.K. Synthesis and pharmacological in vitro and in vivo profile of 3-oxo-1,1-diphenyl-tetrahydro-oxazolo[3,4-a]pyrazine-7-carboxylic acid 4-fluoro-benzylamide (SHA 68), a selective antagonist of the neuropeptide S receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, B.C.; Horowitz, L.F.; Hirdes, W.; Mackie, K.; Hille, B. Regulation of KCNQ2/KCNQ3 current by G protein cycling: The kinetics of receptor-mediated signaling by Gq. J. Gen. Physiol. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootman, M.D.; Collins, T.J.; Mackenzie, L.; Roderick, H.L.; Berridge, M.J.; Peppiatt, C.M. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) is a reliable blocker of store-operated Ca 2+ entry but an inconsistent inhibitor of InsP 3 -induced Ca 2+ release. FASEB J. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Kanaji, T.; Nakade, S.; Kanno, T.; Mikoshiba, K. 2APB, 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate, a membrane-penetrable modulator of Ins(l,4,5)P3-induced Ca2+ release. J. Biochem. 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, K.; Inada, H.; Tominaga, M. Inhibition of the transient receptor potential cation channel TRPM2 by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braas, K.M.; May, V. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptides directly stimulate sympathetic neuron neuropeptide Y release through PAC1 receptor isoform activation of specific intracellular signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27702–27710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kreutzmann, J.C.; Khalil, R.; Köhler, J.C.; Mayer, D.; Florido, A.; Nadal, R.; Andero, R.; Fendt, M. Neuropeptide-S-receptor deficiency affects sex-specific modulation of safety learning by pre-exposure to electric stimuli. Genes Brain Behav. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Iyo, M.; Shimizu, E.; Dempfle, A.; Friedel, S.; Reinscheid, R.K. Gender-specific association of a functional coding polymorphism in the Neuropeptide S receptor gene with panic disorder but not with schizophrenia or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domschke, K.; Reif, A.; Weber, H.; Richter, J.; Hohoff, C.; Ohrmann, P.; Pedersen, A.; Bauer, J.; Suslow, T.; Kugel, H.; et al. Neuropeptide S receptor gene — converging evidence for a role in panic disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.D.; Tran, H.T.; Zeng, J.; Reinscheid, R.K. Importance of extracellular loop one of the neuropeptide S receptor for biogenesis and function. Peptides 2010, 31, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarda, V.; Ruzza, C.; Rizzi, A.; Trapella, C.; Guerrini, R.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Calo, G. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of the novel neuropeptide S receptor ligands QA1 and PI1. Peptides 2013, 48, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bista, P.; Pawlowski, M.; Cerina, M.; Ehling, P.; Leist, M.; Meuth, P.; Aissaoui, A.; Borsotto, M.; Heurteaux, C.; Decher, N.; et al. Differential phospholipase C-dependent modulation of TASK and TREK two-pore domain K+ channels in rat thalamocortical relay neurons. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Talley, E.M.; Patel, N.; Gomis, A.; McIntire, W.E.; Dong, B.; Viana, F.; Garrison, J.C.; Bayliss, D.A. Inhibition of a background potassium channel by Gq protein α-subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3422–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, H.-C.; Jüngling, K.; Seidenbecher, T.; Lesting, J.; Reinscheid, R.K. Neuropeptide S: A transmitter system in the brain regulating fear and anxiety. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, L.F.; Hirdes, W.; Suh, B.C.; Hilgemann, D.W.; Mackie, K.; Hille, B. Phospholipase C in living cells: Activation, inhibition, Ca2+ requirement, and regulation of M current. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005, 126, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.C.; Hechenberger, M.; Weinreich, F.; Kubisch, C.; Jentsch, T.J. KCNQ5, a Novel Potassium Channel Broadly Expressed in Brain, Mediates M-type Currents. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24089–24095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransén, E.; Tigerholm, J. Role of A-type potassium currents in excitability, network synchronicity, and epilepsy. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, D.; Bedoya, M.; Kiper, A.K.; Rinné, S.; Morales-Navarro, S.; Hernández-Rodríguez, E.W.; Sepúlveda, F.V.; Decher, N.; González, W. Structure/activity analysis of task-3 channel antagonists based on a 5,6,7,8 tetrahydropyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selyanko, A.A.; Brown, D.A. Intracellular calcium directly inhibits potassium M channels in excised membrane patches from rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron 1996, 16, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, N.; Zhang, J.S.; Omaki, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Wanaverbecq, N.; Langeberg, L.K.; Yoneda, Y.; Scott, J.D.; Brown, D.A.; et al. AKAP150 signaling complex promotes suppression of the M-current by muscarinic agonists. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altier, C. GPCR and voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC) signaling complexes. Subcell. Biochem. 2012, 63, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zamponi, G.W. Regulation of voltage gated calcium channels by GPCRs and post-translational modification. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, G.E.; Drewe, J.A. Gating-dependent mechanism of 4-aminopyridine block in two related potassium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Ramírez, M.; De Jesús-Pérez, J.J.; Aréchiga-Figueroa, I.A.; Arreola, J.; Adney, S.K.; Villalba-Galea, C.A.; Logothetis, D.E.; Rodríguez-Menchaca, A.A. Regulation of Kv2.1 channel inactivation by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Pignatelli, M.; Xu, S.; Itohara, S.; Tonegawa, S. Antagonistic negative and positive neurons of the basolateral amygdala. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kim, J.; Tonegawa, S. Amygdala Reward Neurons Form and Store Fear Extinction Memory. bioRxiv 2019, 615096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinscheid, R.K.; Mafessoni, F.; Lüttjohann, A.; Jüngling, K.; Pape, H.C.; Schulz, S. Neandertal introgression and accumulation of hypomorphic mutations in the neuropeptide S (NPS) system promote attenuated functionality. Peptides 2021, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasan, R.O.; Verma, D.; Wood, J.; Lach, G.; Hörmer, B.; de Lima, T.C.M.; Herzog, H.; Sperk, G. The role of Neuropeptide Y in fear conditioning and extinction. Neuropeptides 2016, 55, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, J.C.; Jamil, S.; Remmes, J.; Verma, D.; Pape, H.C. Functional deletion of neuropeptide Y receptors type 2 in local synaptic networks of anteroventral BNST facilitates recall and increases return of fear. Mol. Psychiatry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomrenze, M.B.; Giovanetti, S.M.; Maiya, R.; Gordon, A.G.; Kreeger, L.J.; Messing, R.O. Dissecting the Roles of GABA and Neuropeptides from Rat Central Amygdala CRF Neurons in Anxiety and Fear Learning. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 13–21.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, C.A.; Soden, M.E.; Baird, M.A.; Miller, S.M.; Schulkin, J.; Palmiter, R.D.; Clark, M.; Zweifel, L.S. A Central Amygdala CRF Circuit Facilitates Learning about Weak Threats. Neuron 2017, 93, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, F.; Bieler, L.; Nowack, L.M.F.; Leitner, J.; Brunner, S.M.; Zaunmair, P.; Kofler, B.; Couillard-Despres, S. Involvement of Neuropeptide Galanin Receptors 2 and 3 in Learning, Memory and Anxiety in Aging Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, S.M.; Farzi, A.; Locker, F.; Holub, B.S.; Drexel, M.; Reichmann, F.; Lang, A.A.; Mayr, J.A.; Vilches, J.J.; Navarro, X.; et al. GAL3 receptor KO mice exhibit an anxietylike phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7138–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, M.E.; Choi, D.C.; Ressler, K.J. Neuropeptide regulation of fear and anxiety: Implications of cholecystokinin, endogenous opioids, and neuropeptide Y. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressler, K.J.; Mercer, K.B.; Bradley, B.; Jovanovic, T.; Mahan, A.; Kerley, K.; Norrholm, S.D.; Kilaru, V.; Smith, A.K.; Myers, A.J.; et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder is associated with PACAP and the PAC1 receptor. Nature 2011, 470, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustrude, E.T.; Caliman, I.F.; Bernabe, C.S.; Fitz, S.D.; Grafe, L.A.; Bhatnagar, S.; Bonaventure, P.; Johnson, P.L.; Molosh, A.I.; Shekhar, A. Orexin Depolarizes Central Amygdala Neurons via Orexin Receptor 1, Phospholipase C and Sodium-Calcium Exchanger and Modulates Conditioned Fear. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Flüthmann, P.; Wolany, C.; Goedecke, L.; Spenner, H.M.; Budde, T.; Pape, H.-C.; Jüngling, K. Neuropeptide S Receptor Stimulation Excites Principal Neurons in Murine Basolateral Amygdala through a Calcium-Dependent Decrease in Membrane Potassium Conductance. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060519
Park S, Flüthmann P, Wolany C, Goedecke L, Spenner HM, Budde T, Pape H-C, Jüngling K. Neuropeptide S Receptor Stimulation Excites Principal Neurons in Murine Basolateral Amygdala through a Calcium-Dependent Decrease in Membrane Potassium Conductance. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(6):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060519
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sion, Pia Flüthmann, Carla Wolany, Lena Goedecke, Hannah Maleen Spenner, Thomas Budde, Hans-Christian Pape, and Kay Jüngling. 2021. "Neuropeptide S Receptor Stimulation Excites Principal Neurons in Murine Basolateral Amygdala through a Calcium-Dependent Decrease in Membrane Potassium Conductance" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 6: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060519
APA StylePark, S., Flüthmann, P., Wolany, C., Goedecke, L., Spenner, H. M., Budde, T., Pape, H.-C., & Jüngling, K. (2021). Neuropeptide S Receptor Stimulation Excites Principal Neurons in Murine Basolateral Amygdala through a Calcium-Dependent Decrease in Membrane Potassium Conductance. Pharmaceuticals, 14(6), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060519





