Utility of suPAR and NGAL for AKI Risk Stratification and Early Optimization of Renal Risk Medications among Older Patients in the Emergency Department
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics and Incidence of AKI
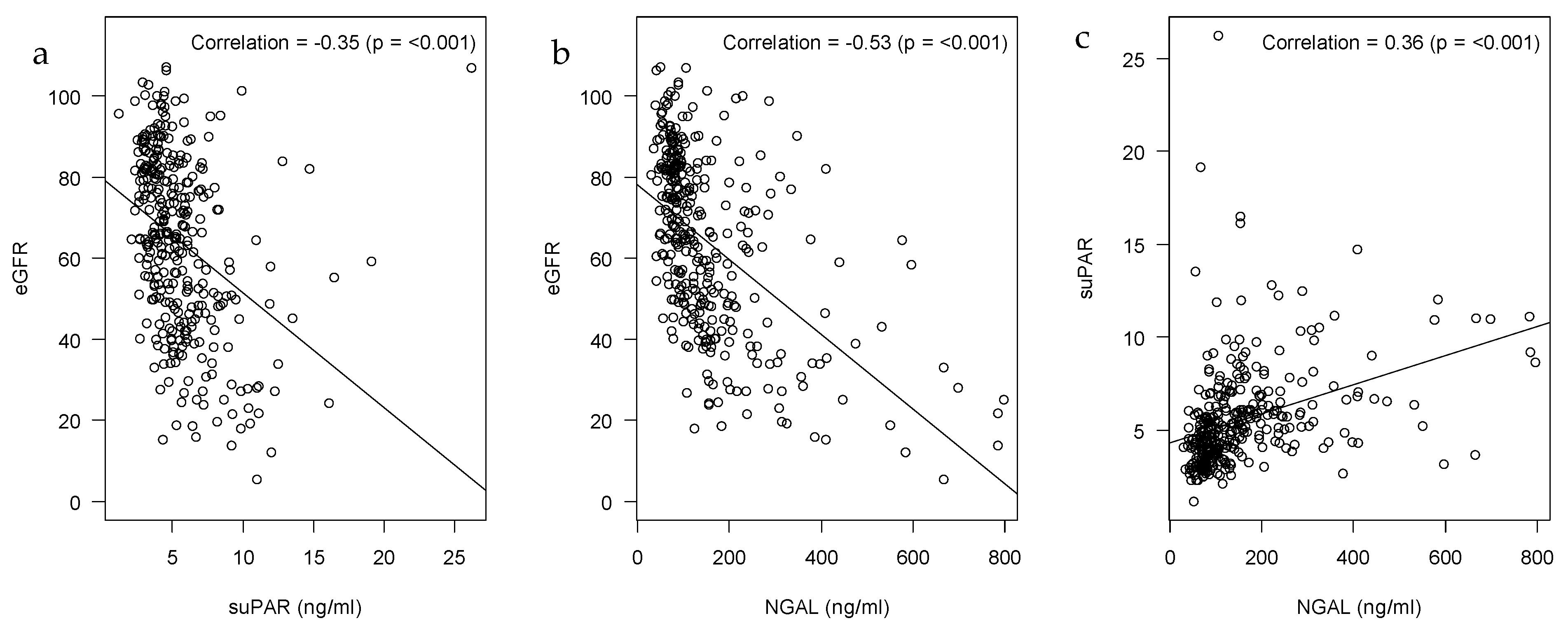
2.2. Correlations of suPAR, NGAL and eGFR
2.3. SuPAR and NGAL Levels in Patients Developing AKI
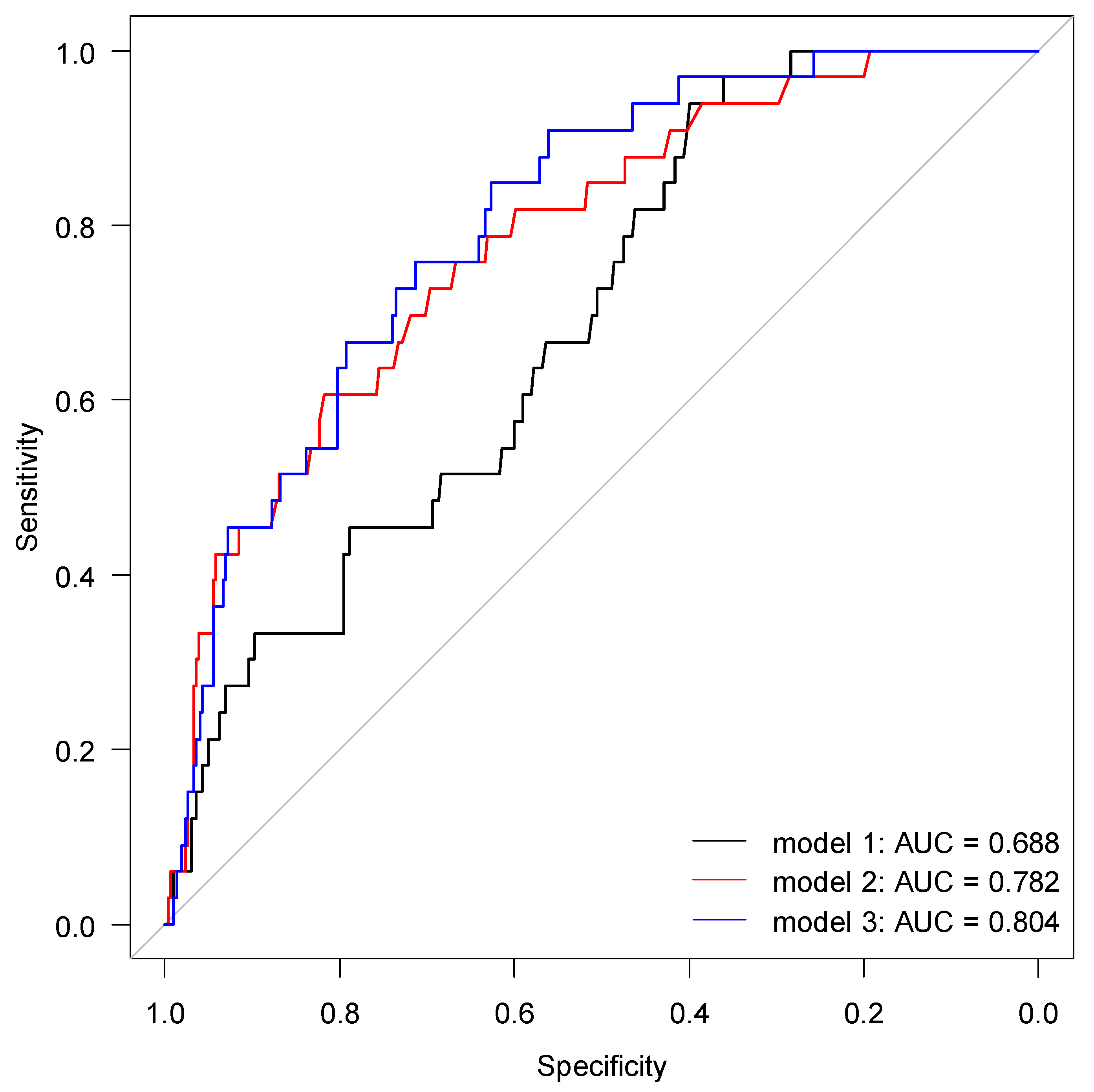
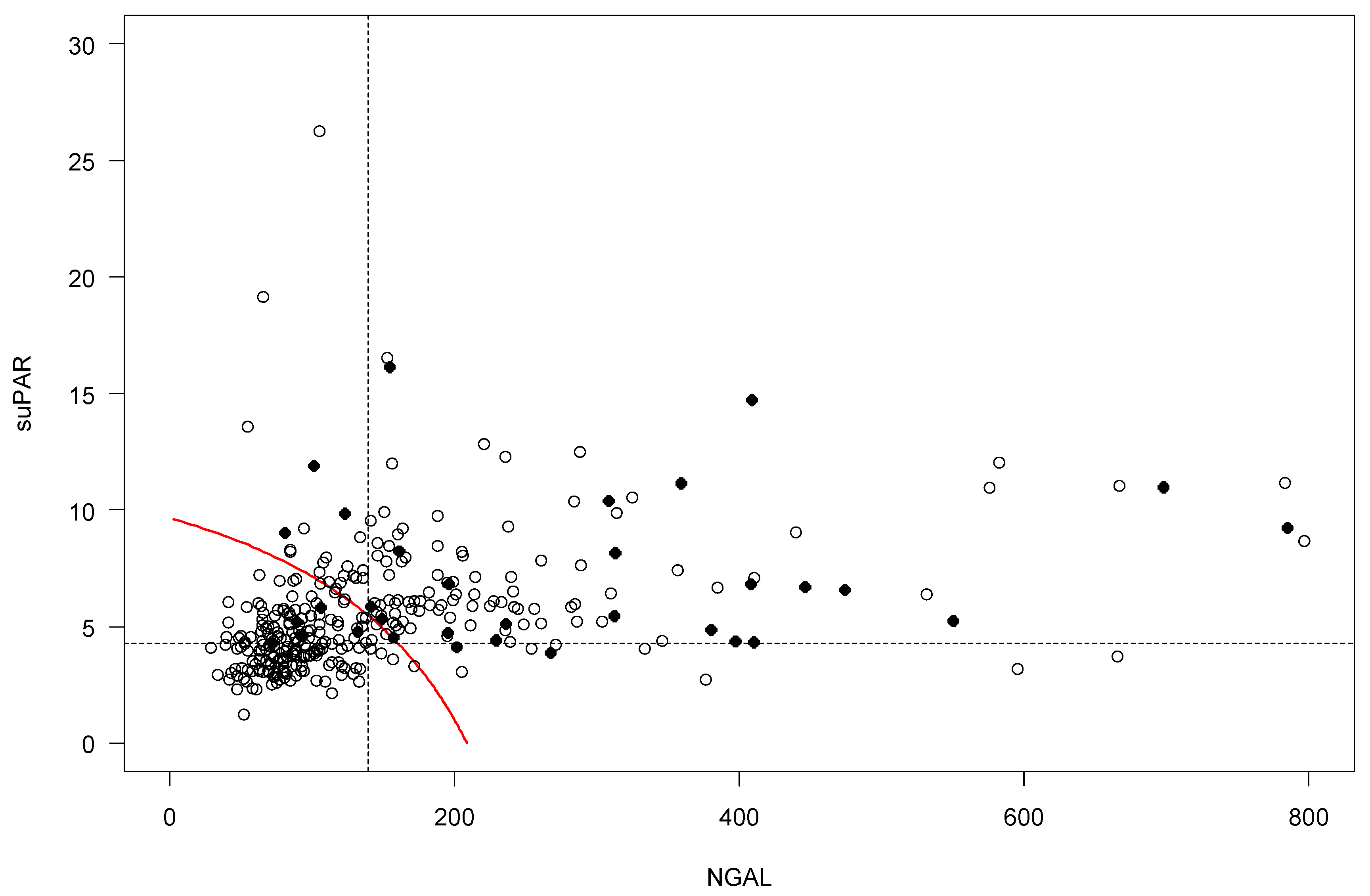
2.4. Risk Prediction for AKI by suPAR and NGAL
2.5. Renal Risk Medications in Patients Developing AKI
3. Discussion
3.1. Main Findings
3.2. AKI in Older Acutely Hospitalized Patients
3.3. Plasma suPAR and NGAL
3.4. Optimization of Medication Prescribing
3.5. Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Setting
4.2. Design and Participants
4.3. Ethical Statement
4.4. Patient Demographic, Length of Stay and Mortality
4.5. Timepoints for Measuring Biomarkers and Calculation of Baseline Plasma Creatinine
4.6. Determination of Biomarkers
4.7. Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate
4.8. Medication
4.9. Outcomes
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Ageing and Health. 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Christensen, K.; Doblhammer, G.; Rau, R.; Vaupel, J.W. Ageing Populations: The Challenges Ahead. Lancet 2009, 374, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health. Styrket Indsats for Den Ældre Medicisnke Patienter—National Handlingsplan. Available online: https://www.sum.dk/~/media/Filer%20-%20Publikationer_i_pdf/2016/Styrket-indsats-for-den-aeldre-medicinske-patient/National_Handlingsplan.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2020). (In Danish).
- Statistics Denmark. StatBank Denmark. Available online: https://www.statistikbanken.dk/IND01 (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Foxwell, D.A.; Pradhan, S.; Zouwail, S.; Rainer, T.H.; Phillips, A.O. Epidemiology of Emergency Department Acute Kidney Injury. Nephrololy 2020, 25, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonnacott, A.; Meran, S.; Amphlett, B.; Talabani, B.; Phillips, A. Epidemiology and Outcomes in Community-Acquired versus Hospital-Acquired AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Nie, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, G.; Zha, Y.; Qian, J.; Liu, B.; Han, S.; Xu, A.; et al. Epidemiology and Clinical Correlates of AKI in Chinese Hospitalized Adults. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, C.J.; Juurlink, I.; Bisset, L.H.; Bavakunji, R.; Mehta, R.L.; Devonald, M.A.J. A Real-Time Electronic Alert to Improve Detection of Acute Kidney Injury in a Large Teaching Hospital. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coca, S.G. Acute Kidney Injury in Elderly Persons. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartin-Ceba, R.; Kashiouris, M.; Plataki, M.; Kor, D.J.; Gajic, O.; Casey, E.T. Risk Factors for Development of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 691013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsittisak, W.; Phonsawang, K.; Jaturapisanukul, S.; Prommool, S.; Kurathong, S. Acute Kidney Injury Outcomes of Elderly and Nonelderly Patients in the Medical Intensive Care Unit of a University Hospital in a Developing Country. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 2391683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, L.G.; Sampaio, B.M.; Rocha, E.P.; Balbi, A.L.; Sousa Prado, I.R.; Ponce, D. Acute Kidney Injury in Elderly Patients: Narrative Review on Incidence, Risk Factors, and Mortality. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2018, 11, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlind, M.B.; Andersen, A.L.; Treldal, C.; Jørgensen, L.M.; Kannegaard, P.N.; Castillo, L.S.; Christensen, L.D.; Tavenier, J.; Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Ankarfeldt, M.Z.; et al. A Collaborative Medication Review Including Deprescribing for Older Patients in an Emergency Department: A Longitudinal Feasibility Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.D.; Reilev, M.; Juul-Larsen, H.G.; Jørgensen, L.M.; Kaae, S.; Andersen, O.; Pottegård, A.; Petersen, J. Use of Prescription Drugs in the Older Adult Population—A Nationwide Pharmacoepidemiological Study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehling, M. (Ed.) Drug Therapy for the Elderly; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2013; ISBN 978-3-7091-0911-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmann, S.; Helms, J.; Joret, A.; Martin-Lefevre, L.; Quenot, J.-P.; Herbrecht, J.-E.; Benzekri-Lefevre, D.; Robert, R.; Desachy, A.; Bellec, F.; et al. Nephrotoxic Drug Burden among 1001 Critically Ill Patients: Impact on Acute Kidney Injury. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, E.L.; Kane-Gill, S.L.; Fuhrman, D.Y.; Kellum, J.A. Drug-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: Who’s at Risk? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miano, T.A.; Shashaty, M.G.S.; Yang, W.; Brown, J.R.; Zuppa, A.; Hennessy, S. Effect of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors on the Comparative Nephrotoxicity of NSAIDs and Opioids during Hospitalization. Kidney360 2020, 1, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, G.N.C.; Leitão, A.C.C.; Alencar, R.L.; Xavier, R.M.F.; Daher, E.D.F.; da Silva, G.B. Pathophysiological Aspects of Nephropathy Caused by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. J. Nephrol. 2019, 41, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury: What’s the Prognosis? Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollitt, J.; Bennett, N.; Darby, D.; Flanagan, E.; Chadwick, P.; Sinha, S.; Kalra, P.A.; Ritchie, J.; Poulikakos, D. The Importance of Acute Kidney Injury in Suspected Community Acquired Infection. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostermann, M.; Joannidis, M. Acute Kidney Injury 2016: Diagnosis and Diagnostic Workup. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, N.I.; Trzeciak, S.; Hollander, J.E.; Birkhahn, R.; Otero, R.; Osborn, T.M.; Moretti, E.; Nguyen, H.B.; Gunnerson, K.; Milzman, D.; et al. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Plasma Neutrophil Gelatinase—Associated Lipocalin in the Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury in Emergency Department Patients with Suspected Sepsis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2010, 56, 52–59.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelow, M.W.; Dall, A.; Regner, K.; Weinberg, C.; Bartz, P.J.; Sowinski, J.; Rudd, N.; Katzmark, L.; Tweddell, J.S.; Earing, M.G. Urinary Interleukin-18 and Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Predict Acute Kidney Injury Following Pulmonary Valve Replacement Prior to Serum Creatinine. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2012, 7, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, E.; Houlind, M.B.; Kallemose, T.; Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Hornum, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Hayek, S.S.; Andersen, O.; Eugen-Olsen, J. Elevated SuPAR Is an Independent Risk Marker for Incident Kidney Disease in Acute Medical Patients. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, E.; Houlind, M.B.; Eugen-Olsen, J. Soluble Urokinase Receptor and Acute Kidney Injury—Letter to the editor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2166–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayek, S.S.; Leaf, D.E.; Samman Tahhan, A.; Raad, M.; Sharma, S.; Waikar, S.S.; Sever, S.; Camacho, A.; Wang, X.; Dande, R.R.; et al. Soluble Urokinase Receptor and Acute Kidney Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, T.U.; Shadid, H.R.; Blakely, P.; O’Hayer, P.; Berlin, H.; Pan, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhao, L.; Pennathur, S.; Pop-Busui, R.; et al. Soluble Urokinase Receptor (SuPAR) in COVID-19-Related AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossanen, J.C.; Pracht, J.; Jansen, T.U.; Buendgens, L.; Stoppe, C.; Goetzenich, A.; Struck, J.; Autschbach, R.; Marx, G.; Tacke, F. Elevated Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor and Proenkephalin Serum Levels Predict the Development of Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiac Surgery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; El Hindi, S.; Li, J.; Fornoni, A.; Goes, N.; Sageshima, J.; Maiguel, D.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Yap, H.-K.; Saleem, M.; et al. Circulating Urokinase Receptor as a Cause of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, S.S.; Koh, K.H.; Grams, M.E.; Wei, C.; Ko, Y.-A.; Li, J.; Samelko, B.; Lee, H.; Dande, R.R.; Lee, H.W.; et al. A Tripartite Complex of SuPAR, APOL1 Risk Variants and Avβ3 Integrin on Podocytes Mediates Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, K.; Papoila, A.L.; Coelho, S.; Bennett, M.; Ma, Q.; Rodrigues, B.; Fidalgo, P.; Frade, F.; Devarajan, P. Plasma NGAL for the Diagnosis of AKI in Patients Admitted from the Emergency Department Setting. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickolas, T.L.; O’Rourke, M.J.; Yang, J.; Sise, M.E.; Canetta, P.A.; Barasch, N.; Buchen, C.; Khan, F.; Mori, K.; Giglio, J.; et al. Sensitivity and Specificity of a Single Emergency Department Measurement of Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Diagnosing Acute Kidney Injury. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.; Zapf, A.; Haase, M.; Röver, C.; Pickering, J.W.; Albert, A.; Bellomo, R.; Breidthardt, T.; Camou, F.; Chen, Z.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Measured on Clinical Laboratory Platforms for the Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury and the Associated Need for Dialysis Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 826–841.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mårtensson, J.; Bellomo, R. The Rise and Fall of NGAL in Acute Kidney Injury. Blood Purif. 2014, 37, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Ma, Q.; Prada, A.; Mitsnefes, M.; Zahedi, K.; Yang, J.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Identification of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Novel Early Urinary Biomarker for Ischemic Renal Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Mori, K.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin: A Novel Early Urinary Biomarker for Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C. N-GAL: Diagnosing AKI as Soon as Possible. Crit. Care 2007, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.B.; Sapra, A. Nephrotoxic Medications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, S.R.; Nielsen, R.V.; Møgelvang, R.; Ostrowski, S.R.; Ravn, H.B. Prognostic Value of SuPAR and HsCRP on Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiac Surgery. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Somma, S.; Magrini, L.; De Berardinis, B.; Marino, R.; Ferri, E.; Moscatelli, P.; Ballarino, P.; Carpinteri, G.; Noto, P.; Gliozzo, B.; et al. Additive Value of Blood Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin to Clinical Judgement in Acute Kidney Injury Diagnosis and Mortality Prediction in Patients Hospitalized from the Emergency Department. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodilsen, A.C.; Klausen, H.H.; Petersen, J.; Beyer, N.; Andersen, O.; Jørgensen, L.M.; Juul-Larsen, H.G.; Bandholm, T. Prediction of Mobility Limitations after Hospitalization in Older Medical Patients by Simple Measures of Physical Performance Obtained at Admission to the Emergency Department. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, H.H.; Bodilsen, A.C.; Petersen, J.; Bandholm, T.; Haupt, T.; Sivertsen, D.M.; Andersen, O. How Inflammation Underlies Physical and Organ Function in Acutely Admitted Older Medical Patients. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 164, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul-Larsen, H.G.; Christensen, L.D.; Andersen, O.; Bandholm, T.; Kaae, S.; Petersen, J. Development of the “Chronic Condition Measurement Guide”: A New Tool to Measure Chronic Conditions in Older People Based on ICD-10 and ATC-Codes. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 10, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, E.; Bodilsen, A.C.; Klausen, H.H.; Treldal, C.; Andersen, O.; Houlind, M.B.; Petersen, J. Kidney Function Estimates Using Cystatin C versus Creatinine: Impact on Medication Prescribing in Acutely Hospitalized Elderly Patients. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, H.H.; Petersen, J.; Bandholm, T.; Juul-Larsen, H.G.; Tavenier, J.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Andersen, O. Association between Routine Laboratory Tests and Long-Term Mortality among Acutely Admitted Older Medical Patients: A Cohort Study. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, A.L.; Henriksen, D.P.; Marinakis, C.; Hellebek, A.; Birn, H.; Nybo, M.; Søndergaard, J.; Nymark, A.; Pedersen, C. Drug Dosing in Patients with Renal Insufficiency in a Hospital Setting Using Electronic Prescribing and Automated Reporting of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harty, J. Prevention and Management of Acute Kidney Injury. Ulst. Med. J. 2014, 83, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. PROC: An Open-Source Package for R and S+ to Analyze and Compare ROC Curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve in Diagnostic Test Assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
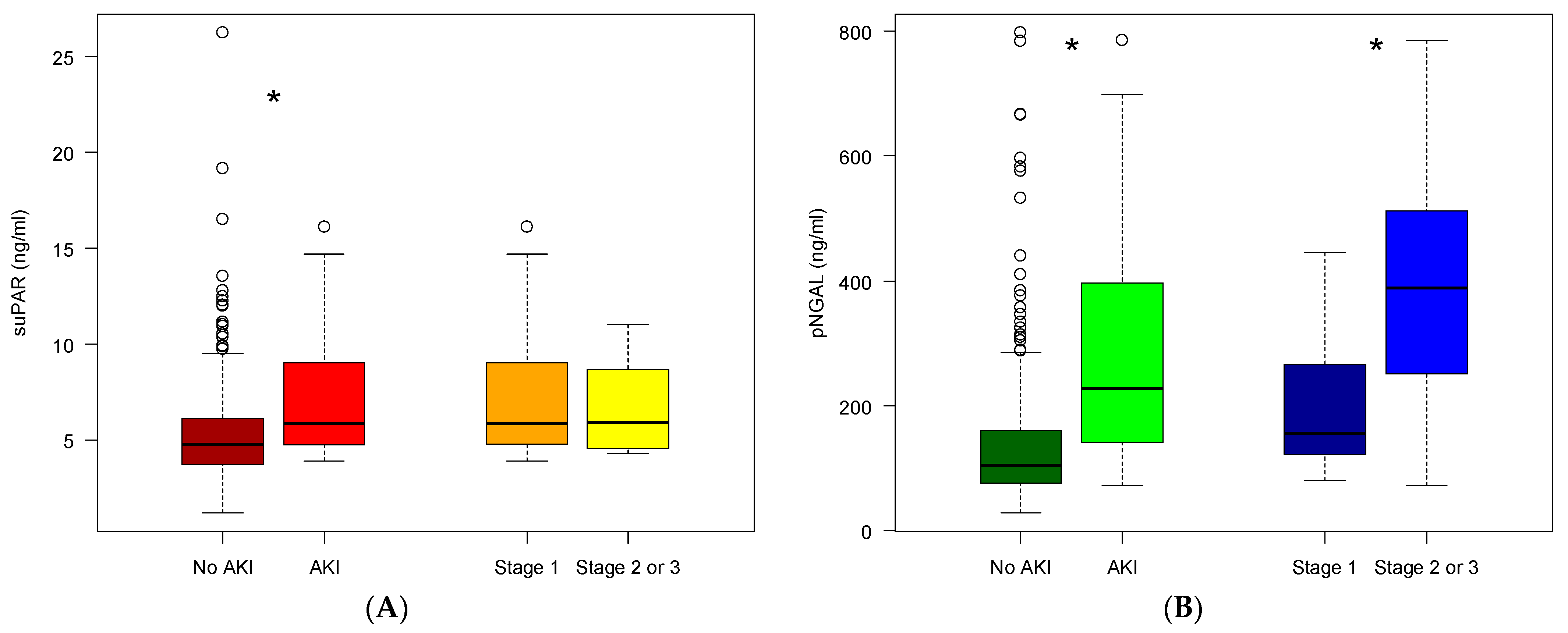
| Variable | All Patients | Patients with AKI | Patients without AKI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Value | N | Value | N | Value | |
| Demographics | ||||||
| Age years, median (IQR) | 339 | 77.6 (70.6; 84.4) | 33 | 75.9 (72.3; 83.0) | 306 | 77.9 (70.5; 84.5) |
| Female, n (%) | - | 212 (62.5) | - | 25 (75.8) | - | 187 (61.1) |
| Body-mass index, median (IQR) | 304 | 25.1 (22.3; 28.8) | 26 | 24.8 (20.7; 28.9) | 278 | 25.1 (22.5; 28.8) |
| Hospitalization-days, median (IQR) | 339 | 2 (1; 6) | 33 | 7 (4; 13) | 306 | 2 (1; 5) |
| 30-day morality, n (%) | 339 | 12 (3.5) | 33 | 3 (9.1) | 306 | 9 (2.9) |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Cardiovascular disease (%) | - | 113 (33.3) | - | 12 (36.4) | - | 101 (33.0) |
| Diabetes (%) | - | 57 (16.8) | - | 5 (15.2) | - | 52 (17.0) |
| Medication | ||||||
| Total number of medications, median (IQR) | 339 | 6 (3; 9) | 33 | 8 (4; 12) | 306 | 6 (3; 9) |
| Biomarkers * | ||||||
| Creatinine µmol/L, median (IQR) | 339 | 84.3 (66.2; 105.4) | 33 | 120.8 (91.1; 169.5) | 306 | 83.0 (65.4; 100.2) |
| Cystatin C mg/L, median (IQR) | 339 | 1.21 (0.95; 1.60) | 1.69 (1.26–2.56) | 306 | 1.17 (0.94; 1.56) | |
| eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2, median (IQR) | 339 | 65.6 (48.2; 81.9) | 33 | 39.1 (26.7; 59.2) | 306 | 67.4 (50.7; 82.3) |
| CRP-µg/mL, median (IQR) | 314 | 15.5 (3.0; 63.7) | 33 | 67.0 (22.3; 120.3) | 281 | 14.0 (3.0; 53.4) |
| IL6-pg/mL, median (IQR) | 336 | 4.6 (1.9; 13.3) | 33 | 9.8 (3.6; 30.4) | 303 | 4.3 (1.8; 11.1) |
| TNF-α–pg/mL, median (IQR) | 336 | 7.4 (5.1; 107) | 33 | 10.1 (6.7; 14.9) | 303 | 7.3 (4.9; 10.5) |
| FI-OutRef, median (IQR) | 314 | 5 (3; 7) | 33 | 7 (6; 8) | 282 | 5 (3; 7) |
| Change in creatinine and eGFR ** | ||||||
| Δcreatinine inclusion to discharge | 339 | −1.0 (−9.0:7.0) | 33 | −33.0 (−57.0:−13.0) | 306 | 0.0 (−7.0:7.0) |
| ΔeGFR inclusion to discharge | 339 | 1.0 (−4.1:7.1) | 33 | 20.4 (4.4:32.2) | 306 | 0.0 (−4.7:4.9) |
| Cutoff | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC (CI 95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| suPAR (ng/mL) | 4.26 | 0.94 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.98 | 0.69 (0.60–0.77) |
| NGAL (ng/mL) | 139.5 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.20 | 0.96 | 0.78 (0.70–0.87) |
| Two-variable interaction | - | 0.82 | 0.73 | 0.25 | 0.97 | 0.82 (0.73–0.90) |
| AKI (n = 33) (%) | |
|---|---|
| Opioids | 13 (39.4) |
| NSAIDs | 4 (12.1) |
| Metformin | 4 (12.1) |
| ACEIs/ARBs | 10 (30.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walls, A.B.; Bengaard, A.K.; Iversen, E.; Nguyen, C.N.; Kallemose, T.; Juul-Larsen, H.G.; Jawad, B.N.; Hornum, M.; Andersen, O.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; et al. Utility of suPAR and NGAL for AKI Risk Stratification and Early Optimization of Renal Risk Medications among Older Patients in the Emergency Department. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090843
Walls AB, Bengaard AK, Iversen E, Nguyen CN, Kallemose T, Juul-Larsen HG, Jawad BN, Hornum M, Andersen O, Eugen-Olsen J, et al. Utility of suPAR and NGAL for AKI Risk Stratification and Early Optimization of Renal Risk Medications among Older Patients in the Emergency Department. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(9):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090843
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalls, Anne Byriel, Anne Kathrine Bengaard, Esben Iversen, Camilla Ngoc Nguyen, Thomas Kallemose, Helle Gybel Juul-Larsen, Baker Nawfal Jawad, Mads Hornum, Ove Andersen, Jesper Eugen-Olsen, and et al. 2021. "Utility of suPAR and NGAL for AKI Risk Stratification and Early Optimization of Renal Risk Medications among Older Patients in the Emergency Department" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 9: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090843
APA StyleWalls, A. B., Bengaard, A. K., Iversen, E., Nguyen, C. N., Kallemose, T., Juul-Larsen, H. G., Jawad, B. N., Hornum, M., Andersen, O., Eugen-Olsen, J., & Houlind, M. B. (2021). Utility of suPAR and NGAL for AKI Risk Stratification and Early Optimization of Renal Risk Medications among Older Patients in the Emergency Department. Pharmaceuticals, 14(9), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090843






