Baicalein Inhibits Metastatic Phenotypes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via a Focal Adhesion Protein Integrin β8
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baicalein Exerts Its Cytotoxicity and Growth Inhibition on NPC Cell Lines
2.2. Baicalein Suppresses Cell Migration, Invasion, and Adhesion In Vitro
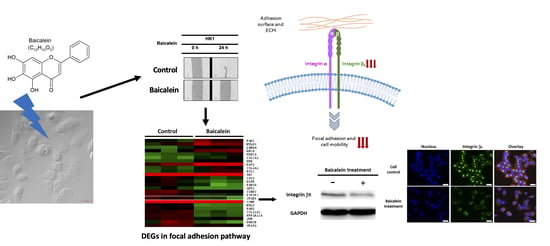
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis of NPC Cells after Baicalein Treatment Reveals the Suppression of Integrin β8 in a Focal Adhesion Pathway
2.4. Integrin β8 Is Suppressed after Baicalein Treatment
3. Discussion

4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Cell Line Maintenance
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. Cell Migration by Wound-Healing Assay
4.4. Cell Invasion Assay
4.5. Cell Adhesion Assay
4.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
4.7. Microarray Hybridization
4.8. Data Processing and Analysis
4.9. Immunofluorescence
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COSMIC | Catalog of somatic mutations in cancer |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| EBV | Epstein-Barr virus |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| ICGC | International Cancer Genome Consortium |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| PPI | Protein-protein interaction |
| SEM | Stand error of mean |
| TRITC | Tetramethylrhodamine-isothiocyanate |
| TPA | 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate |
References
- Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.-O. The Enigmatic Epidemiology of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, P.; Deka, H.; Malakar, A.K.; Halder, B.; Chakraborty, S. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Understanding its molecular biology at a fine scale. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.L.; Chen, W.Q.; Xue, W.Q.; He, Y.Q.; Zheng, R.S.; Zeng, Y.X.; Jia, W.H. Global trends in incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buell, P. The Effect of Migration on the Risk of Nasopharyngeal Cancer among Chinese. Cancer Res. 1974, 34, 1189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richardo, T.; Prattapong, P.; Ngernsombat, C.; Wisetyaningsih, N.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Janvilisri, T. Epstein-Barr Virus Mediated Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.-H.; Xiong, D.; Xu, Y.-F.; Cao, S.-M.; Xue, W.-Q.; Qin, H.-D.; Liu, W.-S.; Cao, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Q.-S.; et al. An Epidemiological and Molecular Study of the Relationship Between Smoking, Risk of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, and Epstein–Barr Virus Activation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1396–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, M.H.; Pan, W.-H.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Li, F.-H.; Brinton, L.A.; Chen, C.-J.; Hsu, M.-M.; Chen, I.H.; Levine, P.H.; Yang, C.-S.; et al. Dietary exposure to nitrite and nitrosamines and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwan. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Chou, S.-P.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chang, Y.; Takada, K.; Chen, J.-Y. The synergistic effect of chemical carcinogens enhances Epstein-Barr Virus reactivation and tumor progression of Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.S.C.; To, K.F.; Lo, K.W.; Mak, K.F.; Pak, W.; Chiu, B.; Tse, G.M.K.; Ding, M.; Li, X.; Lee, J.C.K.; et al. High frequency of chromosome 3p deletion in histologically normal nasopharyngeal epithelia from southern Chinese. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5365. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.S.C.; To, K.F.; Lo, K.W.; Ding, M.; Li, X.; Johnson, P.; Huang, D.P. Frequent chromosome 9p losses in histologically normal nasopharyngeal epithelia from southern Chinese. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 102, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, B. Anti-cancer natural products and their bioactive compounds inducing ER stress-mediated apoptosis: A review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, D.; Zhang, B.; Meng, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Shen, J. Novel synthetic baicalein derivatives caused apoptosis and activated AMP-activated protein kinase in human tumor cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 7287–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Singh, D.; Tali, J.A.; Dheer, D.; Shankar, R. Andrographolide: Chemical modification and its effect on biological activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 95, 103511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Lo, C.-Y.; Feng, J.-Z.; Lin, H.-J.; Chang, P.-Y.; Yang, L.-L.; Chen, L.-G.; Liu, Y.-W.; Kuo, C.-D. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 7-O-lipophilic substituted baicalein derivatives as potential anticancer agents. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, C.; Li, Z. Baicalein: A review of its anti-cancer effects and mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johari, J.; Kianmehr, A.; Mustafa, M.R.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Antiviral activity of baicalein and quercetin against the Japanese encephalitis virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16785–16795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.C.; Ip, M.; Lau, C.B.; Lui, S.L.; Jolivalt, C.; Ganem-Elbaz, C.; Litaudon, M.; Reiner, N.E.; Gong, H.; See, R.H.; et al. Synergistic effects of baicalein with ciprofloxacin against NorA over-expressed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and inhibition of MRSA pyruvate kinase. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Tsang, S.-Y.; Yao, X.; Chen, Z.-Y. Biological properties of baicalein in cardiovascular system. Curr. Drug Targets Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. 2005, 5, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, R.; Xu, B. Antidiabetic properties of dietary flavonoids: A cellular mechanism review. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandrashekar, N.; Selvamani, A.; Subramanian, R.; Pandi, A.; Thiruvengadam, D. Baicalein inhibits pulmonary carcinogenesis-associated inflammation and interferes with COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in-vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 261, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hou, R.; Gao, S.; Song, D.; Feng, Y. Baicalein inhibits proliferation activity of human colorectal cancer cells HCT116 through downregulation of Ezrin. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; You, H.; Li, D. Baicalein exerts anticancer effect in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Choi, H.S.; Seo, E.K.; Kang, D.H.; Oh, E.S. Baicalin and baicalein inhibit transforming growth factor-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Hu, X.; Xing, Z.; Xing, R.; Lv, R.; Cheng, X.; Su, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Nilsson, S.; et al. Baicalein inhibits prostate cancer cell growth and metastasis via the caveolin-1/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 406, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Long, C.; Guo, W.; Sun, X. Baicalein inhibits growth of Epstein-Barr virus-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing the activity of EBNA1 Q-promoter. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Chen, M.C.; Pham, H.; Angst, E.; King, J.C.; Park, J.; Brovman, E.Y.; Ishiguro, H.; Harris, D.M.; Reber, H.A.; et al. Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis by Mcl-1 down-regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, G.; Zheng, D.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Song, Q.; Sun, X.; Tao, C.; Hu, Q.; Gao, T.; et al. Baicalein inhibits progression of osteosarcoma cells through inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86098–86116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, E.-S.; Seiki, M.; Gotte, M.; Chung, J. Cell adhesion in cancer. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 965618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.-B.; Xu, C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Vermorken, J.B.; O’Sullivan, B.; Ma, J. Advances in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Wang, F.-X.; Jia, K.-K.; Kong, L.-D. Natural product interventions for chemotherapy and radiotherapy-induced side effects. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Lu, P.; Guo, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Meng, X.-Y. Baicalein induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through modulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Yan, W.; Dai, Z.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S. Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.-T.; He, M.; Yu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Tai, S.; Teng, C.-B. Baicalein inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion via suppression of NEDD9 expression and its downstream Akt and ERK signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Xin, S.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H. Baicalein inhibits MMP-2 expression in human ovarian cancer cells by suppressing the p38 MAPK-dependent NF-κB signaling pathway. Anticancer. Drugs 2015, 26, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; An, P.; Ren, H.; Liang, R.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. Baicalein inhibits the invasion and metastatic capabilities of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via down-regulation of the ERK pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.-L.; Feng, F.; You, Q.-D.; Lu, N.; Guo, Q.-L. Flavonoid baicalein suppresses adhesion, migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 297, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Baicalein suppresses 17-β-estradiol-induced migration, adhesion and invasion of breast cancer cells via the G protein-coupled receptor 30 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.-W.; Lin, T.-H.; Huang, W.-S.; Teng, C.-Y.; Liou, Y.-S.; Kuo, W.-H.; Lin, W.-L.; Huang, H.-I.; Tung, J.-N.; Huang, C.-Y.; et al. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasive properties of human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 255, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathcart, M.-C.; Useckaite, Z.; Drakeford, C.; Semik, V.; Lysaght, J.; Gately, K.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Pidgeon, G.P. Anti-cancer effects of baicalein in non-small cell lung cancer in-vitro and in-vivo. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, E.-O.; Cho, E.-J.; Jeong, J.-W.; Park, C.; Hong, S.-H.; Hwang, H.-J.; Moon, S.-K.; Son, C.G.; Kim, W.-J.; Choi, Y.H. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasion of B16F10 mouse melanoma cells through inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, K. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of the AKT signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, C.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, B. Coexisting EGFR and TP53 mutations in lung adenocarcinoma patients are associated with COMP and ITGB8 upregulation and poor prognosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mertens-Walker, I.; Fernandini, B.C.; Maharaj, M.S.N.; Rockstroh, A.; Nelson, C.C.; Herington, A.C.; Stephenson, S.-A. The tumour-promoting receptor tyrosine kinase, EphB4, regulates expression of Integrin-β8 in prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reyes, S.B.; Narayanan, A.S.; Lee, H.S.; Tchaicha, J.H.; Aldape, K.D.; Lang, F.F.; Tolias, K.F.; McCarty, J.H. αvβ8 integrin interacts with RhoGDI1 to regulate Rac1 and Cdc42 activation and drive glioblastoma cell invasion. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landemaine, T.; Jackson, A.; Bellahcène, A.; Rucci, N.; Sin, S.; Abad, B.M.; Sierra, A.; Boudinet, A.; Guinebretière, J.-M.; Ricevuto, E.; et al. A six-gene signature predicting breast cancer lung metastasis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, R. Alteration in metastasis potential and gene expression in human lung cancer cell lines by ITGB8 silencing. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, F.; Tian, D.; Wang, T.; Lu, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, P.; Qin, L. miR-199a-3p enhances cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells by targeting ITGB8. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Lee, W.-C.; Aust, D.; Pilarsky, C.; Cordes, N. β8 integrin mediates pancreatic cancer cell radiochemoresistance. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2126–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, B.; Margheri, F.; Rossi, L.; Lapini, I.; Magi, A.; Serratì, S.; Chillà, A.; Laurenzana, A.; Magnelli, L.; Calorini, L.; et al. Desmoglein-2-integrin Beta-8 interaction regulates actin assembly in endothelial cells: Deregulation in systemic sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-S.; Chen, J.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Y. Scutellaria baicalensis and Cancer Treatment: Recent Progress and Perspectives in Biomedical and Clinical Studies. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.Y.; Hsiu, S.L.; Tsai, S.Y.; Hou, Y.C.; Chao, P.D. Comparison of metabolic pharmacokinetics of baicalin and baicalein in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, Y.; Yu, N.; Sun, Y.; Xing, Y.; Yang, F.; Yu, X.; Sun, W.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; et al. Intestinal metabolism of baicalein after oral administration in mice: Pharmacokinetics and mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; He, G.; Song, J.; Wang, S.; Xin, W.; Zhang, D.; Du, G. Pharmacokinetic study of baicalein after oral administration in monkeys. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, A.; Pang, H.; Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Cao, G.; Yan, B.; Dong, F.; Li, K.; Xiao, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of a single ascending dose of baicalein chewable tablets in healthy subjects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Lin, G.; Zuo, Z. Identification and quantification of baicalein, wogonin, oroxylin A and their major glucuronide conjugated metabolites in rat plasma after oral administration of Radix scutellariae product. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, V.; Agrahari, V. Facilitating the translation of nanomedicines to a clinical product: Challenges and opportunities. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 974–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, H.A.; Patwardhan, R.S.; Sharma, D.; Sandur, S.K.; Devarajan, P.V. Pre-clinical evaluation of an innovative oral nano-formulation of baicalein for modulation of radiation responses. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 595, 120181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jin, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Z. Trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles for ocular baicalein delivery: Preparation, optimization, in vitro evaluation, in vivo pharmacokinetic study and molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The ImageJ Program Version 1.52r. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- Ouellet, M.; Adams, P.D.; Keasling, J.D.; Mukhopadhyay, A. A rapid and inexpensive labeling method for microarray gene expression analysis. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DAVID Bioinformatics Resources Version 6.8. Available online: https://david.ncifcrf.gov/ (accessed on 23 May 2020).
- Network Analyst. Available online: https://www.networkanalyst.ca (accessed on 27 May 2020).



| KEGG Pathways | Gene Counts | p Values | Gene Names |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focal adhesion | 26 | 2.33 × 10−4 | CAV1, COL2A1, SRC, MYL9, PAK6, AKT1, PAK2, ITGB8, COMP, BCL2, RHOA, PPP1R12A, COL11A2, PIK3R1, EGFR, PRKCA, MYLK3, RAF1, KDR, PRKCB, LAMA4, CCND3, JUN, VEGFA, COL1A1, PARVA |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 37 | 2.43 × 10−4 | FGFR2, PPP2R3A, FGF9, FGF10, COL2A1, GNG8, AKT1, ITGB8, BCL2, COMP, PPP2CB, CSF3R, COL11A2, FGF1, PIK3R1, SYK, GNG7, PRKCA, EGFR, PPP2R1A, IL2RA, CREB1, YWHAB, PKN2, RAF1, BCL2L11, KDR, NRAS, GNGT1, LAMA4, CDKN1A, CCND3, CHRM2, VEGFA, JAK1, MDM2, COL1A1 |
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | 20 | 7.67 × 10−4 | PRKCA, EGFR, ADCY1, MYLK3, CACNG7, PRKAG2, RAF1, OXTR, KCNJ3, SRC, PRKCB, MYL9, NRAS, CDKN1A, JUN, RHOA, PPP1R12A, CAMK2D, PPP3CC, RYR2 |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 12 | 1.08 × 10−3 | PAK6, AKT1, NRAS, CUL2, HIF1A, PAK2, EPAS1, VHL, JUN, VEGFA, RAF1, PIK3R1 |
| ErbB signaling pathway | 14 | 1.13× 10−3 | PRKCA, EGFR, RAF1, SRC, PRKCB, AKT1, PAK6, NRAS, CDKN1A, EREG, PAK2, JUN, CAMK2D, PIK3R1 |
| Pathways in cancer | 38 | 1.43 × 10−3 | FGFR2, ADCY1, FGF9, FGF10, CXCL12, GNG8, AKT1, CUL2, CDKN2B, BCL2, RHOA, CSF3R, RARB, RUNX1, FGF1, PIK3R1, GNG7, PRKCA, EGFR, PTGER1, BMP2, PTGER4, EPAS1, VHL, RAF1, FZD5, CTNNA3, PRKCB, DAPK1, NRAS, GNGT1, LAMA4, CDKN1A, HIF1A, JUN, VEGFA, JAK1, MDM2 |
| TGF-β signaling pathway | 13 | 2.57 × 10−3 | PPP2R1A, BMP2, SMAD5, DCN, ACVR2A, SP1, CDKN2B, ZFYVE16, PPP2CB, RHOA, TGIF1, ACVR1, BMP8A |
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | 14 | 2.80 × 10−3 | PRKCA, EGFR, VHL, PFKFB3, PRKCB, AKT1, CUL2, CDKN1A, HIF1A, BCL2, VEGFA, CAMK2D, PIK3R1, NPPA |
| Dopaminergic synapse | 16 | 5.66 × 10−3 | PRKCA, PPP2R1A, PPP2R3A, CALY, CREB1, TH, GRIA3, KCNJ3, PRKCB, AKT1, GNG8, GNGT1, PPP2CB, CAMK2D, PPP3CC, GNG7 |
| Viral carcinogenesis | 22 | 5.91 × 10−3 | CREB1, YWHAB, SNW1, SRC, NRAS, CDKN1A, CCND3, CDKN2B, GSN, JUN, RHOA, JAK1, MDM2, HIST1H4C, HIST1H4I, ATP6V0D1, HDAC9, ATP6V0D2, HDAC8, PIK3R1, SYK, HIST1H4H |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiatwuthinon, P.; Narkthong, T.; Ngaokrajang, U.; Kumkate, S.; Janvilisri, T. Baicalein Inhibits Metastatic Phenotypes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via a Focal Adhesion Protein Integrin β8. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010005
Kiatwuthinon P, Narkthong T, Ngaokrajang U, Kumkate S, Janvilisri T. Baicalein Inhibits Metastatic Phenotypes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via a Focal Adhesion Protein Integrin β8. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiatwuthinon, Pichamon, Thana Narkthong, Utapin Ngaokrajang, Supeecha Kumkate, and Tavan Janvilisri. 2022. "Baicalein Inhibits Metastatic Phenotypes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via a Focal Adhesion Protein Integrin β8" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010005
APA StyleKiatwuthinon, P., Narkthong, T., Ngaokrajang, U., Kumkate, S., & Janvilisri, T. (2022). Baicalein Inhibits Metastatic Phenotypes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via a Focal Adhesion Protein Integrin β8. Pharmaceuticals, 15(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010005