HBK-10, A Compound with α1-Adrenolytic Properties, Showed Antiarrhythmic and Hypotensive Effects in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HBK-10 Showed a High Affinity for α1-Adrenoceptors
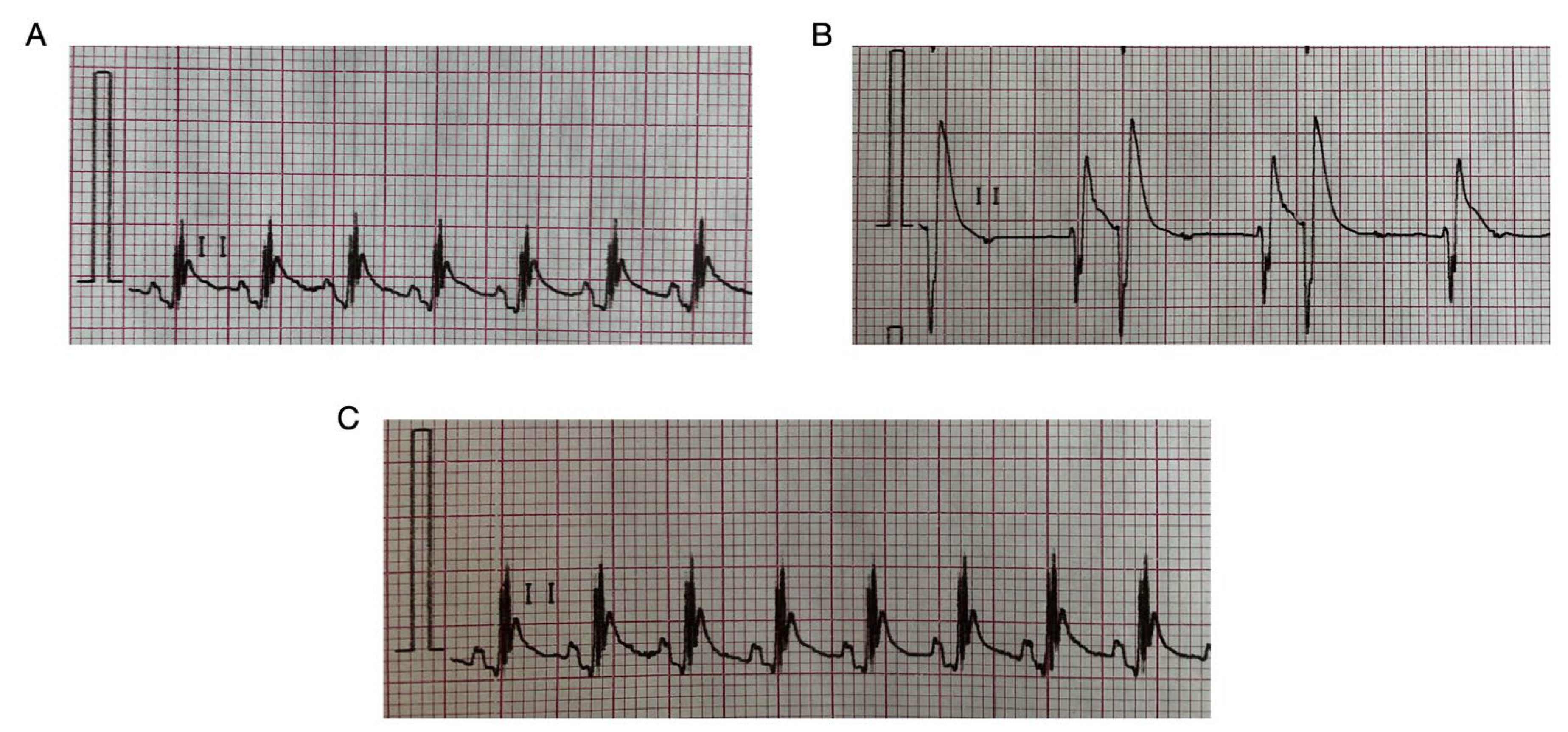
2.2. HBK-10 Showed a Prophylactic Antiarrhythmic Activity in the Adrenaline-Induced Arrhythmia
2.3. HBK-10 Did Not Influence Negatively the Normal Electrocardiogram in Rats
2.4. HBK-10 Showed the Hypotensive Effect in Normotensive Rats
2.5. HBK-10 Attenuates Vasopressor Response after Adrenaline, Noradrenaline, and Methoxamine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Animals
4.3. Radioligand Binding Assay
4.4. Prophylactic Antiarrhythmic Activity in Adrenaline-Induced Arrhythmia
4.5. Effect on a Normal Electrocardiogram in Rats
4.6. Influence on Blood Pressure in Normotensive Rats
4.7. Influence on Blood Vasopressor Response in Rats
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 26 July 2022).
- Crenshaw, B.S.; Ward, S.R.; Granger, C.B.; Stebbins, A.L.; Topol, E.J.; Califf, R.M. Atrial fibrillation in the setting of acute myocardial infarction: The GUSTO-I experience. Global Utilization of Streptokinase and TPA for Occluded Coronary Arteries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1997, 30, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chugh, S.S.; Havmoeller, R.; Narayanan, K.; Singh, D.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Kim, Y.-H.; McAnulty, J.H.J.; Zheng, Z.-J.; et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: A Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014, 129, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brundel, B.J.J.M.; Ai, X.; Hills, M.T.; Kuipers, M.F.; Lip, G.Y.H.; de Groot, N.M.S. Atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2022, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, L.E.; Kitchell, J.B. The incidence of arrhythmias associated with acute myocardial infarction. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 1966, 9, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, A.J. Hopes and disappointments with antiarrhythmic drugs. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 237, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbar, D.; Roden, D.M. Future of antiarrhythmic drugs. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2006, 21, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, O.E.; Aydin, M.; Odabasi, A.Y.; Inc, M.; Payzin, S.; Hasdemir, C. Therapeutic Inefficacy and Proarrhythmic Nature of Metoprolol Succinate and Carvedilol Therapy in Patients with Idiopathic, Frequent, Monomorphic Premature Ventricular Contractions. Am. J. Ther. 2021, 29, e34–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, M.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Darbar, D. Proarrhythmic and Torsadogenic Effects of Potassium Channel Blockers in Patients. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2016, 8, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morganroth, J. Proarrhythmic effects of antiarrhythmic drugs: Evolving concepts. Am. Heart J. 1992, 123, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, M. Proarrhythmic Effects of Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Case Study of Flecainide Induced Ventricular Arrhythmias During Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2015, 8, 1091. [Google Scholar]
- Kurz, T.; Yamada, K.A.; DaTorre, S.D.; Corr, P.B. Alpha1adrenergic system and arrhythmias in ischaemic heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 1991, 12, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culling, W.; Penny, W.J.; Cunliffe, G.; Flores, N.A.; Sheridan, D.J. Arrhythmogenic and electrophysiological effects of alpha adrenoceptor stimulation during myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1987, 19, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, D.J.; Penkoske, P.A.; Sobel, B.E.; Corr, P.B. Alpha adrenergic contributions to dysrhythmia during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in cats. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 65, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilber, D.J.; Lynch, J.J.; Montgomery, D.G.; Lucchesi, B.R. Alpha-adrenergic influences in canine ischemic sudden death: Effects of alpha 1-adrenoceptor blockade with prazosin. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1987, 10, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfey, B.G.; Elfellah, M.S.; Ogilvie, R.I.; Varma, D.R. Anti-arrhythmic effects of prazosin and propranolol during coronary artery occlusion and re-perfusion in dogs and pigs. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 82, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, J.R.; Burmeister, W.E.; Burmeister, J.; Lucchesi, B.R. Electrophysiologic and antiarrhythmic effects of phentolamine in experimental coronary artery occlusion and reperfusion in the dog. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1980, 2, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.T.; Guerrero, J.L.; Leinbach, R.C.; Gold, H.K. Prevention of reperfusion dysrhythmias by selective coronary alpha adrenergic blockade. Am. J. Cardiol. 1982, 49, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandroyen, F.T.; Worthington, M.G.; Higginson, L.M.; Opie, L.H. The effect of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor antagonist agents on reperfusion ventricular fibrillation and metabolic status in the isolated perfused rat heart. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1983, 1, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, P.J.; Vanoli, E.; Zaza, A.; Zuanetti, G. The effect of antiarrhythmic drugs on life-threatening arrhythmias induced by the interaction between acute myocardial ischemia and sympathetic hyperactivity. Am. Heart J. 1985, 109, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.J. The pharmacology of prazosin, an alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist and the basis for its use in the treatment of essential hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. A 1982, 4, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapacz, A.; Sapa, J.; Pytka, K.; Dudek, M.; Filipek, B.; Szkaradek, N.; Marona, H. Antiarrhythmic activity of new 2-methoxyphenylpiperazine xanthone derivatives after ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapacz, A.; Pytka, K.; Sapa, J.; Kubacka, M.; Filipek, B.; Szkaradek, N.; Marona, H. Antiarrhythmic, hypotensive and α1-adrenolytic properties of new 2-methoxyphenylpiperazine derivatives of xanthone. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 735, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytka, K.; Lustyk, K.; Żmudzka, E.; Kotańska, M.; Siwek, A.; Zygmunt, M.; Dziedziczak, A.; Śniecikowska, J.; Olczyk, A.; Gałuszka, A.; et al. Chemically Homogenous Compounds with Antagonistic Properties at All α1-Adrenoceptor Subtypes but not β1-Adrenoceptor Attenuate Adrenaline-Induced Arrhythmia in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sałaciak, K.; Malikowska-Racia, N.; Lustyk, K.; Siwek, A.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Kazek, G.; Popiół, J.; Sapa, J.; Marona, H.; Żelaszczyk, D.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of the Antidepressant-like Properties of HBK-10, a Novel 2-Methoxyphenylpiperazine Derivative Targeting the 5-HT(1A) and D(2) Receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Clerck, F.; Van de Water, A.; D’Aubioul, J.; Lu, H.R.; van Rossem, K.; Hermans, A.; Van Ammel, K. In vivo measurement of QT prolongation, dispersion and arrhythmogenesis: Application to the preclinical cardiovascular safety pharmacology of a new chemical entity. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 16, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubacka, M.; Mogilski, S.; Filipek, B.; Marona, H. The hypotensive activity and alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonistic properties of some aroxyalkyl derivatives of 2-methoxyphenylpiperazine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 698, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdock, C.J.; Hickey, G.M.; Hockings, B.E.; Pitman, G.F.; Taylor, R.R. Effect of alpha 1-adrenoceptor blockade on ventricular ectopic beats inacute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 1990, 26, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzwald-Josefson, E.; Hochhauser, E.; Bogachenko, K.; Harun-Khun, S.; Katz, G.; Aravot, D.; Seidman, J.G.; Seidman, C.E.; Eldar, M.; Shainberg, A.; et al. Alpha blockade potentiates CPVT therapy in calsequestrin-mutant mice. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pytka, K.; Zmudzka, E.; Lustyk, K.; Rapacz, A.; Olczyk, A.; Galuszka, A.; Waszkielewicz, A.; Marona, H.; Sapa, J.; Barbara, F. The antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like activities of new xanthone derivative with piperazine moiety in behavioral tests in mice. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sherif, N.; Turitto, G. Electrophysiologic effects of carvedilol: Is carvedilol an antiarrhythmic agent? Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2005, 28, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccarelli, G.V.; Wolbrette, D.L.; Khan, M.; Bhatta, L.; Hynes, J.; Samii, S.; Luck, J. Old and new antiarrhythmic drugs for converting and maintaining sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation: Comparative efficacy and results of trials. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 15D–26D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starmer, C.F. The cardiac vulnerable period and reentrant arrhythmias: Targets of anti- and proarrhythmic processes. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1997, 20, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdale, J.E.; Chung, M.K.; Campbell, K.B.; Hammadah, M.; Joglar, J.A.; Leclerc, J.; Rajagopalan, B. Drug-Induced Arrhythmias: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 142, e214–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Brügemann, J.; Crijns, H.J. Pharmacological management of arrhythmias in the elderly. Drugs Aging 1997, 11, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TeBay, C.; Hill, A.P.; Windley, M.J. Metabolic and electrolyte abnormalities as risk factors in drug-induced long QT syndrome. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, J.R. The pharmacology of α(1)-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 855, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacka, M.; Mogilski, S.; Filipek, B.; Marona, H. Antiarrhythmic properties of some 1,4-disubstituted piperazine derivatives with α1-adrenoceptor affinities. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 720, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handzlik, J.; Bajda, M.; Zygmunt, M.; MacIg, D.; Dybała, M.; Bednarski, M.; Filipek, B.; Malawska, B.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Antiarrhythmic properties of phenylpiperazine derivatives of phenytoin with α 1-adrenoceptor affinities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2290–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, L.; Papp, J. “Experimental Cardiac Arrhythmias” in Experimental Production of Diseases, Part 3, Heart and Circulation. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield, J.T.; Wilcoxon, F. A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1949, 96, 99–113. [Google Scholar]


| Treatment | Adrenergic Receptors—pKi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| α1 a,b | α2 a,c | β1 a,d | |
| HBK-10 | 8.55 | 5.72 | 5.52 |
| Phentolamine | 8.04 | - | - |
| Clonidine | - | 8.60 | - |
| Propranolol | - | - | 8.12 |
| Treatment | Dose (mg/kg) | Extrasystoles (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 100 |
| HBK-10 | 0.25 | 16.7 |
| 0.125 | 50 | |
| 0.0625 | 83.3 |
| Dose (mg/kg) | Parameters | Time of Observation (min) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | ||
| 10 | PR | 53.9 ± 2.8 | 53.0 ± 3.3 | 55.8 ± 2.0 | 54.9 ± 2.4 | 53.1 ± 4.4 | 52.2 ± 4.4 | 55.6 ± 2.6 | 53.6 ± 4.4 | 54.7 ± 3.1 | 54.9 ± 4.2 |
| QRS | 22.6 ± 1.8 | 21.5 ± 1.4 | 23.2 ± 3.6 | 23.5 ± 2.6 | 23.6 ± 2.9 | 22.9 ± 1.6 | 24.5 ± 1.8 | 23.9 ± 2.5 | 23.2 ± 1.9 | 22.0 ± 1.4 | |
| QTc | 215.3 ± 19.3 | 213.2 ± 20.8 | 214.4 ± 20.0 | 212.4 ± 12.3 | 216.7 ± 13.8 | 213.7 ± 19.0 | 221.4 ± 16.9 | 218.8 ± 11.8 | 217.4 ± 22.0 | 218.3 ± 25.5 | |
| Rate | 357.1 ± 22.6 | 347.3 ± 25.2 | 347.9 ± 29.2 | 345.0 ± 32.7 | 343.4 ± 33.6 | 338.5 ± 26.3 | 337.5 ± 25.0 | 342.2 ± 25.8 | 344.5 ± 28.9 | 350.7 ± 28.1 | |
| 20 | PR | 53.1 ± 2.8 | 52.4 ± 3.4 | 55.3 ± 1.7 | 54.2 ± 2.1 | 52.1 ± 4.2 | 51.3 ± 4.4 | 54.6 ± 2.4 | 52.5 ± 4.6 | 53.7 ± 3.0 | 53.8 ± 4.1 |
| QRS | 21.8 ± 1.7 | 20.9 ± 1.2 | 22.7 ± 3.4 | 22.8 ± 2.2 | 22.7 ± 2.5 | 22.0 ± 1.5 | 23.6 ± 1.5 | 22.9 ± 2.3 | 22.1 ± 1.7 | 21.0 ± 1.3 | |
| QTc | 198.4 ± 6.1 | 190.9 ± 8.4 | 187.8 ± 14.7 | 179.4 ± 16.4 ** | 178.9 ± 21.9 ** | 177.6 ± 21.6l ** | 175.7 ± 20.5 *** | 179.3 ± 20.7 ** | 182.0 ± 30.1 * | 173.0 ± 6.6 *** | |
| Rate | 317.4 ± 26.0 | 304.2 ± 32.0 | 278.4 ± 41.8 *** | 256.2 ± 52.1 **** | 249.9 ± 53.5 **** | 246.5 ± 55.6 **** | 242.1 ± 53.5 *** | 239.2 ± 55.4 *** | 239.5 ± 56.6 *** | 241.0 ± 64.1 *** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lustyk, K.; Sałaciak, K.; Siwek, A.; Filipek, B.; Sapa, J.; Marona, H.; Żelaszczyk, D.; Pytka, K. HBK-10, A Compound with α1-Adrenolytic Properties, Showed Antiarrhythmic and Hypotensive Effects in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101256
Lustyk K, Sałaciak K, Siwek A, Filipek B, Sapa J, Marona H, Żelaszczyk D, Pytka K. HBK-10, A Compound with α1-Adrenolytic Properties, Showed Antiarrhythmic and Hypotensive Effects in Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(10):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101256
Chicago/Turabian StyleLustyk, Klaudia, Kinga Sałaciak, Agata Siwek, Barbara Filipek, Jacek Sapa, Henryk Marona, Dorota Żelaszczyk, and Karolina Pytka. 2022. "HBK-10, A Compound with α1-Adrenolytic Properties, Showed Antiarrhythmic and Hypotensive Effects in Rats" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 10: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101256
APA StyleLustyk, K., Sałaciak, K., Siwek, A., Filipek, B., Sapa, J., Marona, H., Żelaszczyk, D., & Pytka, K. (2022). HBK-10, A Compound with α1-Adrenolytic Properties, Showed Antiarrhythmic and Hypotensive Effects in Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 15(10), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101256






