A Review of the Safety of Interleukin-17A Inhibitor Secukinumab
Abstract
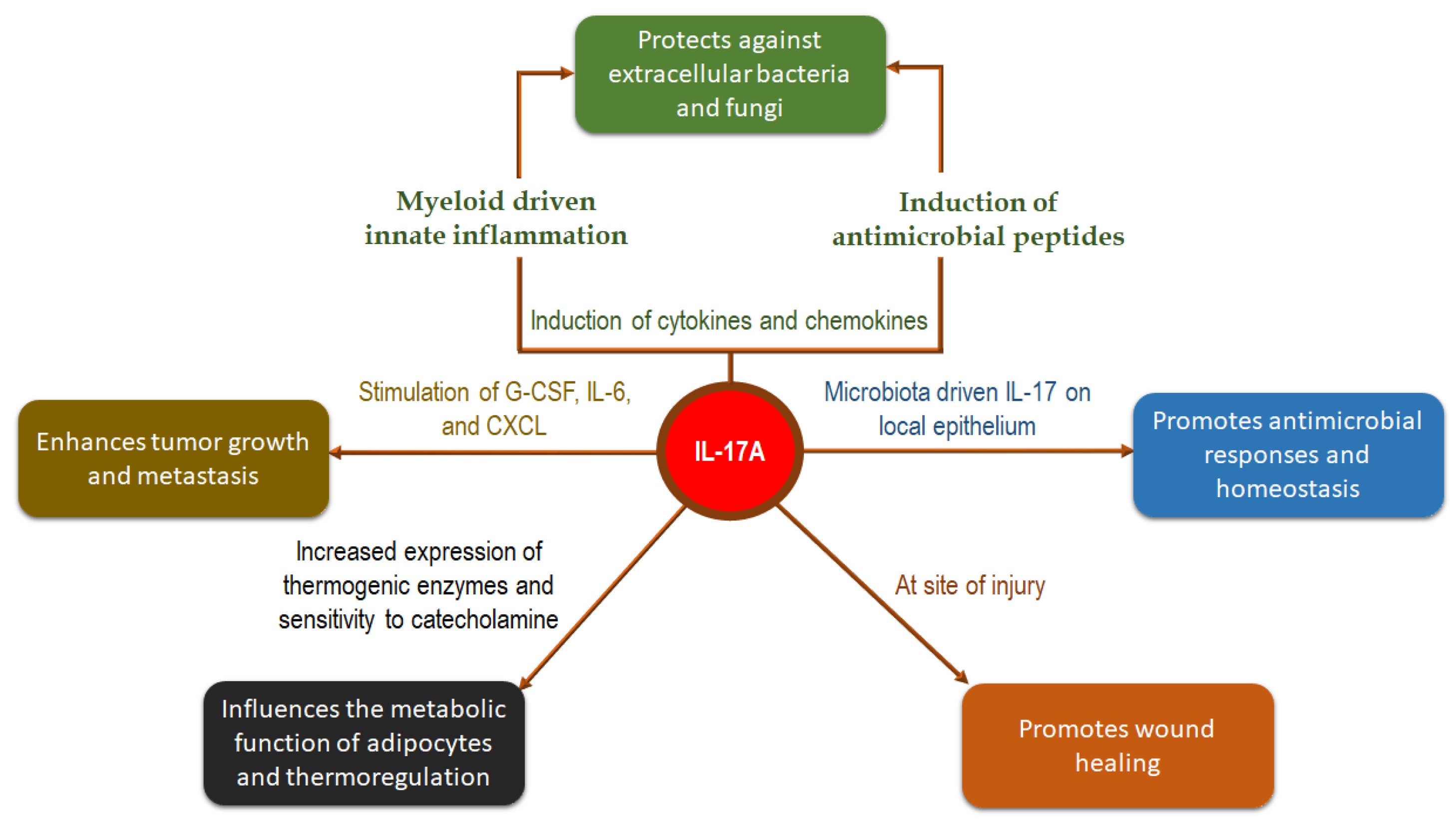
:1. Introduction
2. Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Related Disorders
3. Safety Concerns with IL-17 Inhibitors
4. Important Adverse Effects of Secukinumab
4.1. Infections
4.2. Candidiasis
4.3. Injection Site Reactions
4.4. Neutropenia
4.5. Malignancy
4.6. IBD
4.7. MACE
4.8. Other Adverse Events
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.O.; Chang, S.H.; Nurieva, R.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Hood, L.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, Q.; et al. A Distinct Lineage of CD4 T Cells Regulates Tissue Inflammation by Producing Interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, R.; Maroof, A.; Baker, T.; Lawson, A.D.G.; Oliver, R.; Paveley, R.; Rapecki, S.; Shaw, S.; Vajjah, P.; West, S.; et al. Bimekizumab, a Novel Humanized IgG1 Antibody That Neutralizes Both IL-17A and IL-17F. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miossec, P.; Korn, T.; Kuchroo, V.K. Interleukin-17 and Type 17 Helper T Cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khader, S.; Das, S. Yin and Yang of Interleukin-17 in Host Immunity to Infection. F1000Research 2017, 6, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blake, S.J.; Teng, M.W.L. Role of IL-17 and IL-22 in Autoimmunity and Cancer. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014, 105 (Suppl. 1), 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Herjan, T.; Li, X. The Role of Interleukin-17 in Tumor Development and Progression. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targeting IL-17 in Inflammatory Disease. Available online: https://www.nature.com/collections/vzdlng (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Menter, A.; Strober, B.E.; Kaplan, D.H.; Kivelevitch, D.; Prater, E.F.; Stoff, B.; Armstrong, A.W.; Connor, C.; Cordoro, K.M.; Davis, D.M.R.; et al. Joint AAD-NPF Guidelines of Care for the Management and Treatment of Psoriasis with Biologics. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1029–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, J.A.; Guyatt, G.; Ogdie, A.; Gladman, D.D.; Deal, C.; Deodhar, A.; Dubreuil, M.; Dunham, J.; Husni, M.E.; Kenny, S.; et al. Special Article: 2018 American College of Rheumatology/National Psoriasis Foundation Guideline for the Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, M.M.; Deodhar, A.; Gensler, L.S.; Dubreuil, M.; Yu, D.; Khan, M.A.; Haroon, N.; Borenstein, D.; Wang, R.; Biehl, A.; et al. 2019 Update of the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network Recommendations for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1599–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.K.; Dao, H. Off-Label Dermatologic Uses of IL-17 Inhibitors. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabag, D.A.; Matanes, L.; Bejar, J.; Sheffer, H.; Barzilai, A.; Church, M.K.; Toubi, E.; Maurer, M.; Vadasz, Z. Interleukin-17 Is a Potential Player and Treatment Target in Severe Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.M.; Chiou, A.S.; Shih, Y.; Li, S.; Chang, A.L.S. 17965 An Exploratory, Open-Label Study of Secukinumab in Patients with Moderate to Severe Papulopustular Rosacea. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, AB88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogarajah, J.; Gouveia, C.; Iype, J.; Häfliger, S.; Schaller, A.; Nuoffer, J.M.; Fux, M.; Gautschi, M.; Gautschi, M. Efficacy and Safety of Secukinumab for the Treatment of Severe ABCA12 Deficiency-Related Ichthyosis in a Child. Skin Health Dis. 2021, 1, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieder, J.; Kivelevitch, D.; Menter, A. Secukinumab: A Review of the Anti-IL-17A Biologic for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerkhof, P.C.M.V.D.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Reich, K.; Leonardi, C.L.; Blauvelt, A.; Tsai, T.F.; Gong, Y.; Huang, J.; Papavassilis, C.; Fox, T. Secukinumab Long-Term Safety Experience: A Pooled Analysis of 10 Phase II and III Clinical Studies in Patients with Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, 83–98.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, L.; Shakir, S.A.W. Under-Reporting of Adverse Drug Reactions: A Systematic Review. Drug Saf. 2006, 29, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, A.B.; Deodhar, A.; Mcinnes, I.B.; Baraliakos, X.; Reich, K.; Schreiber, S.; Bao, W.; Marfo, K.; Richards, H.B.; Pricop, L.; et al. Long-Term Safety of Secukinumab Over Five Years in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis: Update on Integrated Pooled Clinical Trial and Post-Marketing Surveillance Data. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2022, 102, adv00698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, M.A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Krueger, J.G. Immunology of Psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, R.M.; Gaffen, S.L. Interleukin-17 and Its Target Genes: Mechanisms of Interleukin-17 Function in Disease. Immunology 2010, 129, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Chiricozzi, A. The Immunologic Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosca, M.; Hong, J.; Hadeler, E.; Hakimi, M.; Liao, W.; Bhutani, T. The Role of IL-17 Cytokines in Psoriasis. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2021, 10, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, M.; Furue, K.; Tsuji, G.; Nakahara, T. Interleukin-17A and Keratinocytes in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gladman, D.; Antoni, C.; Mease, P.; Clegg, D.; Nash, P. Psoriatic Arthritis: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Course, and Outcome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, ii14–ii17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.; Miossec, P. IL-17 in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Precision Medicine: From Synovitis Expression to Circulating Bioactive Levels. Front. Med. 2019, 5, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; He, X.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Qiu, G.; Cao, X.; Weng, X. Ankylosing Spondylitis: Etiology, Pathogenesis, and Treatments. Bone Res. 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sieper, J.; Poddubnyy, D. Axial Spondyloarthritis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2017, 390, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Okamoto, K.; Nakashima, T.; Nitta, T.; Hori, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Takayanagi, H. IL-17-Producing Γδ T Cells Enhance Bone Regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubrano, E.; Perrotta, F.M. Secukinumab for Ankylosing Spondylitis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.K.; King, C.R.; Feldman, S.R. Biologics and Biosimilars. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2015, 26, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. What Are “Biologics” Questions and Answers; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Boyman, O.; Comte, D.; Spertini, F. Adverse Reactions to Biologic Agents and Their Medical Management. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin, F.; Carbonnel, F.; Wendling, D. The Complexity of Adverse Side-Effects to Biological Agents. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hueber, W.; Patel, D.D.; Dryja, T.; Wright, A.M.; Koroleva, I.; Bruin, G.; Antoni, C.; Draelos, Z.; Gold, M.H.; Durez, P.; et al. Effects of AIN457, a Fully Human Antibody to Interleukin-17A, on Psoriasis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Uveitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 52ra72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genovese, M.C.; Bosch, F.V.D.; Roberson, S.A.; Bojin, S.; Biagini, I.M.; Ryan, P.; Sloan-Lancaster, J. LY2439821, a Humanized Anti-Interleukin-17 Monoclonal Antibody, in the Treatment of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Phase I Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Proof-of-Concept Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatt, S.; Helmer, E.; Haier, B.; Strimenopoulou, F.; Price, G.; Vajjah, P.; Harari, O.A.; Lambert, J.; Shaw, S. First-in-Human Randomized Study of Bimekizumab, a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody and Selective Dual Inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F, in Mild Psoriasis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.A.; Leonardi, C.; Menter, A.; Ortonne, J.-P.; Krueger, J.G.; Kricorian, G.; Aras, G.; Li, J.; Russell, C.B.; Thompson, E.H.Z.; et al. Brodalumab, an Anti–Interleukin-17–Receptor Antibody for Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, K.; Warren, R.B.; Lebwohl, M.; Gooderham, M.; Strober, B.; Langley, R.G.; Paul, C.; Cuyper, D.D.; Vanvoorden, V.; Madden, C.; et al. Bimekizumab versus Secukinumab in Plaque Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SILIQTM [Package Insert]; Valeant Pharmaceuticals: Bridgewater, NJ, USA, 2017.
- TALTZTM [Package Insert]; Eli Lily and Company: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2016.
- COSENTYXTM [Package Insert]; Novartis: East Hannover, NJ, USA, 2015.
- Pichler, W.J. Adverse Side-Effects to Biological Agents. Allergy 2006, 61, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Li, G.G.; Liu, Q.; Niu, X.; Li, R.; Ma, H. Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of IL-17, IL-12/23, and IL-23 Inhibitors Brodalumab, Secukinumab, Ixekizumab, Ustekinumab, Guselkumab, Tildrakizumab, and Risankizumab for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 2546161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.A.; Cicala, G.; Cutroneo, P.M.; Gerratana, E.; Palleria, C.; Sarro, C.D.; Vero, A.; Iannone, L.; Manti, A.; Russo, E.; et al. Safety Profile of Biologics Used in Rheumatology: An Italian Prospective Pharmacovigilance Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, L.F.; Bennardo, L.; Palleria, C.; Roberti, R.; de Sarro, C.; Naturale, M.D.; Dastoli, S.; Donato, L.; Manti, A.; Valenti, G.; et al. Safety Profile of Biologic Drugs for Psoriasis in Clinical Practice: An Italian Prospective Pharmacovigilance Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, P.; Tsai, T.F.; Rodins, K.; Hamadah, I.R.; Ammoury, A.; Dayem, H.A.; Abdallah, M.; Crowe, S.; Haas, S.; Pournara, E.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Secukinumab for Psoriasis in a Real-World Clinical Setting in the Asia-Pacific and Middle East Regions: Results from the REALIA Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H.; Ohtsuki, M.; Morita, A.; Nagao, R.; Seko, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Tani, Y.; Terui, T. Safety and Effectiveness of Secukinumab in Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis: Real-world Evidence in Japan. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhou, E.; Ren, T.; Chang, X.; He, M.; Zeng, K.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J. Efficacy and Safety of IL-17 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddur, M.S.; Vani, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Kaveri, S.; Bayry, J. Autoimmunity as a Predisposition for Infectious Diseases. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivas, C.; Odsbu, I.; Linder, M. Risk of Common Infections among Individuals with Psoriasis in Sweden: A Nationwide Cohort Study Comparing Secukinumab to Ustekinumab. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2020, 29, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadeh, H.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Rezaiemanesh, A.; Rajabinejad, M. Immune-Related Adverse Events (IrAEs) in Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) Patients Treated with Interleukin (IL)-17 Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, P.A.; Baddley, J.W. Opportunistic Infections in Biological Therapy, Risk and Prevention. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 43, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahier, J.F.; Magro, F.; Abreu, C.; Armuzzi, A.; Ben-Horin, S.; Chowers, Y.; Cottone, M.; de Ridder, L.; Doherty, G.; Ehehalt, R.; et al. Second European Evidence-Based Consensus on the Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Opportunistic Infections in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2014, 8, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elewski, B.E.; Baddley, J.W.; Deodhar, A.A.; Magrey, M.; Rich, P.A.; Soriano, E.R.; Soung, J.; Bao, W.; Keininger, D.; Marfo, K.; et al. Association of Secukinumab Treatment With Tuberculosis Reactivation in Patients With Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, or Ankylosing Spondylitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.K.; Lee, M.P.; Lee, E.B.; Wu, J.J. Risk of Herpes Zoster with IL-17 Inhibitor Therapy for Psoriasis and Other Inflammatory Conditions. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 31, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, M.; Talamonti, M.; Atzori, L.; Bardazzi, F.; Campanati, A.; Cesare, A.D.; Diotallevi, F.; Flori, M.L.; Mugheddu, C.; Offidani, A.; et al. Secukinumab for the Treatment of Palmoplantar Psoriasis: A 2-Year, Multicenter, Real-Life Observational Study. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2022, 22, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergun, T.; Seckin, D.; Demir, G.; Direskeneli, H. Secukinumab and Infectious Adverse Effects: A Real-Life Experience of 63 Psoriasis Patients. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, e423–e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Dash, M.; Bhatkoti, B.; Krishnan, L.P. Epithelial Herpes Simplex Keratitis in a Patient on Treatment with Secukinumab for Psoriasis: An Effect of Interleukin-17 Blockade? Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2022, 88, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Bueno, J.; Vanaclocha, F.; García-Doval, I.; Torrado, R.; Carretero, G.; Daudén, E.; Ruiz-Genao, D.P.; Alsina-Gibert, M.M.; Pérez-Zafrilla, B.; Pérez-Rial, G.; et al. Risk of Reactivation of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Psoriasis Patients Treated with Biologics: A Retrospective Analysis of 20 Cases from the BIOBADADERM Database. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015, 106, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moneva-Leniz, L.M.; Sahuquillo-Torralba, A.; Vila-Payeras, A.; Mateu-Puchades, A. Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Patients on Secukinumab for Psoriasis: A Series of 4 Cases. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. Engl. Ed. 2020, 111, 613–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Deaner, J.D.; Knapp, A.; Baynes, K.; Srivastava, S.K. Bilateral Infectious Scleritis from Histoplasma Capsulatum in an Immunosuppressed Uveitis Patient. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2021, 23, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Martín, M.; Amores Hernández, I.; Argumánez García, D.; Silva Hernández, M.; De Lucas Laguna, R.; Aracil Santos, F.J.; López López, R.; de Ceano-Vivas La Calle, M. Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome in a Child with Interleukin-17 Inhibitor Treatment for Psoriasis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utiyama, T.O.; Zerbini, C.; Guimarães, G. Infective Dermatitis after Treatment with Secukinumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.; Ziv, M. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in Biological Therapy for Psoriasis—A Case Report and Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard-Anderson, J.; Satola, S.W.; Collins, M.H. Breech at the Border: An Atypical Case of Invasive Haemophilus Influenzae in a Patient on a Novel Immunotherapeutic. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, L.; Baker, B.S. Triggering Psoriasis: The Role of Infections and Medications. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengesha, B.G.; Conti, H.R. The Role of IL-17 in Protection against Mucosal Candida Infections. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, A.; Mease, P.J.; McInnes, I.B.; Baraliakos, X.; Reich, K.; Blauvelt, A.; Leonardi, C.; Porter, B.; Gupta, A.D.; Widmer, A.; et al. Long-Term Safety of Secukinumab in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis: Integrated Pooled Clinical Trial and Post-Marketing Surveillance Data. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, L.; van den Reek, J.M.P.A.; Bruno, M.; van Hunsel, F.; Herings, R.M.C.; Matzaraki, V.; Boahen, C.K.; Kumar, V.; Groenewoud, H.M.M.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; et al. Risk of Candidiasis Associated with Interleukin-17 Inhibitors: A Real-World Observational Study of Multiple Independent Sources. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2022, 13, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.G.; Kauffman, C.A.; Andes, D.R.; Clancy, C.J.; Marr, K.A.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Reboli, A.C.; Schuster, M.G.; Vazquez, J.A.; Walsh, T.J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Candidiasis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, e1–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picciani, B.L.S.; Dziedzic, A.; Werneck, J.T.; Marinho, M.A.; Dick, T.N.A.; Quintanilha, N.R.; Dias, E.P. Atypical Oral Candidiasis in a Psoriatic Patient during Targeted Immunotherapy with an Interleukin 17 Inhibitor (Secukinumab). BMC Oral. Health 2021, 21, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Han, J.H.; Bang, C.H.; Kim, T.Y. Abrupt Development of Esophageal Candidiasis after Secukinumab Treatment in a Psoriatic Patient. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, T.; Dhesi, Z.; Shah, S. Case Report: Death by Antibody. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e225519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, C.S. Concurrent Chronic Hyperplastic Candidosis and Oral Lichenoid Lesion as Adverse Events of Secukinumab Therapy. Aust. Dent. J. 2021, 66, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capusan, T.M.; Herrero-Moyano, M.; Martínez-Mera, C.R.; Freih-Fraih, A.W.; Dauden, E. Oral Lichenoid Reaction in a Psoriatic Patient Treated with Secukinumab: A Drug-Related Rather than a Class-Related Adverse Event? JAAD Case Rep. 2018, 4, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komori, T.; Honda, T.; Endo, Y.; Kaku, Y.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Oral Lichen Planus Associated with Candidiasis during Secukinumab Treatment. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, e60–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreland, L.W.; Schiff, M.H.; Baumgartner, S.W.; Tindall, E.A.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Bulpitt, K.J.; Weaver, A.L.; Keystone, E.C.; Furst, D.E.; Mease, P.J.; et al. Etanercept Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaidou, E.; Ramot, Y. Injection Site Reactions with the Use of Biological Agents. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, G.; Hockey, H.U.P.; Stella, P.L.; Sigurgeirsson, B.; Fu, R.; Patekar, M.; Charef, P.; Woessner, R.; Boutouyrie-Dumont, B. Comparison of Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Secukinumab Administered Subcutaneously Using Different Delivery Systems in Healthy Volunteers and in Psoriasis Patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grace, E.; Goldblum, O.; Renda, L.; Agada, N.; See, K.; Leonardi, C.; Menter, A. Injection Site Reactions in the Federal Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) Post-Marketing Database Vary Among Biologics Approved to Treat Moderate-To-Severe Psoriasis. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- St Clair-Jones, A.; Prignano, F.; Goncalves, J.; Paul, M.; Sewerin, P. Understanding and Minimising Injection-Site Pain Following Subcutaneous Administration of Biologics: A Narrative Review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.K.; Zhu, L.; Procario, M.C.; Weinberg, J.B. IL-17 Contributes to Neutrophil Recruitment but Not to Control of Viral Replication During Acute Mouse Adenovirus Type 1 Respiratory Infection. Virology 2014, 259, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, C.T.; Elson, C.O.; Fouser, L.A.; Kolls, J.K. The Th17 Pathway and Inflammatory Diseases of the Intestines, Lungs, and Skin. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 477–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, A.; Giamarellou, H. Fever of Unknown Origin in Febrile Leukopenia. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 21, 1055–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karataş, A.; Gerçek, A.N.; Öz, B.; Gözel, N.; Sağır, R.P.; Gür, M.; Koca, S.S. The Effect of Secukinumab Treatment on Hematological Parameters in Ankylosing Spondylitis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, G.K.; Newton, G.; Tarrio, M.L.; Bu, D.; Maganto-Garcia, E.; Azcutia, V.; Alcaide, P.; Grabie, N.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Croce, K.J.; et al. IL-17 and TNFα Sustain Neutrophil Recruitment During Inflammation Through Synergistic Effects on Endothelial Activation. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 2012, 188, 6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elkoshi, Z. Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases: A Tale of Two Immunological Opposites? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trafford, A.M.; Parisi, R.; Kontopantelis, E.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Association of Psoriasis With the Risk of Developing or Dying of Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.C.; Glynn, R.J.; Giovannucci, E.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Liu, J.; Feldman, S.; Karlson, E.W.; Schneeweiss, S.; Solomon, D.H. Risk of High-Grade Cervical Dysplasia and Cervical Cancer in Women with Systemic Inflammatory Diseases: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaengebjerg, S.; Skov, L.; Egeberg, A.; Loft, N.D. Prevalence, Incidence, and Risk of Cancer in Patients With Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinato, F.; Gisondi, P.; Girolomoni, G. Risk of Lymphohematologic Malignancies in Patients with Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chang, C.W.; Nguyen, P.A.A.; Chang, T.H.; Shih, Y.L.; Chang, W.Y.; Horng, J.T.; Lee, O.K.S.; Ho, J.H.C. Ankylosing Spondylitis and the Risk of Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebwohl, M.; Deodhar, A.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Menter, M.A.; Poddubnyy, D.; Bao, W.; Jehl, V.; Marfo, K.; Primatesta, P.; Shete, A.; et al. The Risk of Malignancy in Patients with Secukinumab-Treated Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis: Analysis of Clinical Trial and Postmarketing Surveillance Data with up to Five Years of Follow-Up. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Chi, C.C. Association of Psoriasis With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, M.d.F.S.P.d.; Rocha, B.d.O.; Duarte, G.V. Psoriasis: Classical and Emerging Comorbidities. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2015, 90, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hueber, W.; Sands, B.E.; Lewitzky, S.; Vandemeulebroecke, M.; Reinisch, W.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Wehkamp, J.; Feagan, B.G.; Yao, M.D.; Karczewski, M.; et al. Secukinumab, a Human Anti-IL-17A Monoclonal Antibody, for Moderate to Severe Crohn’s Disease: Unexpected Results of a Randomised, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gut 2012, 61, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Lenercept Multiple Sclerosis Study Group; The University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group. TNF Neutralization in MS. Neurology 1999, 53, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Targan, S.R.; Feagan, B.; Vermeire, S.; Panaccione, R.; Melmed, G.Y.; Landers, C.; Li, D.; Russell, C.; Newmark, R.; Zhang, N.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Study of Brodalumab in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onac, I.A.; Clarke, B.D.; Tacu, C.; Lloyd, M.; Hajela, V.; Batty, T.; Thoroughgood, J.; Smith, S.; Irvine, H.; Hill, D.; et al. Secukinumab as a Potential Trigger of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Ankylosing Spondylitis or Psoriatic Arthritis Patients. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2021, 60, 5233–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitpain, N.; D’Amico, F.; Yelehe-Okouma, M.; Jouzeau, J.Y.; Netter, P.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Gillet, P. IL-17 Inhibitors and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Postmarketing Study in Vigibase. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrell, K.A.; Murphrey, M.; Kelm, R.C.; Lee, H.H.; Pease, D.R.; Laumann, A.E.; West, D.P.; Nardone, B. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Events after Exposure to Interleukin 17 Inhibitors Secukinumab and Ixekizumab: Postmarketing Analysis from the RADAR (“Research on Adverse Drug Events And Reports”) Program. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, A.E.; Murakami, T.T. New-Onset Collagenous Colitis in a Patient With Psoriatic Arthritis: Can It Be Secukinumab? Cureus 2021, 13, e16147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achufusi, T.G.; Harnee, P.S.; Rawlins, S. A Rare Case of New-Onset Ulcerative Colitis Following Initiation of Secukinumab. Case Rep. Med. 2019, 2019, 2975631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobelo Lozano, M.J.; Serrano Giménez, R.; Castro Fernández, M. Emergence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease During Treatment With Secukinumab. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 1131–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darch, K.M.; Holland, T.L.; Spelman, L.J. Secukinumab-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Patient Treated for Chronic Plaque Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Case Report and Review of the Role of Novel Biologic Agents Targeting the P19 Subunit of IL-23. Case Rep. Med. 2020, 2020, 9404505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S.W.; Levell, N.J.; Shah, S.N.; Gaffney, K.; Tremelling, M.A.W. Severe Colitis Complicating Secukinumab (Cosentyx®) Therapy. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 344–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, D.; Jamaluddin, N.; Pisegna, J.; Padua, D. A Challenging Case of Severe Ulcerative Colitis Following the Initiation of Secukinumab for Ankylosing Spondylitis. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2018, 2018, 9679287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.N.; Veettil, R. A Case of New Onset Ulcerative Colitis Following Secukinumab Treatment. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 80, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, H.; Fukuda, S.; Iijima, K. Interleukin-17A Inhibitor–Induced Crohn’s Disease/Behçet’s Disease-like Lesions. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, E38–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchida, S.; Oiso, N.; Komeda, Y.; Kudo, M.; Kawada, A. Paradoxical Ulcerative Colitis during Treatment with Secukinumab for Psoriasis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2019, 29, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, W.; Al-Naqshabandi, S.; Ahn, C.S.; Bloomfeld, R.S.; Feldman, S.R. Asymptomatic Crohn’s Disease Identified in a Patient Being treatedwith Secukinumab: A Case Report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2050313X1989358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Neimann, A.L.; Shin, D.B.; Wang, X.; Margolis, D.J.; Troxel, A.B. Risk of Myocardial Infarction in Patients With Psoriasis. JAMA 2006, 296, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samarasekera, E.J.; Neilson, J.M.; Warren, R.B.; Parnham, J.; Smith, C.H. Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease in Individuals with Psoriasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungprasert, P.; Srivali, N.; Kittanamongkolchai, W. Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.Y.; Li, E.K.; Tam, L.S. Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.S.; Packer, M.; Lo, K.H.; Fasanmade, A.A.; Willerson, J.T. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Pilot Trial of Infliximab, a Chimeric Monoclonal Antibody to Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Heart Failure: Results of the Anti-TNF Therapy against Congestive Heart Failure (ATTACH) Trial. Circulation 2003, 107, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coletta, A.P.; Clark, A.L.; Banarjee, P.; Cleland, J.G.F. Clinical Trials Update: RENEWAL (RENAISSANCE and RECOVER) and ATTACH. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2002, 4, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Shin, D.B.; Duffin, K.C.; Armstrong, A.W.; Blauvelt, A.; Tyring, S.K.; Menter, A.; Gottlieb, S.; Lockshin, B.N.; Simpson, E.L.; et al. A Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial of Secukinumab on Aortic Vascular Inflammation in Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis (VIP-S). J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, D.; Simac, P.; Katic, J. IgA Vasculitis during Secukinumab Therapy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020 405 2020, 40, 2071–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelli, C.; Loget, J.; Vanhaecke, C.; Durlach, A.; Gagneux-Lemoussu, L.; Soriano, C.; Viguier, M. Cutaneous Vasculitis with Gut Involvement during Secukinumab Treatment for Psoriatic Arthritis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00077-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, A.A.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Baraliakos, X.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Gladman, D.D.; Blanco, R.; Gupta, A.D.; Martin, R.; Safi, J., Jr.; Brian, P.; et al. Incidence of Uveitis in Secukinumab-treated Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis: Pooled Data Analysis From Three Phase 3 Studies. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadwi, H.; Janaini, M.; Zammo, M.; Cheikh, M.; Almoallim, H. New-Onset Uveitis Possibly Caused by Secukinumab in a 47-Year-Old Male Patient with Long-Standing Ankylosing Spondylitis. Int. Med. Case Rep. J. 2020, 13, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Pan, J.Y. Paradoxical Flare of Psoriasis, Psoriatic Spondyloarthritis, and Psoriatic Uveitis after Switching from Infliximab to Secukinumab. Dermatol. Sin. 2017, 35, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisani-Asenbauer, T.; MacA, S.M.; Mejdoubi, L.; Emminger, W.; MacHold, K.; Auer, H. Uveitis—A Rare Disease Often Associated with Systemic Diseases and Infections—A Systematic Review of 2619 Patients. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Li, S.; Ying, S.; Tang, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiao, J.; Fang, H. The IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Inflammatory Skin Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, R.; Beecker, J. Dyshidrotic Eczema in Two Patients on Secukinumab for Plaque: A Case Report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2050313X2090456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarro-Triviño, F.J.; Sanchez-Parera, R.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Secukinumab-Induced Paradoxical Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sladden, M.J.; Sladden, C.S.; Gulliver, W.P.F. Secukinumab-Induced Psoriasiform Eruption. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 1194–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, M.Z.; Pinheiro, J.R.S.; Enokihara, M.M.S.e.S.; Vasconcellos, M.R.d.A. Biologic Therapy-Induced Pemphigus. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2017, 92, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, S.; Zurgil, N.; Machlav, S.; Shinberg, A.; Langevitz, P.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Deutsch, M. Distinct Effects of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Combined Therapy on TH1/TH2 Balance in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2011, 18, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, M.G.; Papp, K.A.; Marangell, L.B.; Koo, J.; Blauvelt, A.; Gooderham, M.; Wu, J.J.; Rastogi, S.; Harris, S.; Pillai, R.; et al. Psychiatric Adverse Events during Treatment with Brodalumab: Analysis of Psoriasis Clinical Trials. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 81–89.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, M.; Leonardi, C.; Wu, J.J.; Armstrong, A.; Rawnsley, N.; Merchant, M.; Alexander, B.; Jacobson, A. Two-Year US Pharmacovigilance Report on Brodalumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Giuliani, F. The Role of Inflammation in Depression and Fatigue. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattei, D.; Westrin, Å.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; Brundin, L. Cytokine Levels in the Blood May Distinguish Suicide Attempters from Depressed Patients. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ho, R.C.M.; Mak, A. The Role of Interleukin (IL)-17 in Anxiety and Depression of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 15, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, B.E.; Langley, R.G.B.; Menter, A.; Magid, M.; Porter, B.; Fox, T.; Safi, J.; Papavassilis, C. No Elevated Risk for Depression, Anxiety or Suicidality with Secukinumab in a Pooled Analysis of Data from 10 Clinical Studies in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, e105–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komori, T.; Otsuka, A.; Honda, Y.; Kanameishi, S.; Honda, T.; Kabashima, K. Exacerbation of Depression in a Psoriatic Arthritis Patient Possibly Induced by Secukinumab. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2016, 26, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackcloud, P.; Dupuy, E.; Kang, Y.; Smart, C.; Hsiao, J. Bullous Acral Eruption Related to Secukinumab. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhoff, G. Secukinumab-Induced Pompholyx in a Psoriasis Patient. Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 26, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.L.; Tobin, C.A.; Sutton, A.; Missall, T.A. Granuloma Annulare in the Setting of Secukinumab. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2018, 2018, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonomo, L.; Ghoneim, S.; Levitt, J. A Case of Granuloma Annulare Associated with Secukinumab Use. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2017, 2017, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheutlin, A.; Schiopu, E. Relapsing Polychondritis Following Treatment with Secukinumab for Ankylosing Spondylitis: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2018, 2018, 6760806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dastoli, S.; Iannone, L.F.; Bennardo, L.; Silvestri, M.; Palleria, C.; Nisticò, S.P.; De Sarro, G.; Russo, E. A Rare Case of Drug-Induced Erectile Dysfunction with Secukinumab Solved After Switch to Ixekizumab in A Psoriatic Patient: A Case Report. Curr. Drug Saf. 2020, 15, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigottu, M.F.; Montesu, M.A. Adverse Skin Reaction to Secukinumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, e432–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitaka, T.; Sawada, Y.; Okada, E.; Nakamura, M. Recurrent Angular Cheilitis after Secukinumab Injections. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2018, 59, e79–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Sawada, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohmori, S.; Omoto, D.; Haruyama, S.; Yoshioka, M.; Okada, E.; Nakamura, M. Drug Eruption Caused by Secukinumab. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.M.; Cohen, L.M.; Yang, C.S.; Kroumpouzos, G. Severe, Ulcerative, Lichenoid Mucositis Associated with Secukinumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2016, 2, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramalho, D.; Araújo, A.; Rocha, G.; Duarte-Ribeiro, F. Secukinumab, Pituitary Enlargement and Panhypopituitarism: Are They Related? Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2021, 8, 003099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.W.; Zhang, M.H.; Gopee, S.; Lu, Y. Cutaneous Sarcoidosis after Application of Secukinumab in a Patient with Plaque Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, E494–E495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currado, D.; Margiotta, D.P.E.; Conforti, C.; Coppola, R.; Panasiti, V.; Afeltra, A.; Navarini, L. New Onset of Psoriasis Induced by Secukinumab in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case Report. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 49, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammadli, K.; Ceken, K.; Unal, B.; Karakas, A.; Yilmaz, E.; Alpsoy, E. Superficial Thrombophlebitis during Secukinumab Treatment in a Patient with Psoriasis. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2020, 86, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peera, M.; Smith, A. Palmoplantar Pompholyx Secondary to Interleukin 17A Inhibitor Therapy for Psoriasis: A Case Series. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrmann, C.; Sondermann, W.; Körber, A. Secukinumab-Induzierter Subakut-Kutaner Lupus Erythematodes. Hautarzt 2017, 69, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes Roncada, E.V.; Brambilla, V.R.; Freitas Filitto, B.; Genta, M.P.; Morgado De Abreu, M.A.M. Atopic Dermatitis as a Paradoxical Effect of Secukinumab for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2021, 13, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincses, E.; Yurttas, B.; Esatoglu, S.N.; Melikoglu, M.; Hamuryudan, V.; Seyahi, E. Secukinumab Induced Behçet’s Syndrome: A Report of Two Cases. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 2019, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, J.; Tian, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X. Secukinumab-Induced Multiple Lentigines in Areas of Resolved Psoriatic Plaques: A Case Report and Literature Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, S.; Khullar, G. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Antagonists: Side Effects and Their Management. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2013, 79 (Suppl. 7), 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobak, S. Secukinumab-Induced Raynaud’s Phenomenon: First Report in the Literature. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2020, 11, 2042098620905976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermon, C.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Durupt, F.; Sève, P. Aphthous Stomatitis in a Man with Psoriatic Arthritis. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, D.; Magri, F.; Persechino, F.; Lepore, A.; Verde, R.; Capalbo, A.; Persechino, S. Vitiligo with Progressive Repigmentation during Secukinumab Treatment in a Patient with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Case Report. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2021, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, B.; Pilson, Q.; Fulcher, T. Secukinumab-Associated Crystalline Corneal Deposition. Cornea 2019, 38, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, C.; Herlihy, D.; Clarke, L.; Mullan, R. Sarcoidosis Manifesting during Treatment with Secukinumab for Psoriatic Arthritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, 240615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, N.; Sami, N.; Shulman, K.; Bég, S. Secukinumab-Induced Scleroderma: A Case Report. Rheumatology 2021, 60, e99–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, A.J.; Whitley, M.J.; Balaban, A.; Ellington, K.; Marano, A.L. Pyoderma Gangrenosum Induced by Secukinumab in a Patient with Psoriasis Successfully Treated with Ustekinumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oiwa, T.; Honda, T.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Three Cases of Facial Erythema with Dryness and Pruritus in Psoriasis Patients during Treatment with IL-17 Inhibitors. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, e122–e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Igarashi, A.; Okamura, K.; Suzuki, T. Paradoxical Exacerbation of Latent Interstitial Pneumonia by Secukinumab in a Patient with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 684–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajihara, I.; Yamada-Kanazawa, S.; Maeda-Otsuka, S.; Jinnin, M.; Akaike, K.; Ihn, H. Secukinumab-Induced Interstitial Pneumonia in a Patient with Psoriasis Vulgaris. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, e322–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noell, C.; McQuade, B.; Gottlieb, A.; Rosmarin, D. Anti IL-17 Flared Psoriasis in a Patient on Secukinumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, O.L.; Hsu, S. Perianal Dermatophytosis During Secukinumab Therapy for Plaque Psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 486–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, P.H.; Tsai, T.F. Development of Bullous Pemphigoid during Secukinumab Treatment for Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, e220–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranwell, W.C.; Doolan, B.J.; Radulski, B.; Nicolopoulos, J.; Dolianitis, C. Pseudolymphoma Induced by Secukinumab for Treatment of Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2019, 60, e246–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Akasaka, E.; Nakano, H.; Sawamura, D. Pyoderma Gangrenosum Triggered by Switching from Adalimumab to Secukinumab. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, e108–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaquen, M.; Yawalkar, N.; Feldmeyer, L.; Borradori, L.; Schlapbach, C. Herpetiform Aphthous Ulcerations Induced by Secukinumab: Report of 2 Cases. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlando, M.; Cozzani, E.; Russo, R.; Parodi, A. Atopic-like Dermatitis after Secukinumab Injection: A Case Report. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshina, D.; Haga, N.; Furuya, K.; Sakai, M. Paradoxical Localized Exacerbation of Psoriatic Eruptions Triggered by Secukinumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 43, 718–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollina, U.; Schönlebe, J.; Fürll, C. Pyoderma Gangrenosum Induced by Secukinumab—A Late Paradoxical Drug Reaction. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.A.; Hader, I.; Aqel, Z. Novel Presentation of Terminal Ileitis Associated with Secukinumab Therapy. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2021, 2021, 5213876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, P.A.; Kalim, H.; Prawitasari, S.; Raharjo, F.M. Possible Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Induced by Secukinumab: A Case Report. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2022, 41, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.B.; Reich, K.; Langley, R.G.; Strober, B.; Gladman, D.; Deodhar, A.; Bachhuber, T.; Bao, W.; Altemeyer, E.; Hussain, S.; et al. Secukinumab in Pregnancy: Outcomes in Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis from the Global Safety Database. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 1205–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blair, H.A. Secukinumab: A Review in Moderate to Severe Pediatric Plaque Psoriasis. Paediatr. Drugs 2021, 23, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megna, M.; Camela, E.; Cinelli, E.; Fabbrocini, G. Real-Life Efficacy and Safety of Secukinumab in Elderly Patients with Psoriasis over a 2-Year Period. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vana, A.M.; Freyman, A.W.; Reich, S.D.; Yin, D.; Li, R.; Anderson, S.; Jacobs, I.A.; Zacharchuk, C.M.; Ewesuedo, R. Evaluating Imbalances of Adverse Events during Biosimilar Development. mAbs 2016, 8, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Adverse Event Class | Adverse Events |
|---|---|
| Type-α | None reported to date |
| Type-β | Hypersensitivity and injection site reactions |
| Type-γ | Inflammatory bowel disease, infections, allergic and atopic disorders, neutropenia, and paradoxical inflammatory adverse events. |
| Type-δ | None reported to date |
| Type-ε | Major adverse cardiovascular events, malignancy |
| Author(s) | Adverse Drug Event | Indication | Age/Sex | Duration Since Initiation of Secukinumab | Previous History of Biologic Use | Concomitant Medication | Management | Discontinuation of Secukinumab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinha et al. [60] | Herpes keratitis | Psoriasis | 35/M | 4 weeks | No | NA | 3% Acyclovir five times a day, topical moxifloxacin eye drops four times a day, along with topical lubricant eye drops, topical steroids, and emollients for psoriasis | NA |
| Wang [63] | Scleritis due to Histoplasma capsulatum | Ankylosing spondylitis | 45/M | NA | NA | Intravitreal triamcinolone; topical prednisolone; oral prednisone | Left eye: oral itraconazole 200 mg twice daily and fortified topical amphotericin B 0.15% four times daily with a rapid taper of oral prednisone. Right eye: topical amphotericin for two months until the subconjunctival purulence resolved. Maintenance: 6-month course of itraconazole | NA |
| Martin et al. [64] | Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome | Psoriasis | 6/F | 2 weeks | NA | NA | Levofloxacin and rifampin, followed by trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, and cefuroxime unt | Yes |
| Utiyama et al. [65] | Infective dermatitis | Psoriasis | 71/F | 2 months | No | NA | Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim followed by doxycycline. | Yes |
| Fisher et al. [66] | Necrotising fasciitis | Psoriasis | 18/M | 4 weeks | No | NA | Surgical debridement followed by intravenous antibiotics | No |
| Anderson et al. [67] | Invasive Haemophilus influenzae | Psoriatic arthritis | 42/F | 18 months | Yes | NA | Empiric gentamicin and metronidazole, which was narrowed to ceftriaxone and metronidazole | NA |
| Author(s) | Adverse Drug Event | Indication | Age/Sex | Duration Since Initiation of Secukinumab | Previous History of Biologic Use | Concomitant Medication | Management | Discontinuation of Secukinumab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picciani et al. [73] | Oral candidiasis | Psoriasis | 50/F | 6 months | Yes | NA | Miconazole gel | Resumed at a lower dose after management |
| Kang et al. [74] | Oesophageal candidiasis | Psoriasis | 61/M | 3 weeks | NA | NA | Fluconazole 200 mg/day for seven days; switched to guselkumab after infection resolved | Yes |
| Faccini et al. [75] | Candidemia | Psoriatic arthritis | 42/F | 2 months | Yes | NA | Amphotericin B switched to anidulafungin 100 mg OD. | Yes |
| Farah [76] | Hyperplastic candidosis and oral lichenoid lesion | Psoriasis | 52/F | NA | NA | Perindopril arginine, pantoprazole, mometasone furoate. | Oral | No |
| Capusan et al. [77] | Oral lichenoid reaction with candidiasis | Psoriasis | 62/M | 8 months | Yes | NA | Intralesional corticosteroids and itraconazole; switched to apremilast for psoriasis | Yes |
| Komori et al. [78] | Oral lichen planus with candidiasis | Psoriasis | 74/F | 5 months | Yes | NA | Amphotericin B syrup | Yes |
| Author(s) | Adverse Drug Event | Indication | Age/Sex | Duration Since Initiation of Secukinumab | Previous History of Biologic Use | Concomitant Medication | Management | Discontinuation of Secukinumab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Achufusi et al. [105] | Ulcerative colitis | Psoriasis | 39/M | 6 months | NA | NA | Infliximab (symptomatic relief) and apremilast (for psoriasis) | Yes |
| Ehrlich et al. [109] | Ulcerative colitis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 42/M | 6 weeks | Yes | Naproxen; Methotrexate | Methylprednisolone for 1 month (unsatisfactory) followed by ixekizumab | Yes |
| Darch et al. [107] | Inflammatory bowel disease | Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis | 54/F | 14 months | No | NSAIDs | Tildrakizumab | Yes |
| Lozano et al. [106] | Ileocolic Crohn’s disease | Psoriasis | 19/F | 2 months | No | NA | Corticosteroid and switched to ustekinumab | Yes |
| Ulcerative colitis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 60/M | 3 weeks | No | Naproxen; sulphasalazine | Full-dose intravenous steroid treatment, mesalazine enemas, and initiation of infliximab for corticosteroid refractoriness | Yes | |
| Obeidat et al. [104] | Ulcerative colitis | Psoriatic arthritis | 41/F | 9 months | NA | Venlafaxine, NSAIDs, and sulfasalazine | The patient was started on budesonide with significant improvement in her symptoms. Budesonide was eventually tapered, and the patient was started on azathioprine as a steroid-sparing agent and immunomodulator | Yes |
| Johnston et al. [110] | Ulcerative colitis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 27/M | 4 months | Yes | NA | Intravenous cortisone and switch to infliximab. | Yes |
| Shiga et al. [111] | Crohn’s disease/Behcet’s disease–like lesions | Psoriasis | 56/M | 8 weeks | No | NA | Oral prednisolone 40 mg OD | NA |
| Uchida et al. [112] | Ulcerative colitis | Psoriasis | 41/F | 4 months | Yes | NA | Mesalazine 2400 mg daily and switch to adalimumab 20 mg | Yes |
| Lee et al. [108] | Ulcerative colitis | Psoriasis | 52/M | 4 months | Yes | NA | subtotal colectomy | Yes |
| Ulcerative colitis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 38/M | 3 weeks | Yes | NA | IV infliximab 5 mg/kg | Yes | |
| Haidari et al. [113] | Asymptomatic Crohn’s disease | Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis | 69/M | 18 months | Yes | NA | Ustekinumab for CD and switch guselkumab for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. | Yes |
| Author(s) | Adverse Drug Event | Indication | Age/Sex | Duration since Initiation of Secukinumab | Previous History of Biologic Use | Concomitant Medication | Management | Discontinuation of Secukinumab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Navarro-Triviño et al. [129] | Hidradenitis suppurativa | Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis | 58/M | NA | Yes | NA | Ustekinumab (45 mg) 16 weeks | Yes |
| Blackcloud et al. [140] | Bullous acral eruption | Psoriasis | 44/F | ~1 month | Yes | Halobetasol ointment; fluocinonide gel; tacrolimus ointment; metformin; spironolactone; norethindrone-ethinyl estradiol; albuterol | Cyclosporine 100 mg BD and corticosteroid wet wraps | Yes |
| Gerhard Eichhoff [141] | Pompholyx | Psoriasis | 35/M | 3 months | Yes | NA | Clobetasol propionate 0.05% cream | No |
| Clark et al. [142] | Granuloma annulare | Psoriasis | 69/F | 6 months | Yes | Lisinopril; metformin; pravastatin; citalopram; alprazolam | Rifampin, levofloxacin, and minocycline for six months (unsatisfactory), followed by etanercept for six weeks (event resolved) | Yes |
| Bonomo et al. [143] | Granuloma annulare | Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis | 60/M | 2 weeks | Yes | Methotrexate; levothyroxine; omeprazole; duloxetine | Topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% cream | No |
| Zheutlin et al. [144] | Polychondritis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 56/M | 3–4 months | Yes | NA | Prednisone, methotrexate, and folate therapy | Yes |
| Hayashida et al. [131] | Pemphigus | Rheumatoid arthritis | 41/F | 3 months | Yes | Methotrexate; prednisone; paracetamol | Higher dose of methotrexate and topical steroid, and tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis | Yes |
| Sladden et al. [130] | Psoriasiform eruption | Psoriasis | 61/F | 3 months | Yes | NA | 1% Methotrexate gel and ustekinumab | Yes |
| Dastoli et al. [145] | Erectile dysfunction | Psoriasis | 45/M | 2 months | No | NA | Infliximab | Yes |
| Peigottu et al. [146] | Drug eruption | Psoriasis | 57/F | ~3–4 weeks | Yes | NA | Topical and systemic corticosteroids | Yes |
| Hitaka et al. [147] | Angular cheilitis | Psoriasis | 23/F | 2 months (appeared 3 days after every secukinumab injection) | NA | NA | Adalimumab | Yes |
| Shibata et al. [148] | Drug eruption | Psoriatic arthritis | 52/F | ~2–3 weeks | NA | NA | Topical betamethasone butyrate propionate ointment for skin eruption | No |
| Thompson et al. [149] | Ulcerative lichenoid mucositis | Psoriasis | 62/M | 1 week | Yes | NA | 0.1% Triamcinolone in orabase paste | Yes |
| Ramalho et al. [150] | Pituitary enlargement and panhypopituitarism | Psoriasis | 66/M | 3 years | NA | NA | Oral hydrocortisone 40 mg in the morning and 20 mg in the afternoon; levothyroxine 50 μg/day | Yes |
| Nadwi et al. [124] | Anterior uveitis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 47/M | 6 months | Yes | NA | Local corticosteroid eye drops for 2 months | No |
| Su et al. [125] | Uveitis | Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis | 45/M | 3 weeks | Yes | NA | Infliximab 5 mg/kg | Yes |
| Lu et al. [151] | Cutaneous sarcoidosis | Psoriasis | 36/M | 45 days | No | NA | No treatment. Symptoms resolved on their own in 2 months. | Yes |
| Currado et al. [152] | Psoriasis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 54/F | 11 months | Yes | NA | Calcipotriol, betamethasone cream and oral NSAIDs | Yes |
| Mammadli et al. [153] | Thrombophlebitis | Psoriasis | 48/M | 1 week | Yes | NA | Treatment with Ustekinumab | Yes |
| Peera et al. [154] | Palmoplantar pompholyx | Psoriasis | 65/F | 7 weeks | NA | NA | Resolution of symptoms 4 weeks after secukinumab discontinuation. | Yes |
| Palmoplantar pompholyx | Psoriasis | 64/F | 4 months | No | NA | Resolution of symptoms 1 month after secukinumab discontinuation and switch to ustekinumab | Yes | |
| Wehrmann et al. [155] | Drug-induced lupus erythematosus | Psoriasis | 52/F | 5 months | NA | NA | Ustekinumab | Yes |
| Bose et al. [128] | Eczema | Psoriasis | 52/F | 8 months | No | NA | Cyclosporine and guselkumab | Yes |
| Eczema | Psoriasis | 69/F | 7 weeks | NA | NA | Infliximab and apremilast | Yes | |
| Roncada et al. [156] | Atopic dermatitis | Psoriasis | 59/F | 2 months | NA | NA | Cyclosporine, 5 mg/kg/dose; intravenous antibiotic therapy, and skin barrier restorative creams and topical corticosteroids | Yes |
| Dincses et al. [157] | Behçet’s syndrome | Ankylosing spondylitis | 34/M | 3 weeks | Yes | NA | 10 mg/day of prednisolone and certolizumab | Yes |
| Behçet’s syndrome | Ankylosing spondylitis | 29/M | 2 weeks | Yes | NA | Three pulses of methylprednisolone and infliximab 5 mg/kg | Yes | |
| Zhang et al. [158] | Multiple lentigines | Psoriasis | 46/M | 3 months | NA | NA | NA | No |
| Dogra et al. [159] | Paradoxical pustular psoriasis | Psoriasis | 22/M | 9 months | NA | NA | Complete remission was finally attained after intravenous administration of infliximab 300 mg | Yes |
| Kobak [160] | Raynaud’s phenomenon | Ankylosing spondylitis | 35/F | 3 months | Yes | NA | Low-dose aspirin and calcium channel blockers | No |
| Fermon et al. [161] | Aphthous Stomatitis | Psoriatic arthritis | 57/M | 6 months | Yes | Clopidogrel, flecainide and oral potassium. | High dose of corticosteroids and then with adalimumab again | Yes |
| Giordano et al. [162] | Vitiligo | Psoriatic arthritis | 42/F | 1 year | No | NA | NA | No |
| Power et al. [163] | Crystalline corneal deposition | Ankylosing spondylitis | 18/M | 6 months | No | Budesonide, formoterol fumarate, salbutamol, and montelukast | Observed for 12 months. | No |
| Kirby et al. [164] | Multisystem sarcoidosis | Psoriatic arthritis | 52/F | 6 months | Yes | Long-acting beta-agonist and corticosteroid inhalers. | Prednisolone 30 mg by mouth daily, tapered down to 5 mg monthly. | Yes |
| Elias et al. [165] | Scleroderma | Psoriatic arthritis | 46/F | 19 months | NA | Hydrochlorothiazide and levothyroxine | Secukinumab was discontinued, and symptoms resolved gradually. | Yes |
| Petty et al. [166] | Pyoderma gangrenosum | Psoriasis | 50’s/F | 2 weeks | No | NA | Ustekinumab 90 mg | Yes |
| Oiwa et al. [167] | Facial erythema with dryness and pruritus | Psoriasis | 49/M | 3 weeks | NA | NA | Petrolatum | NA |
| Hayashi et al. [168] | Latent interstitial pneumonia | Psoriasis | 66/M | 10 Months | NA | NA | Oral prednisolone and subsequent intravenous high-dose methylprednisolone were administered | Yes |
| Kajihara et al. [169] | Interstitial pneumonia | Psoriasis | 36/M | 18 weeks | Yes | NA | Symptoms resolved 5 weeks after secukinumab discontinuation. | Yes |
| Noell et al. [170] | Flared Psoriasis | Psoriasis | 53/F | Shortly after initiation | Yes | NA | Transition to infliximab after ustekinumab and corticosteroids. | Yes |
| Quach et al. [171] | Perianal dermatophytosis | Psoriasis | 40’s/F | 3 Months | NA | NA | Terbinafine 250 mg OD and butenafine cream BID for 1 month | NA |
| Perianal dermatophytosis | Psoriasis | 60’s/F | 5 weeks | NA | NA | Oral amphotericin B for 14 days and terbinafine cream for 1 month | NA | |
| Ho et al. [172] | Bullous pemphigoid | Psoriasis | 65/F | 8 days | Yes | NA | Clobetasol dipropionate | No |
| Cranwell et al. [173] | Pseudolymphoma | Psoriasis | 56/M | 3 days | NA | NA | Switch to topical therapy | Yes |
| Jin et al. [174] | Pyoderma gangrenosum | Psoriatic arthritis | 47/F | 4 months | Yes | NA | Oral cyclosporin, 2.5 mg/kg per day, | Yes |
| Benzaquen et al. [175] | Herpetiform aphthous ulcerations | SAPHO syndrome | 35/F | 5 weeks | Yes | NA | 3 weeks with betamethasone mouthwash. Reduction of secukinumab dose to 150 mg. | No |
| Herpetiform aphthous ulcerations | Psoriasis | 37/F | 4 weeks | Yes | NA | Switch to ustekinumab, and lesions resolved within 3 weeks. | Yes | |
| Burlando et al. [176] | Atopic like dermatitis | Psoriasis | 70/F | 6 months | No | NA | Symptoms resolved after discontinuation and topicals and phototherapy for psoriasis. | Yes |
| Hoshina et al. [177] | Psoriatic eruptions | Psoriasis | 43/F | 4 weeks | Yes | NA | Cyclosporine 200 mg/day. | Yes |
| Wollina et al. [178] | Pyoderma gangrenosum | Psoriasis | 33/F | 12 months | No | NA | Systemic prednisolone 100 mg/day, pantoprazole, topical corticosteroids. | NA |
| Perkovic et al. [121] | IgA vasculitis | Ankylosing spondylitis | 39/F | 18 months | Yes | NA | Methotrexate reintroduced 15 mg/week, | Yes |
| Chelli et al. [122] | Cutaneous vasculitis with gut involvement | Psoriatic arthritis | 54/F | 1 month | Yes | NA | Prednisone and colchicine for symptomatic management. Methotrexate 15 mg/kg was restarted. | Yes |
| Shaheen et al. [179] | Terminal Ileitis | Psoriatic arthritis | 39/M | 2 months | NA | NA | Ciprofloxacin and metronidazole later switched to piperacillin-tazobactam and received total parenteral nutrition | Yes |
| Rahman et al. [180] | Autoimmune hemolytic anaemia | Psoriasis | 39/M | 8 weeks | NA | NA | No | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eshwar, V.; Kamath, A.; Shastry, R.; Shenoy, A.K.; Kamath, P. A Review of the Safety of Interleukin-17A Inhibitor Secukinumab. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111365
Eshwar V, Kamath A, Shastry R, Shenoy AK, Kamath P. A Review of the Safety of Interleukin-17A Inhibitor Secukinumab. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111365
Chicago/Turabian StyleEshwar, Vishnu, Ashwin Kamath, Rajeshwari Shastry, Ashok K. Shenoy, and Priyanka Kamath. 2022. "A Review of the Safety of Interleukin-17A Inhibitor Secukinumab" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111365
APA StyleEshwar, V., Kamath, A., Shastry, R., Shenoy, A. K., & Kamath, P. (2022). A Review of the Safety of Interleukin-17A Inhibitor Secukinumab. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111365