Challenges in the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Pediatric Asthma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Definition
1.2. Diagnosis
1.3. Asthma Phenotypes, Genotypes and Biomarkers
1.4. Classification of Asthma Severity
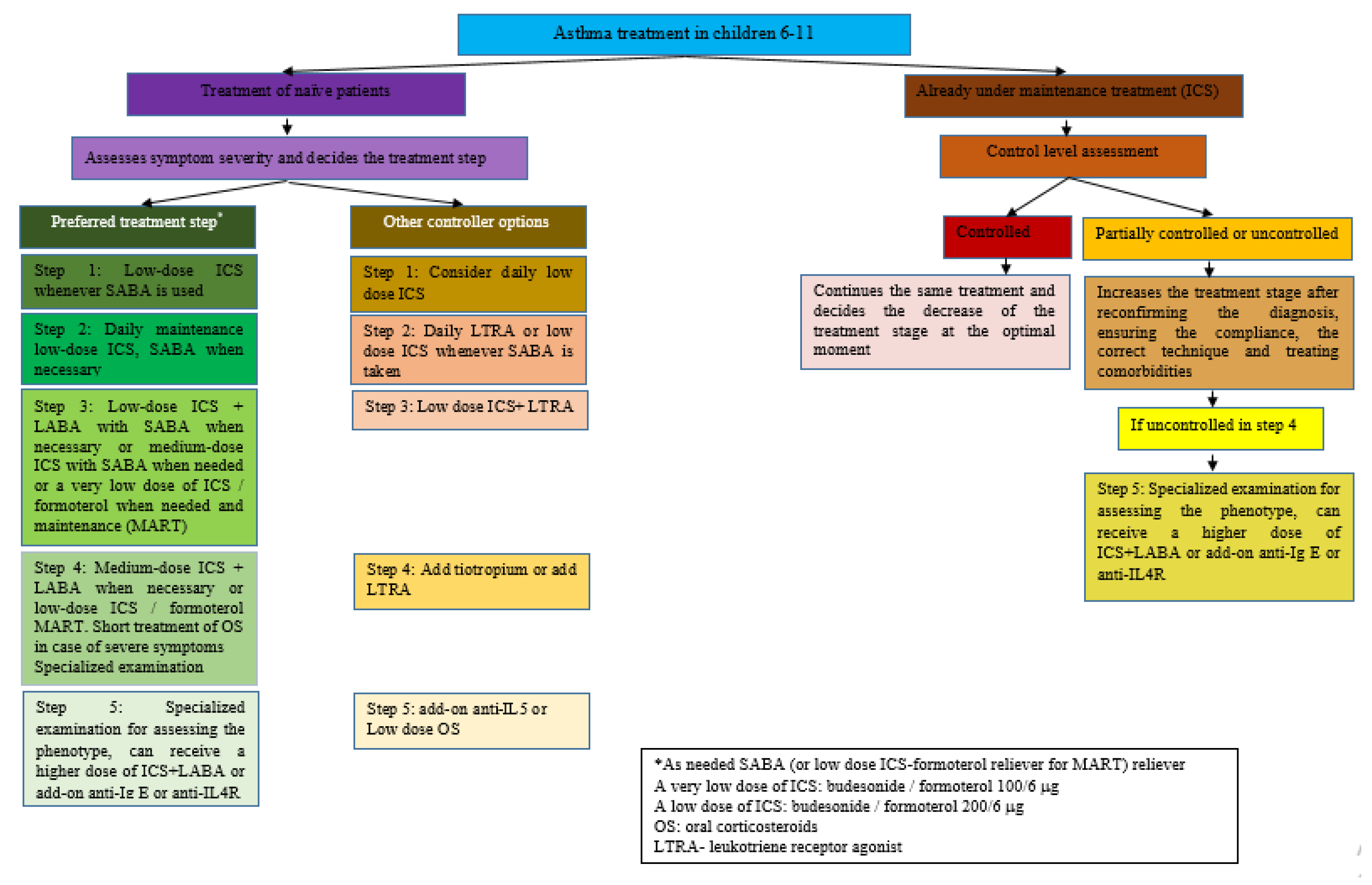
2. Asthma Medication
3. Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
3.1. Uncontrolled, Difficult-to-Treat Asthma and Severe Asthma
3.2. Management of Severe Asthma
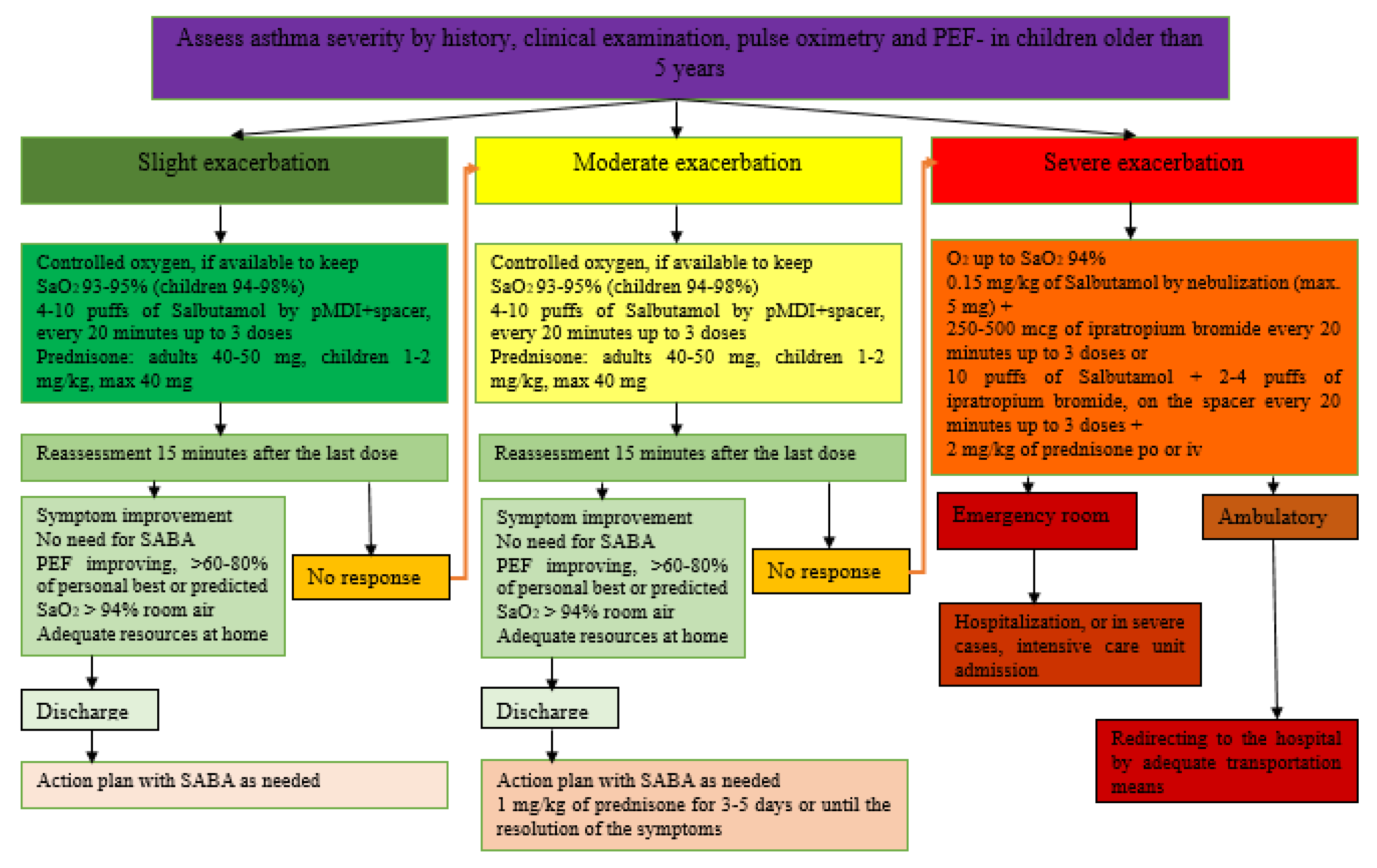
3.3. Management of Exacerbations of Bronchial Asthma
4. Inhaled Corticotherapy Doses Used for Pediatric Patients
5. Vaccination in the Asthmatic Patient
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaillard, E.A.; Kuehni, C.E.; Turner, S.; Goutaki, M.; Holden, K.A.; de Jong, C.C.; Lex, C.; Lo, D.K.; Lucas, J.S.; Midulla, F.; et al. European Respiratory Society clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis of asthma in children aged 5–16 years. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Čustović, A.; Cabana, M.D.; Dell, S.D.; Deschildre, A.; Hedlin, G.; Hossny, E.; Le Souëf, P.; Matricardi, P.M.; Nieto, A.; et al. Pediatric asthma: An unmet need for more effective, focused treatments. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 30, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini Belinchon, J.; Ortega Casanueva, C.; Ariiba Mendez, S. New approach in the treatment pf children with asthma. Pediatr. Integral 2021, XXV, 67–75–EN. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.L.; Custovic, A. Epidemiology of Asthma in Children and Adults. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, O.; Abdelateef, H.; Pozo Beltrán, C.F.; El-Sayed, Z.A.; Gómez, R.M.; Hossny, E.; Morais-Almeida, M.; Nieto, A.; Phipatanakul, W.; Pitrez, P.; et al. Challenges and choices in the pharmacological treatment of non-severe pediatric asthma: A commentary for the practicing physician. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2022. Available online: www.ginasthma.org (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Reddel, H.K.; Bateman, E.D.; Schatz, M.; Krishnan, J.A.; Cloutier, M.M. A Practical Guide to Implementing SMART in Asthma Management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, S31–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Panel Working Group of the National Heart; Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Administered and Coordinated National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Coordinating Committee (NAEPPCC); Cloutier, M.M.; Baptist, A.P.; Blake, K.V.; Brooks, E.G.; Bryant-Stephens, T.; DiMango, E.; Dixon, A.E.; Elward, K.S.; et al. 2020 Focused Updates to the Asthma Management Guidelines: A Report from the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1217–1270, Correction on J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1528–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, V.V.; Miron, I.; Tarca, E.; Trandafir, L.M.; Anton-Paduraru, D.T.; Moisa, S.M.; Starcea, M.; Cernomaz, A.; Miron, L.; Lupu, A. Gastroesophageal reflux in children with asthma. Children 2022, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, J.; Jackson, D.J.; Kent, B.D. Over- and under-diagnosis in asthma. Breathe 2019, 15, e20–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral, L.; Vizmanos, G.; Torres-Borrego, J.; Praena-Crespo, M.; Tortajada-Girbés, M.; Pellegrini, F.; Asensio, Ó. Asthma diagnosis in infants and preschool children: A systematic review of clinical guidelines. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2019, 47, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licari, A.; Castagnoli, R.; Brambilla, I.; Marseglia, A.; Tosca, M.A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Ciprandi, G. Asthma Endotyping and Biomarkers in Childhood Asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2018, 31, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, L.A.; Cabana, M.D.; Rastogi, D. Defining pediatric asthma: Phenotypes to endotypes and beyond. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resiliac, J.; Brooks, C.D.; Grayson, M.H. Immunopathology of Differing Viral Infection in Allergic Asthma Disease. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2022, 42, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coverstone, A.M.; Seibold, M.A.; Peters, M.C. Diagnosis and Management of T2-High Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Hicks, E.; Mitchell, P.; Reisman, J.; Podgers, D.; Hayward, K.M.; Waite, M.; Ramsey, C.D. Canadian Thoracic Society 2021 Guideline update: Diagnosis and management of asthma in preschoolers, children and adults. Can. J. Respir. Crit. 2021, 5, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kama, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Koike, T.; Enseki, M.; Hirai, K.; Mochizuki, H.; Kato, M. Allergic Sensitization Is Crucial for the Suppressive Role of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the Acute Exacerbation of Asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 183, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciprandi, G.; Marseglia, G.L.; Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; Tosca, M.A. Pragmatic Markers in the Management of Asthma: A Real-World-Based Approach. Children 2020, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainardi, V.; Caffarelli, C.; Bergamini, B.M.; Biserna, L.; Bottau, P.; Corinaldesi, E.; Dondi, A.; Fornaro, M.; Guidi, B.; Lombardi, F.; et al. Management of Children with Acute Asthma Attack: A RAND/UCLA Appropriateness Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulhan-Kilroy, J.; Elliott, S.A.; Scott, S.D.; Hartling, L. Parents’ self-reported experiences and information needs related to acute pediatric asthma exacerbations: A mixed studies systematic review. PEC Innov. 2022, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, R.P.; Satia, I.; O’Byrne, P.M. Asthma maintenance and reliever therapy: Should this be the standard of care? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 125, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Hashmi, M.F.; Chakraborty, R.K. Asthma Medications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 18 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Berge, M.; Ten Hacken, N.; Kerstjens, H.; Postma, D. Management of Asthma with ICS and LABAs: Different treatment strategies. Clin. Med. Ther. 2009, 1, CMT-S2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.J.; Dryden, C.; Westwood, J.; Anderson, E.; Thompson, A.; Urquhart, D. Once daily combined inhaled steroid and ultra long-acting bronchodilator prescribing in pediatric asthma: A dual Center retrospective cohort study. J. Asthma 2021, 58, 512–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio Buendía, J.; Patiño, D.G. Fluticasone furoate plus vilanterol in patients with moderate persistent asthma: A cost-utility analysis. J. Asthma. 2022, 1–8, ahead of print.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardana, N.C.; Durham, S.R. New approaches to allergen immunotherapy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perikleous, E.P.; Steiropoulos, P.; Nena, E.; Paraskakis, E. Biologic Therapies in Pediatric Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; McMahon, P.M.; Welch, E.; McMahill-Walraven, C.; Jamal-Allial, A.; Zhang, T.; Draper, C.; Kline, A.M.; Koerner, L.; Brown, J.S.; et al. Use of Mepolizumab in Children and Adolescents with Asthma in the USA. J. Respir. 2022, 2, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Mansfield, L. Step-up and step-down treatments for optimal asthma control in children and adolescents. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Efraij, K.; FitzGerald, J.M. Benralizumab for the add-on maintenance treatment of patients with severe asthma aged 12 years and older with an eosinophilic phenotype. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. PK/PD and Long Term Safety Study of Benralizumab in Children with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma (TATE). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04305405 (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Domingo, C.; Rello, J.; Sogo, A. As-needed ICS-LABA in Mild Asthma: What Does the Evidence Say? Drugs 2019, 79, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, M.L. Precision Medicine Childhood Asthma: AGuide for the Unwary. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancox, R.J.; Cowan, J.O.; Flannery, E.M.; Herbison, G.P.; McLachlan, C.R.; Taylor, D.R. Bronchodilator tolerance and rebound bronchoconstriction during regular inhaled beta-agonist treatment. Respir. Med. 2000, 94, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldridge, R.E.; Hancox, R.J.; Robin Taylor, D.; Cowan, J.O.; Winn, M.C.; Frampton, C.M.; Town, G.I. Effects of terbutaline and budesonide on sputum cells and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, R.H.; Shah, M.B.; D’Souza, A.O.; Dhamane, A.D.; Schatz, M. Short-acting β-agonist use and its ability to predict future asthma-related outcomes. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012, 109, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwaru, B.I.; Ekström, M.; Hasvold, P.; Wiklund, F.; Telg, G.; Janson, C. Overuse of short-acting β2-agonists in asthma is associated with increased risk of exacerbation and mortality: A nationwide cohort study of the global SABINA programme. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suissa, S.; Ernst, P.; Boivin, J.F.; Horwitz, R.I.; Habbick, B.; Cockroft, D.; Blais, L.; McNutt, M.; Buist, A.S.; Spitzer, W.O. A cohort analysis of excess mortality in asthma and the use of inhaled beta-agonists. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149 Pt. 1, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneswarao, J.; Hassali, M.A.; Ibrahim, B.; Saini, B.; Ali, I.A.H.; Verma, A.K. It is time to change the way we manage mild asthma: An update in GINA 2019. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, K.R.; Hong, J.G.; Wandalsen, G.; Larenas-Linnemann, D.; El Beleidy, A.; Zaytseva, O.V.; Pedersen, S.E. Nebulized Inhaled Corticosteroids in Asthma Treatment in Children 5 Years or Younger: A Systematic Review and Global Expert Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizzo, J.M.; Cortes, S. Pediatric Asthma. [Updated 2021 Aug 11]. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551631/ (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Jat, K.R.; Gupta, A. Recent Advances in Long-Term Management of Asthma. Indian J. Pediatr. 2022, 89, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieraj, D.M.; Weeda, E.R.; Nguyen, E.; Coleman, C.I.; White, C.M.; Lazarus, S.C.; Blake, K.V.; Lang, J.E.; Baker, W.L. Association of Inhaled Corticosteroids and Long-Acting β-Agonists as Controller and Quick Relief Therapy With Exacerbations and Symptom Control in Persistent Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2018, 319, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakkasela, J.; Salmela, P.; Juntunen, P.; Karjalainen, J.; Lehtimäki, L. Adherence to treatment guidelines and good asthma control in Finland. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2022, 10, 2149918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijnenburg, M.W.; Fleming, L. Advances in understanding and reducing the burden of severe asthma in children. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.L.; Hicks, E.A.; Mitchell, P.; Reisman, J.; Podgers, D.; Hayward, K.M.; Waite, M.; Ramsey, C.D. 2021 Canadian Thoracic Society Guideline—A focused update on the management of very mild and mild asthma. Can. J. Respir. Crit. Care Sleep Med. 2021, 5, 205–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haktanir Abul, M.; Phipatanakul, W. Severe asthma in children: Evaluation and management. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agache, I.; Beltran, J.; Akdis, C.; Akdis, M.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; Canonica, G.W.; Casale, T.; Chivato, T.; Corren, J.; del Giacco, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of treatment with biologicals (benralizumab, dupilumab, mepolizumab, omalizumab and reslizumab) for severe eosinophilic asthma. A systematic review for the EAACI Guidelines—Recommendations on the use of biologicals in severe asthma. Allergy 2020, 75, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henriksen, D.P.; Bodtger, U.; Sidenius, K.; Maltbaek, N.; Pedersen, L.; Madsen, H.; Andersson, E.A.; Norgaard, O.; Madsen, L.K.; Chawes, B.L. Efficacy of omalizumab in children, adolescents, and adults with severe allergic asthma: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and call for new trials using current guidelines for assessment of severe asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipps, B.E.; Lanier, B.; Milgrom, H.; Deschildre, A.; Hedlin, G.; Szefler, S.J.; Kattan, M.; Kianifard, F.; Ortiz, B.; Haselkorn, T.; et al. Omalizumab in children with uncontrolled allergic asthma: Review of clinical trial and real-world experience. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1431–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowden, R.; Turner, S. Past asthma exacerbation in children predicting future exacerbation: A systematic review. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00174–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, K.M.; Flemyng, E.; Quon, B.S.; Leung, C. Increased versus stable doses of inhaled corticosteroids for exacerbations of chronic asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 9, CD007524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhogal, S.K.; McGillivray, D.; Bourbeau, J.; Benedetti, A.; Bartlett, S.; Ducharme, F.M. Early administration of systemic corticosteroids reduces hospital admission rates for children with moderate and severe asthma exacerbation. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2012, 60, 84–91.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.; Lawton, A.; Gupta, A. Asthma Attacks in Children-Challenges and Opportunities. Indian J. Pediatr. 2022, 89, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, E.D.; Chan, K.; Allain, D.; Chauvin-Kimoff, L. Managing an acute asthma exacerbation in children. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 26, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, B.S.; Miller, N.Z. Analysis of health outcomes in vaccinated and unvaccinated children: Developmental delays, asthma, ear infections and gastrointestinal disorders. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120925344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaratna, S.; Estcourt, M.J.; Burgess, J.; Waidyatillake, N.; Enoh, E.; Lowe, A.J.; Peters, R.; Koplin, J.; Dhamage, S.C.; Lodge, C.J. Childhood vaccination and allergy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2021, 76, 2135–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieckmann, A.; Hærskjold, A.; Benn, C.S.; Aaby, P.; Lange, T.; Sørup, S. Measles, mumps and rubella vs diphtheria-tetanus-acellular-pertussis-inactivated-polio-Haemophilus influenzae type b as the most recent vaccine and risk of early ‘childhood asthma’. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 2026–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, K.L.; Huq, S.I.; Lix, L.M.; Becker, A.B.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Delay in diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus vaccination is associated with a reduced risk of childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, F.; Gu, D.; Kramarz, P.; Truman, B.I.; Iademarco, M.F.; Mullooly, J.P.; Jackson, L.A.; Davis, R.L.; Black, S.B.; Shinefield, H.R.; et al. Childhood vaccinations and risk of asthma. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 21, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogt, H.; Bråbäck, L.; Kling, A.M.; Grünewald, M.; Nilsson, L.; Byington, C.L.; Barnett, E.D.; Dele Davies, H.; Edwards, K.M.; Jackson, M.A.; et al. Pertussis immunization in infancy and adolescent asthma medication. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, J.E.; Mullooly, J.P.; Drew, L.; DeStefano, F. Infant vaccinations and childhood asthma among full-term infants. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2004, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, A.; Bodajko-Grochowska, A.; Klepacz, R.; Szczekala, K.; Zarzycka, D.; Emeryk, A. Clinical form of asthma and vaccine immunity in preschoolers. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Hasan, S.M.T.; Zaman, K.; Takanashi, S.; Hore, S.K.; Yeasmin, S.; Ahmad, S.M.; Alam, J.; Jimba, M.; Iwata, T.; et al. Impact of Haemophilus influenzae type b combination vaccination on asthma symptoms and pneumonia in 5-year-old children in rural Bangladesh: A longitudinal study and comparison with a previous cross-sectional study. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for adults with immunocompromising conditions: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2012, 61, 816–819. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Baz, I.; Navascués, A.; Casado, I.; Portillo, M.E.; Guevara, M.; Gómez-Ibáñez, C.; Burgui, C.; Ezpeleta, C.; Castilla, J. Effect of influenza vaccination in patients with asthma. CMAJ 2021, 193, E1120–E1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, G.T.; Lewis, N.; Goddard, K.; Ross, P.; Duffy, J.; DeStefano, F.; Baxter, R.; Klein, N.P. Asthma exacerbations among asthmatic children receiving live attenuated versus inactivated influenza vaccines. Vaccine 2017, 35, 2668–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Cortright, L.; Buckman, C.; Tumin, D.; Syed, S. Association between asthma and influenza vaccine uptake among US adolescents: A retrospective survey study. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, S.J.; DeLaroche, A.M.; Hill, A.B.; Arora, R.; Gleason-Comstock, J. Influenza vaccination coverage among an urban pediatric asthma population: Implications for population health. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Score * | Respiratory Rate | Wheezing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <6 Years | ≥6 Years | ||
| 0 | <30 | <20 | Without |
| 1 | 31–35 | 21–35 | At end of breath |
| 2 | 46–60 | 36–50 | Throughout exhalation (with stethoscope) |
| 3 | >60 | >50 | Inhaling and exhaling (without stethoscope) ** |
| Lung Score | SaO2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 0–3 | >94% |
| Moderate | 4–6 | 91–94% |
| Severe | 7–9 | <91% |
| Adolescents ≥12 Years Old | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ICS Type | Daily Total Dose of ICS (mcg) | ||
| Low | Medium | High | |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 200–500 | >500–1000 | >1000 |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate (DPI or pMDI, extra fine particles, HFA) | 100–200 | >200–400 | >400 |
| Budesonide (DPI or pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 200–400 | >400–800 | >800 |
| Ciclesonide (pMDI, extra fine particles, HFA) | 800–160 | >160–320 | >320 |
| Fluticasone furoate (DPI) | 100 | 200 | |
| Fluticasone propionate (DPI) | 100–250 | >250–500 | >500 |
| Fluticasone proprionate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 100–250 | >250–500 | >500 |
| Mometasone furoate (DPI) | It depends on the used device—see product information | ||
| Mometasone furoate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 200–400 | >400 | |
| Children Aged 6–11 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ICS Type | Daily Total Dose of ICS (mcg) | ||
| Low | Medium | High | |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 100–200 | >200–400 | >400 |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate (DPI or pMDI, extra fine particles, HFA) | 50–100 | >100–200 | >200 |
| Budesonide (DPI) | 100–200 | >200–400 | >400 |
| Budesonide (nebulization) | 250–500 | >500–1000 | >1000 |
| Ciclesonide (pMDI, extrafine* particles, HFA) | 80 | >80–160 | >160 |
| Fluticasone furoate (DPI) | 50 | Without indications | |
| Fluticasone propionate (DPI) | 50–100 | >100–200 | >200 |
| Fluticasone propionate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 50–100 | >100–200 | >200 |
| Mometasone furoate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 100 | 200 | |
| Children Aged ≤5 | |
|---|---|
| ICS Type | Daily Total Low Dose of ICS (mcg) |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 100 (≥5 years old) |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate (DPI or pMDI, extra fine particles, HFA) | 50 (≥5 years old) |
| Budesonide (nebulization) | 500 (≥5 years old) |
| Fluticasone furoate (DPI) | Without sufficient studies on children ≤5 years old |
| Fluticasone propionate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 50 (≥4 years old) |
| Mometasone furoate (pMDI, standard particles, HFA) | 100 (≥5 years old) |
| Ciclesonide (pMDI, extra fine particles, HFA) | Without sufficient studies on children ≤5 years old |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioniuc, I.; Miron, I.; Lupu, V.V.; Starcea, I.M.; Azoicai, A.; Alexoae, M.; Adam Raileanu, A.; Dragan, F.; Lupu, A. Challenges in the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Pediatric Asthma. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121581
Ioniuc I, Miron I, Lupu VV, Starcea IM, Azoicai A, Alexoae M, Adam Raileanu A, Dragan F, Lupu A. Challenges in the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Pediatric Asthma. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121581
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoniuc, Ileana, Ingrith Miron, Vasile Valeriu Lupu, Iuliana Magdalena Starcea, Alice Azoicai, Monica Alexoae, Anca Adam Raileanu, Felicia Dragan, and Ancuta Lupu. 2022. "Challenges in the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Pediatric Asthma" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121581
APA StyleIoniuc, I., Miron, I., Lupu, V. V., Starcea, I. M., Azoicai, A., Alexoae, M., Adam Raileanu, A., Dragan, F., & Lupu, A. (2022). Challenges in the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Pediatric Asthma. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121581






