Microwave-Assisted Synchronous Nanogold Synthesis Reinforced by Kenaf Seed and Decoding Their Biocompatibility and Anticancer Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
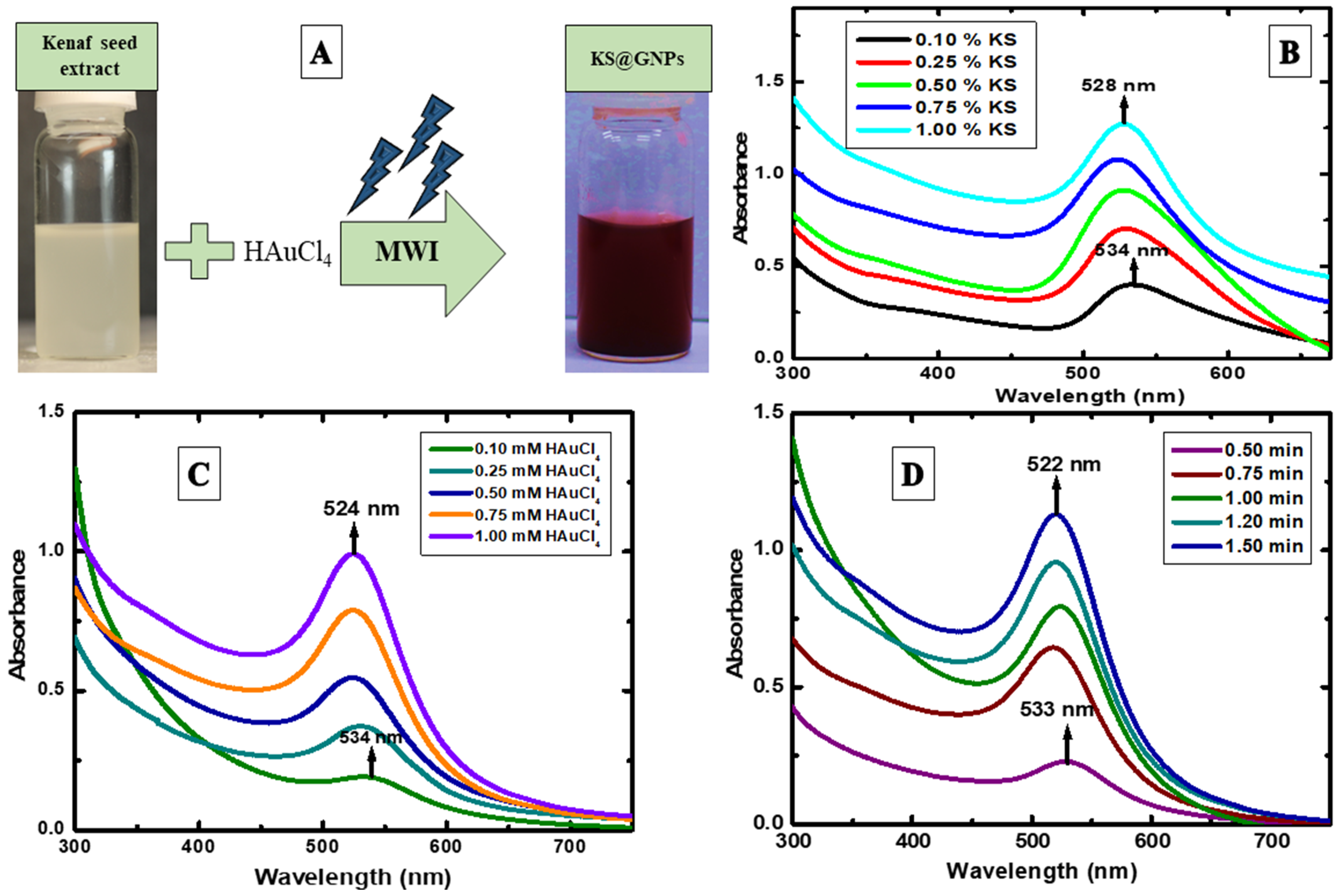
2.1. Synthesis Conditions Optimization
2.2. Effect of Finest KS Concentration
2.3. Effect of Finest HAuCl4 Concentration
2.4. Effect of Ideal MWI Time
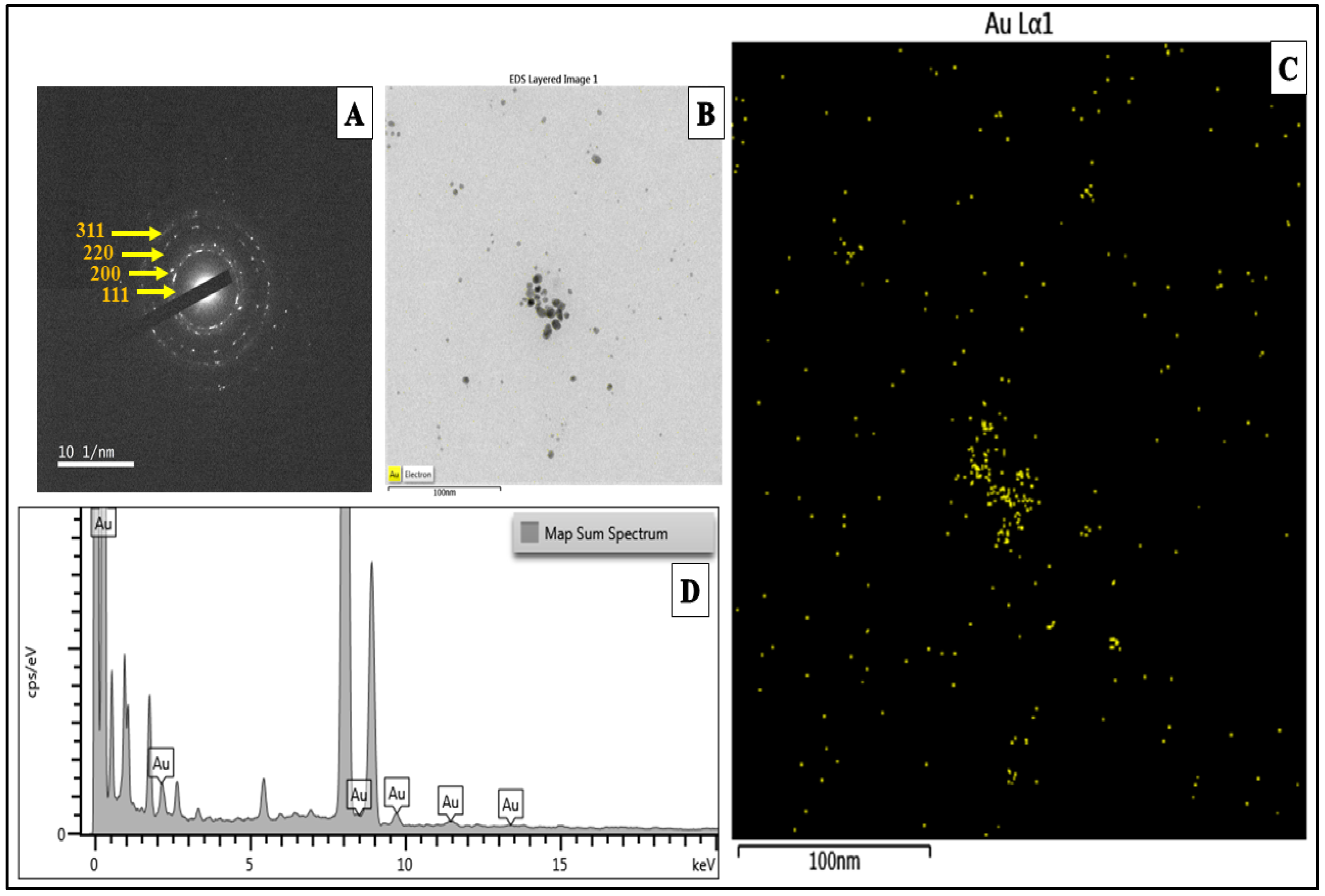
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis of KS@GNPs
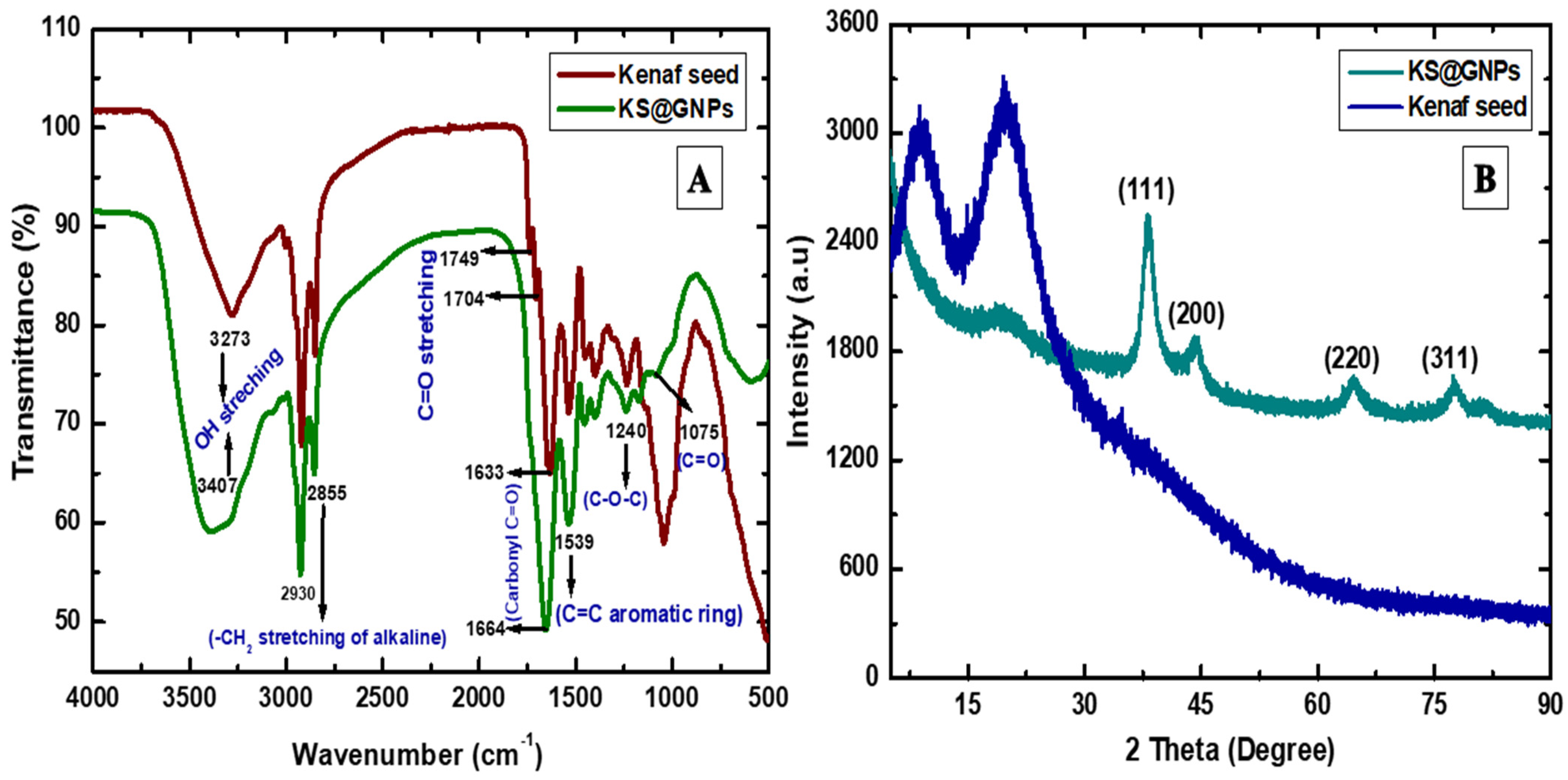
2.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
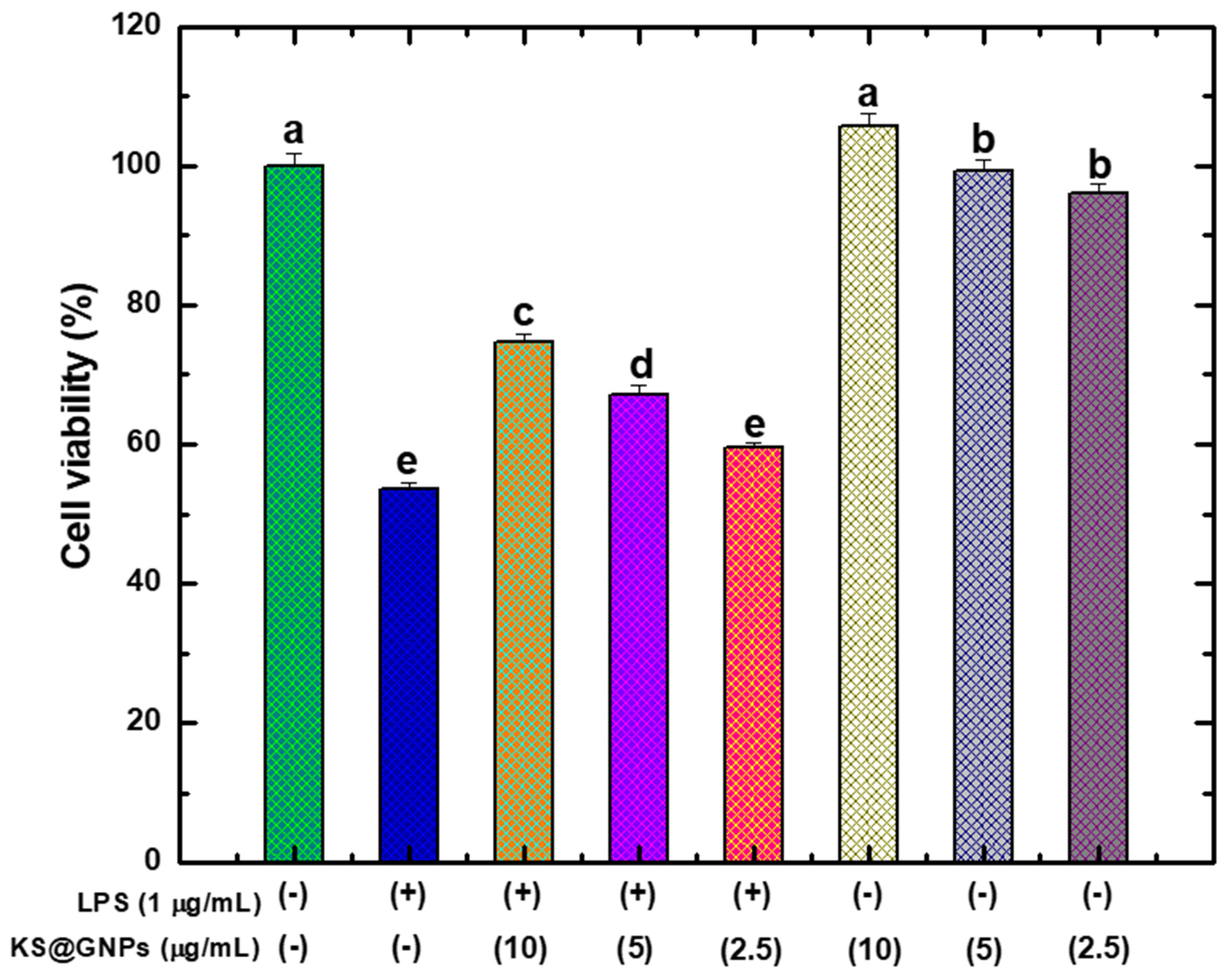
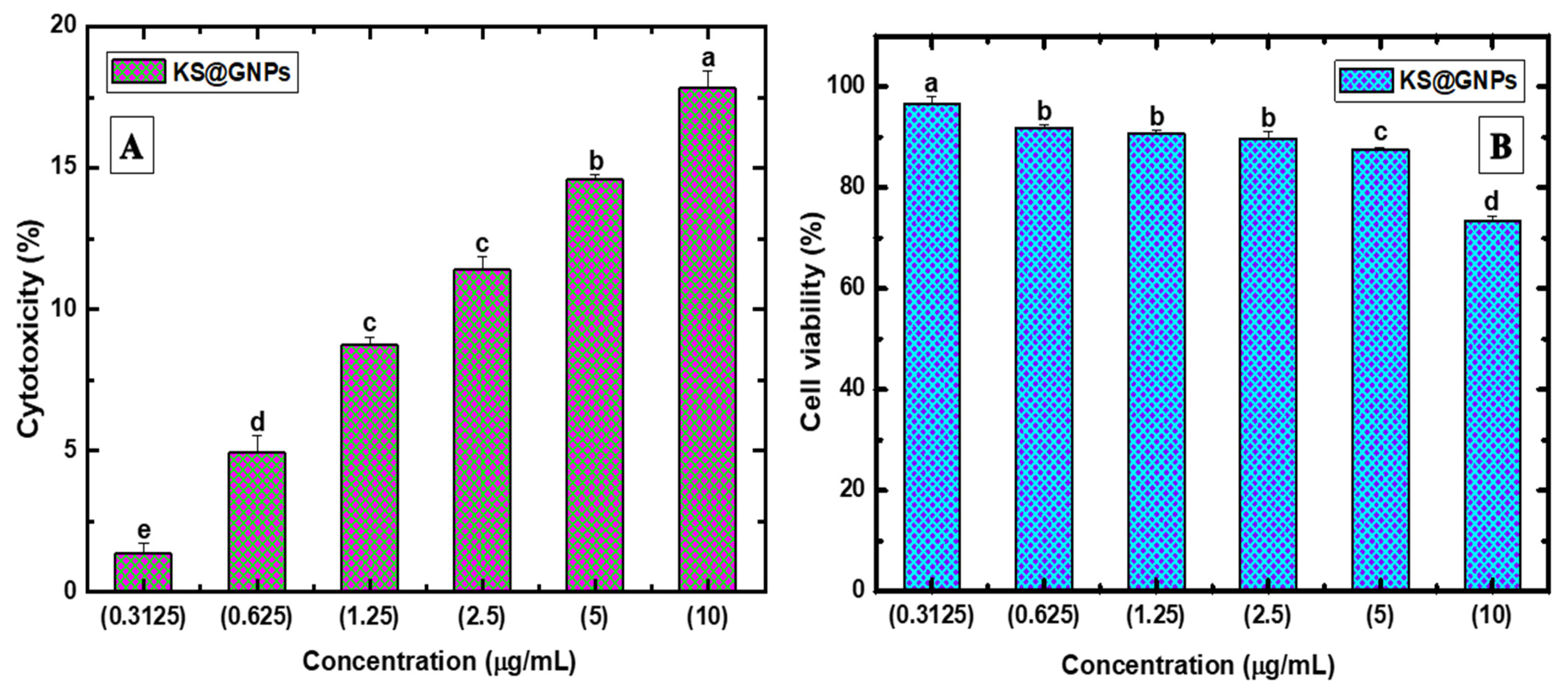
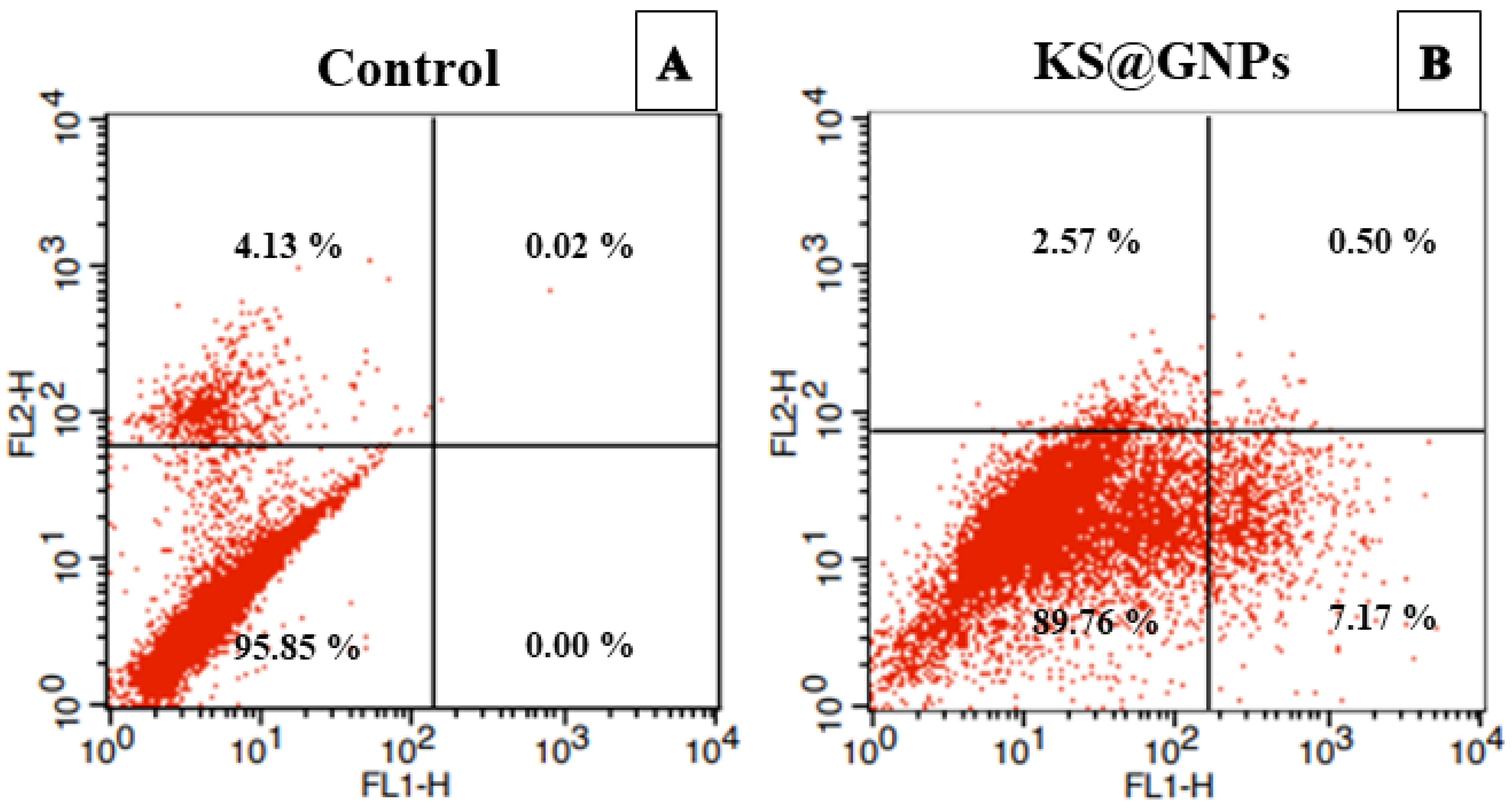
2.7. Biocompatibility Assessment of KS@GNPs
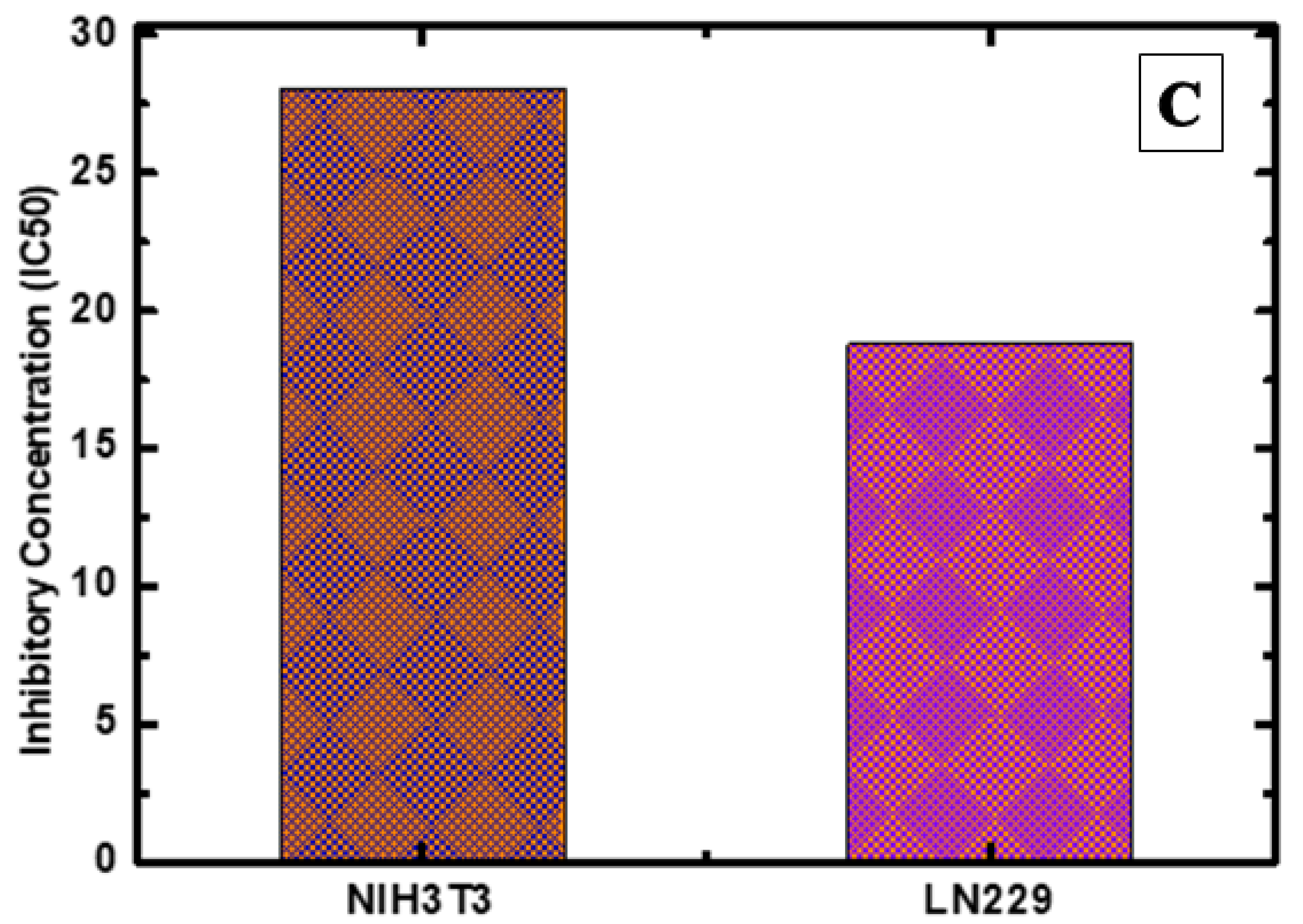
2.8. Anti-Cancer Activity
2.8.1. Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability Assay
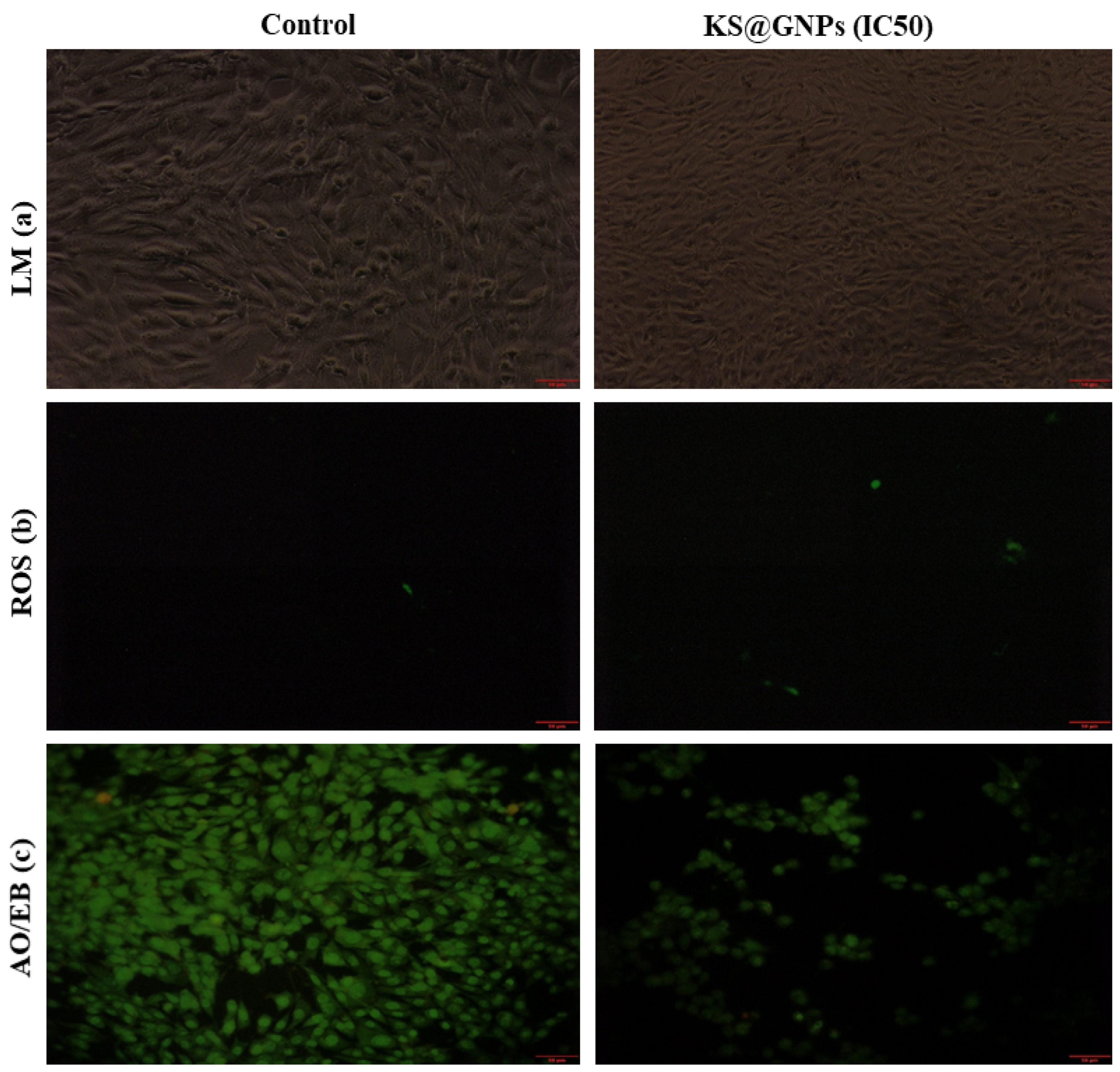
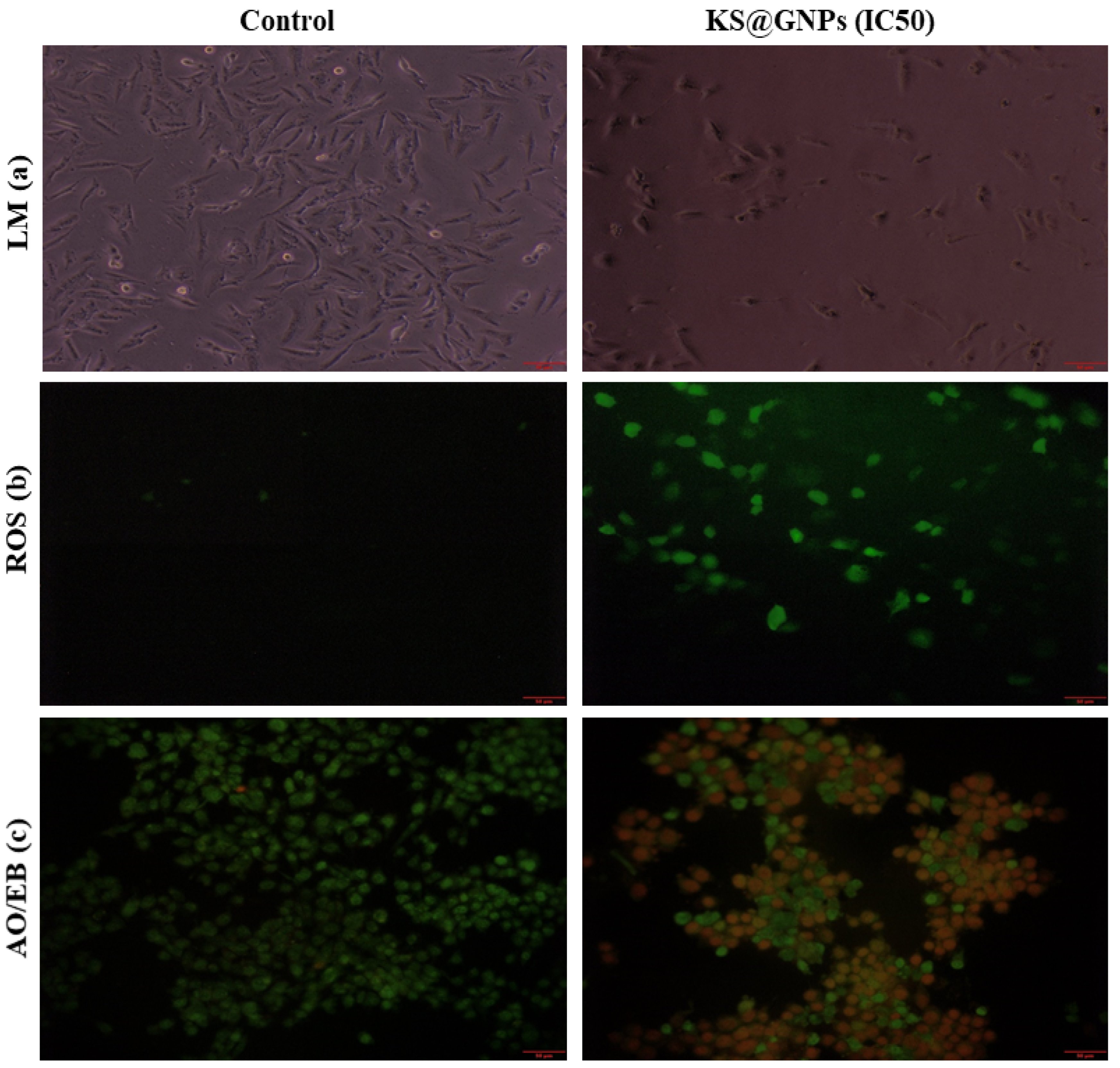
2.8.2. KS@GNPs Induced Cellular Changes, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical and Reagents
3.2. Crude Extract Preparation from Kenaf Seed (KS)
3.3. Kenaf Seed-Mediated Gold Nanoparticles Synthesis (KS@GNPs)
3.4. Characterizations of KS@GNPs
3.5. Biocompatibility Assessment of KS@GNPs
3.6. Cytotoxicity and Anti-Cancer Activity of KS@GNPs
3.6.1. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Determination Induced by KS@GNPs
3.6.2. Acridine Range (AO)/Ethidium Bromide (EB) Staining
3.6.3. Evaluation of Apoptosis by Annexin V-FITC/PI Staining
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, H.; Bhardwaj, K.; Kuča, K.; Kalia, A.; Nepovimova, E.; Verma, R.; Kumar, D. Flower-Based Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles: Applications beyond Fragrance. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, S.K.; Kulkarni, S.K. Nanotechnology: Principles and Practices; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 3319091719. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuter, J. Application of nanoparticles for the delivery of drugs to the brain. In Proceedings of the International Congress Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 1277, pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.; Fawcett, D.; Sharma, S.; Tripathy, S.K.; Poinern, G.E.J. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Materials 2015, 8, 7278–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urruticoechea, A.; Alemany, R.; Balart, J.; Villanueva, A.; Viñals, F.; Capella, G. Recent advances in cancer therapy: An overview. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Cengel, K.A.; Foster, T.H.; Girotti, A.W.; Gollnick, S.O.; Hahn, S.M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Juzeniene, A.; Kessel, D. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, A.G.; Jiang, H.; Hochwald, S.N.; Delano, M.; Cance, W.G.; Grobmyer, S.R. Emerging implications of nanotechnology on cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Cancer 2006, 107, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.C.; Mwakwari, S.C.; Oyelere, A.K. Gold nanoparticles: From nanomedicine to nanosensing. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2008, 1, 45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.S.; Alves, G.G.; Pereira, M.R.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Leite, P.E.C. Advances and potential application of gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 16370–16378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prosective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, X.; Gu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Potential Applications to Treat Cancer. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Chen, X.; Wai, C.M.; Fulton, J.L. Synthesizing and dispersing silver nanoparticles in a water-in-supercritical carbon dioxide microemulsion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 2631–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alle, M.; Kim, T.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-C. Doxorubicin-carboxymethyl xanthan gum capped gold nanoparticles: Microwave synthesis, characterization, and anti-cancer activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhusudhan, A.; Reddy, G.B.; Krishana, I.M. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by Using Natural Gums. In Nanomaterials and Plant Potential; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Desbrières, J.; Petit, C.; Reynaud, S. Microwave-assisted modifications of polysaccharides. Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alle, M.; Park, S.C.; Bandi, R.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-C. Rapid in-situ growth of gold nanoparticles on cationic cellulose nanofibrils: Recyclable nanozyme for the colorimetric glucose detection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus Oliveira, A.C.; Chaves, L.L.; Ribeiro, F.D.O.S.; de Lima, L.R.M.; Oliveira, T.C.; García-Villén, F.; Viseras, C.; de Paula, R.C.M.; Rolim-Neto, P.J.; Hallwass, F. Microwave-initiated rapid synthesis of phthalated cashew gum for drug delivery systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seekaew, Y.; Arayawut, O.; Timsorn, K.; Wongchoosuk, C. Synthesis, characterization, and applications of graphene and derivatives. In Carbon-Based Nanofillers and Their Rubber Nanocomposites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 259–283. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, M.; Azad, M.O.K.; Ju, H.S.; Son, J.M.; Park, C.H.; Shin, M.H.; Alle, M.; Cho, D.H. Development of biopolymer-mediated nanocomposites using hot-melt extrusion to enhance the bio-accessibility and antioxidant capacity of kenaf seed flour. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 10, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Oh, K.K.; Azad, M.O.K.; Shin, M.H.; Wang, M.-H.; Cho, D.H. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Leaves and Seed as a Potential Source of the Bioactive Compounds: Effects of Various Extraction Solvents on Biological Properties. Life 2020, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.K.; Adnan, M.; Ju, I.; Cho, D.H. A network pharmacology study on main chemical compounds from Hibiscus cannabinus L. leaves. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11062–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Azad, M.O.K.; Madhusudhan, A.; Saravanakumar, K.; Hu, X.; Wang, M.H.; Ha, C.D. Simple and cleaner system of silver nanoparticle synthesis using kenaf seed and revealing its anticancer and antimicrobial potential. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 265101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, D. Synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 71, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztandera, K.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Gold nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Božanić, D.K.; Luyt, A.S.; Trandafilović, L.V.; Djoković, V. Glycogen and gold nanoparticle bioconjugates: Controlled plasmon resonance via glycogen-induced nanoparticle aggregation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8705–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanoparticles: Interesting optical properties and recent applications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irfan, M.; Ahmad, T.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Abdullah, B. Size and stability modulation of ionic liquid functionalized gold nanoparticles synthesized using Elaeis guineensis (oil palm) kernel extract. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Jamroz, P.; Sergiel, I.; Kozlecki, T.; Pohl, P. Preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles prepared with aqueous extracts of Lamiaceae plants and the effect of follow-up treatment with atmospheric pressure glow microdischarge. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4118–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Singla, S.K.; Guturu, P.; Frost, M.C.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Shah, V.H.; Patra, C.R. Fabrication and characterization of an inorganic gold and silica nanoparticle mediated drug delivery system for nitric oxide. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 305102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Chiu, H.-W.; Tsai, J.-C.; Fang, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Wang, Y.-J. Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, apoptosis and the autophagic effects of silver nanoparticles in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4706–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Stenzel, M.H. Entry of nanoparticles into cells: The importance of nanoparticle properties. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, W.; Tovmachenko, O.; Rai, U.S.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. Challenge in understanding size and shape dependent toxicity of gold nanomaterials in human skin keratinocytes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 463, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdal Dayem, A.; Hossain, M.K.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.; Saha, S.K.; Yang, G.-M.; Choi, H.Y.; Cho, S.-G. The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the biological activities of metallic nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleury, C.; Mignotte, B.; Vayssière, J.-L. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling. Biochimie 2002, 84, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, S.J.; Rivera-Gil, P.; Montenegro, J.-M.; Parak, W.J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Braeckmans, K. Cellular toxicity of inorganic nanoparticles: Common aspects and guidelines for improved nanotoxicity evaluation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Mason, M.M.; Wise Sr, J.P. Genotoxicity of metal nanoparticles. Rev. Environ. Health 2011, 26, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Brant, J.; Hotze, M.; Sempf, J.; Oberley, T.; Sioutas, C.; Yeh, J.I.; Wiesner, M.R.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1794–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.D.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H. Chemical transformations of nanosilver in biological environments. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9887–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.H.; Ma, J.N.; Park, J.H.; Jung, H.W.; Park, Y. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of MOK, a polyherbal extract, on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adnan, M.; Oh, K.-K.; Husen, A.; Wang, M.-H.; Alle, M.; Cho, D.-H. Microwave-Assisted Synchronous Nanogold Synthesis Reinforced by Kenaf Seed and Decoding Their Biocompatibility and Anticancer Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020111
Adnan M, Oh K-K, Husen A, Wang M-H, Alle M, Cho D-H. Microwave-Assisted Synchronous Nanogold Synthesis Reinforced by Kenaf Seed and Decoding Their Biocompatibility and Anticancer Activity. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020111
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdnan, Md., Ki-Kwang Oh, Azamal Husen, Myeong-Hyeon Wang, Madhusudhan Alle, and Dong-Ha Cho. 2022. "Microwave-Assisted Synchronous Nanogold Synthesis Reinforced by Kenaf Seed and Decoding Their Biocompatibility and Anticancer Activity" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020111
APA StyleAdnan, M., Oh, K.-K., Husen, A., Wang, M.-H., Alle, M., & Cho, D.-H. (2022). Microwave-Assisted Synchronous Nanogold Synthesis Reinforced by Kenaf Seed and Decoding Their Biocompatibility and Anticancer Activity. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020111









