New Applications of JAK/STAT Inhibitors in Pediatrics: Current Use of Ruxolitinib
Abstract
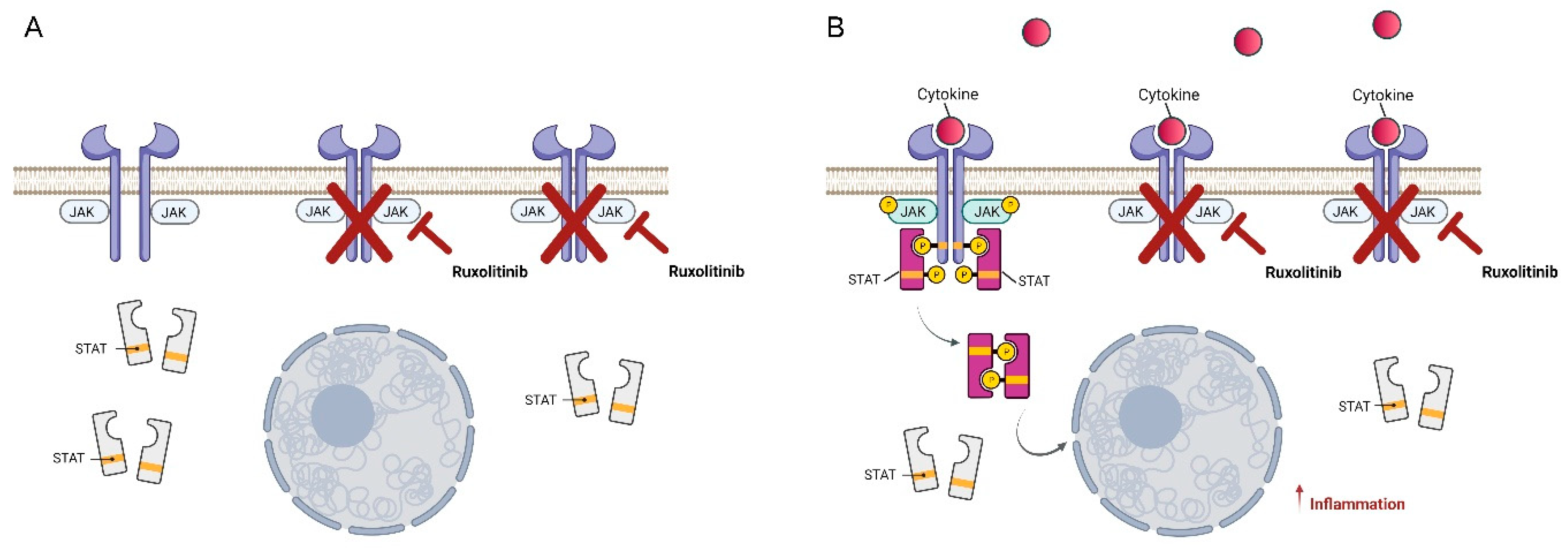
:1. Introduction
2. Ruxolitinib, a Very Promising JAK1/2 Inhibitor
3. Ruxolitinib Use in Pediatric Patients: Indications and Dosages
4. Infectious Complications
5. Clinical Experience of Ruxolitinib Treatment
6. Repositioning Applications of Ruxolitinib: From Autoinflammatory Disease to Viral Infections
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghoreschi, K.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilks, A.F. The JAK kinases: Not just another kinase drug discovery target. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, N.K.; Bamert, R.S.; Patel, O.; Wang, C.; Walden, P.M.; Wilks, A.F.; Fantino, E.; Rossjohn, J.; Lucet, I.S. Dissecting specificity in the Janus kinases: The structures of JAK-specific inhibitors complexed to the JAK1 and JAK2 protein tyrosine kinase domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 387, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alicea-Velázquez, N.L.; Boggon, T.J. The use of structural biology in Janus kinase targeted drug discovery. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Biehl, A.; Gadina, M.; Hasni, S.; Schwartz, D.M. JAK-STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs 2017, 77, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, A.T.; Haikarainen, T.; Raivola, J.; Silvennoinen, O. Selective JAKinibs: Prospects in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. BioDrugs 2019, 33, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seavey, M.M.; Dobrzanski, P. The many faces of Janus kinase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menet, C.J.; Rompaey, L.V.; Geney, R. Advances in the discovery of selective JAK inhibitors. Prog. Med. Chem. 2013, 52, 153–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Alexander, M.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J.; Meylan, F.; Schwartz, D.M. JAK-STAT signaling in human disease: From genetic syndromes to clinical inhibition. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaimowitz, N.S.; Forbes, L.R. Human diseases caused by impaired signal transducer and activator of transcription and Janus kinase signaling. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.O. Development of JAK inhibitors for the treatment of immune-mediated diseases: Kinase-targeted inhibitors and pseudokinase-targeted inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakajima, H.; Saito, Y.; Saito, T.; Leonard, W.J.; Iwamoto, I. Janus kinase 3 (Jak3) is essential for common cytokine receptor gamma chain (gamma(c))-dependent signaling: Comparative analysis of gamma(c), Jak3, and gamma(c) and Jak3 double-deficient mice. Int. Immunol. 2000, 12, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leonard, W.J.; Lin, J.X.; O’Shea, J.J. The γc Family of Cytokines: Basic Biology to Therapeutic Ramifications. Immunity 2019, 50, 832–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.X.; Leonard, W.J. The Common Cytokine Receptor γ Chain Family of Cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, D.; Kröger, N. Janus Kinase Inhibition for Graft-Versus-Host Disease: Current Status and Future Prospects. Drugs 2019, 79, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Vaddi, K.; Liu, P.; Manshouri, T.; Li, J.; Scherle, P.A.; Caulder, E.; Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Waeltz, P.; et al. Preclinical characterization of the selective JAK1/2 inhibitor INCB018424: Therapeutic implications for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2010, 115, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslin, R.; Gardner, D.; Santella, J.; Zhang, Y.; Duncia, J.V.; Liu, C.; Lin, J.; Tokarski, J.S.; Strnad, J.; Pedicord, D.; et al. Identification of imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine TYK2 pseudokinase ligands as potent and selective allosteric inhibitors of TYK2 signalling. Medchemcomm 2016, 8, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Smaill, J.B.; Ding, K. New Promise and Opportunities for Allosteric Kinase Inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 13764–13776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babon, J.J.; Lucet, I.S.; Murphy, J.M.; Nicola, N.A.; Varghese, L.N. The molecular regulation of Janus kinase (JAK) activation. Biochem. J. 2014, 462, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spinelli, F.R.; Meylan, F.; O’Shea, J.J.; Gadina, M. JAK inhibitors: Ten years after. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, J.; Talotta, R.; Roncato, R.; Fornasier, G.; Barbiero, G.; Dal Cin, L.; Brancati, S.; Scaglione, F. JAK-Inhibitors for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Focus on the Present and an Outlook on the Future. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobleski, S.T.; Moslin, R.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Spergel, S.; Kempson, J.; Tokarski, J.S.; Strnad, J.; Zupa-Fernandez, A.; Cheng, L.; et al. Highly Selective Inhibition of Tyrosine Kinase 2 (TYK2) for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases: Discovery of the Allosteric Inhibitor BMS-986165. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8973–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assal, A.; Mapara, M.Y. Janus Kinase Inhibitors and Cell Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 740847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.A.; Choi, J.; Staser, K.; Di Persio, J.F. The Role of Janus Kinase Signaling in Graft-Versus-Host Disease and Graft Versus Leukemia. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018, 24, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, L.M.; Zeiser, R. Kinase Inhibition as Treatment for Acute and Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 760199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raivola, J.; Haikarainen, T.; Abraham, B.G.; Silvennoinen, O. Janus Kinases in Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Gilliland, D.G. The JAK2V617F tyrosine kinase mutation in myeloproliferative disorders: Status report and immediate implications for disease classification and diagnosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campanelli, R.; Massa, M.; Rosti, V.; Barosi, G. New Markers of Disease Progression in Myelofibrosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerk, J.; Kallin, A.; Royer, Y.; Diaconu, C.C.; Dusa, A.; Demoulin, J.B.; Vainchenker, W.; Constantinescu, S.N. JAK2, the JAK2 V617F mutant and cytokine receptors. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 2007, 55, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.J.; Gilliland, D.G. A role for JAK2 mutations in myeloproliferative diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2008, 59, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltro, G.; Vannucchi, A.M. The safety of JAK kinase inhibitors for the treatment of myelofibrosis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirito, K.; Okamoto, S.; Ohishi, K.; Tauchi, T.; Handa, H.; Saito, S.; Takenaka, K.; Shimoda, K.; Oritani, K.; Akashi, K.; et al. Evaluation of the dose and efficacy of ruxolitinib in Japanese patients with myelofibrosis. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 107, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, I.; McLornan, D.; Harrison, C.N. Managing side effects of JAK inhibitors for myelofibrosis in clinical practice. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.J.; Bajel, A.; Burbury, K.; Dunlop, L.; Durrant, S.; Forsyth, C.; Perkins, A.C.; Ross, D.M. A case-based discussion of clinical problems in the management of patients treated with ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesshammer, M.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Besses, C. Thromboembolic events in polycythemia vera. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Ruxolitinib for refractory/relapsed hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica 2020, 105, e210–e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trombetta, A.; Ghirardo, S.; Pastore, S.; Tesser, A.; Piscianz, E.; Tommasini, A.; Bobbo, M.; Taddio, A. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in interferonophaties: A case report and a review of the literature. Pulm. Circ. 2019, 9, 2045894019869837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeiser, R.; von Bubnoff, N.; Butler, J.; Mohty, M.; Niederwieser, D.; Or, R.; Szer, J.; Wagner, E.M.; Zuckerman, T.; Mahuzier, B.; et al. Ruxolitinib for Glucocorticoid-Refractory Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R.; Polverelli, N.; Ram, R.; Hashmi, S.K.; Chakraverty, R.; Middeke, J.M.; Musso, M.; Giebel, S.; Uzay, A.; Langmuir, P.; et al. Ruxolitinib for Glucocorticoid-Refractory Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygun, V.; Karasu, G.; Daloğlu, H.; Öztürkmen, S.; Kılıç, S.Ç.; Yalçın, K.; Çelen, S.S.; Hazar, V.; Yeşilipek, A. Ruxolitinib salvage therapy is effective for steroid-refractory graft-versus-host disease in children: A single-center experience. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28190. [Google Scholar]
- Fitch, T.; Myers, K.C.; Dewan, M.; Towe, C.; Dandoy, C. Pulmonary Complications After Pediatric Stem Cell Transplant. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 755878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoettler, M.; Duncan, C.; Lehmann, L.; Furutani, E.; Subramaniam, M.; Margossian, S. Ruxolitinib is an effective steroid sparing agent in children with steroid refractory/dependent bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogenic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019, 54, 1158–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhu, G.; Qin, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, T. The Effectiveness of Ruxolitinib for Acute/Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children: A Retrospective Study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozo, Y.; Bueno, D.; Sisinni, L.; Fernández-Arroyo, A.; Rosich, B.; Martínez, A.P.; Benítez-Carabante, M.I.; Alonso, L.; Uría, M.L.; Heredia, C.D.; et al. Ruxolitinib for steroid-refractory graft versus host disease in pediatric HSCT: High response rate and manageable toxicity. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 38, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, P.; Teusink-Cross, A.; Davies, S.M.; Nelson, A.S.; Dandoy, C.E.; El-Bietar, J.; Marsh, R.A.; Kumar, A.R.; Grimley, M.S.; Jodele, S.; et al. Ruxolitinib as Salvage Therapy in Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease in Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Patients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017, 23, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coltro, G.; Mannelli, F.; Guglielmelli, P.; Pacilli, A.; Bosi, A.; Vannucchi, A.M. A life-threatening ruxolitinib discontinuation syndrome. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redondo, S.; Esquirol, A.; Novelli, S.; Caballero, A.C.; Garrido, A.; Oñate, G.; López, J.; Moreno, C.; Saavedra, S.D.; Granell, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Ruxolitinib in Steroid-Refractory/Dependent Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: Real-World Data and Challenges. Transpl. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 43.e1–43.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarino, A.V.; Kanno, Y.; O’Shea, A.V.V.Y.K.J.J. Mechanisms and consequences of Jak–STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Stoiber, D.; Sexl, V.; Witalisz-Siepracka, A. Untwining Anti-Tumor and Immunosuppressive Effects of JAK Inhibitors-A Strategy for Hematological Malignancies? Cancers 2021, 13, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarén, H.M.; Virtanen, A.T.; Raivola, J.; Silvennoinen, O. The regulation of JAKs in cytokine signaling and its breakdown in disease. Cytokine 2019, 118, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, T.; Dotta, L.; Giacomelli, M.; Vairo, D.; Badolato, R. STAT mutations as program switchers: Turning primary immunodeficiencies into autoimmune diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 101, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, A.; Shoebridge, S.; Krunic, M.; Simonovi’c, N.; Tebb, G.; Macho-Maschler, S.; Strobl, B.; Müller, M. TYK2 in Tumor Immunosurveillance. Cancers 2020, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hambleton, S.; Goodbourn, S.; Young, D.F.; Dickinson, P.; Mohamad, S.M.B.; Valappil, M.; McGovern, N.; Cant, A.J.; Hackett, S.J.; Ghazal, P.; et al. STAT2 deficiency and susceptibility to viral illness in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3053–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freij, B.J.; Hanrath, A.T.; Chen, R.; Hambleton, S.; Duncan, C.J.A. Life-Threatening Influenza, Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Probable Vaccine-Strain Varicella in a Novel Case of Homozygous STAT2 Deficiency. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimke, L.F.; Hibbard, J.; Martinez-Barricarte, R.; Khan, T.A.; Cavalcante, R.D.S.; Junior, E.B.D.O.; França, T.T.; Iqbal, A.; Yamamoto, G.; Arslanian, C.; et al. Paracoccidioidomycosis Associated With a Heterozygous STAT4 Mutation and Impaired IFN- Immunity. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.A.; Shubitz, L.F.; Butkiewicz, C.D.; Moale, H.; Trinh, H.T.; Doetschman, T.; Hsu, A.P.; Holland, S.M.; Galgiani, J.N.; Frelinger, J.A. Modeling a Human STAT4 Mutation That Predisposes to Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis in Mice. J. Immunol. 2020, 204 (Suppl. 1), 82.6. [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, D.; Iurlo, A. Immune Dysregulation and Infectious Complications in MPN Patients Treated With JAK Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 750346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadian, P.; Wille, K.; Griesshammer, M. Ruxolitinib-Associated Infections in Polycythemia Vera: Review of the Literature, Clinical Significance, and Recommendations. Cancers 2020, 12, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, A.; Held, S.A.; Daecke, S.N.; Wallner, S.; Yajnanarayana, S.P.; Kurts, C.; Wolf, D.; Brossart, P. The JAK-inhibitor ruxolitinib impairs dendritic cell function in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2013, 122, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, A.; Brossart, P.; Wolf, D. Ruxolitinib is a potent immunosuppressive compound: Is it time for anti-infective prophylaxis? Blood 2013, 122, 3843–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussana, F.; Cattaneo, M.; Rambaldi, A.; Squizzato, A. Ruxolitinib-associated infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hultcrantz, M.; Wilkes, S.R.; Kristinsson, S.Y.; Andersson, T.M.; Derolf, A.R.; Eloranta, S.; Samuelsson, J.; Landgren, O.; Dickman, P.W.; Lambert, P.C.; et al. Risk and Cause of Death in Patients Diagnosed With Myeloproliferative Neoplasms in Sweden Between 1973 and 2005: A Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverelli, N.; Breccia, M.; Benevolo, G.; Martino, B.; Tieghi, A.; Latagliata, R.; Sabattini, E.; Riminucci, M.; Godio, L.; Catani, L.; et al. Risk factors for infections in myelofibrosis: Role of disease status and treatment. A multicenter study of 507 patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverelli, N.; Palumbo, G.A.; Binotto, G.; Abruzzese, E.; Benevolo, G.; Bergamaschi, M.; Tieghi, A.; Bonifacio, M.; Breccia, M.; Catani, L.; et al. Epidemiology, outcome, and risk factors for infectious complications in myelofibrosis patients receiving ruxolitinib: A multicenter study on 446 patients. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, D.; King, A.; Li, L.; Moshier, E.; Coltoff, A.; Koshy, A.; Kremyanskaya, M.; Hoffman, R.; Mauro, M.J.; Rampal, R.K.; et al. Risk factors for infections and secondary malignancies in patients with a myeloproliferative neoplasm treated with ruxolitinib: A dual-center, propensity score-matched analysis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, K.; Burns, E.A.; Ensor, J.; Rice, L.; Pingali, S.R. Mycobacterial Infections With Ruxolitinib: A Retrospective Pharmacovigilance Review. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maschmeyer, G.; De Greef, J.; Mellinghoff, S.C.; Nosari, A.; Thiebaut-Bertrand, A.; Bergeron, A.; Franquet, T.; Blijlevens, N.M.A.; Maertens, J.A. Infections Associated With Immunotherapeutic and Molecular Targeted Agents in Hematology and Oncology. A Position Paper by the European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL). Leukemia 2019, 33, 844–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laisne, L.; Neven, B.; Dalle, J.H.; Galambrun, C.; Esvan, M.; Renard, C.; Rialland, F.; Sirvent, A.; Gandemer, V. Pediatric Group of SFGM-TC. Ruxolitinib in children with steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: A retrospective multicenter study of the pediatric group of SFGM-TC. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R.; Burchert, A.; Lengerke, C.; Verbeek, M.; Maas-Bauer, K.; Metzelder, S.K.; Spoerl, S.; Ditschkowski, M.; Ecsedi, M.; Sockel, K.; et al. Ruxolitinib in corticosteroid-refractory graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: A multicenter survey. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, B.; Hernandez-Henderson, M.; Yang, D.; Klein, J.; Dadwal, S.; Kopp, E.; Huelsman, K.; Mokhtari, S.; Ali, H.; Malki, M.M.A.; et al. Ruxolitinib as salvage therapy for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019, 25, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, X.; Liang, D.; Yang, J.; Du, J.; Yue, C.; Deng, L. Ruxolitinib for Treatment of Steroid-Refractory Graft-versus-Host Disease: Real-World Data from Chinese Patients. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4875–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, S.; McKenna, E.; Chhabra, S.; Pasquini, M.; Shah, N.N.; Jerkins, J.; Baim, A.; Runaas, L.; Longo, W.; Drobyski, W.; et al. Efficacy, Toxicity, and Infectious Complications in Ruxolitinib-Treated Patients with Corticosteroid-Refractory Graft-versus-Host Disease after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019, 25, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Wolff, D.; Kitko, C.; Koreth, J.; Inamoto, Y.; Jagasia, M.; Pidala, J.; Olivieri, A.; Martin, P.J.; Przepiorka, D.; et al. Measuring therapeutic response in chronic graft-versus-host disease. National institutes of health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: IV. The 2014 response criteria working group report. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015, 21, 984–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The European Medicines Agency. EudraVigilance—European Data Base of Suspected Adverse Drug Reaction Reports. Available online: http://www.adrreports.eu/index.html (accessed on 20 December 2017).
- Raghuvanshi, R.; Bharate, S.B. Recent Developments in the Use of Kinase Inhibitors for Management of Viral Infections. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 893–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, C. Viral infections: Targeting host kinases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 314. [Google Scholar]
- Gudu, T.; Stober, C.; Cope, A.P.; Cheriyan, J.; Galloway, J.; Wilkinson, I.B.; Kostapanos, M.; Jayne, D.; Hall, F. Baricitinib set to join the Covid-19 therapeutic arsenal? Rheumatology (Oxford) 2021, 60, 1585–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbing, J.; Krishnan, V.; de Bono, S.; Ottaviani, S.; Casalini, G.; Richardson, P.J.; Monteil, V.; Lauschke, V.M.; Mirazimi, A.; Youhanna, S.; et al. Mechanism of baricitinib supports artificial intelligence-predicted testing in COVID-19 patients. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbing, J.; Phelan, A.; Griffin, I.; Tucker, C.; Oechsle, O.; Smith, D.; Richardson, P. COVID-19: Combining antiviral and anti-inflammatory treatments. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeleswaram, S.; Smith, P.; Burn, T.; Covington, M.; Juvekar, A.; Li, Y.; Squier, P.; Langmuir, P. Inhibition of cytokine signaling by ruxolitinib and implications for COVID-19 treatment. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 218, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florescu, D.F.; Kalil, A.C. Janus Kinase inhibitors for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2021, 27, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wei, J.; Zou, L.; Jiang, T.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Meng, F.; Huang, L.; Wang, N.; et al. Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Griesshammer, M.; Masszi, T.; Durrant, S.; Passamonti, F.; Harrison, C.N.; Pane, F.; Zachee, P.; Mesa, R.; et al. Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Rosee, F.; Bremer, H.C.; Gehrke, I.; Kehr, A.; Hochhaus, A.; Birndt, S.; Fellhauer, M.; Henkes, M.; Kumle, B.; Russo, S.G.; et al. The Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib in COVID-19 with severe systemic hyperinflammation. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capochiani, E.; Frediani, B.; Iervasi, G.; Paolicchi, A.; Sani, S.; Roncucci, P.; Cuccaro, A.; Franchi, F.; Simonetti, F.; Carrara, D.; et al. Ruxolitinib Rapidly Reduces Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in COVID-19 Disease. Analysis of Data Collection From RESPIRE Protocol. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessio, A.; Del Poggio, P.; Bracchi, F.; Cesana, G.; Sertori, N.; Di Mauro, D.; Fargnoli, A.; Motta, M.; Giussani, C.; Moro, P.; et al. Low-dose ruxolitinib plus steroid in severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. Leukemia 2021, 35, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, V.; Pagliano, P.; Vatrella, A.; Masullo, A.; Poto, S.; Polverino, B.M.; Gammaldi, R.; Maglio, A.; Sellitto, C.; Vitale, C.; et al. Combination of ruxolitinib and eculizumab for treatment of severe SARS-CoV-2-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: A controlled study. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarker, S.; Tom, A.A.; Shaji, R.A.; Alosious, A.; Luvis, M.; Nampoothiri, M. JAK-STAT Pathway Inhibition and their Implications in COVID-19 Therapy. Postgrad. Med. 2021, 133, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spivak, A.M.; Larragoite, E.T.; Coletti, M.L.; Macedo, A.B.; Martins, L.J.; Bosque, A.; Planelles, V. Janus kinase inhibition suppresses PKC-induced cytokine release without affecting HIV-1 latency reversal ex vivo. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavegnano, C.; Detorio, M.; Montero, C.; Bosque, A.; Planelles, V.; Schinazi, R.F. Ruxolitinib and tofacitinib are potent and selective inhibitors of HIV-1 replication and virus reactivation in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavegnano, C.; Brehm, J.H.; Dupuy, F.P.; Talla, A.; Ribeiro, S.P.; Kulpa, D.A.; Cameron, C.; Santos, S.; Hurwitz, S.J.; Marconi, V.C.; et al. Novel mechanisms to inhibit HIV reservoir seeding using Jak inhibitors. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haile, W.B.; Gavegnano, C.; Tao, S.; Jiang, Y.; Schinazi, R.F.; Tyor, W.R. The Janus kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib reduces HIV replication in human macrophages and ameliorates HIV encephalitis in a murine model. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 92, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onozawa, E.; Shibayama, H.; Takada, H.; Imadome, K.I.; Aoki, S.; Yoshimori, M.; Shimizu, N.; Fujiwara, S.; Koyama, T.; Miura, O.; et al. STAT3 is constitutively activated in chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection and can be a therapeutic target. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31077–31089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z. Long-term survival benefit of ruxolitinib in a patient with relapsed refractory chronic active Epstein-Barr virus. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 2003–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Variables | Value |
|---|---|
| Age at treatment (median, years) | 5.8 (1.1–17.8) |
| Acute GVHD (number, %): | 6 (50.0) |
| Grade 2 | 4 (33.3) |
| Grade 4 | 2 (16.7) |
| Severe chronic GVHD (number, %): | 5 (41.7) |
| Lung involvement | 2 (16.7) |
| Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (number, %) | 1 (8.3) |
| Treatment before ruxolitinib a (number, %): | |
| 1 | 8 (66.7) |
| 2 | 0 |
| ≥3 | 4 (33.3) |
| Response to ruxolitinib b (number, %): | 12 (100) |
| Complete response: | 7 (58.3) |
| Acute GVHD all grade | 6 (100) |
| Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome | 1 (100) |
| Partial response: | 5 (41.7) |
| Chronic GVHD | 5 (100) |
| Ruxolitinib-related adverse events (number, %): | 9 (75.0) |
| Hematological toxicity: [74] | 2 (16.7) |
| Grade 2–3 | 2 (16.7) |
| Grade > 3 | 0 |
| CMV reactivation | 9 (75.0) |
| Dyslipidemia | 2 (16.7) |
| Liver toxicity | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcuzzi, A.; Rimondi, E.; Melloni, E.; Gonelli, A.; Grasso, A.G.; Barbi, E.; Maximova, N. New Applications of JAK/STAT Inhibitors in Pediatrics: Current Use of Ruxolitinib. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030374
Marcuzzi A, Rimondi E, Melloni E, Gonelli A, Grasso AG, Barbi E, Maximova N. New Applications of JAK/STAT Inhibitors in Pediatrics: Current Use of Ruxolitinib. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(3):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030374
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcuzzi, Annalisa, Erika Rimondi, Elisabetta Melloni, Arianna Gonelli, Antonio Giacomo Grasso, Egidio Barbi, and Natalia Maximova. 2022. "New Applications of JAK/STAT Inhibitors in Pediatrics: Current Use of Ruxolitinib" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 3: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030374
APA StyleMarcuzzi, A., Rimondi, E., Melloni, E., Gonelli, A., Grasso, A. G., Barbi, E., & Maximova, N. (2022). New Applications of JAK/STAT Inhibitors in Pediatrics: Current Use of Ruxolitinib. Pharmaceuticals, 15(3), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030374










