Investigation of the Role of the TRPA1 Ion Channel in Conveying the Effect of Dimethyl Trisulfide on Vascular and Histological Changes in Serum-Transfer Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
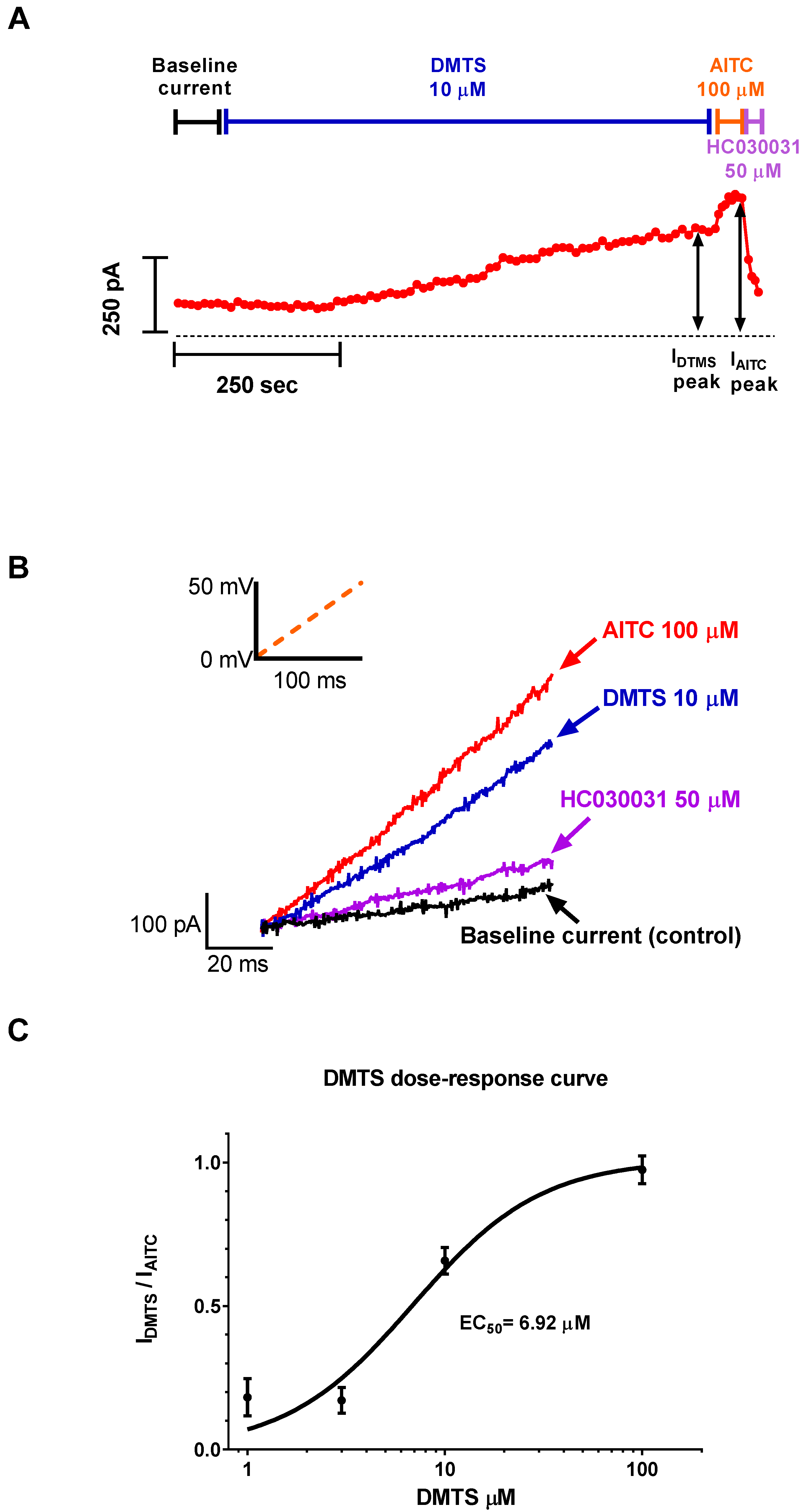
2.1. DMTS Activated TRPA1 Ion Channels Concentration-Dependently
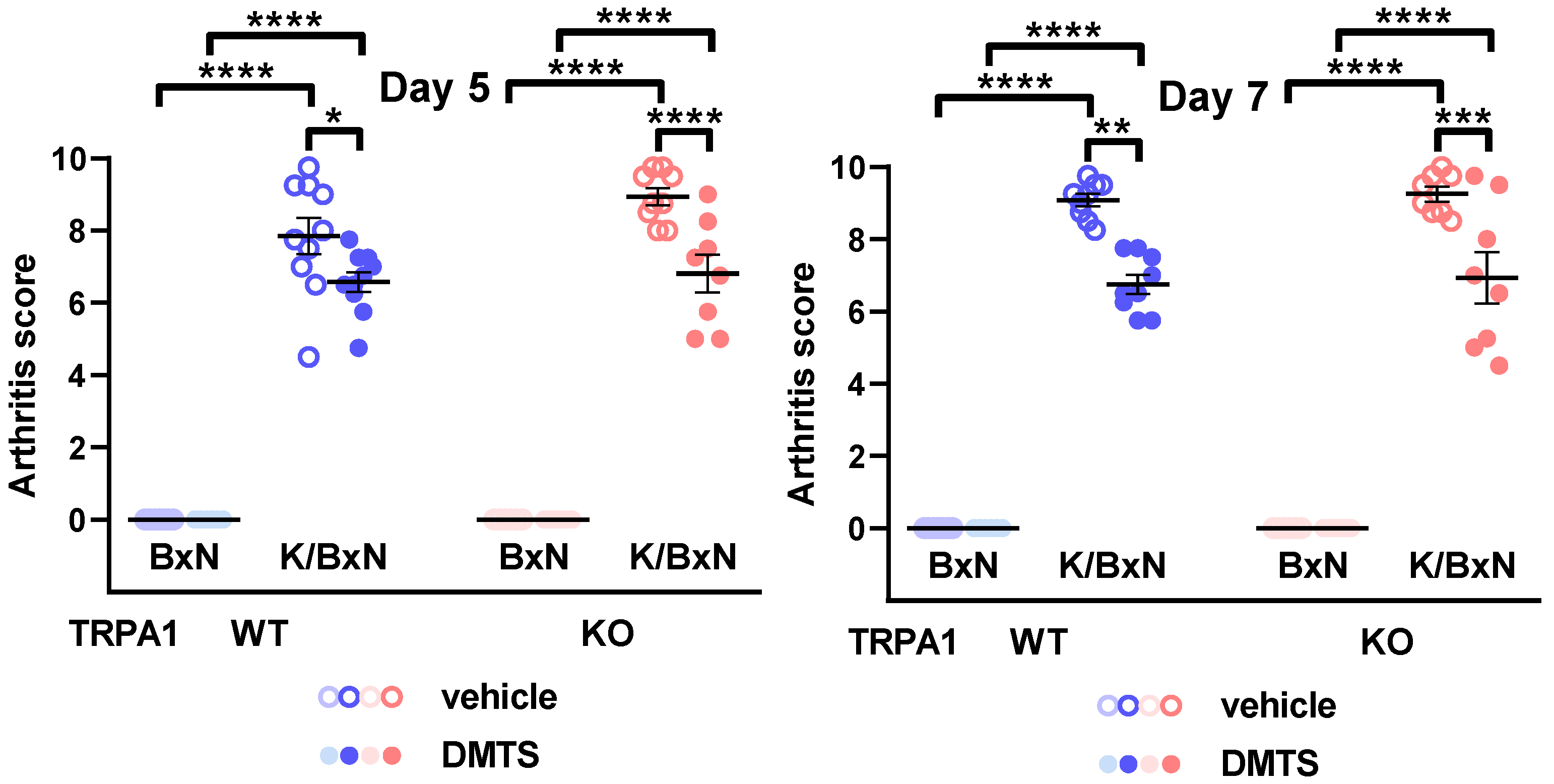
2.2. DMTS Treatment Inhibited Paw Swelling and Arthritis Score Independent of TRPA1 Ion Channels
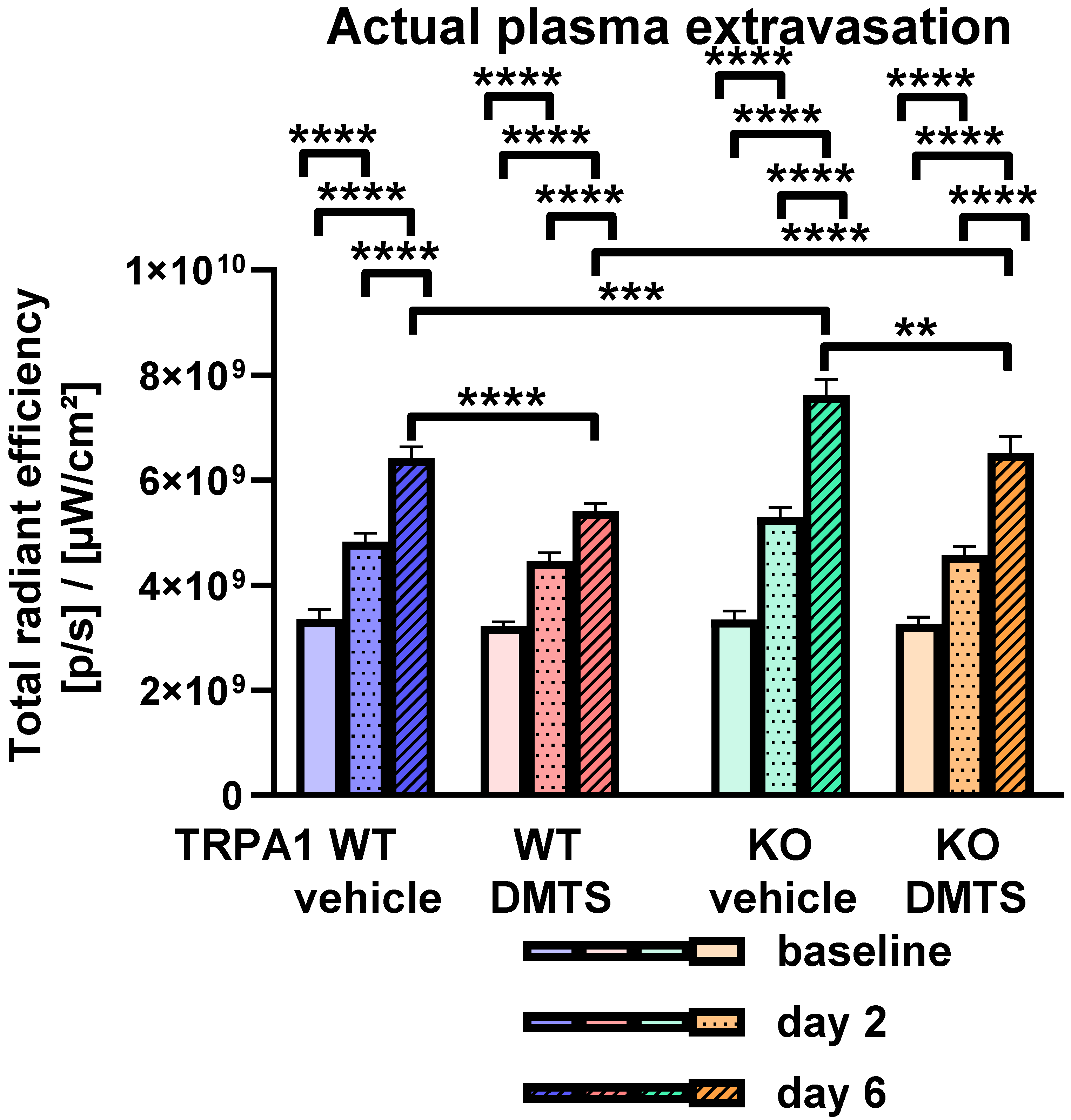
2.3. DMTS Reduced the Actual Rate of Plasma Extravasation in a TRPA1-Independent Manner
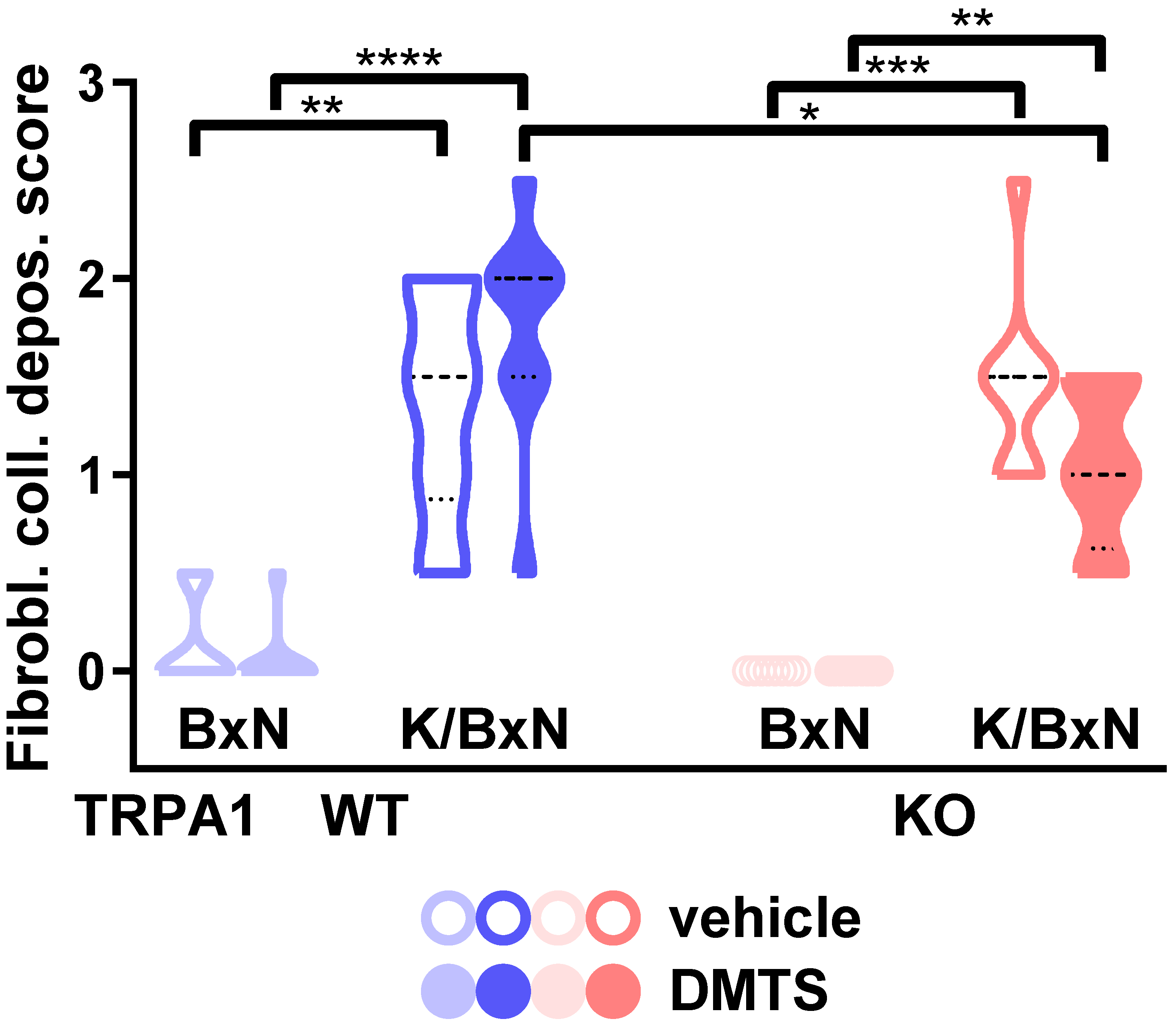
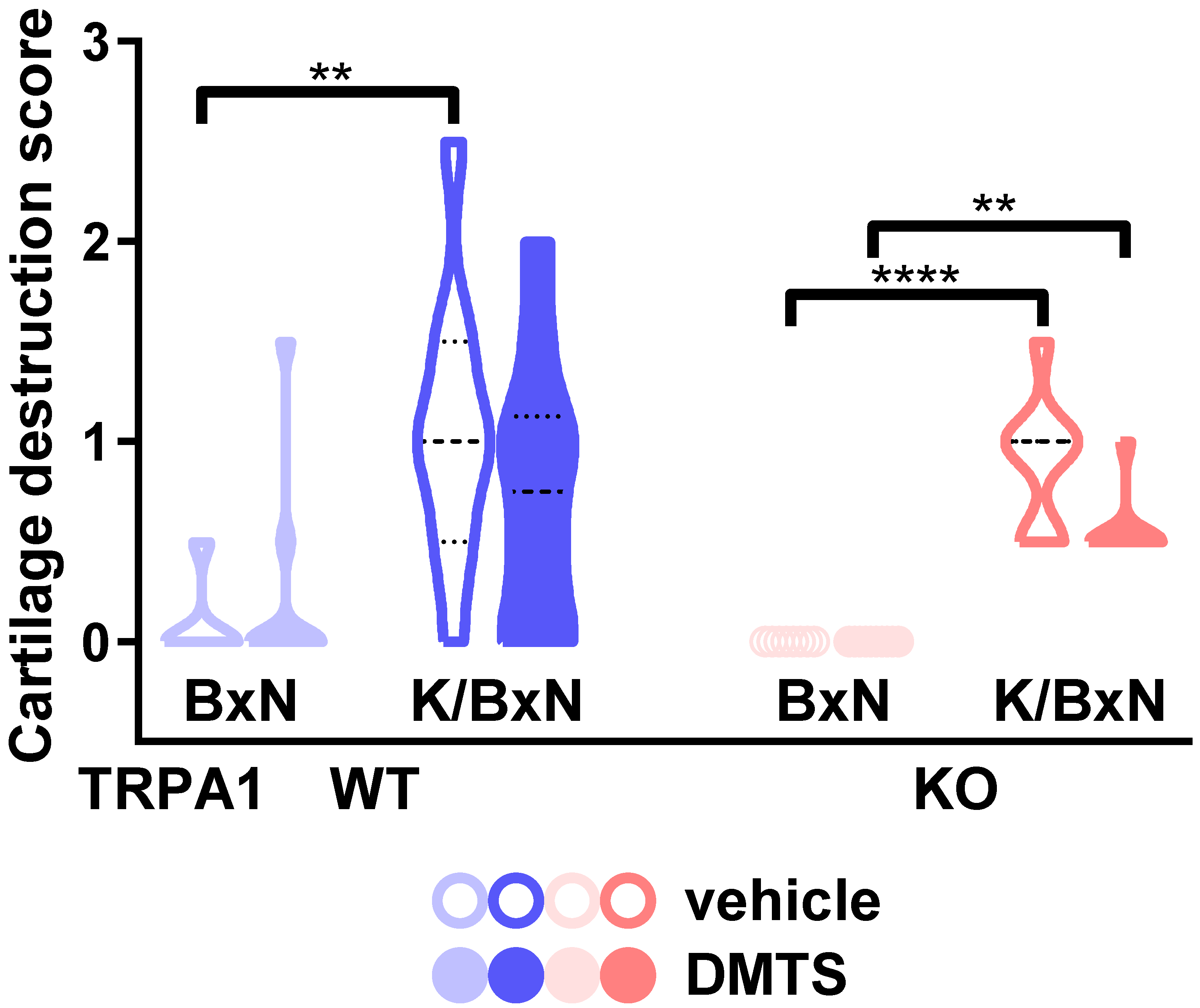
2.4. DMTS-Treated TRPA1 KO Animals Exhibited Milder Collagen Deposition in the Ankle Joints Than WT Ones
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patch Clamp
Data Analysis
4.2. Animals
4.3. Induction of Serum-Transfer Arthritis and Treatment with DMTS
4.4. Measurement of Paw Smwelling
4.5. Arthritis Severity Score
4.6. Detection of the Rate of Plasma Extravasation by Fluorescent Imaging
4.7. Histological Analysis of Arthritic Tibiotarsal Joints
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bollow, M. Rheumatoide Arthritis der Hand. Radiologe 2021, 61, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramaki, T.; Ueki, Y.; Kojima, K.; Kurushima, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Kawachi, N.; Iwamoto, N.; Ichinose, K.; Terada, K.; Eguchi, K.; et al. Clinical predictors of inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) including methotrexate (MTX) in untreated rheumatoid arthritis patients: A single-center observational study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, R.B.; Spaeth, M.; von Restorff, C.; Ackermann, C.; Schulze-Koops, H.; von Kempis, J. Superiority of a Treat-to-Target Strategy over Conventional Treatment with Fixed csDMARD and Corticosteroids: A Multi-Center Randomized Controlled Trial in RA Patients with an Inadequate Response to Conventional Synthetic DMARDs, and New Therapy with Certolizumab Pegol. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.N.; Huri, H.Z.; Yahya, F. Drug-related problems in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 505–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, A.D.; Haase, C.; Cook, A.D.; Hamilton, J.A. K/BxN Serum-Transfer Arthritis as a Model for Human Inflammatory Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bátai, I.Z.; Sár, C.P.; Horváth, Á.; Borbély, É.; Bölcskei, K.; Kemény, Á.; Sándor, Z.; Nemes, B.; Helyes, Z.; Perkecz, A.; et al. TRPA1 Ion Channel Determines Beneficial and Detrimental Effects of GYY4137 in Murine Serum-Transfer Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiner, R.; Pálinkás, Z.; Bäsell, K.; Becher, D.; Antelmann, H.; Nagy, P.; Dick, T.P. Polysulfides Link H2S to Protein Thiol Oxidation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1749–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitvitsky, V.; Yadav, P.K.; An, S.; Seravalli, J.; Cho, U.-S.; Banerjee, R. Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Hemoglobin-catalyzed Hydrogen Sulfide Oxidation and the Fate of Polysulfide Products. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5584–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, R.; Koike, S.; Takano, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Kimura, Y.; Hanaoka, K.; Urano, Y.; Ogasawara, Y.; Kimura, H. Polysulfides (H2Sn) produced from the interaction of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitric oxide (NO) activate TRPA1 channels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Ma, D.; Grubb, B.D.; Wang, M. ROS/TRPA1/CGRP signaling mediates cortical spreading depression. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payrits, M.; Borbely, E.; Godo, S.; Ernszt, D.; Kemeny, A.; Kardos, J.; Szoke, E.; Pinter, E. Genetic deletion of TRPA1 receptor attenuates amyloid beta- 1-42 (Aβ1-42)-induced neurotoxicity in the mouse basal forebrain in vivo. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 189, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheradpezhouh, E.; Choy, J.M.C.; Daria, V.R.; Arabzadeh, E. TRPA1 expression and its functional activation in rodent cortex. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 160314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Souza Monteiro de Araujo, D.; Nassini, R.; Geppetti, P.; De Logu, F. TRPA1 as a therapeutic target for nociceptive pain. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozsgai, G.; Bátai, I.Z.; Pintér, E. Effects of sulfide and polysulfides transmitted by direct or signal transduction-mediated activation of TRPA1 channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozsgai, G.; Payrits, M.; Sághy, É.; Sebestyén-Bátai, R.; Steen, E.; Szőke, É.; Sándor, Z.; Solymár, M.; Garami, A.; Orvos, P.; et al. Analgesic effect of dimethyl trisulfide in mice is mediated by TRPA1 and sst4 receptors. Nitric Oxide 2017, 65, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaiyama, M.; Usui, T.; Nagumo, Y. Non-electrophilic TRPA1 agonists, menthol, carvacrol and clotrimazole, open epithelial tight junctions via TRPA1 activation. J. Biochem. 2020, 168, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naert, R.; Talavera, A.; Startek, J.B.; Talavera, K. TRPA1 gene variants hurting our feelings. Pflüg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrini, A.; Joseph, V.; Dourado, M.; Reese, R.M.; Shields, S.D.; Rougé, L.; Bravo, D.D.; Chernov-Rogan, T.; Austin, C.D.; Chen, H.; et al. A TRPA1 inhibitor suppresses neurogenic inflammation and airway contraction for asthma treatment. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, Á.; Tékus, V.; Bencze, N.; Szentes, N.; Scheich, B.; Bölcskei, K.; Szőke, É.; Mócsai, A.; Tóth-Sarudy, É.; Mátyus, P.; et al. Analgesic effects of the novel semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase inhibitor SZV 1287 in mouse pain models with neuropathic mechanisms: Involvement of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 and ankyrin 1 receptors. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecskés, A.; Pohóczky, K.; Kecskés, M.; Varga, Z.V.; Kormos, V.; Szőke, É.; Henn-Mike, N.; Fehér, M.; Kun, J.; Gyenesei, A.; et al. Characterization of Neurons Expressing the Novel Analgesic Drug Target Somatostatin Receptor 4 in Mouse and Human Brains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) and Polysulfide (H2Sn) Signaling: The First 25 Years. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Q.; Ran, M.; Xia, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Xian, M.; et al. Using resonance synchronous spectroscopy to characterize the reactivity and electrophilicity of biologically relevant sulfane sulfur. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, D.; Lee, S.; Duke, A.; Angalakurthi, S.; Chou, C.-E.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Thompson, D.E.; Petrikovics, I. Intravascular Residence Time Determination for the Cyanide Antidote Dimethyl Trisulfide in Rat by Using Liquid-Liquid Extraction Coupled with High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 6546475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiss, L.; Bocsik, A.; Walter, F.R.; Ross, J.; Brown, D.; Mendenhall, B.A.; Crews, S.R.; Lowry, J.; Coronado, V.; Thompson, D.E.; et al. From the Cover: In Vitro and In Vivo Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration Studies with the Novel Cyanide Antidote Candidate Dimethyl Trisulfide in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 160, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bátai, I.Z.; Horváth, Á.; Pintér, E.; Helyes, Z.; Pozsgai, G. Role of Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Ion Channel and Somatostatin sst4 Receptor in the Antinociceptive and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Sodium Polysulfide and Dimethyl Trisulfide. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolluru, G.K.; Shen, X.; Kevil, C.G. Reactive Sulfur Species. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombi, Á.; Sánta, C.; Bátai, I.Z.; Kormos, V.; Kecskés, A.; Tékus, V.; Pohóczky, K.; Bölcskei, K.; Pintér, E.; Pozsgai, G. Dimethyl Trisulfide Diminishes Traumatic Neuropathic Pain Acting on TRPA1 Receptors in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, P.; Ferulli, F.; Vismara, M.; Tanzi, M.; Negri, S.; Rumolo, A.; Lefkimmiatis, K.; Maestri, M.; Shekha, M.; Pedrazzoli, P.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide-Evoked Intracellular Ca2+ Signals in Primary Cultures of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liu, Y.; Yu, T.; Liu, D.; Shi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y. Hydrogen Sulfide Maintains Dental Pulp Stem Cell Function via TRPV1-Mediated Calcium Influx. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-Z.; Gong, X.-Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.-X.; Nie, Y.-N.; Shang, R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.-C.; Sun, Q.-F.; Gao, P.-F.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Modulates Gastric Acid Secretion in Rats via Involvement of Substance P and Nuclear Factor-ΚB Signaling. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 69, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Sun, Y.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y.; Tang, C.; Du, J.; Jin, H. Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Enhances Carotid Sinus Baroreceptor Sensitivity by Activating the Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily V Member 1 (TRPV1) Channel. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kántás, B.; Szőke, É.; Börzsei, R.; Bánhegyi, P.; Asghar, J.; Hudhud, L.; Steib, A.; Hunyady, Á.; Horváth, Á.; Kecskés, A.; et al. In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Characterization of Novel Analgesic Drug Candidate Somatostatin SST4 Receptor Agonists. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 601887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, N.; Matsubara, M.; Suzuki, H.; Muraki, Y.; Muraki, K. HIF-1α Dependent Upregulation of ZIP8, ZIP14, and TRPA1 Modify Intracellular Zn2+ Accumulation in Inflammatory Synoviocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Wang, P.; Xing, R.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) Mediates Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Primary Human Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Inflammation 2018, 41, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.M.G.; Ueda, T.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Takeda, N.; Fukumitsu, K.; Fukuda, S.; Uemura, T.; Tajiri, T.; Ohkubo, H.; Maeno, K.; et al. AITC inhibits fibroblast-myofibroblast transition via TRPA1-independent MAPK and NRF2/HO-1 pathways and reverses corticosteroids insensitivity in human lung fibroblasts. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowin, T.; Bleck, J.; Schneider, M.; Pongratz, G. Selective killing of proinflammatory synovial fibroblasts via activation of transient receptor potential ankyrin (TRPA1). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 154, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowin, T.; Pongratz, G.; Straub, R.H. The synthetic cannabinoid WIN55,212-2 mesylate decreases the production of inflammatory mediators in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by activating CB2, TRPV1, TRPA1 and yet unidentified receptor targets. J. Inflamm. Lond. Engl. 2016, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.-J.; Jia, W.-W.; Liu, X.-H.; Pan, L.-L.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Yang, D.; Shen, X.-Y.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.Z. S-propargyl-cysteine attenuates inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis by modulating the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sieghart, D.; Liszt, M.; Wanivenhaus, A.; Bröll, H.; Kiener, H.; Klösch, B.; Steiner, G. Hydrogen sulphide decreases IL-1β-induced activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with osteoarthritis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloesch, B.; Liszt, M.; Broell, J. H2S transiently blocks IL-6 expression in rheumatoid arthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes and deactivates p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Cell Biol. Int. 2010, 34, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Li, H.R.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, D.G.; Liang, Z.C.; Shi, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Xin, L.; Zhao, D.B. Diallyl Trisulfide can induce fibroblast-like synovial apoptosis and has a therapeutic effect on collagen-induced arthritis in mice via blocking NF-κB and Wnt pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 71, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, D.; Zietsch, C.; Becher, P.M.; Schulze, K.; Schultheiss, H.-P.; Tschöpe, C.; Westermann, D. Differential Expression of Matrix Metalloproteases in Human Fibroblasts with Different Origins. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, e875742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowin, T.; Tingting, R.; Zurmahr, J.; Classen, T.; Schneider, M.; Pongratz, G. Cannabidiol (CBD): A killer for inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nummenmaa, E.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, L.J.; Paukkeri, E.-L.; Nieminen, R.M.; Moilanen, T.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) is functionally expressed in primary human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthr. Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nummenmaa, E.; Hämäläinen, M.; Pemmari, A.; Moilanen, L.J.; Tuure, L.; Nieminen, R.M.; Moilanen, T.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) Is Involved in Upregulating Interleukin-6 Expression in Osteoarthritic Chondrocyte Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaamonde-García, C.; Burguera, E.F.; Vela-Anero, Á.; Hermida-Gómez, T.; Filgueira-Fernández, P.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.A.; Meijide-Faílde, R.; Blanco, F.J. Intraarticular Administration Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on an In Vivo Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, A.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Albashari, A.A.; Li, J.; Yin, J.; He, Z.; Wang, Q.; et al. pH and enzyme dual-responsive release of hydrogen sulfide for disc degeneration therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela-Anero, Á.; Hermida-Gómez, T.; Gato-Calvo, L.; Vaamonde-García, C.; Díaz-Prado, S.; Meijide-Faílde, R.; Blanco, F.J.; Burguera, E.F. Long-term effects of hydrogen sulfide on the anabolic-catabolic balance of articular cartilage in vitro. Nitric Oxide 2017, 70, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, C.; Tian, S.; Sun, K.; Wang, D.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates IL-1β-induced inflammatory signaling and dysfunction of osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burguera, E.F.; Vela-Anero, A.; Magalhães, J.; Meijide-Faílde, R.; Blanco, F.J. Effect of hydrogen sulfide sources on inflammation and catabolic markers on interleukin 1β-stimulated human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-P.; Tang, J.-L.; Bao, J.-P.; Hu, P.-F.; Yu, C.; Shi, Z.-L.; Wu, L.-D. Effects of diallyl sulphide in chondrocyte and cartilage in experimental osteoarthritis in rabbit. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, D.M.; Jordt, S.-E.; Nikai, T.; Tsuruda, P.R.; Read, A.J.; Poblete, J.; Yamoah, E.N.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. TRPA1 Mediates the Inflammatory Actions of Environmental Irritants and Proalgesic Agents. Cell 2006, 124, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Botz, B.; Bölcskei, K.; Kereskai, L.; Kovács, M.; Németh, T.; Szigeti, K.; Horváth, I.; Máthé, D.; Kovács, N.; Hashimoto, H.; et al. Differential Regulatory Role of Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase–Activating Polypeptide in the Serum-Transfer Arthritis Model. Arthr. Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2739–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakus, Z.; Simon, E.; Balázs, B.; Mócsai, A. Genetic deficiency of Syk protects mice from autoantibody-induced arthritis. Arthr. Rheum. 2010, 62, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borbély, É.; Hunyady, Á.; Pohóczky, K.; Payrits, M.; Botz, B.; Mócsai, A.; Berger, A.; Szőke, É.; Helyes, Z. Hemokinin-1 as a Mediator of Arthritis-Related Pain via Direct Activation of Primary Sensory Neurons. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 594479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bátai, I.Z.; Dombi, Á.; Borbély, É.; Fehér, Á.; Papp, F.; Varga, Z.; Mócsai, A.; Helyes, Z.; Pintér, E.; Pozsgai, G. Investigation of the Role of the TRPA1 Ion Channel in Conveying the Effect of Dimethyl Trisulfide on Vascular and Histological Changes in Serum-Transfer Arthritis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060671
Bátai IZ, Dombi Á, Borbély É, Fehér Á, Papp F, Varga Z, Mócsai A, Helyes Z, Pintér E, Pozsgai G. Investigation of the Role of the TRPA1 Ion Channel in Conveying the Effect of Dimethyl Trisulfide on Vascular and Histological Changes in Serum-Transfer Arthritis. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(6):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060671
Chicago/Turabian StyleBátai, István Z., Ágnes Dombi, Éva Borbély, Ádám Fehér, Ferenc Papp, Zoltan Varga, Attila Mócsai, Zsuzsanna Helyes, Erika Pintér, and Gábor Pozsgai. 2022. "Investigation of the Role of the TRPA1 Ion Channel in Conveying the Effect of Dimethyl Trisulfide on Vascular and Histological Changes in Serum-Transfer Arthritis" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 6: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060671
APA StyleBátai, I. Z., Dombi, Á., Borbély, É., Fehér, Á., Papp, F., Varga, Z., Mócsai, A., Helyes, Z., Pintér, E., & Pozsgai, G. (2022). Investigation of the Role of the TRPA1 Ion Channel in Conveying the Effect of Dimethyl Trisulfide on Vascular and Histological Changes in Serum-Transfer Arthritis. Pharmaceuticals, 15(6), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060671






