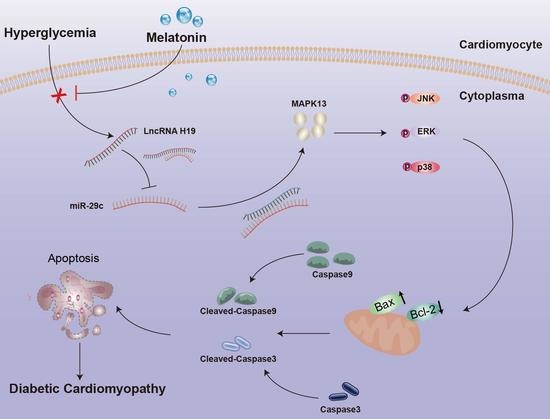
Melatonin Alleviates Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNA H19/miR-29c/MAPK Axis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Diabetes Influenced Body Weight and Blood Glucose of Rats, and Melatonin Improved Myocardial Fiber Disorder, Collagen Accumulation, and Myocardial Dysfunction in Diabetes
2.2. Melatonin Alleviated Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis Caused by Hyperglycemia
2.3. Melatonin Suppressed Phosphorylation of JNK/ERK/p38 in Diabetic Cardiomyocytes
2.4. Melatonin Regulated the Complex Network of lncRNA H19, miRNA-29c, and MAPK13 in Cardiomyocytes
2.5. LncRNA H19 Binds miR-29c Directly and MAPK13 Is a Target of miR-29c
2.6. LncRNA H19-shRNA, miRNA-29c Mimic, and Melatonin Treatments Ameliorated Hyperglycemia-Induced Apoptosis in H9c2 Cells
2.7. Melatonin and lncRNA H19-shRNA Reversed the Pro-Apoptotic Effect of miRNA-29c Inhibitor in High-Glucose-Treated H9c2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Langendorff Perfusion System
4.3. Histology
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Cell Transfection
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Hoechst 33258 Staining
4.8. Luciferase Assay
4.9. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP)
4.10. Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.11. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
4.12. DNA Fragment Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Wintergerst, K.A.; Keller, B.B.; Cai, L. Mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy and potential therapeutic strategies: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Virk, H.; Khalid, M.; Lavie, C.J.; Ventura, H.; Mukherjee, D.; Ramu, V.; Bhogal, S.; Kumar, G.; Shanmugasundaram, M.; et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy—A comprehensive updated review. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 62, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferović, P.M.; Paulus, W.J. Clinical diabetic cardiomyopathy: A two-faced disease with restrictive and dilated phenotypes. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.J.; Kitzman, D.W.; Borlaug, B.A.; van Heerebeek, L.; Zile, M.R.; Kass, D.A.; Paulus, W.J. Phenotype-Specific Treatment of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Multiorgan Roadmap. Circulation 2016, 134, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.; Ke, Z.Q.; Guo, S.; Yang, X.S.; Zhang, F.X.; Liu, X.F.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.G.; Ke, H.Y.; Liu, C. Curcumin protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by promoting autophagy and alleviating apoptosis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 124, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, M.; Jin, T.; An, F. Nicorandil alleviates apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy through PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5349–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, T.; Man, W.; Yin, T.; Guo, W.; Gao, E.; et al. Melatonin protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy through Mst1/Sirt3 signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, V.; Gaikwad, A.B. Telmisartan and thiorphan combination treatment attenuates fibrosis and apoptosis in preventing diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; He, M.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Nie, X.; Yan, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. MiR-30c/PGC-1β protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy via PPARα. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.W.; Chen, Z.F.; Wan, Y.F.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.Q. Long Non-coding RNA H19 Suppression Protects the Endothelium Against Hyperglycemic-Induced Inflammation via Inhibiting Expression of miR-29b Target Gene Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor a through Activation of the Protein Kinase B/Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Tang, W.; He, Y.; Wen, L.; Sun, B.; Li, S. Long non-coding RNA and microRNA-675/let-7a mediates the protective effect of melatonin against early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via targeting TP53 and neural growth factor. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Jin, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Kong, X. lncRNA MIAT functions as a competing endogenous RNA to upregulate DAPK2 by sponging miR-22-3p in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Dong, Z.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, Y. MALAT1-mediated recruitment of the histone methyltransferase EZH2 to the microRNA-22 promoter leads to cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.X. LncRNA H19 promotes atherosclerosis by regulating MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Bitarafan, S.; Yari, M.; Broumand, M.A.; Ghaderian, S.; Rahimi, M.; Mirfakhraie, R.; Azizi, F.; Omrani, M.D. Association of Increased Levels of lncRNA H19 in PBMCs with Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. Cell J. 2019, 20, 564–568. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Gu, J.; Yang, O.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal miRNA-29c Decreases Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibition of Excessive Autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Deng, F.; Song, J.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tang, T.; Zheng, L. Evaluation of miR-29c inhibits endotheliocyte migration and angiogenesis of human endothelial cells by suppressing the insulin like growth factor 1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 866–877. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sainz, R.M.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.; Qin, L. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under promises but over delivers. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzaga, N.A.; Awata, W.; Ficher, S.P.; Assis, V.O.; Alves, J.V.; Tostes, R.C.; Tirapelli, C.R. Melatonin reverses the loss of the anticontractile effect of perivascular adipose tissue in obese rats. J. Pineal Res. 2021, 70, e12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. An evolutionary view of melatonin synthesis and metabolism related to its biological functions in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4677–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilg, A.; Bechstein, P.; Saade, A.; Dick, M.; Li, T.X.; Tosini, G.; Rami, A.; Zemmar, A.; Stehle, J.H. Melatonin modulates daytime-dependent synaptic plasticity and learning efficiency. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 66, e12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Han, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, G.; Wu, X.; Huang, X.; Fang, R.; Baba, K.; Bin, P.; et al. Administration of Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Diurnal Rhythms of the Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. mSystems 2020, 5, e00002-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.M.; Dong, X.; Xue, X.D.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.L.; Wang, Z.S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Liang, Y.X.; et al. Melatonin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy and reduces myocardial vulnerability to ischemia-reperfusion injury by improving mitochondrial quality control: Role of SIRT6. J. Pineal Res. 2021, 70, e12698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Feng, N.; Tang, D.; Feng, J.; Li, Z.; Jia, M.; Liu, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, F.; et al. Melatonin prevents Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission in diabetic hearts through SIRT1-PGC1α pathway. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 65, e12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, F.Y.; Tang, S.T.; Su, H.; Tang, H.Q.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.Q. Melatonin ameliorates myocardial apoptosis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with long-term diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.T.; Su, H.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, H.Q.; Wang, C.J.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhu, H.Q.; Wang, Y. Melatonin Attenuates Aortic Endothelial Permeability and Arteriosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats: Possible Role of MLCK- and MLCP-Dependent MLC Phosphorylation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 21, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhen, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Cheng, F.; Mei, W.; Zheng, D.; Feng, J.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) protects cardiomyocytes against high glucose-induced injuries through inhibiting reactive oxygen species-activated leptin-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 pathways, but not the leptin-c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway in vitro. J. Diabetes Investig. 2017, 8, 434–445. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.L.; Wu, B.Q.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Hao, Y.L.; Liang, J.J.; Fang, F.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.H. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide ameliorates high glucose-induced myocardial injury & inflammation via the CIRP-MAPK signaling pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Life Sci. 2018, 208, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Ares-Carrasco, S.; Picatoste, B.; Camafeita, E.; Carrasco-Navarro, S.; Zubiri, I.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J.; López, J.A.; Tuñón, J.; Lorenzo, O. Proteome changes in the myocardium of experimental chronic diabetes and hypertension: Role of PPARα in the associated hypertrophy. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1816–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.L.; Crossman, D.J. Mechanisms underlying the impaired contractility of diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J. Cardiol. 2014, 6, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, J.H.; Mai, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y. Association between prediabetes and risk of all cause mortality and cardiovascular disease: Updated meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, m2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, H.C.; Abel, E.D. Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, S.S.; Cheng, X.J.; Yang, X.; Cui, X.G.; Zhao, X.R.; Zhao, H.; Hao, M.F.; Li, M.D.; et al. Curcumin alleviates oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via Sirt1-Foxo1 and PI3K-Akt signalling pathways. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12355–12367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, H. Inhibition of miR-223 attenuates the NLRP3 inflammasome activation, fibrosis, and apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; He, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Q.; Xing, J.; et al. Akap1 deficiency exacerbates diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice by NDUFS1-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tran, D.; Yang, H.C.; Nylander, S.; Birnbaum, Y.; Ye, Y. Dapagliflozin and Ticagrelor Have Additive Effects on the Attenuation of the Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and the Progression of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: An AMPK-mTOR Interplay. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2020, 34, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Zhao, L.; Ren, X.M.; Ye, P.; Hu, Z.Y. LCZ696, an angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Damry, N.T.; Attia, H.A.; Al-Rasheed, N.M.; Al-Rasheed, N.M.; Mohamad, R.A.; Al-Amin, M.A.; Dizmiri, N.; Atteya, M. Sitagliptin attenuates myocardial apoptosis via activating LKB-1/AMPK/Akt pathway and suppressing the activity of GSK-3β and p38α/MAPK in a rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Ren, X.; Qian, X.; Ye, P.; Luo, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Inhibition of JNK and p38 MAPK-mediated inflammation and apoptosis by ivabradine improves cardiac function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Man, W.; Lin, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Mst1 knockdown alleviates cardiac lipotoxicity and inhibits the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Yu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.T.; Zhu, H.Q. Inhibition of miR-29b suppresses MAPK signaling pathway through targeting SPRY1 in atherosclerosis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 102, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin and the pathologies of weakened or dysregulated circadian oscillators. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHill, A.W.; Sano, A.; Hilditch, C.J.; Barger, L.K.; Czeisler, C.A.; Picard, R.; Klerman, E.B. Robust stability of melatonin circadian phase, sleep metrics, and chronotype across months in young adults living in real-world settings. J. Pineal Res. 2021, 70, e12720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, Y.B.; Tosun, V.; Güntekin, Ü. Melatonin protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy through the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, X.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, J.; Fan, Y.; et al. Melatonin activates Parkin translocation and rescues the impaired mitophagy activity of diabetic cardiomyopathy through Mst1 inhibition. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5132–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.H.; El-Missiry, M.A.; Othman, A.I. Melatonin ameliorates metabolic risk factors, modulates apoptotic proteins, and protects the rat heart against diabetes-induced apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 747, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Sahil, A.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Dong, R.; Xue, H.; et al. Melatonin alleviates cardiac fibrosis via inhibiting lncRNA MALAT1/miR-141-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome and TGF-β1/Smads signaling in diabetic cardiomyopathy. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 5282–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, X. Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 overexpression promotes viability and inhibits high glucose-induced oxidative stress of cardiomyocytes by targeting microRNA-34a/SIRT1 axis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Zhou, X. LncRNA DCRF regulates cardiomyocyte autophagy by targeting miR-551b-5p in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4558–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Qin, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Che, H.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, A.; Sun, X.; Yue, E.; et al. Silencing long non-coding RNA Kcnq1ot1 alleviates pyroptosis and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Song, L.; Yu, H.; Feng, S.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; He, Y. Knockdown of LncRNA-H19 Ameliorates Kidney Fibrosis in Diabetic Mice by Suppressing miR-29a-Mediated EndMT. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 586895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, M.S.; Abdelghany, A.A.; Toraih, E.A.; Mohamed, A.M. Circulating long noncoding RNAs H19 and GAS5 are associated with type 2 diabetes but not with diabetic retinopathy: A preliminary study. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Yang, X.C.; Chen, M.L.; Zhuang, Z.W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.J. LncRNA H19/Runx2 axis promotes VSMCs transition via MAPK pathway. Am. J. Transl Res. 2020, 12, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, M.; Villena, J.A. Contribution of Impaired Insulin Signaling to the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Zhong, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, S.; Zhu, H. Melatonin Alleviates Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNA H19/miR-29c/MAPK Axis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070821
Tang H, Zhong H, Liu W, Wang Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Tang S, Zhu H. Melatonin Alleviates Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNA H19/miR-29c/MAPK Axis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(7):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070821
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Haitao, Hongli Zhong, Wanqing Liu, Yi Wang, Yuan Wang, Liuqing Wang, Songtao Tang, and Huaqing Zhu. 2022. "Melatonin Alleviates Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNA H19/miR-29c/MAPK Axis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 7: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070821
APA StyleTang, H., Zhong, H., Liu, W., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Tang, S., & Zhu, H. (2022). Melatonin Alleviates Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNA H19/miR-29c/MAPK Axis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Pharmaceuticals, 15(7), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070821