Endocannabinoid System: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
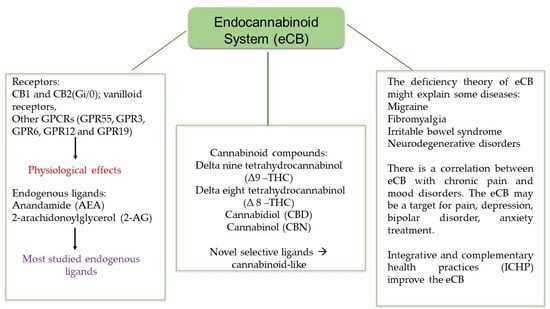
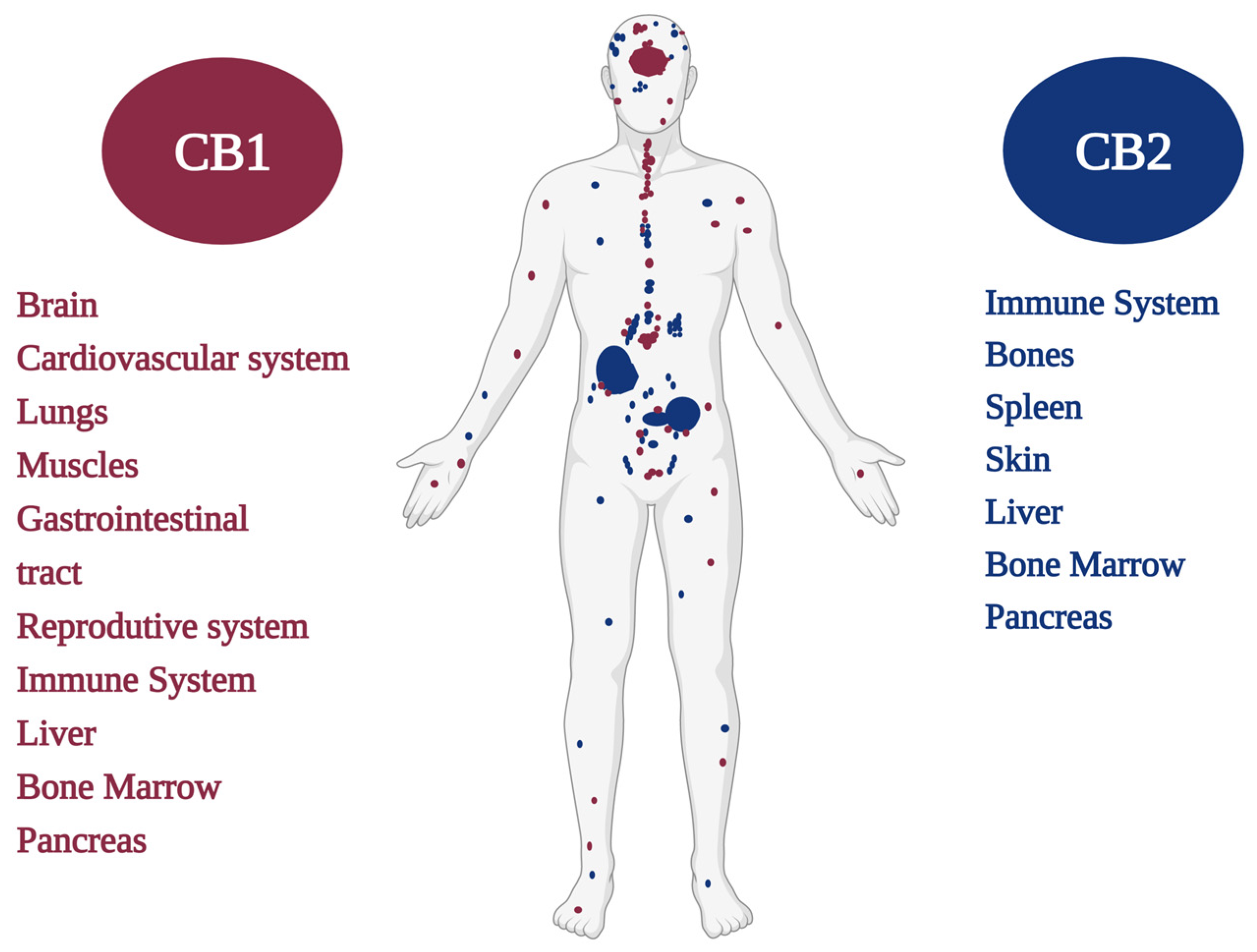
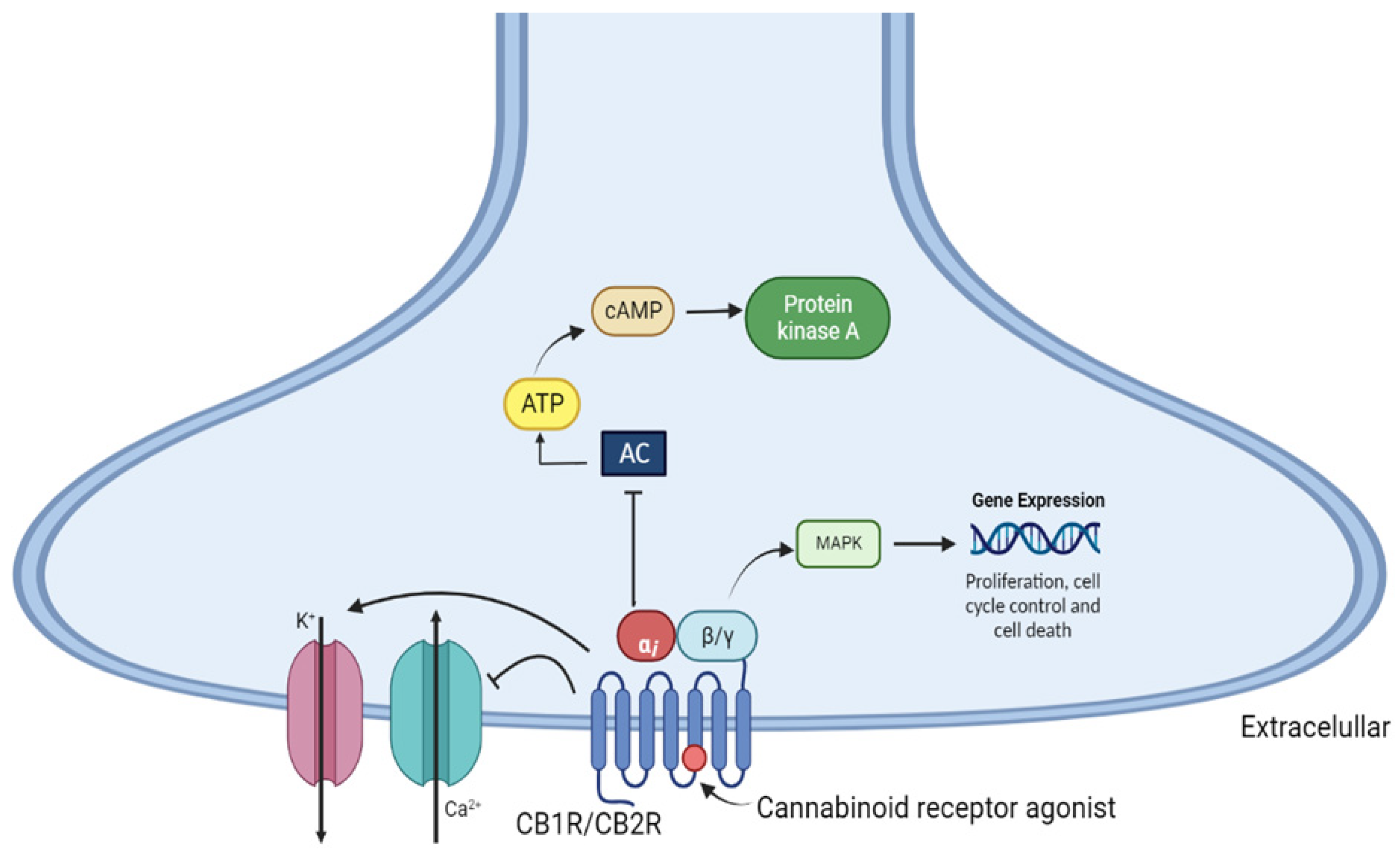
2. Cannabinoid Receptors
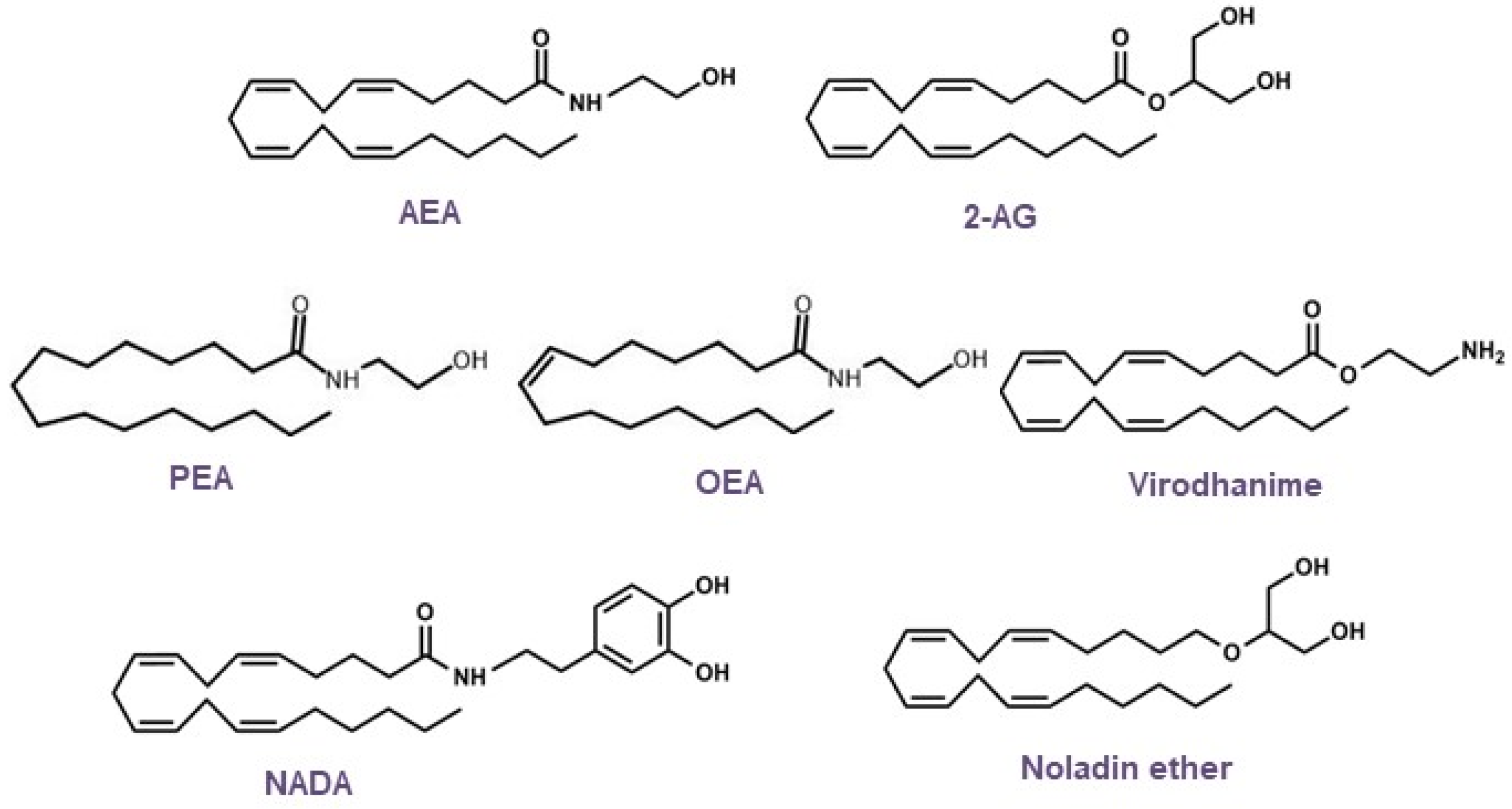
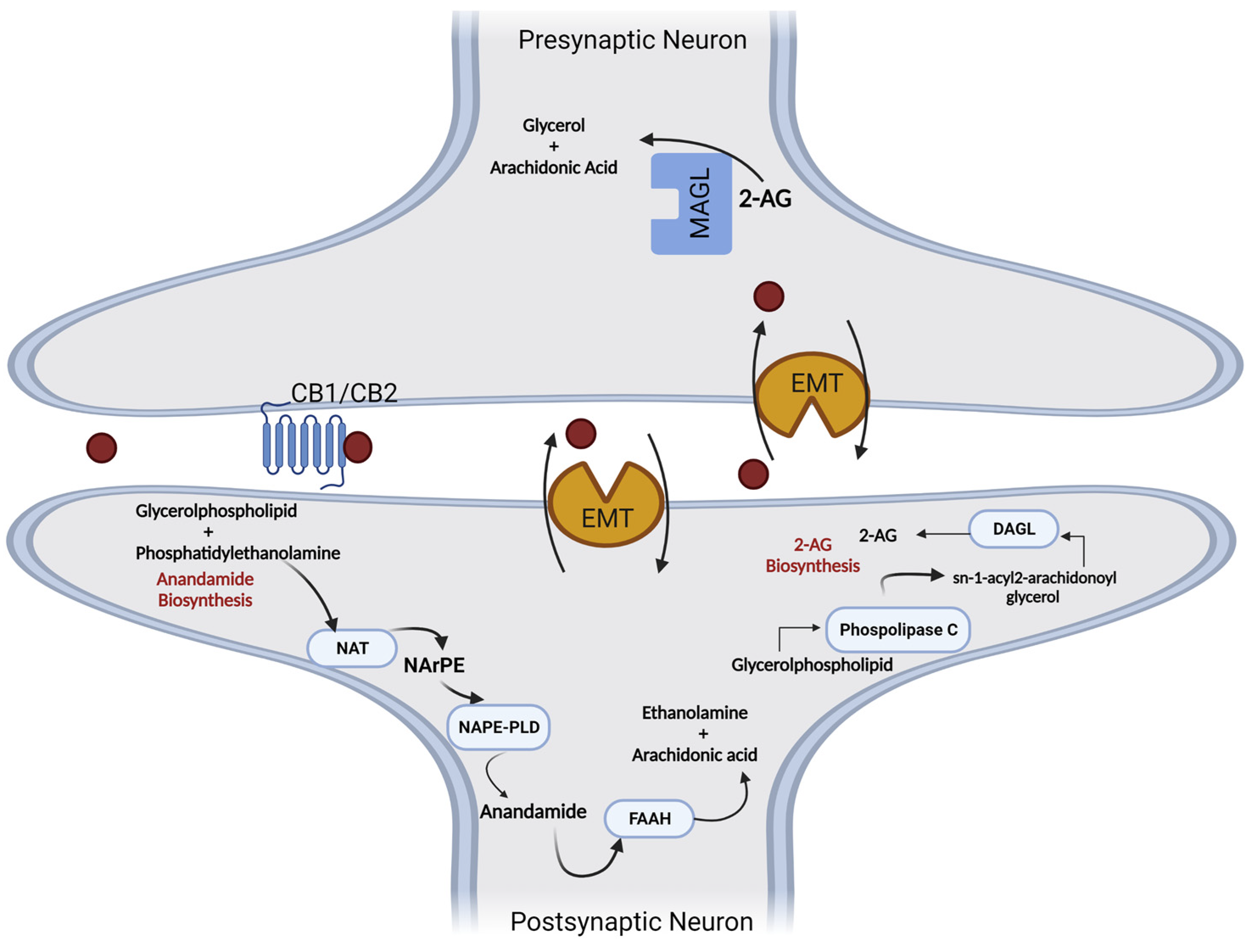
3. Endocannabinoids: Synthesis, Release, and Metabolism
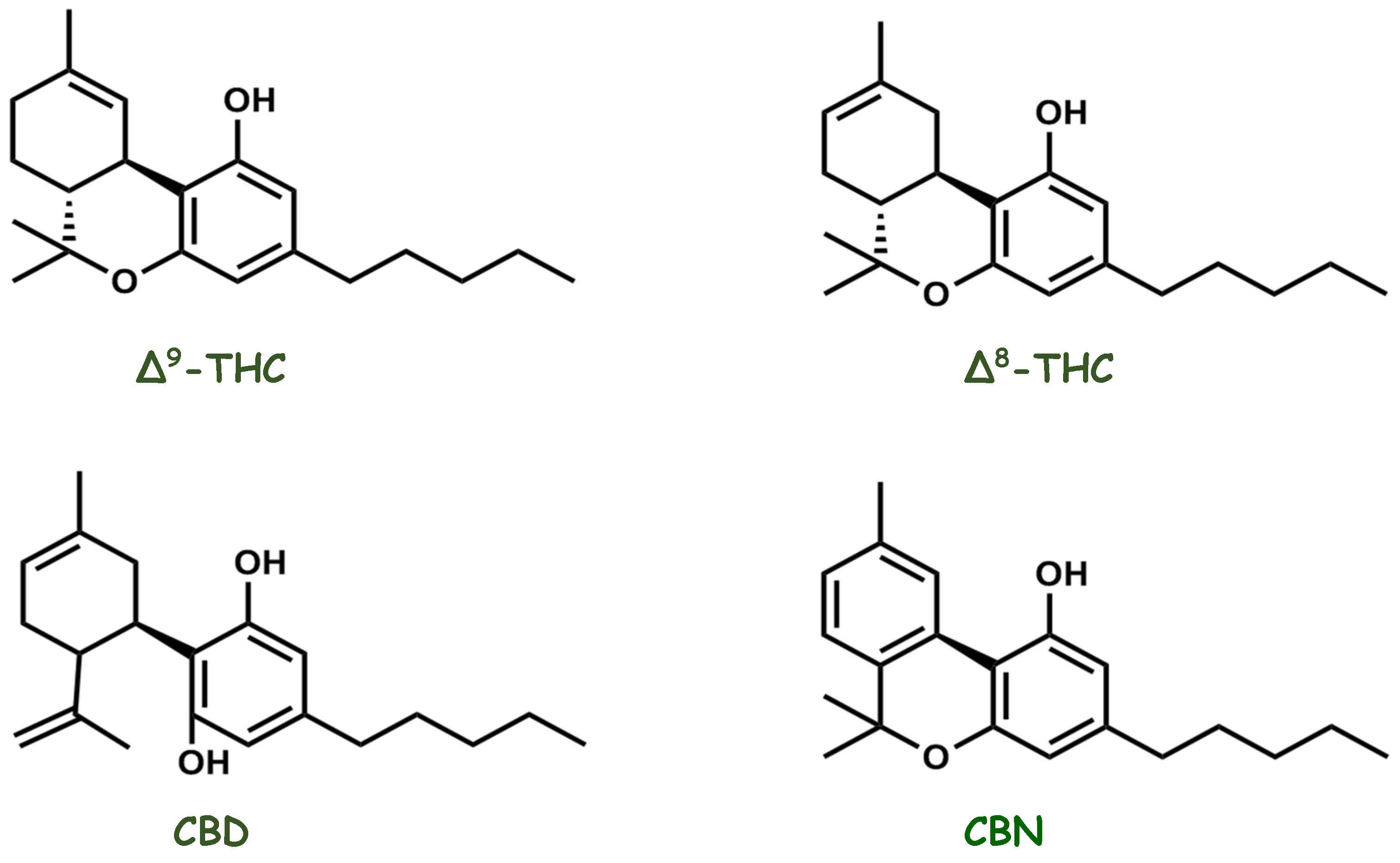
4. Molecules That Modulate the Endocannabinoid System
5. Endocannabinoid System Emerging as a Pharmacotherapy Target for Chronic Pain and Mood Disorders
6. Harmonization of the Endocannabinoid System through Integrative and Complementary Health Practices (ICHP)
7. Research Perspectives and Trends in the Endocannabinoid System
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urits, I.; Charipova, K.; Gress, K.; Li, N.; Berger, A.A.; Cornett, E.M.; Kassem, H.; Ngo, A.L.; Kaye, A.D.; Viswanath, O. Adverse Effects of Recreational and Medical Cannabis. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 2021, 51, 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Legare, C.A.; Raup-Konsavage, W.M.; Vrana, K.E. Therapeutic Potential of Cannabis, Cannabidiol, and Cannabinoid-Based Pharmaceuticals. Pharmacology 2022, 107, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, Z.; Callaway, R.; Belle-Isle, L.; Capler, R.; Kay, R.; Lucas, P.; Holtzman, S. Cannabis for therapeutic purposes: Patient characteristics, access, and reasons for use. Int. J. Drug Policy 2013, 24, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuardi, A.W. History of cannabis as a medicine: A review. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2006, 28, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlimme, J.; Rada, D.; Schneider, U. Cannabis consumption and its psychosocial effects in a comparison of different cultures. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 2001, 69, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Becker, T.; Di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoids and energy homeostasis: An update. Biofactors 2014, 40, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Reis, R.A.; Isaac, A.R.; Freitas, H.R.; de Almeida, M.M.; Schuck, P.F.; Ferreira, G.C.; Andrade-da-Costa, B.; Trevenzoli, I.H. Quality of Life and a Surveillant Endocannabinoid System. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 747229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.S.; Paddibhatla, I.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Malleswarapu, M.; Sangeeth, A.; Kovuru, N.; Dahariya, S.; Gautam, D.K.; Pallepati, A.; Gutti, R.K. Endocannabinoid system: Role in blood cell development, neuroimmune interactions and associated disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 353, 577501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.C.; Yang, D.; Nicolaescu, V.; Best, T.J.; Gula, H.; Saxena, D.; Gabbard, J.D.; Chen, S.N.; Ohtsuki, T.; Friesen, J.B.; et al. Cannabidiol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication through induction of the host ER stress and innate immune responses. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabi6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocchio, L.; Bordea, I.R.; Ballini, A.; Lorusso, F.; Hazballa, D.; Isacco, C.G.; Malcangi, G.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, F.; et al. Environmental Issues and Neurological Manifestations Associated with COVID-19 Pandemic: New Aspects of the Disease? Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.P. Cannabinoids and the Coronavirus. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020, 5, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis-Gray, K.; Tupal, S.; Premkumar, L.S. TRPV1: A Common Denominator Mediating Antinociceptive and Antiemetic Effects of Cannabinoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, R.; Glaser, T.; Villegas, C.; Burgos, V.; Ulrich, H.; Paz, C. Therapeutic Effects of Cannabinoids and Their Applications in COVID-19 Treatment. Life 2022, 12, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurman, L.D.; Lu, D.; Kendall, D.A.; Howlett, A.C.; Lichtman, A.H. Molecular Mechanism and Cannabinoid Pharmacology. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 258, 323–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.E.; Williams, C.M.; Iversen, L.; Whalley, B.J. Molecular Pharmacology of Phytocannabinoids. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2017, 103, 61–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, W.A.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Pertwee, R.G.; Stevenson, L.A.; Griffin, G.; Gibson, D.; Mandelbaum, A.; Etinger, A.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992, 258, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; De Petrocellis, L.; Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Potential biosynthetic connections between the two cannabimimetic eicosanoids, anandamide and 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol, in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 227, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Pharmacology of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 74, 129–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanolkar, A.D.; Palmer, S.L.; Makriyannis, A. Molecular probes for the cannabinoid receptors. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 108, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, J.L.; Martin, B.R. Cannabinoid pharmacology: Implications for additional cannabinoid receptor subtypes. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2002, 121, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E. CB1 and CB2 Receptor Pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Cao, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhou, N. New Insights in Cannabinoid Receptor Structure and Signaling. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Ligresti, A.; Moriello, A.S.; Allara, M.; Bisogno, T.; Petrosino, S.; Stott, C.G.; Di Marzo, V. Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1479–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muller, C.; Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H. Cannabinoid Ligands Targeting TRP Channels. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veilleux, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Silvestri, C. The Expanded Endocannabinoid System/Endocannabinoidome as a Potential Target for Treating Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2019, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Silvestri, C. Lifestyle and Metabolic Syndrome: Contribution of the Endocannabinoidome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piscitelli, F.; Silvestri, C. Role of the Endocannabinoidome in Human and Mouse Atherosclerosis. Curr. Pharmacol. Des. 2019, 25, 3147–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Walder, K.; Kloiber, S.; Amminger, P.; Berk, M.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Maes, M.; Puri, B.K.; Carvalho, A.F. The endocannabinoidome in neuropsychiatry: Opportunities and potential risks. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, M.; Hogenauer, C.; Blesl, A.; Haybaeck, J.; Golob-Schwarzl, N.; Ferreiros, N.; Thomas, D.; Gurke, R.; Trotzmuller, M.; Kofeler, H.C.; et al. Members of the endocannabinoid system are distinctly regulated in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; Piscitelli, F. The Endocannabinoid System and its Modulation by Phytocannabinoids. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castonguay-Paradis, S.; Lacroix, S.; Rochefort, G.; Parent, L.; Perron, J.; Martin, C.; Lamarche, B.; Raymond, F.; Flamand, N.; Di Marzo, V.; et al. Dietary fatty acid intake and gut microbiota determine circulating endocannabinoidome signaling beyond the effect of body fat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, F.; Turco, F.; Iannotta, M.; De Gregorio, D.; Palumbo, I.; Sarnelli, G.; Furiano, A.; Napolitano, F.; Boccella, S.; Luongo, L.; et al. Antibiotic-induced microbiota perturbation causes gut endocannabinoidome changes, hippocampal neuroglial reorganization and depression in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 67, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Li, C.; Jaffe, A.E.; Shin, J.H.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Yamin, R.; Weinberger, D.R.; Hyde, T.M.; Kleinman, J.E. Cannabinoid receptor CNR1 expression and DNA methylation in human prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and caudate in brain development and schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkenham, M.; Groen, B.G.; Lynn, A.B.; De Costa, B.R.; Richfield, E.K. Neuronal localization of cannabinoid receptors and second messengers in mutant mouse cerebellum. Brain Res. 1991, 552, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, C.; Mollereau, C.; Vassart, G.; Parmentier, M. Nucleotide sequence of a human cannabinoid receptor cDNA. Nucleic. Acids Res. 1990, 18, 7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerard, C.M.; Mollereau, C.; Vassart, G.; Parmentier, M. Molecular cloning of a human cannabinoid receptor which is also expressed in testis. Biochem. J. 1991, 279 Pt 1, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Onaivi, E.S.; Chaudhuri, G. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the mouse brain-type cannabinoid receptor protein. DNA Seq. 1995, 5, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, C.; Campillo, N.E.; Goya, P.; Paez, J.A. Homology models of the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. A docking analysis study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 40, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.S.; Ashton, J.C.; Glass, M. Cannabinoid Receptors: A brief history and what not. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2009, 14, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Lynskey, M.T. Candidate genes for cannabis use disorders: Findings, challenges and directions. Addiction 2009, 104, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Grzemska, M.; Clark, L.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glass, M.; Dragunow, M.; Faull, R.L. Cannabinoid receptors in the human brain: A detailed anatomical and quantitative autoradiographic study in the fetal, neonatal and adult human brain. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaFrance, E.M.; Stueber, A.; Glodosky, N.C.; Mauzay, D.; Cuttler, C. Overbaked: Assessing and predicting acute adverse reactions to Cannabis. J. Cannabis Res. 2020, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stella, N. Endocannabinoid signaling in microglial cells. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56 (Suppl. S1), 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, P.E.; Younts, T.J.; Chavez, A.E.; Hashimotodani, Y. Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 2012, 76, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kano, M. Control of synaptic function by endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde signaling. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2014, 90, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abuhasira, R.; Schleider, L.B.; Mechoulam, R.; Novack, V. Epidemiological characteristics, safety and efficacy of medical cannabis in the elderly. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 49, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehra, A.; Burns, J.; Liu, C.K.; Manza, P.; Wiers, C.E.; Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J. Cannabis Addiction and the Brain: A Review. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smiarowska, M.; Bialecka, M.; Machoy-Mokrzynska, A. Cannabis and cannabinoids: Pharmacology and therapeutic potential. Neurol. Neurochir Pol. 2022, 56, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K. Distribution of cannabinoid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. Handb Exp. Pharmacol. 2005, 168, 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Bab, I.; Biro, T.; Cabral, G.A.; Dey, S.K.; Di Marzo, V.; Konje, J.C.; Kunos, G.; Mechoulam, R.; Pacher, P.; et al. Endocannabinoid signaling at the periphery: 50 years after THC. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuce, B.; Kemmer, M.; Qian, G.; Muller, M.; Sibaev, A.; Li, Y.; Kreis, M.E.; Storr, M. Cannabinoid 1 receptors modulate intestinal sensory and motor function in rat. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 672-e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, R.A.A.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; Abdel-Salam, O.M.E.; Khattab, M.M.; Salem, N.A.; El-Khyat, Z.A.; Morsy, F.A.; Eldenshary, E.D.S. Modulation of gastric acid secretion by cannabinoids in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol 2019, 33, e22256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruginsk, S.G.; Vechiato, F.M.; Uchoa, E.T.; Elias, L.L.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J. Type 1 cannabinoid receptor modulates water deprivation-induced homeostatic responses. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R1358–R1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibarra-Lecue, I.; Diez-Alarcia, R.; Uriguen, L. Serotonin 2A receptors and cannabinoids. Prog. Brain. Res. 2021, 259, 135–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunos, G. Understanding metabolic homeostasis and imbalance: What is the role of the endocannabinoid system? Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, S18–S24; discussion S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwad, M.A.; Couch, D.G.; Theophilidou, E.; Sarmad, S.; Barrett, D.A.; Larvin, M.; Wright, K.L.; Lund, J.N.; O’Sullivan, S.E. The role of CB(1) in intestinal permeability and inflammation. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3267–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, J.; Trembovler, V.; Di Marzo, V.; Petrosino, S.; Leo, G.; Alexandrovich, A.; Regev, E.; Casap, N.; Shteyer, A.; Ledent, C.; et al. The cannabinoid CB1 receptor regulates bone formation by modulating adrenergic signaling. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izzo, A.A.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoids and the gut: New developments and emerging concepts. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.K.; Devi, L.A. The highs and lows of cannabinoid receptor expression in disease: Mechanisms and their therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, S.; Luquin, N.; Navarro-Otano, J. The endocannabinoid system in cardiovascular function: Novel insights and clinical implications. Clin. Auton. Res. 2018, 28, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecucco, F.; Di Marzo, V. At the heart of the matter: The endocannabinoid system in cardiovascular function and dysfunction. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booz, G.W. Cannabidiol as an emergent therapeutic strategy for lessening the impact of inflammation on oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajesh, M.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Batkai, S.; Patel, V.; Saito, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Kashiwaya, Y.; Horvath, B.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Becker, L.; et al. Cannabidiol attenuates cardiac dysfunction, oxidative stress, fibrosis, and inflammatory and cell death signaling pathways in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendizabal-Zubiaga, J.; Melser, S.; Benard, G.; Ramos, A.; Reguero, L.; Arrabal, S.; Elezgarai, I.; Gerrikagoitia, I.; Suarez, J.; Rodriguez De Fonseca, F.; et al. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Are Localized in Striated Muscle Mitochondria and Regulate Mitochondrial Respiration. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shire, D.; Calandra, B.; Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Oustric, D.; Pessegue, B.; Bonnin-Cabanne, O.; Le Fur, G.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P. Molecular cloning, expression and function of the murine CB2 peripheral cannabinoid receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1307, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G.; Tao, Q.; Abood, M.E. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of the rat CB(2) cannabinoid receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McPartland, J.M.; Glass, M.; Matias, I.; Norris, R.W.; Kilpatrick, C.W. A shifted repertoire of endocannabinoid genes in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2007, 277, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndong, C.; O’Donnell, D.; Ahmad, S.; Groblewski, T. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of the dog cannabinoid CB(2)receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 669, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Bi, G.H.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Qu, H.; Zhang, S.J.; Li, C.Y.; Onaivi, E.S.; Gardner, E.L.; Xi, Z.X.; et al. Species differences in cannabinoid receptor 2 and receptor responses to cocaine self-administration in mice and rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Shen, L.; Hua, T.; Liu, Z.J. Structural and Functional Insights into Cannabinoid Receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.; Khawaja, K.; Muller-Ladner, U. G protein-coupled receptors in rheumatology. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Hashimotodani, Y.; Uchigashima, M.; Watanabe, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 309–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Whiteside, G.; Fowler, C.J.; Hohmann, A.G. Targeting CB2 receptors and the endocannabinoid system for the treatment of pain. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turu, G.; Hunyady, L. Signal transduction of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol 2010, 44, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackie, K.; Devane, W.A.; Hille, B. Anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid, inhibits calcium currents as a partial agonist in N18 neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 44, 498–503. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, B.R.; Mechoulam, R.; Razdan, R.K. Discovery and characterization of endogenous cannabinoids. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 573–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goutopoulos, A.; Makriyannis, A. From cannabis to cannabinergics: New therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 95, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Tsuboi, K.; Uyama, T. Enzymological studies on the biosynthesis of N-acylethanolamines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; Bifulco, M.; De Petrocellis, L. The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, S.; Ligresti, A.; Di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoid chemical biology: A tool for the development of novel therapies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilaru, A.; Chapman, K.D. The endocannabinoid system. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N.E.; Schatz, A.R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R.; et al. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Nakane, S.; Shinoda, A.; Itoh, K.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: A possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez de Fonseca, F.; Navarro, M.; Gomez, R.; Escuredo, L.; Nava, F.; Fu, J.; Murillo-Rodriguez, E.; Giuffrida, A.; LoVerme, J.; Gaetani, S.; et al. An anorexic lipid mediator regulated by feeding. Nature 2001, 414, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanus, L.; Abu-Lafi, S.; Fride, E.; Breuer, A.; Vogel, Z.; Shalev, D.E.; Kustanovich, I.; Mechoulam, R. 2-arachidonyl glyceryl ether, an endogenous agonist of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3662–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, A.C.; Sauer, J.M.; Knierman, M.D.; Becker, G.W.; Berna, M.J.; Bao, J.; Nomikos, G.G.; Carter, P.; Bymaster, F.P.; Leese, A.B.; et al. Characterization of a novel endocannabinoid, virodhamine, with antagonist activity at the CB1 receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 301, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.M.; Bisogno, T.; Trevisani, M.; Al-Hayani, A.; De Petrocellis, L.; Fezza, F.; Tognetto, M.; Petros, T.J.; Krey, J.F.; Chu, C.J.; et al. An endogenous capsaicin-like substance with high potency at recombinant and native vanilloid VR1 receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8400–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisogno, T.; Maurelli, S.; Melck, D.; De Petrocellis, L.; Di Marzo, V. Biosynthesis, uptake, and degradation of anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide in leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.C.; Mackie, K. An Introduction to the Endogenous Cannabinoid System. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piette, C.; Cui, Y.; Gervasi, N.; Venance, L. Lights on Endocannabinoid-Mediated Synaptic Potentiation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, K.D. Emerging physiological roles for N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in plants: Signal transduction and membrane protection. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2000, 108, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Tsuboi, K. Endocannabinoid-related enzymes as drug targets with special reference to N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Tsuboi, K.; Uyama, T.; Ohnishi, T. Biosynthesis and degradation of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Biofactors 2011, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Gao, F.; Chen, C. Endocannabinoid Metabolism and Traumatic Brain Injury. Cells 2021, 10, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N. Endocannabinoid hydrolases. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002, 68–69, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavarajappa, B.S.; Shivakumar, M.; Joshi, V.; Subbanna, S. Endocannabinoid system in neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neurochem 2017, 142, 624–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo, E.B. Clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD): Can this concept explain therapeutic benefits of cannabis in migraine, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome and other treatment-resistant conditions? Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 2004, 25, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.N.; Gorzalka, B.B. Is there a role for the endocannabinoid system in the etiology and treatment of melancholic depression? Behav. Pharmacol. 2005, 16, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlabritz-Loutsevitch, N.; German, N.; Ventolini, G.; Larumbe, E.; Samson, J. Fetal Syndrome of Endocannabinoid Deficiency (FSECD) In Maternal Obesity. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 96, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boger, D.L.; Patterson, J.E.; Jin, Q. Structural requirements for 5-HT2A and 5-HT1A serotonin receptor potentiation by the biologically active lipid oleamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4102–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, E.B. Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Reconsidered: Current Research Supports the Theory in Migraine, Fibromyalgia, Irritable Bowel, and Other Treatment-Resistant Syndromes. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walitt, B.; Klose, P.; Fitzcharles, M.A.; Phillips, T.; Hauser, W. Cannabinoids for fibromyalgia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 7, CD011694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurshid, H.; Qureshi, I.A.; Jahan, N.; Went, T.R.; Sultan, W.; Sapkota, A.; Alfonso, M. A Systematic Review of Fibromyalgia and Recent Advancements in Treatment: Is Medicinal Cannabis a New Hope? Cureus 2021, 13, e17332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, S.M.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Sarnelli, G.; Sharkey, K.A.; Storr, M.; Tack, J. Targeting the endocannabinoid system for the treatment of abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraguas-Sanchez, A.I.; Torres-Suarez, A.I. Medical Use of Cannabinoids. Drugs 2018, 78, 1665–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, Y.; Woo, M.; Andrews, C.N. Cannabis in Gastroenterology: Watch Your Head! A Review of Use in Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Functional Gut Disorders, and Gut-Related Adverse Effects. Curr. Treat. Opt. Gastroenterol. 2020, 18, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carlo, G.; Izzo, A.A. Cannabinoids for gastrointestinal diseases: Potential therapeutic applications. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2003, 12, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, A.; Yiangou, Y.; Facer, P.; Walters, J.R.; Anand, P.; Ghosh, S. Increased capsaicin receptor TRPV1-expressing sensory fibres in irritable bowel syndrome and their correlation with abdominal pain. Gut 2008, 57, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisogno, T.; Hanus, L.; De Petrocellis, L.; Tchilibon, S.; Ponde, D.E.; Brandi, I.; Moriello, A.S.; Davis, J.B.; Mechoulam, R.; Di Marzo, V. Molecular targets for cannabidiol and its synthetic analogues: Effect on vanilloid VR1 receptors and on the cellular uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis of anandamide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leweke, F.M.; Piomelli, D.; Pahlisch, F.; Muhl, D.; Gerth, C.W.; Hoyer, C.; Klosterkotter, J.; Hellmich, M.; Koethe, D. Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pisani, A.; Fezza, F.; Galati, S.; Battista, N.; Napolitano, S.; Finazzi-Agro, A.; Bernardi, G.; Brusa, L.; Pierantozzi, M.; Stanzione, P.; et al. High endogenous cannabinoid levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of untreated Parkinson’s disease patients. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, R.; Gupta, V.; Suphioglu, C. Current Aspects of the Endocannabinoid System and Targeted THC and CBD Phytocannabinoids as Potential Therapeutics for Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases: A Review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4878–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, A.J.; Zubko, O.; Reeves, S.J.; Howard, R.J. Endocannabinoid system alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review of human studies. Brain Res. 2020, 1749, 147135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets-Garcia, A.; Gomis-Gonzalez, M.; Guegan, T.; Agustin-Pavon, C.; Pastor, A.; Mato, S.; Perez-Samartin, A.; Matute, C.; de la Torre, R.; Dierssen, M.; et al. Targeting the endocannabinoid system in the treatment of fragile X syndrome. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro-Romero, A.; Vazquez-Oliver, A.; Gomis-Gonzalez, M.; Garzon-Montesinos, C.; Falcon-Moya, R.; Pastor, A.; Martin-Garcia, E.; Pizarro, N.; Busquets-Garcia, A.; Revest, J.M.; et al. Cannabinoid type-1 receptor blockade restores neurological phenotypes in two models for Down syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 125, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro-Romero, A.; Galera-Lopez, L.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Llorente-Ovejero, A.; de Los Reyes-Ramirez, L.; Bengoetxea de Tena, I.; Garcia-Elias, A.; Mas-Stachurska, A.; Reixachs-Sole, M.; Pastor, A.; et al. Cannabinoid signaling modulation through JZL184 restores key phenotypes of a mouse model for Williams-Beuren syndrome. Elife 2022, 11, e72560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, M.M.; Chandra, S.; Gul, S.; ElSohly, M.A. Cannabinoids, Phenolics, Terpenes and Alkaloids of Cannabis. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommano, S.R.; Chittasupho, C.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Jantrawut, P. The Cannabis Terpenes. Molecules 2020, 25, 5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Gaoni, Y. A Total Synthesis of Dl-Delta-1-Tetrahydrocannabinol, the Active Constituent of Hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 3273–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odieka, A.E.; Obuzor, G.U.; Oyedeji, O.O.; Gondwe, M.; Hosu, Y.S.; Oyedeji, A.O. The Medicinal Natural Products of Cannabis sativa Linn.: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, E.C.D.; Baldasso, G.M.; Bicca, M.A.; Paes, R.S.; Capasso, R.; Dutra, R.C. Terpenoids, Cannabimimetic Ligands, beyond the Cannabis Plant. Molecules 2020, 25, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atakan, Z. Cannabis, a complex plant: Different compounds and different effects on individuals. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 2, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procaccia, S.; Lewitus, G.M.; Lipson Feder, C.; Shapira, A.; Berman, P.; Meiri, D. Cannabis for Medical Use: Versatile Plant Rather Than a Single Drug. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 894960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huestis, M.A.; Solimini, R.; Pichini, S.; Pacifici, R.; Carlier, J.; Busardo, F.P. Cannabidiol Adverse Effects and Toxicity. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britch, S.C.; Babalonis, S.; Walsh, S.L. Cannabidiol: Pharmacology and therapeutic targets. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, L. Cannabis and the brain. Brain 2003, 126, 1252–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soethoudt, M.; Hoorens, M.W.H.; Doelman, W.; Martella, A.; van der Stelt, M.; Heitman, L.H. Structure-kinetic relationship studies of cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonists reveal substituent-specific lipophilic effects on residence time. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Wohlfarth, A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Gorelick, D.A.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids pharmacokinetics and detection methods in biological matrices. Drug Metab. Rev. 2015, 47, 124–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.K.; Murumkar, P.R.; Kanhed, A.M.; Giridhar, R.; Yadav, M.R. Prospective therapeutic agents for obesity: Molecular modification approaches of centrally and peripherally acting selective cannabinoid 1 receptor antagonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 79, 298–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, K.; Dolle, R.E. Simultaneous optimization of potency, selectivity and physicochemical properties for cannabinoid CB(2) ligands. Curr. Pharmacol. Des. 2009, 15, 3345–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2019, 160, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, D.S.; McGee, S.J. Pain as a global public health priority. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dydyk, A.M.; Conermann, T. Chronic Pain. In StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA, StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
- Aronoff, G.M. What Do We Know About the Pathophysiology of Chronic Pain? Implications for Treatment Considerations. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 100, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzke, F.; Tolle, T.; Fitzcharles, M.A.; Hauser, W. Cannabis-Based Medicines and Medical Cannabis for Chronic Neuropathic Pain. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, R.D.; Nalepa, S.D.; Harakal, J.J.; Vassar, H.B. Anti-edema and analgesic properties of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1973, 186, 646–655. [Google Scholar]
- Formukong, E.A.; Evans, A.T.; Evans, F.J. Analgesic and antiinflammatory activity of constituents of Cannabis sativa L. Inflammation 1988, 12, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calignano, A.; La Rana, G.; Giuffrida, A.; Piomelli, D. Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids. Nature 1998, 394, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulugol, A.; Ozyigit, F.; Yesilyurt, O.; Dogrul, A. The additive antinociceptive interaction between WIN 55,212-2, a cannabinoid agonist, and ketorolac. Anesth Analg. 2006, 102, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.; Colleoni, M.; Conti, S.; Parolaro, D.; Franke, C.; Trovato, A.E.; Giagnoni, G. Oral anti-inflammatory activity of cannabidiol, a non-psychoactive constituent of cannabis, in acute carrageenan-induced inflammation in the rat paw. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2004, 369, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.J.; Hohmann, A.G.; Walker, J.M. Suppression of noxious stimulus-evoked activity in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus by a cannabinoid agonist: Correlation between electrophysiological and antinociceptive effects. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 6601–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, J.; Beaulieu, P. Antihyperalgesic effects of local injections of anandamide, ibuprofen, rofecoxib and their combinations in a model of neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 2006, 50, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Rodrigues, B.M.; Coimbra, N.C. CB(1) receptor signalling mediates cannabidiol-induced panicolytic-like effects and defensive antinociception impairment in mice threatened by Bothrops jararaca lancehead pit vipers. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 1384–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberg, U.; Eliav, E.; Bennett, G.J.; Kopin, I.J. The analgesic effects of R(+)-WIN 55,212-2 mesylate, a high affinity cannabinoid agonist, in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 221, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, D.; Ahmad, K.; Rice, A.S. The synthetic cannabinoid WIN55,212-2 attenuates hyperalgesia and allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; Kesingland, A.; Gentry, C.; McNair, K.; Patel, S.; Urban, L.; James, I. The role of central and peripheral Cannabinoid1 receptors in the antihyperalgesic activity of cannabinoids in a model of neuropathic pain. Pain 2001, 92, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, S.L.; Mitchell, V.A.; Sokolaj, E.E.; Winters, B.L.; Vaughan, C.W. Intrathecal Actions of the Cannabis Constituents Delta(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol in a Mouse Neuropathic Pain Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, J.; De Lean, A.; Beaulieu, P. Local interactions between anandamide, an endocannabinoid, and ibuprofen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, in acute and inflammatory pain. Pain 2006, 121, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinger-Gratz, P.P.; Ralvenius, W.T.; Neumann, E.; Kato, A.; Nyilas, R.; Lele, Z.; Katona, I.; Zeilhofer, H.U. Acetaminophen Relieves Inflammatory Pain through CB1 Cannabinoid Receptors in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottani, A.; Leone, S.; Sandrini, M.; Ferrari, A.; Bertolini, A. The analgesic activity of paracetamol is prevented by the blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 531, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, M.; Guindon, J.; Lambert, C.; Beaulieu, P. The local antinociceptive effects of paracetamol in neuropathic pain are mediated by cannabinoid receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 573, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, S.; Gould, G.G.; Antonucci, N.; Brigida, A.L.; Siniscalco, D. Endocannabinoid System Dysregulation from Acetaminophen Use May Lead to Autism Spectrum Disorder: Could Cannabinoid Treatment Be Efficacious? Molecules 2021, 26, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucke, M.; Phillips, T.; Radbruch, L.; Petzke, F.; Hauser, W. Cannabis-based medicines for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 3, CD012182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, C.; Mawani, S.; Brady, S.; Chan, C.; Liu, C.; Mehina, E.; Garven, A.; Bestard, J.; Korngut, L. An enriched-enrolment, randomized withdrawal, flexible-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel assignment efficacy study of nabilone as adjuvant in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 2012, 153, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimrigk, S.; Marziniak, M.; Neubauer, C.; Kugler, E.M.; Werner, G.; Abramov-Sommariva, D. Dronabinol Is a Safe Long-Term Treatment Option for Neuropathic Pain Patients. Eur. Neurol. 2017, 78, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Schley, M.; Casutt, M.; Gerber, H.; Schuepfer, G.; Rukwied, R.; Schleinzer, W.; Ueberall, M.; Konrad, C. Tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta 9-THC) Treatment in Chronic Central Neuropathic Pain and Fibromyalgia Patients: Results of a Multicenter Survey. Anesth. Res. Pr. 2009, 2009, 827290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.J.; Chen, W.W.; Zhang, X. Endocannabinoid system: Role in depression, reward and pain control (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2899–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vimal, D.; D’Souza, L.C.; Rai, V.; Lal, S.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, S.C. Efficacy of cannabis and its constituents in disease management: Insights from clinical studies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 30, 178–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, M.A.; Wang, T.; Shapiro, S.; Robinson, A.; Ducruet, T.; Huynh, T.; Gamsa, A.; Bennett, G.J.; Collet, J.P. Smoked cannabis for chronic neuropathic pain: A randomized controlled trial. CMAJ. 2010, 182, E694–E701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, D.I.; Jay, C.A.; Shade, S.B.; Vizoso, H.; Reda, H.; Press, S.; Kelly, M.E.; Rowbotham, M.C.; Petersen, K.L. Cannabis in painful HIV-associated sensory neuropathy: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 2007, 68, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennici, A.; Mannucci, C.; Calapai, F.; Cardia, L.; Ammendolia, I.; Gangemi, S.; Calapai, G.; Griscti Soler, D. Safety of Medical Cannabis in Neuropathic Chronic Pain Management. Molecules 2021, 26, 6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinals, X.; Moreno, E.; Lanfumey, L.; Cordomi, A.; Pastor, A.; de La Torre, R.; Gasperini, P.; Navarro, G.; Howell, L.A.; Pardo, L.; et al. Cognitive Impairment Induced by Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol Occurs through Heteromers between Cannabinoid CB1 and Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptors. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallo, M.; Moreno, E.; Defaus, S.; Ortega-Alvaro, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Robledo, P.; Cavaco, M.; Neves, V.; Castanho, M.; Casado, V.; et al. Orally Active Peptide Vector Allows Using Cannabis to Fight Pain While Avoiding Side Effects. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 6937–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmani, N.A. Cannabinoids of diverse structure inhibit two DOI-induced 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated behaviors in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2001, 68, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Parker, L.A. The endocannabinoid system and the brain. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puighermanal, E.; Busquets-Garcia, A.; Maldonado, R.; Ozaita, A. Cellular and intracellular mechanisms involved in the cognitive impairment of cannabinoids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bombardi, C.; Di Giovanni, G. Functional anatomy of 5-HT2A receptors in the amygdala and hippocampal complex: Relevance to memory functions. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 230, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, Y.; Tang, Y. The central cannabinoid receptor type-2 (CB2) and chronic pain. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Chico, A.; Tepavcevic, V.; Manterola, A.; Utrilla, C.; Matute, C.; Mato, S. Endocannabinoid signaling in brain diseases: Emerging relevance of glial cells. Glia 2023, 71, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanero, D.; Ramirez-Lopez, A.; Drews, E.; Schmole, A.; Otte, D.M.; Wawrzczak-Bargiela, A.; Huerga Encabo, H.; Kummer, S.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.; Przewlocki, R.; et al. Protective role of neuronal and lymphoid cannabinoid CB(2) receptors in neuropathic pain. Elife 2020, 9, e55582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curto-Reyes, V.; Llames, S.; Hidalgo, A.; Menendez, L.; Baamonde, A. Spinal and peripheral analgesic effects of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist AM1241 in two models of bone cancer-induced pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacher, P.; Batkai, S.; Kunos, G. The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 389–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacher, P.; Kecskemeti, V. Trends in the development of new antidepressants. Is there a light at the end of the tunnel? Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 925–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hen-Shoval, D.; Weller, A.; Weizman, A.; Shoval, G. Examining the Use of Antidepressants for Adolescents with Depression/Anxiety Who Regularly Use Cannabis: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Wolff, R.F.; Deshpande, S.; Di Nisio, M.; Duffy, S.; Hernandez, A.V.; Keurentjes, J.C.; Lang, S.; Misso, K.; Ryder, S.; et al. Cannabinoids for Medical Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2015, 313, 2456–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graczyk, M.; Lukowicz, M.; Dzierzanowski, T. Prospects for the Use of Cannabinoids in Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 620073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, D.; Gasparyan, A.; Navarrete, F.; Torregrosa, A.B.; Rubio, G.; Marin-Mayor, M.; Acosta, G.B.; Garcia-Gutierrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Molecular Alterations of the Endocannabinoid System in Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, P.; Bifulco, M.; Maina, G.; Tortorella, A.; Gazzerro, P.; Proto, M.C.; Di Filippo, C.; Monteleone, F.; Canestrelli, B.; Buonerba, G.; et al. Investigation of CNR1 and FAAH endocannabinoid gene polymorphisms in bipolar disorder and major depression. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minocci, D.; Massei, J.; Martino, A.; Milianti, M.; Piz, L.; Di Bello, D.; Sbrana, A.; Martinotti, E.; Rossi, A.M.; Nieri, P. Genetic association between bipolar disorder and 524A>C (Leu133Ile) polymorphism of CNR2 gene, encoding for CB2 cannabinoid receptor. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 134, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitjans, M.; Gasto, C.; Catalan, R.; Fananas, L.; Arias, B. Genetic variability in the endocannabinoid system and 12-week clinical response to citalopram treatment: The role of the CNR1, CNR2 and FAAH genes. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domschke, K.; Dannlowski, U.; Ohrmann, P.; Lawford, B.; Bauer, J.; Kugel, H.; Heindel, W.; Young, R.; Morris, P.; Arolt, V.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1) gene: Impact on antidepressant treatment response and emotion processing in major depression. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micale, V.; Drago, F. Endocannabinoid system, stress and HPA axis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, A.H.; Salem, V.; Ghatei, M.A. Rimonabant: From RIO to Ban. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 432607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, L.D.; Wills, K.L.; Segsworth, B.; Dashney, B.; Rock, E.M.; Limebeer, C.L.; Parker, L.A. Effect of chronic exposure to rimonabant and phytocannabinoids on anxiety-like behavior and saccharin palatability. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 103, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettaro, R.; Laudermilk, L.; Clark, S.D.; Maitra, R. Behavioral assessment of rimonabant under acute and chronic conditions. Behav. Brain. Res. 2020, 390, 112697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, C.H.; Moore, P.B.; Gallagher, P.; Young, A.H. Cannabinoids in bipolar affective disorder: A review and discussion of their therapeutic potential. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 19, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinspoon, L.; Bakalar, J.B. The use of cannabis as a mood stabilizer in bipolar disorder: Anecdotal evidence and the need for clinical research. J. Psychoact. Drugs 1998, 30, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botsford, S.L.; Yang, S.; George, T.P. Cannabis and Cannabinoids in Mood and Anxiety Disorders: Impact on Illness Onset and Course, and Assessment of Therapeutic Potential. Am. J. Addict. 2020, 29, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinchii, D.; Dremencov, E. Mechanism of Action of Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs in Mood Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Park, H.J.; Chae, Y.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, H.; Chung, J.H. Effect of acupuncture on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system in maternal separation rats. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPartland, J.M.; Guy, G.W.; Di Marzo, V. Care and feeding of the endocannabinoid system: A systematic review of potential clinical interventions that upregulate the endocannabinoid system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.H.; Shi, J.; Pan, H.L.; Li, M. Endogenous anandamide and cannabinoid receptor-2 contribute to electroacupuncture analgesia in rats. J. Pain 2009, 10, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Su, T.; Cao, F.; Meng, X.; Pei, L.; Shi, J.; Pan, H.L.; Li, M. Electroacupuncture increases CB2 receptor expression on keratinocytes and infiltrating inflammatory cells in inflamed skin tissues of rats. J. Pain 2010, 11, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.F.; Zhang, L.H.; Peng, M.; Wu, C.H.; Pan, W.; Tian, B.; Shi, J.; Pan, H.L.; Li, M. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors contribute to upregulation of beta-endorphin in inflamed skin tissues by electroacupuncture. Mol. Pain 2011, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Chen, S.; Gou, X.; Hu, B.; Du, J.; Lu, Y.; Xiong, L. Pretreatment with electroacupuncture induces rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia through regulation of endocannabinoid system. Stroke 2009, 40, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, F.; Guo, F.; Gao, Z.; Marsicano, G.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, L. Activation of STAT3 is involved in neuroprotection by electroacupuncture pretreatment via cannabinoid CB1 receptors in rats. Brain. Res. 2013, 1529, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhasivam, S.; Alankar, S.; Maturi, R.; Vishnubhotla, R.V.; Mudigonda, M.; Pawale, D.; Narayanan, S.; Hariri, S.; Ram, C.; Chang, T.; et al. Inner Engineering Practices and Advanced 4-day Isha Yoga Retreat Are Associated with Cannabimimetic Effects with Increased Endocannabinoids and Short-Term and Sustained Improvement in Mental Health: A Prospective Observational Study of Meditators. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 8438272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanton, H.L.; Barnes, R.C.; McHann, M.C.; Bilbrey, J.A.; Wilkerson, J.L.; Guindon, J. Sex differences and the endocannabinoid system in pain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 202, 173107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhams, S.G.; Chapman, V.; Finn, D.P.; Hohmann, A.G.; Neugebauer, V. The cannabinoid system and pain. Neuropharmacology 2017, 124, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, S.E. Endocannabinoids and the Cardiovascular System in Health and Disease. Handb Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 231, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calixto, J.B.; Beirith, A.; Ferreira, J.; Santos, A.R.; Filho, V.C.; Yunes, R.A. Naturally occurring antinociceptive substances from plants. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeredo, E.L.; Dos Santos, F.B.; Barbosa, L.S.; Souza, T.M.A.; Badolato-Corrêa, J.; Sánchez-Arcila, J.C.; Nunes, P.C.G.; de-Oliveira-Pinto, L.M.; de Filippis, A.M.; Dal Fabbro, M.; et al. Clinical and Laboratory Profile of Zika and Dengue Infected Patients: Lessons Learned From the Co-circulation of Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya in Brazil. PLoS Curr. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarabian, K.; Wannon, A.; Chin, M.; Kogan, M. The intersection between integrative medicine and neuropathic pain: A case report. Explore 2022, 18, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.L.; Hurst, D.P.; Reggio, P.H. The Nucleotide-Free State of the Cannabinoid CB2/Gi Complex. Cell 2020, 180, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C. The cannabinoid receptors. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002, 68–69, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Devane, W.A.; Breuer, A.; Zahalka, J. A random walk through a cannabis field. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerich, B.L.; Ferreira, R.C.; Cordeiro, M.N.; Borges, M.H.; Pimenta, A.M.; Figueiredo, S.G.; Duarte, I.D.; de Lima, M.E. delta-Ctenitoxin-Pn1a, a Peptide from Phoneutria nigriventer Spider Venom, Shows Antinociceptive Effect Involving Opioid and Cannabinoid Systems, in Rats. Toxins 2016, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima, L.S.; Loyola, V.; Bicca, J.; Faro, L.; Vale, C.L.C.; Lotufo Denucci, B.; Mortari, M.R. Innovative treatments for epilepsy: Venom peptides, cannabinoids, and neurostimulation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 100, 1969–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Peigneur, S.; Hendrickx, L.A.; Tytgat, J. Targeting Cannabinoid Receptors: Current Status and Prospects of Natural Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezende, B.; Alencar, A.K.N.; de Bem, G.F.; Fontes-Dantas, F.L.; Montes, G.C. Endocannabinoid System: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020148
Rezende B, Alencar AKN, de Bem GF, Fontes-Dantas FL, Montes GC. Endocannabinoid System: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020148
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezende, Bismarck, Allan Kardec Nogueira Alencar, Graziele Freitas de Bem, Fabrícia Lima Fontes-Dantas, and Guilherme Carneiro Montes. 2023. "Endocannabinoid System: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020148
APA StyleRezende, B., Alencar, A. K. N., de Bem, G. F., Fontes-Dantas, F. L., & Montes, G. C. (2023). Endocannabinoid System: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020148