Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Zaltoprofen in Healthy Adults: Exploring the Dosage Regimen
Abstract
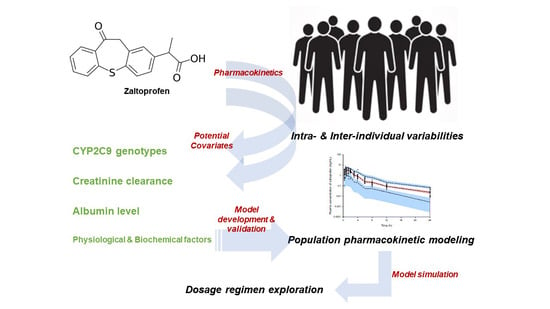
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling
2.2. Model Qualification
2.3. External Model Validation
2.4. Exploring the Simulation-Based Dosage Regimen
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Workflow
4.2. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling
4.3. Model Validation
4.4. External Model Validation
4.5. Model Simulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hatori, M.; Kokubun, S. The long-term efficacy and tolerability of the new anti-inflammatory agent zaltoprofen in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1998, 14, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komiya, A.; Endo, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kim, W.; Araki, K.; Naya, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Tobe, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Fuse, H. Oral analgesia by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug zaltoprofen to manage cystoscopy-related pain: A prospective study. Int. J. Urol. 2009, 16, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.M.; Jun, S.; Chung, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, C.A.; Kim, J.S. Efficacy and Safety of Miniscalpel Acupuncture, Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs or Combined Treatment for Chronic Neck Pain: An Assessor-Blinded Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Korean J. Acupunct. 2020, 37, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santenna, C.; Kumar, S.; Balakrishnan, S.; Jhaj, R.; Ahmed, S.N. A comparative experimental study of analgesic activity of a novel non-steroidal anti-inflammatory molecule–zaltoprofen, and a standard drug–piroxicam, using murine models. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 11, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuvaraj, S.; Kumar, B.P. Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor-γ as A Novel and Promising Target For Treating Cancer via Regulation of Inflammation: A Brief Review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Hiramoto, K.; Maruyama, K.; Ooi, K. Relationships of pain-causing substances with dry skin and effects of zaltoprofen on alleviation of symptoms in arthritis model mice. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.A.; Patel, R.P. Statistical modeling of zaltoprofen loaded biopolymeric nanoparticles: Characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of nanoparticles loaded gel. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, H.; Quan, P.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, L. Development of a drug-in-adhesive patch combining ion pair and chemical enhancer strategy for transdermal delivery of zaltoprofen: Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and in vitro/in vivo correlation evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3461–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaltoprofen-Drug-Details. Database(Zaltoprofen). Available online: http://www.health.kr/searchDrug/result_drug.asp (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Pareek, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Chandurkar, N.B.; Sirsikar, A.D.; Ambade, R.E.; Jesalpura, B.H.; Swamy, A.P. Zaltoprofen, a noninferior alternative to diclofenac for the treatment of primary knee osteoarthritis–a comparative evaluation of efficacy and safety in a 4-week, multicentric, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy trial. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2011, 12, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Prabhavalkar, K.S.; Bhatt, L.K. Preparation, optimization, and evaluation of Zaltoprofen-loaded microemulsion and microemulsion-based gel for transdermal delivery. J. Liposome Res. 2016, 26, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-M. To market, to market-1993. In Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 29, pp. 331–354. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.-Y.; Seo, K.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-M. Evaluation of NSAIDs Prescription for the Prevention of Gastrointestinal and Cardiovascular Risk in Geriatric Patients. J. Korean Soc. Health Syst. Pharm. 2017, 34, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wicha, S.G.; Märtson, A.G.; Nielsen, E.I.; Koch, B.C.; Friberg, L.E.; Alffenaar, J.W.; Minichmayr, I.K.; International Society of Anti-Infective Pharmacology; The PK/PD Study Group of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology, Infectious Diseases. From therapeutic drug monitoring to model-informed precision dosing for antibiotics. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 109, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.; Lapa, R.; Vale, N. PBPK modeling and simulation and therapeutic drug monitoring: Possible ways for antibiotic dose adjustment. Processes 2021, 9, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.; Davis, G.; Conner, T.M.; Zhang, T. Utilization of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in clinical pharmacology and therapeutics: An overview. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 6, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorr, A.F.; Bruno, C.J.; Zhang, Z.; Jensen, E.; Gao, W.; Feng, H.-P.; Huntington, J.A.; Yu, B.; Rhee, E.G.; De Anda, C. Ceftolozane/tazobactam probability of target attainment and outcomes in participants with augmented renal clearance from the randomized phase 3 ASPECT-NP trial. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, N.S.J.D.; Draibe, S.A.; Kamimura, M.A.; Canziani, M.E.F.; Cendoroglo, M.; Júnior, A.G.; Cuppari, L. Is serum albumin a marker of nutritional status in hemodialysis patients without evidence of inflammation? Artif. Organs 2003, 27, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Cho, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.-B. Comparison of UPLC-MS/MS and HPLC-UV methods for the determination of zaltoprofen in human plasma. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, S.; Akagawa, N.; Kamada, E.; Hiyama, A.; Kawabata, Y.; Kowata, N.; Inaba, A.; Matthews, A.; Hall, M.; Kurimoto, T. Involvement of CYP2C9 and UGT2B7 in the metabolism of zaltoprofen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, and its lack of clinically significant CYP inhibition potential. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, Y.-J.; Cha, E.-Y.; Jung, H.-E.; Ghim, J.-L.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, E.-Y.; Shin, J.-G. Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5 in Vietnamese-Koreans. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 22, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kindla, J.; Müller, F.; Mieth, M.; Fromm, M.F.; König, J. Influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1-and OATP1B3-mediated drug transport. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, K.; Iizuka, K.; Sano, H.; Miwa, M.; Harnki, S. Pharmacokinetics of CN-100 for 80 mg tablet of final preparation in healthy volunteers. Jpn. Pharmacol. Ther. 1992, 20, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, H.; Segawa, Y.; Furuta, S.; Yoshino, Y.; Kamishiro, T.; Esumi, Y. Drug interaction of zaltoprofen, a novel anti-inflammatory drug, and its effect on hepatic drug metabolizing enzyme. Jpn. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 23, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.-A.; Park, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-H.; Yun, H.; Kim, K.-R.; Yoo, H.-D.; Park, E.-J.; Cho, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.-B. Bioequivalence of SCD Zaltoprofen Tablet to Soleton® Tablet (Zaltoprofen 80 mg). J. Pharm. Investig. 2006, 36, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ma, P.; Cao, Y.; Tao, L.; Tao, Y. Single-dose and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of zaltoprofen after oral administration in healthy Chinese volunteers. J. Biomed. Res. 2011, 25, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, K.T. Determination of zaltoprofen in human plasma by liquid chromatography with electrospray tandem mass spectrometry: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2675–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Zaltoprofen in Healthy Adults: Exploring the Dosage Regimen. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020161
Jang J-H, Jeong S-H, Lee Y-B. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Zaltoprofen in Healthy Adults: Exploring the Dosage Regimen. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020161
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Ji-Hun, Seung-Hyun Jeong, and Yong-Bok Lee. 2023. "Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Zaltoprofen in Healthy Adults: Exploring the Dosage Regimen" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020161
APA StyleJang, J. -H., Jeong, S. -H., & Lee, Y. -B. (2023). Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Zaltoprofen in Healthy Adults: Exploring the Dosage Regimen. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020161