Pharmacological Profiling of KATP Channel Modulators: An Outlook for New Treatment Opportunities for Migraine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Functional Characterization of KATP Channel Activators
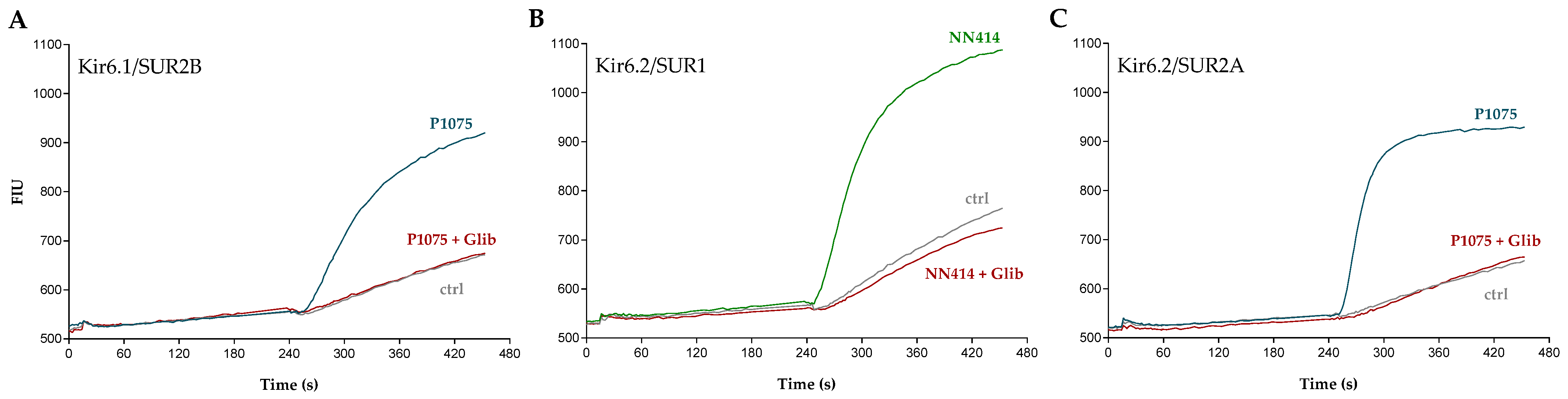
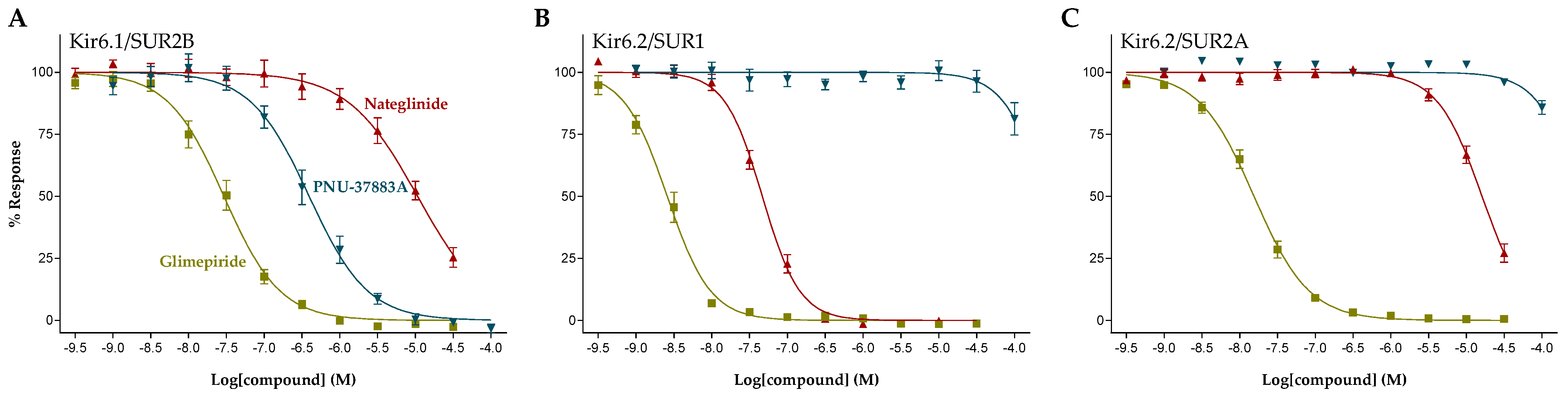
2.2. Functional Characterization of KATP Channel Inhibitors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Generation of Stable Cell Lines
4.3. Thallium-Flux Assays
4.4. Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [Google Scholar]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Davidsson, O.B.; Olofsson, A.I.; Kogelman, L.J.; Andersen, M.A.; Rostgaard, K.; Hjalgrim, H.; Olesen, J.; Hansen, T.F. Twenty-five years of triptans—A nationwide population study. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tfelt-Hansen, P.; Loder, E. The Emperor’s New Gepants: Are the Effects of the New Oral CGRP Antagonists Clinically Meaningful? Headache 2019, 59, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, A.; Guo, S.; Jansen-Olesen, I.; Christensen, S.L. ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels in Migraine: Translational Findings and Therapeutic Potential. Cells 2022, 11, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.S.; Hansen, A.E.; Amin, F.M.; van der Geest, R.J.; van der Koning, P.; Larsson, H.B.W.; Olesen, J.; Ashina, M. Evidence for a vascular factor in migraine. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 69, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.M.; Asghar, M.S.; Guo, S.; Hougaard, A.; Hansen, A.E.; Schytz, H.W.; van der Geest, R.; de Koning, P.J.; Larsson, H.B.; Olesen, J.; et al. Headache and prolonged dilatation of the middle meningeal artery by PACAP38 in healthy volunteers. Cephalalgia 2011, 32, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karagholi, M.A.M.; Ghanizada, H.; Hansen, J.M.; Skovgaard, L.T.; Olesen, J.; Larsson, H.B.; Amin, F.M.; Ashina, M. Levcromakalim, an Adenosine Triphosphate-Sensitive Potassium Channel Opener, Dilates Extracerebral but not Cerebral Arteries. Headache 2019, 59, 1468–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karagholi, M.A.-M.; Hansen, J.M.; Severinsen, J.; Jansen-Olesen, I.; Ashina, M. The KATP channel in migraine pathophysiology: A novel therapeutic target for migraine. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karagholi, M.A.-M.; Ghanizada, H.; Nielsen, C.A.W.; Hougaard, A.; Ashina, M. Opening of ATP sensitive potassium channels causes migraine attacks with aura. Brain 2021, 144, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.L.; Munro, G.; Petersen, S.; Shabir, A.; Jansen-Olesen, I.; Kristensen, D.M.; Olesen, J. ATP sensitive potassium (KATP) channel inhibition: A promising new drug target for migraine. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploug, K.B.; Baun, M.; Hay-Schmidt, A.; Olesen, J.; Jansen-Olesen, I. Presence and vascular pharmacology of KATP channel subtypes in rat central and peripheral tissues. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 637, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploug, K.B.; Sørensen, M.A.; Strøbech, L.; Klaerke, D.A.; Hay-Schmidt, A.; Sheykhzade, M.; Olesen, J.; Jansen-Olesen, I. K ATP channels in pig and human intracranial arteries. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 601, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.L.; Rasmussen, R.H.; Cour, S.L.; Ernstsen, C.; Hansen, T.F.; Kogelman, L.J.; Lauritzen, S.P.; Guzaite, G.; Styrishave, B.; Janfelt, C.; et al. Smooth muscle ATP-sensitive potassium channels mediate migraine-relevant hypersensitivity in mouse models. Cephalalgia 2022, 42, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinker, A.; Aziz, Q.; Li, Y.; Specterman, M. ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels and Their Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1463–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, C.G.; Shyng, S.-L.; Nestorowicz, A.; Glaser, B.; Clement, J.P.; Gonzalez, G.; Aguilar-Bryan, L.; Permutt, M.A.; Bryan, J. Adenosine Diphosphate as an Intracellular Regulator of Insulin Secretion. Science 1996, 272, 1785–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ji, J.J.; Yuan, H.; Miki, T.; Sato, S.; Horimoto, N.; Shimizu, T.; Seino, S.; Inagaki, N. Protective Role of ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels in Hypoxia-Induced Generalized Seizure. Science 2001, 292, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standen, N.B.; Quayle, J.M.; Davies, N.W.; Brayden, J.E.; Huang, Y.; Nelson, M.T. Hyperpolarizing Vasodilators Activate ATP-sensitive K + Channels in Arterial Smooth Muscle. Science 1989, 245, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, C.G. KATP channels as molecular sensors of cellular metabolism. Nature 2006, 440, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, S.; Miki, T. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2003, 81, 133–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Gonoi, T.; Clement, J.P., IV; Namba, N.; Inazawa, J.; Gonzalez, G.; Aguilar-Bryan, L.; Seino, S.; Bryan, J. Reconstitution of IKATP: An inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science 1995, 270, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, N.; Gonoi, T.; Iv JP, C.; Wang, C.Z.; Aguilar-Bryan, L.; Bryan, J.; Seino, S. A family of sulfonylurea receptors determines the pharmacological properties of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Neuron 1996, 16, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Isomoto, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Kondo, C.; Shindo, T.; Horio, Y.; Kurachi, Y. Sulphonylurea receptor 2B and Kir6.1 form a sulphonylurea-sensitive but ATP-insensitive K+ channel. J. Physiol. 1997, 499, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwanstecher, M.; Sieverding, C.; Dörschner, H.; Gross, I.; Aguilar-Bryan, L.; Schwanstecher, C.; Bryan, J. Potassium channel openers require ATP to bind to and act through sulfonylurea receptors. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5529–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, G.; O’Rourke, B.; Marbán, E.; Seharaseyon, J. Pharmacological comparison of native mitochondrial K(ATP) channels with molecularly defined surface K(ATP) channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, M.; Larsen, T.; Ashcroft, F.M.; Hansen, J.B.; Wahl, P. Potent and selective activation of the pancreatic beta-cell type K ATP channel by two novel diazoxide analogues. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M. Adenosine 5’-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev. Neurosci. 1988, 11, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen-Olesen, I.; Mortensen, C.H.; El-Bariaki, N.; Ploug, K.B. Characterization of K(ATP)-channels in rat basilar and middle cerebral arteries: Studies of vasomotor responses and mRNA expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 523, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploug, K.B.; Amrutkar, D.V.; Baun, M.; Ramachandran, R.; Iversen, A.; Lund, T.M.; Gupta, S.; Hay-Schmidt, A.; Olesen, J.; Jansen-Olesen, I. K(ATP) channel openers in the trigeminovascular system. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karagholi, M.A.-M.; Hansen, J.M.; Guo, S.; Olesen, J.; Ashina, M. Opening of ATP-sensitive potassium channels causes migraine attacks: A new target for the treatment of migraine. Brain 2019, 142, 2644–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.; Weston, A. Potassium channel openers and vascular smooth muscle relaxation. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 48, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Ito, S.; Shafiq, J.; Suzuki, H. Effects of a newly synthesized K+ channel opener, Y-26763, on noradrenaline-induced Ca2+ mobilization in smooth muscle of the rabbit mesenteric artery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 111, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, G.J.; D’Alonzo, A.J.; Garlid, K.; Bajgar, R.; Lodge, N.J.; Sleph, P.G.; Darbenzio, R.B.; Hess, A.T.; Smith, A.M.; Paucek, P.; et al. Pharmacologic characterization of BMS-191095, a mitochondrial K(ATP) opener with no peripheral vasodilator or cardiac action potential shortening activity. Experiment 2001, 297, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigoni-Martelli, E.; Nielsen, C.K.; Olsen, U.B.; Petersen, H.J. N″-cyano-N-4-pyridyl-N′-1,2,2-trimethylpropylguanidine, monohydrate (P 1134): A new, potent vasodilator. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1980, 36, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, J.K.; Steinberg, M.I. Cardiac electrophysiological effects of pinacidil and related pyridylcyanoguanidines: Relationship to antihypertensive activity. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1988, 12, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.L.; Ohnmacht, C.J.; Howe, B.B. Anilide tertiary carbinols: A novel series of K+ channel openers. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1994, 15, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, A.M.; Bialecki, A.R.; Elhilali, M.M. Effects of ZD6169 and ZD0947, 2 potassium adenosine triphosphate channel openers, on bladder function of spinalized rats. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, M.; Buckner, S.A.; Whiteaker, K.L.; Shieh, C.C.; Molinari, E.J.; Milicic, I.; Daza, A.V.; Davis-Taber, R.; Scott, V.E.; Sellers, D.; et al. (-)-(9S)-9-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-2,3,5,6,7,9-hexahydrothieno[3,2-b]quinolin-8(4H)-one 1,1-dioxide (A-278637): A novel ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener efficacious in suppressing urinary bladder contractions I. In Vitro characterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheon, D.E.; Barthalmus, K.S. Antihypertensive action of diazoxide. A new benzothiazine with antidiuretic properties. Br. Med. J. 1962, 2, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphemot, R.; Swale, D.R.; Dadi, P.K.; Jacobson, D.A.; Cooper, P.; Wojtovich, A.P.; Banerjee, S.; Nichols, C.G.; Denton, J.S. Direct Activation Of Beta-Cell Katp Channels With A Novel Xanthine Derivative. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, R.D.; Brand, C.L.; Bodvarsdottir, T.B.; Hansen, J.B.; Sturis, J. NN414, a SUR1/Kir6.2-Selective Potassium Channel Opener, Reduces Blood Glucose and Improves Glucose Tolerance in the VDF Zucker Rat. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharade, S.V.; Sanchez-Andres, J.V.; Fulton, M.G.; Shelton, E.L.; Blobaum, A.L.; Engers, D.W.; Hofmann, C.S.; Dadi, P.K.; Lantier, L.; Jacobson, D.A.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationships, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of the Kir6.2/SUR1-Specific Channel Opener VU0071063. Experiment 2019, 370, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.L.; Rasmussen, R.H.; Ernstsen, C.; La Cour, S.; David, A.; Chaker, J.; Haane, K.A.; Christensen, S.T.; Olesen, J.; Kristensen, D.M. CGRP-dependent signalling pathways involved in mouse models of GTN- cilostazol- and levcromakalim-induced migraine. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, H.; Elbahi, F.A.; Al-Karagholi, M.A.-M.; Ghanizada, H.; Sheykhzade, M.; Ashina, M. The Effect of K ATP Channel Blocker Glibenclamide on CGRP-Induced Headache and Hemodynamic in Healthy Volunteers. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 652136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Karagholi, M.A.-M.; Ghanizada, H.; Nielsen, C.A.W.; Ansari, A.; Gram, C.; Younis, S.; Vestergaard, M.B.; Larsson, H.B.; Skovgaard, L.T.; Amin, F.M.; et al. Cerebrovascular effects of glibenclamide investigated using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in healthy volunteers. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 41, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfour, J.A.; Plosker, G.L. Rosiglitazone. Drugs 1999, 57, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C. Thiazolidinediones: A new class of antidiabetic drugs. Diabet. Med. 1999, 16, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Tabrizchi, R. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma as a drug target in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Jin, X.; Cui, N.; Wu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, D.; Jiang, C. Rosiglitazone selectively inhibits K(ATP) channels by acting on the K(IR) 6 subunit. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, E.R.; Heyen, J.; Hemkens, M.; McHarg, A.; Ecelbarger, C.M.; Tiwari, S. Effects of Chronic PPAR-Agonist Treatment on Cardiac Structure and Function, Blood Pressure, and Kidney in Healthy Sprague-Dawley Rats. PPAR Res. 2009, 2009, 237865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, S.C.; Humphrey, S.J.; Skaletzky, L.L.; Graham, B.E.; Zandt, R.A.; Zins, G.R. Synthesis and Diuretic Activity of Alkyl- and Arylguanidine Analogs of N,N′-Dicyclohexyl-4-morpholinecarboxamidine in Rats and Dogs. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3693–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisheri, K.D.; Humphrey, S.J.; Khan, A.S.; Cipkus-Dubray, A.L.; Smith, M.P.; Jones, A.W. 4-morpholinecarboximidine-N-1-adamantyl-N′-cyclohexylhydrochloride (U-37883A): Pharmacological characterization of a novel antagonist of vascular ATP-sensitive K+ channel openers. Experiment 1993, 266, 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Wellman, G.C.; Barrett-Jolley, R.; Köppel, H.; Everitt, D.; Quayle, J.M. Inhibition of vascular K(ATP) channels by U-37883A: A comparison with cardiac and skeletal muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Tinker, A.; Clapp, L.H. Different molecular sites of action for the KATP channel inhibitors, PNU-99963 and PNU-37883A. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, S.J.; Smith, M.P.; Cimini, M.G.; Buchanan, L.V.; Gibson, J.K.; Khan, A.S.; Meisheri, K.D. Cardiovascular effects of the K-ATP channel blocker U-37883A and structurally related morpholinoguanidines. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 18, 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, S.; Dyhring, T.; Brown, D.T.; Strøbæk, D.; Christophersen, P.; Demnitz, J. A high-throughput screening campaign for detection of Ca2+-activated K+ channel activators and inhibitors using a fluorometric imaging plate reader-based Tl+-influx assay. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2013, 11, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
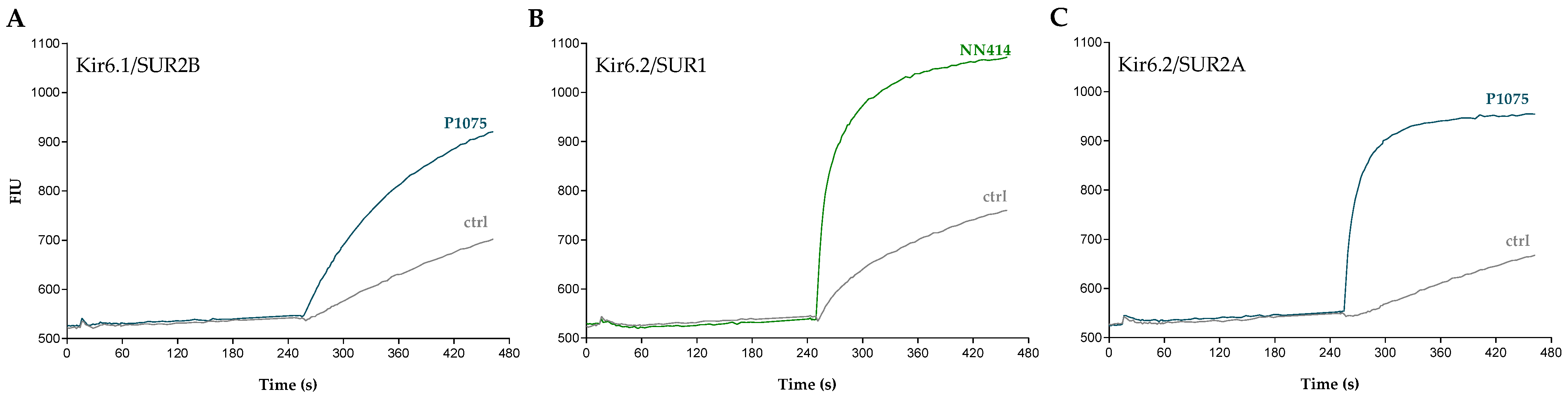
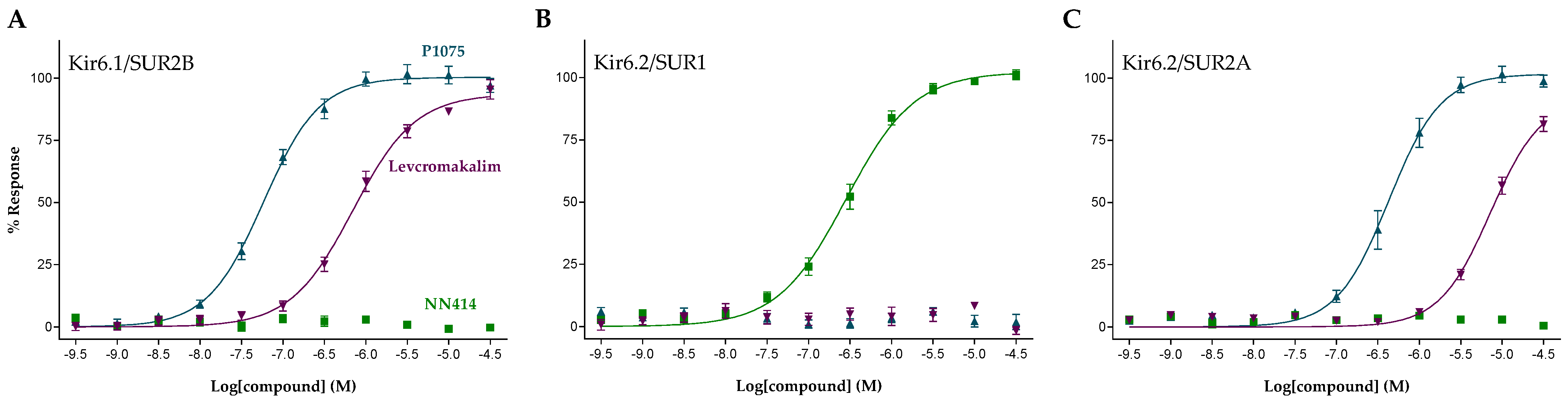
| Compound | Structure | Kir6.1/SUR2B | Kir6.2/SUR1 | Kir6.2/SUR2A | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC50 (µM) | Efficacy (%) | EC50 (µM) | Efficacy (%) | EC50 (µM) | Efficacy (%) | ||
| Levcromakalim | 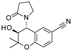 | 0.55 ± 0.29 (7) | 90 ± 6 (7) | >30 (7) | 0 (7) | 6.9 ± 2.2 (7) | 85 ± 11 (7) |
| Y-26763 | 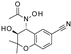 | 0.075 ± 0.042 (6) | 96 ± 3 (6) | 4.1 ± 2.1 (7) | 98 ± 2 (7) | 1.3 ± 0.97 (7) | 71 ± 5 (7) |
| BMS-191095 | 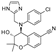 | >30 (5) | 0 (5) | 1.4 ± 0.95 (5) | 82 ± 10 (5) | >30 (6) | 0 (6) |
| Pinacidil | 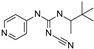 | 1.1 ± 0.60 (6) | 76 ± 9 (6) | >30 (6) | 0 (6) | 17 ± 5.8 (6) | 73 ± 14 (6) |
| P1075 | 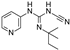 | 0.052 ± 0.024 (10) | 100 (10) | >30 (10) | 0 (10) | 0.51 ± 0.27 (10) | 100 (10) |
| ZM226600 | 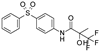 | 0.15 ± 0.090 (5) | 87 ± 6 (5) | >30 (5) | 0 (5) | 2.8 ± 2.2 (5) | 54 ± 10 (5) |
| ZD0947 | 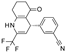 | 0.52 ± 0.22 (6) | 57 ± 2 (6) | >30 (6) | 0 (6) | 11 ± 5.9 (6) | 33 ± 9 (6) |
| A-278637 | 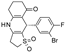 | 0.17 ± 0.089 (5) | 88 ± 6 (5) | >30 (6) | 0 (6) | 1.6 ± 0.89 (6) | 95 ± 4 (6) |
| NN414 | 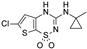 | >30 (9) | 0 (9) | 0.26 ± 0.16 (9) | 100 (9) | >30 (9) | 0 (9) |
| Diazoxide | 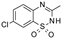 | 9.7 ± 5.7 (7) | 38 ± 9 (7) | 6.2 ± 4.8 (7) | 97 ± 5 (7) | >100 (7) | 0 (7) |
| VU0071063 | 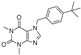 | >30 (5) | 0 (5) | 1.1 ± 0.62 (6) | 100 ± 1 (6) | >30 (6) | 0 (6) |
| Compound | Structure | Kir6.1/SUR2B | Kir6.2/SUR1 | Kir6.2/SUR2A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µM) | IC50 (µM) | IC50 (µM) | ||
| Glibenclamide | 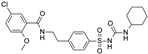 | 0.021 ± 0.014 (5) | 0.00087 ± 0.0005 (5) | 0.0099 ± 0.0041 (5) |
| Glimepiride | 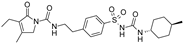 | 0.033 ± 0.023 (6) | 0.0023 ± 0.0012 (6) | 0.017 ± 0.009 (5) |
| Gliquidone | 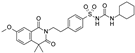 | 4.5 ± 3.6 (6) | 0.0069 ± 0.0050 (6) | 0.78 ± 0.58 (6) |
| Gliclazide | 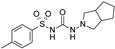 | 24 ± 11 (5) | 0.61 ± 0.45 (7) | 55 ± 22 (6) |
| Tolbutamide | 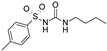 | 41 ± 11 (5) | 7.5 ± 4.1 (6) | 71 ± 12 (5) |
| Repaglinide | 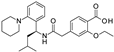 | 0.0011 ± 0.0006 (5) | 0.0039 ± 0.0014 (5) | 0.00094 ± 0.00046 (5) |
| Nateglinide | 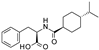 | 14 ± 6.7 (6) | 0.044 ± 0.013 (5) | 16 ± 7.3 (5) |
| Troglitazone | 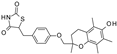 | 10 ± 6.5 (8) | 14 ± 3.1 (5) | 30 ± 16 (5) |
| Rosiglitazone | 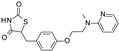 | 8.5 ± 4.6 (6) | >100 (5) | >100 (5) |
| PNU-37883A | 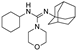 | 0.29 ± 0.21 (6) | >100 (6) | >100 (6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dyhring, T.; Jansen-Olesen, I.; Christophersen, P.; Olesen, J. Pharmacological Profiling of KATP Channel Modulators: An Outlook for New Treatment Opportunities for Migraine. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020225
Dyhring T, Jansen-Olesen I, Christophersen P, Olesen J. Pharmacological Profiling of KATP Channel Modulators: An Outlook for New Treatment Opportunities for Migraine. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020225
Chicago/Turabian StyleDyhring, Tino, Inger Jansen-Olesen, Palle Christophersen, and Jes Olesen. 2023. "Pharmacological Profiling of KATP Channel Modulators: An Outlook for New Treatment Opportunities for Migraine" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020225
APA StyleDyhring, T., Jansen-Olesen, I., Christophersen, P., & Olesen, J. (2023). Pharmacological Profiling of KATP Channel Modulators: An Outlook for New Treatment Opportunities for Migraine. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020225







