Therapeutic Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas for Alzheimer’s Disease Patients and Subsequent Long-Term Follow-Up as a Disease-Modifying Treatment: An Open Label Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hydrogen Treatment Improved AD as Assessed by ADAS-cog
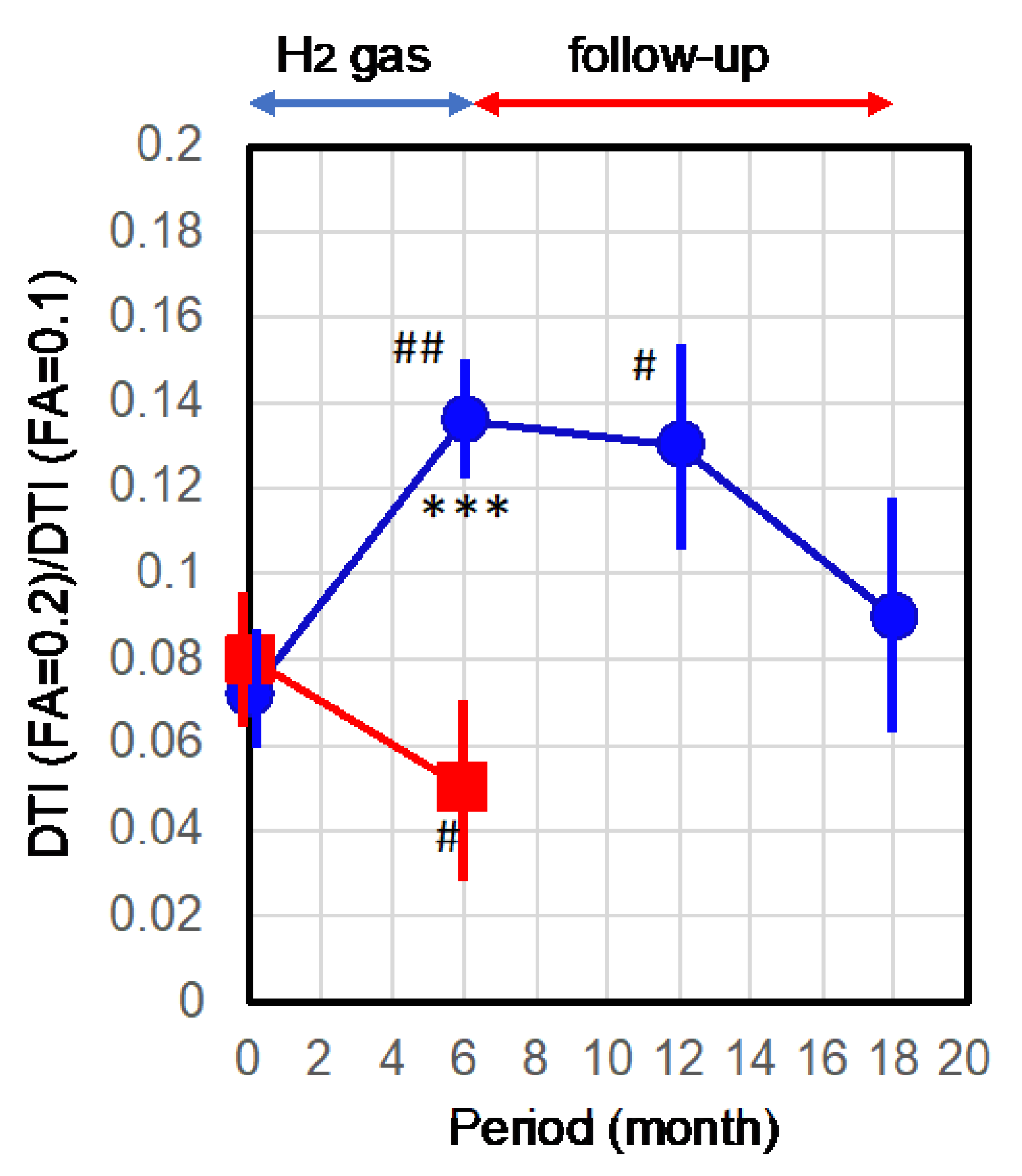
2.2. Improvement of Neurons by H2 Inhalation as Assessed by Diffusion Tensor Imaging
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Approval for This Study
4.2. Patient Selection
4.3. Collection of Data from Untreated Control Patients
4.4. Treatment
4.5. ADAS-cog Examination
4.6. Measurement of the Integrity of Neurons by Diffusion Tensor Imaging
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umar, T. Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systemic Review of Substantial Therapeutic Targets and the Leading Multi-functional Molecules. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 17, 3370–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhong, R.-J.; Cheng, C.; Li, S.; Le, W.-D. New therapeutics beyond amyloid-β and tau for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 42, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecocci, P.; Boccardi, V.; Cecchetti, R.; Bastiani, P.; Scamosci, M.; Ruggiero, C.; Baroni, M. A Long Journey into Aging, Brain Aging, and Alzheimer’s Disease Following the Oxidative Stress Tracks. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 1319–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Freitas Silva, M.; Dias, K.S.T.; Gontijo, V.S.; Ortiz, C.J.C.; Viegas, C., Jr. Multi-Target Directed Drugs as a Modern Approach for Drug Design Towards Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3491–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.-X.; Dai, C.-L.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K. Multi-Targets: An Unconventional Drug Development Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piton, M.; Hirtz, C.; Desmetz, C.; Milhau, J.; Lajoix, A.D.; Bennys, K.; Lehmann, S.; Gabelle, A. Alzheimer’s Disease: Advances in Drug Development. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.-I.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: Initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohta, S. Development of Hydrogen Medicine and Biology: Potential for Various Applications in Diverse Fields. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iketani, M.; Ohsawa, I. Molecular Hydrogen as a Neuroprotective Agent. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, H.; Bajgai, J.; Fadriquela, A.; Sharma, S.; Trinh, T.T.; Akter, R.; Jeong, Y.J.; Goh, S.H.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, K.-J. Therapeutic Potential of Natural Products in Treating Neurodegenerative Disorders and Their Future Prospects and Challenges. Molecules 2021, 26, 5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.R.B.; Sperotto, F.; DiNardo, J.A.; Carlisle, S.; Rivkin, M.J.; Sleeper, L.A.S.; Kheir, J.N. Safety of Prolonged Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas in Air in Healthy Adults. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.-L.; Yang, Y.; Tan, X.; Shen, F.; Chen, G. The role of hydrogen in Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Gas Res. 2018, 8, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimaki, K.; Asada, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Nakajima, E.; Ikejima, C.; Yokota, T.; Kamimura, N.; Ohta, S. Effects of Molecular Hydrogen Assessed by an Animal Model and a Randomized Clinical Study on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donix, M.; Small, G.W.; Bookheimer, S.Y. Family History and APOE-4 Genetic Risk in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2012, 22, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Kitamura, S.; Naitoh, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Fujii, N.; Kikura, R.; Ohta, S. Long-Term Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas for Patients with Advanced Alzheimer’s Disease: A Case Report Showing Improvement in Fecal Incontinence. Med. Res. Arch. 2022, 10. (in press). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, T.C.; Wen, W.; Slavin, M.J.; Sachdev, P.S. Diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2008, 21, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amlien, I.; Fjell, A. Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroscience 2014, 276, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniolo, S.; Serra, L.; Olivito, G.; Caltagirone, C.; Mercuri, N.B.; Marra, C.; Cercignani, M.; Bozzali, M. Cerebellar White Matter Disruption in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 74, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, W.G.; Mohs, R.C.; Davis, K.L. A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Psychiatry 1984, 141, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, S.; Doody, R.; Pratt, R.; Ieni, J. Long-term efficacy and safety of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Final analysis of a US multicentre open-label study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2000, 10, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Cocuzza, E.; Marchiaro, L.; Bogetto, F. Donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 26, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, D.; Sun, L. Amyloid-β PET in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis. Brain Behav. 2022, 13, e2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Guo, J.; Ye, X.-Y.; Xie, Y.; Xie, T. Oxidative stress: The core pathogenesis and mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 77, 101619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, H.; Barger, S.; Barnum, S.; Bradt, B.; Bauer, J.; Cole, G.M.; Cooper, N.R.; Eikelenboom, P.; Emmerling, M.; Fiebich, B.L.; et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 383–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Patil, I.; Cadenas, E. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Ortiz, S.; Lista, S.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Pinto-Fraga, J.; Carmona, R.; Caraci, F.; Caruso, G.; Toschi, N.; Emanuele, E.; Gabelle, A.; et al. Effects of physical activity and exercise interventions on Alzheimer’s disease: An umbrella review of existing meta-analyses. J. Neurol. 2022, 270, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcău, M.C.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Jurcău, A.; Marcu, F.; Ţiț, D.M.; Pașcalău, N.; Nistor-Cseppentö, D.C. The Link between Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Therapeutic Implications and Future Perspectives. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botek, M.; Krejčí, J.; Valenta, M.; McKune, A.; Sládečková, B.; Konečný, P.; Klimešová, I.; Pastucha, D. Molecular Hydrogen Positively Affects Physical and Respiratory Function in Acute Post-COVID-19 Patients: A New Perspective in Rehabilitation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-G.; Sun, W.-Z.; Hu, J.-Y.; Jie, Z.-J.; Xu, J.-F.; Cao, J.; Song, Y.-L.; Wang, C.-H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; et al. Hydrogen/oxygen therapy for the treatment of an acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group controlled trial. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilova, D.A.; Deryugina, A.V.; Brichkin, Y.D.; Taranov, E.V.; Nazarov, E.I.; Pichugin, V.V.; Medvedev, A.P.; Riazanov, M.V.; Fedorov, S.A.; Andrej, Y.S.; et al. Molecular hydrogen exposure improves functional state of red blood cells in the early postoperative period: A randomized clinical study. Med. Gas Res. 2023, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W.; Yang, C.; Xue, Y.; Song, G.; Qin, S. A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of hydrogen/oxygen inhalation for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4113–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, P.; Gong, W.; Ding, W.; He, Q. Fe-porphyrin: A redox-related biosensor of hydrogen molecule. Nano Res. 2022, 16, 2020–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2—A therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iuchi, K.; Nishimaki, K.; Kamimura, N.; Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen suppresses free-radical-induced cell death by mitigating fatty acid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, Y.; Ohsawa, I.; Terasaki, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kunugi, S.; Dedong, K.; Urushiyama, H.; Amenomori, S.; Kaneko-Togashi, M.; Kuwahara, N.; et al. Hydrogen therapy attenuates irradiation-induced lung damage by reducing oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L415–L426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, J.; Wei, Y. Hydrogen, a Novel Therapeutic Molecule, Regulates Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, H.M.; Sama, M.A.; Furman, J.L.; Mathis, D.M.; Beckett, T.L.; Weidner, A.M.; Patel, E.S.; Baig, I.; Murphy, M.P.; LeVine, H.; et al. Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease Is Associated with Selective Changes in Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12957–12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hudry, E.; Wu, H.-Y.; Arbel-Ornath, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Matsouaka, R.; Fan, Z.; Spires-Jones, T.L.; Betensky, R.A.; Bacskai, B.J.; Hyman, B.T. Inhibition of the NFAT Pathway Alleviates Amyloid Beta Neurotoxicity in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 3176–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamimura, N.; Nishimaki, K.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen Improves Obesity and Diabetes by Inducing Hepatic FGF21 and Stimulating Energy Metabolism in db/db Mice. Obesity 2011, 19, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, N.; Ichimiya, H.; Iuchi, K.; Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen stimulates the gene expression of transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α to enhance fatty acid metabolism. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2016, 2, 16008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birks, J.S.; Harvey, R. Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, 3, CD001190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.; Perdomo, C.; Pratt, R.D.; Birks, J.; Wilcock, G.K.; Evans, J.G. Donepezil for the symptomatic treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised controlled trials. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2004, 19, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H., Jr.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caro, J.; Ward, A.; Ishak, K.; Migliaccio-Walle, K.; Getsios, D.; Papadopoulos, G.; Torfs, K. To what degree does cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease predict dependence of patients on caregivers? BMC Neurol. 2002, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Ohta, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kinone, K.; Horikosi, T.; Tamaki, M.; Takeshita, H.; Futatuki, T.; Ohishi, W.; et al. Hydrogen Gas Inhalation Treatment in Acute Cerebral Infarction: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study on Safety and Neuroprotection. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
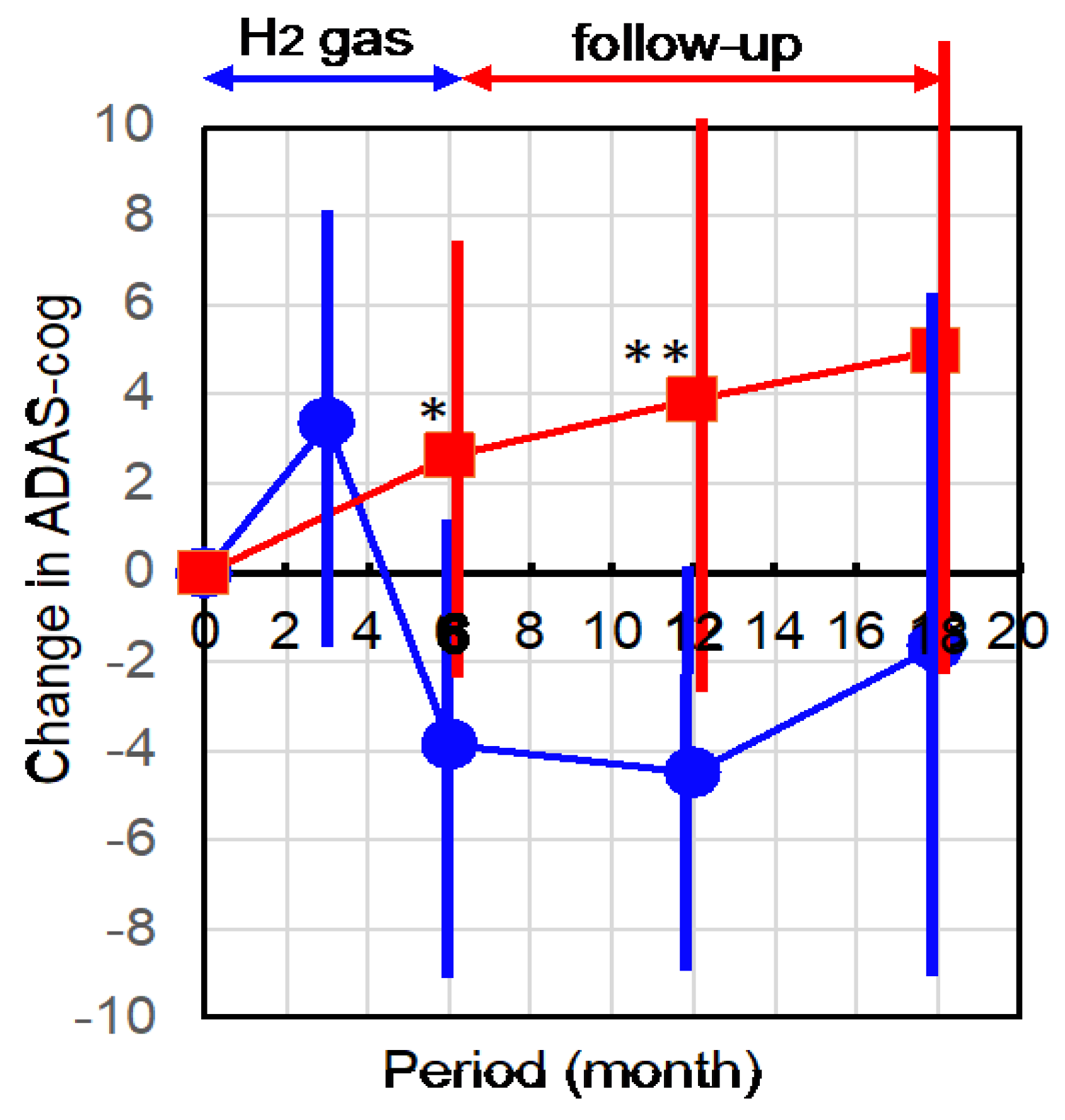
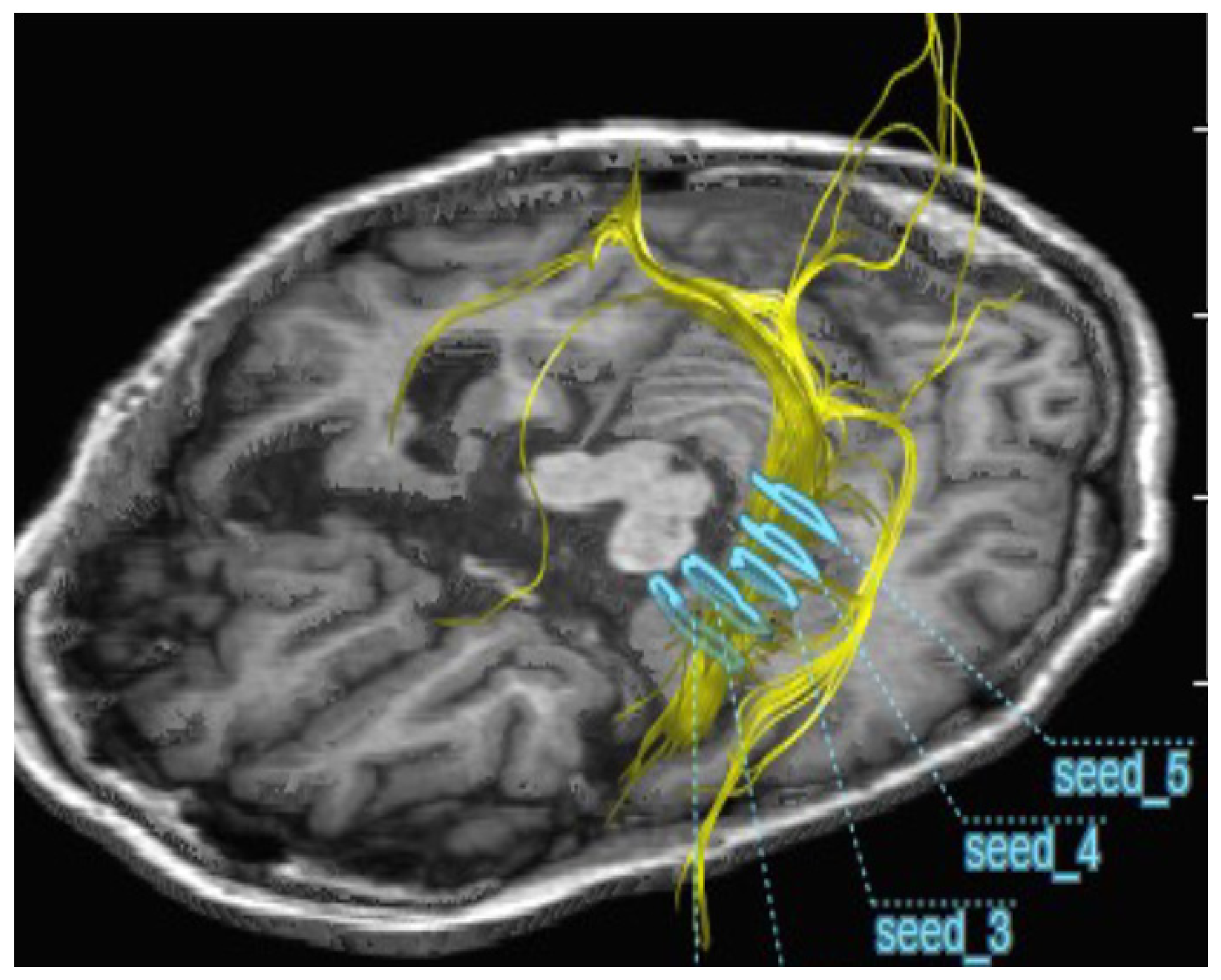
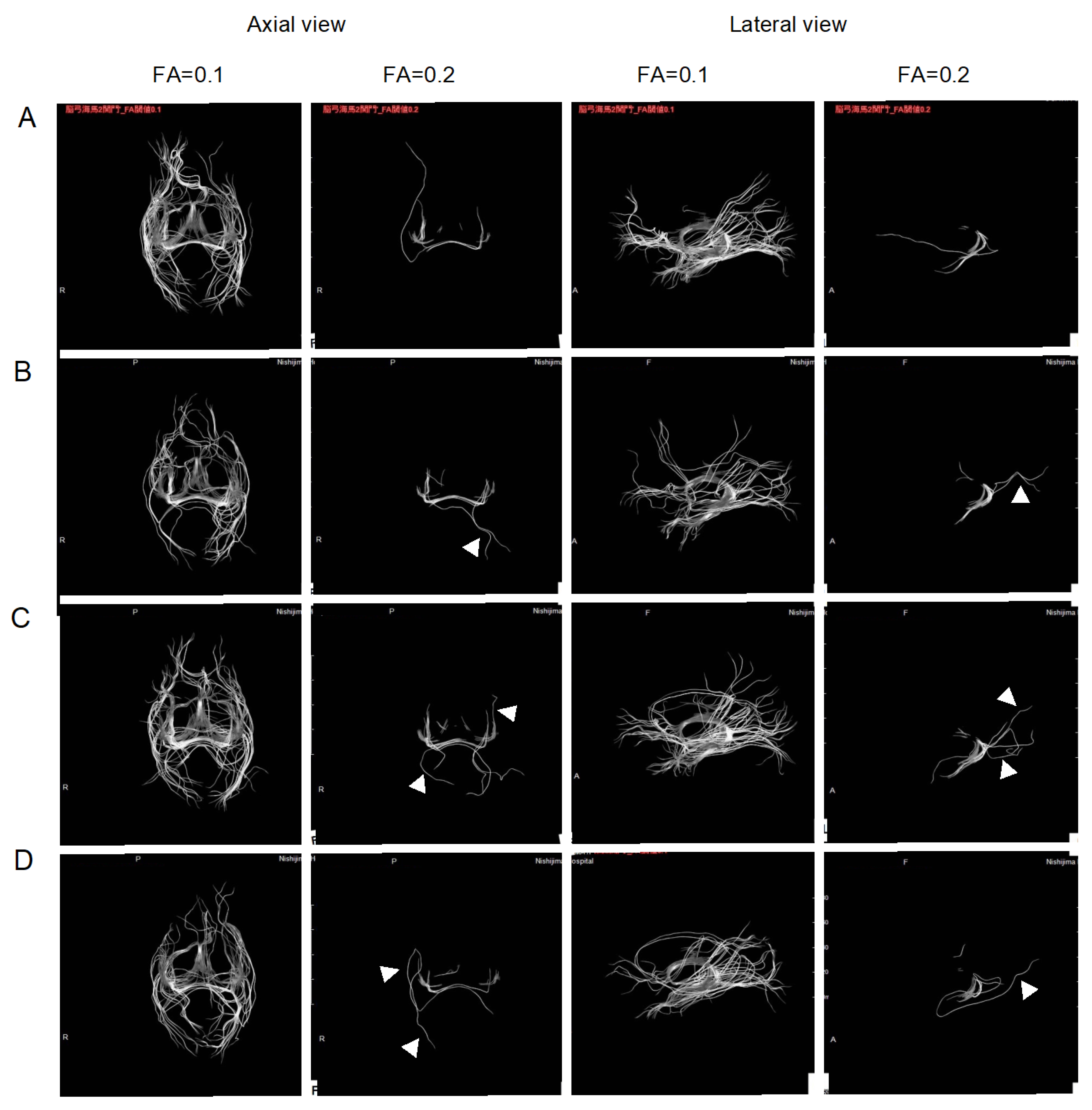
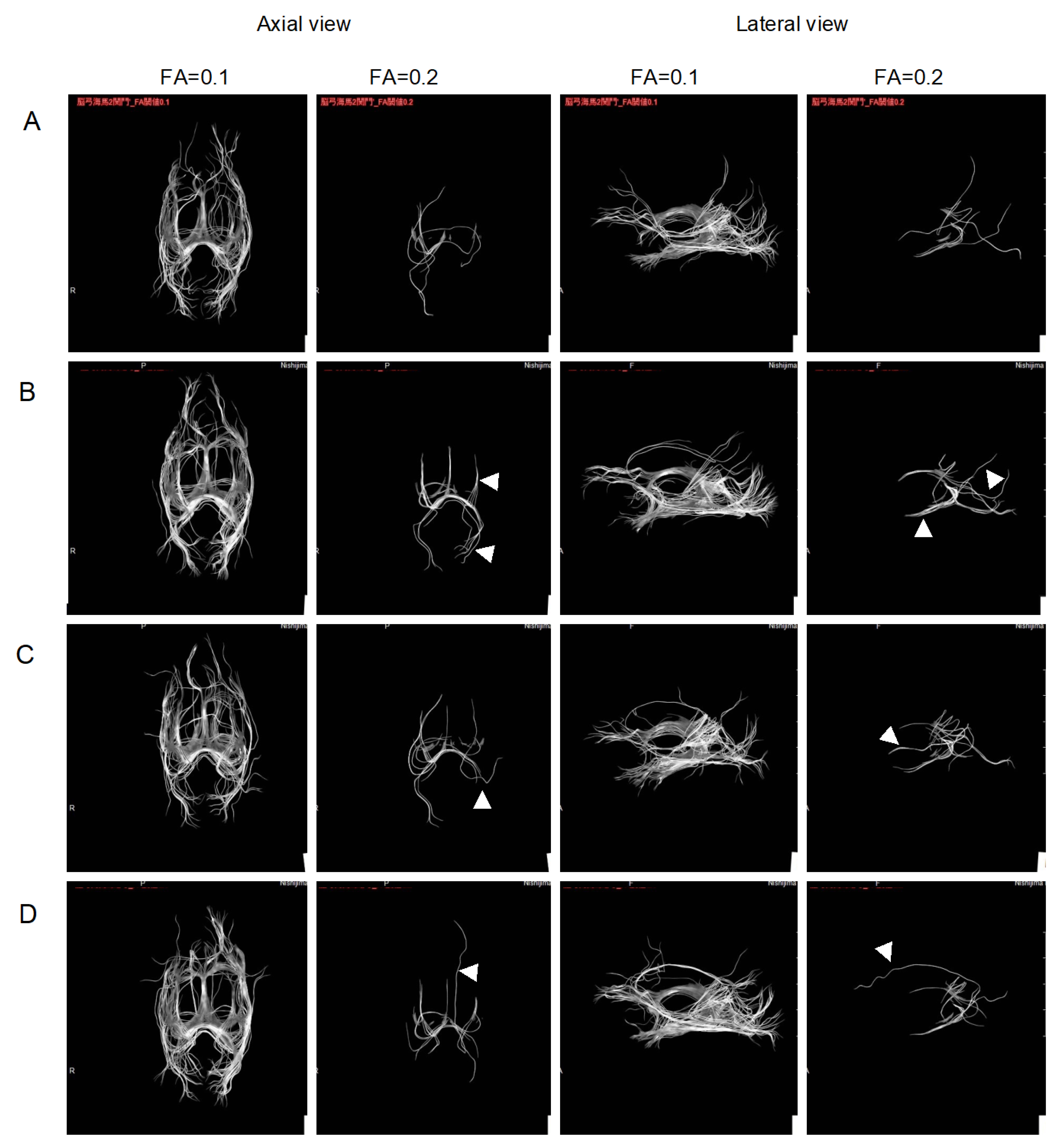
| H2-Treated Group | Control for DTI | Control for ADAS-cog | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 8 | 5 | 19 | |||
| Age (±SD) | 79.4 | ±6.11 | 80.4 | ±1.8 | - | - |
| Creatine (mg/dL) (±SD) | 0.675 | ±0.104 | 0.66 | ±0.114 | - | - |
| Female (%) | 87.5 | 80 | - | - | ||
| Diabetes (%) | 12.5 | 20 | - | - | ||
| Lipidemia (%) | 25 | 60 | - | - | ||
| Mean of ADAS-cog (±SD) | 29.74 | ±8.03 | 27.6 | ±6.5 | 27.83 | ±3.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Ohta, S. Therapeutic Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas for Alzheimer’s Disease Patients and Subsequent Long-Term Follow-Up as a Disease-Modifying Treatment: An Open Label Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030434
Ono H, Nishijima Y, Ohta S. Therapeutic Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas for Alzheimer’s Disease Patients and Subsequent Long-Term Follow-Up as a Disease-Modifying Treatment: An Open Label Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(3):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030434
Chicago/Turabian StyleOno, Hirohisa, Yoji Nishijima, and Shigeo Ohta. 2023. "Therapeutic Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas for Alzheimer’s Disease Patients and Subsequent Long-Term Follow-Up as a Disease-Modifying Treatment: An Open Label Pilot Study" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 3: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030434
APA StyleOno, H., Nishijima, Y., & Ohta, S. (2023). Therapeutic Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas for Alzheimer’s Disease Patients and Subsequent Long-Term Follow-Up as a Disease-Modifying Treatment: An Open Label Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030434







