Antiplatelet Aggregation Properties of Cirsilineol: A Novel Inhibitor of Blood Coagulation Factor Xa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
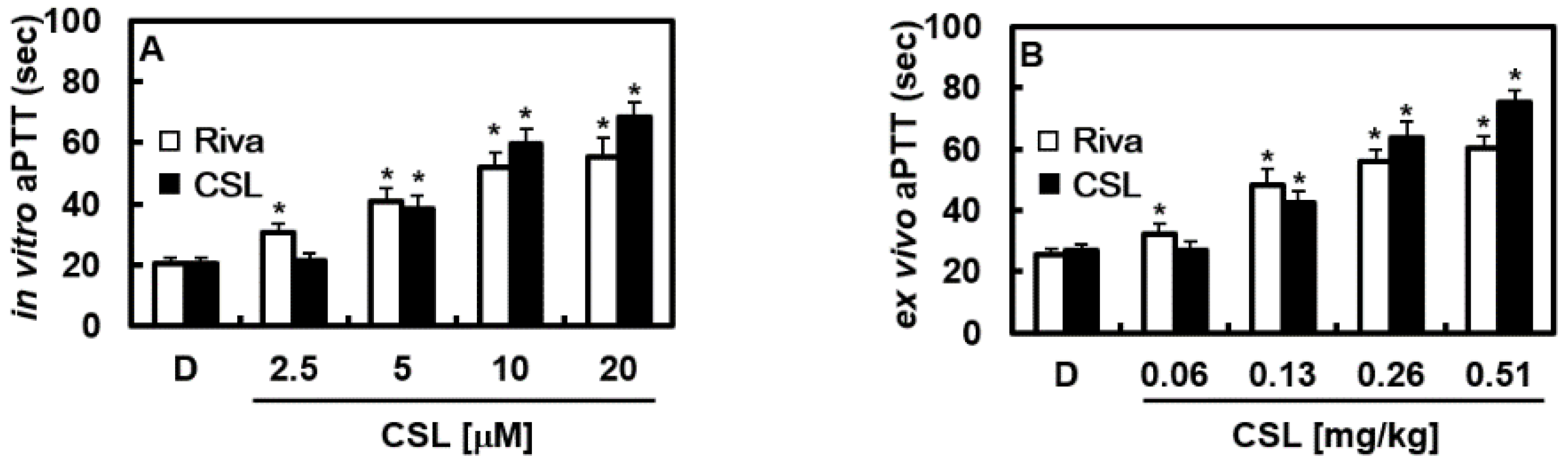
2.1. Effects of CSL on Cellular Viability, Clotting Time In Vitro and Ex Vivo
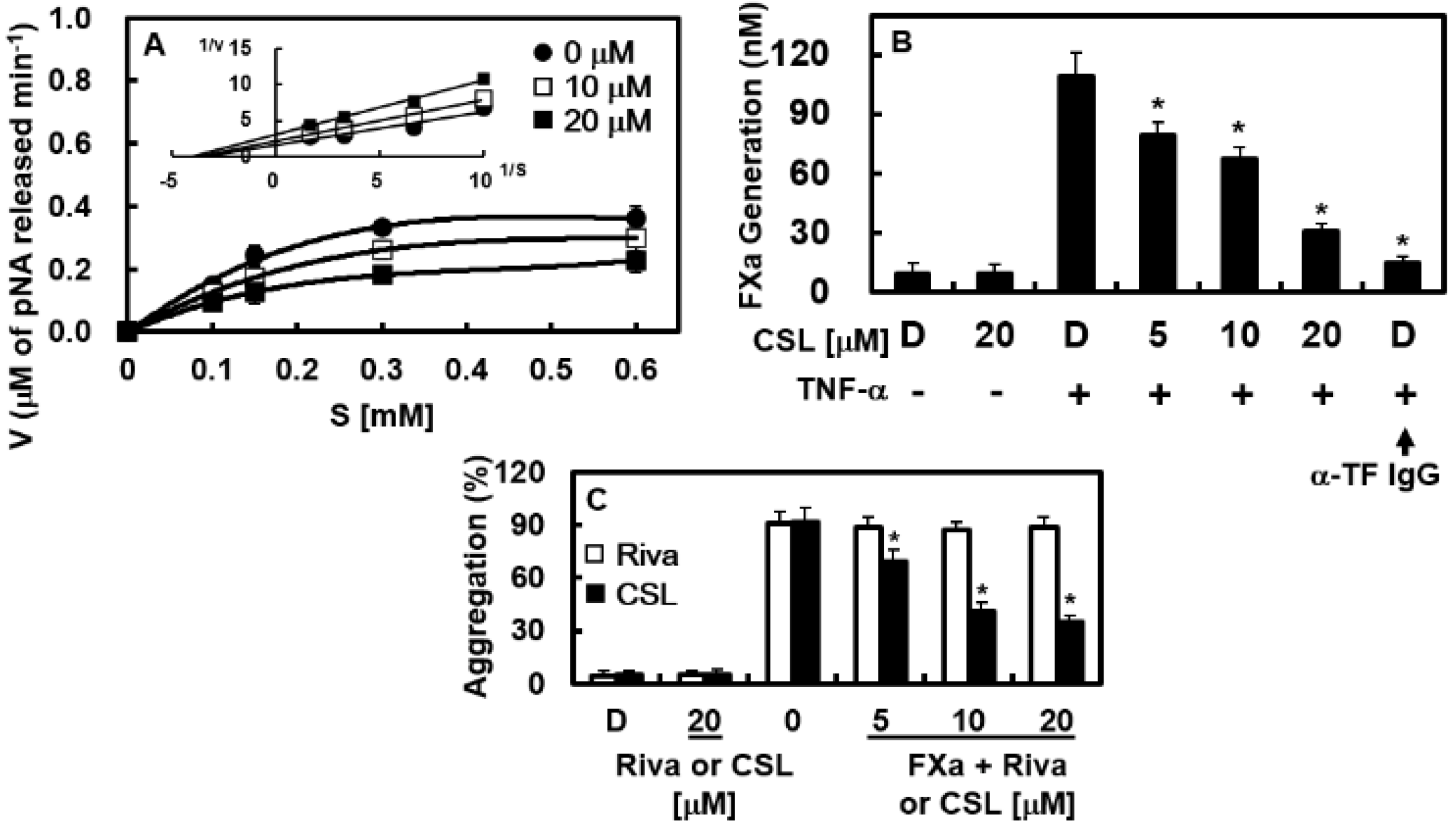
2.2. Effects of CSL on Platelet Aggregation In Vitro
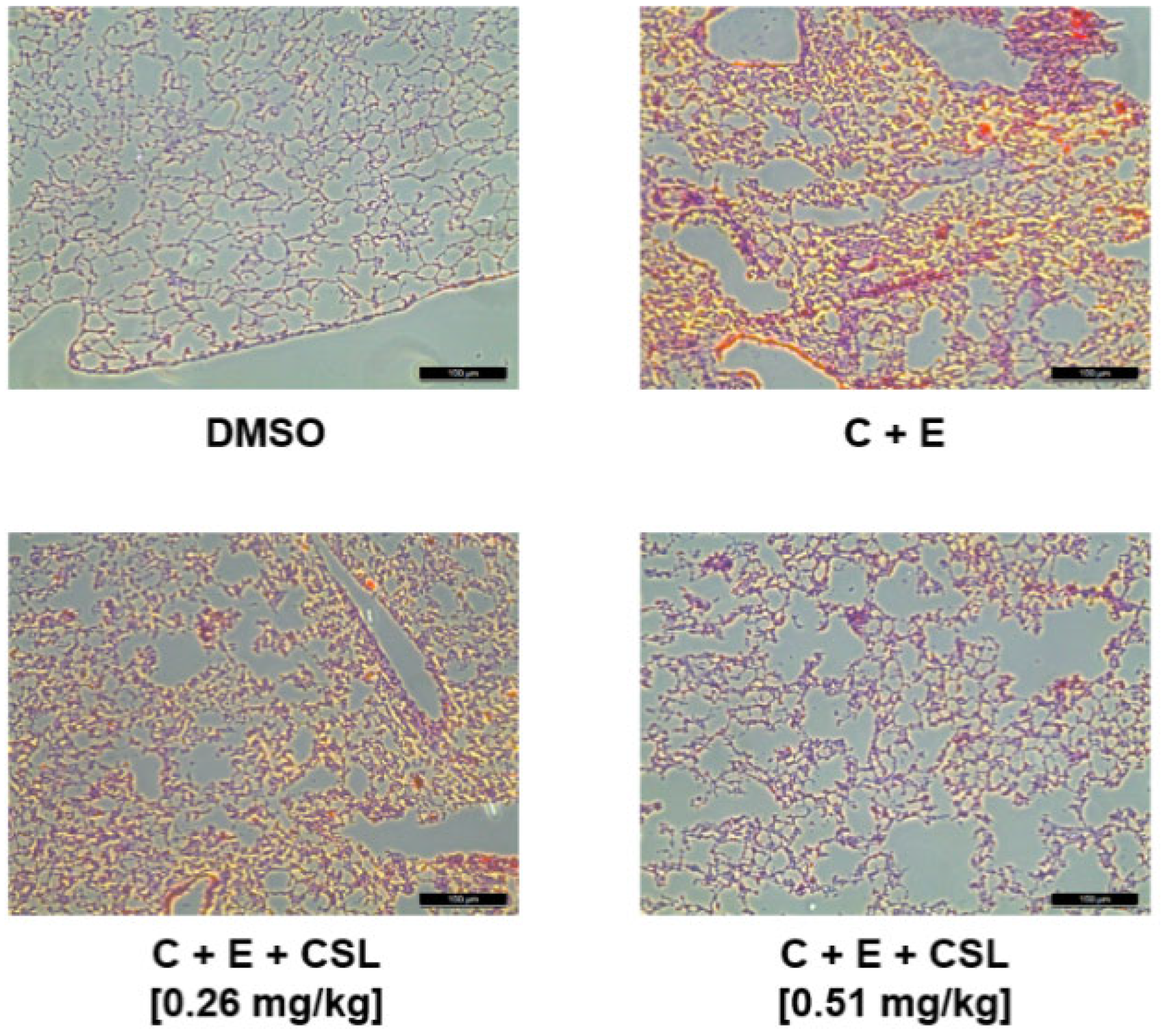
2.3. Effects of CSL on Animal Models of Arterial and Pulmonary Thrombosis
2.4. Effects of CSL on the Catalytic Activity and Production of FXa In Vitro
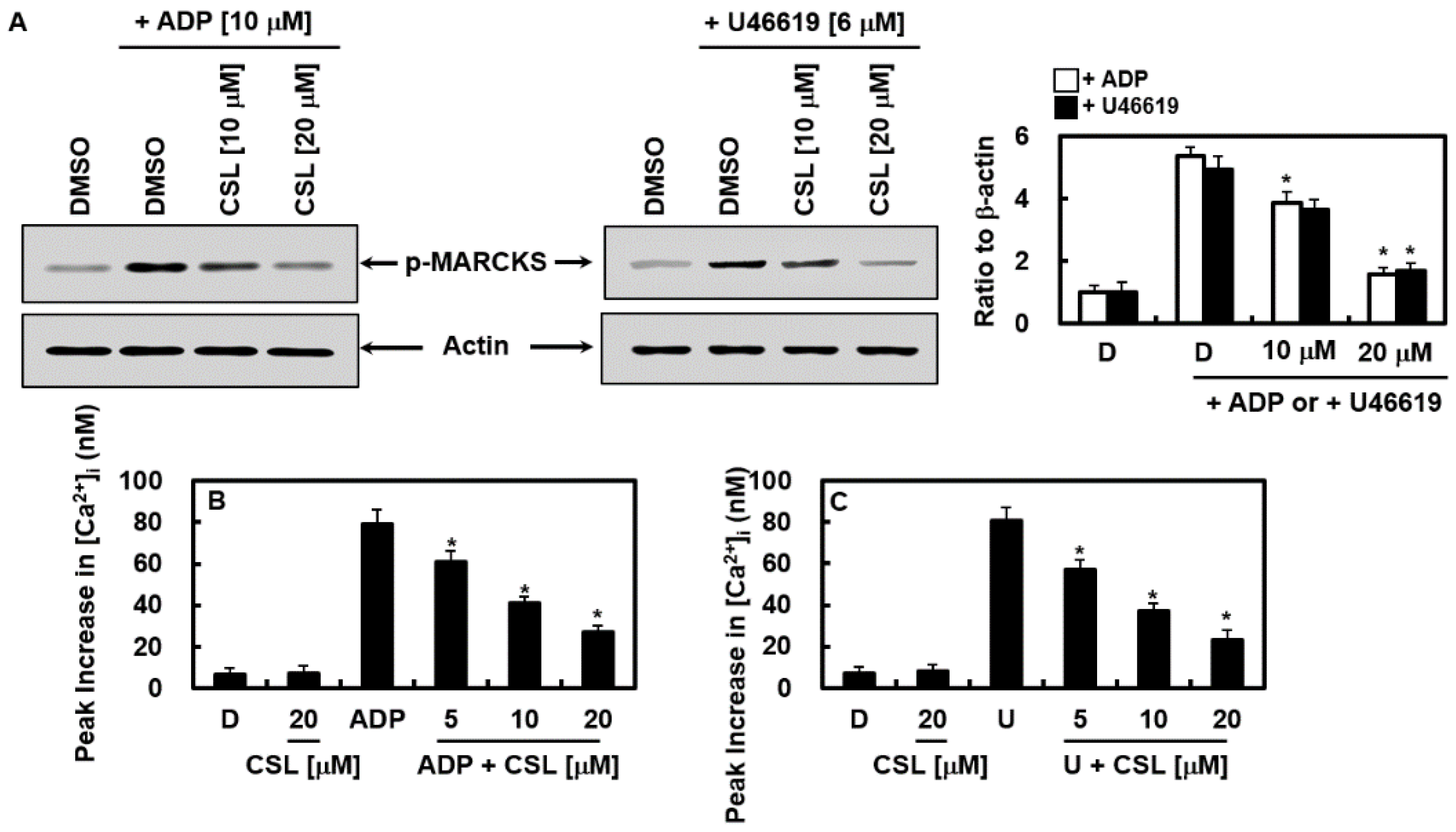
2.5. Effects of CSL on the Activation of Protein Kinase C and Mobilization of Intracellular Calcium
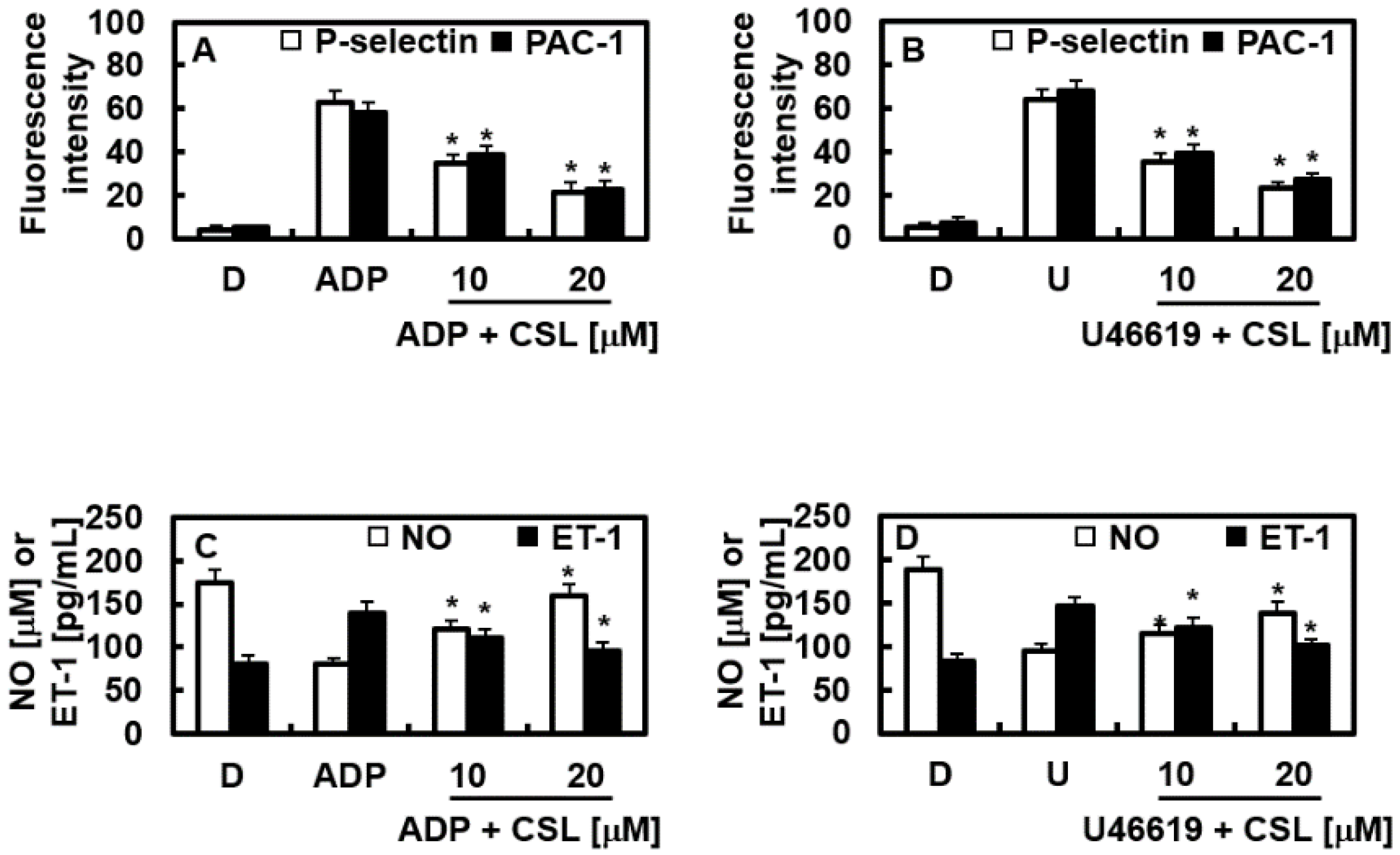
2.6. Effects of CSL on the Expression of P-Selectin and PAC-1
2.7. Effects of CSL on NO and ET-1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Animal Care and Blood Correction
4.3. Care Preparation of Human Plasma and Platelets
4.4. In Vitro Coagulation Assay
4.5. In Vitro Platelet Aggregation Assay
4.6. Inhibition of FXa Amidolytic Activity
4.7. Inhibitory Constant for FXa
4.8. Production of FXa on the Surface of HUVECs
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Measurement of Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization
4.12. Measurement of PAC-1 and P-Selectin Expression
4.13. Quantification of Nitrogen Monoxide (NO) and Endothelin-1 (ET-1)
4.14. Arterial Thrombosis Animal Model
4.15. Acute Pulmonary Thrombosis Induced by Combined Treatment of Collagen and Epinephrine in an Animal Model
4.16. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, G.; Qin, Y.; Huang, W. Anti-thrombosis effect of diosgenin extract from Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H. Wright in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberti, R.; Iannone, L.F.; Palleria, C.; Curcio, A.; Rossi, M.; Sciacqua, A.; Armentaro, G.; Vero, A.; Manti, A.; Cassano, V.; et al. Direct oral anticoagulants: From randomized clinical trials to real-world clinical practice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 684638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milling, T.J., Jr.; Ziebell, C.M. A review of oral anticoagulants, old and new, in major bleeding and the need for urgent surgery. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, M.; Benjanuwattra, J.; Okasha, O.; Almaghraby, A.; Saleh, Y.; Gerges, F. Switching from warfarin to direct-acting oral anticoagulants: It is time to move forward! Egypt Heart J. 2022, 74, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozi, W.; Rahhal, A.; Ali, E.A.; Al-Mashdali, A.; Hilan, Y.; Khamees, I.; Fernyhough, L.J.; Yassin, M.A. Direct oral anticoagulants in sickle cell disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 5061–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustem Gulluoglu, F.; Souverein, P.C.; van den Ham, H.A.; de Boer, A.; Komen, J. Comparative effectiveness and safety of direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in uk patients with atrial fibrillation and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2021, 30, 1293–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobesh, P.P.; Kernan, M.M.; Lueshen, J.J. Direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of venous thromboembolism: Use in patients with advanced renal impairment, obesity, or other weight-related special populations. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 42, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavalia, R.; Middeldorp, S.; Weisser, G.; Espinola-Klein, C. Treatment of venous thromboembolism in special populations with direct oral anticoagulants. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Ruff, C.T.; Antman, E.M.; Giugliano, R.P. The efficacy and safety of non-vitamin k antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2019, 8, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grymonprez, M.; Simoens, C.; Steurbaut, S.; De Backer, T.L.; Lahousse, L. Worldwide trends in oral anticoagulant use in patients with atrial fibrillation from 2010 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace 2022, 24, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.H.; Gong, S.; Gong, T.L.; Zhou, L.Y.; Hu, C.; Xu, W.H. New oral anticoagulants for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in total hip and knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 775126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupo, P.; Szakacs, Z.; Solymar, M.; Habon, T.; Czopf, L.; Hategan, L.; Csanyi, B.; Borbas, J.; Tringer, A.; Varga, G.; et al. Direct anticoagulants and risk of myocardial infarction, a multiple treatment network meta-analysis. Angiology 2020, 71, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, R.D.; Heizer, G.; Aronson, R.; Vora, A.N.; Massaro, T.; Mehran, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Windecker, S.; Darius, H.; Li, J.; et al. Antithrombotic therapy after acute coronary syndrome or pci in atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szapary, L.; Tornyos, D.; Kupo, P.; Lukacs, R.; El Alaoui El Abdallaoui, O.; Komocsi, A. Combination of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy, component network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1036609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, Z.M. Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, P. P-selectin in haemostasis. Brit. J. Haematol. 2004, 126, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, M. Antiplatelet therapy after aspirin-induced upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforen. 2006, 126, 2802–2804. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.P.; Jia, H.W.; Xiao, C.; Lu, Q.P. Theory of traditional chinese medicine and therapeutic method of diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 1854–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, F.P.; Pinheiro, N.M.; Mernak, M.I.; Righetti, R.F.; Martins, M.A.; Lago, J.H.; Lopes, F.D.; Tiberio, I.F.; Prado, C.M. Evidences of herbal medicine-derived natural products effects in inflammatory lung diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 2348968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Gong, F.Y.; Wu, X.X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Chen, T.; Xu, Q. Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effect of flavones isolated from artemisia vestita. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, T.; Xu, Q. Cirsilineol inhibits proliferation of cancer cells by inducing apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.S.; He, K.; Zhou, Z.; Lai, C.S.; Zhang, L.; Quan, Z.; Shao, X.; Pan, M.H.; Ho, C.T. Flavonoids from rabdosia rubescens exert anti-inflammatory and growth inhibitory effect against human leukemia hl-60 cells. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.P.; Silva, A.L.N.; Viana, L.; Silva, M.G.; Lavor, E.M.; Oliveira, R.G.; Alencar, E.B.; Lima, R.S.; Mendes, R.L.; Rolim, L.A.; et al. Beta-cyclodextrin complex improves the bioavailability and antitumor potential of cirsiliol, a flavone isolated from leonotis nepetifolia (lamiaceae). Heliyon 2019, 5, e01692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.; Song, K.S.; Yang, E.J.; Bae, J.S. Isolation, synthesis, and antisepsis effects of a c-methylcoumarinochromone isolated from abronia nana cell culture. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Nangaku, M.; Takizawa, S.; Ishida, H.; Kurokawa, K.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C.; Hirayama, N.; Miyata, T. Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: Its mechanism and effectiveness on coagulation and fibrosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hahn, D.; Bae, J.S. Recent progress in the discovery of bioactive components from edible natural sources with antithrombotic activity. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, M.A.; Bae, J.S. Anti-factor xa activities of zingerone with anti-platelet aggregation activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 105, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, T.; Thienel, M.; Dannenberg, L.; Mourikis, P.; Helten, C.; Ayhan, A.; M’Pembele, R.; Achilles, A.; Trojovky, K.; Konsek, D.; et al. Rivaroxaban reduces arterial thrombosis by inhibition of fxa-driven platelet activation via protease activated receptor-1. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzagallaai, A.; Rose, S.D.; Trifaro, J.M. Platelet secretion induced by phorbol esters stimulation is mediated through phosphorylation of marcks: A marcks-derived peptide blocks marcks phosphorylation and serotonin release without affecting pleckstrin phosphorylation. Blood 2000, 95, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.H.; Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Andrews, R.K.; Jackson, S.P. New insights into the haemostatic function of platelets. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 147, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merten, M.; Thiagarajan, P. P-selectin expression on platelets determines size and stability of platelet aggregates. Circulation 2000, 102, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredt, D.S.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric oxide: A physiologic messenger molecule. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994, 63, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, M.; Kurihara, H.; Kimura, S.; Tomobe, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Mitsui, Y.; Yazaki, Y.; Goto, K.; Masaki, T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 1988, 332, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- d’Uscio, L.V.; Barton, M.; Shaw, S.; Luscher, T.F. Endothelin in atherosclerosis: Importance of risk factors and therapeutic implications. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2000, 35, S55–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Spanke, S.; Schipke, J.D. Potential role of endothelin-1 and endothelin antagonists in cardiovascular diseases. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2000, 95, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhamme, P.; Hoylaerts, M.F. The pivotal role of the endothelium in haemostasis and thrombosis. Acta Clin. Belg. 2006, 61, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, V.A.; Ferraris, S.P.; Saha, S.P. Antiplatelet drugs: Mechanisms and risks of bleeding following cardiac operations. Int. J. Angiol. 2011, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Hirsh, J.; Spencer, F.A.; Baglin, T.P.; Weitz, J.I. Antiplatelet drugs: Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American college of chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, e89S–e119S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahlback, B. Blood coagulation. Lancet 2000, 355, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, L.; Perri, L.; Violi, F. Myocardial infarction and atrial fibrillation: Different impact of anti-iia vs anti-xa new oral anticoagulants: A meta-analysis of the interventional trials. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 178, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.A. New anticoagulants: Anti iia vs anti xa--is one better? J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2006, 21, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauch, E.C.; Saver, J.L.; Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bruno, A.; Connors, J.J.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Khatri, P.; McMullan, P.W., Jr.; Qureshi, A.I.; Rosenfield, K.; et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2013, 44, 870–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, D.; Flaumenhaft, R.; Furie, B. Interactions of platelets, blood-borne tissue factor, and fibrin during arteriolar thrombus formation in vivo. Microcirculation 2005, 12, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perzborn, E.; Heitmeier, S.; Laux, V. Effects of rivaroxaban on platelet activation and platelet-coagulation pathway interaction: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 20, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olivier, C.B.; Weik, P.; Meyer, M.; Weber, S.; Diehl, P.; Bode, C.; Moser, M.; Zhou, Q. Dabigatran and rivaroxaban do not affect aa- and adp-induced platelet aggregation in patients receiving concomitant platelet inhibitors. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 42, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perzborn, E.; Roehrig, S.; Straub, A.; Kubitza, D.; Mueck, W.; Laux, V. Rivaroxaban: A new oral factor xa inhibitor. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdi, G.; Bachelot-Loza, C.; Mazoyer, E.; Poirault-Chassac, S.; Duchemin, J.; Fontenay, M.; Gaussem, P. Effect of rivaroxaban and dabigatran on platelet functions: In vitro study. Thromb. Res. 2019, 183, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, N.; Lee, W.; Bae, J.-S. Renal protective effects of sparstolonin b in a mouse model of sepsis. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2022, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.C.; Bae, J.S. Hepatic protective effects of jujuboside b through the modulation of inflammatory pathways. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2022, 27, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Jeon, C.; Kim, C.; Ryu, S.H.; Lee, W.; Bae, J.S. Inhibition of factor xa activity, platelet aggregation, and experimentally induced thrombosis by sparstolonin B. Phytomedicine 2022, 99, 153987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Wu, C.I.; Wang, W.Y.; Wu, Y.C. Low concentrations of resveratrol potentiate the antiplatelet effect of prostaglandins. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grynkiewicz, G.; Poenie, M.; Tsien, R.Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frojmovic, M.; Wong, T.; van de Ven, T. Dynamic measurements of the platelet membrane glycoprotein iib-iiia receptor for fibrinogen by flow cytometry. I. Methodology, theory and results for two distinct activators. Biophys. J. 1991, 59, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DiMinno, G.; Silver, M.J. Mouse antithrombotic assay: A simple method for the evaluation of antithrombotic agents in vivo. Potentiation of antithrombotic activity by ethyl alcohol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1983, 225, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Bae, O.N.; Lim, K.M.; Noh, J.Y.; Kang, S.; Chung, K.Y.; Chung, J.H. Novel antiplatelet activity of protocatechuic acid through the inhibition of high shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, T.; Satoh, K.; Yaoita, N.; Kikuchi, N.; Omura, J.; Kurosawa, R.; Numano, K.; Al-Mamun, E.; Siddique, M.A.; Sunamura, S.; et al. Activated tafi promotes the development of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A possible novel therapeutic target. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1246–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Time to Large Thrombus Formation (min) | ||||
| mg/kg | Rivaroxaban | CSL | ||
| DMSO | 7.4 ± 0.5 | 7.1 ± 0.4 | ||
| 0.13 | 15.3 ± 1.1 * | 13.1 ± 1.1 * | ||
| 0.26 | 21.8 ± 1.9 * | 27.2 ± 2.1 * | ||
| 0.51 | 44.3 ± 3.1 * | 51.4 ± 3.1 * | ||
| Scored thrombus formation | ||||
| mg/kg | Rivaroxaban | CSL | ||
| DMSO | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 4.1 ± 0.1 | ||
| 0.13 | 3.5 ± 0.1 * | 3.7 ± 0.2 * | ||
| 0.26 | 3.1 ± 0.3 * | 2.7 ± 0.1 * | ||
| 0.51 | 2.3 ± 0.1 * | 1.8 ± 0.1 * | ||
| In vivo pulmonary thrombosis model (Mortality % and Scored thrombus formation, n = 20) | ||||
| mg/kg | Rivaroxaban | CSL | ||
| % | Thrombi | % | Thrombi | |
| DMSO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| C + E | 95 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 95 | 4.1± 0.2 |
| 0.13 | 85 # | 3.1 ± 0.1 # | 85 # | 3.5 ± 0.1 # |
| 0.26 | 75 # | 2.6 ± 0.1 # | 80 # | 2.5 ± 0.1 # |
| 0.51 | 55 # | 1.9 ± 0.2 # | 60 # | 1.8 ± 0.2 # |
| MA | ||
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | Ki a | Ratio b |
| Factor Xa | 3.70 ± 0.19 | 1 |
| α-Thrombin | >300 | >100 |
| Trypsin | >300 | >100 |
| Plasmin | >300 | >100 |
| Protein Ca | >300 | >100 |
| tPA c | >300 | >100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.O.; Heo, J.B.; Park, D.H.; Song, G.Y.; Bae, J.-S. Antiplatelet Aggregation Properties of Cirsilineol: A Novel Inhibitor of Blood Coagulation Factor Xa. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040588
Kim GO, Heo JB, Park DH, Song GY, Bae J-S. Antiplatelet Aggregation Properties of Cirsilineol: A Novel Inhibitor of Blood Coagulation Factor Xa. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040588
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Go Oun, Jong Beom Heo, Dong Ho Park, Gyu Yong Song, and Jong-Sup Bae. 2023. "Antiplatelet Aggregation Properties of Cirsilineol: A Novel Inhibitor of Blood Coagulation Factor Xa" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040588
APA StyleKim, G. O., Heo, J. B., Park, D. H., Song, G. Y., & Bae, J. -S. (2023). Antiplatelet Aggregation Properties of Cirsilineol: A Novel Inhibitor of Blood Coagulation Factor Xa. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040588








