Manganese (II) Complex of 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane-1,4,7-Triacetic Acid (NOTA) as a Hepatobiliary MRI Contrast Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Relaxivities and Human Serum Albumin (HSA)-Binding of Mn-NOTA-NP
| Compound | Water | HSA (0.67 mM) | HSA Binding Constant (Ka) | logP oct/wat | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r1 (mM−1 s−1) | r2 (mM−1 s−1) | r2/r1 | r1 (mM−1 s−1) | r2 (mM−1 s−1) | r2/r1 | |||
| Mn-NOTA-NP | 3.57 ± 0.20 | 18.08 ± 0.50 | 5.0 | 9.01 ± 0.50 | 42.83 ± 2.70 | 4.8 | 36.6 M−1 | −0.93 |
| Mn-EDTA | 1.79 ± 0.05 | 3.85 ± 0.05 | 2.2 | 2.93 ± 0.30 | 5.54 ± 0.10 | 1.9 | - | −2.72 |
| Mn-DPDP b | 1.50 ± 0.40 | 2.30 ± 0.60 | 1.5 | - | - | - | - | −3.07 |
| Gd-DTPA | 4.12 ± 0.10 | 5.20 ± 0.20 | 1.3 | - | - | - | - | −3.16 |
| Gd-DTPA-EOB b | 4.30 ± 0.60 | 5.50 ± 0.60 | 1.3 | 9.97 ± 1.00 | 10.76 ± 0.10 | 1.1 | 27 M−1 | −2.11 |
| Gd-BOPTA b | 4.00 ± 0.60 | 4.70 ± 0.60 | 1.2 | 8.27 ± 0.10 | 10.84 ± 0.10 | 1.3 | - | −2.23 |
2.3. Lipophilicity of Mn-NOTA-NP
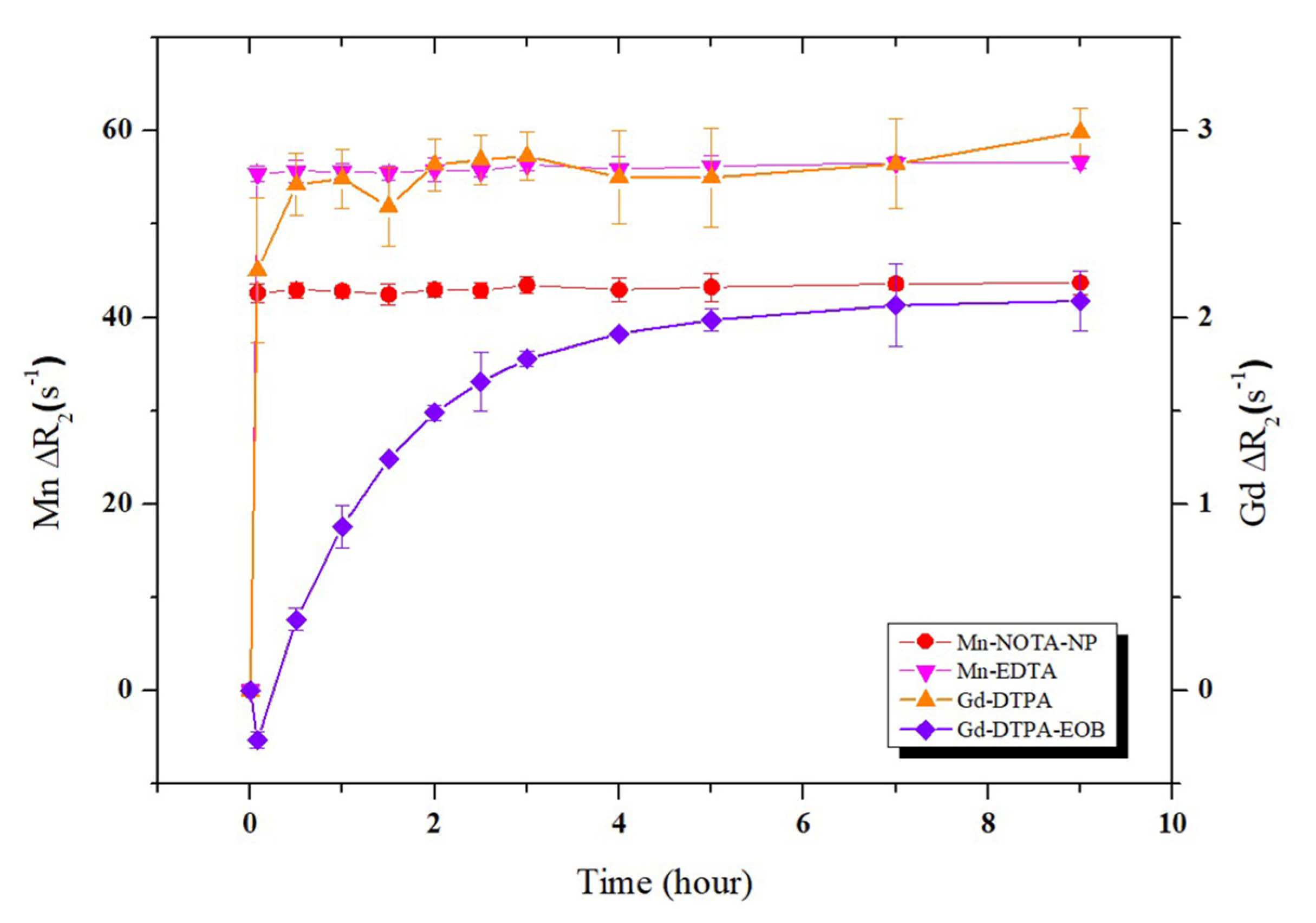
2.4. Kinetic Inertness and pH Stability of Mn-NOTA-NP
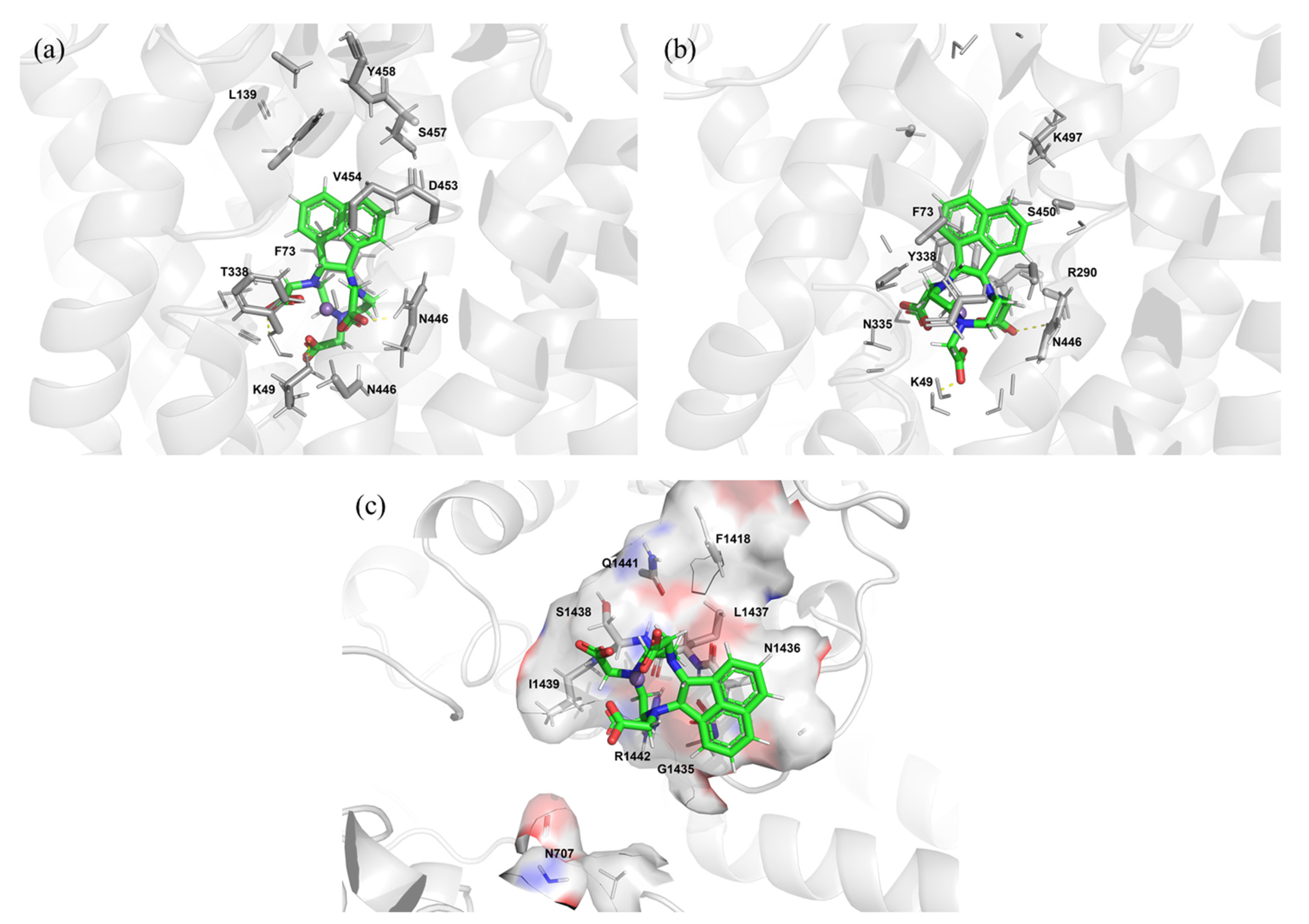
2.5. Protein–Ligand Docking Simulations of Mn-NOTA-NP
2.6. Cytotoxicity of Mn-NOTA-NP
2.7. In Vivo MR Images of Normal Mice Using Mn-NOTA-NP
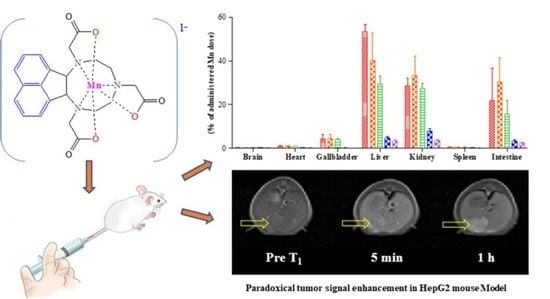
2.8. In Vivo Biodistribution of Mn-NOTA-NP
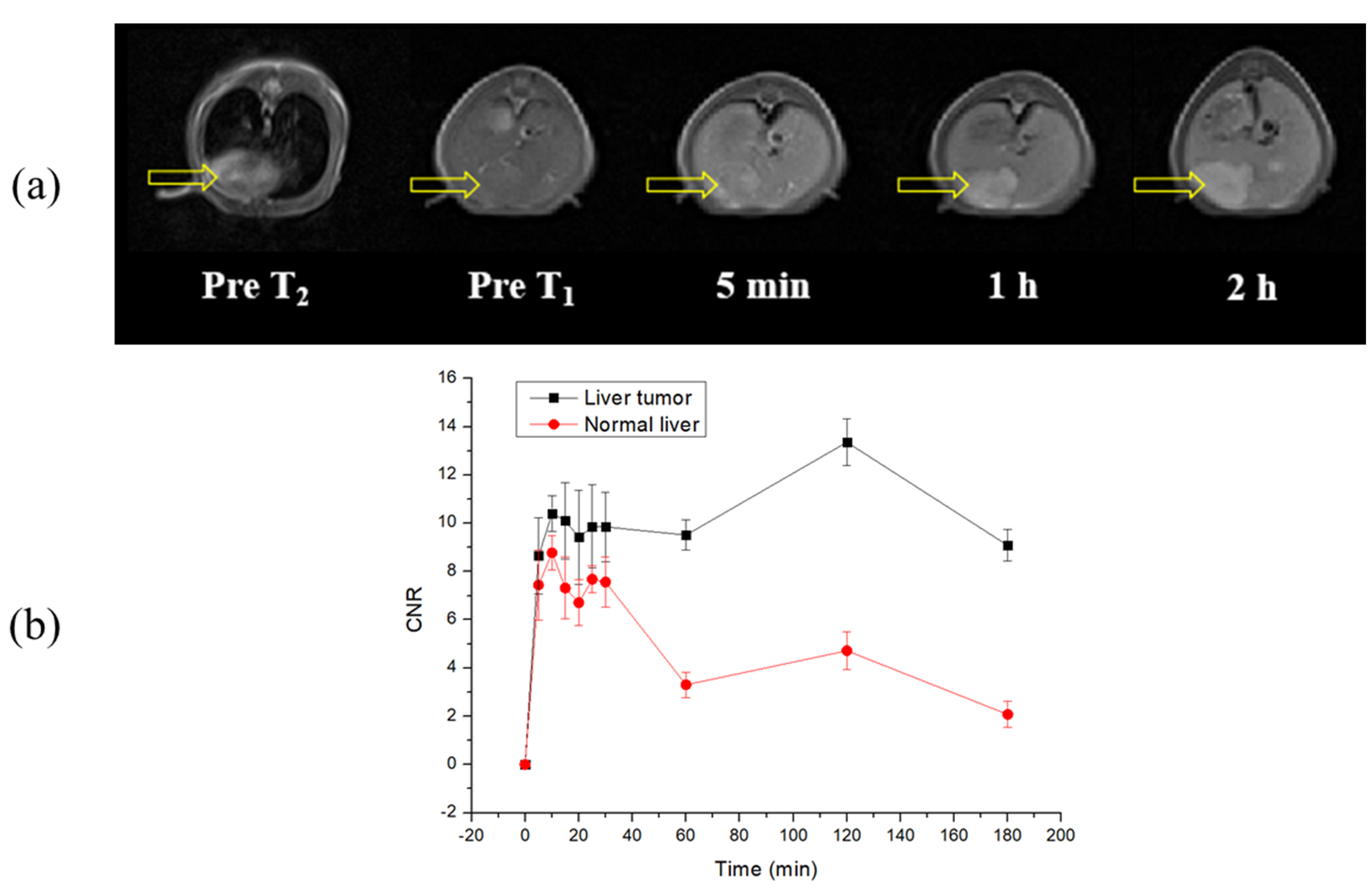
2.9. In Vivo MR Images of the Liver Tumor Model Using Mn-NOTA-NP
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2.1. Synthesis of Compound 2
3.2.2. Synthesis of Compound 3
3.2.3. Synthesis of NOTA-NP
3.2.4. Synthesis of Mn-NOTA-NP
3.3. Relaxivity
3.4. Octanol−Water Partition Coefficients
3.5. Determination of Binding Constants
3.6. Transmetalation Kinetics
3.7. pH Stability
3.8. Molecular Modeling Method
3.9. Cell Culture
3.10. Cell Viability Assay
3.11. Biodistribution
3.12. In Vivo MRI of Normal Mice
3.13. Liver Tumor Model and In Vivo MRI
3.14. Image Analysis
3.15. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, A.; Caravan, P.; Price, W.S.; Platas-Iglesias, C.; Gale, E.M. Applications for Transition-Metal Chemistry in Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 6648–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI Contrast Agents: Current Challenges and New Frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 957–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, G.H.; Chang, Y. Gadolinium as an MRI contrast agent. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, A.P.; Velloni, F.; Ramalho, M.; AlObaidy, M.; Rajapaksha, A.; Semelka, R.C. Focal liver lesions: Practical magnetic resonance imaging approach. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitclerc, L.; Sebastiani, G.; Gilbert, G.; Cloutier, G.; Tang, A. Liver fibrosis: Review of current imaging and MRI quantification techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 1276–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T. Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Liver and Pancreas. In Medical Imaging Contrast Agents: A Clinical Manual; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 131–148. [Google Scholar]
- Grobner, T. Gadolinium—A specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, G.; Frenzel, T.; Boyken, J.; Schoeckel, L.; Pietsch, H. Gadolinium presence in the brain after administration of the liver-specific gadolinium-based contrast agent gadoxetate: A systematic comparison to multipurpose agents in rats. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, J.; Sherry, A.D. Advances in gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent designs for monitoring biological processes in vivo. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 45, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, S.; Hoffmann, S.H.L.; Carniato, F.; Kenning, L.; Price, T.W.; Prior, T.J.; Botta, M.; Martins, A.F.; Stasiuk, G.J. A Single-Pot Template Reaction Towards a Manganese-Based T1 Contrast Agent. Angew. Chem. 2021, 60, 10736–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, D.; Sy, M.; Pallier, A.; Meme, S.; de Silva, I.; Lacerda, S.; Nonat, A.M.; Charbonniere, L.J.; Toth, E. Unprecedented Kinetic Inertness for a Mn(2+) -Bispidine Chelate: A Novel Structural Entry for Mn(2+) -Based Imaging Agents. Angew. Chem. 2020, 59, 11958–11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, P.; Luo, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, B.; Lin, H.; Gao, J. Multinuclear Mn (II) united-DOTA complexes with enhanced inertness and high MRI contrast ability. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.A.; Lazar, B. Manganese-Based Contrast Agents as a Replacement for Gadolinium. Radiol. Technol. 2021, 93, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merbach, A.E.H.L.; Tóth, E. The Chemistry of Contrast Agent in Medical Magnetic Resonance Imaging; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, J.; Ponzoni, S.; Aschner, M. Manganese homeostasis and transport. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2013, 12, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.S.; Gore, J.C. Studies of tissue NMR relaxation enhancement by manganese. Dose and time dependences. Investig. Radiol. 1984, 19, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Baron, R.L.; Peterson, M.S.; Oliver, J.H., 3rd; Davis, P.L.; Confer, S.R.; Federle, M.P. Hepatocellular carcinoma: MR imaging with mangafodipir trisodium (Mn-DPDP). Radiology 1996, 200, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, P.; Zhu, C.; Xia, Z.; Xia, Q.; Zhong, L.; Xiao, B.; Cheng, T.; Wu, C.; Shen, C.; et al. Mn(II) Complex of Lipophilic Group-Modified Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) as a New Hepatobiliary MRI Contrast Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9182–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Choi, G.; Baek, A.R.; Sung, B.K.; Kim, M.; Cho, A.E.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Manganese(II)-Based Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid-Ethoxybenzyl Conjugate as a Highly Stable Hepatobiliary Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3614–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.; Lee, G.H.; Kang, H.J.; Jung, J.C.; Park, J.S.; Kim, T.J.; Chang, Y. Manganese Complex of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA)-Benzothiazole Aniline (BTA) Conjugate as a Potential Liver-Targeting MRI Contrast Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Willich, H. Stability of linear and macrocyclic gadolinium based contrast agents. Br. J. Radiol. 2007, 80, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Ramsay, I.A.; Erstad, D.J.; Fuchs, B.C.; Tanabe, K.K.; Caravan, P.; Gale, E.M. Manganese-Based Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Liver Tumors: Structure-Activity Relationships and Lead Candidate Evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8811–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, T.J.; Parmelee, D.J.; Sajiki, H.; Scott, D.M.; Ouellet, H.S.; Walovitch, R.C.; Tyeklar, Z.; Dumas, S.; Bernard, P.; Nadler, S.; et al. The effect of a phosphodiester linking group on albumin binding, blood half-life, and relaxivity of intravascular diethylenetriaminepentaacetato aquo gadolinium(III) MRI contrast agents. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 3465–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Woolley, F.R.; Zingaro, R.A. In vitro anticancer activities and optical imaging of novel intercalative non-cisplatin conjugates. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7192–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzal-Varela, R.; Valencia, L.; Lalli, D.; Maneiro, M.; Esteban-Gomez, D.; Platas-Iglesias, C.; Botta, M.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A. Understanding the Effect of the Electron Spin Relaxation on the Relaxivities of Mn(II) Complexes with Triazacyclononane Derivatives. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 15055–15068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, C.; Sherry, A.; Brown III, R.; Koenig, S. Magnetic field dependence of solvent proton relaxation rates induced by Gd3+ and Mn2+ complexes of various polyaza macrocyclic ligands: Implications for NMR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1986, 3, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacheris, W.; Nickle, S.; Sherry, A. Thermodynamic study of lanthanide complexes of 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-N, N′, N″-triacetic acid and 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-N, N′, N″, N‴-tetraacetic acid. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drahos, B.; Lukes, I.; Toth, E. Manganese(II) Complexes as Potential Contrast Agents for MRI. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyon Bin Na, I.C.S. Taeghwan Hyeon. Inorganic Nanoparticles for MRI Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J. Interplay between longitudinal and transverse contrasts in Fe3O4 nanoplates with (111) exposed surfaces. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7976–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kang, M.K.; Jung, K.H.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Jung, J.C.; Lee, G.H.; Chang, Y.; Kim, T.J. Gadolinium complex of DO3A-benzothiazole aniline (BTA) conjugate as a theranostic agent. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8104–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, M.; Bauer, H.; Mintorovitch, J.; Requardt, M.; Weinmann, H.J. Comparison of magnetic properties of MRI contrast media solutions at different magnetic field strengths. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, M.J. Lipophilicity in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, Z.; Brucher, E.; Uggeri, F.; Maiocchi, A.; Toth, I.; Andrasi, M.; Gaspar, A.; Zekany, L.; Aime, S. The role of equilibrium and kinetic properties in the dissociation of Gd[DTPA-bis(methylamide)] (Omniscan) at near to physiological conditions. Chemistry 2015, 21, 4789–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, E.M.; Atanasova, I.P.; Blasi, F.; Ay, I.; Caravan, P. A Manganese Alternative to Gadolinium for MRI Contrast. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15548–15557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federle, M.P.; Chezmar, J.L.; Rubin, D.L.; Weinreb, J.C.; Freeny, P.C.; Semelka, R.C.; Brown, J.J.; Borrello, J.A.; Lee, J.K.; Mattrey, R. Safety and efficacy of mangafodipir trisodium (MnDPDP) injection for hepatic MRI in adults: Results of the US multicenter phase III clinical trials (safety). J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Gianolio, E.; Terreno, E.; Giovenzana, G.; Pagliarin, R.; Sisti, M.; Palmisano, G.; Botta, M.; Lowe, M.; Parker, D. Ternary Gd (III) L-HSA adducts: Evidence for the replacement of inner-sphere water molecules by coordinating groups of the protein. Implications for the design of contrast agents for MRI. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 5, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput. -Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascolo, L.; Petrovic, S.; Cupelli, F.; Bruschi, C.V.; Anelli, P.L.; Lorusso, V.; Visigalli, M.; Uggeri, F.; Tiribelli, C. Abc protein transport of MRI contrast agents in canalicular rat liver plasma vesicles and yeast vacuoles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 282, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, M.; Neuhoff, S.; Carlson, G.; Warhurst, G.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Absolute abundance and function of intestinal drug transporters: A prerequisite for fully mechanistic in vitro–in vivo extrapolation of oral drug absorption. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2013, 34, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, M.; Keiser, M.; Oswald, S.; Kühn, J.; Jia, J.; Grube, M.; Kroemer, H.K.; Siegmund, W.; Weitschies, W. Hepatic uptake of the magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA: Role of human organic anion transporters. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; Secky, L.; Wlcek, K.; Svoboda, M.; Kounnis, V.; Briasoulis, E.; Tzakos, A.G.; Jaeger, W.; Thalhammer, T. Tumor-specific expression of organic anion-transporting polypeptides: Transporters as novel targets for cancer therapy. J. Drug Deliv. 2013, 2013, 863539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idee, J.M.; Fretellier, N.; Robic, C.; Corot, C. The role of gadolinium chelates in the mechanism of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: A critical update. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 895–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, A.R.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.; Lee, G.H.; Kang, H.J.; Jung, J.C.; Park, J.S.; Ryeom, H.K.; Kim, T.J.; Chang, Y. Gadolinium Complex of 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-trisacetic Acid (DO3A)-Ethoxybenzyl (EOB) Conjugate as a New Macrocyclic Hepatobiliary MRI Contrast Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4861–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, A.R.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, S.; Yang, J.-u.; Kang, M.-K.; Lee, J.J.; Sung, B.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Cho, A.E. Effect of Structural Fine-Tuning on Chelate Stability and Liver Uptake of Anionic MRI Contrast Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 6313–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Marchal, G.; Yu, J.; Muhler, A.; Lukito, G.; Baert, A.L. Prolonged positive contrast enhancement with Gd-EOB-DTPA in experimental liver tumors: Potential value in tissue characterization. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1994, 4, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboyama, T.; Onishi, H.; Kim, T.; Akita, H.; Hori, M.; Tatsumi, M.; Nakamoto, A.; Nagano, H.; Matsuura, N.; Wakasa, K. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Hepatocyte-selective enhancement at gadoxetic acid–enhanced MR imaging—Correlation with expression of sinusoidal and canalicular transporters and bile accumulation. Radiology 2010, 255, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Marchal, G. Enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for tissue characterization of liver abnormalities with hepatobiliary contrast agents: An overview of preclinical animal experiments. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging TMRI 1998, 9, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Compounds | OATP1B1 | OATP1B3 | MRP2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-NOTA-NP | −9.281 | −5.532 | −4.579 |
| Gd-DTPA-EOB c | −13.25 | −11.54 | −3.976 |
| Mn-EDTA-BTA | −7.392 | −10.172 | −5.731 |
| Mn-EDTA-EOB c | −9.36 | −11.58 | −5.149 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.K.; Baek, A.-R.; Yang, B.-W.; Kim, S.; Hwang, D.W.; Nam, S.-W.; Lee, G.-H.; Chang, Y. Manganese (II) Complex of 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane-1,4,7-Triacetic Acid (NOTA) as a Hepatobiliary MRI Contrast Agent. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040602
Islam MK, Baek A-R, Yang B-W, Kim S, Hwang DW, Nam S-W, Lee G-H, Chang Y. Manganese (II) Complex of 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane-1,4,7-Triacetic Acid (NOTA) as a Hepatobiliary MRI Contrast Agent. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040602
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md. Kamrul, Ah-Rum Baek, Byeong-Woo Yang, Soyeon Kim, Dong Wook Hwang, Sung-Wook Nam, Gang-Ho Lee, and Yongmin Chang. 2023. "Manganese (II) Complex of 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane-1,4,7-Triacetic Acid (NOTA) as a Hepatobiliary MRI Contrast Agent" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040602
APA StyleIslam, M. K., Baek, A.-R., Yang, B.-W., Kim, S., Hwang, D. W., Nam, S.-W., Lee, G.-H., & Chang, Y. (2023). Manganese (II) Complex of 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane-1,4,7-Triacetic Acid (NOTA) as a Hepatobiliary MRI Contrast Agent. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040602