PET Imaging in Bladder Cancer: An Update and Future Direction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. [18F]FDG PET/CT
2.1. Initial Staging and Relapse
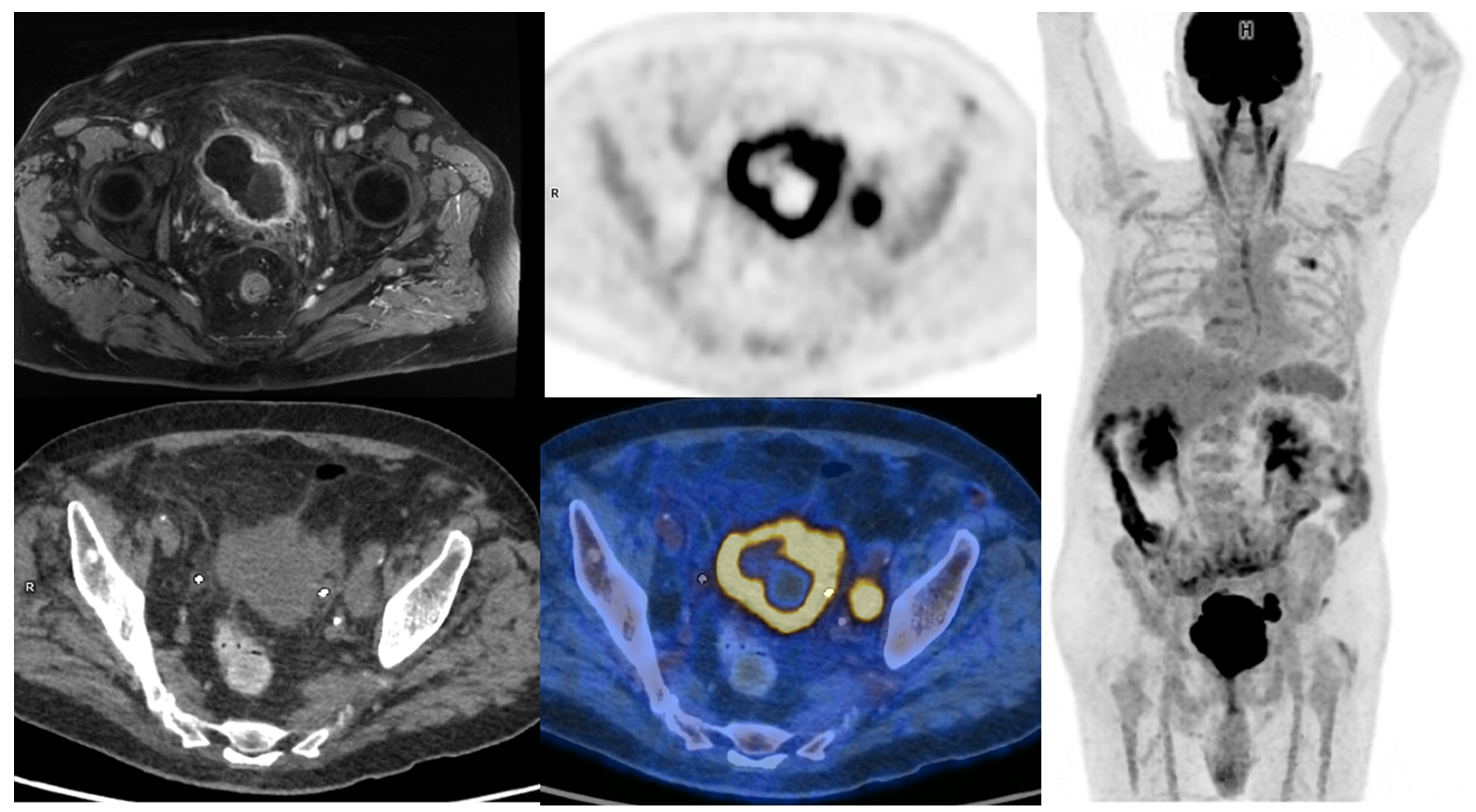
2.1.1. Primary Tumor Evaluation
2.1.2. Regional Nodal Staging
2.1.3. Distant Metastatic Staging
2.2. Follow-Up
2.2.1. Neoadjuvant and Induction Chemotherapy
2.2.2. Chemotherapy in a Metastatic Setting
2.2.3. Detecting and Restaging Relapse
3. Future Directions
3.1. Treatment Guided by [18F]FDG-PET/CT
3.2. PET/MRI
3.3. PET Tracers beyond [18F]FDG
3.3.1. Limits of Metabolic Radiotracers
3.3.2. FAPI-PET
3.3.3. ICI Tracers and Targeted Therapies
3.4. Artificial Intelligence
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| ANN | artificial neural networks |
| AUA | American Urological Association |
| BC | bladder cancer |
| CT | computed tomography |
| EAU | European Association of Urology |
| ESMO | European Society of Medical Oncology |
| ePLND | extended pelvic lymph node dissection |
| FAP | fibroblast activation protein |
| FAPI | fibroblast activation protein inhibitor |
| [18F]FDG | 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose |
| MIBC | muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| NMIBC | non-muscle invasive bladder cancer |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-ligand 1 |
| RC | radical cystectomy |
| TURBT | bransurethral resection of the bladder tumor |
| UC | urothelial carcinomas |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Babjuk, M.; Bellmunt, J.; Bruins, H.M.; De Reijke, T.M.; De Santis, M.; Gillessen, S.; James, N.; Maclennan, S.; Palou, J.; et al. EAU-ESMO consensus statements on the management of advanced and variant bladder cancer-an international collaborative multistakeholder effort: Under the auspices of the eau-esmo guidelines committees. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, D.S.; Shipley, W.U.; Feldman, A.S. Bladder cancer. Lancet 2009, 374, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumberbatch, M.G.K.; Jubber, I.; Black, P.C.; Esperto, F.; Figueroa, J.D.; Kamat, A.M.; Kiemeney, L.; Lotan, Y.; Pang, K.; Silverman, D.T.; et al. Epidemiology of bladder cancer: A systematic review and contemporary update of risk factors in 2018. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magers, M.J.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Montironi, R.; Williamson, S.R.; Kaimakliotis, H.Z.; Cheng, L. Staging of bladder cancer. Histopathology 2019, 74, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Bellmunt, J.; Comperat, E.; De Santis, M.; Huddart, R.; Loriot, Y.; Necchi, A.; Valderrama, B.; Ravaud, A.; Shariat, S.; et al. Bladder cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: Update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. Eur. Urol. 2005, 48, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumberbatch, M.G.; Foerster, B.; Catto, J.W.; Kamat, A.M.; Kassouf, W.; Jubber, I.; Shariat, S.F.; Sylvester, R.J.; Gontero, P. Repeat transurethral resection in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, V.; Narumi, Y.; Altun, E.; Bochner, B.H.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Hafeez, S.; Huddart, R.; Kennish, S.; Lerner, S.; Montironi, R.; et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for bladder cancer: Development of VI-RADS (vesical imaging-reporting and data system). Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiang, P.; Lu, Y. Is Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography useful for detecting bladder lesions? A meta-analysis of the literature. Urol. Int. 2013, 92, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, A.; Komori, T.; Juri, H.; Inada, Y.; Azuma, H.; Narumi, Y. Detectability of residual invasive bladder cancer in delayed 18F-FDG PET imaging with oral hydration using 500 mL of water and voiding-refilling. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, B.; Dogra, P.N.; Naswa, N.; Kumar, R. Diuretic 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for detection and locoregional staging of urinary bladder cancer: Prospective evaluation of a novel technique. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 40, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.J.; Yoo, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, B.S. Enhanced Application of 18F-FDG PET/ CT in bladder cancer by adding early dynamic acquisition to a standard delayed PET Protocol. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, H.W.; Bochner, B.H.; Dalbagni, G.; Donat, S.M.; Reuter, V.E.; Bajorin, D.F. Impact of the number of lymph nodes retrieved on outcome in patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, J.P.; Lieskovsky, G.; Cote, R.; Groshen, S.; Feng, A.-C.; Boyd, S.; Skinner, E.; Bochner, B.; Thangathurai, D.; Mikhail, M.; et al. Radical Cystectomy in the Treatment of Invasive Bladder Cancer: Long-Term Results in 1054 Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacVicar, A.D. Bladder cancer staging. BJU Int. 2000, 86, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einerhand, S.M.H.; van Gennep, E.J.; Mertens, L.S.; Hendriksen, K.; Donswijk, M.L.; van der Poel, H.G.; van Rijhn, B.W. 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyD-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2020, 30, 654–664. [Google Scholar]
- Lodde, M.; Lacombe, L.; Friede, J.; Morin, F.; Saourine, A.; Fradet, Y. Evaluation of fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography with computed tomography for staging of urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int. 2010, 106, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.G.; Hong, S.; You, D.; Hong, J.H.; Ahn, H.; Kim, C.S. FDG PET-CT for lymph node staging of bladder cancer: A prospective study of patients with extended pelvic lymphadenectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.K.; Koo, P.J.; Kim, S.-J. Diagnostic Accuracy of F-18 FDG PET/CT for Preoperative Lymph Node Staging in Newly Diagnosed Bladder Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncology 2018, 95, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubra, A.; Hayward, D.; Dahm, P.; Goldfarb, R.; Froehlich, J.; Jha, G.; Konety, B.R. The diagnostic accuracy of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography in staging bladder cancer: A single-institution study and a systematic review with meta-analysis. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, A.; Rouanne, M.; Taconet, S.; Radulescu, C.; Neuzillet, Y.; Girma, A.; Beaufrere, A.; Lebret, T.; Le Stanc, E.; Grellier, J.-F. Integrated analysis of 18F-FDG PET/CT improves preoperative lymph node staging for patients with invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4286–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dason, S.; Cha, E.K.; Falavolti, C.; Vertosick, E.A.; Dean, L.W.; McPherson, V.A.; Sjoberg, D.D.; Benfante, N.E.; Donahue, T.F.; Dalbagni, G.; et al. Late Recurrences Following Radical Cystectomy Have Distinct Prognostic and Management Considerations. J. Urol. 2020, 204, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinagare, A.B.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Jagannathan, J.P.; Fennessy, F.M.; Taplin, M.-E.; Abbeele, A.D.V.D. Metastatic Pattern of Bladder Cancer: Correlation With the Characteristics of the Primary Tumor. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, H. Detecting metastatic bladder cancer using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/computed tomography. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolo, A.B.; Riches, J.; Schöder, H.; Akin, O.; Trout, A.; Milowsky, M.I.; Bajorin, D.F. Clinical Value of Fluorine-18 2-Fluoro-2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Bladder Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3973–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Pan, L.; Hu, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Ye, D.; Zhang, Y. Is whole-body fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT plus additional pelvic images (oral hydration– voiding–refilling) useful for detecting recurrent bladder cancer? Ann. Nucl. Med. 2012, 26, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, H.; Viney, Z.; Hughes, P.; Rankin, S.; Rottenberg, G.; Hughes, S.; Evison, F.; Dasgupta, P.; O’Brien, T.; Khan, M.S. Role of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET)- computed tomography (CT) in the staging of bladder cancer: FDG pet in the staging of bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2014, 114, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K. Role of PET/CT in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 2908–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouanne, M.; Alhammadi, A.; Vilain, D.; Radulescu, C.; Lebret, T. Value of positron emission tomography in diagnosing synchronous penile metastasis from urothelial bladder cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, L.S.; Fioole-Bruining, A.; Vegt, E.; Vogel, W.V.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Horenblas, S. Impact of18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-positron-emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) on management of patients with carcinoma invading bladder muscle. BJU Int. 2013, 112, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibel, A.S.; Dehdashti, F.; Katz, M.D.; Klim, A.P.; Grubb, R.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Siegel, C.; Cao, D.; Gao, F.; Siegel, B.A. Prospective Study of [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography for Staging of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4314–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voskuilen, C.S.; van Gennep, E.J.; Einerhand, S.M.; Vegt, E.; Donswijk, M.L.; Bruining, A.; van der Poel, H.G.; Horenblas, S.; Hendricksen, K.; van Rhijn, B.W.; et al. Staging 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Changes Treatment Recommendation in Invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 5, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghote, F.; Poppe, L.; Verbeke, S.; Dirix, P.; Albersen, M.; De Meerleer, G.; Berghen, C.; Ost, P.; Villeirs, G.; De Visschere, P.; et al. Evaluating the impact of 18F-FDG-PET-CT on risk stratification and treatment adaptation for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (EFFORT-MIBC): A phase II prospective trial. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaig, T.W.; Spiess, P.E.; Agarwal, N.; Bangs, R.; Boorjian, S.A. Bladder Cancer, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.S.; Bochner, B.H.; Chou, R.; Dreicer, R.; Kamat, A.M.; Lerner, S.P.; Lotan, Y.; Meeks, J.J.; Michalski, J.M.; Morgan, T.M.; et al. Treatment of Non-Metastatic Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO Guideline. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, J.J.; Bellmunt, J.; Bochner, B.H.; Clarke, N.W.; Daneshmand, S.; Galsky, M.D.; Hahn, N.M.; Lerner, S.P.; Mason, M.; Powles, T.; et al. A systematic review of neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, T.J.; van de Putte, E.E.F.; Horenblas, S.; Meijer, R.P.; Boormans, J.L.; Aben, K.K.; van der Heijden, M.S.; de Wit, R.; Beerepoot, L.V.; Verhoeven, R.H.; et al. Pathological downstaging and survival after induction chemotherapy and radical cystectomy for clinically node-positive bladder cancer-Results of a nationwide population-based study. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 69, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubra, A.; Gencturk, M.; Froelich, J.; Balaji, P.; Gupta, S.; Jha, G.; Konety, B.R. FDG-PET/CT for Assessing the Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Bladder Cancer Patients. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2018, 16, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Putte, E.F.; Vegt, E.; Mertens, L.S.; Bruining, A.; Hendricksen, K.; Van Der Heijden, M.S.; Horenblas, S.; Van Rhijn, B.W.G. FDG-PET/CT for response evaluation of invasive bladder cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollberg, P.; Almquist, H.; Bläckberg, M.; Cwikiel, M.; Gudjonsson, S.; Lyttkens, K.; Patschan, O.; Liedberg, F. [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography response evaluation can predict histological response at surgery after induction chemotherapy for oligometastatic bladder cancer. Scand. J. Urol. 2017, 51, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, J.; Kollberg, P.; Almquist, H.; Bläckberg, M.; Brändstedt, J.; Lyttkens, K.; Simoulis, A.; Sjödahl, G.; Sörenby, A.; Trägårdh, E.; et al. Complete metabolic response with [ 18 F]fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography predicts survival following induction chemotherapy and radical cystectomy in clinically lymph node positive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2021, 129, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandino, L.; Capozza, A.; Bandini, M.; Raggi, D.; Farè, E.; Pederzoli, F.; Gallina, A.; Capitanio, U.; Bianchi, M.; Gandaglia, G.; et al. [18F]Fluoro-Deoxy-Glucose positron emission tomography to evaluate lymph node involvement in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer receiving neoadjuvant pembrolizumab. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2021, 39, 235.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H. Comparing RECIST with EORTC criteria in metastatic bladder cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannatempo, P.; Alessi, A.; Miceli, R.; Raggi, D.; Farè, E.; Nicolai, N.; Serafini, G.; Padovano, B.; Piva, L.; Biasoni, D.; et al. Interim Fluorine-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography for Early Metabolic Assessment of Therapeutic Response to Chemotherapy for Metastatic Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2014, 12, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, A.; Campi, R.; Tellini, R.; Gandaglia, G.; Albisinni, S.; Abufaraj, M.; Hatzichristodoulou, G.; Montorsi, F.; Van Velthoven, R.; Carini, M.; et al. Patterns and predictors of recurrence after open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: A comprehensive review of the literature. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, P.; Caobelli, F.; Gentile, R.; Stefano, A.; Russo, G.; Albano, D.; Baldari, S.; Gilardi, M.C.; Midiri, M. Recurrent bladder carcinoma: Clinical and prognostic role of 18 F-FDG PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 44, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, H.; Karapolat, İ. Efficacy of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography in restaging muscle-invasive bladder cancer following radical cystectomy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zattoni, F.; Incerti, E.; Moro, F.D.; Moschini, M.; Castellucci, P.; Panareo, S.; Picchio, M.; Fallanca, F.; Briganti, A.; Gallina, A.; et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT and Urothelial Carcinoma: Impact on Management and Prognosis—A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zattoni, F.; Incerti, E.; Colicchia, M.; Castellucci, P.; Panareo, S.; Picchio, M.; Fallanca, F.; Briganti, A.; Moschini, M.; Gallina, A.; et al. Comparison between the diagnostic accuracies of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography and conventional imaging in recurrent urothelial carcinomas: A retrospective, multicenter study. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Liu, L.; Du, G.; Fu, Z. Diagnostic Evaluation of 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging in Recurrent or Residual Urinary Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Urol. J. 2020, 17, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04724928 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Mansi, L.; Ciarmiello, A.; Cuccurullo, V. PET/MRI and the revolution of the third eye. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 39, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, O.A.; Rosen, B.R.; Sahani, D.V.; Hahn, P.F.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Vangel, M.G.; Nicolai, E.; Soricelli, A.; Salvatore, M. Clinical Impact of PET/MR Imaging in Patients with Cancer Undergoing Same-Day PET/CT: Initial Experience in 134 Patients—A Hypothesis-generating Exploratory Study. Radiology 2013, 269, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.C.; Sung, D.J. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in tumor staging and follow-up for bladder cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 2890–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Friedman, K.P.; Ponzo, F.; Raad, R.A.; Jackson, K.; Huang, W.C.; Balar, A.V. Prospective Pilot Study to Evaluate the Incremental Value of PET Information in Patients With Bladder Cancer Undergoing 18F-FDG Simultaneous PET/MRI. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, e8–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulitt, P.J.; Altun, E.; Sheikh, A.; Wong, T.Z.; Woods, M.E.; Rose, T.L.; Wallen, E.M.; Pruthi, R.S.; Smith, A.B.; Nielsen, M.E.; et al. Pilot Study of [18F] Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography (FDG-PET)/Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for Staging of Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC). Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, 378–386.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Jambor, I.; Merisaari, H.; Ettala, O.; Virtanen, J.; Koskinen, I.; Veskimae, E.; Sairanen, J.; Taimen, P.; Kemppainen, J.; et al. 11C-acetate PET/MRI in bladder cancer staging and treatment response evaluation to neoadjuvant chemo-therapy: A prospective multicenter study (ACEBIB trial). Cancer Imaging 2018, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Suh, C.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H. The Diagnostic Performance of MRI for Detection of Lymph Node Metastasis in Bladder and Prostate Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Diagnostic Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, W95–W109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Okudaira, H.; Ono, M.; Schuster, D.M.; Goodman, M.M.; Kawai, K.; Shirakami, Y. Differences in Transport Mechanisms of trans-1-Amino-3-[18F]Fluorocyclobutanecarboxylic Acid in Inflammation, Prostate Cancer, and Glioma Cells: Comparison with l-[Methyl-11C]Methionine and 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]Fluoro-d-Glucose. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2014, 16, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Koo, P.J.; Pak, K.; Kim, I.-J.; Kim, K. Diagnostic accuracy of C-11 choline and C-11 acetate for lymph node staging in patients with bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, T.; Seidl, C.; Schiemann, M.; Senekowitsch-Schmidtke, R.; Krause, B.J. Increased choline uptake in macrophages and prostate cancer cells does not allow for differentiation between benign and malignant prostate pathologies. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2016, 43, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, Y.; Sato, T.; Hozumi, C.; Han, Q.; Aoki, Y.; Masaki, N.; Obara, K.; Tsunoda, T.; Hoffman, R.M. Superiority of [11C]methionine over [18F]deoxyglucose for PET Imaging of Multiple Cancer Types Due to the Methionine Addiction of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterrainer, L.M.; Lindner, S.; Eismann, L.; Casuscelli, J.; Gildehaus, F.-J.; Bui, V.N.; Albert, N.L.; Holzgreve, A.; Beyer, L.; Todica, A.; et al. Feasibility of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46 PET/CT for detection of nodal and hematogenous spread in high-grade urothelial carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 49, 3571–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novruzov, E.; Dendl, K.; Ndlovu, H.; Choyke, P.L.; Dabir, M.; Beu, M.; Mehdi, E.; Guliyev, F.; Koerber, S.A.; Lawal, I.; et al. Head-to-head Intra-individual Comparison of [68Ga]-FAPI and [18F]-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Bladder Cancer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeijer, A.-L.N.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Huisman, M.C.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Boellaard, R.; Veen, B.J.D.W.-V.D.; Bahce, I.; Vugts, D.J.; van Dongen, G.A.; Thunnissen, E.; et al. Study of 89Zr-Pembrolizumab PET/CT in Patients With Advanced-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, E.; Fujita, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Adomi, S.; Kawashima, A.; Minami, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Uemura, H.; Nonomura, N. Comparison of molecular profiles of upper tract urothelial carcinoma vs. urinary bladder cancer in the era of targeted therapy: A narrative review. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2022, 11, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltas, B.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Govindan, S.V.; Wilhelm, F.; Sharkey, R.M.; Hajdenberg, J.; Hodes, G.; Nanus, D.M.; Tagawa, S.T. Sacituzumab Govitecan, a Novel Antibody–Drug Conjugate, in Patients With Metastatic Platinum-Resistant Urothelial Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2016, 14, e75–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.T.; Mandleywala, K.; Viray, T.; Tan, K.V.; Lewis, J.S.; Pereira, P.M.R. EGFR-Targeted ImmunoPET of UMUC3 Orthotopic Bladder Tumors. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Fujita, K.; Tomiyama, E.; Fujimoto, S.; Adomi, S.; Banno, E.; Minami, T.; Takao, T.; Nozawa, M.; Fushimi, H.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis of HER2, EGFR, and Nectin-4 Expression in Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2023, 43, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.L.; Hosny, A.; Schabath, M.B.; Giger, M.L.; Birkbak, N.J.; Mehrtash, A.; Allison, T.; Arnaout, O.; Abbosh, C.; Dunn, I.F.; et al. Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: Clinical challenges and applications. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadaghiani, M.S.; Rowe, S.P.; Sheikhbahaei, S. Applications of artificial intelligence in oncologic 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging: A systematic review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, A.F.; Kors, J.A.; Rijnbeek, P.R. The role of explainability in creating trustworthy artificial intelligence for health care: A comprehensive survey of the terminology, design choices, and evaluation strategies. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 113, 103655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Materka, A.; Langs, G.; Häggström, I.; Szczypiński, P.; Gibbs, P.; Cook, G. Introduction to Radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, A.; Dercle, L.; Vila-Reyes, H.; Schwartz, L.H.; Girma, A.; Bertaux, M.; Radulescu, C.; Lebret, T.; Delcroix, O.; Rouanne, M. A machine-learning-based combination of criteria to detect bladder cancer lymph node metastasis on [18F]FDG PET/CT: A pathology-controlled study. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 33, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Du, P.; Li, S.; Tian, Q.; Ling, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Elaboration of a multisequence MRI-based radiomics signature for the preoperative prediction of the muscle-invasive status of bladder cancer: A double-center study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4816–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L.; Mao, L.; Li, X.; Jin, Z.; Sun, H. CT-based radiomics to predict the pathological grade of bladder cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6749–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shi, S.; Huang, M.; Yu, H.; Dong, W.; Huang, J.; Lin, T. Development and Validation of an MRI-Based Radiomics Signature for the Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Bladder Cancer. Ebiomedicine 2018, 34, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.H.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Cohan, R.H.; Chan, H.-P.; Caoili, E.M.; Davenport, M.S.; Samala, R.K.; Weizer, A.Z.; Alva, A.; Kirova-Nedyalkova, G.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of CT for Prediction of Bladder Cancer Treatment Response with and without Computerized Decision Support. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaish, H.; Mutasa, S.; Makkar, J.; Chang, P.; Schwartz, L.; Ahmed, F. Prediction of Lymph Node Maximum Standardized Uptake Value in Patients With Cancer Using a 3D Convolutional Neural Network: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysouw, M.C.; Jansen, B.H.; van de Brug, T.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Pfaehler, E.; de Vries, B.M.; van Moorselaar, R.J.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Vis, A.N.; Boellaard, R.; et al. Machine learning-based analysis of [18F]DCFPyL PET radiomics for risk stratification in primary prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentinuzzi, D.; Vrankar, M.; Boc, N.; Ahac, V.; Zupancic, Z.; Unk, M.; Skalic, K.; Zagar, I.; Studen, A.; Simoncic, U.; et al. [18F]FDG PET immunotherapy radiomics signature (iRADIOMICS) predicts response of non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with pembrolizumab. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, P.; Yang, G.; Wang, N.; Yan, L.; Miao, W.; Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gong, A.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. Additional value of metabolic parameters to PET/CT-based radiomics nomogram in predicting lymphovascular invasion and outcome in lung. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang-Yin, J.; Girard, A.; Marchal, E.; Lebret, T.; Homo Seban, M.; Uhl, M.; Bertaux, M. PET Imaging in Bladder Cancer: An Update and Future Direction. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040606
Zhang-Yin J, Girard A, Marchal E, Lebret T, Homo Seban M, Uhl M, Bertaux M. PET Imaging in Bladder Cancer: An Update and Future Direction. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040606
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang-Yin, Jules, Antoine Girard, Etienne Marchal, Thierry Lebret, Marie Homo Seban, Marine Uhl, and Marc Bertaux. 2023. "PET Imaging in Bladder Cancer: An Update and Future Direction" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040606
APA StyleZhang-Yin, J., Girard, A., Marchal, E., Lebret, T., Homo Seban, M., Uhl, M., & Bertaux, M. (2023). PET Imaging in Bladder Cancer: An Update and Future Direction. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040606






