Hybrid Dissolving Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Ibuprofen: Solubilization, Fabrication, and Characterization
Abstract
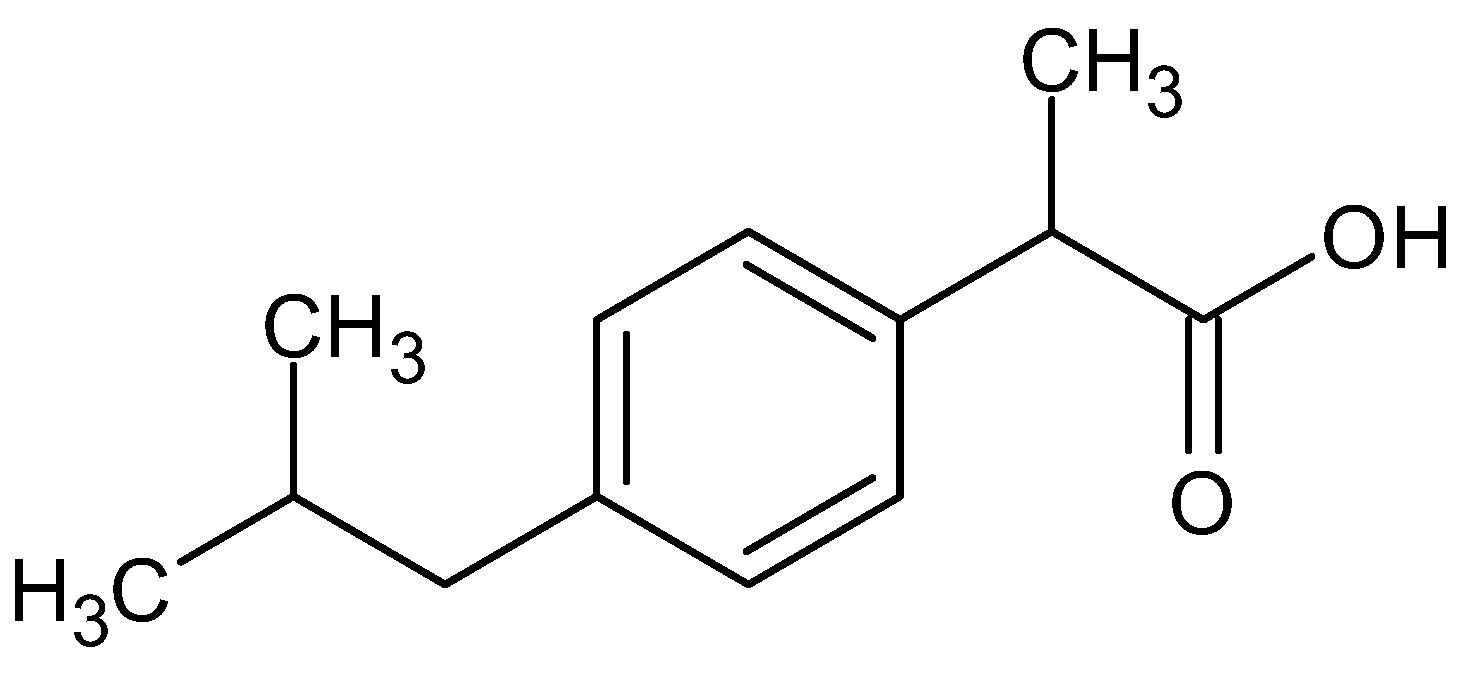
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2. Thermal Analysis (DSC/TGA)
2.3. Solubilization of Ibuprofen
2.4. Fabrication of Drug-Loaded Microneedles
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Mechanical Strength/Breaking Strength
2.7. Insertion Studies
2.8. Drug Content
2.9. In Vitro Drug Release Profile
2.10. In Vivo Release Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Analytical Instruments
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Preformulation Studies
FTIR
Thermal Analysis (DSC/TGA)
3.2.2. Solubilization of Ibuprofen
3.2.3. Preparation of Casting Material (Drug-Polymer Blend)
3.2.4. Fabrication of Drug-Loaded Microneedles
3.3. Characterization of Ibuprofen Microneedles
3.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3.2. Mechanical Strength/Breaking Strength
3.3.3. Insertion Test
3.3.4. Drug Content
3.3.5. In Vitro Drug Release Profile
3.3.6. In Vivo Release Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, A.; Prabhu, P.; Kamath, J. Nano Structured lipid carriers: A Novel Topical drug delivery system. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2012, 4, 705–714. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, J.D.; Meinardi, M.M. The 500 Dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs. Exp. Dermatol. 2000, 9, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, B.W. Novel mechanisms and devices to enable successful transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldvari, M. Non-invasive administration of drugs through the skin: Challenges in delivery system design. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, M.J.; Migalska, K.; Mahmood, T.M.T.; Singh, T.R.R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle arrays as medical devices for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2011, 8, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gera, A.K.; Burra, R.K. The Rise of Polymeric Microneedles: Recent Developments, Advances, Challenges, and Applications with Regard to Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, J.N.; Guo, X.D. In Vitro and in vivo assessment of polymer microneedles for controlled transdermal drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.L.; Ren, J.W.; Chen, B.Z.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C.Y.; Guo, X.D. Effect of humidity on mechanical properties of dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkenne, C.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Hadgraft, J.; Guy, R.H. Ibuprofen transport into and through skin from topical formulations: In vitro–in vivo comparison. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, T.J.; Laurent, A.L.; Leyva, R.; Kellstein, D. Ibuprofen sodium is absorbed faster than standard ibuprofen tablets: Results of two open-label, randomized, crossover pharmacokinetic studies. Drugs R&d 2014, 14, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Shin, W.S.; Kim, H.T. Effects of pH, dissolved organic matter, and salinity on ibuprofen sorption on sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22882–22889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Aller, M.; Guillarme, D.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Gurny, R. Strategies for formulating and delivering poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 30, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Mittal, A.; Chauhan, N.; Alam, S. Role of surfactants as penetration enhancer in transdermal drug delivery system. J. Mol. Pharm. Org. Process Res. 2014, 2, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrudden, M.T.; Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, C.M.; McAlister, E.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and physicochemical characterisation of novel dissolving polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal delivery of high dose, low molecular weight drugs. J. Control. Release 2014, 180, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjani, Q.K.; Sabri, A.H.B.; Utomo, E.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Donnelly, R.F. Elucidating the impact of surfactants on the performance of dissolving microneedle array patches. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 1191–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, N.; Yuan, W.; Jin, T. A scalable fabrication process of polymer microneedles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 12, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Luo, G.; Xing, M. Biomedical applications of polymeric microneedles for transdermal therapeutic delivery and diagnosis: Current status and future perspectives. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 1900140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Niu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, A.; Yang, H.; Xu, F.; Li, F. A hydrogel microneedle patch for point-of-care testing based on skin interstitial fluid. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.G.; Hwang, S.Y.; Na, Y.H. Fabrication of a PVA-Based Hydrogel Microneedle Patch. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25179–25185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradossi, G.; Cavalieri, F.; Chiessi, E.; Spagnoli, C.; Cowman, M.K. Poly(vinyl alcohol) as versatile biomaterial for potential biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatello, R.; Corsaro, R.; Bonaccorso, A.; Zingale, E.; Carbone, C.; Musumeci, T. Soluplus® polymeric nanomicelles improve solubility of BCS-class II drugs. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1991–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Smith, G.; Khan, K.A.; Bukhari, N.I.; Pedge, N.I.; Ermolina, I. Solubility and dissolution rate enhancement of ibuprofen by co-milling with polymeric excipients. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.-Q.; Lai, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.-M.; Li, Z.-Q.; Qi, X.-R. On the inherent properties of Soluplus and its application in ibuprofen solid dispersions generated by microwave-quench cooling technology. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekko, I.A.; Chen, G.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Hamdan, I.M.; Vora, L.; Larrañeta, E.; McElnay, J.C.; McCarthy, H.O.; Rooney, M. Development and characterisation of novel poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)-based hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays for enhanced and sustained transdermal delivery of methotrexate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makvandi, P.; Kirkby, M.; Hutton, A.R.; Shabani, M.; Yiu, C.K.; Baghbantaraghdari, Z.; Jamaledin, R.; Carlotti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V. Engineering microneedle patches for improved penetration: Analysis, skin models and factors affecting needle insertion. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, A.J.; McAlister, E.; McCrudden, M.T.; Vora, L.; Steiner, L.; Levin, G.; Levy-Nissenbaum, E.; Shterman, N.; Kearney, M.-C.; McCarthy, H.O. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays as a therapeutic option for transdermal esketamine delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfante, G.; Lee, H.; Bao, L.; Park, J.; Takama, N.; Kim, B. Comparison of polymers to enhance mechanical properties of microneedles for bio-medical applications. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Moore, J.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; González-Vázquez, P.; Lutton, R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A proposed model membrane and test method for microneedle insertion studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Bozorg, B.D.; Kim, Y.; Wieber, A.; Birk, G.; Lubda, D.; Banga, A.K. Poly(vinyl alcohol) microneedles: Fabrication, characterization, and application for transdermal drug delivery of doxorubicin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 129, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, B.L.; Chen, B.Z.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Fei, W.M.; Cui, Y.; Guo, X.D. Dissolving microneedle rollers for rapid transdermal drug delivery. Drug. Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguzzi, C.; Cerezo, P.; Salcedo, I.; Sánchez, R.; Viseras, C. Mathematical models describing drug release from biopolymeric delivery systems. Mater. Technol. 2010, 25, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Kumar, P.; Thakkar, H.P. Lopinavir metered-dose transdermal spray through microporated skin: Permeation enhancement to achieve therapeutic needs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laracuente, M.-L.; Marina, H.Y.; McHugh, K.J. Zero-order drug delivery: State of the art and future prospects. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 834–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Stewart, S.; Fallows, S.J.; Birkhäuer, L.L.; McCrudden, M.T.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A facile system to evaluate in vitro drug release from dissolving microneedle arrays. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 497, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Model | R2 | K | n | Regression Equation (y=) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero order | 0.98 | 2.220 | -- | 2.2055x−2.2204 |
| First order | 0.572 | 0.280 | -- | 0.0606x−0.2803 |
| Hixson and Crowell | 0.98 | 102.2 | -- | −2.2055x + 102.22 |
| Higuchi | 0.95 | 22.5 | -- | 16.6x−22.5 |
| Korsemeyer and Peppas | 0.947 | -- | 1.885 | 1.8853x−0.82 |
| Parameter | Unit | Tablet | Cream | Ibu 25% MNs | Sig. (Post HOC Analysis) | Sig. (Post HOC Analysis) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | MN- Cream | MN-Tab | ||
| t1/2 | Hr | 2.48 ± 0.33 | 2.29 ± 0.16 | 5.2 ± 0.1 | * 0.009 | * 0.013 |
| Tmax | Hr | 2.66 ± 0.41 | 2.33 ± 0.41 | 24.0 ± 0.0 | * 0.000 | * 0.000 |
| Cmax | μg/ml | 32.66 ± 1.73 | 5.73 ± 0.24 | 28.7 ± 0.5 | * 0.000 | * 0.078 |
| AUC0-t | μg/mL·h | 157.84 ± 0.83 | 43.90 ± 2.44 | 831.9 ± 30.8 | * 0.000 | * 0.000 |
| AUC0–∞ | μg/mL·h | 167.05 ± 4.72 | 43.95 ± 2.45 | 841.0 ± 31.1 | * 0.000 | * 0.000 |
| AUMC0–∞ | μg/mL·h2 | 780.63 ± 90.88 | 259.23 ± 7.73 | 16,387.0 ± 463.3 | * 0.000 | * 0.000 |
| MRT0–∞ | H | 4.66 ± 0.42 | 5.91 ± 0.19 | 19.5 ± 0.3 | * 0.000 | * 0.000 |
| Cl/F | (mg)/(μg/mL)/h | 4.94 ± 0.14 | 18.85 ± 1.09 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | * 0.000 | * 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hidayatullah, T.; Nasir, F.; Khattak, M.A.; Pervez, S.; Almalki, W.H.; Alasmari, F.; Maryam, G.e.; Rahman, A.u.; Ali, A.T. Hybrid Dissolving Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Ibuprofen: Solubilization, Fabrication, and Characterization. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050677
Hidayatullah T, Nasir F, Khattak MA, Pervez S, Almalki WH, Alasmari F, Maryam Ge, Rahman Au, Ali AT. Hybrid Dissolving Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Ibuprofen: Solubilization, Fabrication, and Characterization. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(5):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050677
Chicago/Turabian StyleHidayatullah, Talaya, Fazli Nasir, Muzna Ali Khattak, Sadia Pervez, Waleed H. Almalki, Fawaz Alasmari, Gul e Maryam, Altaf ur Rahman, and Arbab Tahir Ali. 2023. "Hybrid Dissolving Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Ibuprofen: Solubilization, Fabrication, and Characterization" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 5: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050677
APA StyleHidayatullah, T., Nasir, F., Khattak, M. A., Pervez, S., Almalki, W. H., Alasmari, F., Maryam, G. e., Rahman, A. u., & Ali, A. T. (2023). Hybrid Dissolving Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Ibuprofen: Solubilization, Fabrication, and Characterization. Pharmaceuticals, 16(5), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050677








