Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there were mistakes in Figures 5 and 9 as published. In Figure 5C, the molecular weight of URAT1 protein was labeled incorrectly. The correct size of URAT1 protein in this experiment should be 46 KDa. In Figure 9, the dosage of hypoxanthine (Hypox) was incorrectly stated in the original publication. The dosage of Hypox should be 500 mg/kg. The corrected Figure 5 and Figure 9 appear below.
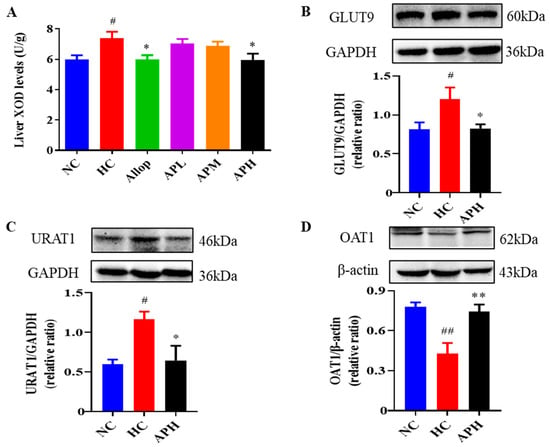
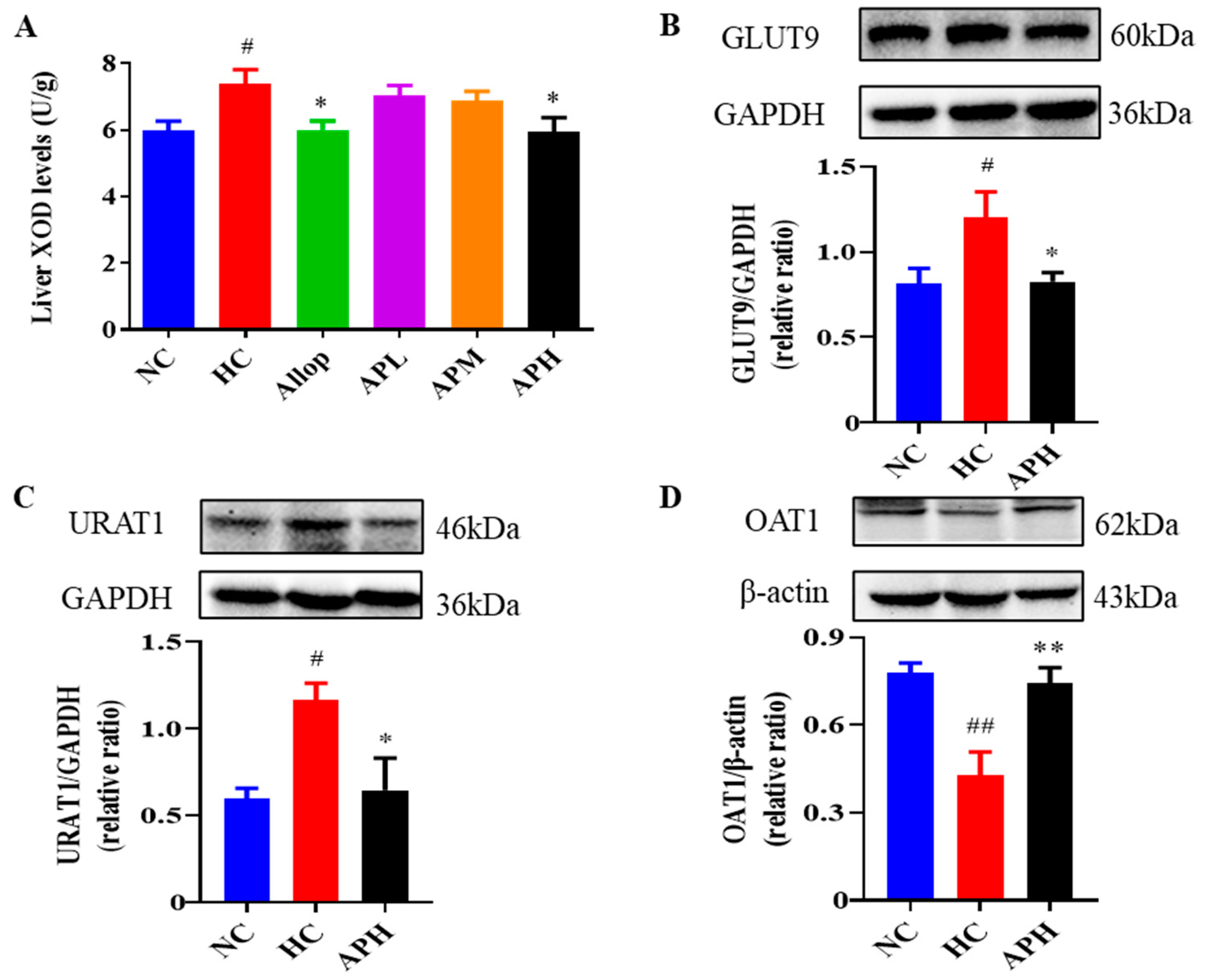
Figure 5.
Apigenin decreases liver XOD levels (A; U/g, n = 10) and renal expression levels of GLUT9 and URAT1, and increases renal expression levels of OAT1 in HUA mice. Representative images of western blot and their analyses show GLUT9 (B), URAT1 (C), and OAT1 (D) expressions in the kidneys (n ≥ 3). ## p < 0.01, # p < 0.05 vs. the NC group. ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05 vs. the HC group.
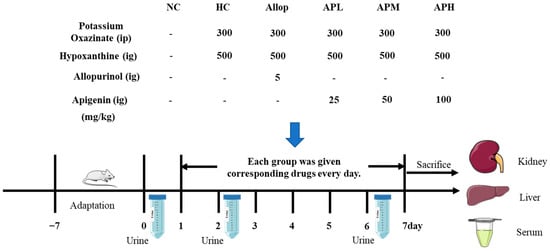
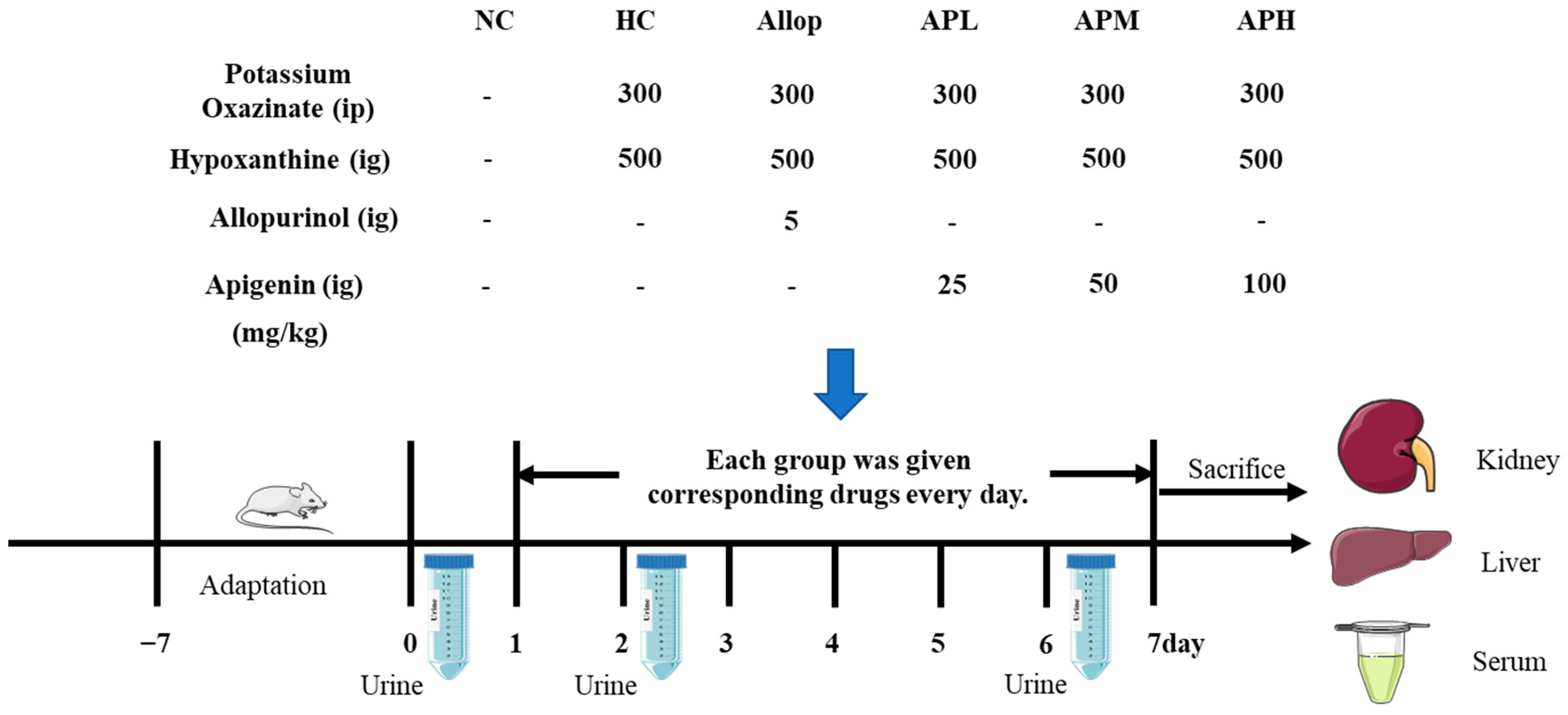
Figure 9.
Experimental design on action of apigenin on acute HUA mice. ig denotes intragastrical administration, ip denotes intraperitoneal administration.
Text Correction
There was an error in the original publication. The dosage of hypoxanthine (Hypox) was incorrectly stated in the original publication. The dosage of Hypox should be 500 mg/kg.
A correction has been made to Section 3. Discussion, Paragraph 8:
“In this study, Allop was demonstrated to decrease the levels of liver XOD and serum UA, and increase the levels of urine CRE (day 6) in this rapid HUA mouse model. However, Allop did not reverse the increased serum levels of CRE and BUN in HUA mice. By contrast, Chen et al. [64] reported that Allop was able to decrease serum levels of CRE and BUN in HUA mice. The underlying cause to explain the conflicting findings may be attributed to the differences in the approaches to establish HUA mouse model. In their study, the authors employed intraperitoneal injection with PO to establish the HUA mouse model. However, in the present study, Hypox (500 mg/kg, gavage) was used to induce HUA mice in addition to PO exposure.”
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Liu, T.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, M.; Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Xu, T.; Yin, J.; et al. Apigenin Ameliorates Hyperuricemia and Renal Injury through Regulation of Uric Acid Metabolism and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).