Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Indole-2-carboxamides as Potential Multi-Target Antiproliferative Agents
Abstract
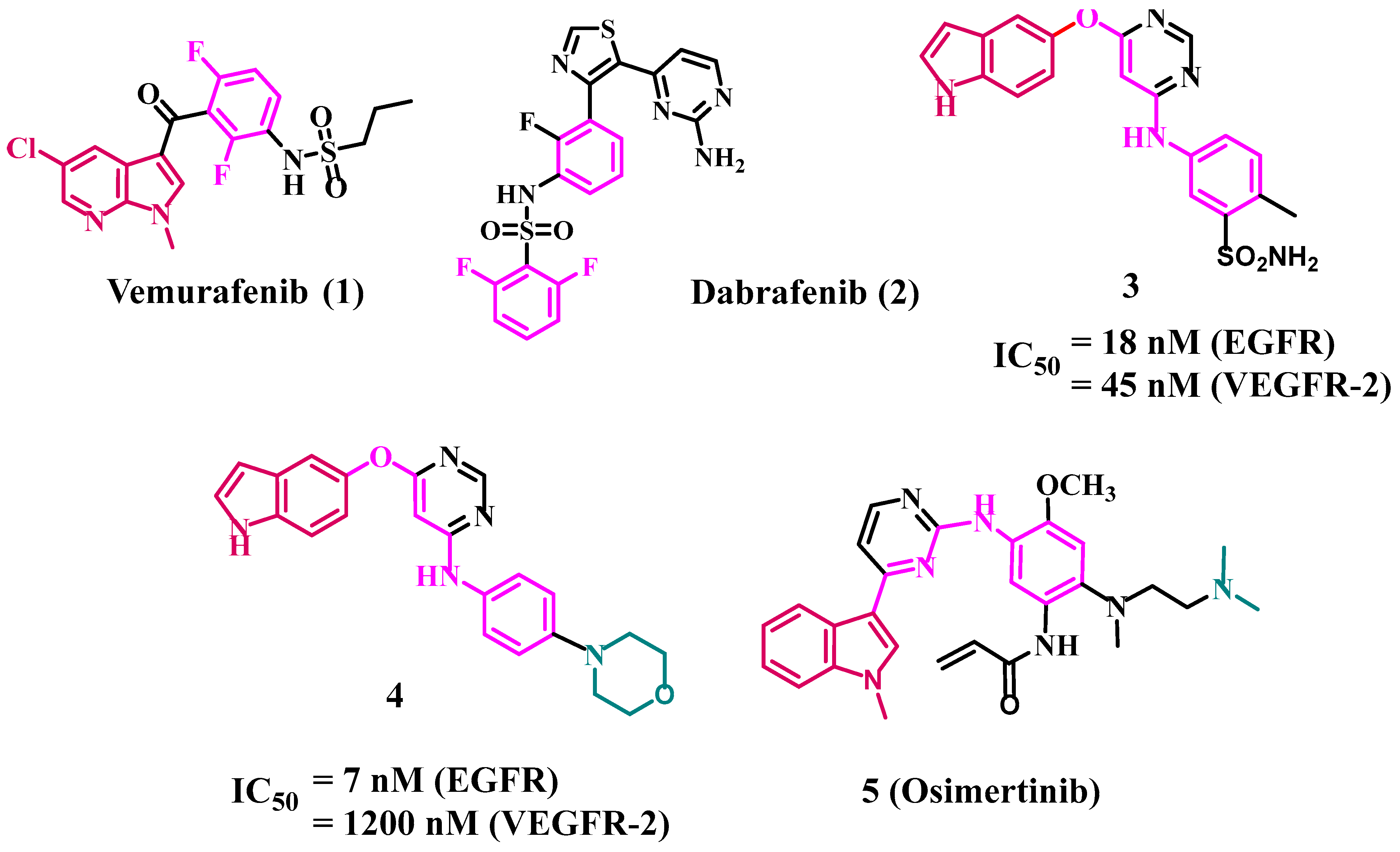
:1. Introduction
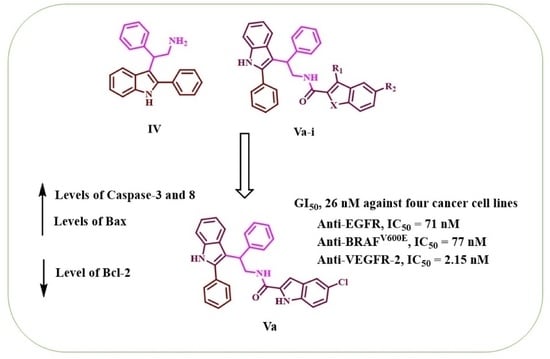
2. Results and Discussion
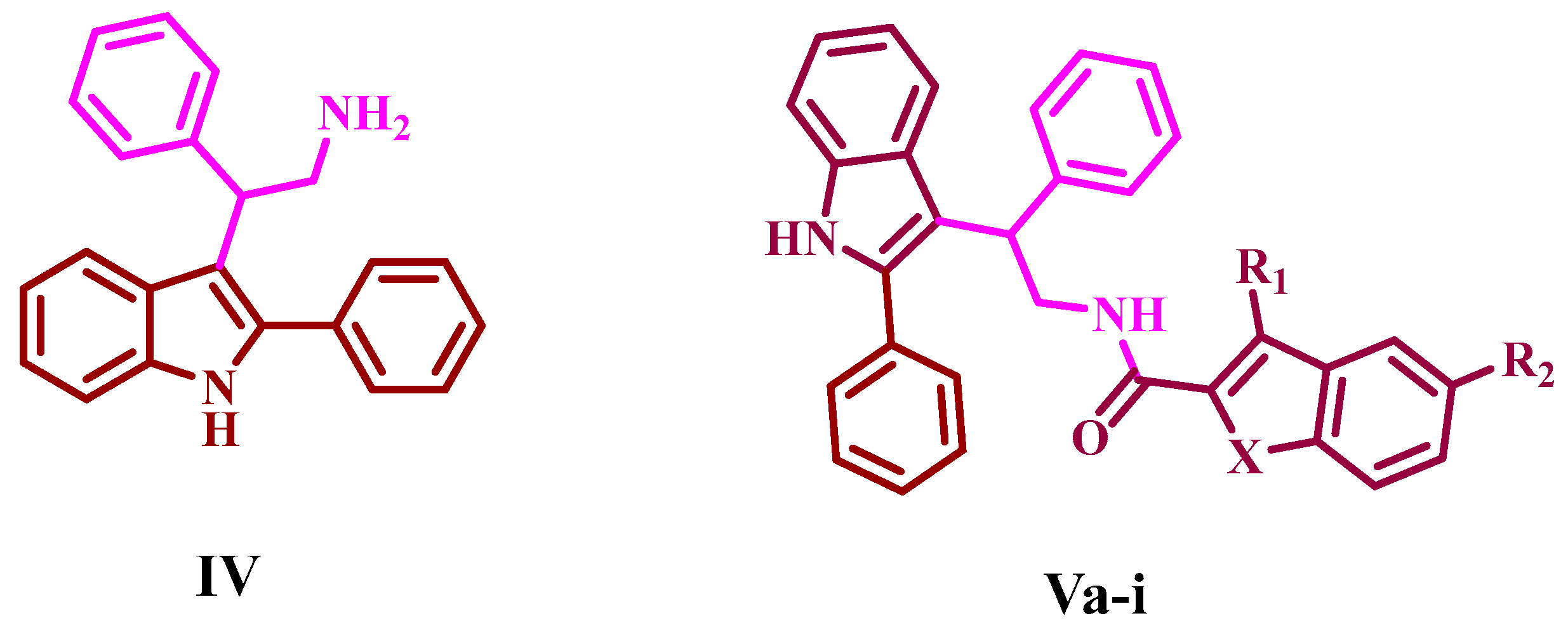
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biology
2.2.1. Assay for Cell Viability
2.2.2. Antiproliferative Assay
2.2.3. EGFR Inhibitory Assay
2.2.4. BRAFV600E Inhibitory Assay
2.2.5. VEGFR-2 Inhibitory Assay
2.3. Apoptotic Marker Assays
2.3.1. Caspase 3 Assay
2.3.2. Caspase-8, Bax, and Bcl-2 Level Assays
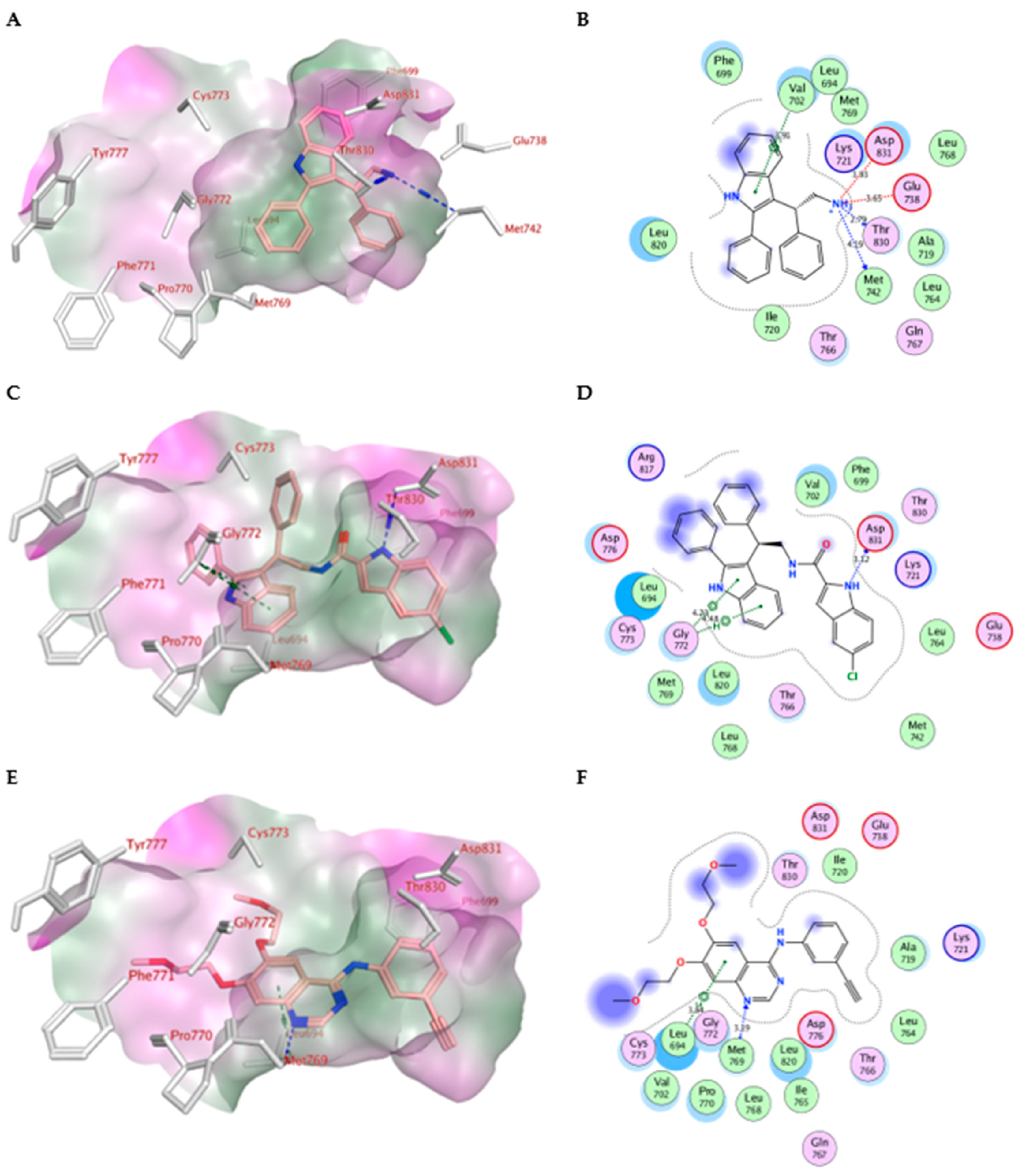
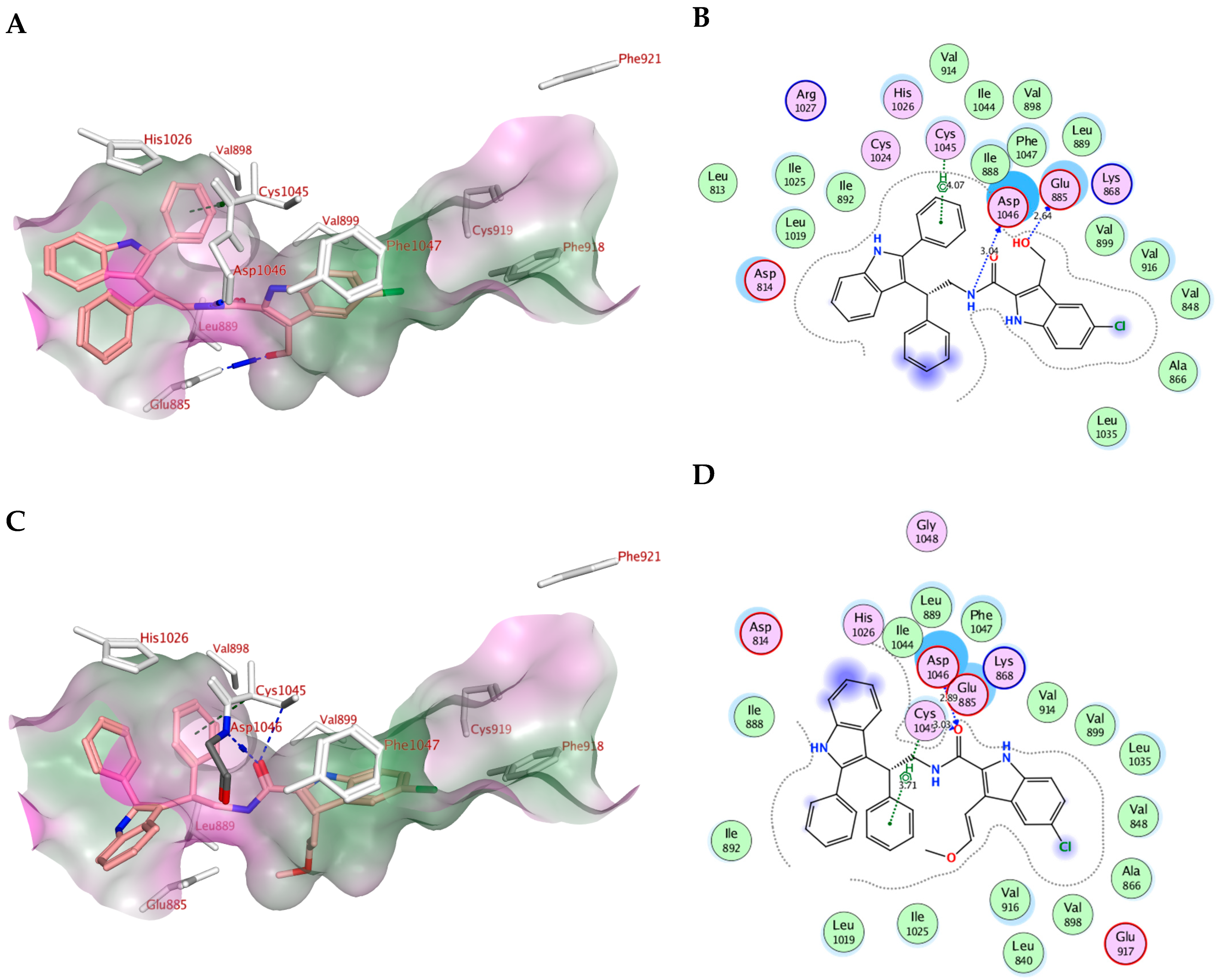
2.4. Molecular Modeling
2.5. In Silico ADME/Pharmacokinetics Studies
3. Materials and Methods
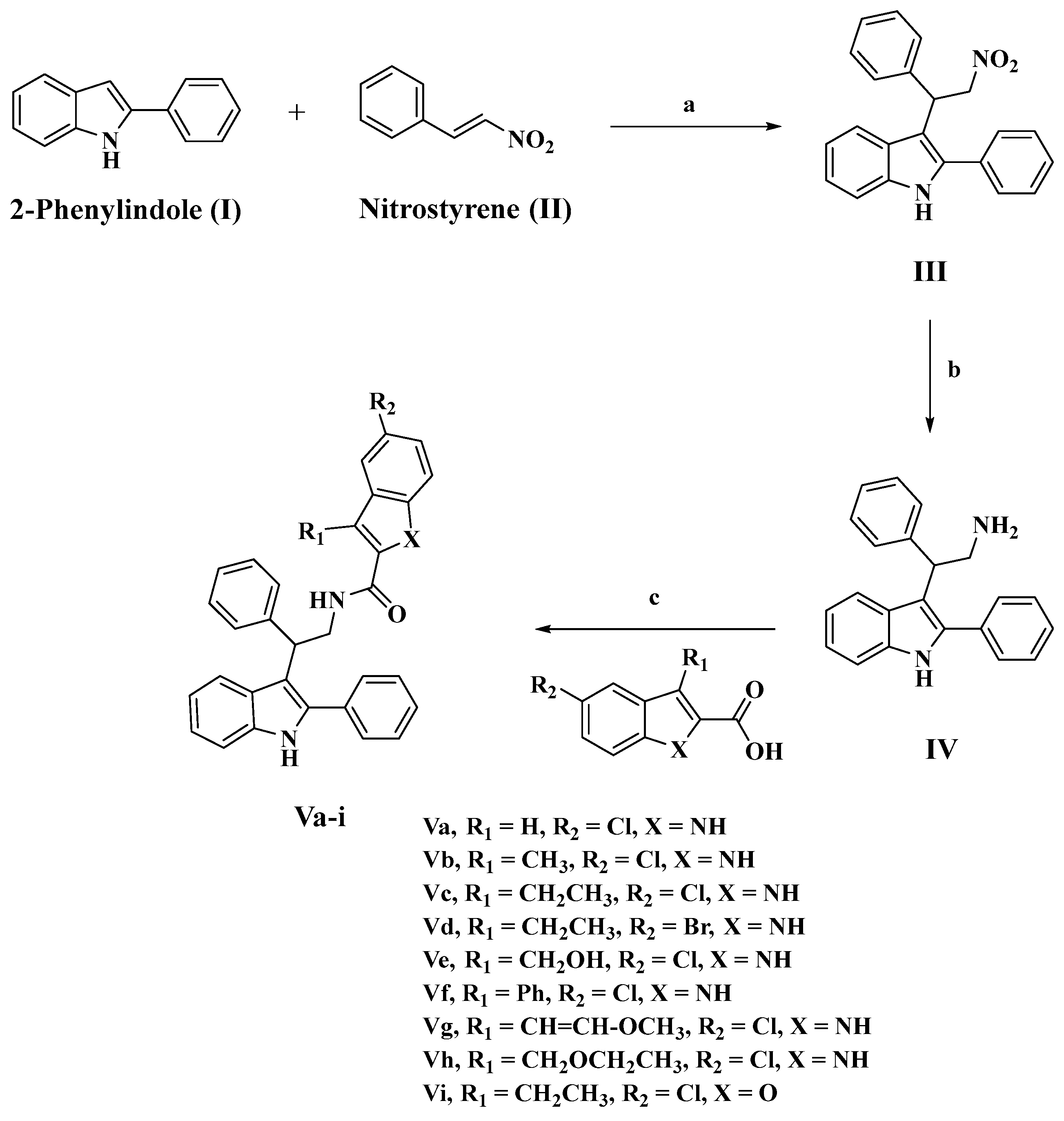
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 3-(2-nitro-1-phenylethyl)-2-phenyl-1H-indole (III)
3.1.2. Synthesis of 2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-amine (IV)
3.1.3. Synthesis of N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamides (Va-i)
5-Chloro-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Va)
5-Chloro-3-methyl-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Vb)
5-Chloro-3-ethyl-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Vc)
5-Bromo-3-ethyl-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Vd)
5-Chloro-3-(hydroxymethyl)-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Ve)
5-Chloro-3-phenyl-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Vf)
(E)-5-Chloro-3-(2-methoxyvinyl)-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Vg)
5-Chloro-3-(ethoxymethyl)-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (Vh)
5-Chloro-3-ethyl-N-(2-phenyl-2-(2-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)benzofuran-2-carboxamide (Vi)
3.2. Biology
3.2.1. Cell Viability Assay
3.2.2. Antiproliferative Assay
3.2.3. EGFR Inhibitory Assay
3.2.4. BRAFV600E Inhibitory Assay
3.2.5. VEGFR-2 Inhibitory Assay
3.3. Apoptotic Markers Assays
3.3.1. Caspase-3 Assay
3.3.2. Caspase-8, Bax, and Bcl-2 Level Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, P.A.; Murray, B.W. Protein kinase biochemistry and drug discovery. Bioorg. Chem. 2011, 39, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannaiyan, R.; Mahadevan, D. A comprehensive review of protein kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 1249–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhullar, K.S.; Lagarón, N.O.; McGowan, E.M.; Parmar, I.; Jha, A.; Hubbard, B.P.; Rupasinghe, H.V. Kinase-targeted cancer therapies: Progress, challenges and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asati, V.; Mahapatra, D.K.; Bharti, S.K. PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibitors as anticancer agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 314–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2021 update. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Yang, X.; Duan, Y.; Han, J.; Liao, C. Small-molecule kinase inhibitors for the treatment of nononcologic diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1283–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ko, Y.T. Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in glioblastoma. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yan, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Luo, P. Cutaneous toxicity of FDA-approved small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivy, S.P.; Wick, J.Y.; Kaufman, B.M. An overview of small-molecule inhibitors of VEGFR signaling. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, N.E.; Dhingra, S.; Jois, S.D.; Vicente, M.d.G.H. Molecular targeting of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR). Molecules 2021, 26, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Queralt, C.; Porta, R.; Cardenal, F.; Camps, C.; Majem, M.; Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Isla, D.; Provencio, M. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Concurrent gene alterations with EGFR mutation and treatment efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagy, J.A.; Dvorak, A.M.; Dvorak, H.F. VEGF-A164/165 and PlGF: Roles in angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2003, 13, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kitadai, Y.; Bucana, C.D.; Cleary, K.R.; Ellis, L.M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3964–3968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poon, R.T.-P.; Fan, S.-T.; Wong, J. Clinical implications of circulating angiogenic factors in cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1207–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Akhtar, S. Tumor angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: Mechanism, pathways and current biological therapeutic interventions. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Azzoli, C.G.; Baker, S., Jr.; Temin, S.; Pao, W.; Aliff, T.; Brahmer, J.; Johnson, D.H.; Laskin, J.L.; Masters, G.; Milton, D. American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update on chemotherapy for stage IV non–small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Jian, H.; Tong, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, F.; Shao, Y.W.; Zhao, X. Variability of EGFR exon 20 insertions in 24 468 Chinese lung cancer patients and their divergent responses to EGFR inhibitors. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Huang, Z.; Bai, Z.; Xie, R.; Sun, L.; Lin, K. Development and strategies of VEGFR-2/KDR inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1839–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enokida, T.; Tahara, M. Management of VEGFR-Targeted TKI for thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitoia, F.; Jerkovich, F. Selective use of sorafenib in the treatment of thyroid cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 2016, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wellbrock, C.; Karasarides, M.; Marais, R. The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, U.M.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.S.; Oh, C.-H. Recent advances of RAF (rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma) inhibitors as anti-cancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 144–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyssonnaux, C.; Eychène, A. The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway: New concepts of activation. Biol. Cell 2001, 93, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. RAF protein-serine/threonine kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samatar, A.A.; Poulikakos, P.I. Targeting RAS–ERK signalling in cancer: Promises and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Gouda, A.M.; Abou-Ghadir, O.F.; Salem, O.I.; Ali, A.T.; Farghaly, H.S.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Trembleau, L.; Abdu-Allah, H.H.; Youssif, B.G. Design and synthesis of novel 2, 3-dihydropyrazino [1, 2-a] indole-1, 4-dione derivatives as antiproliferative EGFR and BRAFV600E dual inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 104, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohassab, A.M.; Hassan, H.A.; Abdelhamid, D.; Gouda, A.M.; Youssif, B.G.; Tateishi, H.; Fujita, M.; Otsuka, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M. Design and synthesis of novel quinoline/chalcone/1, 2, 4-triazole hybrids as potent antiproliferative agent targeting EGFR and BRAFV600E kinases. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 106, 104510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollag, G.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Ibrahim, P.; Nolop, K.; Hirth, P. Vemurafenib: The first drug approved for BRAF-mutant cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoja, L.; Hogg, D. Dabrafenib in the treatment of metastatic or unresectable melanoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2015, 15, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahallad, A.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Salazar, R.; Zecchin, D.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Bardelli, A.; Bernards, R. Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF (V600E) inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR. Nature 2012, 483, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, W.-g.; Song, Q.-b.; Wei, J. BRAF V600E mutation as a predictive factor of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies therapeutic effects in metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2014, 29, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporali, S.; Amaro, A.; Levati, L.; Alvino, E.; Lacal, P.M.; Mastroeni, S.; Ruffini, F.; Bonmassar, L.; Antonini Cappellini, G.C.; Felli, N. miR-126-3p down-regulation contributes to dabrafenib acquired resistance in melanoma by up-regulating ADAM9 and VEGF-A. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-I.; Liao, C.-B.; Chen, C.-S.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Chung, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Ciou, S.-Y.; Hsueh, W.-Y.; Lo, T.-H.; Huang, G.-R. Design and synthesis of 4-anilinoquinazolines as Raf kinase inhibitors. Part 1. Selective B-Raf/B-RafV600E and potent EGFR/VEGFR2 inhibitory 4-(3-hydroxyanilino)-6-(1H-1, 2, 3-triazol-4-yl) quinazolines. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 109, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, K.; Brungs, D.; Szeto, E.; Epstein, R. Anticancer activity of combination targeted therapy using cetuximab plus vemurafenib for refractory BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2014, 21, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothey, A.; Fakih, M.; Tabernero, J. Management of BRAF-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: A review of treatment options and evidence-based guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondevila, F.; Méndez-Blanco, C.; Fernández-Palanca, P.; González-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, J.L. Anti-tumoral activity of single and combined regorafenib treatments in preclinical models of liver and gastrointestinal cancers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comunanza, V.; Corà, D.; Orso, F.; Consonni, F.M.; Middonti, E.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Buzdin, A.; Sica, A.; Medico, E.; Sangiolo, D. VEGF blockade enhances the antitumor effect of BRAFV 600E inhibition. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Collado, A.X.; Knott, J.; Jazirehi, A.R. Reversal of resistance in targeted therapy of metastatic melanoma: Lessons learned from Vemurafenib (BRAFV600E-specific inhibitor). Cancers 2018, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Tu, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, J.; Ren, X.; Ding, K. Identification and optimization of new dual inhibitors of B-Raf and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases for overcoming resistance against vemurafenib. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, O.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. Anticancer potential of plants and natural products. Am J Pharmacol Sci 2013, 1, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sravanthi, T.; Manju, S. Indoles—A promising scaffold for drug development. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, A.; Sharma, R.; Singh, R.K. Target-based anticancer indole derivatives and insight into structure‒activity relationship: A mechanistic review update (2018–2021). Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3006–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssif, B.G.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Salem, O.I.; Mohamed, M.F.; Treambleau, L.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Design, synthesis, mechanistic and histopathological studies of small-molecules of novel indole-2-carboxamides and pyrazino [1, 2-a] indol-1 (2H)-ones as potential anticancer agents effecting the reactive oxygen species production. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Dong, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, L. The importance of indole and azaindole scaffold in the development of antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 203, 112506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman, D.J. Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qi, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Gan, Y.Y.; Shao, L.H.; Zhang, L.Q.; Tang, Z.H.; Zhu, M.; Tang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.C. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of sorafenib derivatives containing indole (ketone) semicarbazide analogs as antitumor agents. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2020, 57, 2548–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Silakari, O. Molecular dynamics guided development of indole based dual inhibitors of EGFR (T790M) and c-MET. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 79, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. Three generations of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors developed to revolutionize the therapy of lung cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Yoo, J.; Kwon, A.; Kim, D.; Nguyen, H.K.; Lee, B.-Y.; Suh, W.; Min, K.H. Structure-activity relationship of indole-tethered pyrimidine derivatives that concurrently inhibit epidermal growth factor receptor and other angiokinases. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, P.; Choudhary, A. Kinase Inhibitor Drugs. Success. Drug Discov. 2018, 3, 65–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.A.; Goldberg, F.W. Kinase Drug Discovery: Modern Approaches; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Mohammed, A.F.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Trembleau, L.; Youssif, B.G. Design, Synthesis, and Antiproliferative Activity of New 5-Chloro-indole-2-carboxylate and Pyrrolo [3, 4-b] indol-3-one Derivatives as Potent Inhibitors of EGFRT790M/BRAFV600E Pathways. Molecules 2023, 28, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Mostafa, Y.A.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; El-Bahrawy, A.H.; Trembleau, L.; Youssif, B.G. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Indole-2-Carboxamides with Potent Apoptotic Antiproliferative Activity as EGFR/CDK2 Dual Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H.A.; Shaker, M.E.; Alzarea, S.I.; Hendawy, O.; Mohamed, F.A.; Gouda, A.M.; Ali, A.T.; Morcoss, M.M.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Trembleau, L. Optimization and SAR investigation of novel 2, 3-dihydropyrazino [1, 2-a] indole-1, 4-dione derivatives as EGFR and BRAFV600E dual inhibitors with potent antiproliferative and antioxidant activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 120, 105616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.A.; Gomaa, H.A.; Hendawy, O.; Ali, A.T.; Farghaly, H.S.; Gouda, A.M.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Trembleau, L.; Youssif, B.G. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel EGFR inhibitors containing 5-chloro-3-hydroxymethyl-indole-2-carboxamide scaffold with apoptotic antiproliferative activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 112, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.A.; Alakilli, S.Y.; El Azab, E.F.; Baawad, F.A.; Shaaban, E.I.A.; Alrub, H.A.; Hendawy, O.; Gomaa, H.A.; Bakr, A.G.; Abdelrahman, M.H. Discovery of new 5-substituted-indole-2-carboxamides as dual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/cyclin dependent kinase-2 (CDK2) inhibitors with potent antiproliferative action. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H.A.; El-Sherief, H.A.; Hussein, S.; Gouda, A.M.; Salem, O.I.; Alharbi, K.S.; Hayallah, A.M.; Youssif, B.G. Novel 1, 2, 4-triazole derivatives as apoptotic inducers targeting p53: Synthesis and antiproliferative activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 105, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzouk, A.A.; Abdel-Aziz, S.A.; Abdelrahman, K.S.; Wanas, A.S.; Gouda, A.M.; Youssif, B.G.; Abdel-Aziz, M. Design and synthesis of new 1, 6-dihydropyrimidin-2-thio derivatives targeting VEGFR-2: Molecular docking and antiproliferative evaluation. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 102, 104090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell viability assays. In Assay Guidance Manual; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Mohammed, A.F.; Salem, O.I.; Gomaa, H.A.; Youssif, B.G. New 1, 3, 4-oxadiazoles linked with the 1, 2, 3-triazole moiety as antiproliferative agents targeting the EGFR tyrosine kinase. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, 2200009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, S.A.; Taher, E.S.; Lan, P.; Asaad, G.F.; Gomaa, H.A.; El-Koussi, N.A.; Youssif, B.G. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile derivatives bearing 1, 3-thiazole moiety as novel anti-inflammatory EGFR inhibitors with cardiac safety profile. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 111, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Zied, H.A.; Beshr, E.A.; Gomaa, H.A.; Mostafa, Y.A.; Youssif, B.G.; Hayallah, A.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M. Discovery of new cyanopyridine/chalcone hybrids as dual inhibitors of EGFR/BRAFV600E with promising antiproliferative properties. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 356, e2200464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, D.S.; Belzile, J.; Bready, J.V.; Coxon, A.; DeMelfi, T.; Doerr, N.; Estrada, J.; Flynn, J.C.; Flynn, S.R.; Graceffa, R.F. Novel 2, 3-dihydro-1, 4-benzoxazines as potent and orally bioavailable inhibitors of tumor-driven angiogenesis. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Liang, N.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, D.; Yu, X.; Tian, Y. Advanced research on vasculogenic mimicry in cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Ikemori-Kawada, M.; Jestel, A.; von König, K.; Funahashi, Y.; Matsushima, T.; Tsuruoka, A.; Inoue, A.; Matsui, J. Distinct binding mode of multikinase inhibitor lenvatinib revealed by biochemical characterization. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Colbert, L.S.; Fuller, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in breast cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2010, 1806, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Mohammed, A.F.; Salem, O.I.; Rabea, S.M.; Youssif, B.G. Design, synthesis, and antiproliferative properties of new 1, 2, 3-triazole-carboximidamide derivatives as dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 inhibitors. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1282, 135165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zied, H.A.; Youssif, B.G.; Mohamed, M.F.; Hayallah, A.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M. EGFR inhibitors and apoptotic inducers: Design, synthesis, anticancer activity and docking studies of novel xanthine derivatives carrying chalcone moiety as hybrid molecules. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Wei, Z.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. The role of BCL-2 family proteins in regulating apoptosis and cancer therapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 985363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Lim, B. Targeting apoptosis in cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, Z.; Fakhri, S.; Nouri, K.; Wallace, C.E.; Farzaei, M.H.; Bishayee, A. Targeting multiple signaling pathways in cancer: The rutin therapeutic approach. Cancers 2020, 12, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S. Caspases: Executioners of apoptosis. Pathobiol. Hum. Dis. 2014, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, G.S.; Al-Harbi, S.; Almasan, A. Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. In Apoptosis Cancer: Methods and Protocol; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1219, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder, S.; Plesca, D.; Almasan, A. Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. In Apoptosis Cancer: Methods and Protocol; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 414, pp. 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, T.S.; Bokhtia, R.M.; Al-Mahmoudy, A.M.; Taher, E.S.; AlAwadh, M.A.; Elagawany, M.; Abdel-Aal, E.H.; Panda, S.; Gouda, A.M.; Asfour, H.Z. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 5-((substituted quinolin-3-yl/1-naphthyl) methylene)-3-substituted imidazolidin-2, 4-dione as HIV-1 fusion inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.K.; Labute, P. Assessment of fully automated antibody homology modeling protocols in molecular operating environment. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2014, 82, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Lemmon, M.A.; Radhakrishnan, R. Erlotinib binds both inactive and active conformations of the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain. Biochem. J. 2012, 448, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Mostafa, Y.A.; Raslan, A.E.; Youssif, B.G. Novel piperine-carboximidamide hybrids: Design, synthesis, and antiproliferative activity via a multi-targeted inhibitory pathway. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.S.; Voell, S.A.; Sosič, I.; Proj, M.; Rossanese, O.W.; Schnakenburg, G.; Gütschow, M.; Collins, I.; Steinebach, C. Encoding BRAF inhibitor functions in protein degraders. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakchi, B.; Krishna, A.D.; Sreecharan, E.; Ganesh, V.B.J.; Niharika, M.; Maharshi, S.; Puttagunta, S.B.; Sigalapalli, D.K.; Bhandare, R.R.; Shaik, A.B. An overview on applications of SwissADME web tool in the design and development of anticancer, antitubercular and antimicrobial agents: A medicinal chemist’s perspective. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1259, 132712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dulsat, J.; López-Nieto, B.; Estrada-Tejedor, R.; Borrell, J.I. Evaluation of Free Online ADMET Tools for Academic or Small Biotech Environments. Molecules 2023, 28, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoud, N.E.-H.; Borah, P.; Deb, P.K.; Venugopala, K.N.; Hourani, W.; Alzweiri, M.; Bardaweel, S.K.; Tiwari, V. ADMET profiling in drug discovery and development: Perspectives of in silico, in vitro and integrated approaches. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
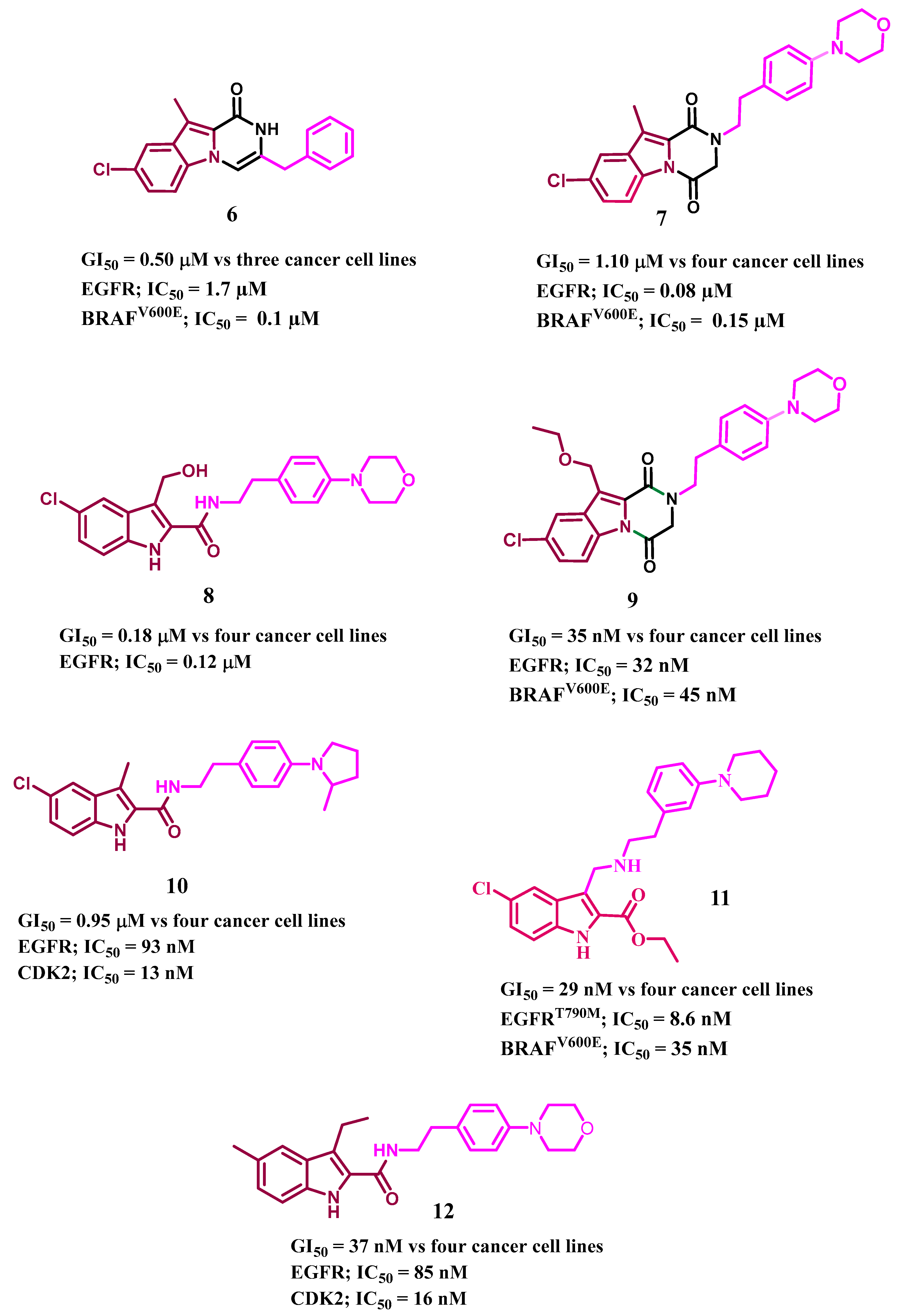

 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp. | R1 | R2 | X | Cell Viability % | Antiproliferative Activity IC50 ± SEM (nM) | ||||
| A-549 | MCF-7 | Panc-1 | HT-29 | Average (GI50) | |||||
| IV | -- | -- | -- | 92 | 102 ± 10 | 106 ± 10 | 104 ± 10 | 104 ± 10 | 104 |
| Va | H | Cl | NH | 91 | 25 ± 2 | 28 ± 2 | 26 ± 2 | 26 ± 2 | 26 |
| Vb | CH3 | Cl | NH | 88 | 58 ± 5 | 61 ± 6 | 58± 5 | 59 ± 5 | 59 |
| Vc | CH2CH3 | Cl | NH | 91 | 54 ± 5 | 57 ± 5 | 56± 5 | 55 ± 5 | 56 |
| Vd | CH2CH3 | Br | NH | 89 | 64 ± 6 | 68 ± 6 | 66 ± 6 | 66 ± 6 | 66 |
| Ve | CH2OH | Cl | NH | 90 | 42 ± 4 | 46 ± 4 | 44 ± 4 | 45 ± 4 | 44 |
| Vf | Ph | Cl | NH | 91 | 46 ± 4 | 49 ± 4 | 48 ± 4 | 48 ± 4 | 48 |
| Vg | CH=CH-OCH3 | Cl | NH | 89 | 30 ± 2 | 33 ± 3 | 30 ± 2 | 30 ± 2 | 31 |
| Vh | CH2OCH2CH3 | Cl | NH | 90 | 34 ± 3 | 38 ± 3 | 36 ± 3 | 38 ± 3 | 37 |
| Vi | CH2CH3 | Cl | O | 89 | 86 ± 8 | 89 ± 8 | 85 ± 8 | 85 ± 8 | 86 |
| Erlotinib | -- | -- | -- | ND | 30 ± 3 | 40 ± 3 | 30 ± 3 | 30 ± 3 | 33 |
| Compd. | EGFR Inhibition IC50 ± SEM (nM) | BRAFV600E Inhibition IC50 ± SEM (nM) | VEGFR-2 Inhibition IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Va | 71 ± 6 | 77 ± 6 | 2.15 ± 0.20 |
| Ve | 94 ± 7 | 97 ± 8 | 1.10 ± 0.08 |
| Vf | 103 ± 8 | 107 ± 9 | 2.50 ± 0.20 |
| Vg | 79 ± 6 | 83 ± 6 | 1.60 ± 0.10 |
| Vh | 85 ± 7 | 89 ± 7 | 3.25 ± 0.25 |
| Erlotinib | 80 ± 5 | 60 ± 5 | -- |
| Sorafenib | -- | -- | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| Compd. No. | Caspase-3 | Caspase-8 | Bax | Bcl-2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc (pg/mL) | Fold Change | Conc (ng/mL) | Fold Change | Conc (pg/mL) | Fold Change | Conc (ng/mL) | Fold Reduction | |
| Va | 726± 6 | 11 | 3.50 | 35 | 410 | 45 | 0.75 | 7 |
| Ve | 462 ± 4 | 7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Vg | 528 ± 5 | 8 | 2.20 | 22 | 320 | 35 | 0.85 | 6 |
| Vh | 460 ± 4 | 7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Doxorubicin | 505 ± 4 | 7.5 | 1.80 | 18 | 280 | 31 | 0.90 | 6 |
| Control | 66 | 1 | 0.10 | 1 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| Compd. | MOE Score kcal/mol | Hydrogen Bond Interactions | Hydrophobic Interactions | Other Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erlotinib | −10.70 | Met769 | Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722, Thr766, Thr830 | Leu694 |
| IV | −7.79 | Met769 Thr830 | Leu820, Val702, Phe699, Asp831 | Glu738 (ionic) Asp831 (ionic) Val702 (pi-H) |
| Va | −10.52 | Asp831 | Gly722, Thr766, Pro770, Glu780Leu694, Leu820, Val702 | Gly772 (pi-H) |
| Vb | −8.89 | Asp831 Asp776 | Thr766, Pro770, Glu780, Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722 | Cys773 (pi-H) |
| Vc | −9.38 | Asp831 Arg817 | Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722, Thr766, Pro770, Glu780, His781 | -------------------- |
| Vd | −9.35 | Leu764 Asp831 | Leu820, Val702, Gly722, Thr766, Leu694, Asp776, Glu780 | Leu820 (pi-H) |
| Ve | −9.89 | Asp831 | Glu780, Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722, Thr766, Asp776, | Leu694 (pi-H) |
| Vf | −9.90 | Asp831 Asp776 | Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722, Thr766, Asp776, Glu780 | Val702 (pi-H) |
| Vg | −10.05 | Asp831 | Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722, Thr766, Asp776, Glu780 | ------------------ |
| Vh | −10.13 | Asp831 Arg817 | Thr766, Asp776, Glu780, Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722 | Gly695, Val702 (pi-H) |
| Vi | −9.58 | ---------- | Leu694, Leu820, Val702, Gly722, Thr766, Asp776, Glu780 | Gly772 (pi-H) |
| Compd. | MOE Score kcal/mol | Hydrogen Bond Interactions | Hydrophobic Interactions | Other Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vemurafenib | −11.78 | Thr529 Gln530 Cys532 Asp594 Gly596 | Trp531, Phe583, Cys532, Ile463, Thr592, val471, Lys483, Leu514 | Lys483 (ionic) |
| Va | −7.97 | Thr529 | Phe583, Cys532, Thr592, val471, Lys483, Leu514 | -------------------- |
| Ve | −4.21 | Leu505 Thr508 Lys483 | Trp531, Phe583, Cys532, Ile463, Thr592, val471, Lys483, Leu514 | -------------------- |
| Vf | −4.30 | ---------- | Trp531, Phe583, Cys532, Ile463, Thr592, val471, Lys483, Leu514 | Val471 (pi-H) Leu514 (pi-H) Phe583 (pi-pi) |
| Vg | −7.32 | ---------- | Trp531, Phe583, Cys532, Ile463, Thr592, val471, Lys483, Leu514 | Val471 (pi-H) |
| Vh | −7.44 | Asp594 | Trp531, Phe583, Cys532, Ile463, Thr592, val471, Lys483, Leu514, Gly596 | Val471 (pi-H) Ile527 (pi-H) |
| Compd. | MOE Score kcal/mol | Hydrogen Bond Interactions | Hydrophobic Interactions | Pi-H Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorafenib | −10.73 | Cys919, Glu885 | Val916, Leu889, Leu840, Asp1046, Cys1045 and Phe1047 | Phe1047 |
| Va | −9.61 | Glu885, Asp1046 | Leu889, Asp814, Asp1046, Glu885 and Leu886 | ----------- |
| Ve | −9.77 | Glu885, Asp1046 | Leu889, Asp814, Asp1046, Glu885 and Leu886, Cys1045 and His1026 | Cys1045 |
| Vf | −8.18 | Glu885, Asp1046 | Leu889, Asp814, Asp1046, Glu885 and Leu886, Cys1045 and Phe1047 | Cys1045 |
| Vg | −9.07 | Cys1045, Asp1046 | Leu889, Asp814, Asp1046, Glu885 and Leu886, Cys1045 and Phe1047 | Cys1045 |
| Vh | −9.09 | Glu885, Asp1046, Cys1045 | Leu889, Asp814, Asp1046, Glu885 and Leu886, Cys1045 and Phe1047 | ------------- |
| Compd. | MW | nROTB | HBA | HBD | Violations | MR | TPSA | Log P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | 312 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 100 | 41.81 | 4.25 |
| Va | 490 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 147 | 60.68 | 6.22 |
| Vb | 504 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 152 | 60.68 | 6.61 |
| Vc | 518 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 157 | 60.68 | 6.79 |
| Vd | 563 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 160 | 60.68 | 6.91 |
| Ve | 520 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 154 | 80.91 | 5.72 |
| Vf | 566 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 173 | 60.68 | 7.59 |
| Vg | 546 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 164 | 69.91 | 6.54 |
| Vh | 548 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 163 | 69.91 | 6.5 |
| Vi | 519 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 155 | 58.03 | 7.12 |
| Compd. | GI Abs. | BBB | P-gp Substrate | CYP1A2 Inhibitor | CYP2C19 Inhibitor | CYP2C9 Inhibitor | CYP2D6 Inhibitor | CYP3A4 Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | High | ++ | - | + | --- | --- | + | - |
| Va | Low | ++ | --- | + | + | + | + | ++ |
| Vb | Low | ++ | --- | + | + | + | + | + |
| Vc | Low | ++ | --- | + | - | + | + | + |
| Vd | Low | ++ | --- | + | + | + | - | + |
| Ve | Low | ++ | --- | - | - | + | + | - |
| Vf | Low | ++ | --- | + | - | + | + | - |
| Vg | Low | ++ | --- | - | - | + | + | ++ |
| Vh | Low | + | --- | - | --- | + | + | + |
| Vi | Low | ++ | --- | + | + | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Mohammed, A.F.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Trembleau, L.; Youssif, B.G.M. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Indole-2-carboxamides as Potential Multi-Target Antiproliferative Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071039
Al-Wahaibi LH, Mohammed AF, Abdelrahman MH, Trembleau L, Youssif BGM. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Indole-2-carboxamides as Potential Multi-Target Antiproliferative Agents. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Wahaibi, Lamya H., Anber F. Mohammed, Mostafa H. Abdelrahman, Laurent Trembleau, and Bahaa G. M. Youssif. 2023. "Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Indole-2-carboxamides as Potential Multi-Target Antiproliferative Agents" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071039
APA StyleAl-Wahaibi, L. H., Mohammed, A. F., Abdelrahman, M. H., Trembleau, L., & Youssif, B. G. M. (2023). Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Indole-2-carboxamides as Potential Multi-Target Antiproliferative Agents. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071039