CP-673451, a Selective Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis in Opisthorchis viverrini-Associated Cholangiocarcinoma via Nrf2 Suppression and Enhanced ROS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression Level of PDGFs and PDGFRs in CCA Tissues and CCA Cell Lines
2.2. Sensitivity of PDGFR Inhibitors
2.3. CP-673451 Induced Apoptosis in HuCCA-1 Cells
2.4. CP-673451 Induced ROS Elevation
2.5. CP-673451 Suppressed Nrf2 Protein Expression and Nuclear Translocation and Inhibited PI3K/Akt Pathway
2.6. CP-673451 Decreased the Expression of Antioxidant Genes in HuCCA-1 Cells
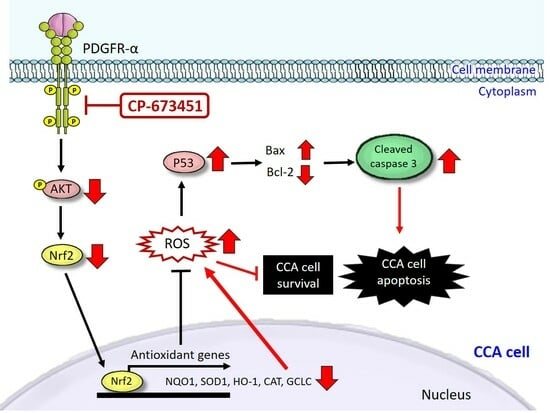
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and CCA Tissue Samples
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Analysis of RNA Expression
4.4. Drug-Sensitivity Assay In Vitro
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Apoptosis Analysis
4.6.1. DAPI Staining
4.6.2. Flow-Cytometry
4.7. Intracellular Reactive Oxidative Species (ROS) Level
4.8. Immunofluorescence
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IARC. Infection with liver flukes (Opisthorchis viverrivi, Opisthorchis felineus and Clonorchis sinensis). IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1994, 61, 121–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sripa, B.; Brindley, P.J.; Mulvenna, J.; Laha, T.; Smout, M.; Mairiang, E.; Bethony, J.M.; Loukas, A. The tumorigenic liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini-multiple pathways to cancer. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montori, M.; Scorzoni, C.; Argenziano, M.E.; Balducci, D.; De Blasio, F.; Martini, F.; Buono, T.; Benedetti, A.; Marzioni, M.; Maroni, L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and possible implications for therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Davidson, B.R.; Goldin, R.; Pereira, S.P.; Rosenberg, W.M.C.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Thillainayagam, A.V.; Thomas, H.C.; Thursz, M.R.; Wasan, H. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma: Consensus document. Gut 2002, 51, VI1–VI9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewater, J.A.; Palmer, D.; Cunningham, D.; Iveson, T.; Gillmore, R.; Waters, J.; Harrison, M.; Valle, J.W.; Wasan, H.; Corrie, P. Second-line therapy in advanced biliary tract cancer: Baseline data from a retrospective multi-centre series. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 224–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, D.; Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Roayaie, S.; Ferrer, J.; Tabak, B.; Peix, J.; Sole, M.; Tovar, V.; Alsinet, C.; et al. Integrative molecular analysis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reveals 2 classes that have different outcomes. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, D.; Ojima, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Hiraoka, N.; Kosuge, T.; Kasai, S.; Hirohashi, S.; Shibata, T. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of EGFR, VEGF, and HER2 expression in cholangiocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Hendifar, A.; Osipov, A.; Cho, M.; Li, D.; Gong, J. Targeting the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) in advanced cholangiocarcinoma: Clinical trial progress and future considerations. Cancers 2021, 13, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W. ErBb family proteins in cholangiocarcinoma and clinical implications. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, E.C.; Sclafani, F.; Cunningham, D. Emerging molecular targets in oncology: Clinical potential of MET/hepatocyte growth-factor inhibitors. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuzillet, C.; Seitz, J.-F.; Fartoux, L.; Malka, D.; Lledo, G.; Tijeras-Raballand, A.; Gramont, A.D.; Ronot, M.; Bouattour, M.; Dreyer, C.; et al. Sunitinib as second-line treatment in patients with advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (SUN-CK phase II trial): Safety, efficacy, and updated translational results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinmuth, N.; Liersch, R.; Raedel, M.; Fehrmann, F.; Fehrmann, N.; Bayer, M.; Schwoeppe, C.; Kessler, T.; Berdel, W.; Thomas, M.; et al. Combined anti-PDGFRα and PDGFRβ targeting in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.J.; Small, E.J.; Kabbinavar, F.; Chachoua, A.; Taneja, S.; Reese, D.; DePaoli, A.; Hannah, A.; Balk, S.P.; Bubley, G.J. A multi-institutional phase ii study of SU101, a platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibitor, for patients with hor-mone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Demetri, G.D.; Blanke, C.D.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; McGreevey, L.S.; Chen, C.J.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadamuro, M.; Nardo, G.; Indraccolo, S.; Dall’olmo, L.; Sambado, L.; Moserle, L.; Franceschet, I.; Colledan, M.; Massani, M.; Stecca, T.; et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-D and Rho GTPases regulate recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wang, D.; Yao, Y.; Wang, M. PDGF signaling in cancer progression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 9918–9929. [Google Scholar]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Essaghir, A. PDGF receptor signaling networks in normal and cancer cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonjaraspinyo, S.; Wu, Z.; Boonmars, T.; Kaewkes, S.; Loilome, W.; Sithithaworn, P.; Nagano, I.; Takahashi, Y.; Yongvanit, P.; Bhudhisawasdi, V. Overexpression of PDGFA and its receptor during carcinogenesis of Opisthorchis viverrini-associated chol-angiocarcinoma. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenetti, A.; Popov, Y.; Jung, Y.; Choi, S.S.; Witek, R.P.; Yang, L.; Brown, K.D.; Schuppan, D.; Diehl, A.M. The hedgehog pathway regulates remodelling responses to biliary obstruction in rats. Gut 2008, 57, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonjaraspinyo, S.; Boonmars, T.; Wu, Z.; Loilome, W.; Sithithaworn, P.; Nagano, I.; Pinlaor, S.; Yongvanit, P.; Nielsen, P.S.; Pairojkul, C.; et al. Platelet-derived growth factor may be a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 1785–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, C.D.; Mertens, J.C.; Razumilava, N.; Bronk, S.F.; Sirica, A.E.; Gores, G.J. Targeting PDGFR-β in cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.G.; Whalen, P.M.; Soderstrom, E.; Moraski, G.; Lyssikatos, J.P.; Wang, H.F.; Cooper, B.; Baker, D.A.; Savage, D.; Dalvie, D.; et al. Antiangiogenic and antitumor activity of a selective PDGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, CP-673,451. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Li, D. CP-673451, a platelet-derived growth-factor receptor inhibitor, suppresses lung cancer cell proliferation and migration. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B. Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant re-sponse element. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Lu, W.; et al. Over-expression of PDGFR-β promotes PDGF-induced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of EPCs through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.S.; Jun, M.; Kong, A.N. Nrf2: A potential molecular target for cancer chemoprevention by natural compounds. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, G.; Tuveson, D.A. Diversity and biology of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 147–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, B.J.; Riehle, K.J.; Shimizu-Albergine, M.; Bauer, R.L.; Hudkins, K.L.; Johansson, F.; Yeh, M.M.; Mahoney, W.M., Jr.; Yeung, R.S.; Campbell, J.S. Activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha contributes to liver fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabayoglu, P.; Lade, A.; Lee, Y.A.; Dragomir, A.C.; Sun, X.; Fiel, M.I.; Thung, S.; Aloman, C.; Soriano, P.; Hoshida, Y.; et al. β-PDGF receptor expressed by hepatic stellate cells regulates fibrosis in murine liver injury, but not carcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, M.W.; Mossner, J. Molecular targeted therapy of biliary tract cancer-results of the first clinical studies. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 834–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, D.B.; Laird, A.D.; Xin, X.; Louie, S.G.; Christensen, J.G.; Li, G.; Schreck, R.E.; Abrams, T.J.; Ngai, T.J.; Lee, L.B.; et al. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and plate-let-derived growth factor receptors: Determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basciani, S.; De Luca, G.; Dolci, S.; Brama, M.; Arizzi, M.; Mariani, S.; Rosano, G.; Spera, G.; Gnessi, L. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor β-subtype regulates proliferation and migration of gonocytes. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6226–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehner, M.; Beuthien-Baumann, B.; Dittert, D.D.; Schuler, U.; Wirth, M.P. Lack of efficacy of imatinib in a patient with metastatic Leydig cell tumor. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, S.; Ohashi, A.; Nishida, T.; Isozaki, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Shinomura, Y.; Kitamura, Y. Gain-of-function mutations of platelet-derived growth factor receptor α gene in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, D.K.; Mouradov, D.; Wasenang, W.; Luk, I.Y.; Scott, C.M.; Williams, D.S.; Yeung, Y.H.; Limpaiboon, T.; Iatropoulos, G.F.; Jenkins, L.J.; et al. Genomic profiling of biliary tract cancer cell lines reveals molecular subtypes and actionable drug targets. iScience 2019, 21, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Petracci, E.; Delmonte, A.; Chiadini, E.; Dazzi, C.; Papi, M.; Capelli, L.; Casanova, C.; De Luigi, N.; Mariotti, M.; et al. Impact of TP53 mutations on outcome in EGFR-mutated patients treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonsri, B.; Yacqub-Usman, K.; Thintharua, P.; Myint, K.Z.; Sae-Lao, T.; Collier, P.; Suriyonplengsaeng, C.; Larbcharoensub, N.; Balasubramanian, B.; Venkatraman, S.; et al. Effect of combining EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and cytotoxic agents on cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, F.A.; Rodrigues Pereira, J.; Ciuleanu, T.; Tan, E.H.; Hirsh, V.; Thongprasert, S.; Campos, D.; Maoleekoonpiroj, S.; Smylie, M.; Martins, R.; et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, M.; Yano, S.; Giaccone, G.; Tamura, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Douillard, J.Y.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Kudoh, S.; Rischin, D.; et al. Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial). J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Ohnishi, H.; Ohtsuka, K.; Matsushima, S.; Ohkura, Y.; Furuse, J.; Watanabe, T.; Mori, T.; Sugiyama, M. KRAS mutation as a potential prognostic biomarker of biliary tract cancers. Jpn. Clin. Med. 2016, 7, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saensa-Ard, S.; Leuangwattanawanit, S.; Senggunprai, L.; Namwat, N.; Kongpetch, S.; Chamgramol, Y.; Loilome, W.; Khansaard, W.; Jusakul, A.; Prawan, A. Establishment of cholangiocarcinoma cell lines from patients in the endemic area of liver fluke infection in Thailand. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317725925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamnongsong, S.; Kueanjinda, P.; Buraphat, P.; Sakornsakolpat, P.; Vaeteewoottacharn, K.; Okada, S.; Jirawatnotai, S.; Sam-pattavanich, S. Comprehensive drug response profiling and pan-omic analysis identified therapeutic candidates and prognostic biomarkers for Asian cholangiocarcinoma. iScience 2022, 25, 105182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuishi, Y.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. The Keap1-Nrf2 system in cancers: Stress response and anabolic metabolism. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E.H.; Wei, M.C.; Weiler, S.; Flavell, R.A.; Mak, T.W.; Lindsten, T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L) sequester BH3 do-main-only molecules preventing Bax and Bak-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.S.; Xu, X.X.; Hu, M.; Chen, L.; Fu, Q.; Pu, D.M.; Hong, L. Realgar-induced apoptosis of cervical cancer cell line Siha via cytochrome c release and caspase-3 and caspase-9 activation. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2012, 18, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononen, J.; Bubendorf, L.; Kallionimeni, A.; Bärlund, M.; Schraml, P.; Leighton, S.; Torhorst, J.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.P. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazières, J.; Brugger, W.; Cappuzzo, F.; Middel, P.; Frosch, A.; Bara, I.; Klingelschmitt, G.; Klughammer, B. Evaluation of EGFR protein expression by immunohistochemistry using H-score and the magnification rule: Re-analysis of the SATURN study. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDGFR-α | F: TTGAAGGCAGGCACATTTACA R: GCGACAAGGTATAATGGCAGAAT | 119 | NM_006206.5 |
| PDGFR-β | F: CCTGCAATGTGACGGAGAGT R: GGTGCGGTTGTCTTTGAACC | 200 | NM_002609.3 |
| PDGF-A | F: GCAAGACCAGGACGGTCATTT R: GGCACTTGACACTGCTCGT | 135 | NM_033023.4 |
| PDGF-B | F: CACTCGATCCGCTCCTTTGA R: CGGGTCATGTTCAGGTCCAA | 92 | NM_033016.3 |
| PDGF-C | F: GCCAGGTTGTCTCCTGGTTA R: TGCTTGGGACACATTGACAT | 86 | NM_016205.3 |
| PDGF-D | F: GTGGAGGAAATTGTGGCTGT R: CGTTCATGGTGATCCAACTG | 172 | NM_033135.3 |
| NRF2 | F: AGGTTGCCCACATTCCCAAA R: AGTGACTGAAACGTAGCCGA | 118 | NM_006164.5 |
| NQO1 | F: GTTTGGAGTCCCTGCCATTC R: AAGCACTGCCTTCTTACTCCG | 118 | NM_000903.3 |
| HO-1 | F: AACTTTCAGAAGGGCCAGGT R: CTGGGCTCTCCTTGTTGC | 112 | NM_002133.3 |
| SOD1 | F: ACAAAGATGGTGTGGCCGAT R: AACGACTTCCAGCGTTTCCT | 162 | NM_000454.5 |
| CAT | F: GCCACAGGAAAGTACCCCTC R: GAGGCCAAACCTTGGTGAGA | 106 | NM_001752.4 |
| GCLC | F: GAGGTCAAACCCAACCCAGT R: AAGGTACTGAAGCGAGGGTG | 92 | NM_001498.4 |
| GAPDH | F: CTGACTTCAACAGCGACACC R: TGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGTTG | 114 | NM_002046.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duangdara, J.; Boonsri, B.; Sayinta, A.; Supradit, K.; Thintharua, P.; Kumkate, S.; Suriyonplengsaeng, C.; Larbcharoensub, N.; Mingphruedhi, S.; Rungsakulkij, N.; et al. CP-673451, a Selective Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis in Opisthorchis viverrini-Associated Cholangiocarcinoma via Nrf2 Suppression and Enhanced ROS. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010009
Duangdara J, Boonsri B, Sayinta A, Supradit K, Thintharua P, Kumkate S, Suriyonplengsaeng C, Larbcharoensub N, Mingphruedhi S, Rungsakulkij N, et al. CP-673451, a Selective Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis in Opisthorchis viverrini-Associated Cholangiocarcinoma via Nrf2 Suppression and Enhanced ROS. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuangdara, Jinchutha, Boonyakorn Boonsri, Apinya Sayinta, Kittiya Supradit, Pakpoom Thintharua, Supeecha Kumkate, Chinnawut Suriyonplengsaeng, Noppadol Larbcharoensub, Somkit Mingphruedhi, Narongsak Rungsakulkij, and et al. 2024. "CP-673451, a Selective Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis in Opisthorchis viverrini-Associated Cholangiocarcinoma via Nrf2 Suppression and Enhanced ROS" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010009
APA StyleDuangdara, J., Boonsri, B., Sayinta, A., Supradit, K., Thintharua, P., Kumkate, S., Suriyonplengsaeng, C., Larbcharoensub, N., Mingphruedhi, S., Rungsakulkij, N., Muangkaew, P., Tangtawee, P., Vassanasiri, W., Suragul, W., Janvilisri, T., Tohtong, R., Bates, D. O., & Wongprasert, K. (2024). CP-673451, a Selective Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis in Opisthorchis viverrini-Associated Cholangiocarcinoma via Nrf2 Suppression and Enhanced ROS. Pharmaceuticals, 17(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010009