A Selective Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor, JSH-23, Exhibits Antidepressant-like Effects and Reduces Brain Inflammation in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of JSH-23 on LPS-Induced Inflammation
2.1.1. Effect of JSH-23 on LPS-Induced Hypothermia
2.1.2. Effects of JSH-23 on Plasma Levels of IL-6, PGE2 and TNF-α in LPS-Treated Rats
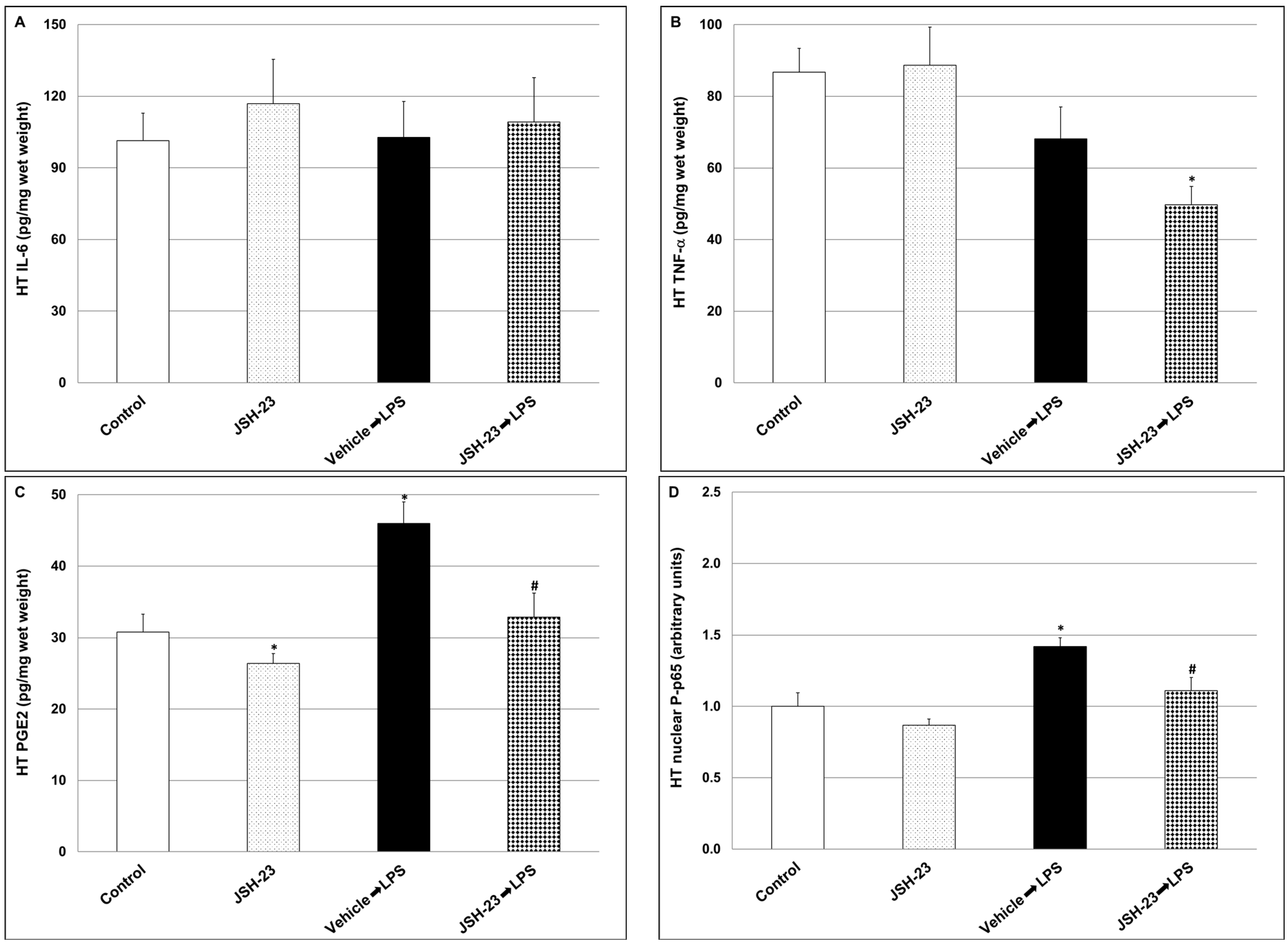
2.1.3. Effects of JSH-23 on Brain Levels of IL-6, PGE2, TNF-α and P-p65 in LPS-Treated Rats
2.2. Effects of Chronic JSH-23 Treatment on Behavioral Phenotypes and Brain Inflammation in Depression-like and Mania-like Models in Rats
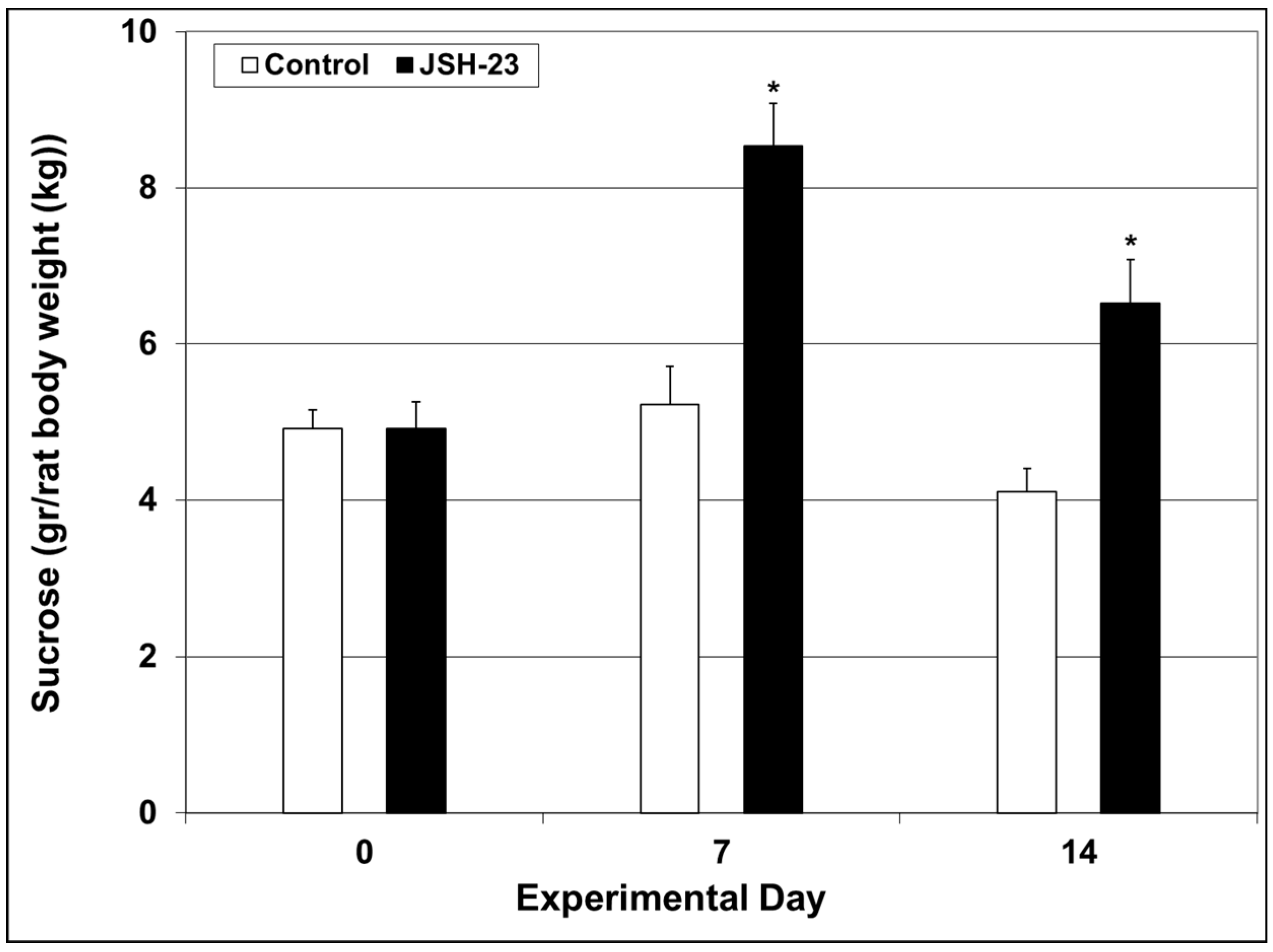
2.2.1. Efficacy of Chronic JSH-23 Treatment in Depression-Modeling Paradigms
2.2.2. Effects of Chronic JSH-23 Treatment on Brain Levels of IL-6, PGE2 and TNF-α in Post-FST Rats
2.2.3. Efficacy of Chronic JSH-23 Treatment in a Mania-Modeling Paradigm
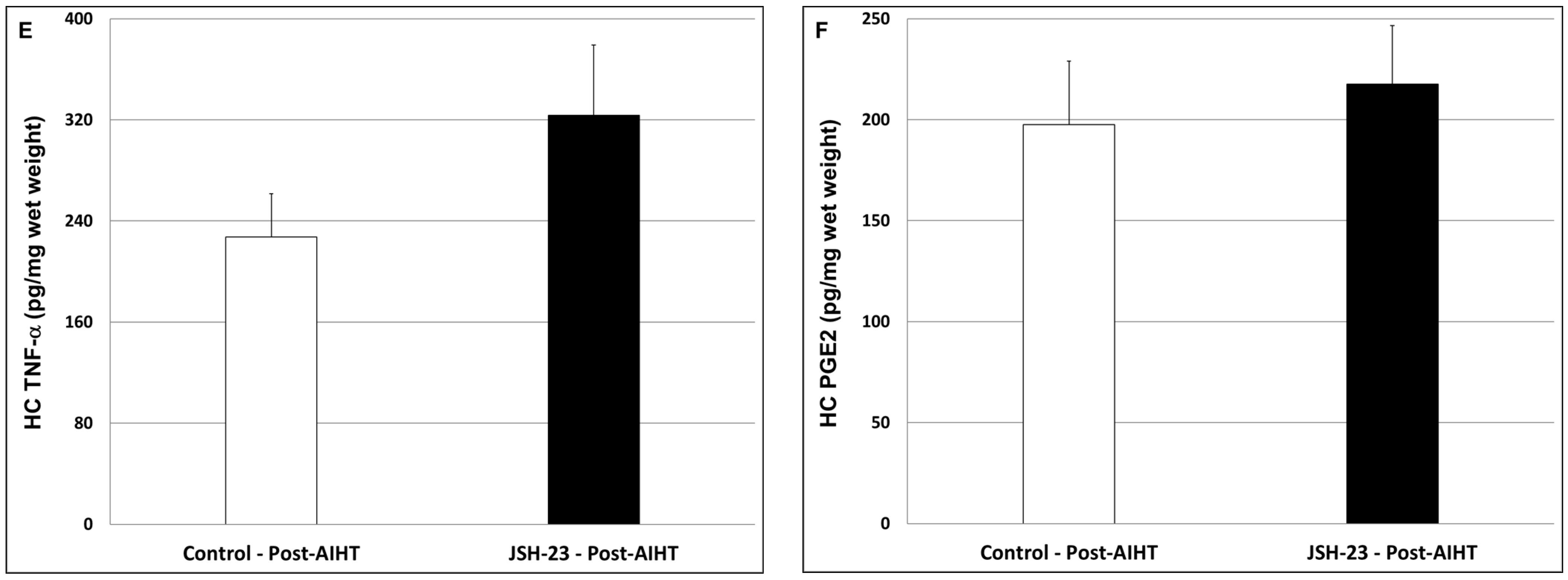
2.2.4. Effects of Chronic JSH-23 Treatment on Brain Levels of IL-6, PGE2 and TNF-α in Post-AIHT Rats
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Treatment with JSH-23
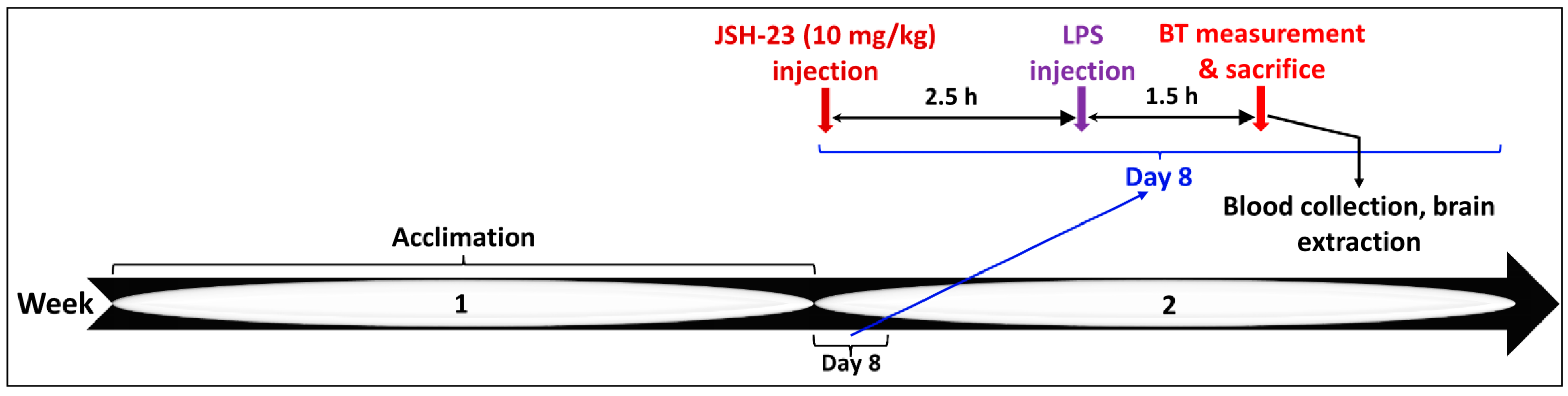
4.2.1. Acute JSH-23 Treatment and Induction of Inflammation by LPS
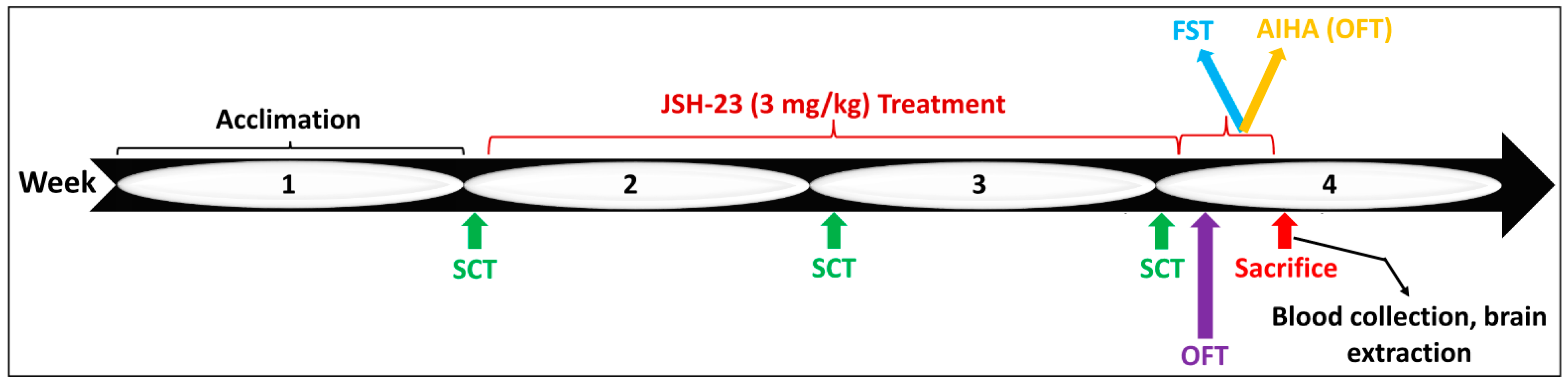
4.2.2. Chronic JSH-23 Treatment in Rats Subjected to Behavioral Tests
4.3. Behavioral Tests
4.3.1. SCT
4.3.2. OFT
4.3.3. Porsolt’s FST
4.3.4. AIHT
4.4. Tissue Collection and Processing of the Samples
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global regional and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Santomauro, D.F.; Aali, A.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abdelmasseh, M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdollahi, A.; et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2024, 403, 2133–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Bromet, E.; Andrade, L.H.; Hwang, I.; Sampson, A.N.; Alonso, J.; de Girolamo, G.; de Graaf, R.; Demyttenaere, K.; Hu, C.; Iwata, N.; et al. Cross-national epidemiology of DSM-IV major depressive episode. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, B.; Steptoe, A.; Zaninotto, P. Depression and anxiety in people with cognitive impairment and dementia during the COVID-19 pandemic: Analysis of the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Stockings, E.; Khoo, J.P.; Erskine, H.E.; Degenhardt, L.; Vos, T.; Whiteford, H.A. The prevalence and burden of bipolar disorder: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.L.R.; Van Meter, A.; Genzlinger, J.; Youngstrom, E.A. Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiologic Studies of Adult Bipolar Disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, e1259–e1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, K.; Goodman, M.; Xu, H. The associations of late-life depression with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: The NHANES 2005–2014. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 300, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazus, T.B.; Beraldi, G.H.; Tokeshi, L.; Rotenberg, L.D.S.; Dragioti, E.; Carvalho, A.F.; Solmi, M.; Lafer, B. All-cause and cause-specific mortality among people with bipolar disorder: A large-scale systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2508–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.E.; Teixeira, A.L. Inflammation in psychiatric disorders: What comes first? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1437, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhie, S.J.; Jung, E.Y.; Shim, I. The role of neuroinflammation on pathogenesis of affective disorders. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2020, 16, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmawati, N.A.; Karimah, A.; Amin, M.M. Inflammation in Depression. JPS 2021, 10, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.E.; Teixeira, L. Neuroinflammation in Mood Disorders: Role of Regulatory Immune Cells. Neuroimmunomodulation 2021, 28, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuring, J.K.; Mathias, J.L.; Ward, L.; Tachas, G. Inflammatory markers in persons with clinically-significant depression, anxiety or PTSD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 168, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modabbernia, A.; Taslimi, S.; Brietzke, E.; Ashrafi, M. Cytokine alterations in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of 30 studies. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkholm, K.; Mäkinen, I.J.O.; Maigaard, K.; Coello, K.; Pagsberg, A.K.; Kessing, L.V. Inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers in children and adolescents with bipolar disorder—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 163, 105766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: Comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.K.; Miller, B.J. Meta-analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytokine and Tryptophan Catabolite Alterations in Psychiatric Patients: Comparisons between Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and Depression. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakici, N.; Sutterland, A.L.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; De Haan, L.; Van Beveren, N.J.M. Changes in peripheral blood compounds following psychopharmacological treatment in drug-naïve first-episode patients with either schizophrenia or major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michopoulos, V.; Powers, A.; Gillespie, C.F.; Ressler, K.J.; Jovanovic, T. Inflammation in Fear-and Anxiety-Based Disorders: PTSD, GAD, and beyond. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, N.; O’Gorman, C.; Horgan, I.; Weeratunga, M.; Halstead, S.; Moussiopoulou, J.; Campana, M.; Yakimov, V.; Wagner, E.; Siskind, D. Inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid markers in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 69 studies with 5710 participants. Schizophr. Res. 2024, 266, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappelmann, N.; Lewis, G.; Dantzer, R.; Jones, P.B.; Khandaker, G.M. Antidepressant activity of anti-cytokine treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of chronic inflammatory conditions. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Rapoport, S.I.; Rao, J.S. Altered arachidonic acid cascade enzymes in postmortem brain from bipolar disorder patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohishi, K.; Ueno, R.; Nishino, S.; Sakai, T.; Hayaishi, O. Increased level of salivary prostaglandins in patients with major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1988, 23, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditzen, C.; Tang, N.; Jastorff, A.M.; Teplytska, L.; Yassouridis, A.; MacCarrone, G.; Uhr, M.; Bronisch, T.; Miller, C.A.; Holsboer, F.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for major depression confirm relevance of associated pathophysiology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Hernández, D.; Caso, J.R.; Javier Meana, J.; Callado, L.F.; Madrigal, J.L.M.; García-Bueno, B.; Leza, J.C. Intracellular inflammatory and antioxidant pathways in postmortem frontal cortex of subjects with major depression: Effect of antidepressants. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.; Khodadadi, H.; Fathalizadeh, J.; Hassanshahi, G.; Bidaki, R.; Ayoobi, F.; Hajebrahimi, B.; Bagheri, F.; Arababadi, M.K. Defective NF-kB Transcription Factor as the Mediator of Inflammatory Responses: A Study on Depressed Iranian Medical Students. Clin. Lab. 2013, 59, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, K.M.; Jenkins, A.K.; Lewis, D.A.; Volk, D.W. Involvement of the nuclear factor-κB transcriptional complex in prefrontal cortex immune activation in bipolar disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.I.; Hung, Y.Y.; Wu, M.K.; Huang, Y.L.; Kang, H.Y. TNIP2 mediates GRβ-promoted inflammation and is associated with severity of major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 95, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, R.C.; Claiborne, J.; Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Reddy, R.; Aschner, M.; Lewis, D.A.; Mirnics, K. Altered expression of genes involved in inflammation and apoptosis in frontal cortex in major depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler-Forsberg, O.; NLydholm, C.; Hjorthøj, C.; Nordentoft, M.; Mors, O.; Benros, M.E. Efficacy of anti-inflammatory treatment on major depressive disorder or depressive symptoms: Meta-analysis of clinical trials. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2019, 139, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brás, J.P.; Bravo, J.; Freitas, J.; Barbosa, M.A.; Santos, S.G.; Summavielle, T.; Almeida, M.I. TNF-alpha-induced microglia activation requires miR-342: Impact on NF-kB signaling and neurotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olugbemide, A.S.; Ben-Azu, B.; Bakre, A.G.; Ajayi, A.M.; Femi-Akinlosotu, O.; Umukoro, S. Naringenin improves depressive- and anxiety-like behaviors in mice exposed to repeated hypoxic stress through modulation of oxido-inflammatory mediators and NF-kB/BDNF expressions. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 169, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.J.; Cole, S.W.; Bower, J.E.; Irwin, M.R.; Taylor, S.E.; Arevalo, J.; Fuligni, A.J. Depressive symptoms and immune transcriptional profiles in late adolescents. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Sayeed, M.S.; Shams, T.; Fahim Hossain, S.; Rahman, M.R.; Mostofa, A.; Fahim Kadir, M.; Mahmood, S.; Asaduzzaman, M. Nigella sativa L. seeds modulate mood, anxiety and cognition in healthy adolescent males. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. IL-6 and IL-8 are likely associated with psychological status in treatment naïve general population. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 298, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshnizi, S.A.; Shahani, P.; Taheri, M.; Hussen, B.M.; Eslami, S.; Sadeghzadeh, Z.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Sayad, A. Expression analysis of NF-ƙB-related long non-coding RNAs in bipolar disorder. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirbalouti, R.G.; Mohseni, M.M.; Taheri, M.; Neishabouri, S.M.; Shirvani-Farsani, Z. Deregulation of NF-κB associated long non-coding RNAs in bipolar disorder. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023, 38, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, C. Inflammation-related biomarkers in major psychiatric disorders: A cross-disorder assessment of reproducibility and specificity in 43 meta-analyses. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, R.; Seol, S.; Kang, H.J.; Suk, K. Brain-immune interactions in neuropsychiatric disorders: Lessons from transcriptome studies for molecular targeting. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 188, 114532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Ringel, K.; Kubera, M.; Berk, M.; Rybakowski, J. Increased autoimmune activity against 5-HT: A key component of depression that is associated with inflammation and activation of cell-mediated immunity, and with severity and staging of depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 136, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roohi, E.; Jaafari, N.; Hashemian, F. On inflammatory hypothesis of depression: What is the role of IL-6 in the middle of the chaos? J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaini, G.; Mason, B.L.; Diaz, A.P.; Jha, M.K.; Soares, J.C.; Trivedi, M.H.; Quevedo, J. Dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy and apoptosis in major depressive disorder: Does inflammation play a role? Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tridon, V.; May, M.J.; Ghosh, S.; Dantzer, R.; Ame, T. NFkB activates in vivo the synthesis of inducible Cox-2 in the brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, M.; Rao, R.; Inoue, H.; Hao, C.M. C/EBPβ and Its Binding Element Are Required for NFκB-induced COX2 Expression Following Hypertonic Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16354–16359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayet, B.; Gélinas, C. Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6938–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Kumar, R. Crosstalk between NFkB and glucocorticoid signaling: A potential target of breast cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2012, 322, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Wang, Q.M. The IKK NF-κB system: A treasure trove for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yde, P.; Mengel, B.; Jensen, M.H.; Krishna, S.; Trusina, A. Modeling the NF-κB mediated inflammatory response predicts cytokine waves in tissue. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, P. Cellular & Molecular Immunology NF-κB and Its Regulation on the Immune System. Immunology 2004, 1, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, R.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: A mini review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Ma, Q.; Tang, H.; Zou, X.; Guo, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Liu, R. LTB4 Promotes Acute Lung Injury via Upregulating the PLC ε-1/TLR4/NF-κ B Pathway in One-Lung Ventilation. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1839341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.F.; Greene, W.C. Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.W.; Russo, S.J.; Ferguson, D.; Nestler, E.J.; Duman, R.S. Nuclear factor-kappaB is a critical mediator of stress-impaired neurogenesis and depressive behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2669–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sundaram, C.; Reuter, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a therapeutic strategy. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, E.; Pippione, A.C.; Boyko, M.; Einaudi, G.; Sainas, S.; Collino, M.; Cifani, C.; Lolli, M.L.; Abu-Freha, N.; Kaplanski, J.; et al. A New NF-κB Inhibitor, MEDS-23, Reduces the Severity of Adverse Post-Ischemic Stroke Outcomes in Rats. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.H.C.N.; Fraga, C.A.M. NF-κB-IKKβ Pathway as a Target for Drug Development: Realities, Challenges and Perspectives. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.M.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, B.H.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, H.J.; Hong, J.T.; Min, K.R.; Kim, Y. Inhibitory action of novel aromatic diamine compound on lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB without affecting IκB degradation. FEBS Lett. 2004, 571, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Salvatierra, D.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Acosta-Saavedra, L.C.; Calderon-Aranda, E.S. Role of nitric oxide produced by iNOS through NF-κB pathway in migration of cerebellar granule neurons induced by Lipopolysaccharide. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Negi, G.; Sharma, S.S. JSH-23 targets nuclear factor-kappa B and reverses various deficits in experimental diabetic neuropathy: Effect on neuroinflammation and antioxidant defence. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, X.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Lin, Y.; Kang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. JSH-23 prevents depressive-like behaviors in mice subjected to chronic mild stress: Effects on inflammation and antioxidant defense in the hippocampus. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 169, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, H.; Wang, Y. Upregulated Long Non-coding RNA ALMS1-IT1 Promotes Neuroinflammation by Activating NF-κB Signaling in Ischemic Cerebral Injury. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4270–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.S.; Harry, G.J.; Rapoport, S.I.; Kim, H.W. Increased excitotoxicity and neuroinflammatory markers in postmortem frontal cortex from bipolar disorder patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaik, E.; Zandi, P. Dysregulation of the NF-κB pathway as a potential inducer of bipolar disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 70, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Johnston, N.L.; Torrey, E.F.; Yolken, R.H. Serial analysis of gene expression in the frontal cortex of patients with bipolar disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry 2001, 178, s137–s141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.G.; Nogueira, C.R.C.; Rocha, N.P.; Queiroz, A.L.L.; Vago, J.P.; Tavares, L.P.; Assis, F.; Fagundes, C.T.; Huguet, R.B.; Bauer, M.E.; et al. Altered intracellular signaling cascades in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from BD patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklowitz, D.J.; Portnoff, L.C.; Armstrong, C.C.; Keenan-Miller, D.; Breen, E.C.; Muscatell, K.A.; Eisenberger, N.I.; Irwin, M.R. Inflammatory cytokines and nuclear factor-kappa B activation in adolescents with bipolar and major depressive disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 241, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzan, S.; Azab, A.N. Anti-TNF-α Compounds as a Treatment for Depression. Molecules 2021, 26, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, N.; Schwarz, M.J.; Dehning, S.; Douhe, A.; Cerovecki, A.; Goldstein-Müller, B.; Spellmann, I.; Hetzel, G.; Maino, K.; Kleindienst, N.; et al. The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib has therapeutic effects in major depression: Results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, add-on pilot study to reboxetine. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, S.H.; Hosseini, F.; Modabbernia, A.; Ashrafi, M.; Akhondzadeh, S. Effect of celecoxib add-on treatment on symptoms and serum IL-6 concentrations in patients with major depressive disorder: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 141, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabzadeh, S.; Ameli, N.; Zeinoddini, A.; Rezaei, F.; Farokhnia, M.; Mohammadinejad, P.; Ghaleiha, A.; Akhondzadeh, S. Celecoxib adjunctive therapy for acute bipolar mania: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Bipolar Disord. 2015, 17, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBattista, C.; Posener, J.A.; Kalehzan, B.M.; Schatzberg, A.F. Acute antidepressant effects of intravenous hydrocortisone and CRH in depressed patients: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.; Azab, A.N. Effects of lithium on inflammation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troib, A.; Azab, A.N. Effects of psychotropic drugs on Nuclear Factor kappa B. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar]
- TourTourjman, V.; Koué, M.È.; Kouassi, E.; Potvin, S. In vivo immunomodulatory effects of antipsychotics on inflammatory mediators: A review. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2012, 3, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Keating, B.A.; Dale, R.C. Anti-inflammatory properties of commonly used psychiatric drugs. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1039379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlola, S.R.; Donohoe, G.; McKernan, D.P. Anti-inflammatory effects of 2nd generation antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 160, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Ren, P.; Cui, L.Y.; Duan, J.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Zeng, Z.R.; Li, Y.F. Astrocyte-specific activation of sigma-1 receptors in mPFC mediates the faster onset antidepressant effect by inhibiting NF-κB-induced neuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 120, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvartsur, R.; Agam, G.; Uzzan, S.; Azab, A.N. Low-Dose Aspirin Augments the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Low-Dose Lithium in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Rats. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, A.; Azab, A.N. Effects of Dexamethasone and Pentoxifylline on Mania-like and Depression-like Behaviors in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzzan, S.; Rostevanov, I.S.; Rubin, E.; Benguigui, O.; Marazka, S.; Kaplanski, J.; Agbaria, R.; Azab, A.N. Chronic Treatment with Nigella sativa Oil Exerts Antimanic Properties and Reduces Brain Inflammation in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostevanov, I.S.; Boyko, M.; Ferorelli, S.; Scilimati, A.; Grazia, M.; Kaplanski, J.; Zlotnik, A.; Azab, A.N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Modelling the dynamic interaction of systemic inflammation and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during and after cardiac surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 22, 467–475. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, M.D.; Ataoglu, H.; Akarsu, E.S. Effects of selective cyclooxygenase enzyme inhibitors on lipopolysaccharide-induced dual thermoregulatory changes in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2002, 57, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanski, J.; Nassar, A.; Sharon-Granit, Y.; Jabareen, A.; Kobal, S.L.; Azab, A.N. Lithium attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, A.; Sharon-Granit, Y.; Azab, A.N. Psychotropic drugs attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia by altering hypothalamic levels of inflammatory mediators in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 626, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ali, T.; Abid, M.N.; Jo, M.H.; Khan, A.; Kim, M.W.; Yoon, G.H.; Cheon, E.W.; Rehman, S.U.; Kim, M.O. Lithium ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the cortex and hippocampus of the adult rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 108, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.N.; Kobal, S.; Rubin, M.; Kaplanski, J. Effects of nimesulide, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on cardiovascular alterations in endotoxemia. Cardiology 2005, 103, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munhoz, C.D.; Lepsch, L.B.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Malta, M.B.; De Sá Lima, L.; Avellar, M.C.W.; Sapolsky, R.M.; Scavone, C. Chronic unpredictable stress exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of nuclear factor-κB in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via glucocorticoid secretion. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3813–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, L.; Fraifeld, V.; Kaplanski, J. Evidence supporting involvement of leukotrienes in LPS-induced hypothermia in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1999, 276, R52–R58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.A.; Molchanova, A.Y.; Dogan, M.D.; Patel, S.; Pétervári, E.; Balaskó, M.; Wanner, S.P.; Eales, J.; Oliveira, D.L.; Gavva, N.R.; et al. The hypothermic response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide critically depends on brain CB1, but not CB2 or TRPV1, receptors. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 2415–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.E.; Walker, A.K.; Weickert, C.S. Neuroinflammation in schizophrenia: The role of nuclear factor kappa B. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Guleria, R.S. Involvement of Nuclear Factor-κB in Inflammation and Neuronal Plasticity Associated with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Cells 2022, 11, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.E.; Walker, A.K.; O’Donnell, M.; Galletly, C.; Lloyd, A.R.; Liu, D.; Weickert, C.S.; Weickert, T.W. Peripheral NF-κB dysregulation in people with schizophrenia drives inflammation: Putative anti-inflammatory functions of NF-κB kinases. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Lv, L.X.; Li, W.Q.; Hao, Y.H.; Zhao, J.P. The Interaction of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and Cytokines Is Associated with Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, D.W.; Moroco, A.E.; Roman, K.M.; Edelson, J.R.; Lewis, D.A. The Role of the Nuclear Factor-κB Transcriptional Complex in Cortical Immune Activation in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, K.; Zhang, Q.; Luan, Q.; Chen, W.; Liu, D. Antidepressant-like effects of curcumin in chronic mild stress of rats: Involvement of its anti-inflammatory action. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yang, C.C.; Rao, C.L.; Zhou, C.J.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, L.B.; Fang, L.; et al. Pioglitazone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behaviors, modulates NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3, CREB/BDNF pathways and central serotonergic neurotransmission in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Zhang, H.N.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Xu, R.A.; Hu, L.F.; Zhang, C.H.; Xu, H.Q.; An, Y.Q.; Tang, C.R.; et al. Simvastatin prevents and ameliorates depressive behaviors via neuroinflammatory regulation in mice. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 245, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.Y.; Khezri, R.; Karkhaneh-Yousefi, M.A.; Mohammadinejad, P.; Gholamian, F.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Zeinoddini, A.; Akhondzadeh, S. A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial on Effectiveness and Safety of Celecoxib Adjunctive Therapy in Adolescents with Acute Bipolar Mania. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fond, G.; Hamdani, N.; Kapczinski, F.; Boukouaci, W.; Drancourt, N.; Dargel, A.; Oliveira, J.; Le Guen, E.; Marlinge, E.; Tamouza, R.; et al. Effectiveness and tolerance of anti-inflammatory drugs’ add-on therapy in major mental disorders: A systematic qualitative review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2014, 129, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominiak, M.; Adam, G.; Sikorska, M.; Mierzejewski, P.; Wojnar, M. Acetylsalicylic Acid and Mood Disorders: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvassori, S.S.; Tonin, P.T.; Dal-Pont, G.C.; Varela, R.B.; Cararo, J.H.; Garcia, A.F.; Gava, F.F.; Menegas, S.; Soares, J.C.; Quevedo, J. Coadministration of lithium and celecoxib reverses manic-like behavior and decreases oxidative stress in a dopaminergic model of mania induced in rats. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvassori, S.S.; Dal-Pont, G.C.; Tonin, P.T.; Varela, R.B.; Ferreira, C.L.; Gava, F.F.; Andersen, M.L.; Soares, J.C.; Quevedo, J. Coadministration of lithium and celecoxib attenuates the behavioral alterations and inflammatory processes induced by amphetamine in an animal model of mania. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 183, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; An, L.T.; Qiu, Y.; Shan, X.X.; Zhao, W.L.; Zhao, J.P.; Li, L.H.; Lang, B.; Wu, R.R. Effects of Aspirin in Rats with Ouabain Intracerebral Treatment-Possible Involvement of Inflammatory Modulation? Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Kaltschmidt, C. Potential involvement of the transcription factor NF-κB in neurological disorders. Mol. Asp. Med. 1993, 14, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardado, P.; Olivera, A.; Rusch, H.L.; Roy, M.; Martin, C.; Lejbman, N.; Lee, H.; Gill, J.M. Altered gene expression of the innate immune, neuroendocrine, and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) systems is associated with posttraumatic stress disorder in military personnel. J. Anxiety Disord. 2016, 38, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.C. Exploring the positive and negative consequences of NF-kappaB inhibition for the treatment of human disease. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussos, P.; Katsel, P.; Davis, K.L.; Giakoumaki, S.G.; Siever, L.J.; Bitsios, P.; Haroutunian, V. Convergent findings for abnormalities of the NF-κB signaling pathway in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yang, K.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Chronic Fluoxetine Treatment Upregulates the Activity of the ERK1/2-NF-κB Signaling Pathway in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex of Rats Exposed to Forced-Swimming Stress. Med. Princ. Pract. 2016, 25, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitychoutis, P.M.; Nakamura, K.; Tsonis, P.A.; Papadopoulou-Daifoti, Z. Neurochemical and behavioral alterations in an inflammatory model of depression: Sex differences exposed. Neuroscience 2009, 159, 1216–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, W.; Greiner, E.; Buczek, L.; Migliaccio, J.; Corbett, E.; Madden, A.M.K.; Petrovich, G.D. Sex differences in activation of extra-hypothalamic forebrain areas during hedonic eating. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 2857–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G.E.; Bangasser, D.; Sotiropoulos, I.; Kokras, N.; Dalla, C. Sex Differences in Stress Response: Classical Mechanisms and Beyond. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla, C.; Pitychoutis, P.M.; Kokras, N.; Papadopoulou-Daifoti, Z. Sex differences in animal models of depression and antidepressant response. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 106, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostevanov, I.S.; Betesh-abay, B.; Nassar, A.; Rubin, E.; Uzzan, S.; Kaplanski, J.; Biton, L.; Azab, A.N. Montelukast induces beneficial behavioral outcomes and reduces inflammation in male and female rats. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 981440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvartsur, R.; Agam, G.; Shnaider, A.; Uzzan, S.; Nassar, A.; Jabarin, A.; Abu-Freha, N.; Meir, K.; Azab, A.N. Safety and efficacy of combined low-dose lithium and low-dose aspirin: A pharmacological and behavioral proof-of-concept study in rats. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaisher-Grinberg, S.; Einat, H. Strain-specific battery of tests for domains of mania: Effects of valproate, lithium and imipramine. Front. Psychiatry 2010, 1, 1416. [Google Scholar]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Anton, G.; Blavet, N.; Jalfre, M. Behavioural despair in rats: A new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1978, 47, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, D.A.; Cryan, J.F. Using the rat forced swim test to assess antidepressant-like activity in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, D.K.E.; Freund, N. Animal models for bipolar disorder: From bedside to the cage. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2017, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Sahakian, B.J. Cognitive neuroscience and brain imaging in bipolar disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 10, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepenik, L.G.; Wang, F.; Spencer, L.; Spann, M.; Kalmar, J.H.; Womer, F.; Kale Edmiston, E.; Pittman, B.; Blumberg, H.P. Structure-function associations in hippocampus in bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychol. 2012, 90, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.L.; Maguire, J. Pathophysiological mechanisms implicated in postpartum depression. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 52, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 indicate inhibition/blocking;
indicate inhibition/blocking;  indicates reduction. Abbreviations: I-κB, inhibitor κB; IKK, I-κB kinase; IL, interleukin; P, phosphate; PG, prostaglandin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
indicates reduction. Abbreviations: I-κB, inhibitor κB; IKK, I-κB kinase; IL, interleukin; P, phosphate; PG, prostaglandin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
 indicate inhibition/blocking;
indicate inhibition/blocking;  indicates reduction. Abbreviations: I-κB, inhibitor κB; IKK, I-κB kinase; IL, interleukin; P, phosphate; PG, prostaglandin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
indicates reduction. Abbreviations: I-κB, inhibitor κB; IKK, I-κB kinase; IL, interleukin; P, phosphate; PG, prostaglandin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.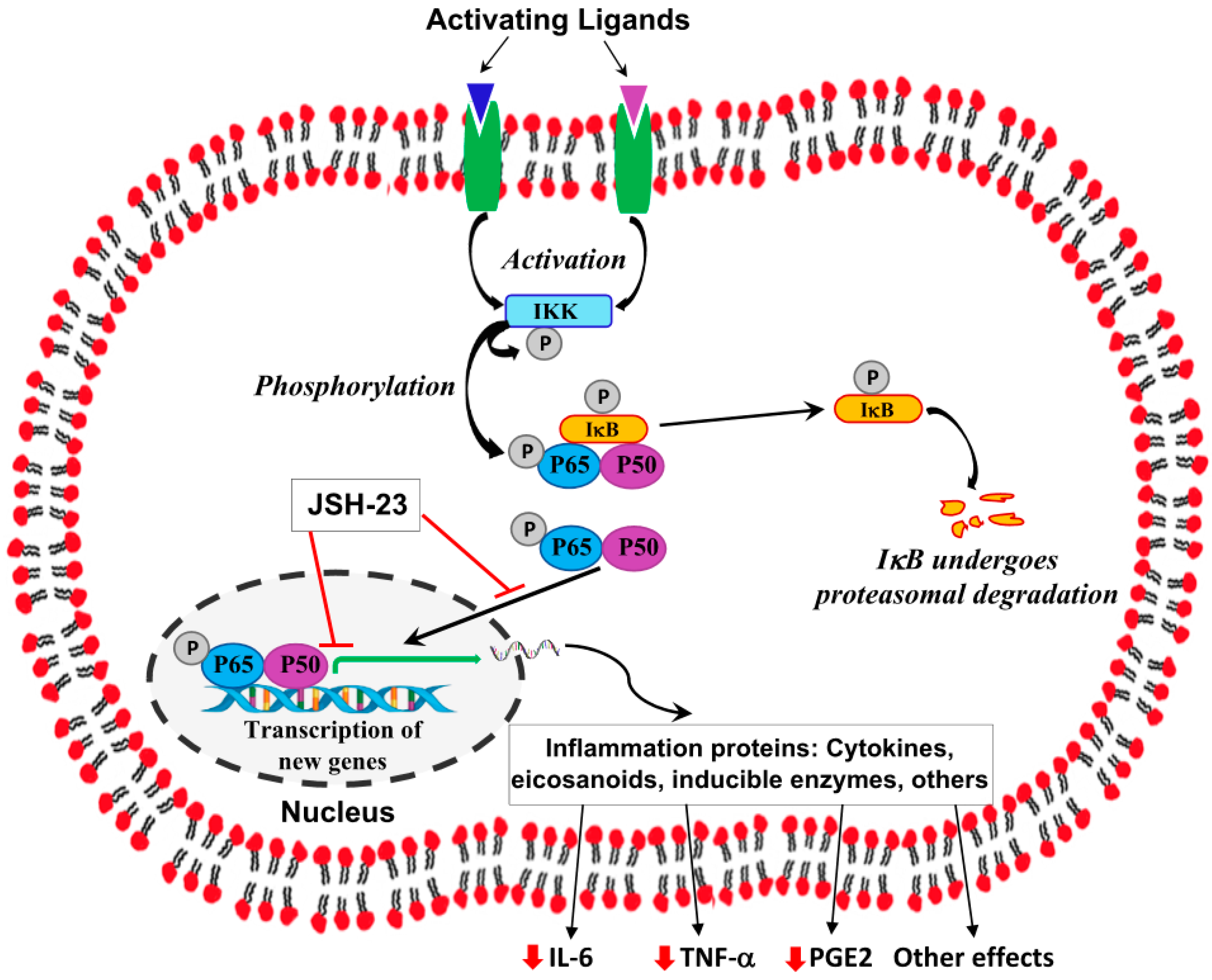








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nassar, A.; Kaplanski, J.; Azab, A.N. A Selective Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor, JSH-23, Exhibits Antidepressant-like Effects and Reduces Brain Inflammation in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101271
Nassar A, Kaplanski J, Azab AN. A Selective Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor, JSH-23, Exhibits Antidepressant-like Effects and Reduces Brain Inflammation in Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101271
Chicago/Turabian StyleNassar, Ahmad, Jacob Kaplanski, and Abed N. Azab. 2024. "A Selective Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor, JSH-23, Exhibits Antidepressant-like Effects and Reduces Brain Inflammation in Rats" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101271
APA StyleNassar, A., Kaplanski, J., & Azab, A. N. (2024). A Selective Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor, JSH-23, Exhibits Antidepressant-like Effects and Reduces Brain Inflammation in Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101271





