Heterobivalent Dual-Target Peptide for Integrin-αvβ3 and Neuropeptide Y Receptors on Breast Tumor
Abstract
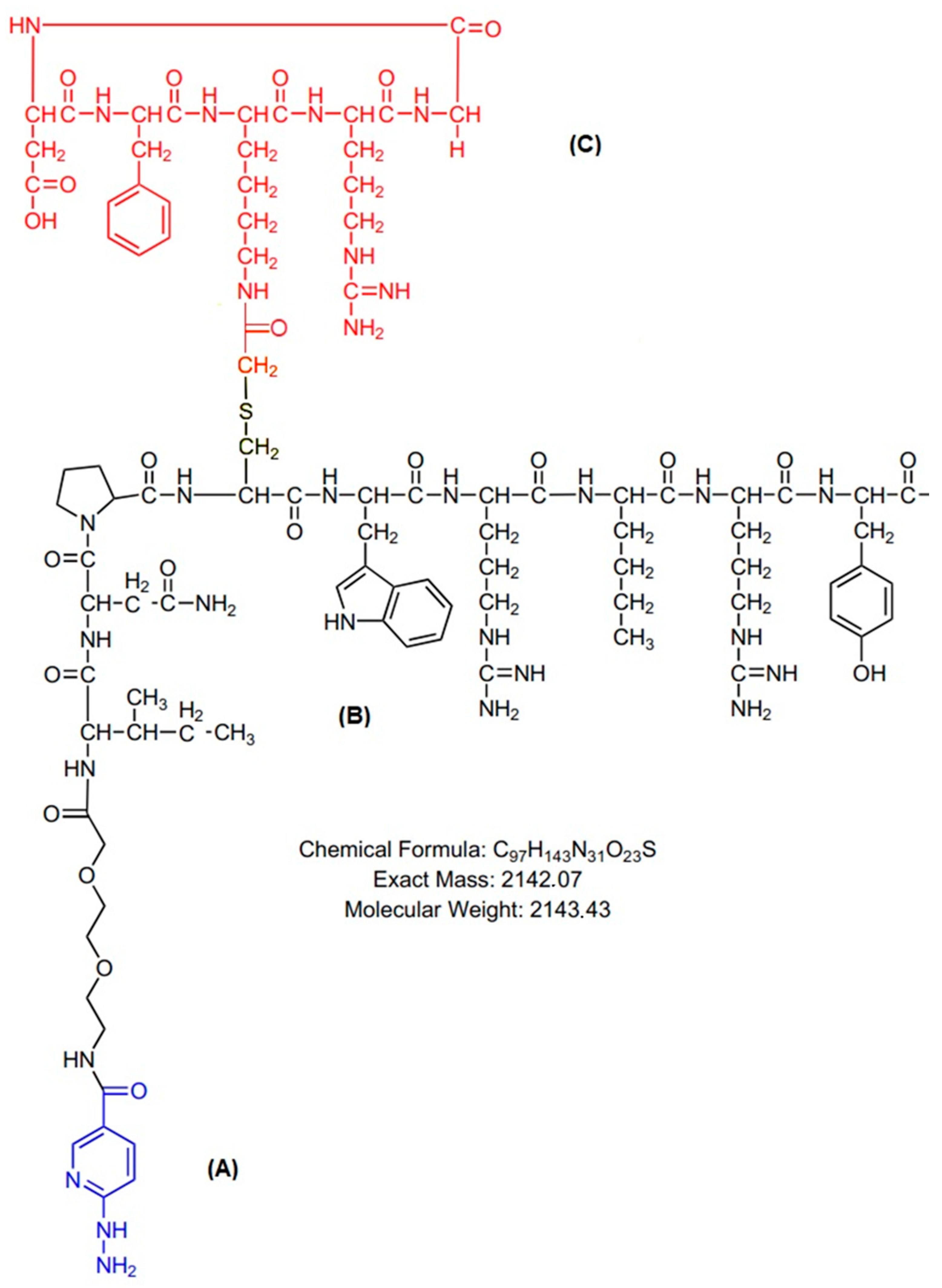
1. Introduction
2. Results
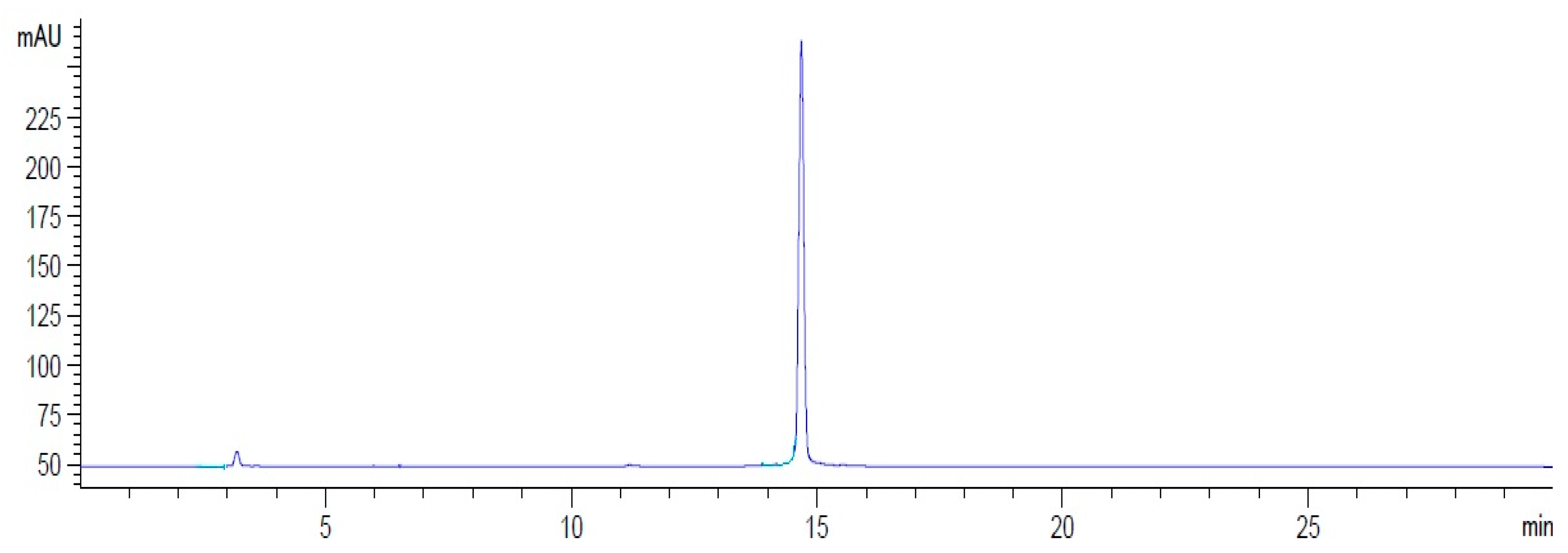
2.1. Radiolabeling of HYNIC-cRDGfK-NPY Peptide
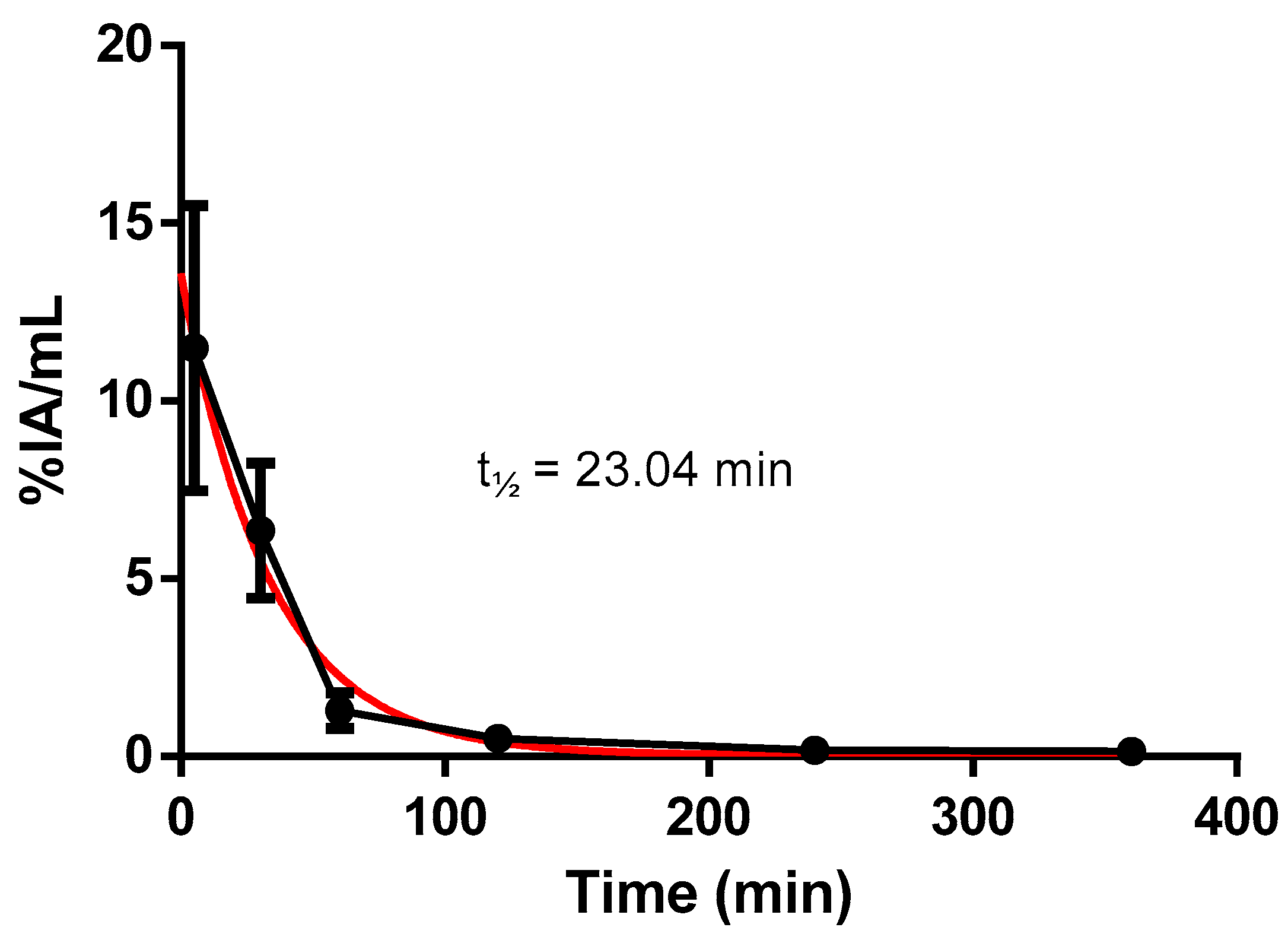
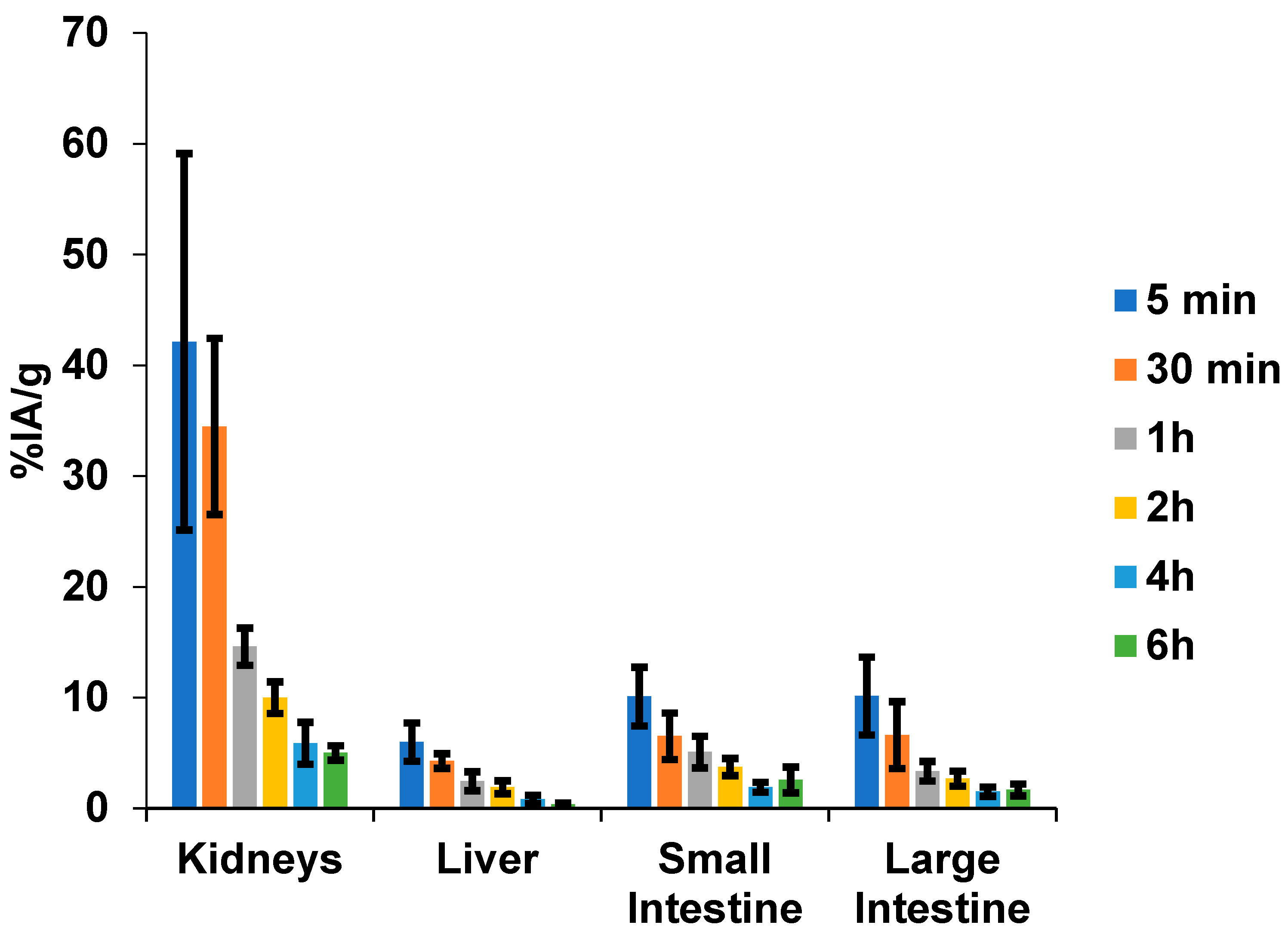
2.2. [99mTc]HYNIC-cRDGfk-NPY Biodistribution in Balb/c Healthy Mice
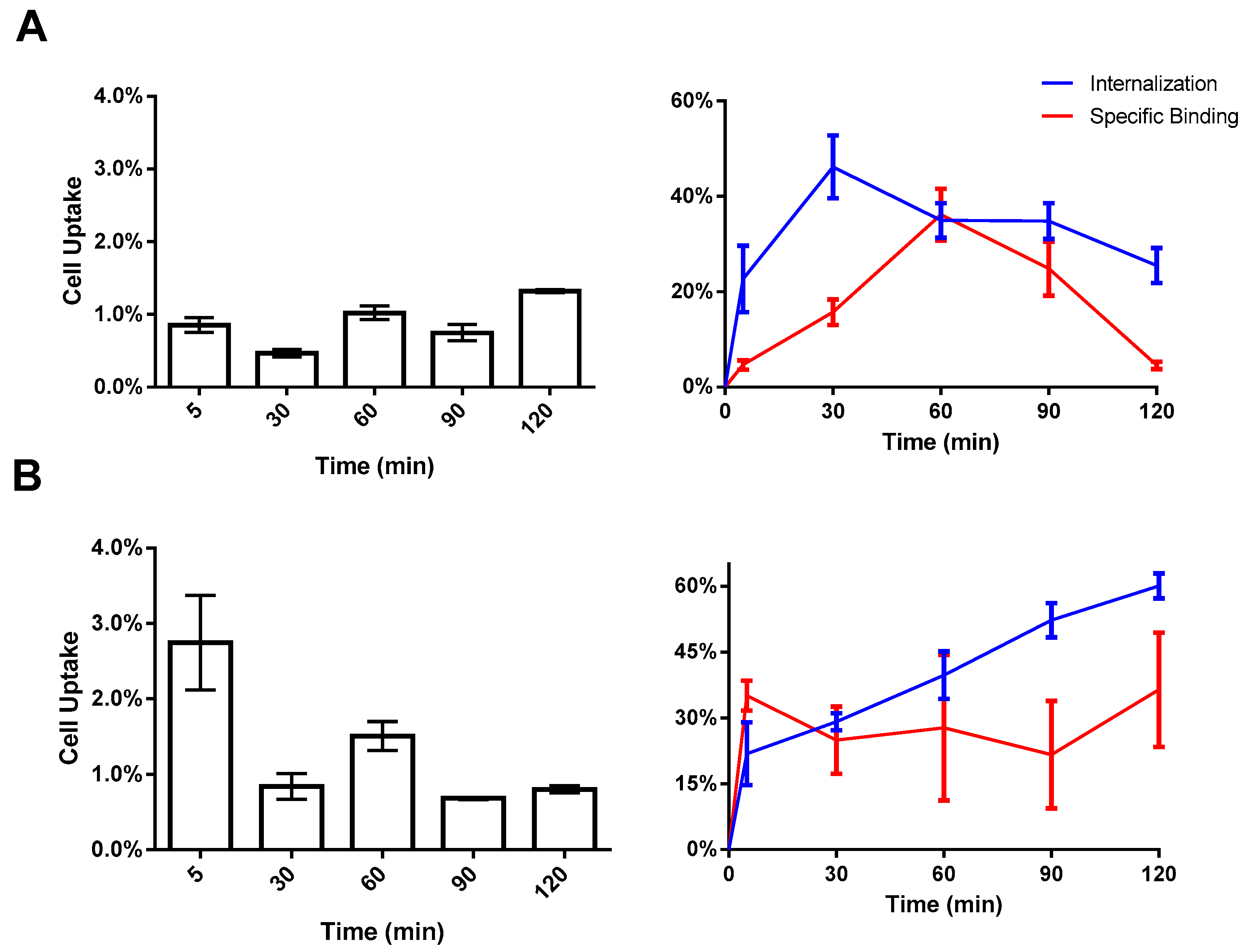
2.3. In Vitro Cell Binding
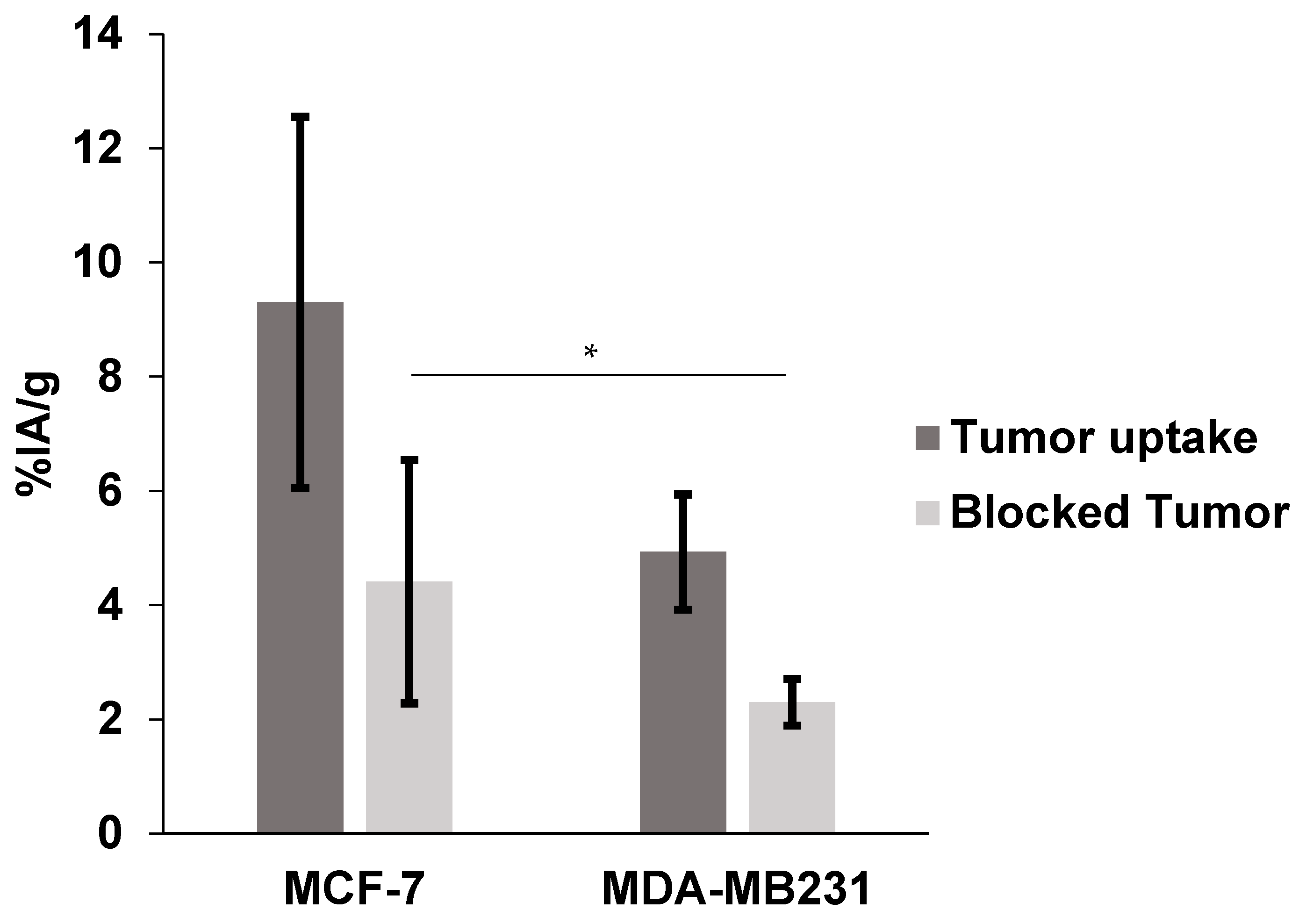
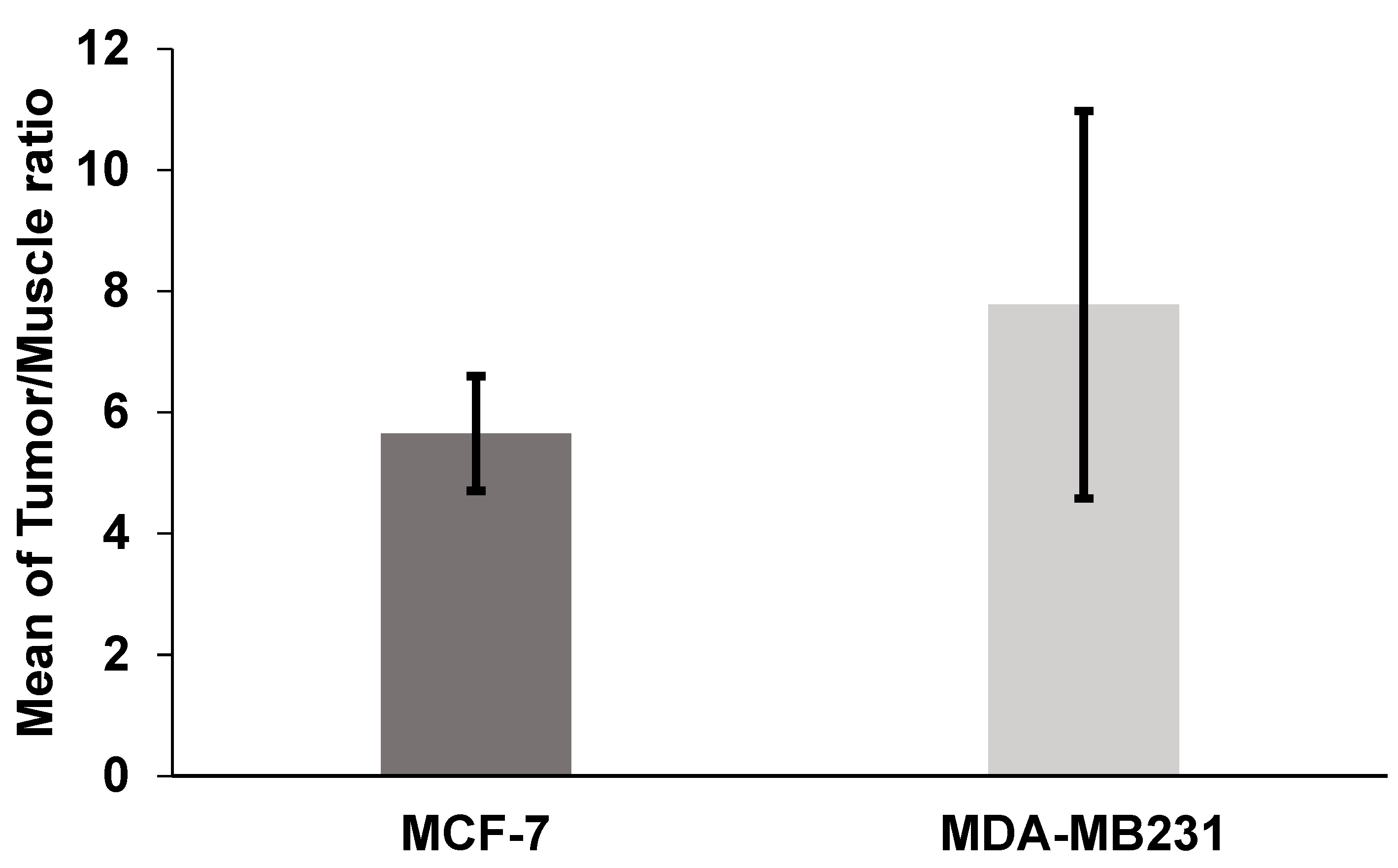
2.4. Biodistribution in Nude Mice Bearing MCF-7 and MDA-MB231 Human Breast Cancer Xenografts
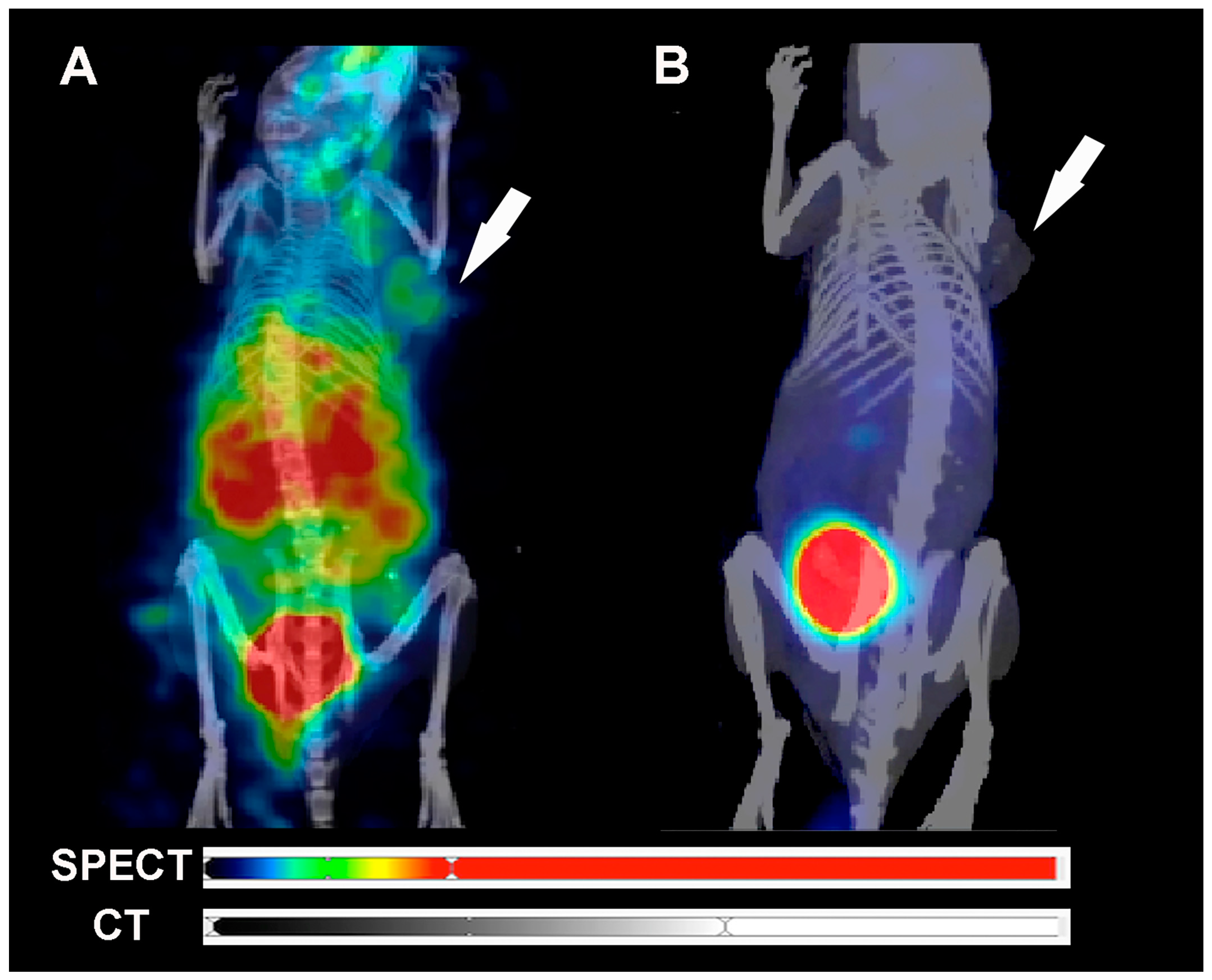
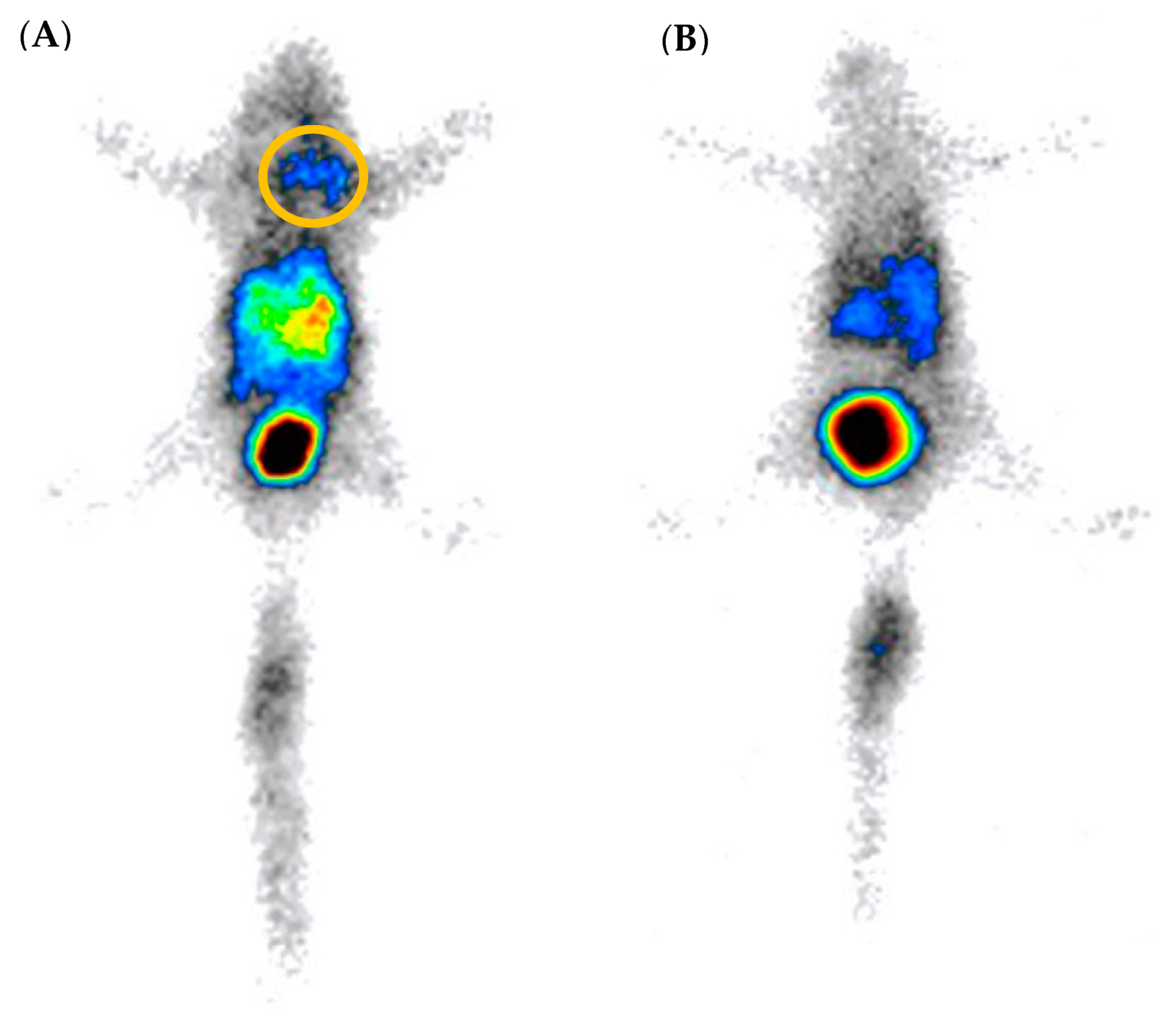
2.5. SPECT/CT Image and Scintigraphy Image
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. 99mTc Radiolabeling of HYNIC-cRDGfK-NPY
4.2. Radiochemical Control
4.3. Partition Coefficient (P) Determination
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. In Vitro Specific Binding to MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 Cells
4.6. Breast Cancer Tumor-Bearing Animal Model
4.7. Ex Vivo Biodistribution Studies
4.8. SPECT/CT Image and Scintigraphy Image
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Aboian, M.S.; Zhu, X.; Marquez-Nostra, B. Clinical Evaluation of Nuclear Imaging Agents in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luining, W.I.; Cysouw, M.C.F.; Meijer, D.; Hendrikse, N.H.; Boellaard, R.; Vis, A.N.; Oprea-Lager, D.E. Targeting PSMA Revolutionizes the Role of Nuclear Medicine in Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krȩcisz, P.; Czarnecka, K.; Królicki, L.; Mikiciuk-Olasik, E.; Szymański, P. Radiolabeled Peptides and Antibodies in Medicine. Bioconjug Chem. 2021, 32, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vall-Sagarra, A.; Litau, S.; Decristoforo, C.; Wängler, B.; Schirrmacher, R.; Fricker, G.; Wängler, C. Design, Synthesis, In Vitro, and Initial In Vivo Evaluation of Heterobivalent Peptidic Ligands Targeting Both NPY(Y1)- and GRP-Receptors—An Improvement for Breast Cancer Imaging? Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judmann, B.; Braun, D.; Wängler, B.; Schirrmacher, R.; Fricker, G.; Wängler, C. Current State of Radiolabeled Heterobivalent Peptidic Ligands in Tumor Imaging and Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, X. Peptide Heterodimers for Molecular Imaging. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Hübner, R.; von Kiedrowski, V.; Fricker, G.; Schirrmacher, R.; Wängler, C.; Wängler, B. Design, Synthesis, in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Heterobivalent Sifalin-Modified Peptidic Radioligands Targeting Both Integrin Av Β3 and the Mc1 Receptor—Suitable for the Specific Visualization of Melanomas? Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, S.; Rudolf, H.; Palumbo, G.; Oos, R.; Antons, M.; Hübner, R.; Bartenstein, P.; Schirrmacher, R.; Wängler, B.; Wängler, C. Are Heterobivalent GRPR- and VPAC1R-Bispecific Radiopeptides Suitable for Efficient in Vivo Tumor Imaging of Prostate Carcinomas? Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 48, 128241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xu, H. Integrins as Attractive Targets for Cancer Therapeutics. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, M.; Baneshi, M.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Mahmoudi, R.; Jabari Arabzadeh, A.; Akrami, M.; Mehrzad, J.; Bardania, H. Recent Progress in Biomedical Applications of RGD-Based Ligand: From Precise Cancer Theranostics to Biomaterial Engineering: A Systematic Review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2020, 108, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Niu, G.; Lang, L.; Li, F.; Fan, X.; Yan, X.; Yao, S.; Yan, W.; Huo, L.; Chen, L.; et al. Clinical Translation of a Dual Integrin Avβ3- and Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptor-Targeting PET Radiotracer, 68Ga-BBN-RGD. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shen, Z.; Ma, X.; Ren, W.; Xiang, L.; Gong, A.; Xia, T.; Guo, J.; Wu, A. Neuropeptide Y Y1 Receptors Mediate [Corrected] Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Drug with Encapsulated Nanoparticles to Breast Cancer Cells with High Selectivity and Its Potential for Breast Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5574–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y1-Mediated Effect of Neuropeptide Y in Cancer|Cancer Research|American Association for Cancer Research. Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/61/11/4636/507863/Y1-Mediated-Effect-of-Neuropeptide-Y-in (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Lin, S.T.; Li, Y.Z.; Sun, X.Q.; Chen, Q.Q.; Huang, S.F.; Lin, S.; Cai, S.Q. Update on the Role of Neuropeptide Y and Other Related Factors in Breast Cancer and Osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memminger, M.; Keller, M.; Lopuch, M.; Pop, N.; Bernhardt, G.; von Angerer, E.; Buschauer, A. The Neuropeptide Y Y1 Receptor: A Diagnostic Marker? Expression in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells Is Down-Regulated by Antiestrogens In Vitro and in Xenografts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Nguyen, Q.T. Molecular Imaging for Cancer Diagnosis and Surgery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, L.F.; Ferreira, A.H.; Thipe, V.C.; Varca, G.H.C.; Lima, C.S.A.; Batista, J.G.S.; Riello, F.N.; Nogueira, K.; Cruz, C.P.C.; Mendes, G.O.A.; et al. The State of the Art of Theranostic Nanomaterials for Lung, Breast, and Prostate Cancers. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Chen, X. Integrin Alpha(v)Beta(3)-Targeted Cancer Therapy. Drug Dev. Res. 2008, 69, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Bauwens, M. Molecular Imaging of Angiogenesis in Oncology: Current Preclinical and Clinical Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanovas, O.; Pons-Cursach, R. Mechanisms of Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. In Tumor Angiogenesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelstuen, O.K. Technetium-99m Chelators in Nuclear Medicine. A Review. Analyst 1995, 120, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, N.; Hosseinimehr, S.J.; Khalaj, A.; Noaparast, Z.; Abedi, S.M.; Sabzevari, O. 99mTc-Radiolabeled GE11-Modified Peptide for Ovarian Tumor Targeting. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 25, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decristoforo, C.; Mather, S.J. 99m-Technetium-Labelled Peptide-HYNIC Conjugates: Effects of Lipophilicity and Stability on Biodistribution. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1999, 26, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaonkar, R.H.; Ganguly, S.; Dewanjee, S.; Sinha, S.; Gupta, A.; Ganguly, S.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Chatterjee Debnath, M. Garcinol Loaded Vitamin E TPGS Emulsified PLGA Nanoparticles: Preparation, Physicochemical Characterization, in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunello, S.; Salvarese, N.; Carpanese, D.; Gobbi, C.; Melendez-Alafort, L.; Bolzati, C. A Review on the Current State and Future Perspectives of [99mTc]Tc-Housed PSMA-i in Prostate Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, I.C.F.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Cavadas, C.; Abrunhosa, A.J. PET Imaging of the Neuropeptide Y System: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Kim, J.; Ko, S.B.; Choi, Y.K.; Jeong, H.; Woo, H.; Kang, H.; Bang, I.; Kim, S.A.; Yoon, T.Y.; et al. Structural Basis of Neuropeptide Y Signaling through Y1 Receptor. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, Q.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. A Promising Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases: Neuropeptide Y Receptors in Humans. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Reichmann, F.; Farzi, A. Neuropeptide Y, Peptide YY and Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Gut–Brain Axis. Neuropeptides 2012, 46, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitto, J.M.; Huang, Z.; McCarthy, D.B. Molecular Cloning of NPY-Y1 Receptor CDNA from Rat Splenic Lymphocytes: Evidence of Low Levels of MRNA Expression and [125I]NPY Binding Sites. J. Neuroimmunol. 1994, 54, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmström, R.E.; Hökfelt, T.; Björkman, J.A.; Nihlén, C.; Byström, M.; Ekstrand, A.J.; Lundberg, J.M. Characterization and Molecular Cloning of Vascular Neuropeptide Y Receptor Subtypes in Pig and Dog. Regul. Pept. 1998, 75–76, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.C.; Liu, Y.B.; Liu, W.F.; Zhou, Y.Y.; He, H.F.; Lin, S. Neuropeptide Y Is an Immunomodulatory Factor: Direct and Indirect. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, A. Neuropeptide Y Receptors: A Promising Target for Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Regen. Biomater. 2015, 2, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xie, Y.; Fu, T.; Qiu, F.; Yu, F.; Qu, W.; Yao, X.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Z.; Shao, G.; et al. [99mTc]Tc-Galacto-RGD2 Integrin Avβ3-Targeted Imaging as a Surrogate for Molecular Phenotyping in Lung Cancer: Real-World Data. EJNMMI Res. 2021, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.; Maschauer, S.; Brennauer, A.; Tripal, P.; Koglin, N.; Dittrich, R.; Bernhardt, G.; Kuwert, T.; Wester, H.J.; Buschauer, A.; et al. Prototypic 18F-Labeled Argininamide-Type Neuropeptide Y Y1R Antagonists as Tracers for PET Imaging of Mammary Carcinoma. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decristoforo, C.; Faintuch-Linkowski, B.; Rey, A.; von Guggenberg, E.; Rupprich, M.; Hernandez-Gonzales, I.; Rodrigo, T.; Haubner, R. [99mTc]HYNIC-RGD for Imaging Integrin Avβ3 Expression. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadpour, S.; Noaparast, Z.; Abedi, S.M.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. 99mTc-HYNIC-(Tricine/EDDA)-FROP Peptide for MCF-7 Breast Tumor Targeting and Imaging. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, K.; Mukherjee, D.; Sinha, S.; Ganguly, S. HYNIC and DOMA Conjugated Radiolabeled Bombesin Analogs as Receptor-Targeted Probes for Scintigraphic Detection of Breast Tumor. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organ/Time | 5 min | 30 min | 1 h | 2 h | 4 h | 6 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | 4.30 ± 1.32 | 3.21 ± 1.22 | 1.04 ± 0.23 | 0.55 ± 0.07 | 0.35 ± 0.12 | 0.33 ± 0.09 |
| Lung | 9.80 ± 3.16 | 4.80 ± 2.67 | 2.64 ± 0.83 | 1.17 ± 0.20 | 0.63 ± 0.17 | 1.65 ± 2.02 |
| Spleen | 6.06 ± 2.90 | 6.14 ± 2.29 | 3.41 ± 1.17 | 2.22 ± 0.37 | 1.69 ± 0.34 | 1.98 ± 0.63 |
| Stomach | 8.05 ± 2.56 | 7.17 ± 1.38 | 3.97 ± 0.78 | 2.62 ± 0.68 | 1.81 ± 0.50 | 1.79 ± 0.58 |
| Pancreas | 3.39 ± 0.92 | 2.52 ± 0.89 | 1.17 ± 0.45 | 0.53 ± 0.10 | 0.35 ± 0.12 | 0.34 ± 0.11 |
| Muscle | 2.16 ± 0.62 | 1.50 ± 0.41 | 0.68 ± 0.33 | 0.39 ± 0.09 | 0.22 ± 0.07 | 0.21 ± 0.03 |
| Bone | 3.19 ± 0.76 | 3.71 ± 1.37 | 2.52 ± 1.67 | 0.71 ± 0.22 | 0.46 ± 0.14 | 0.54 ± 0.28 |
| Brain | 0.37 ± 0.11 | 0.22 ± 0.15 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| Organ/Tumor Model | MCF-7 | MDA-MB231 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Block | Block | Non-Block | Block | |
| Blood * | 1.66 ± 0.89 | 0.92 ± 0.07 | 1.80 ± 1.03 | 1.40 ± 0.21 |
| Heart | 1.53 ± 0.45 | 0.65 ± 0.24 | 1.48 ± 0.29 | 0.74 ± 0.20 |
| Lungs | 3.58 ± 1.22 | 1.59 ± 0.34 | 3.27 ± 0.47 | 1.95 ± 0.60 |
| Kidneys | 24.55 ± 8.60 | 20.80 ± 7.02 | 19.30 ± 2.89 | 12.99 ± 2.68 |
| Spleen | 5.33 ± 1.88 | 2.53 ± 0.74 | 5.02 ± 0.63 | 1.51 ± 0.22 |
| Stomach | 6.04 ± 1.15 | 2.98 ± 0.57 | 5.63 ± 0.96 | 2.05 ± 0.33 |
| Pancreas | 1.62 ± 0.30 | 1.12 ± 0.42 | 1.35 ± 0.35 | 0.70 ± 0.21 |
| Liver | 3.61 ± 0.73 | 1.84 ± 0.13 | 3.75 ± 0.51 | 1.41 ± 0.62 |
| Large Intestine | 6.41 ± 1.63 | 3.91 ± 2.11 | 5.18 ± 0.87 | 2.22 ± 0.98 |
| Small Intestine | 10.32 ± 2.18 | 3.77 ± 0.95 | 8.30 ± 1.36 | 2.16 ± 0.74 |
| Muscle | 1.56 ± 1.41 | 0.59 ± 0.37 | 0.88 ± 0.13 | 0.33 ± 0.02 |
| Bone | 1.40 ± 0.72 | 1.08 ± 0.77 | 1.22 ± 0.28 | 0.53 ± 0.16 |
| Brain | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.01 |
| Tumor | 9.30 ± 3.25 | 4.41 ± 2.13 | 4.93 ± 1.01 | 2.30 ± 0.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, A.H.; Real, C.C.; Malafaia, O. Heterobivalent Dual-Target Peptide for Integrin-αvβ3 and Neuropeptide Y Receptors on Breast Tumor. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101328
Ferreira AH, Real CC, Malafaia O. Heterobivalent Dual-Target Peptide for Integrin-αvβ3 and Neuropeptide Y Receptors on Breast Tumor. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101328
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Aryel H., Caroline C. Real, and Osvaldo Malafaia. 2024. "Heterobivalent Dual-Target Peptide for Integrin-αvβ3 and Neuropeptide Y Receptors on Breast Tumor" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101328
APA StyleFerreira, A. H., Real, C. C., & Malafaia, O. (2024). Heterobivalent Dual-Target Peptide for Integrin-αvβ3 and Neuropeptide Y Receptors on Breast Tumor. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101328








