GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Promising Therapy for Modern Lifestyle Diseases with Unforeseen Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Structure, Synthesis, Action, and Catabolism of GLP-1
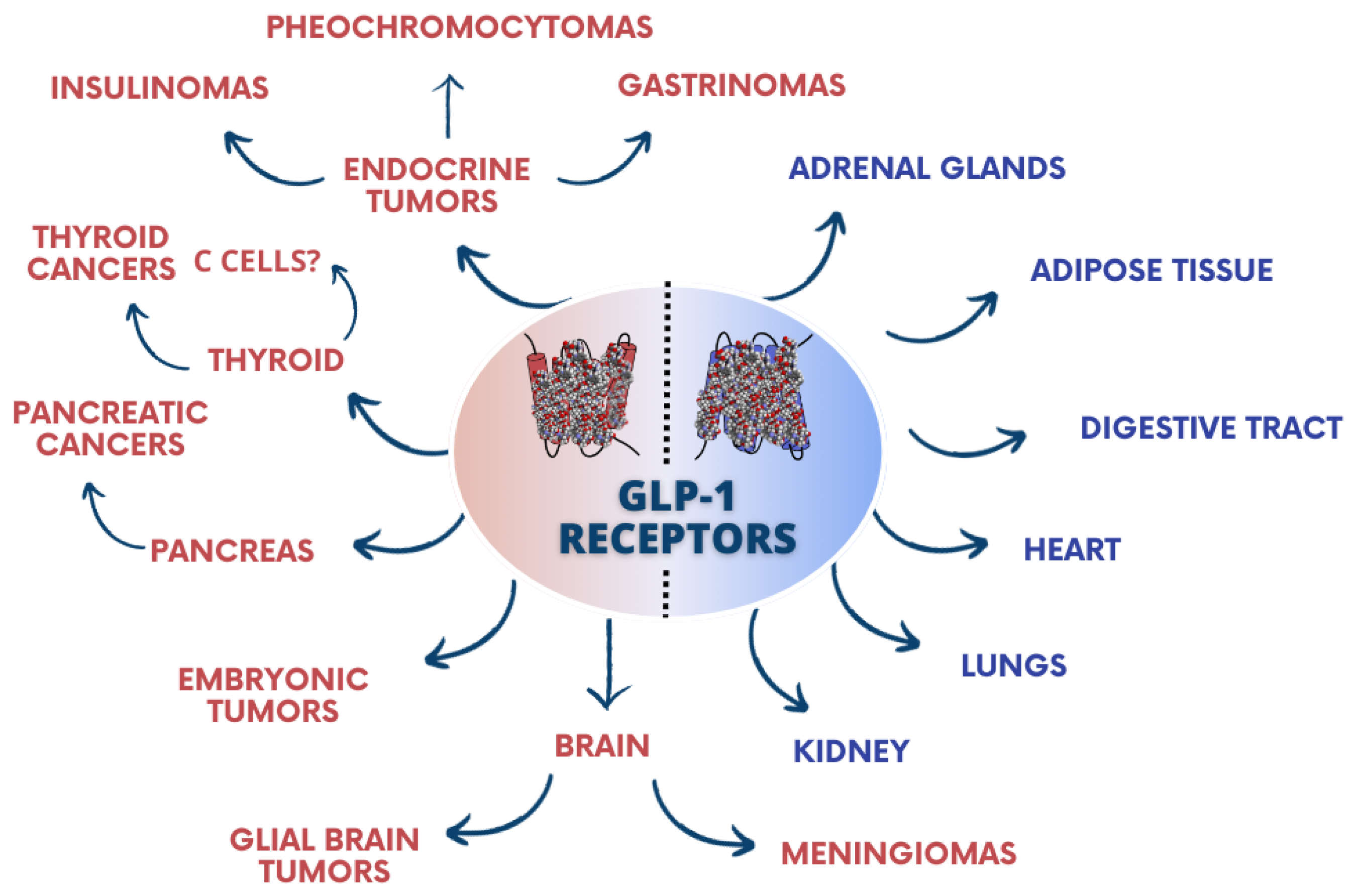
1.2. GLP-1 Receptors
1.3. GLP-1RA and Receptor Agonists and Their Application
2. Methods
Eligibility Criteria
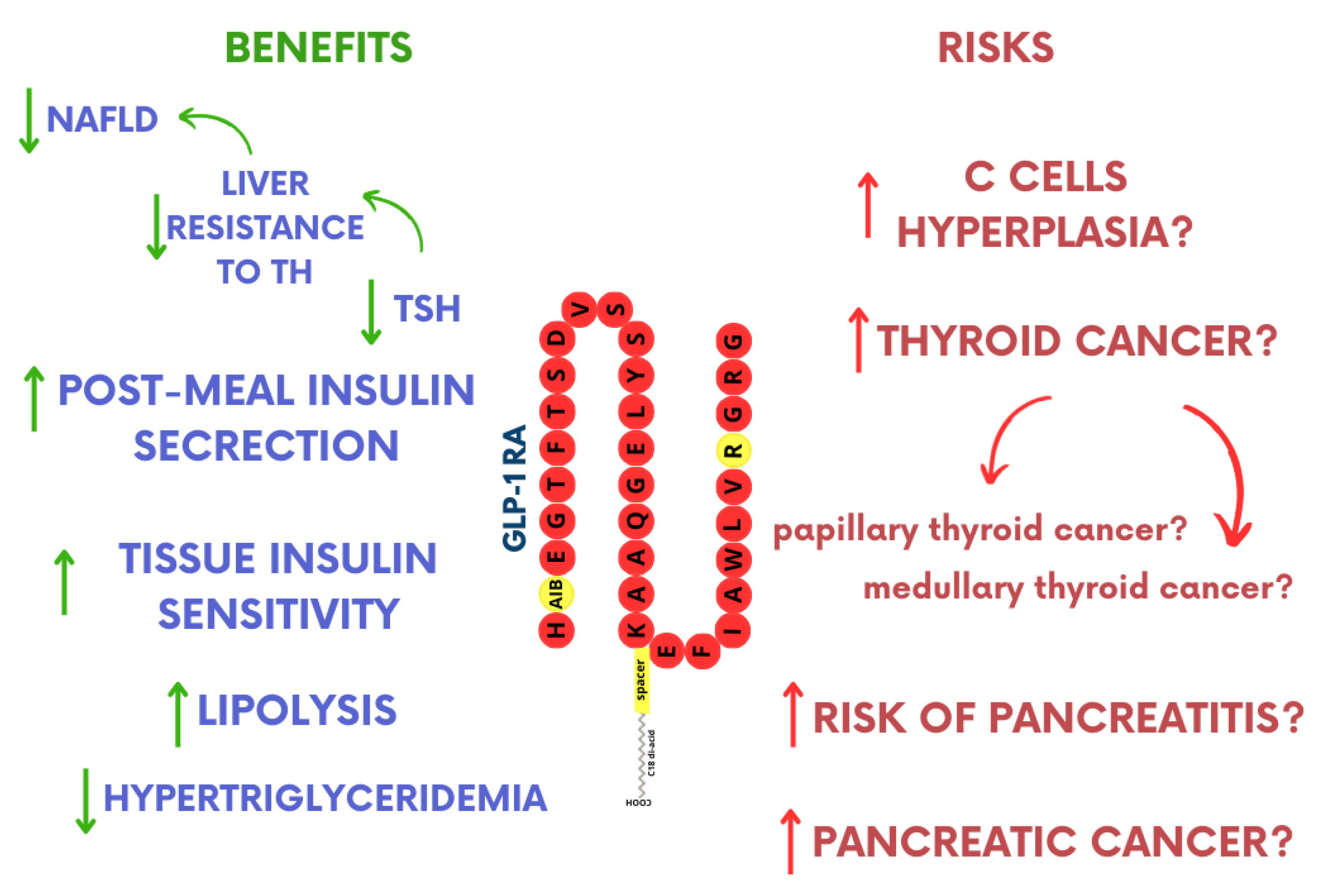
3. GLP-1RA Influence on Thyroid Function
3.1. The Influence on TSH Levels
3.2. C-Cell Hyperplasia and Thyroid Cancer
GLP-1RA and Safety of Use
3.3. C-Cell Hyperplasia and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
3.4. Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
4. The Impact of GLP-1RA on the Pancreas
4.1. GLP-1RA and the Function of Beta Cells
4.2. Pancreatitis Risk
4.3. GLP-1RA and Pancreatic Cancer
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Challenges, Limitations, and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| Aib-2 | Aminoisobutyric acid |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CCH | C-cell hyperplasia |
| CFDA | China Food and Drug Administration |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FAERS | FDA Adverse Event Reporting System |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FT3 | Triiodothyronine |
| FT4 | Thyroxine |
| GLP-1RA | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists |
| GLP-2 | Glucagon-like peptide-2 |
| GRPP | Glicentin-related pancreatic polypeptide |
| HIF-1 | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1- α |
| HOMA-B | Homeostasis model assessment index of β-cel |
| IP-2 | Intervening peptide-2 |
| MEN 2 | Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NMPA | National Medical Products Administration |
| PC 1/3 | Prohormone convertase 1/3 |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PTC | Papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| SCD | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TH | Thyroid hormones |
| TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| TZD | Thiazolidinediones |
References
- Xu, D.; Nair, A.; Sigston, C.; Ho, C.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Liao, X.; Chen, W.; Kuang, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Potential Roles of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in Nondiabetic Populations. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2007, 3, 154–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, F.K.; Aroda, V.R.; Vale, R.D.D.; Holst-Hansen, T.; Laursen, P.N.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubino, D.M.; Garvey, W.T. Oral semaglutide 50 mg taken once per day in adults with overweight or obesity (OASIS 1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliaki, C.; Doupis, J. Incretin-based therapy: A powerful and promising weapon in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2011, 2, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.K.; Chang, R.B.; Strochlic, D.E.; Umans, B.D.; Lowell, B.B.; Liberles, S.D. Sensory Neurons that Detect Stretch and Nutrients in the Digestive System. Cell 2016, 166, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirra, J.; Göke, B. The physiological role of GLP-1 in human: Incretin, ileal brake or more? Regul. Pept. 2005, 128, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, D. Is GLP-1 a hormone: Whether and When? J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Akindehin, S.E.; Orsso, C.E.; Waldner, R.C.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Müller, T.D.; Haqq, A.M. Recent Advances in Incretin-Based Pharmacotherapies for the Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 838410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Guan, Y.; Hua, X. Glucagon-like peptide 1-potentiated insulin secretion and proliferation of pancreatic β-cells. J. Diabetes. 2014, 6, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plamboeck, A.; Holst, J.J.; Carr, R.D.; Deacon, C.F. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 and dipeptidyl peptidase IV are both mediators of the degradation of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the anaesthetised pig. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Verma, S.; Vaidya, S.; Kalia, K.; Tiwari, V. Recent updates on GLP-1 agonists: Current advancements & challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoffel, M.; Espinosa, R.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bell, G.I. Human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene. Localization to chromosome band 6p21 by fluorescence in situ hybridization and linkage of a highly polymorphic simple tandem repeat DNA polymorphism to other markers on chromosome 6. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; de Graaf, C.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, K.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Lin, G.; et al. Human GLP-1 receptor transmembrane domain structure in complex with allosteric modulators. Nature 2017, 546, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, P.L.; Drucker, D.J. Structure-function of the glucagon receptor family of G protein-coupled receptors: The glucagon, GIP, GLP-1, and GLP-2 receptors. Recept Channels 2002, 8, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Lau, J. The Discovery and Development of Liraglutide and Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, C.; Heller, R.S.; Kirk, R.K.; Ørskov, C.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Kaastrup, P.; Hvelplund, A.; Bardram, L.; Calatayud, D.; Knudsen, L.B. GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: Novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrell, J.; El Bekay, R.; Peral, B.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Megia, A.; Macías-González, M.; Fernández Real, J.; Jiménez-Gómez, Y.; Escoté, X.; Pachón, G.; et al. Study of the potential association of adipose tissue GLP-1 receptor with obesity and insulin resistance. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, M.; Stöckli, M.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.C. GLP-1 receptor expression in human tumors and human normal tissues: Potential for in vivo targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Madsen, L.W.; Andersen, S.; Almholt, K.; de Boer, A.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Gotfredsen, C.; Egerod, F.L.; Hegelund, A.C.; Jacobsen, H.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists activate rodent thyroid C-cells causing calcitonin release and C-cell proliferation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gier, B.; Butler, P.C.; Lai, C.K.; Kirakossian, D.; DeNicola, M.M.; Yeh, M.W. Glucagon like peptide-1 receptor expression in the human thyroid gland. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Secher, A.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Pyke, C. Long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists have direct access to and effects on pro-opiomelanocortin/cocaine- and amphetamine-stimulated transcript neurons in the mouse hypothalamus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malendowicz, L.K.; Neri, G.; Nussdorfer, G.G.; Nowak, K.W.; Zyterska, A.; Ziolkowska, A. Prolonged exendin-4 administration stimulates pituitary-adrenocortical axis of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 12, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malendowicz, L.K.; Nussdorfer, G.G.; Nowak, K.W.; Ziolkowska, A.; Tortorella, C.; Trejter, M. Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, stimulates pituitary-adrenocortical axis in the rat: Investigations into the mechanism(s) underlying Ex4 effect. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 12, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J. Treatment of type 2 diabetes. Internist 2016, 57, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists for individualized treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes—State-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; He, L.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, D.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Hou, D.; Ouyang, C.; et al. Polyethylene Glycol Loxenatide Injection (GLP-1) Protects Vascular Endothelial Cell Function in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients With Type 2 Diabetes by Regulating Gut Microbiota. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 879294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadouh, H.; Chedid, V.; Halawi, H.; Burton, D.D.; Clark, M.M.; Khemani, D.; Vella, A.; Acosta, A.; Camilleri, M. GLP-1 Analog Modulates Appetite, Taste Preference, Gut Hormones, and Regional Body Fat Stores in Adults with Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Neil, P.M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; McGowan, B.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; Wharton, S.; Carson, C.G.; Jepsen, C.H.; Kabisch, M.; Wilding, J.P.H. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, D.M.; Greenway, F.L.; Khalid, U.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Sørrig, R.; Wadden, T.A.; Wizert, A.; Garvey, W.T. Effect of Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs. Daily Liraglutide on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity Without Diabetes: The STEP 8 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maselli, D.B.; Camilleri, M. Effects of GLP-1 and Its Analogs on Gastric Physiology in Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1307, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Saxena, N.K.; Lin, S.; Gupta, N.A.; Anania, F.A. Exendin-4, a glucagon-like protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, reverses hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatology 2006, 43, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wretlind, A.; Zobel, E.H.; de Zawadzki, A.; Ripa, R.S.; Curovic, V.R.; von Scholten, B.J.; Mattila, I.M.; Hansen, T.W.; Kjær, A.; Vestergaard, H.; et al. Liraglutide Lowers Palmitoleate Levels in Type 2 Diabetes. A Post Hoc Analysis of the LIRAFLAME Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2022, 3, 856485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Gaunt, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Barton, D.; Hull, D.; Parker, R.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Guo, K.; Abouda, G.; Aldersley, M.A.; et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.R.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Oh, I.J.; Choi, D.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, I.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.H.; et al. A GLP-1/GLP-2 receptor dual agonist to treat NASH: Targeting the gut-liver axis and microbiome. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, M.K.; Thomsen, M.; Wortwein, G.; Fink-Jensen, A. The role of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in addictive disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuong, V.; Farokhnia, M.; Khom, S.; Pince, C.L.; Elvig, S.K.; Vlkolinsky, R.; Marchette, R.C.; Koob, G.F.; Roberto, M.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; et al. The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue semaglutide reduces alcohol drinking and modulates central GABA neurotransmission. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e170671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kahng, M.W.; Elkind, J.A.; Weir, V.R.; Hernandez, N.S.; Stein, L.M.; Schmidt, H.D. Activation of GLP-1 receptors attenuates oxycodone taking and seeking without compromising the antinociceptive effects of oxycodone in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuesta, L.M.; Chen, Z.; Duncan, A.; Fowler, C.D.; Ishikawa, M.; Lee, B.R.; Liu, X.-A.; Lu, Q.; Cameron, M.; Hayes, M.R.; et al. GLP-1 acts on habenular avoidance circuits to control nicotine intake. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, F. Successful Pregnancy after Improving Insulin Resistance with the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue in a Woman with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2016, 81, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highlights of Prescribing Information. 2017. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209637lbl.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Greco, D. Normal pregnancy outcome after first-trimester exposure to liraglutide in a woman with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2015, 32, e29–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezin, J.; Gouverneur, A.; Pénichon, M.; Mathieu, C.; Garrel, R.; Hillaire-Buys, D.; Pariente, A.; Faillie, J.-L. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Duan, X.X.; Yuan, M.C.; Yu, J.; Hu, X.; Han, X.; Lan, L.; Liu, B.W.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J.F. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation by liraglutide promotes breast cancer through NOX4/ROS/VEGF pathway. Life Sci. 2022, 294, 120370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sande, C.M.; Tondi Resta, I.; Livolsi, V.A. The Thyroid Pathologist Meets Therapeutic Pharmacology. Endocr. Pathol. 2023, 34, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.W.; Knauf, J.A.; Gotfredsen, C.; Pilling, A.; Sjögren, I.; Andersen, S.; Andersen, L.; de Boer, A.S.; Manova, K.; Barlas, A.; et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists and the thyroid: C-cell effects in mice are mediated via the GLP-1 receptor and not associated with RET activation. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Friedrich, N. Do GLP-1-based therapies increase cancer risk? Diabetes Care 2013, 36, S245–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, F.K.; Brønden, A.; Vilsbøll, T. Exenatide: Pharmacokinetics, clinical use, and future directions. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, S.A.; Tsatlidis, V.; Razvi, S. The GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide reduces serum TSH by its effect on body weight in people with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Endocrinol. 2023, 99, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, O.M.; Sofopoulos, M.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Dincer, F.; Thakkar, B.; Sahin-Efe, A.; Filippaios, A.; Bowers, J.; Srnka, A.; Gavrieli, A.; et al. GLP-1 receptors exist in the parietal cortex, hypothalamus and medulla of human brains and the GLP-1 analogue liraglutide alters brain activity related to highly desirable food cues in individuals with diabetes: A crossover, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lin, Z.; Wang, H.; Teng, W.; Shan, Z. Causal Association Between Serum Thyrotropin and Obesity: A Bidirectional, Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e4251–e4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, C. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Thyroid Function in Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 3292–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lips, M.A.; Pijl, H.; van Klinken, J.B.; de Groot, G.H.; Janssen, I.M.; Van Ramshorst, B.; Van Wagensveld, B.A.; Swank, D.J.; Van Dielen, F.; Smit, J.W. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and calorie restriction induce comparable time-dependent effects on thyroid hormone function tests in obese female subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencar, M.E.; Sakiz, D.; Calapkulu, M.; Hepsen, S.; Kizilgul, M.; Ozturk, I.U.; Ucan, B.; Bayram, M.; Cagir, B.B.; Akin, S.; et al. The Effect of Exenatide on Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Volume. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2019, 8, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köseoğlu, D.; Özdemir Başer, Ö.; Berker, D.; Güler, S. Exenatide Treatment Reduces Thyroid Gland Volume, but Has No Effect on The Size of Thyroid Nodules. Acta Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Albores-Saavedra, J.A.; Krueger, J.E. C-cell hyperplasia and medullary thyroid microcarcinoma. Endocr. Pathol. 2001, 12, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, G.; Bhargav, P.M. A Study of Hormonal Abnormalities in Chronic Liver Disease. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2019, 67, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Borges-Canha, M.; Neves, J.S.; Mendonça, F.; Silva, M.M.; Costa, C.; Cabral, P.M.; Guerreiro, V.; Lourenço, R.; Meira, P.; Salazar, D.; et al. Thyroid Function and the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Morbid Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 572128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Xu, J.; Wen, W.; Huang, B. Effect of Liraglutide on Serum TSH Levels in Patients with NAFLD and its Underlying Mechanisms. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 1786559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouwels, S.; Sakran, N.; Graham, Y.; Leal, A.; Pintar, T.; Yang, W.; Kassir, R.; Singhal, R.; Mahawar, K.; Ramnarain, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mali, G.; Ahuja, V.; Dubey, K. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues and thyroid cancer: An analysis of cases reported in the European pharmacovigilance database. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Yu, M.; Mei, M.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, S.; Li, R. GLP-1 receptor agonist-associated tumor adverse events: A real-world study from 2004 to 2021 based on FAERS. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 925377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, B.H. Current Guidelines for Management of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, H.; Koo, H.L. Medullary thyroid carcinoma with diabetic ketoacidosis: An autopsy case report and literature review. Forensic. Sci. Med. Pathol. 2021, 17, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodish, M.B.; Stratakis, C.A. RET oncogene in MEN2, MEN2B, MTC and other forms of thyroid cancer. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2008, 8, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra, L.; Bg, H.; Sharma, M.; Dutta, D. Semaglutide and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2023, 17, 102834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.Y.; Shih, S.R.; Tseng, C.H. A review on the association between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 924168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.J.; Waller, P.C.; Davis, S. Use of proportional reporting ratios (PRRs) for signal generation from spontaneous adverse drug reaction reports. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2001, 10, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Agrawal, V.; Pani, K.C.; Verma, R.; Jaiswal, S.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, R. C-cell hyperplasia in sporadic and familial medullary thyroid carcinoma. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2018, 61, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machens, A.; Hoffmann, F.; Sekulla, C.; Dralle, H. Importance of gender-specific calcitonin thresholds in screening for occult sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costante, G.; Meringolo, D.; Durante, C.; Bianchi, D.; Nocera, M.; Tumino, S.; Crocetti, U.; Attard, M.; Maranghi, M.; Torlontano, M.; et al. Predictive value of serum calcitonin levels for preoperative diagnosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma in a cohort of 5817 consecutive patients with thyroid nodules. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulchandani, D.; Nachnani, J.S.; Herndon, B.; Molteni, A.; Pathan, M.H.; Quinn, T.; Hamdan, H.A.; Alba, L.M.; Graves, L. Effect of exendin (exenatide)--GLP 1 receptor agonist on the thyroid and parathyroid gland in a rat model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 691, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedüs, L.; Sherman, S.I.; Tuttle, R.M.; von Scholten, B.J.; Rasmussen, S.; Karsbøl, J.D.; Daniels, G.H. No Evidence of Increase in Calcitonin Concentrations or Development of C-Cell Malignancy in Response to Liraglutide for up to 5 Years in the LEADER Trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedüs, L.; Moses, A.C.; Zdravkovic, M.; Le Thi, T.; Daniels, G.H. GLP-1 and calcitonin concentration in humans: Lack of evidence of calcitonin release from sequential screening in over 5000 subjects with type 2 diabetes or nondiabetic obese subjects treated with the human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; McDow, A.D.; Saeed, Z.; Hou, T. Multifocal C-cell Hyperplasia and Marked Hypercalcitoninemia in a Diabetic Patient Treated With Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Agonist With Concurrent Multinodular Goiter and Hyperparathyroidism. Cureus 2023, 15, e33384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, P.F.; Baruch, H. Is calcitonin an important physiological substance? Endocrine 2003, 21, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lewin, E.; Olgaard, K. Role of calcitonin in the rapid minute-to-minute regulation of plasma Ca2+ homeostasis in the rat. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosol, T.J. On-target effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on thyroid C-cells in rats and mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, B.; Blank, A.; Karamitopoulou, E.; Perren, A.; Reubi, J.C. Glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor expression in normal and diseased human thyroid and pancreas. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, M.; Cao, Y.; Qi, J.; Geng, J.; Liu, X. Expression of GLP-1 receptor and CD26 in human thyroid C-cells: The association of thyroid C-cell tumorigenesis with incretin-based medicine. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2684–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Gu, L.; Guo, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z. GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide inhibits the proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cells. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, M.M.; Van Raalte, D.H. Safety of Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 645563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randle, R.W.; Balentine, C.J.; Leverson, G.E.; Havlena, J.A.; Sippel, R.S.; Schneider, D.F.; Pitt, S.C. Trends in the presentation, treatment, and survival of patients with medullary thyroid cancer over the past 30 years. Surgery 2017, 161, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, S.A.; Asa, S.L.; Dralle, H.; Elisei, R.; Evans, D.B.; Gagel, R.F.; Lee, N.; Machens, A.; Moley, J.F.; Pacini, F.; et al. Revised American Thyroid Association guidelines for the management of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 2015, 25, 567–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschebrook-Kilfoy, B.; Ward, M.H.; Sabra, M.M.; Devesa, S.S. Thyroid cancer incidence patterns in the United States by histologic type, 1992-2006. Thyroid 2011, 21, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chair, R.T.K.; Eng, C.; Evans, D.B.; Francis, G.L.; Gagel, R.F.; Gharib, H.; Moley, J.F.; Pacini, F.; Ringel, M.D.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Medullary thyroid cancer: Management guidelines of the American Thyroid Association. Thyroid 2009, 19, 565–612. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: Established and emerging indications. Lancet 2021, 398, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespel, A.; De Boisvilliers, F.; Gros, L.; Kervran, A. Effects of glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide on C cells from rat thyroid and medullary thyroid carcinoma CA-77 cell line. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 3674–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.; Welch, H.G. Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973–2002. JAMA 2006, 295, 2164–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.J.; Kwon, S.K. Expression of glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its clinicopathologic significance. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 29, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Maksoud, R.S.; Elsayed, W.S.H.; Rashad, N.M.; Elsayed, R.S.; Elshorbagy, S.; Hamed, M.G. GLP-1R polymorphism (rs1042044) and expression are associated with the risk of papillary thyroid cancer among the Egyptian population. Gene 2022, 834, 146597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternak, B.; Wintzell, V.; Hviid, A.; Eliasson, B.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Jonasson, C.; Hveem, K.; Svanström, H.; Melbye, M.; Ueda, P. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist use and risk of thyroid cancer: Scandinavian cohort study. BMJ 2024, 385, e078225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bea, S.; Son, H.; Bae, J.H.; Cho, S.W.; Shin, J.Y.; Cho, Y.M. Risk of thyroid cancer associated with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, P.S. Overview of the pancreas. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 690, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, M.P.; Pratley, R.E. GLP-1 Analogs and DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Therapy: Review of Head-to-Head Clinical Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashoff, M.; Matveyenko, A.V.; Gier, B.; Elashoff, R.; Butler, P.C. Pancreatitis, pancreatic, and thyroid cancer with glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsbøll, T. The effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on the beta cell. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlessi, R.; Chen, Y.; Rowlands, J.; Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.N.; Egan, L.; Mamotte, C.; Stokes, R.; Gunton, J.E.; Bittencourt, P.I.H.; et al. GLP-1 receptor signalling promotes β-cell glucose metabolism via mTOR-dependent HIF-1α activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, M.; Madsbad, S.; Madsen, J.L.; Holst, J.J. Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: A parallel-group study. Lancet 2002, 359, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Rosenstock, J.; Sesti, G.; Schmidt, W.E.; Montanya, E.; Brett, J.H.; Zychma, M.; Blonde, L.; LEAD-6 Study Group. Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: A 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet 2009, 374, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.N.; Ndefo, U.A.; Oliver, A.; Payton, E. Albiglutide: A once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2015, 72, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, A.B.; Knop, F.K.; Christensen, M. Lixisenatide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Drugs Today 2013, 49, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. Dulaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, M.A.; Halter, J.B.; Porte, D. Insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Med. 1981, 70, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsbøll, T.; Brock, B.; Perrild, H.; Levin, K.; Lervang, H.H.; Kølendorf, K.; Krarup, T.; Schmitz, O.; Zdravkovic, M.; Le-Thi, T.; et al. Liraglutide, a once-daily human GLP-1 analogue, improves pancreatic B-cell function and arginine-stimulated insulin secretion during hyperglycaemia in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Z. GLP-1 receptor agonists and pancreatic safety concerns in type 2 diabetic patients: Data from cardiovascular outcome trials. Endocrine 2020, 68, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Kawamura, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Nieda, M.; Okazawa, T.; Takemoto, M.; Shimada, F. A low-grade increase of serum pancreatic exocrine enzyme levels by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 100, e66–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lando, H.M.; Alattar, M.; Dua, A.P. Elevated amylase and lipase levels in patients using glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonists or dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitors in the outpatient setting. Endocr. Pract. 2012, 18, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.M.; Tonneijck, L.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Diamant, M.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Cahen, D.L.; van Raalte, D.H. Acute plasma amylase increase after glucagon-like peptide -1 receptor agonist exenatide administration in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, W.M.; Buse, J.B.; Ghorbani, M.L.M.; Ørsted, D.D.; Nauck, M.A.; LEADER Steering Committee; LEADER Trial Investigators. Amylase, Lipase, and Acute Pancreatitis in People with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Liraglutide: Results From the LEADER Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cure, P.; Pileggi, A.; Alejandro, R. Exenatide and rare adverse events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1969–1970; discussion 1971–1972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Richards, T.M.; Weiner, J.P.; Clark, J.M.; Segal, J.B. Glucagonlike peptide 1-based therapies and risk of hospitalization for acute pancreatitis in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population-based matched case-control study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Lin, Y.H.; Dai, L.Z.; Lin, C.S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.Y. Efficacy and safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists versus SGLT-2 inhibitors in overweight/obese patients with or without diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e061807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tang, H.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, B.; Yu, C. Exenatide-induced chronic damage of pancreatic tissue in rats. Pancreas 2012, 41, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Duke, J. Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies and risk of pancreatitis: A self-controlled case series analysis. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2014, 23, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, D.D.; Seeger, J.D.; Arnold Chan, K. Use of a claims-based active drug safety surveillance system to assess the risk of acute pancreatitis with exenatide or sitagliptin compared to metformin or glyburide. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2009, 25, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funch, D.; Gydesen, H.; Tornøe, K.; Major-Pedersen, A.; Chan, K.A. A prospective, claims-based assessment of the risk of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer with liraglutide compared to other antidiabetic drugs. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Batel-Marques, F.; Macedo, A.F. A meta-analysis of serious adverse events reported with exenatide and liraglutide: Acute pancreatitis and cancer. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 98, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenten, M.; Gaebler, J.A.; Hussein, M.; Pelletier, E.M.; Smith, D.B.; Girase, P.; Noel, R.A.; Braun, D.K.; Bloomgren, G.L. Relative risk of acute pancreatitis in initiators of exenatide twice daily compared with other anti-diabetic medication: A follow-up study. Diabet. Med. 2012, 29, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhite, K.; Reid, J.M.; Lane, M. Risk of Pancreatitis With Incretin Therapies Versus Thiazolidinediones in the Veterans Health Administration. Ann. Pharmacother. 2024, 58, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, L.E.M.; Marinho, T.S.; Martins, F.F.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Treatment with semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, improves extracellular matrix remodeling in the pancreatic islet of diet-induced obese mice. Life Sci. 2023, 319, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukherjee, A.; Morales-Scheihing, D.; Butler, P.C.; Soto, C. Type 2 diabetes as a protein misfolding disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.; Weinstock, R.S.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Guerci, B.; Skrivanek, Z.; Milicevic, Z. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide versus sitagliptin after 52 weeks in type 2 diabetes in a randomized controlled trial (AWARD-5). Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.B.; Shah, A.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, M.I.; Amir, A. Dulaglutide (Trulicity)-Induced Acute Pancreatitis: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e38630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nreu, B.; Dicembrini, I.; Tinti, F.; Mannucci, E.; Monami, M. Pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Minerva Endocrinol. 2023, 48, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, A.G.; Blind, E.; Dunder, K.; de Graeff, P.A.; Hummer, B.T.; Bourcier, T.; Rosebraugh, C. Pancreatic safety of incretin-based drugs--FDA and EMA assessment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebours, V.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Schnee, M.; Ferec, C.; Le Marechal, C.; Hentic, O.; Maire, F.; Hammel, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Levy, P. The natural history of hereditary pancreatitis: A national series. Gut 2009, 58, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoud, R.; Drucker, D.J. Beyond the pancreas: Contrasting cardiometabolic actions of GIP and GLP1. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, M.H.; Pereira, M.J.; Eriksson, J.W. Glucose-dependent inflammatory responses in obese compared to lean individuals. Endocrine 2023, 81, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiri, A.; Al Qarni, A.; Bakillah, A. The Interlinking Metabolic Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Insights. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemesh, E.; Zafrir, B. Hypertriglyceridemia-Related Pancreatitis In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Links And Risks. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Half-Life | Dosage | Approved Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exenatide | 2.4 h | twice-daily injections | April 2005 (FDA) |
| Liraglutide | 13 h | once-daily injections | January 2010 (FDA) |
| Exenatide | Exenatide extended-release, peak at 840 h [3] | once-weekly injections | January 2012 (FDA) |
| Albiglutide | 120 h | once-weekly injections | April 2014 (FDA) |
| Dulaglutide | 90 h | once-weekly injections | September 2014 (FDA) |
| Lixisenatide | 3–4 h | once-daily injections | July 2016 (FDA) |
| Beinaglutide | 1–2 min | three times-daily injections | December 2016 (NMPA) |
| Semaglutide | 160 h | once-weekly injections | December 2017 (FDA) |
| 7 days | once-daily oral | September 2019 | |
| PEG-loxenatide | 80 h | once-weekly injections | May 2019 (CFDA) |
| Tirzepatide | 5 days | once-weekly injections | May 2022 (CFDA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kupnicka, P.; Król, M.; Żychowska, J.; Łagowski, R.; Prajwos, E.; Surówka, A.; Chlubek, D. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Promising Therapy for Modern Lifestyle Diseases with Unforeseen Challenges. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111470
Kupnicka P, Król M, Żychowska J, Łagowski R, Prajwos E, Surówka A, Chlubek D. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Promising Therapy for Modern Lifestyle Diseases with Unforeseen Challenges. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(11):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111470
Chicago/Turabian StyleKupnicka, Patrycja, Małgorzata Król, Justyna Żychowska, Ryszard Łagowski, Eryk Prajwos, Anna Surówka, and Dariusz Chlubek. 2024. "GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Promising Therapy for Modern Lifestyle Diseases with Unforeseen Challenges" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 11: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111470
APA StyleKupnicka, P., Król, M., Żychowska, J., Łagowski, R., Prajwos, E., Surówka, A., & Chlubek, D. (2024). GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Promising Therapy for Modern Lifestyle Diseases with Unforeseen Challenges. Pharmaceuticals, 17(11), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111470





