Integrated Network-Based Analysis of Diseases Associated with Amyloid Deposition Through a Disease–Protein–Drug Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
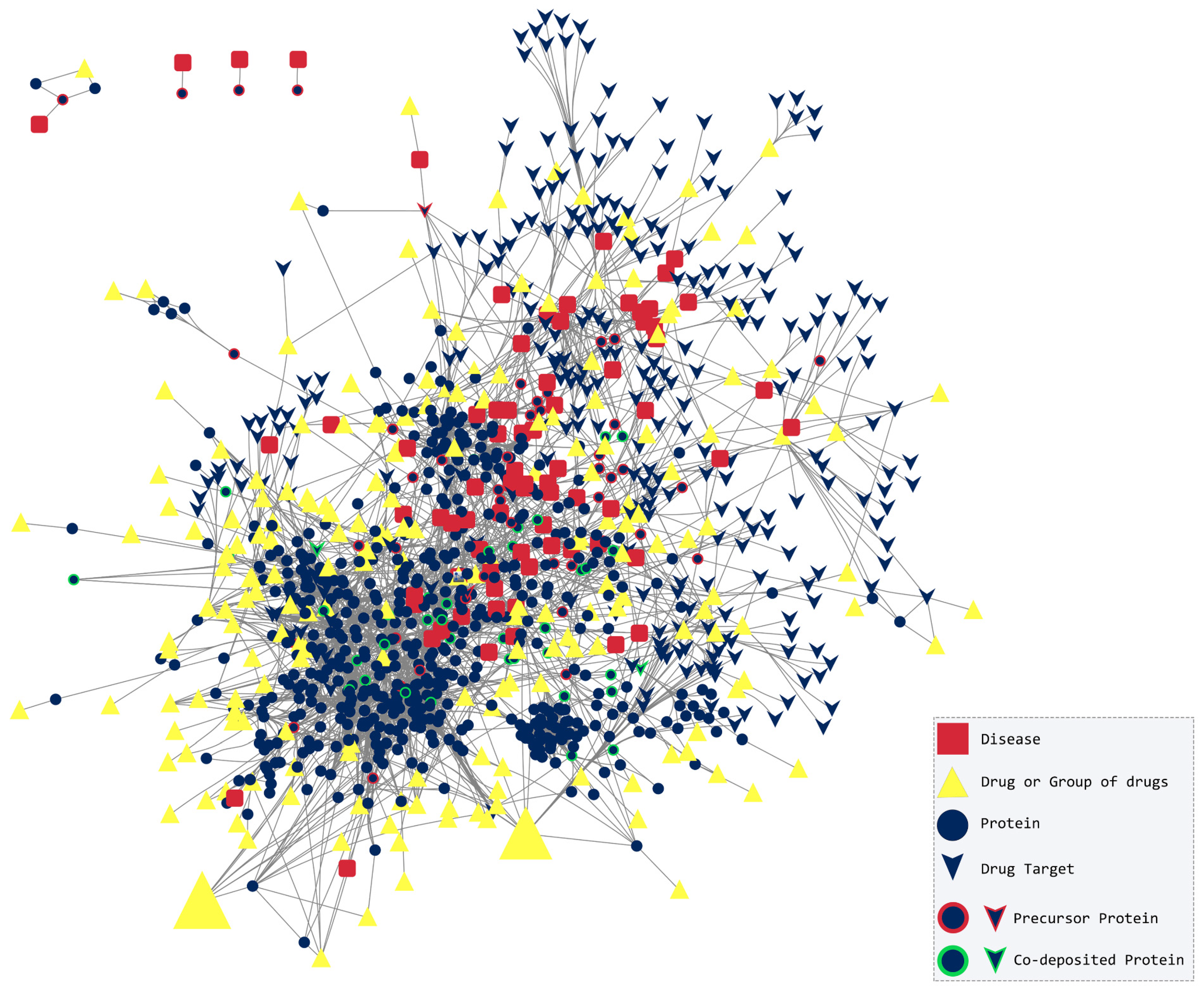
2.1. Topological Analysis
2.2. The Amyloidogenic Proteins
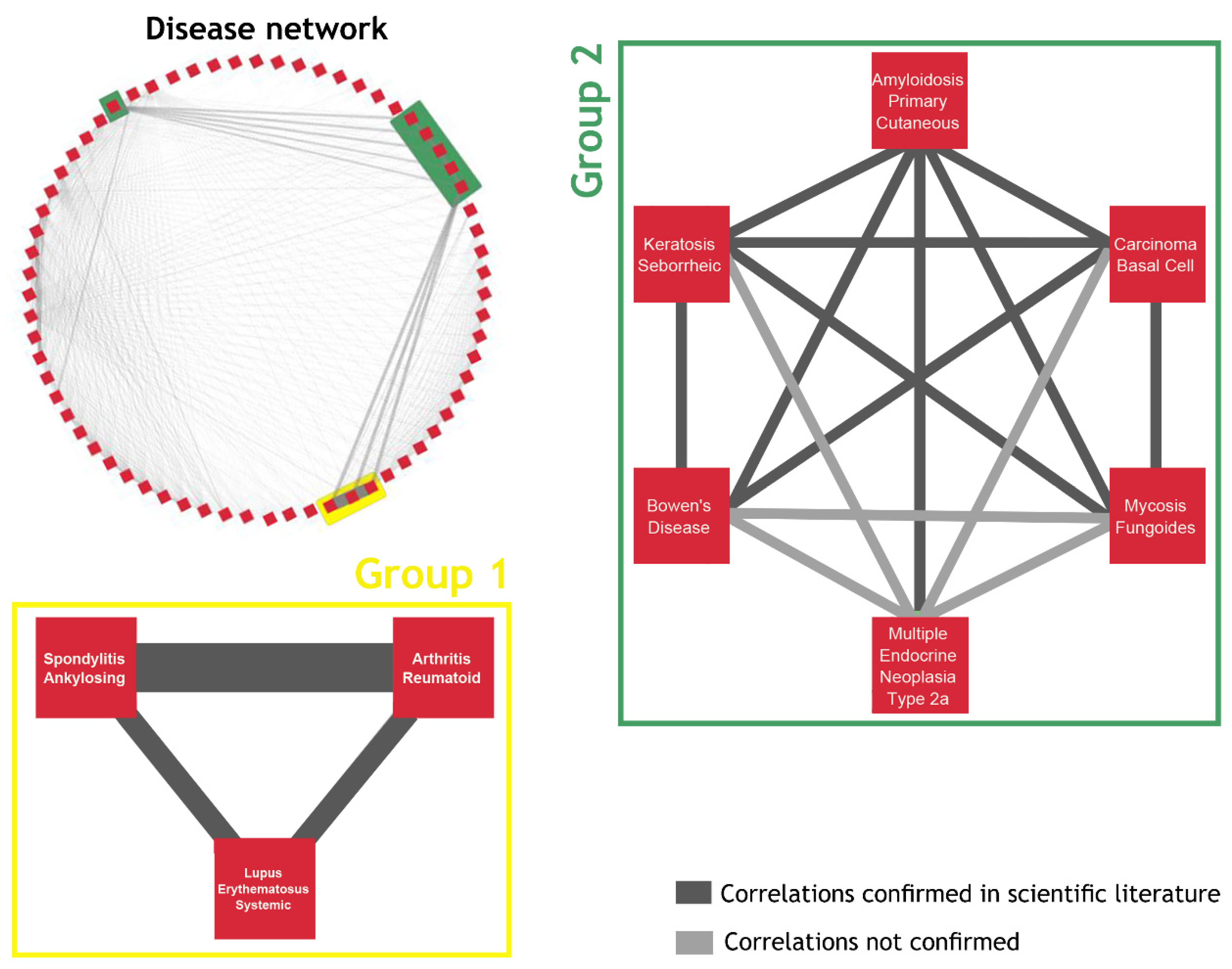
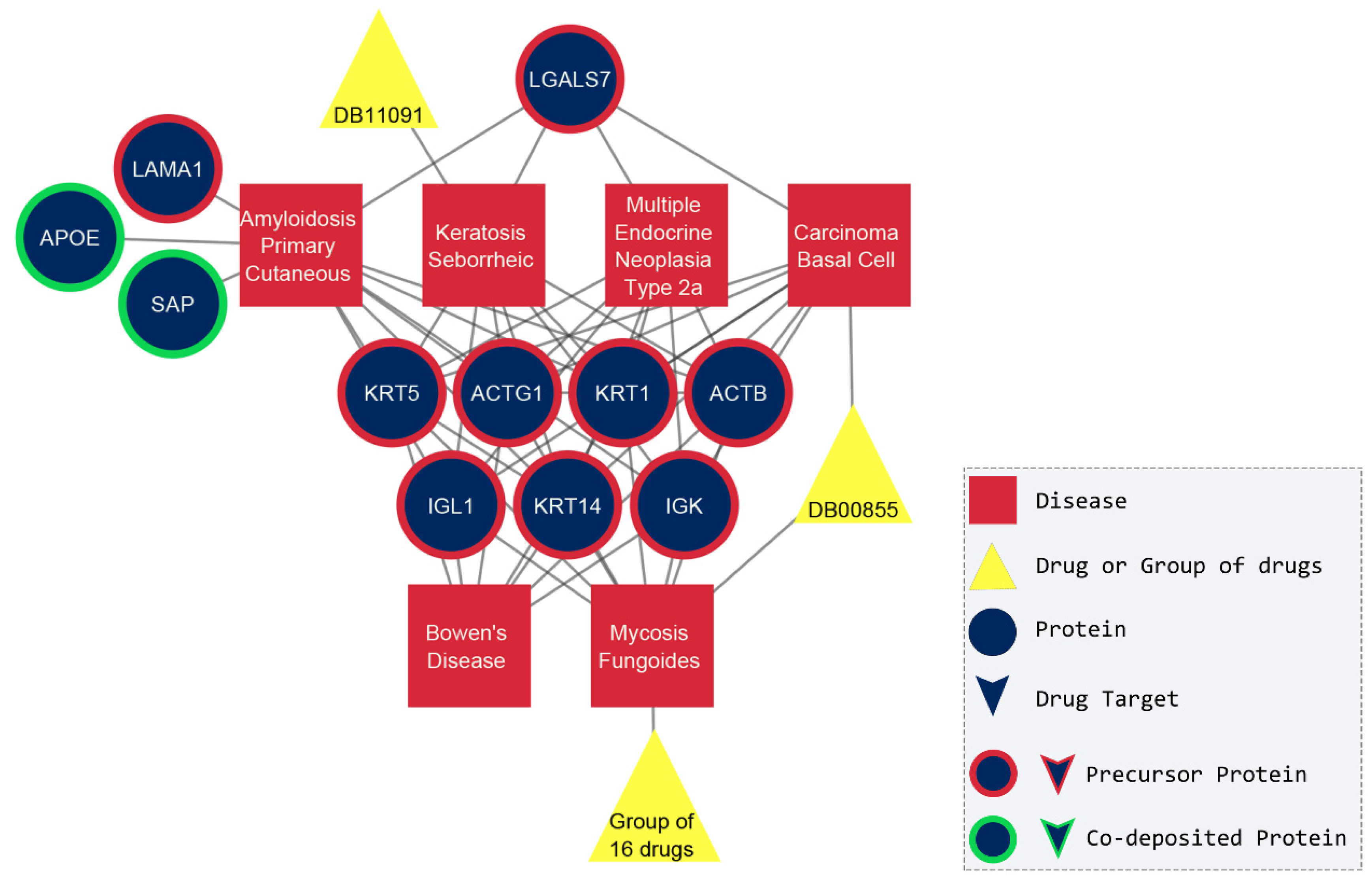
2.3. The Network of Diseases
2.4. Drug-Based Approach
3. Materials and Methods
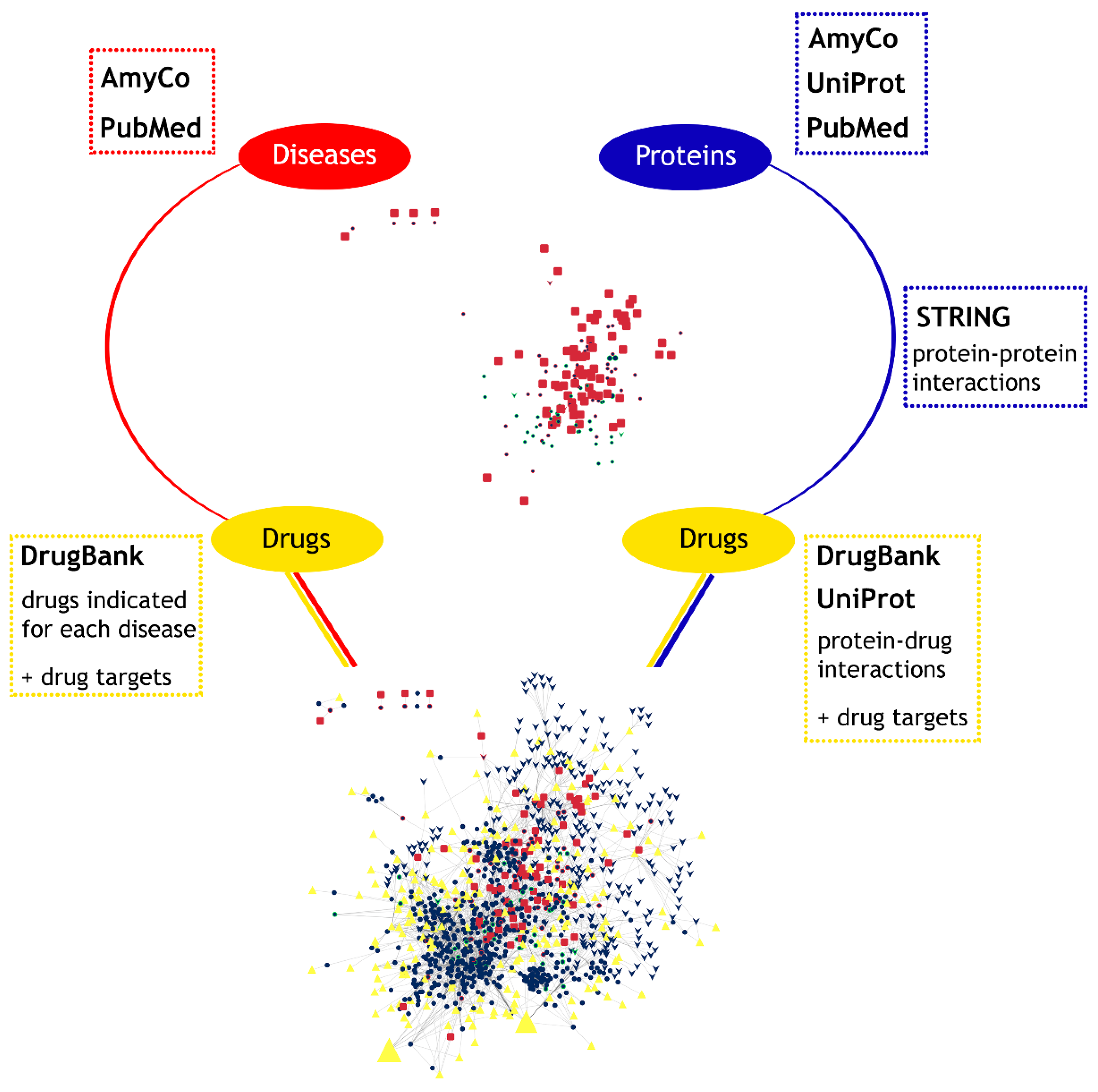
3.1. Disease–Protein Associations
3.2. Protein–Protein Interactions
3.3. Drug–Disease and Drug-Protein Interactions
3.4. Disease–Protein–Drug Interactions Network
- (1)
- Diseases and proteins;
- (2)
- Proteins and proteins;
- (3)
- Proteins and drugs;
- (4)
- Diseases and drugs.
3.5. A Disease-Based and Drug-Based Approach
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tolani, P.; Gupta, S.; Yadav, K.; Aggarwal, S.; Yadav, A.K. Big Data, Integrative Omics and Network Biology. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 127, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Gulbahce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Network Medicine: A Network-Based Approach to Human Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.-I.; Cusick, M.E.; Valle, D.; Childs, B.; Vidal, M.; Barabási, A.-L. The Human Disease Network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8685–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.-I.; Choi, I.-G. Exploring the Human Diseasome: The Human Disease Network. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2012, 11, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Network-Based Drug Repositioning. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Handa, H. Molecular Mechanisms of Thalidomide and Its Derivatives. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2020, 96, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancas-Mejía, L.M.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Systemic Amyloidoses. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 745–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Talapatra, A.; Gillespie, J.R.; Fink, A.L. Protein Deposits as the Molecular Basis of Amyloidosis. Part I. Syst. Amyloidoses. Med. Sci. Monit. 1999, 5, RA1001–RA1012. [Google Scholar]
- Spatharas, P.M.; Nasi, G.I.; Tsiolaki, P.L.; Theodoropoulou, M.K.; Papandreou, N.C.; Hoenger, A.; Trougakos, I.P.; Iconomidou, V.A. Clusterin in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Amyloidogenic Inhibitor of Amyloid Formation? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yee, A.; Brewer, H.B.; Das, S.; Potter, H. Amyloid-Associated Proteins Alpha 1-Antichymotrypsin and Apolipoprotein E Promote Assembly of Alzheimer Beta-Protein into Filaments. Nature 1994, 372, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepys, M.B.; Dyck, R.F.; de Beer, F.C.; Skinner, M.; Cohen, A.S. Binding of Serum Amyloid P-Component (SAP) by Amyloid Fibrils. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1979, 38, 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum, J.N.; Dispenzieri, A.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Fändrich, M.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.M.; Sekijima, Y.; Westermark, P. Amyloid Nomenclature 2022: Update, Novel Proteins, and Recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) Nomenclature Committee. Amyloid 2022, 29, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J.N.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Fändrich, M.; McPhail, E.D.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.; Sekijima, Y.; Westermark, P. Amyloid Nomenclature 2024: Update, Novel Proteins, and Recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) Nomenclature Committee. Amyloid 2024, 31, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, R.; Green, K.M.; Soto, C. Cross Currents in Protein Misfolding Disorders: Interactions and Therapy. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 8, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S. Protein Misfolding Diseases. Future Sci. OA 2015, 1, FSO38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, R.; Bapat, S.; Jain, E.; Karthikeyan, M.; Tambe, S.; Kulkarni, B.D. Building and Analysis of Protein-Protein Interactions Related to Diabetes Mellitus Using Support Vector Machine, Biomedical Text Mining and Network Analysis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 65, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, G.; Molzahn, C.; Mayor, T. Protein Interaction Networks in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Physiological Function to Aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Secrier, M.; Moschopoulos, C.N.; Soldatos, T.G.; Kossida, S.; Aerts, J.; Schneider, R.; Bagos, P.G. Using Graph Theory to Analyze Biological Networks. BioData Min. 2011, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective Dynamics of “small-World” Networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broido, A.D.; Clauset, A. Scale-Free Networks Are Rare. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, T.P.J.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. The Amyloid State and Its Association with Protein Misfolding Diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhondi, H.; Varacallo, M. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, M.; Parodis, I.; Nikiphorou, E. Fatigue in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Mechanisms, Measures and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörner, T.; Vital, E.M.; Ohrndorf, S.; Alten, R.; Bello, N.; Haladyj, E.; Burmester, G. A Narrative Literature Review Comparing the Key Features of Musculoskeletal Involvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 781–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhan, F.; Argın, M.; Can, G.; Özmen, M.; Keser, G. Coexistence of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Ankylosing Spondylitis: Another Case Report and Review of the Literature. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 1, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-H.; Chen, D.-Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lai, K.-L. Health-Related Quality of Life and Utility: Comparison of Ankylosing Spondylitis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients in Taiwan. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Deng, J.-H.; Mao, G.-F.; He, Y.-L.; Shi, X. Serum Amyloid A: A Potential Biomarker Assessing Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e923290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.-L.; Fu, S.; Huang, R.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L.-F.; Lv, Y.-J. The Value of Serum Amyloid A in the Diagnosis and Management of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2715–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, M.; Cui, C.; Zhou, J. Association between Serum Amyloid A Levels and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 38, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, S.; Azhari, V.; Bidari-Zerehpoosh, F.; Asadi-Kani, Z.; Talebi, A. The Diagnostic Value of P63, P16, and P53 Immunohistochemistry in Distinguishing Seborrheic Keratosis, Actinic Keratosis, and Bowen’s Disease. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka, T.; Kon, S. Two Cases of Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising in Seborrheic Keratosis. J. Dermatol. 1997, 24, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazza, M.A.; Ryatt, K.S.; Dharmagunawardena, P.V.B. Mycosis Fungoides Masquerading as Seborrhoeic Keratosis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 1264–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedir, R.; Yurdakul, C.; Güçer, H.; Sehitoglu, I. Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising within Seborrheic Keratosis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, YD06–YD07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, R.; Shinkuma, S.; Tomii, K.; Aizawa, A.; Abe, R. Multiple Seborrheic Keratosis-like Lesions of Mycosis Fungoides Masquerading as the Leser-Trèlat Sign. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, e96–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolkow, N.; Yoon, M.K. Seborrheic Keratosis Concealing a Basal Cell Carcinoma. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 37, S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebas, E.; Chapelier, C.; Quatresooz, P.; Seidel, L.; Nikkels, A.F. Exploratory Assessment of Oxygen Flow-Assisted Cutaneous Administration of Methotrexate for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma, Mycosis Fungoides, and Extramammary Paget Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genouw, E.; Verheire, B.; Ongenae, K.; de Schepper, S.; Creytens, D.; Verhaeghe, E.; Boone, B. Laser-Assisted Photodynamic Therapy for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma and Bowen’s Disease: A Randomized Intrapatient Comparison between a Continuous and a Fractional Ablative CO2 Laser Mode. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, L.C.; Keeling, C.P. Cryosurgery + 5% 5-Fluorouracil for Treatment of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma and Bowen’s Disease. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2018, 22, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, C.H.; Park, M.K.; Choi, M.S.; Hong, S.P.; Park, B.C.; Kim, M.H. Secondary Cutaneous Amyloidosis in a Patient with Mycosis Fungoides. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, S.B.; Brown, C.S. Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis. Arch. Dermatol. 1965, 92, 344–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miura, Y.; Harumiya, S.; Ono, K.; Fujimoto, E.; Akiyama, M.; Fujii, N.; Kawano, H.; Wachi, H.; Tajima, S. Galectin-7 and Actin Are Components of Amyloid Deposit of Localized Cutaneous Amyloidosis. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, T.; Illing, T.; Elsner, P. Primary Localized Cutaneous Amyloidosis: A Systematic Treatment Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 18, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, F.; Ueo, D.; Okubo-Gunge, Y.; Usui, A.; Kuwatsuka, S.; Mine, Y.; Hamada, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Sasaki, T.; Nomizu, M.; et al. Fibulin-4 Accelerates Amyloid Formation by Binding with a Keratin 5 Peptide Fragment. JID Innov. 2022, 2, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapineli, J.O.; Ceolin, L.; Puñales, M.K.; Dora, J.M.; Maia, A.L. MEN 2A-Related Cutaneous Lichen Amyloidosis: Report of Three Kindred and Systematic Literature Review of Clinical, Biochemical and Molecular Characteristics. Fam. Cancer 2016, 15, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, R.; Boro, H.; Shamim, S.A.; Khadgawat, R. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2A with Cutaneous Lichen Amyloidosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e238423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badkas, A.; de Landtsheer, S.; Sauter, T. Topological Network Measures for Drug Repositioning. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J. A Measure of Betweenness Centrality Based on Random Walks. Soc. Netw. 2005, 27, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somolinos, F.J.; León, C.; Guerrero-Aspizua, S. Drug Repurposing Using Biological Networks. Processes 2021, 9, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahata, K.; Shimazu, S.; Katsuki, H.; Yoneda, F.; Akaike, A. Effects of Selegiline on Antioxidant Systems in the Nigrostriatum in Rat. J. Neural Transm. 2006, 113, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleutherio, E.C.A.; Silva Magalhães, R.S.; de Araújo Brasil, A.; Monteiro Neto, J.R.; de Holanda Paranhos, L. SOD1, More than Just an Antioxidant. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 697, 108701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trist, B.G.; Davies, K.M.; Cottam, V.; Genoud, S.; Ortega, R.; Roudeau, S.; Carmona, A.; de Silva, K.; Wasinger, V.; Lewis, S.J.G.; et al. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-like Superoxide Dismutase 1 Proteinopathy Is Associated with Neuronal Loss in Parkinson’s Disease Brain. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solana-Manrique, C.; Sanz, F.J.; Martínez-Carrión, G.; Paricio, N. Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Effects of Carnosine: Therapeutic Implications in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nastou, K.C.; Nasi, G.I.; Tsiolaki, P.L.; Litou, Z.I.; Iconomidou, V.A. AmyCo: The Amyloidoses Collection. Amyloid 2019, 26, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Treeck, B.J.; Dasari, S.; Kurtin, P.J.; Theis, J.D.; Nasr, S.H.; Zhang, L.; Yasir, S.; Graham, R.P.; McPhail, E.D.; Said, S. Somatostatin-Derived Amyloidosis: A Novel Type of Amyloidosis Associated with Well-Differentiated Somatostatin-Producing Neuroendocrine Tumours. Amyloid 2022, 29, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING Database in 2021: Customizable Protein-Protein Networks, and Functional Characterization of User-Uploaded Gene/Measurement Sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenov, Y.; Ramírez, F.; Schelhorn, S.-E.; Lengauer, T.; Albrecht, M. Computing Topological Parameters of Biological Networks. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosadori, G.; Bestvina, I.; Spoto, F.; Laudanna, C.; Scardoni, G. Creating, Generating and Comparing Random Network Models with NetworkRandomizer. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizou, A.E.I.; Nasi, G.I.; Apostolakou, A.E.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Kastritis, E.; Iconomidou, V.A. Integrated Network-Based Analysis of Diseases Associated with Amyloid Deposition Through a Disease–Protein–Drug Network. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121736
Rizou AEI, Nasi GI, Apostolakou AE, Dimopoulos MA, Kastritis E, Iconomidou VA. Integrated Network-Based Analysis of Diseases Associated with Amyloid Deposition Through a Disease–Protein–Drug Network. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(12):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121736
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizou, Aikaterini E. I., Georgia I. Nasi, Avgi E. Apostolakou, Meletios A. Dimopoulos, Efstathios Kastritis, and Vassiliki A. Iconomidou. 2024. "Integrated Network-Based Analysis of Diseases Associated with Amyloid Deposition Through a Disease–Protein–Drug Network" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 12: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121736
APA StyleRizou, A. E. I., Nasi, G. I., Apostolakou, A. E., Dimopoulos, M. A., Kastritis, E., & Iconomidou, V. A. (2024). Integrated Network-Based Analysis of Diseases Associated with Amyloid Deposition Through a Disease–Protein–Drug Network. Pharmaceuticals, 17(12), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121736







