Unveiling Epigenetic Vulnerabilities in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through 3D Organoid Drug Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Establishment of Patient-Derived TNBC Organoids and a High-Throughput Drug Screening System
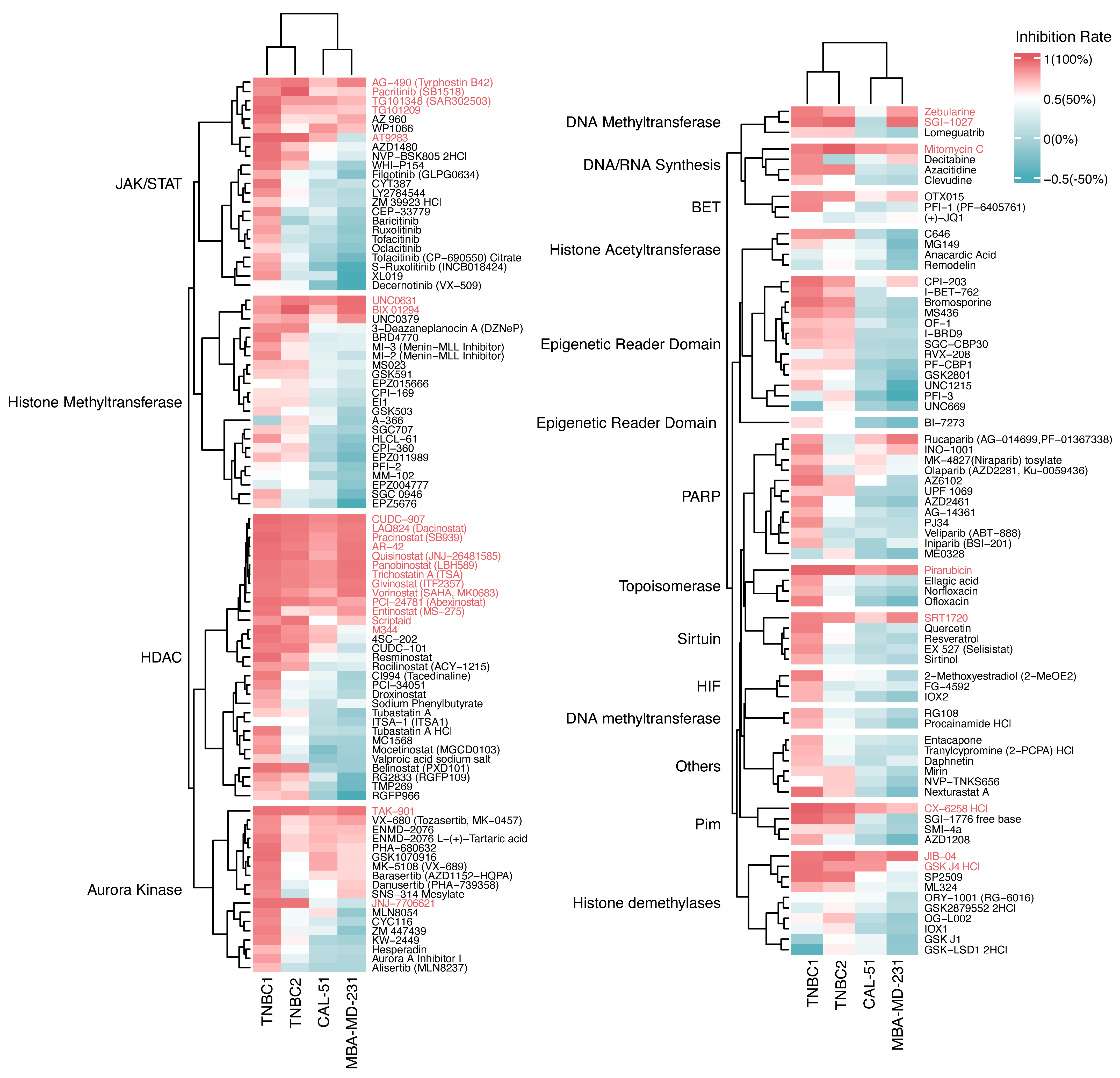
2.2. Growth Inhibition Profiling of Epigenetic Drugs on TNBC Organoids and Cell Lines
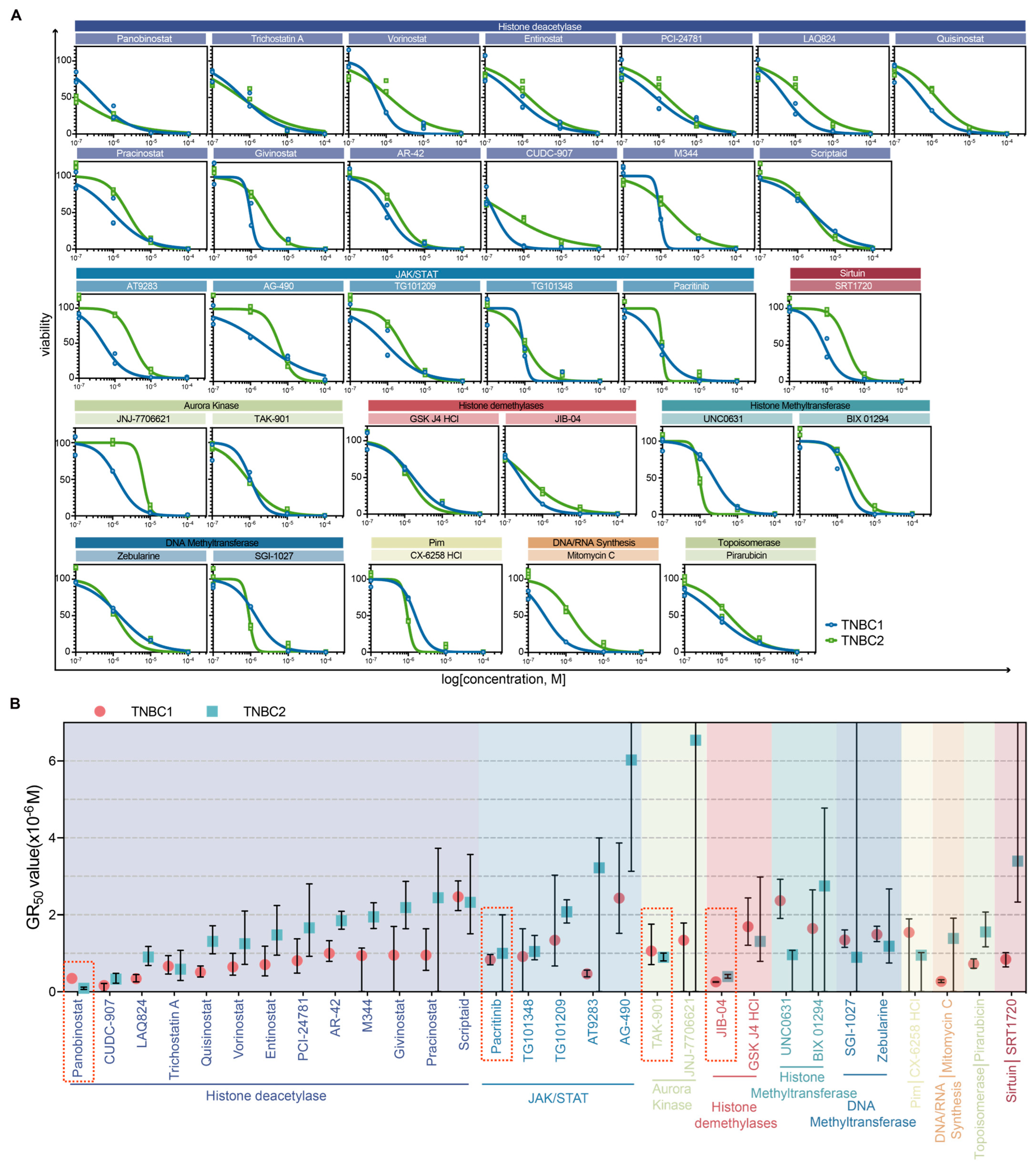
2.3. Dose–Response Characterization and Drug Sensitivity Analysis of Selected Drugs in TNBC Organoids
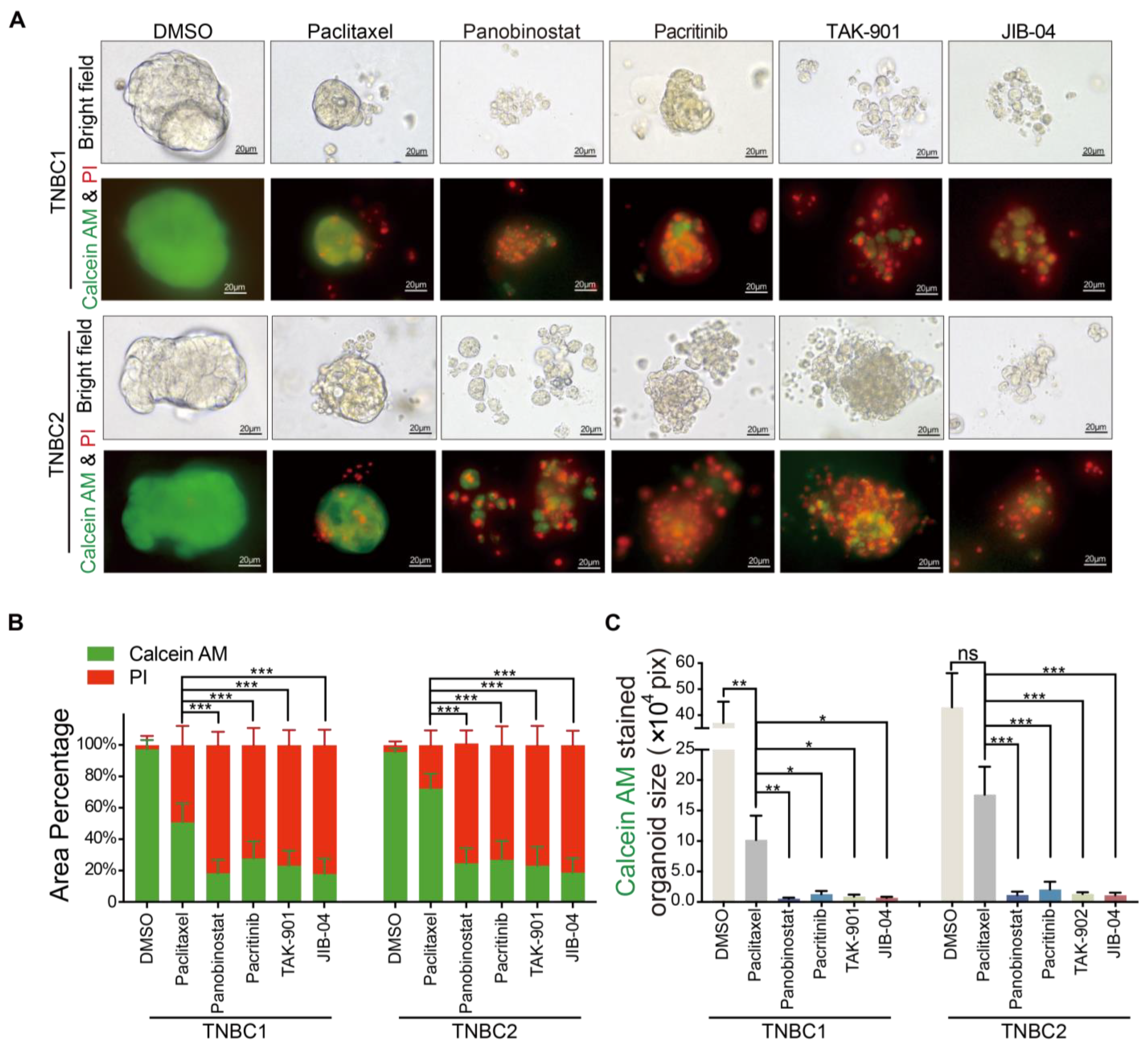
2.4. Superior Cytotoxicity of Novel Agents Panobinostat, Pacritinib, TAK-901, and JIB-04 over Paclitaxel in TNBC Organoid Models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Tissue Processing and Organoid Culture
4.3. Organoid Passaging
4.4. Cell Cultures
4.5. Drug Screening
4.6. Histology, Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence Staining
4.7. Fluorescence (Calcein-AM/PI) Staining of Organoids
4.8. Imaging of Organoids
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianchini, G.; Balko, J.M.; Mayer, I.A.; Sanders, M.E.; Gianni, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malorni, L.; Shetty, P.B.; De Angelis, C.; Hilsenbeck, S.; Rimawi, M.F.; Elledge, R.; Osborne, C.K.; De Placido, S.; Arpino, G. Clinical and biologic features of triple-negative breast cancers in a large cohort of patients with long-term follow-up. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.E.; Tung, N.; Conte, P.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Armstrong, A.; et al. OlympiAD final overall survival and tolerability results: Olaparib versus chemotherapy treatment of physician’s choice in patients with a germline BRCA mutation and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutt, A.N.J.; Garber, J.E.; Kaufman, B.; Viale, G.; Fumagalli, D.; Rastogi, P.; Gelber, R.D.; de Azambuja, E.; Fielding, A.; Balmaña, J.; et al. Adjuvant Olaparib for Patients with BRCA1- or BRCA2-Mutated Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, J.K.; Rugo, H.S.; Ettl, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Gonçalves, A.; Lee, K.H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Yerushalmi, R.; Mina, L.A.; Martin, M.; et al. Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer and a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, J.K.; Scoggins, M.E.; Hess, K.R.; Adrada, B.E.; Murthy, R.K.; Damodaran, S.; DeSnyder, S.M.; Brewster, A.M.; Barcenas, C.H.; Valero, V.; et al. Neoadjuvant Talazoparib for Patients With Operable Breast Cancer With a Germline BRCA Pathogenic Variant. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Schmid, P.; Rugo, H.S.; Winer, E.P.; Loirat, D.; Awada, A.; Cescon, D.W.; Iwata, H.; Campone, M.; Nanda, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab monotherapy for previously treated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: Cohort A of the phase II KEYNOTE-086 study. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Loi, S.; Toppmeyer, D.; Cescon, D.W.; De Laurentiis, M.; Nanda, R.; Winer, E.P.; Mukai, H.; Tamura, K.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab monotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-positive, metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: Cohort B of the phase II KEYNOTE-086 study. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Hegg, R.; Im, S.A.; Shaw Wright, G.; et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Rugo, H.S.; Adams, S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Henschel, V.; Molinero, L.; Chui, S.Y.; et al. Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel as first-line treatment for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion130): Updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; Harbeck, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Haiderali, A.; Pan, W.; Hu, P.; Chaudhuri, M.; Le Bailly De Tilleghem, C.; Cappoen, N.; Fasching, P.A. Q-TWiST analysis of pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy as first-line treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer that expresses PD-L1. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 177, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Zhang, H.; Barrios, C.H.; Saji, S.; Jung, K.H.; Hegg, R.; Koehler, A.; Sohn, J.; Iwata, H.; Telli, M.L.; et al. Neoadjuvant atezolizumab in combination with sequential nab-paclitaxel and anthracycline-based chemotherapy versus placebo and chemotherapy in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion031): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, R.; Liu, M.C.; Yau, C.; Shatsky, R.; Pusztai, L.; Wallace, A.; Chien, A.J.; Forero-Torres, A.; Ellis, E.; Han, H.; et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab Plus Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Pathologic Complete Response in Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: An Analysis of the Ongoing Phase 2 Adaptively Randomized I-SPY2 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passalacqua, M.I.; Rizzo, G.; Santarpia, M.; Curigliano, G. Why is survival with triple negative breast cancer so low? insights and talking points from preclinical and clinical research. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2022, 31, 1291–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, E.A.; Chan, S. Metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Oncol. R Coll. Radiol. 2011, 23, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Gao, R.; Sei, E.; Brandt, R.; Hartman, J.; Hatschek, T.; Crosetto, N.; Foukakis, T.; Navin, N.E. Chemoresistance Evolution in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Delineated by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2018, 173, 879–893.e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, A.; Franzese, E.; Centonze, S.; Carlino, F.; Della Corte, C.M.; Ventriglia, J.; Petrillo, A.; De Vita, F.; Alfano, R.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: Systematic Review of the Literature on Molecular and Clinical Features with a Focus on Treatment with Innovative Drugs. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, J.; Haddad, F.G.; Eid, R.; Lambertini, M.; Kourie, H.R. Triple-negative breast cancer: Current perspective on the evolving therapeutic landscape. Int. J. Womens Health 2019, 11, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylin, S.B.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetic Determinants of Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a019505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, H.; Ushijima, T. Accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations in normal cells and cancer risk. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdasco, M.; Esteller, M. Clinical epigenetics: Seizing opportunities for translation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolota, V.; Tzelepi, V.; Piperigkou, Z.; Kourea, H.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Argentou, Μ.I.; Karamanos, N.K. Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer-The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix. Cancers 2021, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, T.; Cui, S.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Geng, C.; et al. Tucidinostat plus exemestane for postmenopausal patients with advanced, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (ACE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, D.A.; Ismail-Khan, R.R.; Melichar, B.; Lichinitser, M.; Munster, P.N.; Klein, P.M.; Cruickshank, S.; Miller, K.D.; Lee, M.J.; Trepel, J.B. Randomized phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of exemestane with or without entinostat in postmenopausal women with locally recurrent or metastatic estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer progressing on treatment with a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandhasin, C.; Dang, V.; Perabo, F.; Del Rosario, J.; Chen, Y.K.; Filvaroff, E.; Stafford, J.A.; Clarke, M. TACH101, a first-in-class pan-inhibitor of KDM4 histone demethylase. Anticancer. Drugs 2023, 34, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhu, J.; Wan, J.; Shen, L.; Xia, F.; Fu, G.; Deng, Y.; Pan, M.; et al. Patient-Derived Organoids Predict Chemoradiation Responses of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 17–26.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.H.N.; Siu, H.C.; Law, S.; Ho, S.L.; Yue, S.S.K.; Tsui, W.Y.; Chan, D.; Chan, A.S.; Ma, S.; Lam, K.O.; et al. A Comprehensive Human Gastric Cancer Organoid Biobank Captures Tumor Subtype Heterogeneity and Enables Therapeutic Screening. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 882–897.e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, N.; de Ligt, J.; Kopper, O.; Gogola, E.; Bounova, G.; Weeber, F.; Balgobind, A.V.; Wind, K.; Gracanin, A.; Begthel, H.; et al. A Living Biobank of Breast Cancer Organoids Captures Disease Heterogeneity. Cell 2018, 172, 373–386.e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopper, O.; de Witte, C.J.; Lõhmussaar, K.; Valle-Inclan, J.E.; Hami, N.; Kester, L.; Balgobind, A.V.; Korving, J.; Proost, N.; Begthel, H.; et al. An organoid platform for ovarian cancer captures intra- and interpatient heterogeneity. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broutier, L.; Mastrogiovanni, G.; Verstegen, M.M.; Francies, H.E.; Gavarró, L.M.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Allen, G.E.; Arnes-Benito, R.; Sidorova, O.; Gaspersz, M.P.; et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, A.; Gjorevski, N.; Lutolf, M.P. Drug discovery through stem cell-based organoid models. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2014, 69–70, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuveson, D.; Clevers, H. Cancer modeling meets human organoid technology. Science 2019, 364, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tang, P.; Cai, S.; Peng, J.; Hua, G. Organoid based personalized medicine: From bench to bedside. Cell Regen. 2020, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, J.F.; van Vliet, E.J.; Sachs, N.; Rosenbluth, J.M.; Kopper, O.; Rebel, H.G.; Wehrens, E.J.; Piani, C.; Visvader, J.E.; Verissimo, C.S.; et al. Long-term culture, genetic manipulation and xenotransplantation of human normal and breast cancer organoids. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 1936–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Lu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Wen, L.; Fu, W.; Tang, F. Drug repurposing screening and mechanism analysis based on human colorectal cancer organoids. Protein Cell 2023, 2023, pwad038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Ding, R.; Yang, L.; Lyu, X.; Zeng, J.; Lei, J.H.; Wang, L.; Bi, J.; Shao, N.; et al. Patient-Derived Organoids Can Guide Personalized-Therapies for Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fu, G.; Zhang, L.; Guan, R.; Tang, P.; Zhang, J.; Rao, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Assay establishment and validation of a high-throughput organoid-based drug screening platform. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Kramer, M.; Russo, S.; Naik, P.; Arun, G.; Brophy, K.; Andrews, P.; Fan, C.; Perou, C.M.; Preall, J.; et al. Patient-Derived Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Organoids Provide Robust Model Systems That Recapitulate Tumor Intrinsic Characteristics. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1174–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.K.; Huang, S.S.; Northey, J.J.; Liao, W.Y.; Hsu, C.C.; Cheng, L.H.; Werner, M.E.; Chuu, C.P.; Chatterjee, C.; Lakins, J.N.; et al. Screening of organoids derived from patients with breast cancer implicates the repressor NCOR2 in cytotoxic stress response and antitumor immunity. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 734–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachogiannis, G.; Hedayat, S.; Vatsiou, A.; Jamin, Y.; Fernández-Mateos, J.; Khan, K.; Lampis, A.; Eason, K.; Huntingford, I.; Burke, R.; et al. Patient-derived organoids model treatment response of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Science 2018, 359, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.A.; Sahu, K.K.; Sengupta, S.; Partap, S.; Karpoormath, R.; Kumar, B.; Kumar, D. Recent advancement of HDAC inhibitors against breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccallini, C.; Ammazzalorso, A.; De Filippis, B.; Fantacuzzi, M.; Giampietro, L.; Amoroso, R. HDAC Inhibitors for the Therapy of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, C.R.; Rhodes, L.V.; Segar, H.C.; Driver, J.L.; Pounder, F.N.; Burow, M.E.; Collins-Burow, B.M. Targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells with the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, N.; Marano, F.; Bandino, A.; Frairia, R.; Catalano, M.G.; Boccuzzi, G. The pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 (panobinostat) alters the invasive breast cancer cell phenotype. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, A.; Qi, Q.; Peng, X.; Yan, L.; Takabe, K.; Hait, N.C. Class I histone deacetylase inhibitor suppresses vasculogenic mimicry by enhancing the expression of tumor suppressor and anti-angiogenesis genes in aggressive human TNBC cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yao, Y.; Yao, M.; Fu, P.; Wang, W. Interleukin-22 promotes triple negative breast cancer cells migration and paclitaxel resistance through JAK-STAT3/MAPKs/AKT signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Mei, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Nie, W. FRZB is Regulated by the Transcription Factor EGR1 and Inhibits the Growth and Invasion of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating the JAK/STAT3 Pathway. Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Tan, Q.; Su, X.; Yuan, Y.; Hou, L.; Li, J. Adjuvant radiation therapy for older women with early-stage breast cancer: A propensity-matched SEER analysis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doheny, D.; Sirkisoon, S.; Carpenter, R.L.; Aguayo, N.R.; Regua, A.T.; Anguelov, M.; Manore, S.G.; Arrigo, A.; Jalboush, S.A.; Wong, G.L.; et al. Combined inhibition of JAK2-STAT3 and SMO-GLI1/tGLI1 pathways suppresses breast cancer stem cells, tumor growth, and metastasis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6589–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sarli, V.N.; Lucci, A. Sensitization of Resistant Breast Cancer Cells with a Jumonji Family Histone Demethylase Inhibitor. Cancers 2022, 14, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalirad, M.; Haddad, T.C.; Salisbury, J.L.; Radisky, D.; Zhang, M.; Schroeder, M.; Tuma, A.; Leof, E.; Carter, J.M.; Degnim, A.C.; et al. Aurora-A kinase oncogenic signaling mediates TGF-β-induced triple-negative breast cancer plasticity and chemoresistance. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2509–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, D.; Yan, M.; Kamran, M.; Liu, Q.; Xu, B. Aurora kinase A stabilizes FOXM1 to enhance paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6442–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xia, D.; Li, Z.; Zhou, T.; Chen, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, J. Aurora-A/ERK1/2/mTOR axis promotes tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer and dual-targeting Aurora-A/mTOR shows synthetic lethality. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.L.; Ionkina, A.A.; Bagby, S.M.; Orth, J.D.; Gittleman, B.; Marcus, J.M.; Lam, E.T.; Corr, B.R.; O’Bryant, C.L.; Glode, A.E.; et al. Preclinical and Dose-Finding Phase I Trial Results of Combined Treatment with a TORC1/2 Inhibitor (TAK-228) and Aurora A Kinase Inhibitor (Alisertib) in Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, J.R.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Pitts, T.M.; van Bokhoven, A.; Aisner, D.; Gustafson, D.L.; Capasso, A.; Sams, S.; Kabos, P.; Zolman, K.; et al. A phase II clinical trial of the Aurora and angiogenic kinase inhibitor ENMD-2076 for previously treated, advanced, or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
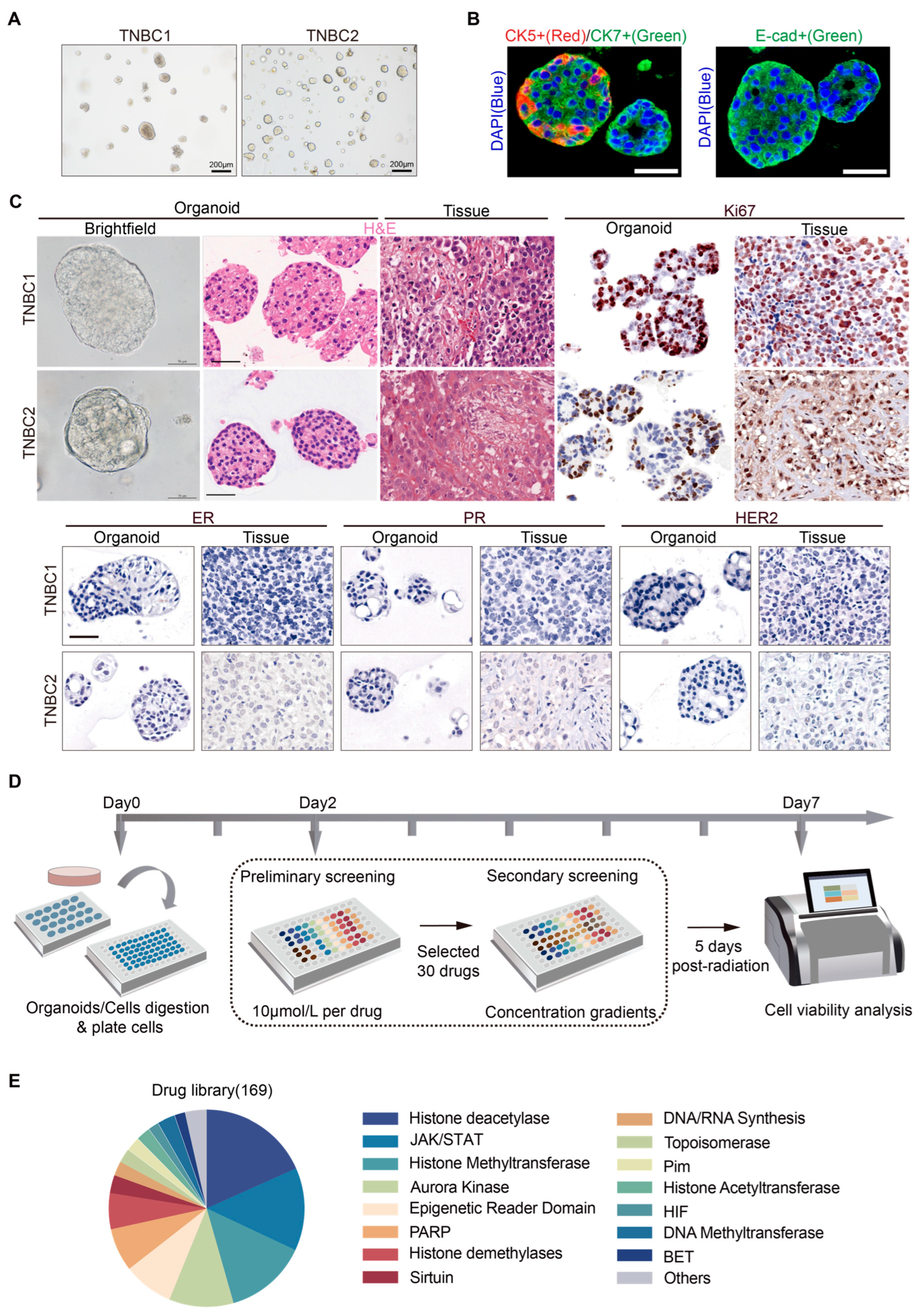
| Patient | Age (Years) | Gender | Clinical Stage | Histological Type | Histologic Grade | Molecular Subtype | Laterality | Tumor Location | Sample Type | Pre-Sampling Therapeutic History |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNBC1 | 45 | Female | cT2N0M0 | Invasive Ductal Carcinoma | II | TNBC | Left | Central/ Medial | Surgical | Modified Radical Mastectomy |
| TNBC2 | 50 | Female | cT4N1M0 | Invasive Ductal Carcinoma | II | TNBC | Left | Central/ Medial | Biopsy | Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy(Paclitaxel and Carboplatin, PCb Protocol) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, X.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Guo, X. Unveiling Epigenetic Vulnerabilities in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through 3D Organoid Drug Screening. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020225
Rao X, Qiao Z, Yang Y, Deng Y, Zhang Z, Yu X, Guo X. Unveiling Epigenetic Vulnerabilities in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through 3D Organoid Drug Screening. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020225
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Xinxin, Zhibin Qiao, Yang Yang, Yun Deng, Zhen Zhang, Xiaoli Yu, and Xiaomao Guo. 2024. "Unveiling Epigenetic Vulnerabilities in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through 3D Organoid Drug Screening" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 2: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020225
APA StyleRao, X., Qiao, Z., Yang, Y., Deng, Y., Zhang, Z., Yu, X., & Guo, X. (2024). Unveiling Epigenetic Vulnerabilities in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through 3D Organoid Drug Screening. Pharmaceuticals, 17(2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020225






