Demethyleneberberine Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Disruption of USP11 Deubiquitinating GREM1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
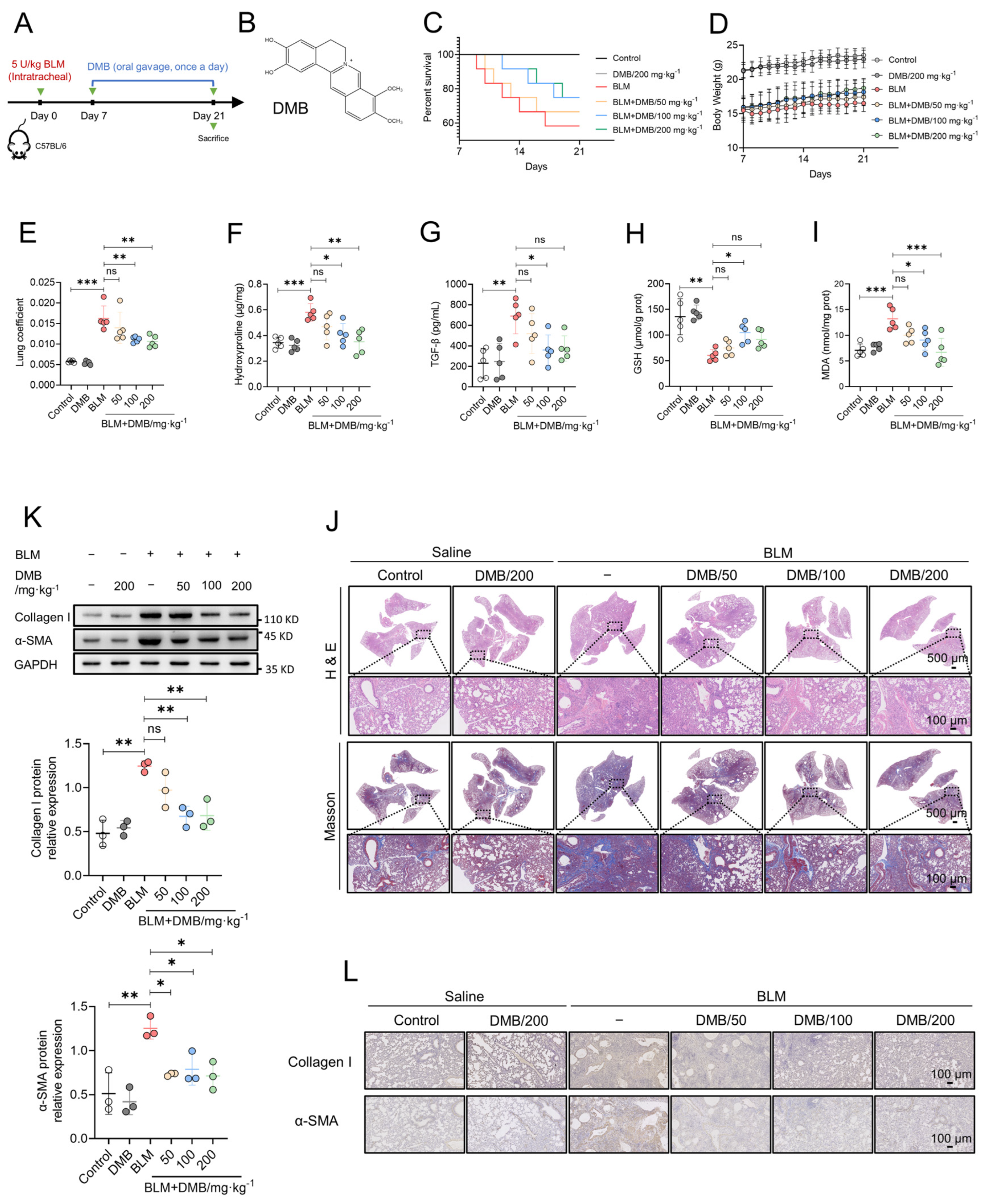
2.1. DMB Alleviates BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice
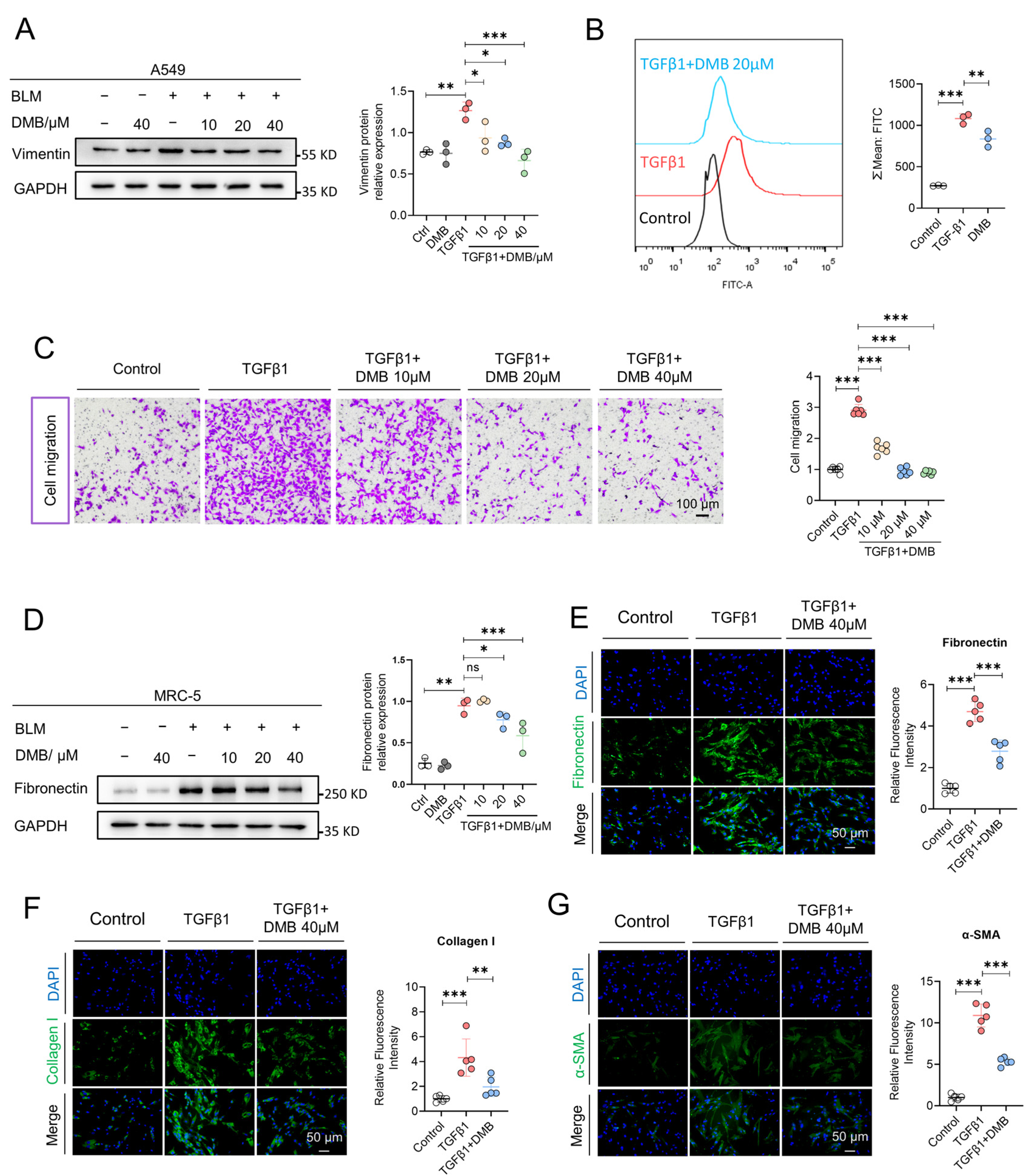
2.2. DMB Inhibits Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transition
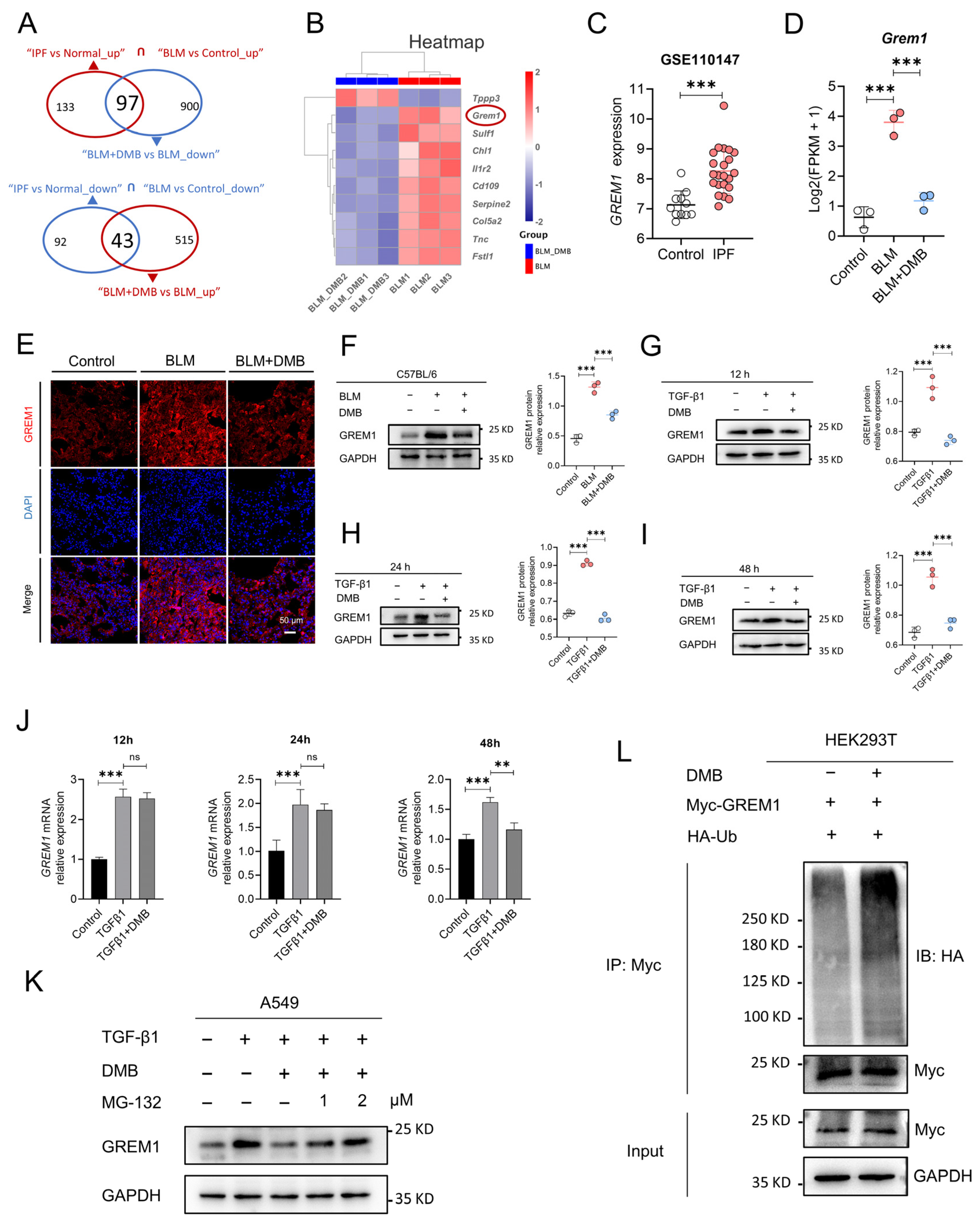
2.3. DMB Promotes the Degradation of GREM1 byt Ub/Proteasome Pathway
2.4. USP11 Stabilizes GREM1 by Deubiquitination
2.5. DMB Directly Binds to USP11 and Inhibits Its Deubiquitination on GREM1
2.6. Met776 of USP11 Is Critical for DMB Binding to USP11
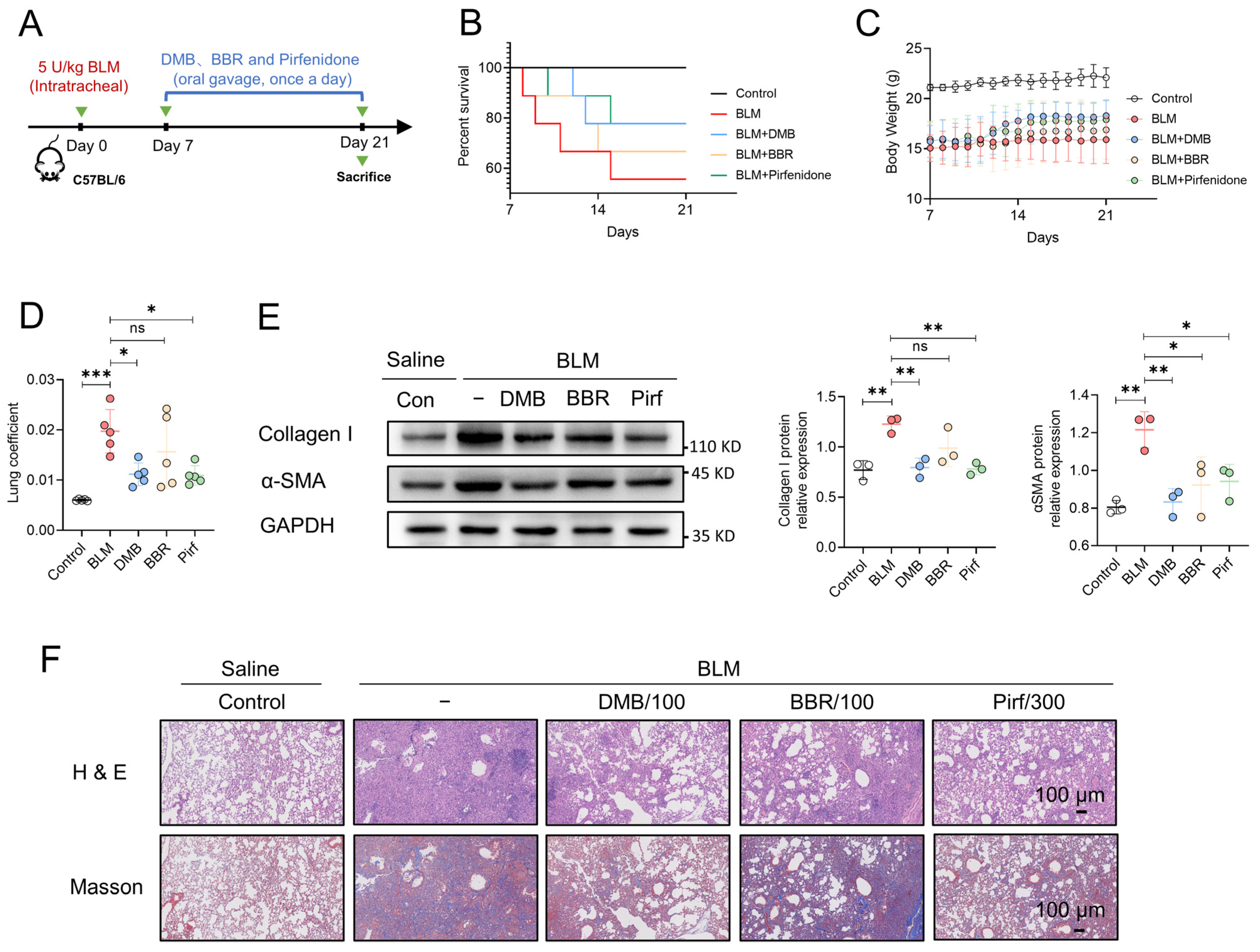
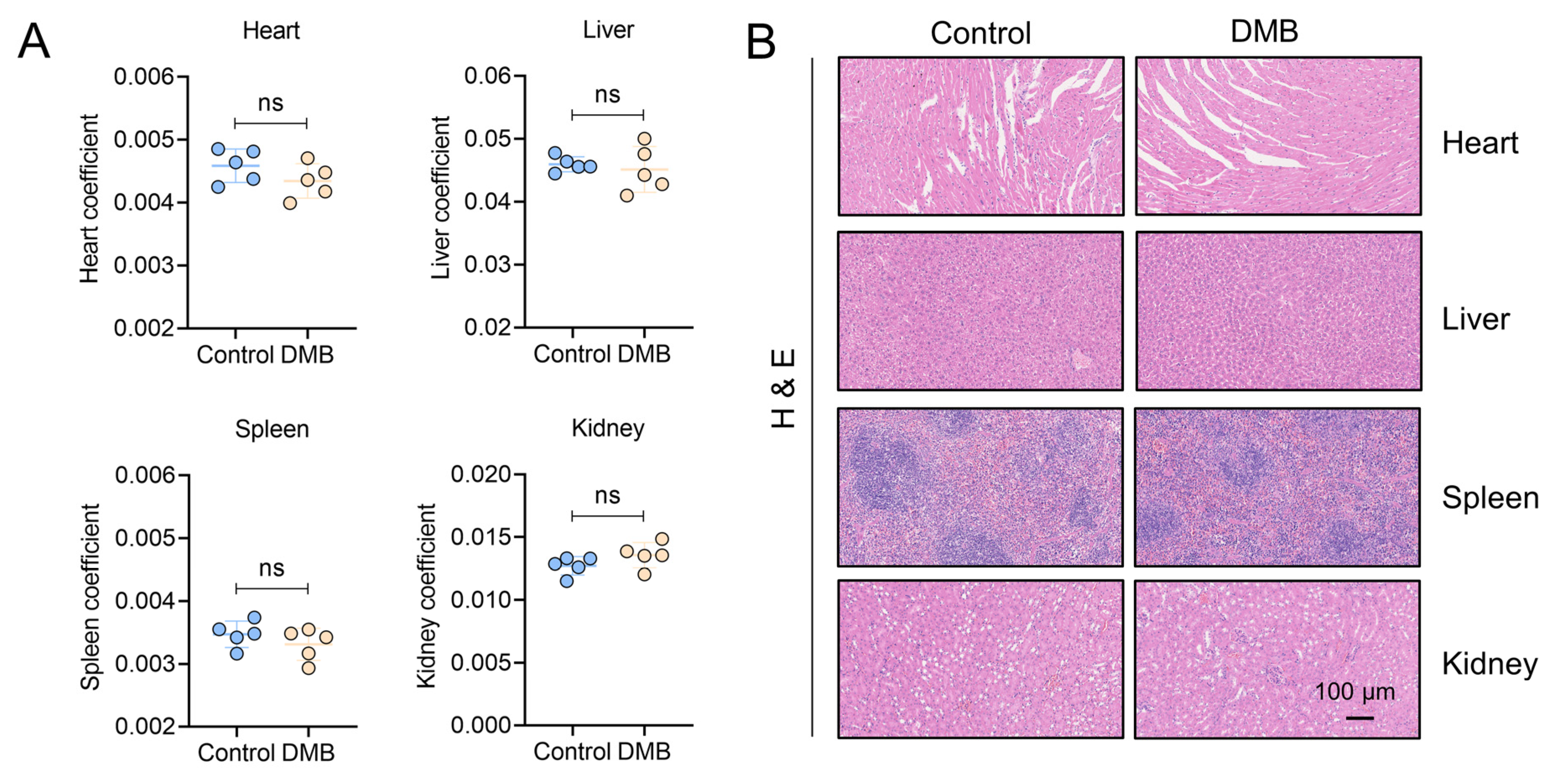
2.7. DMB Exhibits Preferable Antifibrotic Efficacy without Obvious Toxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection
4.6. Hydroxyproline, GSH and MDA Assay
4.7. ELISA
4.8. Cell Migration
4.9. Immunoprecipitation
4.10. In Vivo Ubiquitination Assay
4.11. RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.12. CRISPR/Cas9 Plasmid Construction
- SgRNA 1#-F: CACCGAGATAGAAAACGGCGAGAGT
- SgRNA 1#-R: AAACACTCTCGCCGTTTTCTATCTC
- SgRNA 2#-F: CACCGTGGGCGAGAACGTCCACTG
- SgRNA 2#-R: AAACCAGTGGACGTTCTCGCCCAC
4.13. Synthesis of Biotin-Conjugated DMB (Biotin-DMB)
4.14. Biotin-DMB Binding Assay
4.15. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
- Met776 F: CTGTGGGCACTGCCGGAGATTCTCATCATCCACCTGAAACGC
- Met776 R: CGGCAGTGCCCACAGGTCCAGCTTCTTGGTTGCCAGCTGGTG
- Leu777 F: TGGATGGCACCGGAGATTCTCATCATCCACCTGAAACGCTTT
- Leu777 R: CTCCGGTGCCATCCACAGGTCCAGCTTCTTGGTTGCCAGCTG
- Glu779 F: CTGCCGGCAATTCTCATCATCCACCTGAAACGCTTTTCCTAC
- Glu779 R: GAGAATTGCCGGCAGCATCCACAGGTCCAGCTTCTTGGTTGC
- Arg886 F: TACCAAGCACAGGACGTGGCGCGACGCCTGCTGTCCCCGGCC
- Arg886 R: GTCCTGTGCTTGGTAGAAGAGGACATAGGCTGCCTTGGACTC
4.16. Molecular Docking
4.17. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
- GREM1 F: CGGAGCGCAAATACCTGAAG
- GREM1 R: GGTTGATGATGGTGCGACTGT
- GAPDH F: ACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG
- GAPDH R: GCCATCACGCCACAGTTTC
4.18. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hewlett, J.C.; Kropski, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions and emerging therapeutic targets. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokland, K.E.C.; Waters, D.W.; Schuliga, M.; Read, J.; Pouwels, S.D.; Grainge, C.L.; Jaffar, J.; Westall, G.; Mutsaers, S.E.; Prele, C.M.; et al. Senescence of IPF Lung Fibroblasts Disrupt Alveolar Epithelial Cell Proliferation and Promote Migration in Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, P.; Volpe, M.C.; Jacob, J.; Maiocchi, S.; Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, M.; Braga, L. Regeneration or Repair? The Role of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Cells 2022, 11, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, P.; Confalonieri, M. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: A Major Pathogenic Driver in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Medicina 2020, 56, 10608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. The leading role of epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Signal 2020, 66, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Molina-Molina, M.; Raghu, G. Highlights for the Clinical Practice in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis: From the ATS/ERS/ALAT/JRS 2022 Guideline. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, J.A.; Pandya, A.; Vega-Olivo, M.; Dass, C.; Zhao, H.; Criner, G.J. Pirfenidone and nintedanib for pulmonary fibrosis in clinical practice: Tolerability and adverse drug reactions. Respirology 2017, 22, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazil, D.P.; Church, R.H.; Surae, S.; Godson, C.; Martin, F. BMP signalling: Agony and antagony in the family. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Langhe, E.; Cailotto, F.; De Vooght, V.; Aznar-Lopez, C.; Vanoirbeek, J.A.; Luyten, F.P.; Lories, R.J. Enhanced endogenous bone morphogenetic protein signaling protects against bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dituri, F.; Cossu, C.; Mancarella, S.; Giannelli, G. The Interactivity between TGFbeta and BMP Signaling in Organogenesis, Fibrosis, and Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, Y.; Enomoto, Y.; Muto, S.; Meguro, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Kosugi, I.; Fujisawa, T.; Enomoto, N.; Inui, N.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Gremlin-1 for the Differential Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Versus Other Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Clinical and Pathophysiological Analysis. Lung 2021, 199, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koli, K.; Myllarniemi, M.; Vuorinen, K.; Salmenkivi, K.; Ryynanen, M.J.; Kinnula, V.L.; Keski-Oja, J. Bone morphogenetic protein-4 inhibitor gremlin is overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllarniemi, M.; Lindholm, P.; Ryynanen, M.J.; Kliment, C.R.; Salmenkivi, K.; Keski-Oja, J.; Kinnula, V.L.; Oury, T.D.; Koli, K. Gremlin-mediated decrease in bone morphogenetic protein signaling promotes pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, L.; Farkas, D.; Gauldie, J.; Warburton, D.; Shi, W.; Kolb, M. Transient overexpression of Gremlin results in epithelial activation and reversible fibrosis in rat lungs. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Luo, W.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Y.; Chao, J. GREM1/PPP2R3A expression in heterogeneous fibroblasts initiates pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, R.H.; Ali, I.; Tate, M.; Lavin, D.; Krishnakumar, A.; Kok, H.M.; Hombrebueno, J.R.; Dunne, P.D.; Bingham, V.; Goldschmeding, R.; et al. Gremlin1 plays a key role in kidney development and renal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2017, 312, F1141–F1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zeng, Q.S.; Zou, M.; Zeng, J.; Nie, J.; Chen, D.; Gan, H.T. Targeting Gremlin 1 Prevents Intestinal Fibrosis Progression by Inhibiting the Fatty Acid Oxidation of Fibroblast Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 663774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, G.; Keskin, O.; Fraternali, F.; Gursoy, A. Emerging role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system as drug targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 3175–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komander, D.; Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S. Breaking the chains: Structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Salihi, M.A.; Herhaus, L.; Macartney, T.; Sapkota, G.P. USP11 augments TGFbeta signalling by deubiquitylating ALK5. Open Biol. 2012, 2, 120063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.W.; Seong, D.; Seo, J.; Jeong, M.; Lee, H.K.; Song, J. USP11-dependent selective cIAP2 deubiquitylation and stabilization determine sensitivity to Smac mimetics. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Tan, X.; Shi, Y.; Xu, G.; Mao, R.; Gu, X.; Fan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Burlingame, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. USP11 negatively regulates TNFalpha-induced NF-kappaB activation by targeting on IkappaBalpha. Cell Signal 2010, 22, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Li, L.; Dai, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Ling, N.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. The regulation of NONO by USP11 via deubiquitination is linked to the proliferation of melanoma cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ou, B.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Song, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Peng, Z. USP11 promotes growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer via PPP1CA-mediated activation of ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. eBioMedicine 2019, 48, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacko, A.M.; Nan, L.; Li, S.; Tan, J.; Zhao, J.; Kass, D.J.; Zhao, Y. De-ubiquitinating enzyme, USP11, promotes transforming growth factor beta-1 signaling through stabilization of transforming growth factor beta receptor II. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Cao, J.; Luo, J.; Jiao, Y. Targeting USP11 may alleviate radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating endothelium tight junction. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Xian, Y.F.; Ip, S.P.; Tsai, S.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Che, C.T. Chemical and biological differentiation of Cortex Phellodendri Chinensis and Cortex Phellodendri Amurensis. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Lu, H.J.; Lin, C.H.; Wu, T.S. A rapid and simple determination of protoberberine alkaloids in cortex phellodendri by 1H NMR and its application for quality control of commercial traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.F.; Lin, Z.X.; Ip, S.P.; Su, Z.R.; Chen, J.N.; Lai, X.P. Comparison the neuropreotective effect of Cortex Phellodendri chinensis and Cortex Phellodendri amurensis against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.F.; Mao, Q.Q.; Ip, S.P.; Lin, Z.X.; Che, C.T. Comparison on the anti-inflammatory effect of Cortex Phellodendri Chinensis and Cortex Phellodendri Amurensis in 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate-induced ear edema in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Li, R.Y.; Shi, M.J.; Zhao, Y.X.; Yan, Y.; Xu, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.T.; Zhang, Y.B. Demethyleneberberine alleviates inflammatory bowel disease in mice through regulating NF-kappaB signaling and T-helper cell homeostasis. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ge, C.; Ye, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y. Demethyleneberberine alleviates Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute pneumonia by inhibiting the AIM2 inflammasome and oxidative stress. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 83, 102259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Demethyleneberberine attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with activation of AMPK and inhibition of oxidative stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 472, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, Y.; Qiang, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y. Demethyleneberberine Protects against Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice by Modulating NF-kappaB Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qiang, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y. Demethyleneberberine, a natural mitochondria-targeted antioxidant, inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and steatosis in alcoholic liver disease mouse model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Luan, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R. Demethyleneberberine blocked the maturation of IL-1beta in inflammation by inhibiting TLR4-mitochondria signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 113, 109319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoupalova, E.; Smith, S.; Cheng, G.; Thannickal, V.J. Oxidative Stress in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Compr. Physiol. 2020, 10, 509–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkauskas, C.E.; Noble, P.W. Cellular mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. 7. New insights into the cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 306, C987–C996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, I.A.; Schimmel, J.; Eifler, K.; Olsen, J.V.; Vertegaal, A.C.O. Ubiquitin-specific Protease 11 (USP11) Deubiquitinates Hybrid Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO)-Ubiquitin Chains to Counteract RING Finger Protein 4 (RNF4). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15526–15537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Feng, X.; Chai, L.; Cao, S.; Qiu, F. The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, D.; Ji, K.; Tao, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J. Demethyleneberberine induces cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence of NSCLC cells via c-Myc/HIF-1alpha pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, B.; Sun, X.; Xie, Y.; Yang, H.; Zi, C.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. Demethyleneberberine promotes apoptosis and suppresses TGF-beta/Smads induced EMT in the colon cancer cells HCT-116. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2021, 39, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.K.; Ward, C.; Eapen, M.S.; Myers, S.; Hallgren, O.; Levine, H.; Sohal, S.S. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a spectrum of states: Role in lung development, homeostasis, and disease. Dev. Dyn. 2018, 247, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coward, W.R.; Saini, G.; Jenkins, G. The pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2010, 4, 367–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, I.E.; Eickelberg, O. New cellular and molecular mechanisms of lung injury and fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2012, 380, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontake, V.; Kasam, R.K.; Sinner, D.; Korfhagen, T.R.; Reddy, G.B.; White, E.S.; Jegga, A.G.; Madala, S.K. Wilms’ tumor 1 drives fibroproliferation and myofibroblast transformation in severe fibrotic lung disease. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e121252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, M.S.; Kwon, Y.W.; Lee, S.; Fang, L.T.; Choi, H.; Ray, R.; Kang, H.C.; Mao, J.H.; Jablons, D.; Kim, I.J. Gremlin is overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma and increases cell growth and proliferation in normal lung cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S.; Komander, D. Breaking the chains: Deubiquitylating enzyme specificity begets function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaid, S.; Brandts, C.H.; Serve, H.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitination and selective autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, S.; Gutierrez Barrera, A.M.; Liu, D.; Pusztai, L.; Litton, J.; Valero, V.; Hunt, K.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Wu, Y.; Symmans, F.; et al. USP-11 as a predictive and prognostic factor following neoadjuvant therapy in women with breast cancer. Cancer J. 2013, 19, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, R.A.; Peng, Y.; Norris, Z.A.; Tholey, R.M.; Talbott, V.A.; Liang, Q.; Ai, Y.; Miller, K.; Lal, S.; Cozzitorto, J.A.; et al. Mitoxantrone targets human ubiquitin-specific peptidase 11 (USP11) and is a potent inhibitor of pancreatic cancer cell survival. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Luo, A.; Shrivastava, I.; He, M.; Huang, Y.; Bahar, I.; Liu, Z.; Wan, Y. Regulation of XIAP Turnover Reveals a Role for USP11 in Promotion of Tumorigenesis. eBioMedicine 2017, 15, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, H.Y.; Yang, N.H.; Li, J.Y.; Sun, X.A.; Guo, H.J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme USP11 promotes renal tubular cell senescence and fibrosis via inhibiting the ubiquitin degradation of TGF-beta receptor II. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 44, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Tao, M.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Cui, B.; Qiu, A.; et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 11 promotes partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by deubiquitinating the epidermal growth factor receptor during kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2022, 103, 544–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, C.; Huang, M.; Han, Y.; Shou, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y. Demethyleneberberine Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Disruption of USP11 Deubiquitinating GREM1. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030279
Ge C, Huang M, Han Y, Shou C, Li D, Zhang Y. Demethyleneberberine Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Disruption of USP11 Deubiquitinating GREM1. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Chuang, Mengsheng Huang, Yanhong Han, Chang Shou, Dongyin Li, and Yubin Zhang. 2024. "Demethyleneberberine Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Disruption of USP11 Deubiquitinating GREM1" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030279
APA StyleGe, C., Huang, M., Han, Y., Shou, C., Li, D., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Demethyleneberberine Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Disruption of USP11 Deubiquitinating GREM1. Pharmaceuticals, 17(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030279




