In Silico Exploration of Novel EGFR Kinase Mutant-Selective Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Computational Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
2.1. Pharmacophore Model Generation
2.2. Virtual Screening
2.3. Pharmacophore Validation
2.4. ADMET Properties
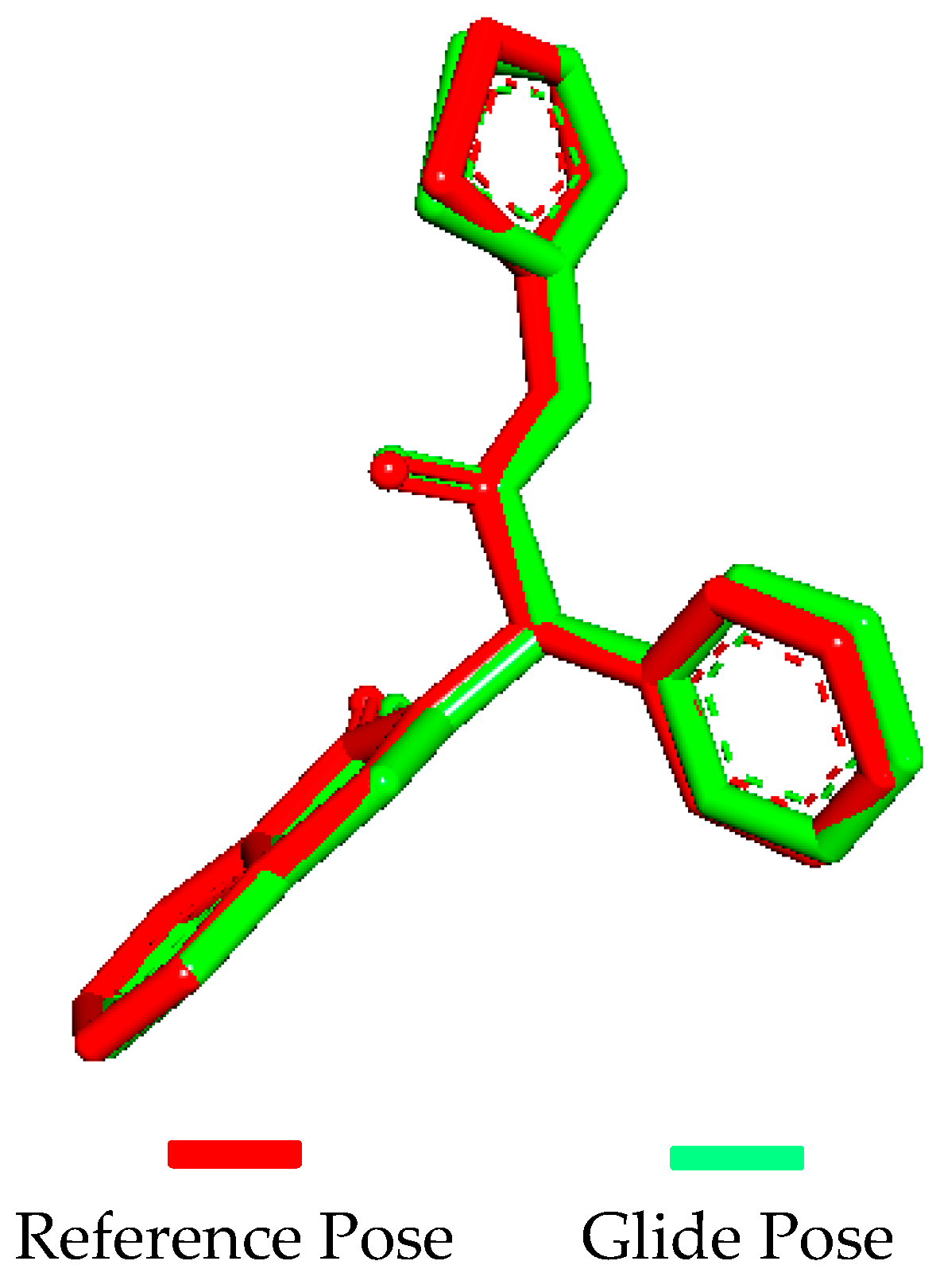
2.5. Molecular Docking Validation
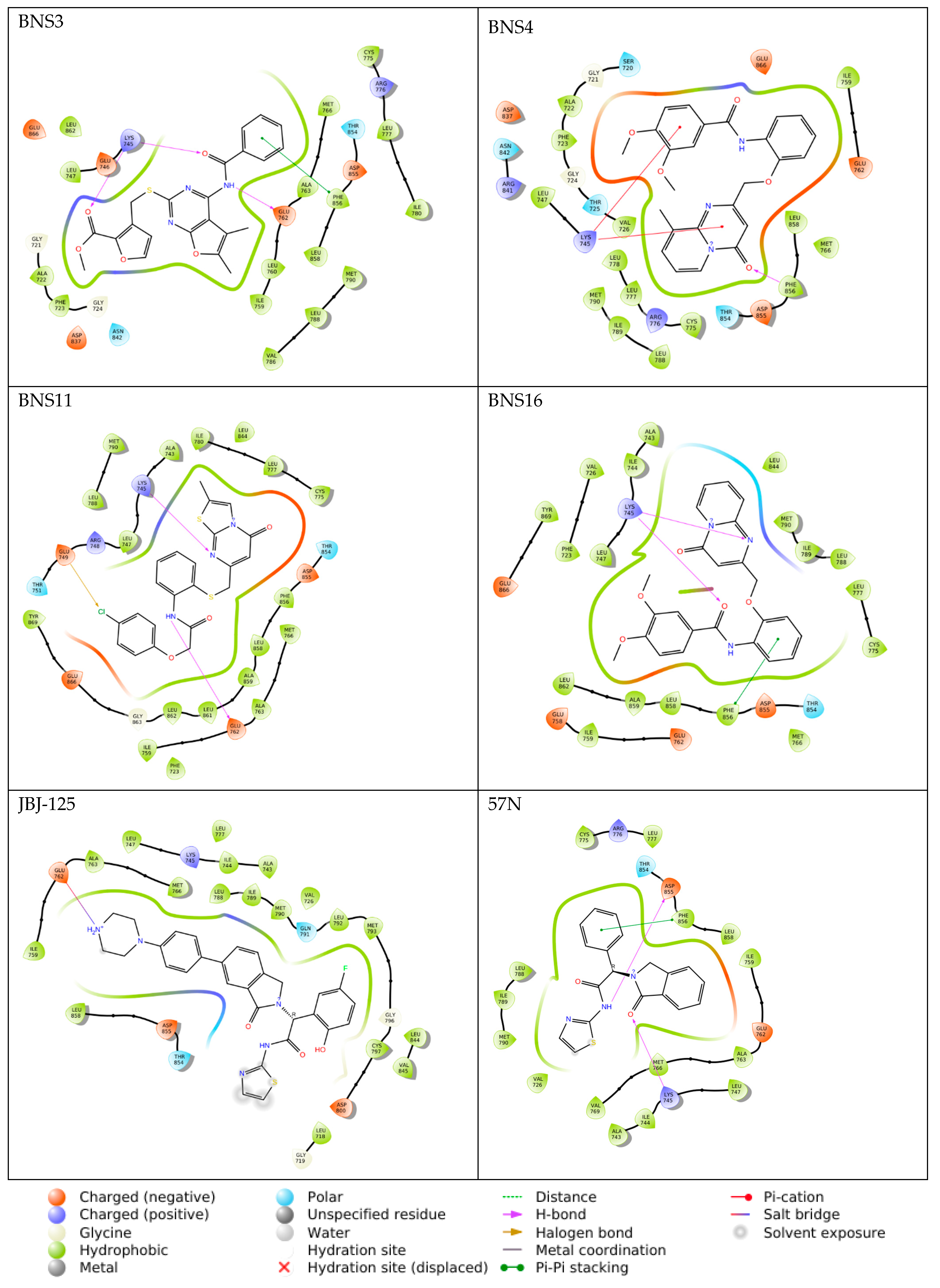
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Induced Fit Docking
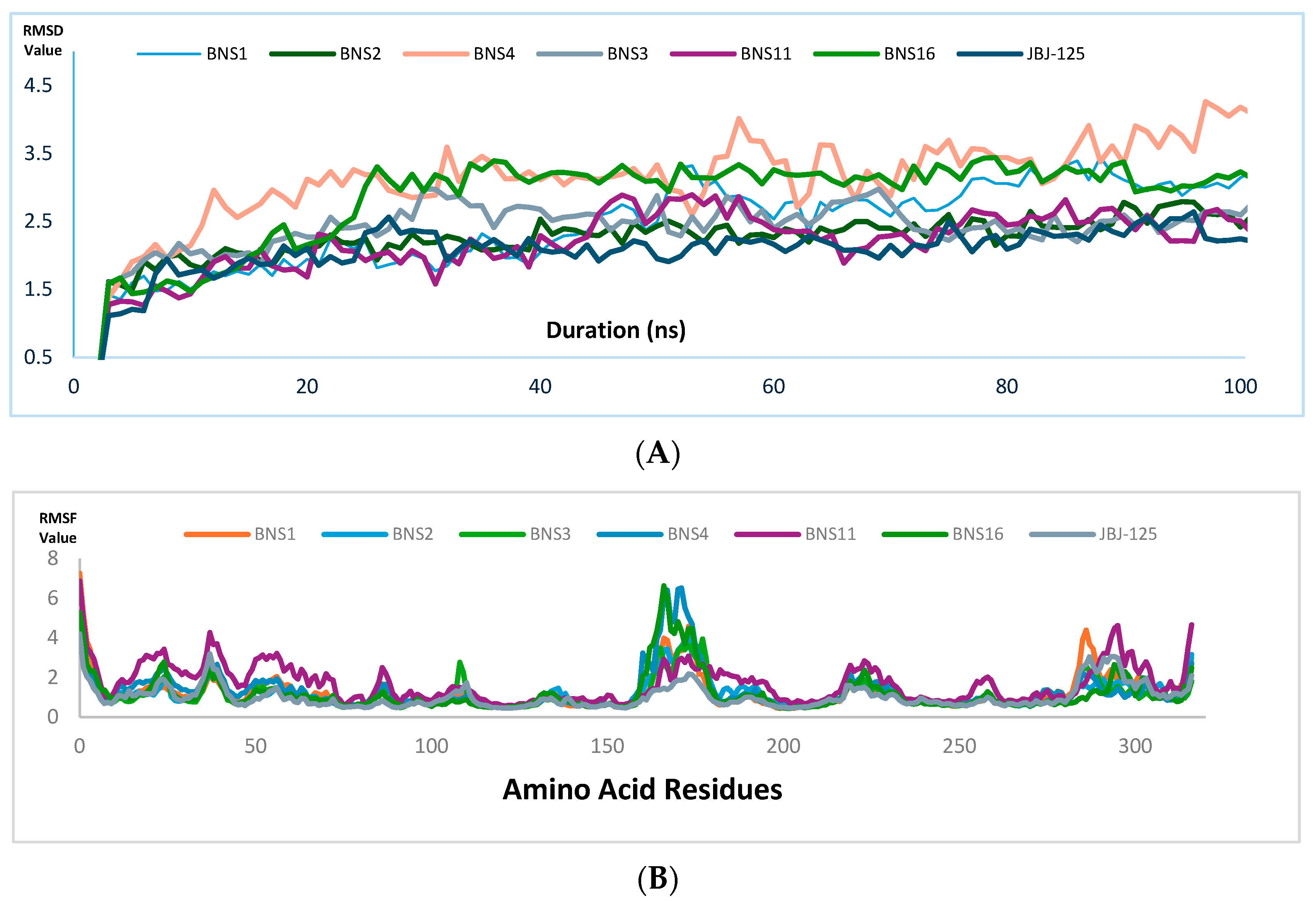
2.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Pharmacophore Designing/Modeling
4.2. Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening
4.3. Pharmacophore Validation
4.4. ADME Profile
4.5. Ligand Preparation
4.6. Protein Preparation
4.7. Docking Simulation Validation
4.8. Molecular Docking
4.9. Induced Fit Docking
4.10. Molecular Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fawwaz, M.; Mishiro, K.; Nishii, R.; Sawazaki, I.; Shiba, K.; Kinuya, S.; Ogawa, K. Synthesis and Fundamental Evaluation of RadioiodinatedRociletinib (CO-1686) as a Probe to Lung Cancer with L858R/T790M Mutations of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR). Molecules 2020, 25, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cuan, X.; Zhu, W.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sheng, J.; Zi, C.; Wang, X. An EGCG Derivative in Combination with Nimotuzumab for the Treatment of Wild-Type EGFR NSCLC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 34–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schechter, A.; Stern, D.; Vaidyanathan, L.; Decker, S.J.; Drebin, J.A.; Greene, M.I.; Weinberg, R.A. Neu Oncogene: An erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature 1984, 312, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, T.; Kartasasmita, R.E.; Ohwada, T.; Tjahjono, D.H. Structural Insight and Development of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.; Kumari, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Singh, A.; Mishra, A. Discovery of the allosteric inhibitor from actinomyces metabolites to target EGFRCSTMLR mutant protein: Molecular modeling and free energy approach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, P.A.; Moody, C.; Murali, R. Allosteric modulation of Ras and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Emerging therapeutic opportunities. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, S.; Pai, K.S.R.; Nayak, Y. Advances in targeting EGFR allosteric site as anti-NSCLC therapy to overcome the drug resistance. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Classification of small molecule protein kinase inhibitors based upon the structures of their drug-enzyme complexes. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purba, E.; Saita, E.; Maruyama, I. Activation of the EGF receptor by ligand binding and oncogenic mutations: The “rotation model”. Cell 2017, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyett, T.S.; To, C.; Heppner, D.E.; Rana, J.K.; Schmoker, A.M.; Jang, J.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Gomez, G.; Scott, D.A.; Gray, N.S.; et al. Molecular basis for cooperative binding and synergy of ATP-site and allosteric EGFR inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, H.; Palumbo, R.; Petrosyan, S.; Mkrtchyan, A.; Galstyan, A.; Saghyan, A.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Vicidomini, C.; Fik-Jaskólka, M.; Roviello, G.N. BSA Binding and Aggregate Formation of a Synthetic Amino Acid with Potential for Promoting Fibroblast Proliferation: An In Silico, CD Spectroscopic, DLS, and Cellular Study. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, J.A. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curves. In Wiley StatsRef:Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Teugels, F.R.J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rácz, A.; Bajusz, D.; Héberger, K. Multi-level comparison of machine learningclassifiers and their performance metrics. Molecules 2019, 24, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imrie, F.; Bradley, A.R.; Deane, C.M. Generating property-matched decoy molecules using deep learning. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drwal, M.N.; Banerjee, P.; Dunkel, M.; Wettig, M.R.; Preissner, R. ProTox: A web server for the in silico prediction of rodent oral toxicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W53–W58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, K.J.; Chow, E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Gregersen, B.A.; Klepeis, J.L.; Kolossvary, I.; Moraes, M.A.; Sacerdoti, F.D.; et al. Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing ( SC ‘06), Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vemula, D.; Maddi, D.R.; Bhandari, V. Homology modeling, virtual screening, molecular docking, and dynamics studies for discovering Staphylococcus epidermidis FtsZ inhibitors. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1087676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyambo, K.; Tapfuma, K.I.; Adu-Amankwaah, F.; Julius, L.; Baatjies, L.; Niang, I.S.; Smith, L.; Govender, K.K.; Ngxande, M.; Watson, D.J.; et al. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations and binding free energy studies of interactions between Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pks13, PknG and bioactive constituents of extremophilic bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Singh, A.V.; Paudel, N.; Kanase, A.; Falletta, E.; Kerkar, P.; Heyda, J.; Barghash, R.F.; Pratap Singh, S.; Soos, M. Herbal concoction Unveiled: A computational analysis of phytochemicals’ pharmacokinetic and toxicological profiles using novel approach methodologies (NAMs). Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arnott, J.A.; Planey, S.L. The influence of lipophilicity in drug discovery and design. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug solubility: Importance and enhancement techniques. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J. Prediction of blood–brain barrier permeation in drug discovery from in vivo, in vitro and in silico models. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.B. Drugs as P-glycoprotein substrates, inhibitors, and inducers. Drug Metab. Rev. 2002, 34, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farid, R.; Day, T.; Friesner, R.A.; Pearlstein, R.A. New insights about HERG blockade obtained from protein modeling, potentialenergy mapping, and docking studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3160–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, W.; Day, T.; Jacobson, M.P.; Friesner, R.A.; Farid, R. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenk, R.; Schipani, A.; James, D.; Krasowski, A.; Gilbert, I.H.; Frearson, J.; Wyatt, P.G. Lessons Learnt from Assembling Screening Libraries for Drug Discovery for Neglected Diseases. ChemMedChem Chem. Enabling Drug Discov. 2007, 3, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.S.; Singh, S.R.; Sahoo, A.; Hussain, T.; Pati, S. Anti-HIV-drug and phyto-flavonoid combination against SARS-CoV-2: A molecular docking-simulation base assessment. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 40, 6463–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Randive, V.; Mahadik, I.; Asgaonkar, K. Design, In Silico Molecular Docking, and ADMET Prediction of Amide Derivatives of Chalcone Nucleus as EGFR Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2024, 21, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Lu, W. Identification of Dual-Target Inhibitors for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and AKT: Virtual Screening Based on Structure and Molecular Dynamics Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, Y.; Zou, W.; Peng, L.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Q.; Chen, M.; Jia, S.; Zhang, H.; Lan, Z.; Zheng, P.; et al. Design, Synthesis, Antiproliferative Activity and Docking Studies of Quinazoline Derivatives Bearing 2,3-dihydro-indole or 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline As Potential EGFR Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 154, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourad, M.A.; Abo Elmaaty, A.; Zaki, I.; Mourad, A.A.; Hofni, A.; Khodir, A.E.; Elkamhawyf, A.; Roh, E.J.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Novel topoisomerase II/EGFR dual inhibitors: Design, synthesis and docking studies of naphtho[2′,3′:4,5]thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidine hybrids as potential anticancer agents with apoptosis inducing activity. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2205043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunseri, J.; Koes, D.R. Pharmit: Interactive exploration of chemical space. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W442–W448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Agarwal, P.; Rathi, E.; Kini, S.G. Computer-aided identification of human carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme VII inhibitors 211as potential antiepileptic agents. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 4850–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S. Pharmacophore modeling and applications in drug discovery: Challenges and recent advances. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J.J.; Tang, K.G.; Young, J.; Dandarchuluun, C.; Wong, B.R.; Khurelbaatar, M.; Moroz, Y.S.; Mayfield, J.; Sayle, R.A. ZINC20—A Free Ultralarge-Scale Chemical Database for Ligand Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 6065–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Rao, S.N. PHASE: A novel approach to pharmacophore modeling and 3D database searching. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yun, C.H.; Park, E.; Ercan, D.; Manuia, M.; Juarez, J.; Xu, C.; Rhee, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature 2016, 534, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schödinger Release, S. 2: Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.K.; Muttineni, R.; Singh, S.K. Extra precision docking, free energy calculation and molecular dynamics simulation studies of CDK2 inhibitors. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 334, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelley, J.C.; Cholleti, A.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Timlin, M.R.; Uchimaya, M. Epik: A software program for pKa prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
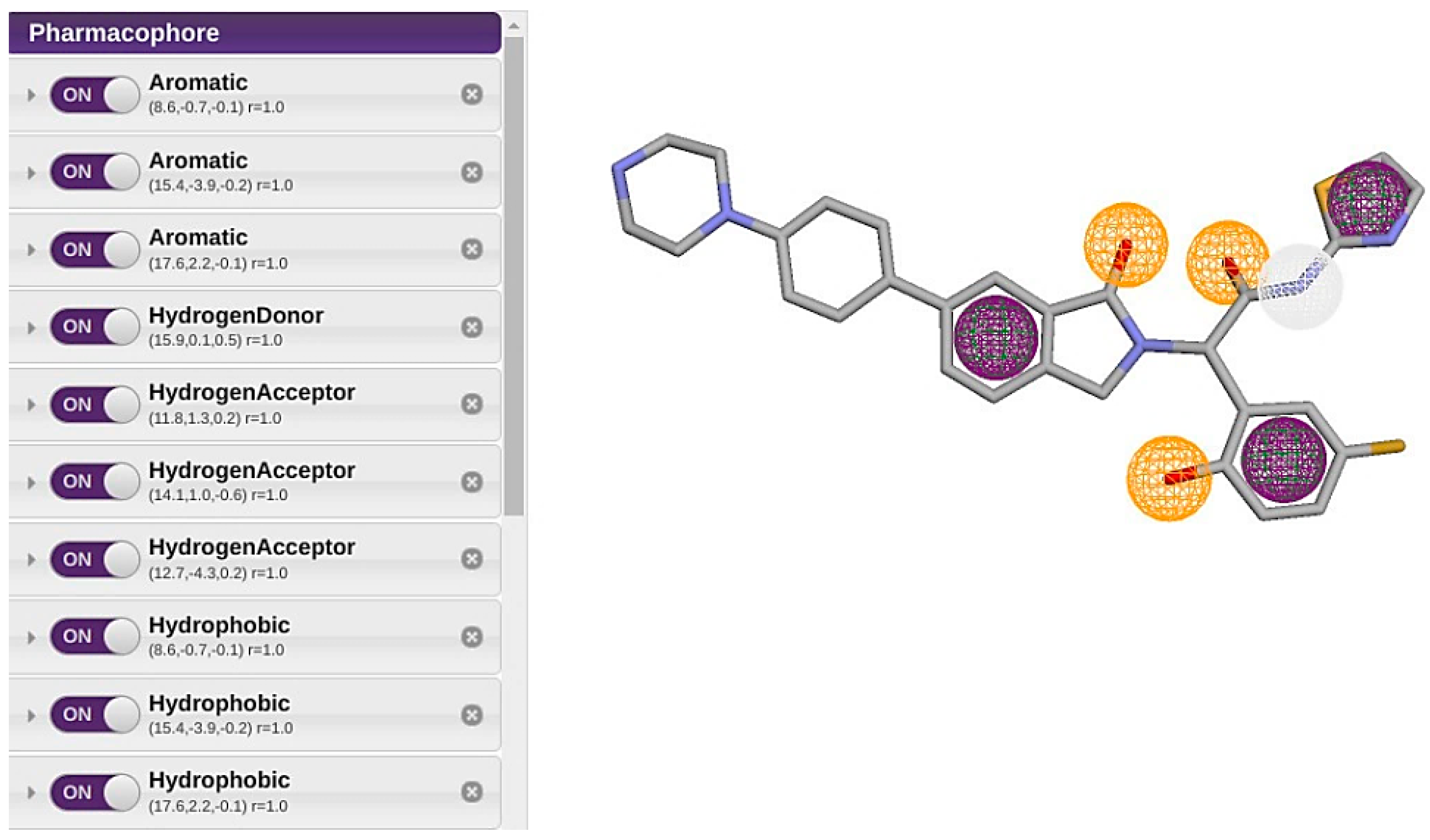


| Feature | X | Y | Z | Radious |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aromatic Ring 1 | 8.6 | −0.7 | −0.1 | 1 |
| Aromatic Ring 2 | 15.4 | −3.9 | −0.2 | 1 |
| Aromatic Ring 3 | 17.6 | 2.2 | −0.1 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 15.9 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor 1 | 11.8 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor 2 | 14.1 | 1 | −0.6 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor 3 | 12.7 | −4.3 | 0.2 | 1 |
| Hydrophobic Bond 1 | 8.6 | −0.7 | −0.1 | 1 |
| Hydrophobic Bond 2 | 15.4 | −3.9 | −0.2 | 1 |
| Hydrophobic Bond 3 | 17.6 | 2.2 | −0.1 | 1 |
| Scheme | Compound ID | Code Number | SMILE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ZINC000012638703 | BNS1 | COc1cc(OC)cc(C(=O)Nc2ccccc2-c2nnn(CC(=O)N3CCCc4ccccc43)n2)c1 |
| 2 | ZINC000016694801 | BNS2 | COc1ccccc1N(CC(=O)Nc1ccccc1Oc1ccccc1)S(=O)(=O)c1cccs1 |
| 3 | ZINC000012777271 | BNS3 | COC(=O)c1occc1CSc1nc(NC(=O)c2ccccc2)c2c(C)c(C)oc2n1 |
| 4 | ZINC000033067859 | BNS4 | COc1ccc(C(=O)Nc2ccccc2OCc2cc(=O)n3cccc(C)c3n2)cc1OC |
| 5 | ZINC000020617126 | BNS5 | COc1ccc(C)cc1NC(=O)c1cn(C)nc1C(=O)Nc1cc(C)ccc1OC |
| 6 | ZINC000020617150 | BNS6 | COc1ccccc1NC(=O)c1cn(C)nc1C(=O)Nc1ccccc1OC |
| 7 | ZINC000059488018 | BNS7 | Oc1ccc(Br)cc1/C=N/N=C1/c2ccccc2-c2nc3ccccc3nc21 |
| 8 | ZINC000059488022 | BNS8 | O=[N+]([O-])c1ccc(O)c(/C=N/N=C2/c3ccccc3-c3nc4ccccc4nc32)c1 |
| 9 | ZINC000059488016 | BNS9 | Oc1cc(Cl)ccc1/C=N/N=C1/c2ccccc2-c2nc3ccccc3nc21 |
| 10 | ZINC000013577005 | BNS10 | COc1ccc(NC(=O)C[C@H]2C(=O)N(c3ccccc3)C(=S)N2CCc2ccccc2OC)cc1 |
| 11 | ZINC000021535964 | BNS11 | Cc1cn2c(=O)cc(CSc3ccccc3NC(=O)COc3ccc(Cl)cc3)nc2s1 |
| 12 | ZINC000059488021 | BNS12 | COc1ccc(O)c(/C=N/N=C2/c3ccccc3-c3nc4ccccc4nc32)c1 |
| 13 | ZINC000229934991 | BNS13 | O=C(Nc1ccc(Cl)cc1)[C@@H]1[C@H](c2cccc([N+](=O)[O-])c2)C2(C(=O) c3ccccc3C2=O)[C@H]2c3ccccc3C=NN12 |
| 14 | ZINC000041077159 | BNS14 | COc1cccc(C(=O)Nc2ccccc2OCc2cc(=O)n3c(ncn3C(C)C)n2)c1 |
| 15 | ZINC000000831474 | BNS15 | COc1ccccc1NC(=O)c1nc[nH]c1C(=O)Nc1ccccc1OC |
| 16 | ZINC000033067751 | BNS16 | COc1ccc(C(=O)Nc2ccccc2OCc2cc(=O)n3ccccc3n2)cc1OC |
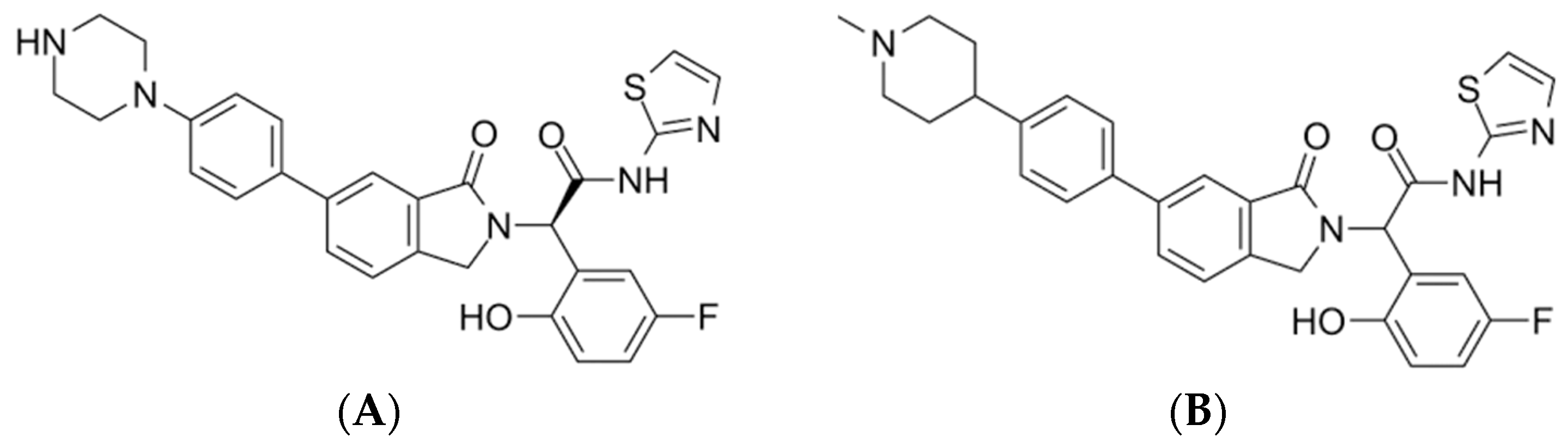
| 17 | Pubchem CID 124173751 | JBJ-125 | C1CN(CCN1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC4=C(CN(C4=O)C(C5=C(C=CC(=C5)F)O)C(=O)NC6=NC=CS6)C=C3 |
| Compounds. | Lipinski #Violations | Ghose #Violations | Veber #Violations | Egan #ViolAtions | Muegge #Violations | Bioavailability Score | PAINS #Alert | Brenk #Alert | Lead Likeness #Violations | Synthetic Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNS1 | Yes, 0 violations | No#2 | yes | yes | yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#3 | 3.75 |
| BNS2 | Yes, 0 violations | No#3 | yes | No | No | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#3 | 3.93 |
| BNS3 | Yes, 0 Violation | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#3 | 3.73 |
| BNS4 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#2 | 3.32 |
| BNS5 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#2 | 3.04 |
| BNS6 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#2 | 2.81 |
| BNS7 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 1 | 1 | No#2 | 3.3 |
| BNS8 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 1 | 3 | No#2 | 3.37 |
| BNS9 | Yes, 0 violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 1 | 1 | No#2 | 3.25 |
| BNS10 | Yes, 0 Violations | No#2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 1 | No#3 | 3.88 |
| BNS11 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#3 | 3.5 |
| BNS12 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 1 | 1 | No#2 | 3.37 |
| BNS13 | Yes, 1 Violation | No#2 | Yes | Yes | No#1 | 0.55 | 1 | 3 | No#2 | 5.32 |
| BNS14 | Yes,0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#2 | 3.34 |
| BNS15 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#2 | 2.66 |
| BNS16 | Yes, 0 Violations | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | No#2 | 3.17 |
| JBJ-125 | Yes, 1 Violations | No#2 | No#2 | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 1 | 0 | No#2 | 4.26 |
| Compounds | Hepato-Toxicity | Neuro Toxicity | Respiratory Toxicity | Carcino Genicity | Immuno Toxicity | Muta Genicity | Cyto Toxicity | Toxicity Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNS1 | Inactive | Active | Active | inactive | inactive | Moderately active | Moderately active | IV |
| BNS2 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Moderately inactive | inactive | inactive | inactive | VI |
| BNS3 | Moderately active | Inactive | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Inactive | V |
| BNS4 | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | Active | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | III |
| BNS5 | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Inactive | Moderately inactive | Inactive | IV |
| BNS6 | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Inactive | Moderately inactive | Inactive | IV |
| BNS7 | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | IV |
| BNS8 | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Active | Moderately inactive | Active | inactive | V |
| BNS9 | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | inactive | Moderately inactive | inactive | V |
| BNS10 | Moderately inactive | Active | Active | Moderately inactive | inactive | inactive | inactive | IV |
| BNS11 | Moderately active | Moderately active | Active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | IV |
| BNS12 | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | Active | Moderately active | inactive | V |
| BNS13 | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | inactive | Active | inactive | IV |
| BNS14 | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | Active | Moderately active | inactive | IV |
| BNS15 | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | inactive | Moderately inactive | inactive | IV |
| BNS16 | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | Active | Moderately inactive | Moderately active | Moderately active | Moderately inactive | IV |
| JBJ-125 | Moderately inactive | Active | Active | Moderately inactive | Active | Moderately inactive | Moderately inactive | IV |
| Compound | Glide Score (Kcal/mol) | IFD Score | Total Amino Acid Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| BNS1 | −11.625 | −667.73 | 29 |
| BNS2 | −10.313 | −663.75 | 29 |
| BNS3 | −9.874 | −666.74 | 27 |
| BNS4 | −10.408 | −671.39 | 27 |
| BNS5 | −10.217 | −664.96 | 25 |
| BNS6 | −9.853 | −664.44 | 23 |
| BNS11 | −10.193 | −665.93 | 27 |
| BNS14 | −10.442 | −671.61 | 25 |
| BNS15 | −9.692 | −663.93 | 21 |
| BNS16 | −11.237 | −673.11 | 24 |
| 57N | −10.388 | −662.43 | 20 |
| JBJ-125 | −11.119 | −659.97 | 26 |
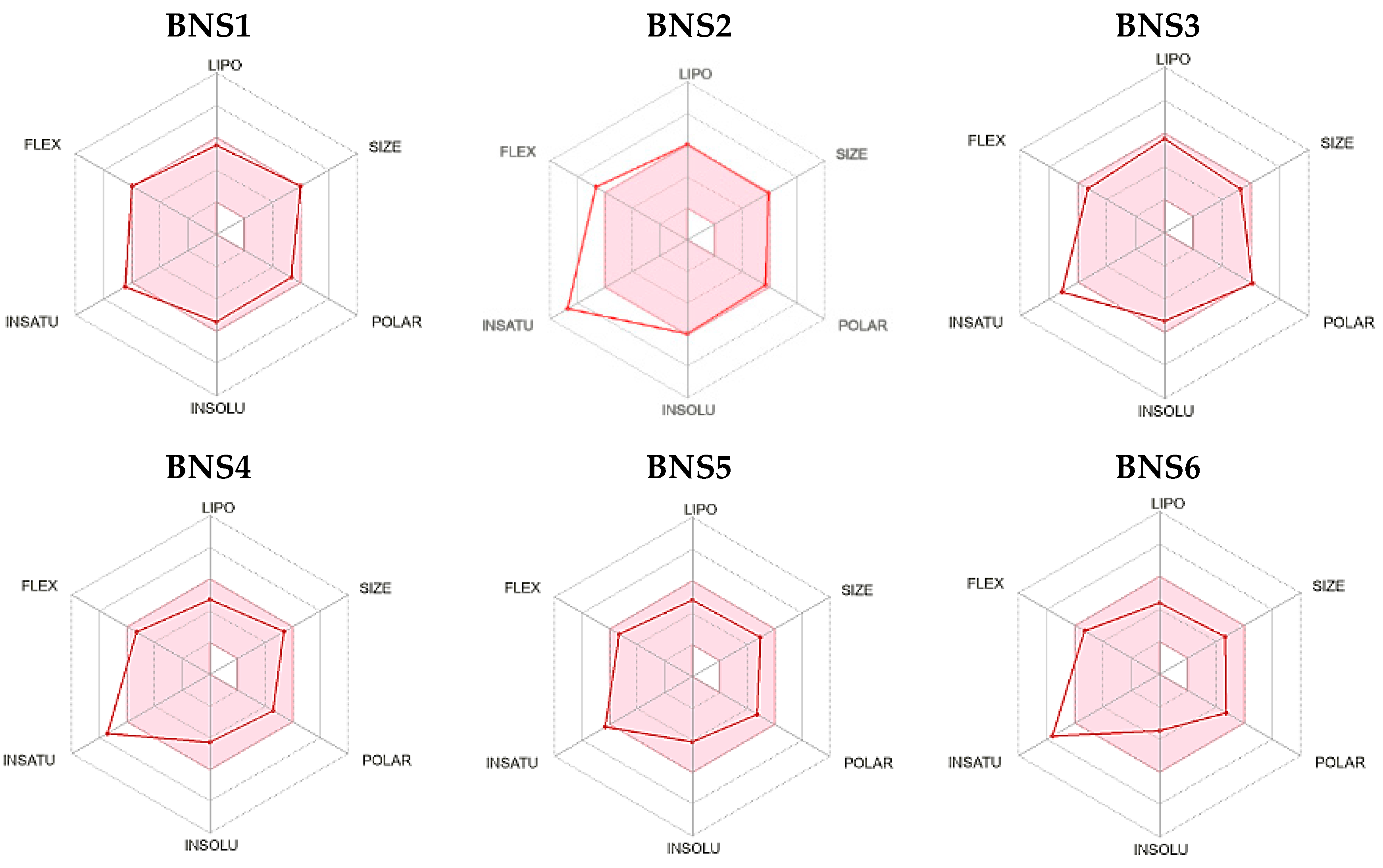
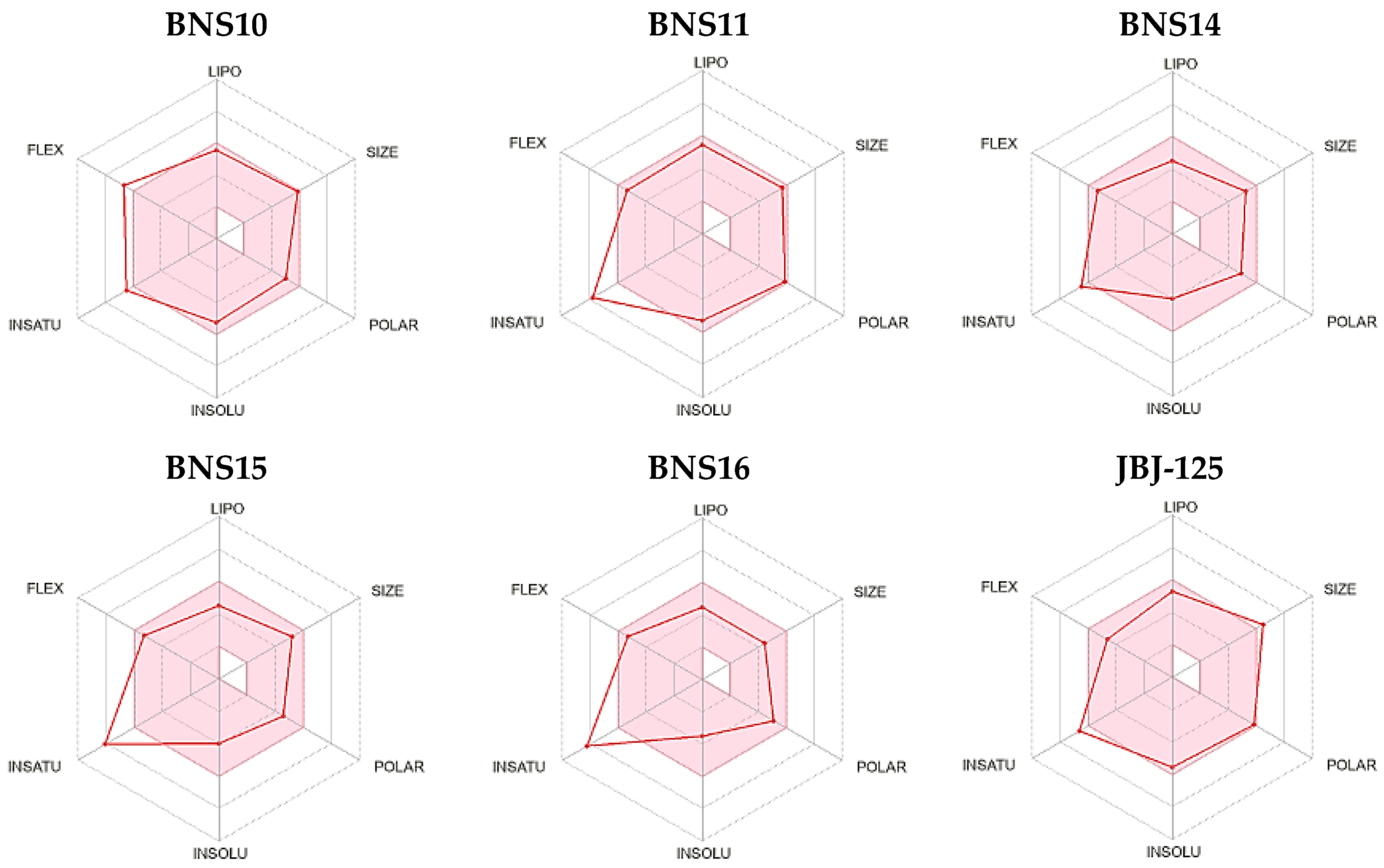
| Compound ID | RMSD | Mass | RBnds |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZINC000012777271 | 0.617 | 437 | 8 |
| ZINC000013577005 | 0.642 | 490 | 10 |
| ZINC000229934991 | 0.687 | 577 | 5 |
| ZINC000033067751 | 0.699 | 431 | 8 |
| ZINC000012638703 | 0.701 | 499 | 9 |
| ZINC000041077159 | 0.714 | 433 | 8 |
| ZINC000020617150 | 0.750 | 380 | 8 |
| ZINC000020617126 | 0.751 | 408 | 8 |
| ZINC000033067859 | 0.754 | 445 | 8 |
| ZINC000000831474 | 0.762 | 366 | 8 |
| ZINC000059488016 | 0.797 | 385 | 2 |
| ZINC000059488018 | 0.798 | 429 | 2 |
| ZINC000059488021 | 0.798 | 380 | 3 |
| ZINC000059488022 | 0.798 | 395 | 3 |
| ZINC000016694801 | 0.807 | 495 | 10 |
| ZINC000021535964 | 0.821 | 472 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, M.A.A.; Haq, M.M.; Chowdhury, M.A.R.; Tayara, H.; Shim, H.; Chong, K.T. In Silico Exploration of Novel EGFR Kinase Mutant-Selective Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Computational Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091107
Noor MAA, Haq MM, Chowdhury MAR, Tayara H, Shim H, Chong KT. In Silico Exploration of Novel EGFR Kinase Mutant-Selective Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Computational Approach. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091107
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Md Ali Asif, Md Mazedul Haq, Md Arifur Rahman Chowdhury, Hilal Tayara, HyunJoo Shim, and Kil To Chong. 2024. "In Silico Exploration of Novel EGFR Kinase Mutant-Selective Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Computational Approach" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091107
APA StyleNoor, M. A. A., Haq, M. M., Chowdhury, M. A. R., Tayara, H., Shim, H., & Chong, K. T. (2024). In Silico Exploration of Novel EGFR Kinase Mutant-Selective Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Computational Approach. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091107









