Demystifying the Antidepressant Mechanism of Action of Stinels, a Novel Class of Neuroplastogens: Positive Allosteric Modulators of the NMDA Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The NMDAR as a Therapeutic Target
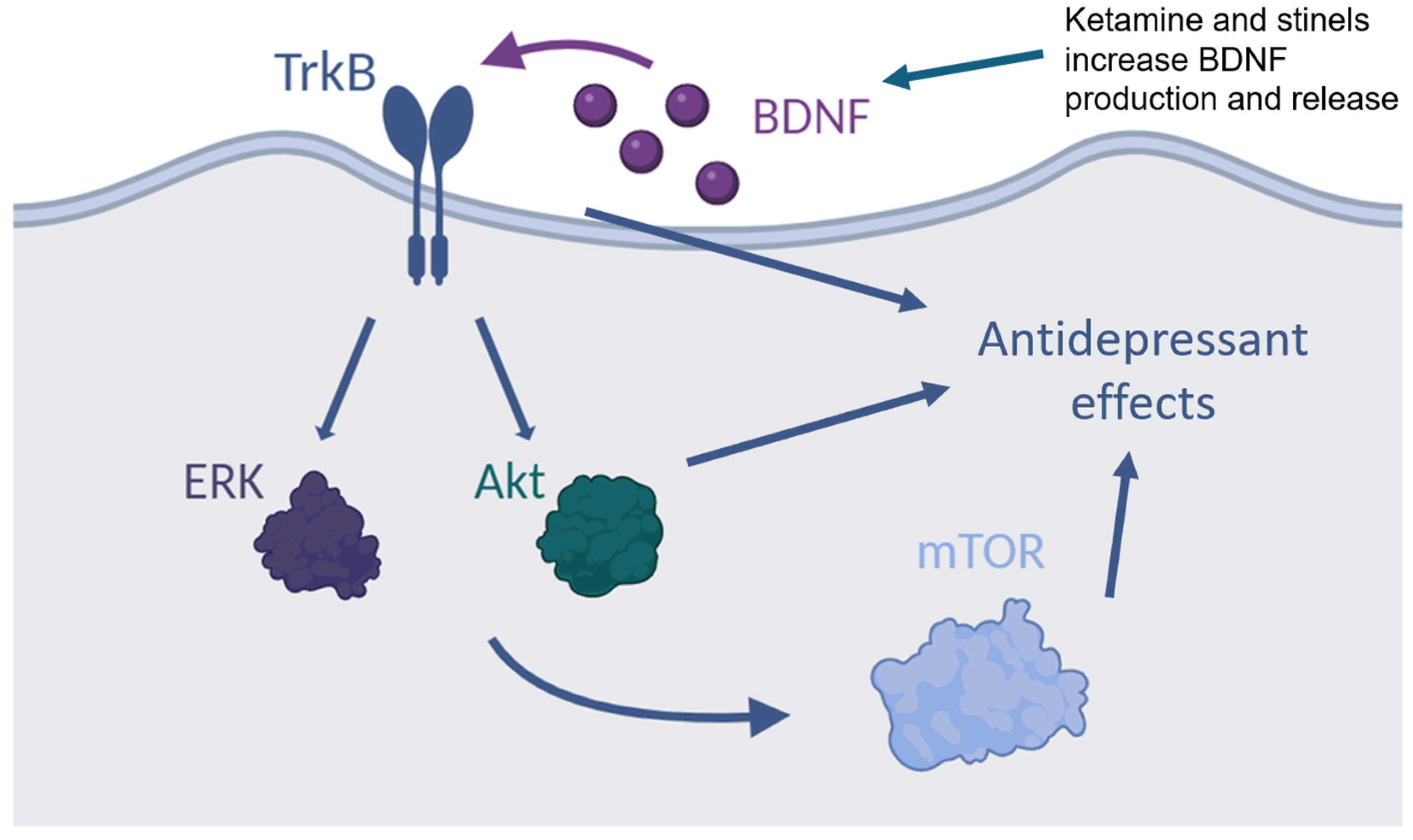
3. NMDAR, BDNF, and Depression
4. NMDAR Modulators
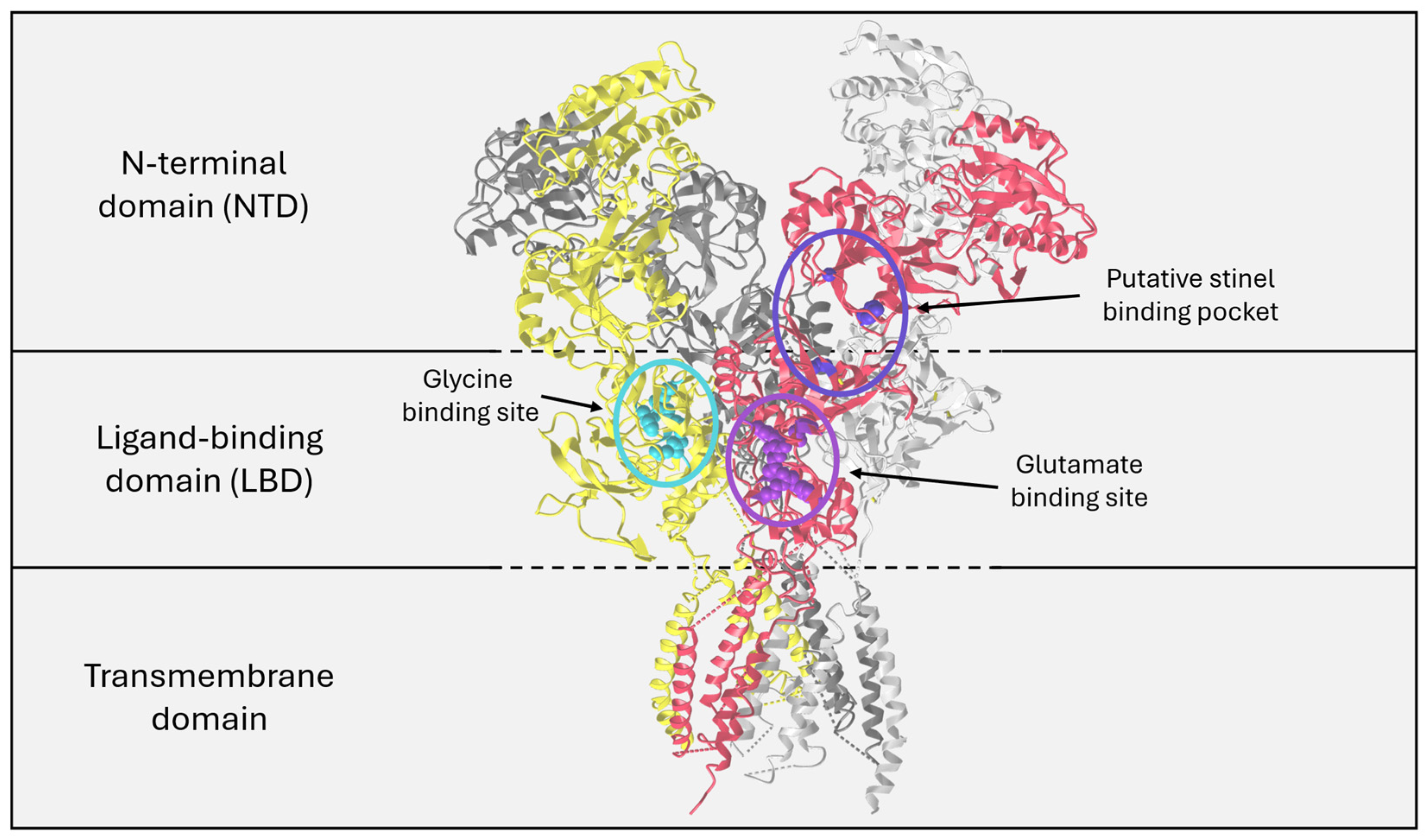
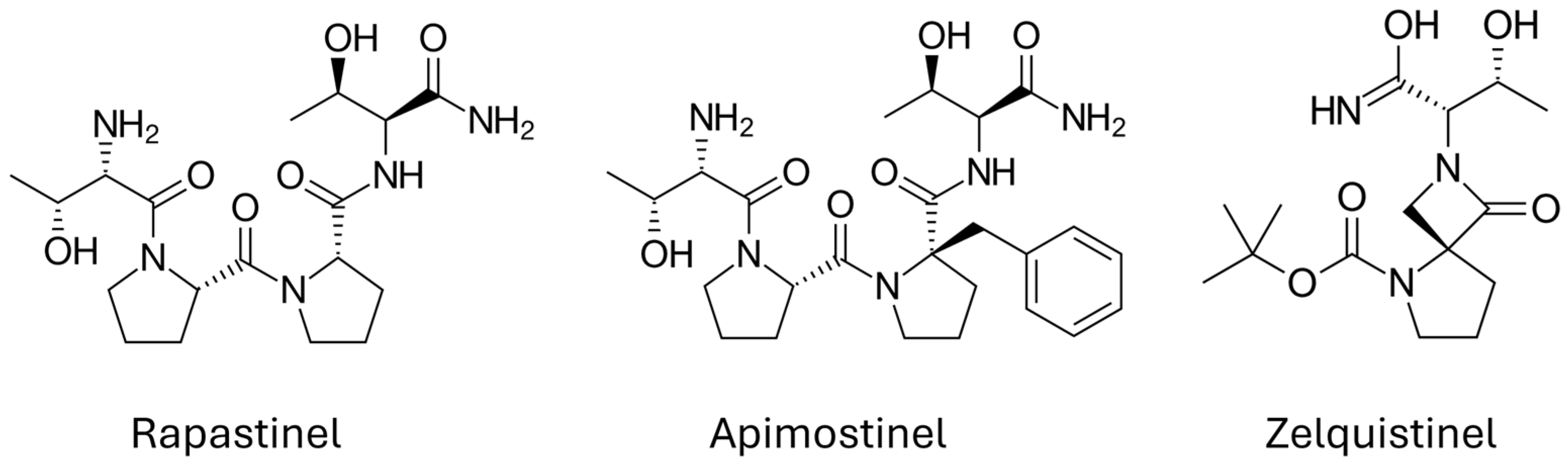
5. Stinels Are NMDAR PAMs
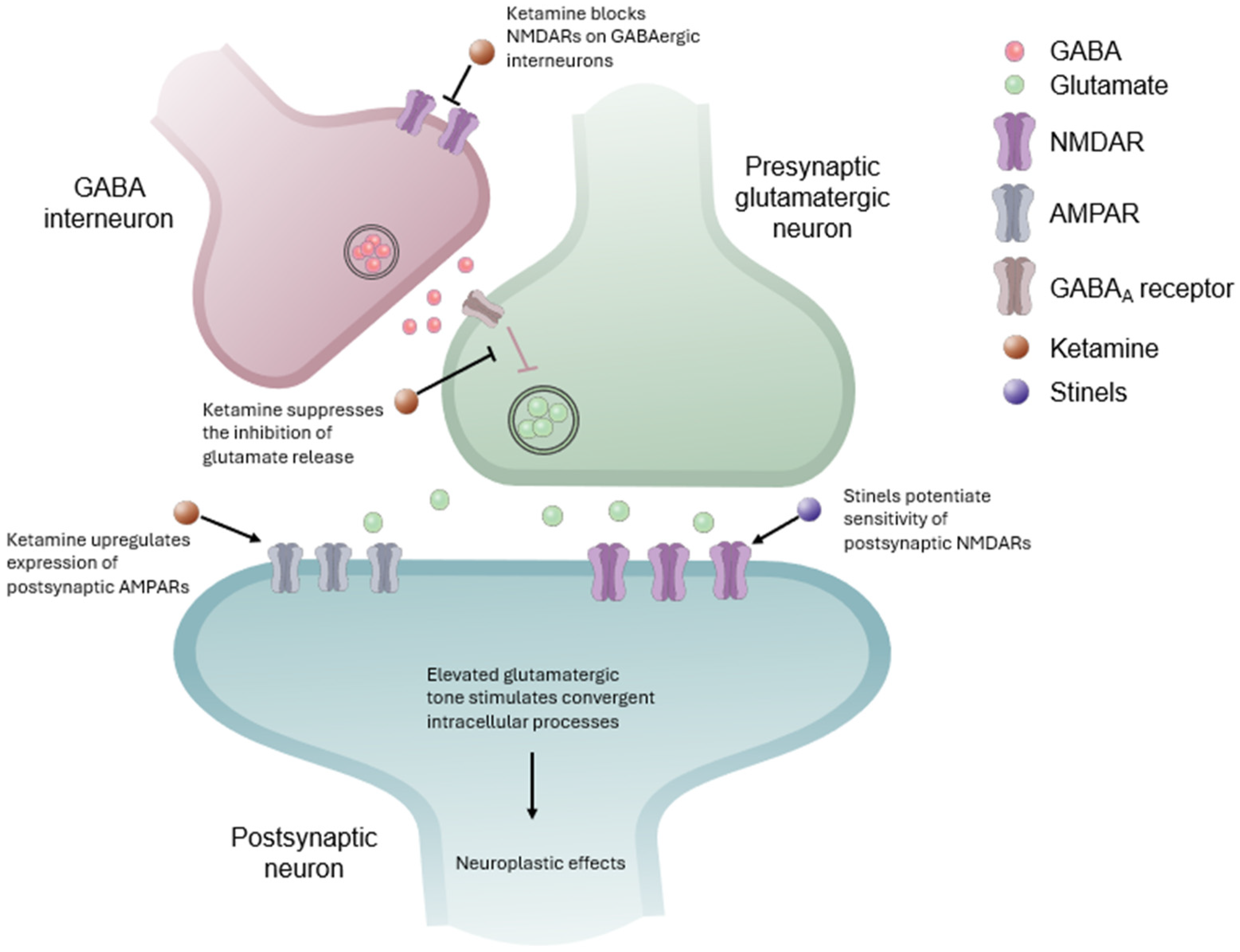
6. Convergent Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine and Stinels
7. Current Challenges and Future Efforts
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harmer, C.J.; Duman, R.S.; Cowen, P.J. How do antidepressants work? New perspectives for refining future treatment approaches. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, S.M. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific Basis and Practical Applications, 5th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Newport, D.J.; Carpenter, L.L.; McDonald, W.M.; Potash, J.B.; Tohen, M.; Nemeroff, C.B.; The APA Council of Research Task Force on Novel Biomarkers and Treatments. Ketamine and other NMDA antagonists: Early clinical trials and possible mechanisms in depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, T.; Seigler, M.D.; Stahl, S. Rapid onset brain plasticity at novel pharmacologic targets hypothetically drives innovations for rapid onset antidepressant actions. J. Psychopharmacol. 2023, 37, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, C.; Greb, A.C.; Cameron, L.P.; Wong, J.M.; Barragan, E.V.; Wilson, P.C.; Burbach, K.F.; Soltanzadeh Zarandi, S.; Sood, A.; Paddy, M.R.; et al. Psychedelics promote structural and functional neural plasticity. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3170–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.E. Psychoplastogens: A promising class of plasticity-promoting neurotherapeutics. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1179069518800508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castren, E.; Antila, H. Neuronal plasticity and neurotrophic factors in drug responses. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgdorf, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Nicholson, K.L.; Balster, R.L.; Leander, J.D.; Stanton, P.K.; Gross, A.L.; Kroes, R.A.; Moskal, J.R. GLYX-13, a NMDA receptor glycine-site functional partial agonist, induces antidepressant-like effects without ketamine-like side effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgdorf, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Weiss, C.; Gross, A.; Boikess, S.R.; Kroes, R.A.; Khan, M.A.; Burch, R.M.; Rex, C.S.; Disterhoft, J.F.; et al. The long-lasting antidepressant effects of rapastinel (GLYX-13) are associated with a metaplasticity process in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 2015, 308, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskal, J.R.; Burch, R.; Burgdorf, J.S.; Kroes, R.A.; Stanton, P.K.; Disterhoft, J.F.; Leander, J.D. GLYX-13, an NMDA receptor glycine site functional partial agonist enhances cognition and produces antidepressant effects without the psychotomimetic side effects of NMDA receptor antagonists. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2014, 23, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothula, S.; Liu, R.J.; Wu, M.; Sliby, A.N.; Picciotto, M.R.; Banerjee, P.; Duman, R.S. Positive modulation of NMDA receptors by AGN-241751 exerts rapid antidepressant-like effects via excitatory neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, I.D.; de Sousa, R.T.; Zarate, C.A. Glutamatergic modulators in depression. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, S.T.; Sanacora, G. A new generation of antidepressants: An update on the pharmaceutical pipeline for novel and rapid-acting therapeutics in mood disorders based on glutamate/GABA neurotransmitter systems. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henter, I.D.; Park, L.T.; Zarate, C.A., Jr. Novel glutamatergic modulators for the treatment of mood disorders: Current status. CNS Drugs 2021, 35, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrobak, A.A.; Siwek, M. Drugs with glutamate-based mechanisms of action in psychiatry. Pharmacol. Rep. 2024, 76, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haring, R.; Stanton, P.K.; Scheideler, M.A.; Moskal, J.R. Glycine-like modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by a monoclonal antibody that enhances long-term potentiation. J. Neurochem. 1991, 57, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroebel, D.; Paoletti, P. Architecture and function of NMDA receptors: An evolutionary perspective. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 2615–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.B.; Yi, F.; Perszyk, R.E.; Furukawa, H.; Wollmuth, L.P.; Gibb, A.J.; Traynelis, S.F. Structure, function, and allosteric modulation of NMDA receptors. J. Gen. Physiol. 2018, 150, 1081–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyklicky, V.; Korinek, M.; Smejkalova, T.; Balik, A.; Krausova, B.; Kaniakova, M.; Lichnerova, K.; Cerny, J.; Krusek, J.; Dittert, I.; et al. Structure, function, and pharmacology of NMDA receptor channels. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63, S191–S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasgow, N.G.; Siegler Retchless, B.; Johnson, J.W. Molecular bases of NMDA receptor subtype-dependent properties. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.A. Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 87–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoll, R.A. A brief history of long-term potentiation. Neuron 2017, 93, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volianskis, A.; France, G.; Jensen, M.S.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Jane, D.E.; Collingridge, G.L. Long-term potentiation and the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Brain Res. 2015, 1621, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüscher, C.; Malenka, R.C. NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation and long-term depression (LTP/LTD). Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a005710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, C.; Sanacora, G.; Krystal, J.H. The NMDA receptor as a therapeutic target in major depressive disorder. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 6, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.E.; Yuan, H.; Perszyk, R.E.; Banke, T.G.; Xing, H.; Tsai, M.C.; Menniti, F.S.; Traynelis, S.F. Therapeutic potential of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulators in psychiatry. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 49, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Ascher, P.; Neyton, J. High-affinity zinc inhibition of NMDA NR1-NR2A receptors. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5711–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrilli, M.A.; Kranz, T.M.; Kleinhaus, K.; Joe, P.; Getz, M.; Johnson, P.; Chao, M.V.; Malaspina, D. The emerging role for zinc in depression and psychosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.T.; Radford, R.J.; Zastrow, M.L.; Zhang, D.Y.; Apfel, U.P.; Lippard, S.J.; Tzounopoulos, T. Modulation of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors by synaptic and tonic zinc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2705–E2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, Y.; Auberson, Y.P.; Zorumski, C.F. Zinc modulates bidirectional hippocampal plasticity by effects on NMDA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7181–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, G.; Comprido, D.; Duarte, C.B. BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt C, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci-D’Amato, L.; Speranza, L.; Volpicelli, F. Neurotrophic factor BDNF, physiological functions and therapeutic potential in depression, neurodegeneration and brain cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkholm, C.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF—A key transducer of antidepressant effects. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casarotto, P.; Umemori, J.; Castren, E. BDNF receptor TrkB as the mediator of the antidepressant drug action. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1032224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwag, B.J.; Springer, J.E. Activation of NMDA receptors increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA expression in the hippocampal formation. Neuroreport 1993, 5, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkbeiner, S. Calcium regulation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 2000, 57, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, M.V.; Melo, C.V.; Pereira, D.B.; Carvalho, R.F.; Carvalho, A.L.; Duarte, C.B. BDNF regulates the expression and traffic of NMDA receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 35, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, P.C.; Wu, K.; Levine, E.S.; Mount, H.T.; Xu, J.L.; Lin, S.Y.; Black, I.B. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor rapidly enhances phosphorylation of the postsynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8191–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanos, P.; Gould, T.D. Mechanisms of ketamine action as an antidepressant. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adell, A. Brain NMDA receptors in schizophrenia and depression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, J.B.; Moody, G.R.; Wollmuth, L.P. From bedside-to-bench: What disease-associated variants are teaching us about the NMDA receptor. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Rodrigues, N.B.; Lipsitz, O.; Chen-Li, D.; Lee, J.G.; Nasri, F.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Kratiuk, K.; Wang, A.; et al. The effect of intravenous ketamine on cognitive functions in adults with treatment-resistant major depressive or bipolar disorders: Results from the Canadian Rapid Treatment Center of Excellence (CRTCE). Psychiatry Res. 2021, 302, 113993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, W.N. Stressor-induced NMDAR dysfunction as a unifying hypothesis for the aetiology, pathogenesis and comorbidity of clinical depression. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 77, 508–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaut, O.; Schmitt, I.; Hofmann, A.; Hoffmann, P.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Wullner, U.; Hurlemann, R. Aberrant NMDA receptor DNA methylation detected by epigenome-wide analysis of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in major depression. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 265, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niciu, M.J.; Ionescu, D.F.; Richards, E.M.; Zarate, C.A. Glutamate and its receptors in the pathophysiology and treatment of major depressive disorder. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Peng, D.; Hong, W.; Yuan, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S.; et al. A study of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor gene (GRIN2B) variants as predictors of treatment-resistant major depression. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Alsuwaidan, M.; Baune, B.T.; Berk, M.; Demyttenaere, K.; Goldberg, J.F.; Gorwood, P.; Ho, R.; Kasper, S.; Kennedy, S.H.; et al. Treatment-resistant depression: Definition, prevalence, detection, management, and investigational interventions. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, C.; Paoletti, P.; Mony, L. Positive allosteric modulation of NMDA receptors: Mechanisms, physiological impact and therapeutic potential. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, K.K.; Traynelis, S.F. New advances in NMDA receptor pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, S.A. Failures and successes of NMDA receptor antagonists: Molecular basis for the use of open-channel blockers like memantine in the treatment of acute and chronic neurologic insults. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Magid, A.F. Allosteric modulators: An emerging concept in drug discovery. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.M.; Quast, R.B.; Fatemi, F.; Rondard, P.; Pin, J.P.; Margeat, E. Allosteric modulators enhance agonist efficacy by increasing the residence time of a GPCR in the active state. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, B.; Mikkelsen, S.; Thorkildsen, C.; Borgbjerg, F.M. Norketamine, the main metabolite of ketamine, is a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist in the rat cortex and spinal cord. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 333, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Zhang, T.; Lv, S.; Zhou, L.; Du, D.; Lin, H.; Guo, F.; Luo, C.; Zhu, S. Author correction: Structural basis of ketamine action on human NMDA receptors. Nature 2021, 598, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorumski, C.F.; Izumi, Y.; Mennerick, S. Ketamine: NMDA receptors and beyond. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 11158–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.P.; Traynelis, S.F.; Siffert, J.; Pope, L.E.; Matsumoto, R.R. Pharmacology of dextromethorphan: Relevance to dextromethorphan/quinidine (Nuedexta®) clinical use. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 164, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, R.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; McCauley, J.A.; Bednar, R.A.; Gaul, S.L.; Mosser, S.D.; Kiss, L.; Lynch, J.J.; Patel, S.; Fandozzi, C.; et al. Preclinical pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of CERC-301, a GluN2B-selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettini, E.; Stahl, S.M.; De Martin, S.; Mattarei, A.; Sgrignani, J.; Carignani, C.; Nola, S.; Locatelli, P.; Pappagallo, M.; Inturrisi, C.E.; et al. Pharmacological comparative characterization of REL-1017 (esmethadone-HCl) and other NMDAR channel blockers in human heterodimeric N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Jensen, M.O.; Jogini, V.; Stein, R.A.; Lee, C.H.; McHaourab, H.S.; Shaw, D.E.; Gouaux, E. Mechanism of NMDA receptor channel block by MK-801 and memantine. Nature 2018, 556, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevtović-Todorović, V.; Todorovć, S.M.; Mennerick, S.; Powell, S.; Dikranian, K.; Benshoff, N.; Zorumski, C.F.; Olney, J.W. Nitrous oxide (laughing gas) is an NMDA antagonist, neuroprotectant and neurotoxin. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanacora, G.; Smith, M.A.; Pathak, S.; Su, H.L.; Boeijinga, P.H.; McCarthy, D.J.; Quirk, M.C. Lanicemine: A low-trapping NMDA channel blocker produces sustained antidepressant efficacy with minimal psychotomimetic adverse effects. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doble, A. The pharmacology and mechanism of action of riluzole. Neurology 1996, 47, S233–S241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourque, M.; Gregoire, L.; Patel, W.; Dickens, D.; Snodgrass, R.; Di Paolo, T. AV-101, a pro-drug antagonist at the NMDA receptor glycine site, reduces L-dopa induced dyskinesias in MPTP monkeys. Cells 2022, 11, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Lin, Y.R.; Tu, Y.S.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chan, M.H.; Chen, H.H. Effects of sarcosine and N, N-dimethylglycine on NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory field potentials. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, S.; Paulus, W. D-cycloserine in neuropsychiatric diseases: A systematic review. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, pyv102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Mancilla, B.; Levy, J.A.; Ganesan, S.; Faller, T.; Issachar, G.; Peremen, Z.; Laufer, O.; Shani-Hershkovich, R.; Biliouris, K.; Walker, E.; et al. MIJ821 (onfasprodil) in healthy volunteers: First-in-human, randomized, placebo-controlled study (single ascending dose and repeated intravenous dose). Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 16, 2236–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcin, L.R.; Warrier, J.; Thangathirupathy, S.; Shi, J.; Karageorge, G.N.; Pearce, B.C.; Ng, A.; Park, H.; Kempson, J.; Li, J.; et al. BMS-986163, a negative allosteric modulator of GluN2B with potential utility in major depressive disorder. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskal, J.R.; Burgdorf, J.S.; Stanton, P.K.; Kroes, R.A.; Disterhoft, J.F.; Burch, R.M.; Khan, M.A. The development of rapastinel (formerly GLYX-13); a rapid acting and long lasting antidepressant. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donello, J.E.; Banerjee, P.; Li, Y.X.; Guo, Y.X.; Yoshitake, T.; Zhang, X.L.; Miry, O.; Kehr, J.; Stanton, P.K.; Gross, A.L.; et al. Positive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulation by rapastinel promotes rapid and sustained antidepressant-like effects. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasipe, O.J. The emergence of new antidepressants for clinical use: Agomelatine paradox versus other novel agents. IBRO Rep. 2019, 6, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgdorf, J.S.; Zhang, X.L.; Stanton, P.K.; Moskal, J.R.; Donello, J.E. Zelquistinel is an orally bioavailable novel NMDA receptor allosteric modulator that exhibits rapid and sustained antidepressant-like effects. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 25, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Li, Y.X.; Berglund, N.; Burgdorf, J.S.; Donello, J.E.; Moskal, J.R.; Stanton, P.K. Zelquistinel acts at an extracellular binding domain to modulate intracellular calcium inactivation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Neuropharmacology 2024, 259, 110100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Berglund, N.A.; Burgdorf, J.S.; Donello, J.E.; Moskal, J.R.; Stanton, P.K. Extracellular application of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor allosteric modulator rapastinel acts remotely to regulate Ca2+ inactivation at an intracellular locus. Neuroreport 2022, 33, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, N.K.; Carrillo, E.; Durham, R.J.; Berka, V.; Jayaraman, V. Allosteric changes in the NMDA receptor associated with calcium-dependent inactivation. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lee, B.; Liu, R.J.; Banasr, M.; Dwyer, J.M.; Iwata, M.; Li, X.Y.; Aghajanian, G.; Duman, R.S. mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 2010, 329, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zang, T.; Birnbaum, S.G.; Wang, Z.; Johnson, J.E.; Zhang, C.L.; Parada, L.F. TrkB dependent adult hippocampal progenitor differentiation mediates sustained ketamine antidepressant response. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S. Pathophysiology of depression and innovative treatments: Remodeling glutamatergic synaptic connections. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 16, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.A.; Gould, T.D. Targeting metaplasticity mechanisms to promote sustained antidepressant actions. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Pothula, S.; Duman, R.S. NMDAR modulators as rapid antidepressants: Converging and distinct signaling mechanisms. Integr. Clin. Med. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Lv, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, C. ERK/mTOR signaling may underlying the antidepressant actions of rapastinel in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepack, A.E.; Bang, E.; Lee, B.; Dwyer, J.M.; Duman, R.S. Fast-acting antidepressants rapidly stimulate ERK signaling and BDNF release in primary neuronal cultures. Neuropharmacology 2016, 111, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Fogaca, M.V.; Deyama, S.; Li, X.Y.; Fukumoto, K.; Duman, R.S. BDNF release and signaling are required for the antidepressant actions of GLYX-13. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widman, A.J.; McMahon, L.L. Disinhibition of CA1 pyramidal cells by low-dose ketamine and other antagonists with rapid antidepressant efficacy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3007–E3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsellino, P.; Krider, R.I.; Chea, D.; Grinnell, R.; Vida, T.A. Ketamine and the disinhibition hypothesis: Neurotrophic factor-mediated treatment of depression. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Suzuki, K.; Kavalali, E.; Monteggia, L. Bridging rapid and sustained antidepressant effects of ketamine. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P.J.; Georgiou, P.; Fischell, J.; Elmer, G.I.; Alkondon, M.; Yuan, P.; Pribut, H.J.; Singh, N.S.; et al. NMDAR inhibition-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolites. Nature 2016, 533, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P.J.; Riggs, L.M.; Highland, J.N.; Georgiou, P.; Pereira, E.F.R.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Thomas, C.J.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; et al. Ketamine and ketamine metabolite pharmacology: Insights into therapeutic mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 621–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Maeng, S.; Martinowich, K.; Manji, H.K.; Zarate, C.A., Jr. Enhancing AMPA to NMDA throughput as a convergent mechanism for antidepressant action. Drug Discov. Today Ther. Strateg. 2006, 3, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackos, D.H.; Lupardus, P.J.; Grand, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.M.; Reynen, P.; Gustafson, A.; Wallweber, H.J.; Volgraf, M.; Sellers, B.D.; et al. Positive allosteric modulators of GluN2A-containing NMDARs with distinct modes of action and impacts on circuit function. Neuron 2016, 89, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackos, D.H.; Hanson, J.E. Diverse modes of NMDA receptor positive allosteric modulation: Mechanisms and consequences. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanos, P.; Brown, K.A.; Georgiou, P.; Yuan, P.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Thompson, S.M.; Gould, T.D. NMDA receptor activation-dependent antidepressant-relevant behavioral and synaptic actions of ketamine. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothula, S.; Kato, T.; Liu, R.J.; Wu, M.; Gerhard, D.; Shinohara, R.; Sliby, A.N.; Chowdhury, G.M.I.; Behar, K.L.; Sanacora, G.; et al. Cell-type specific modulation of NMDA receptors triggers antidepressant actions. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5097–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.J.; Alami, A.; Alexander, G.C.; Mattison, D.R. Safety and effectiveness of NMDA receptor antagonists for depression: A multidisciplinary review. Pharmacotherapy 2022, 42, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mechanism | NMDAR Modulator |
|---|---|
| NMDAR antagonists | |
| Uncompetitive antagonism | Ketamine |
| Esketamine | |
| Arketamine | |
| Dextromethorphan | |
| Lanicemine | |
| Riluzole | |
| CERC-301 | |
| Memantine | |
| Methadone | |
| Esmethadone | |
| Nitrous oxide | |
| Glycine site competitive antagonism | AV-101 |
| NMDAR agonists | |
| Glycine site NMDAR agonist | Sarcosine |
| Glycine site NMDAR partial agonist | D-cycloserine |
| NMDAR negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) | |
| Noncompetitive antagonism | Zinc Ifenprodil |
| Traxoprodil (CP-101606) | |
| Ro 25-6891 | |
| BMS-986163 | |
| YY-23 | |
| Onfasprodil (MIJ821) | |
| NMDAR positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) | |
| Noncompetitive agonism | GNE-6901 |
| GNE-8324 | |
| Rapastinel (GLYX-13) | |
| Apimostinel (NRX-1074) | |
| Zelquistinel (AGN-241751) |
| Stinel * | Stinel Generation | Chemistry | NMDAR Potency † | Oral Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapastinel | First | Peptide | - | No |
| Apimostinel | Second | Peptide | 10–30× | No |
| Zelquistinel | Third | Small molecule | 3–10× | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donello, J.E.; McIntyre, R.S.; Pickel, D.B.; Stahl, S.M. Demystifying the Antidepressant Mechanism of Action of Stinels, a Novel Class of Neuroplastogens: Positive Allosteric Modulators of the NMDA Receptor. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020157
Donello JE, McIntyre RS, Pickel DB, Stahl SM. Demystifying the Antidepressant Mechanism of Action of Stinels, a Novel Class of Neuroplastogens: Positive Allosteric Modulators of the NMDA Receptor. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(2):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020157
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonello, John E., Roger S. McIntyre, Donald B. Pickel, and Stephen M. Stahl. 2025. "Demystifying the Antidepressant Mechanism of Action of Stinels, a Novel Class of Neuroplastogens: Positive Allosteric Modulators of the NMDA Receptor" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 2: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020157
APA StyleDonello, J. E., McIntyre, R. S., Pickel, D. B., & Stahl, S. M. (2025). Demystifying the Antidepressant Mechanism of Action of Stinels, a Novel Class of Neuroplastogens: Positive Allosteric Modulators of the NMDA Receptor. Pharmaceuticals, 18(2), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020157







