Synergistic Efficacy of Policosanol (Raydel®) and Banaba Leaf Extract to Treat Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic and Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Protection of Liver and Kidney with Enhanced Tissue Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
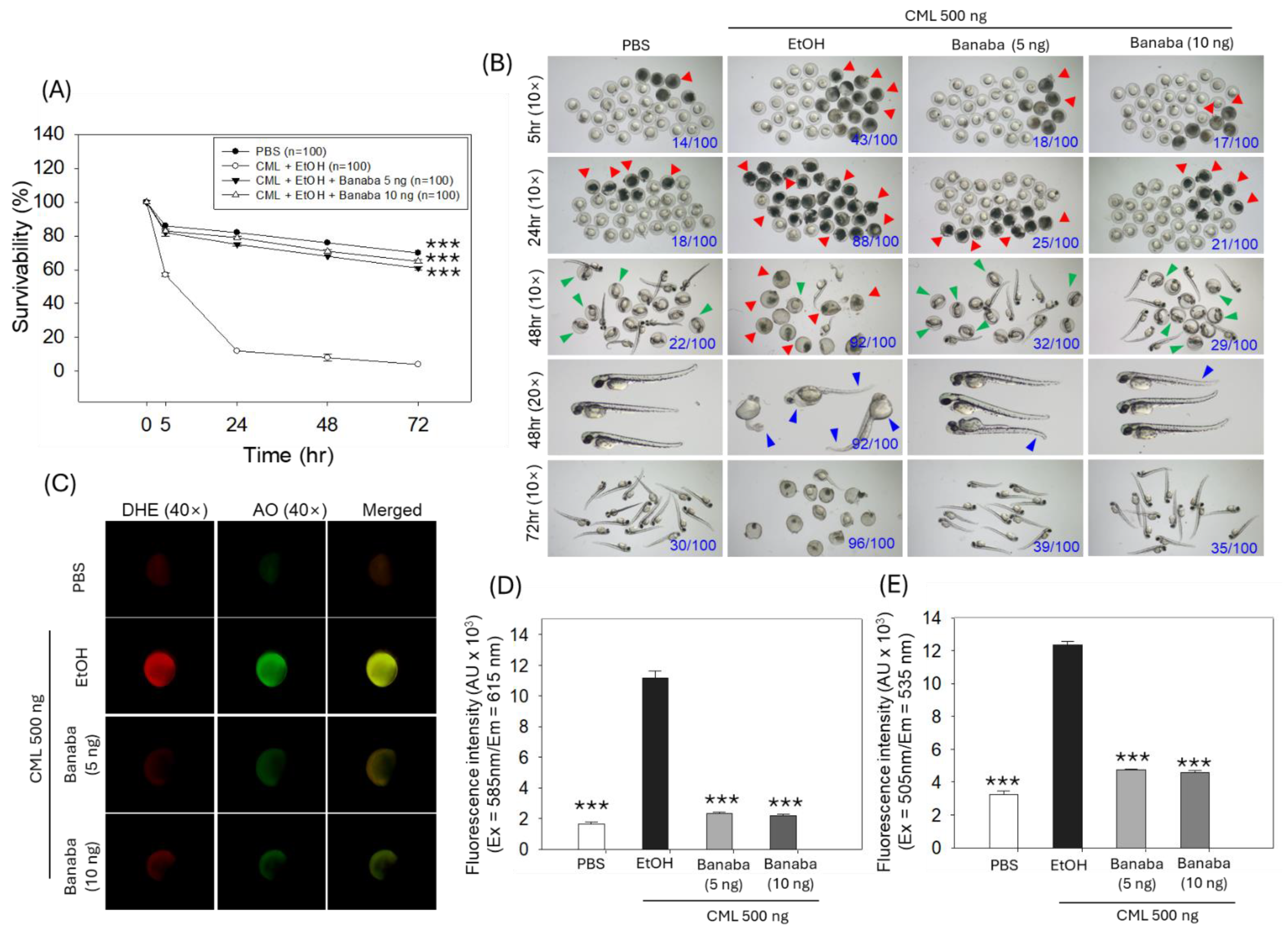
2.1. Zebrafish Embryo Protective Effect of Banaba
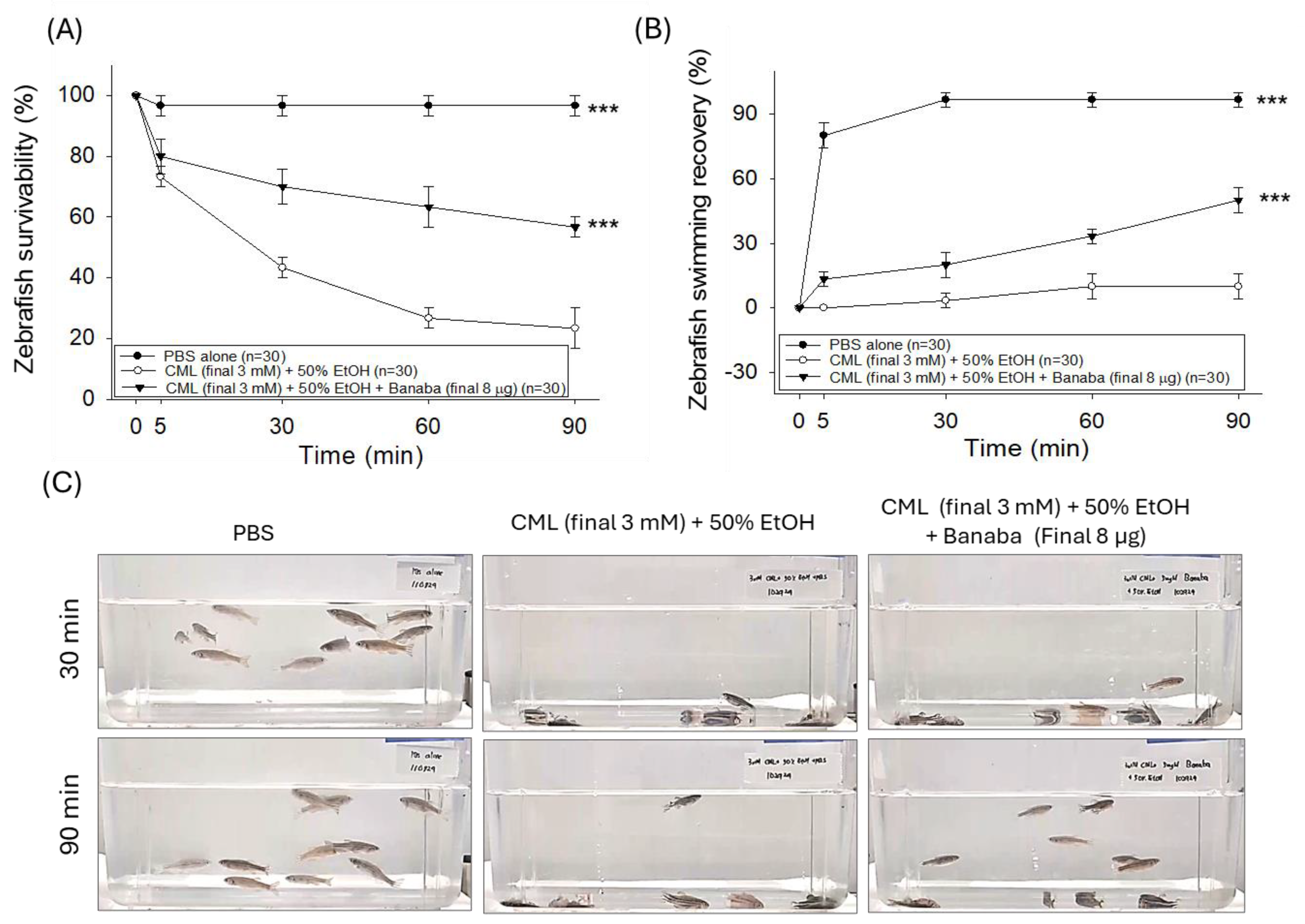
2.2. Banaba Mitigates CML-Induced Paralysis and Mortality in Adult Zebrafish
2.3. Banaba Extract Augmented CML-Impaired Plasma Antioxidant Variables
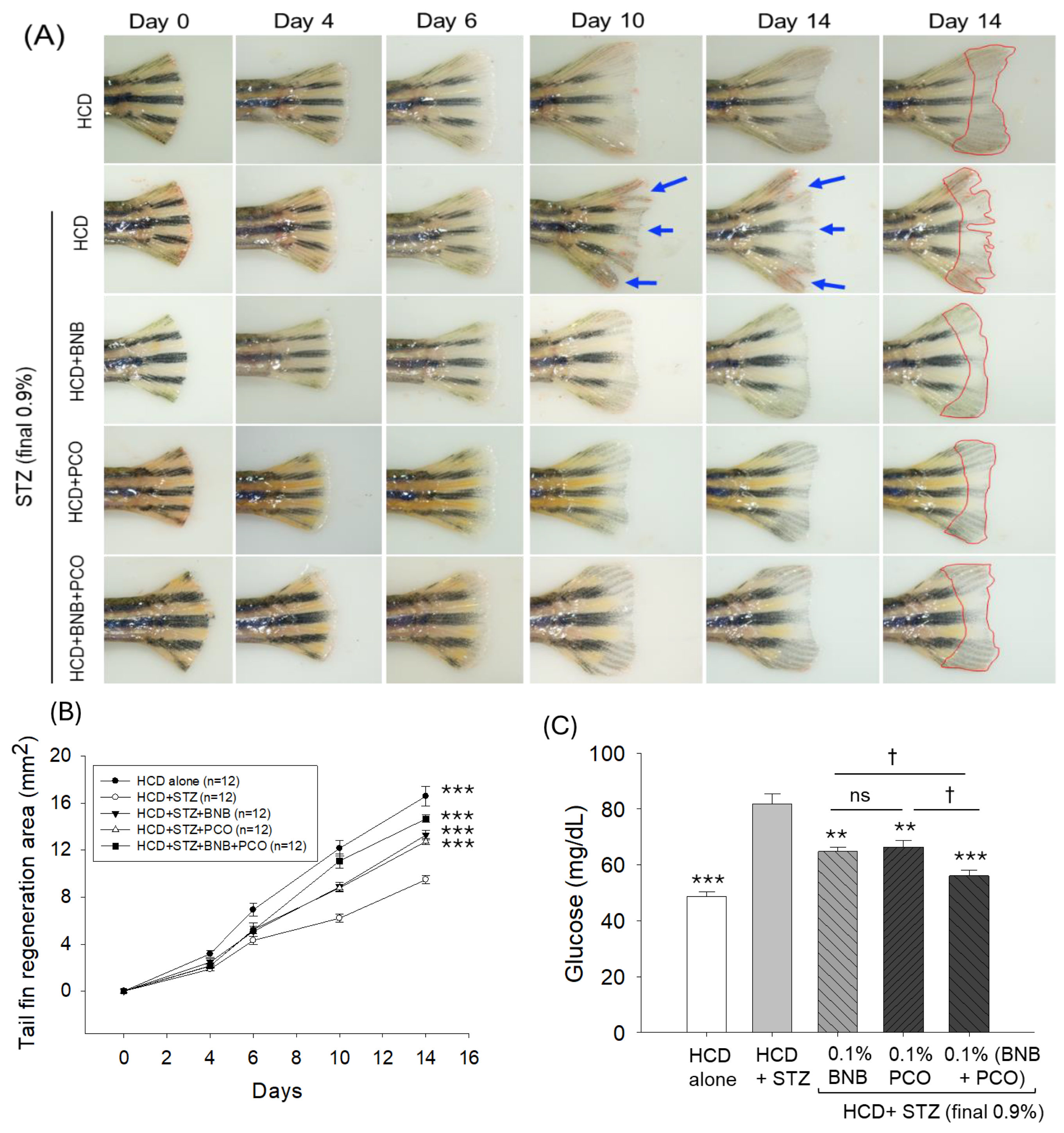
2.4. Banaba and Policosanol Improved STZ-Impaired Tail Fin Regeneration
2.5. Banaba and Policosanol Displayed a Hypoglycemic Effect
2.6. Blood Lipid Profile
2.7. Effect of Banaba and Policosanol Consumption on Blood Antioxidant Status
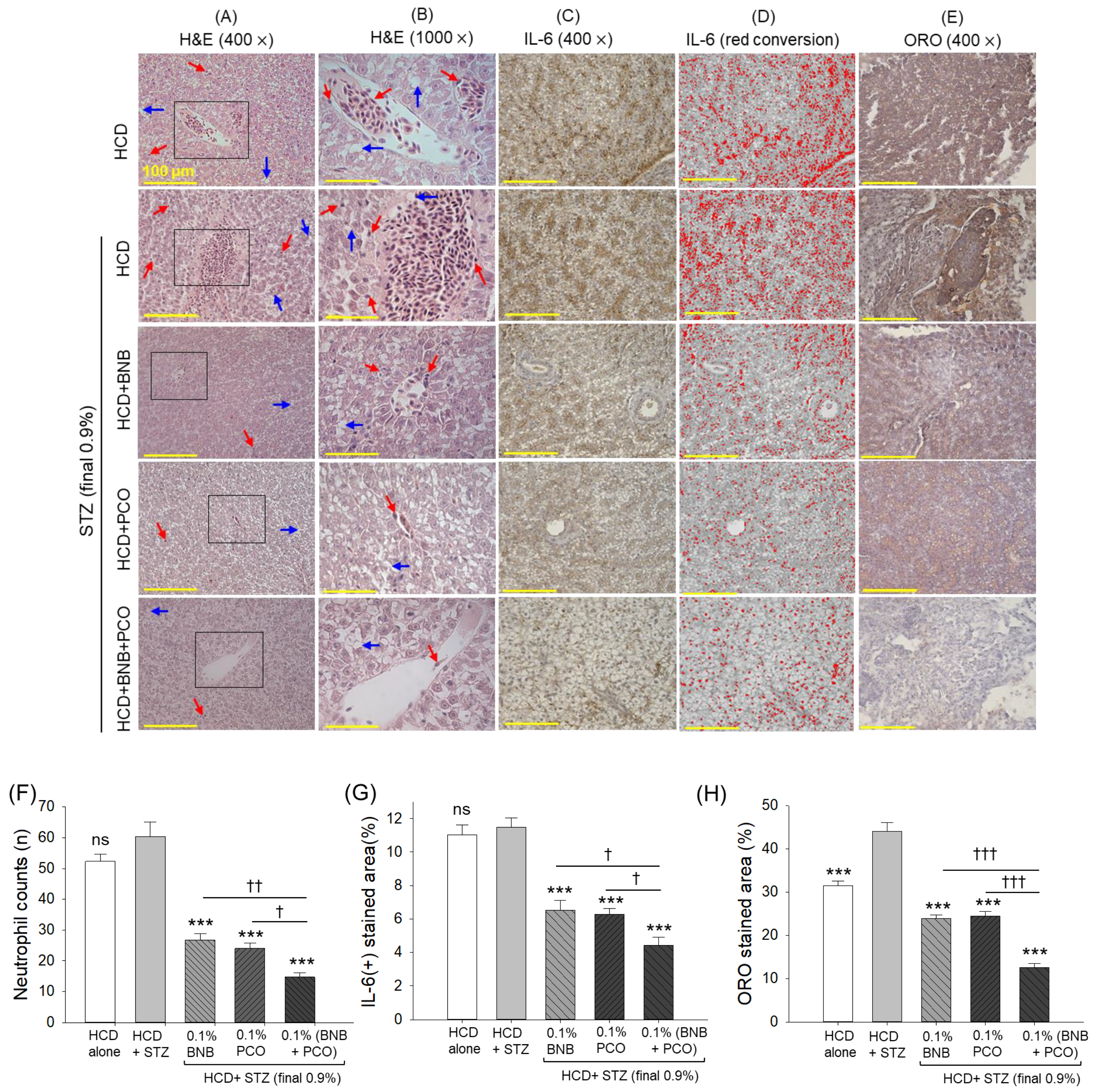
2.8. Hepatic Histology and Inflammation
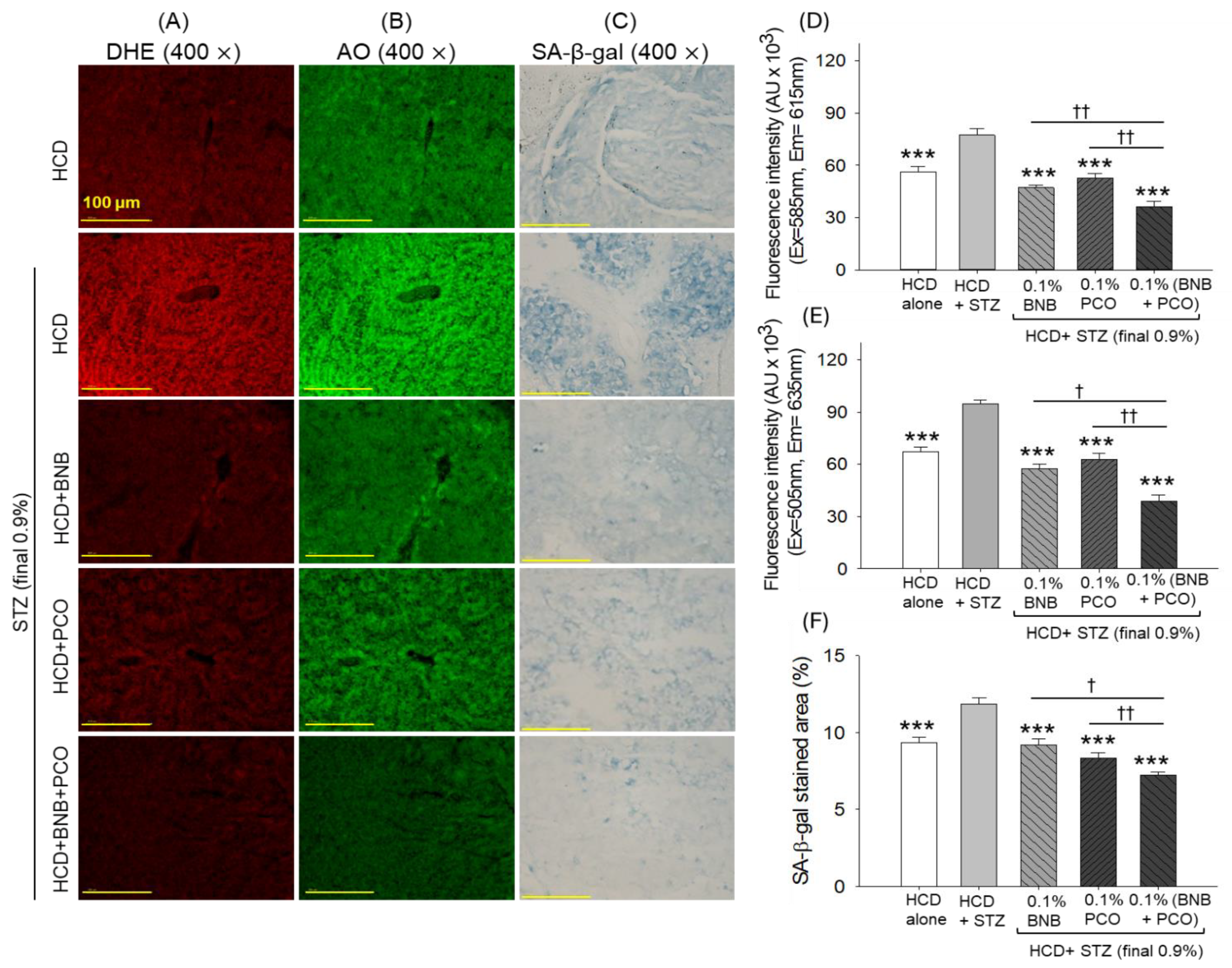
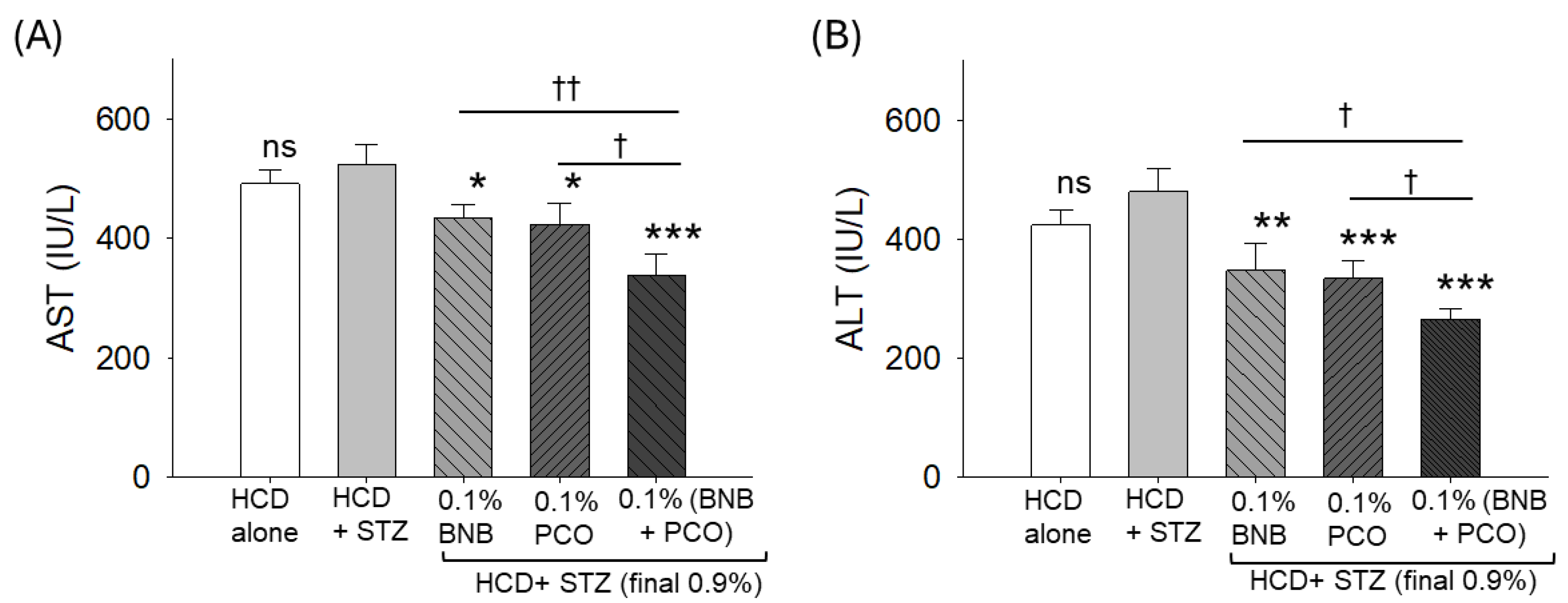
2.9. ROS Production, Apoptosis, Senescence, and Hepatic Function Biomarkers
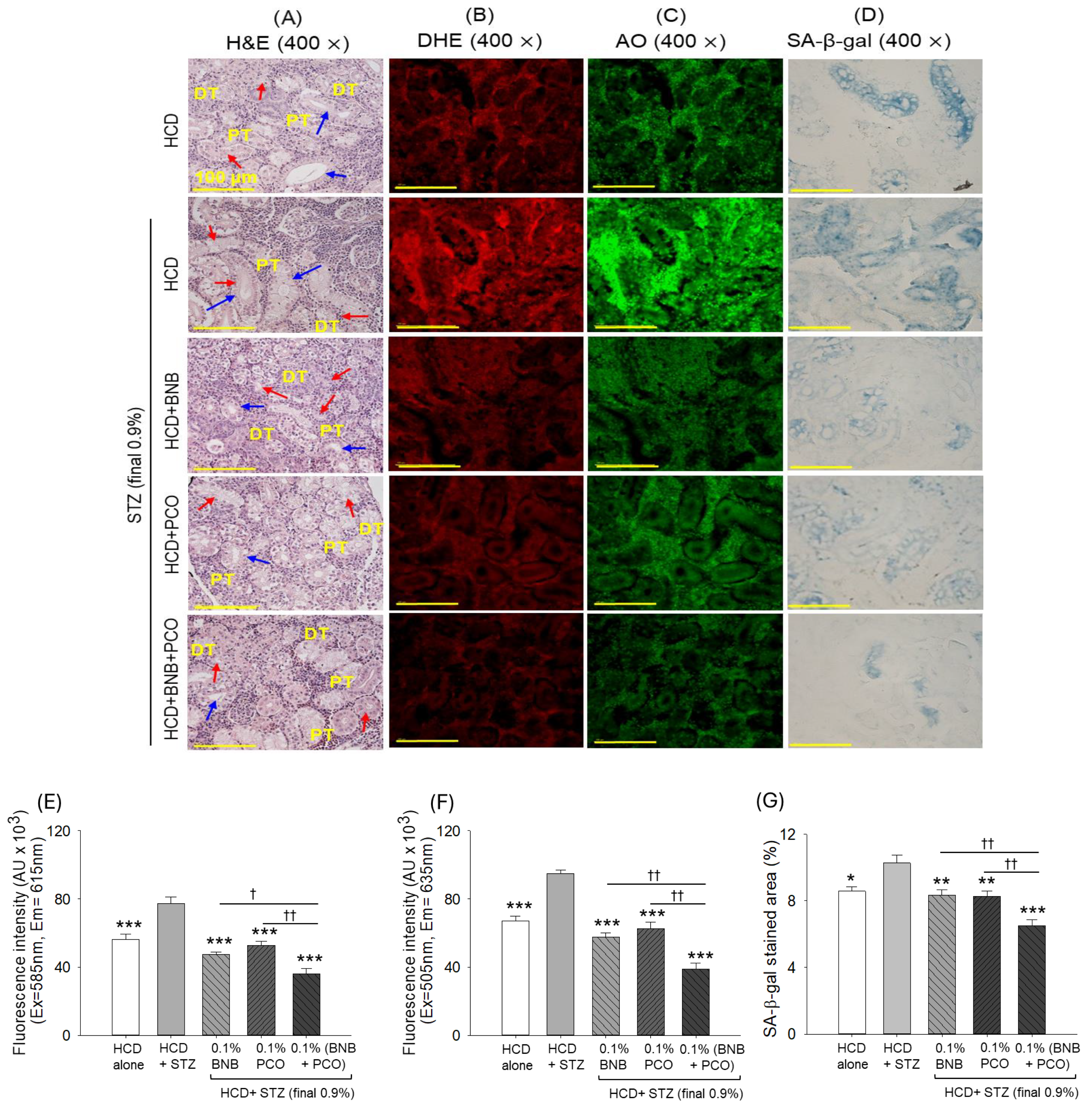
2.10. Histological Analysis of the Kidney
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Zebrafish Husbandry and Production of Embryos
4.3. Microinjection of Zebrafish Embryos
4.4. Acute Toxicity in Adult Zebrafish
4.5. Blood Analysis for Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels and Antioxidant Variables
4.6. Formulation of Different Diets
4.7. Induction of Hyperglycemia in Zebrafish and Tail Fin Regeneration
4.8. Blood Analysis and Collection of Organs
4.9. Histological Analysis and Cellular Senescence
4.10. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Fluorescence Imaging
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abduh, M.S.; Alzoghaibi, M.A.; Alzoghaibi, A.M.; Bin-Ammar, A.; Alotaibi, M.F.; Kamel, E.M.; Mahmoud, A.M. Arbutin ameliorates hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and oxidative stress and modulates adipocytokines and PPARγ in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2023, 321, 121612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahito, S.; Kitahata, H.; Oshita, S. Problems associated with glucose toxicity: Role of hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4137–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddatu, J.; Anderson-Baucum, E.; Evans-Molina, C. Smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes. Transl. Res. 2017, 184, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Del Prato, S. Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Perspectives on the past, present, and future. Lancet 2014, 383, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, J.; Nazratun Nafizah, A.H.; Zariyantey, A.H.; Budin, S.B. Mechanisms of diabetes-induced liver damage: The role of oxidative stress and inflammation. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2016, 16, e132–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S.K. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration, and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, A.G.; Hundley, W.G.; Massing, M.W.; Bonds, D.E.; Burke, G.L.; Goff, D.C., Jr. Heart failure prevalence, incidence, and mortality in the elderly with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinthal, G.N.; Tavill, A.S. Liver disease and diabetes mellitus. Clin. Diabetes 1999, 17, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Schaper, N.; Rayman, G. Microangiopathy: Is it relevant to wound healing in diabetic foot disease? Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Petroianu, G.; Adem, A. Advanced glycation end products and diabetes mellitus: Mechanisms and perspectives. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blahova, J.; Martiniakova, M.; Babikova, M.; Kovacova, V.; Mondockova, V.; Omelka, R. Pharmaceutical drugs and natural therapeutic products for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Islam, M.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Gan, S.H. Updates on managing type 2 diabetes mellitus with natural products: Towards antidiabetic drug development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 5395–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Jiao, R.; Ma, K.Y. Cholesterol-lowering nutraceuticals and functional foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8761–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Yoo, J.A.; Lim, S.M.; Cho, K.H. Anti-aging and tissue regeneration ability of policosanol along with lipid-lowering effect in hyperlipidemic zebrafish via enhancement of high-density lipoprotein functionality. Rejuvenation Res. 2016, 19, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Yoo, J.A.; Lee, E.Y.; Cho, K.H. Enhancement of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol functions by encapsulation of policosanol exerts anti-senescence and tissue regeneration effects via improvement of anti-glycation, anti-apoptosis, and cholesteryl ester transfer inhibition. Rejuvenation Res. 2016, 19, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Throne Research. Monograph. Policosanol. Altern. Med. Rev. 2004, 9, 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.-H.; Nam, H.-S.; Baek, S.-H.; Kang, D.-J.; Na, H.; Komatsu, T.; Uehara, Y. Beneficial effect of Cuban policosanol on blood pressure and serum lipoproteins accompanied with lowered glycated hemoglobin and enhanced high-density lipoprotein functionalities in a randomized, placebo-controlled, and double-blinded trial with healthy Japanese. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, L.K.; Jimoh, A.O.; Tukur, U.M.; Imam, M.U. A review of the effects of policosanol on metabolic syndrome. Clin. Complement. Med. Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Kim, J.-R.; Cho, K.-H. Consumption of policosanol enhances HDL functionality via CETP inhibition and reduces blood pressure and visceral fat in young and middle-aged subjects. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Sasaki, K.; Abe, S.; Nakashima, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kim, J.-E.; Cho, K.-H. Cuban policosanol improves high-density lipoprotein cholesterol efflux capacity in healthy Japanese subjects. Front. Nutr. 2024, 10, 1297008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, N.; Illnait, J.; Mas, R.; Fernandez, L.; Fernandez, J.; Castano, G. Comparative study of the efficacy and tolerability of policosanol and lovastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia and noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 1999, 29, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Stohs, S.J.; Miller, H.; Kaats, G.R. A review of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L.) and corosolic acid. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, A.M.; El-Sammad, N.M.; Abdel-Halim, A.H.; Anwar, N.; Khalil, W.K.B.; Nawwar, M.; Hashim, A.N.; Elsayed, E.A.; Hassan, S.K. Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) pers leaf extract attenuates lung tumorigenesis via alleviating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Yuan, B.; Gothai, S.; Arulselvan, P.; Song, X.; Chen, L. Dietary triterpenes in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: To date. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.S.; Singh, W.S. Multifaceted therapeutic potential of corosolic acid: A novel bioactive compound. Obes. Med. 2024, 49, 100548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Hsu, W.H.; Hsu, Y.W.; Pan, T.M. Suppression of dimerumic acid on hepatic fibrosis caused from carboxymethyl-lysine (CML) by attenuating oxidative stress depends on Nrf2 activation in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G.; Xiao, S.; Qiao, X.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z. Toxicological evaluation of advanced glycation end product Nε-(carboxymethyl)lysine: Acute and subacute oral toxicity studies. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2016, 77, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, A.; Suthar, M.; Rathore, G.S.; Bansal, V.; Kumawat, T. In vitro antioxidant studies of Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves. Pharmacogn. J. 2010, 2, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidke, P.S.; Patil, C.R. Nrf2 activator corosolic acid meliorates alloxan induced diabetic nephropathy in mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Jian, Z. Nrf2 regulates oxidative stress and Its role in cerebral ischemic stroke. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Nam, H.-S.; Kim, J.-E.; Na, H.-J.; del Carmen Dominguez-Horta, M.; Martinez-Donato, G. CIGB-258 exerts potent anti-inflammatory activity against carboxymethyllysine-induced acute inflammation in hyperlipidemic zebrafish via the protection of apolipoprotein AI. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, T.T.; Sabu, M.C.; Jolly, C.I. Free radical scavenging and anti-inflammatory properties of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L). Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaweł, S.; Wardas, M.; Niedworok, E.; Wardas, P. Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad. Lek. 2004, 57, 453–455. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Bourgonje, M.F.; Binnenmars, S.H.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; la Bastide-van Gemert, S.; Kieneker, L.M.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Serum free sulfhydryl status associates with new-onset chronic kidney disease in the general population. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Bourgonje, M.F.; Post, A.; Gemert, S.L.B.-V.; Kieneker, L.M.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Gordijn, S.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.; Mulder, D.J.; et al. Systemic oxidative stress associates with new-onset hypertension in the general population. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 187, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-L. Measurement of protein thiol groups and glutathione in plasma. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 233, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgrowder, D.; Riley, C.; Morrison, E.Y.S.A.; Gordon, L. The role of high-density lipoproteins in reducing the risk of vascular diseases, neurogenerative disorders, and cancer. Cholesterol 2011, 2011, 496925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tréguier, M.; Briand, F.; Boubacar, A.; André, A.; Magot, T.; Nguyen, P.; Krempf, M.; Sulpice, T.; Ouguerram, K. Diet-induced dyslipidemia impairs reverse cholesterol transport in hamsters. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagaméry, F.; Varga, K.; Kecsmár, K.; Vincze, I.; Szökő, É.; Tábi, T. Lack of insulin resistance in response to streptozotocin treatment in neuronal SH-SY5Y cell line. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheibi, S.; Kashfi, K.; Ghasemi, A. A practical guide for induction of type-2 diabetes in rat: Incorporating a high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, B.L. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic models in mice and rats. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Ma, J.; Fang, Y.; Lei, P.; Wang, L.; Qu, L.; Wu, W.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Advances in zebrafish for diabetes mellitus with wound model. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, M.R.; Kazeminejad, S.; Jalalzadeh, M.; Majd, S.S.; Kavyani, Z.; Askari, G.; Hekmatdoost, A. The effects of policosanol supplementation on blood glucose: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 212, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Leng, J.; Li, J.J.; Tang, J.F.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.L.; Wen, X.D. Corosolic acid inhibits adipose tissue inflammation and ameliorates insulin resistance via AMPK activation in high-fat fed mice. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2016, 23, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X.; Peng, A.; Chen, L.; Wei, Y. Triterpene acids isolated from Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves as α-glucosidase inhibitors. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharchil, C.; Vijay, A.; Ramachandran, V.; Bhagavatheeswaran, S.; Devarajan, R.; Koul, B.; Yadav, D.; Balakrishnan, A. Zebrafish: A model to study and understand the diabetic nephropathy and other microvascular complications of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, N.; Jiang, A.; Skochdopole, A.; Chung, J.; Reece, E.M.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Winocour, S. Updates in diabetic wound healing, inflammation, and scarring. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ge, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, X.; Ngan, A.H.W.; Tang, B. Vascular endothelial cellular mechanics under hyperglycemia and its role in tissue regeneration. Regen. Biomater. 2024, 11, rbae004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accipe, L.; Abadie, A.; Neviere, R.; Bercion, S. Antioxidant activities of natural compounds from caribbean plants to enhance diabetic wound healing. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarella, R.; Garofalo, V.; Calogero, A.E. Anti-dyslipidemic and anti-diabetic properties of corosolic acid: A narrative review. Endocrines 2023, 4, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jia, Y.; Thach, T.T.; Han, Y.; Kim, B.; Wu, C.; Kim, Y.; Seo, W.D.; Lee, S.J. Hexacosanol reduces plasma and hepatic cholesterol by activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and suppression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 in HepG2 and C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Res. 2017, 43, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ma, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Ran, X. Association of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikura, K.; Hanai, K.; Shinjyo, T.; Uchigata, Y. HDL cholesterol as a predictor for the incidence of lower extremity amputation and wound-related death in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Atherosclerosis 2015, 239, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.T.M.; Prosser, H.C.; Dunn, L.L.; Vanags, L.Z.; Ridiandries, A.; Tsatralis, T.; Leece, L.; Clayton, Z.E.; Yuen, S.C.G.; Robertson, S.; et al. High-density lipoproteins rescue diabetes-impaired angiogenesis via scavenger receptor class B type I. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3091–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsatralis, T.; Ridiandries, A.; Robertson, S.; Vanags, L.Z.; Lam, Y.T.; Tan, J.T.M.; Ng, M.K.; Bursill, C.A. Reconstituted high-density lipoproteins promote wound repair and blood flow recovery in response to ischemia in aged mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-Y.; Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, Y.-P.; Chiu, H.-Y.; Yeh, N.-L.; Wu, T.-K.; Wu, J.-S. Wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats using atmospheric-pressure argon plasma Jet. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Zhou, S.; Qiu, J.; Shi, C.; Liu, R.; Zhou, H.; Lu, L. Hyperglycemia aggravates acute liver injury by promoting liver-resident macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the inhibition of AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy induction. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Cheng, X.-F.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Q.-Z.; Liu, G.-L.; Zhang, J.-G.; Li, X.-Y. Potential nexus of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Insulin resistance between hepatic and peripheral tissues. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Jain, S.K. Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 2000, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraonio, R. Oxidative stress and cell senescence process. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanami, D.; Matoba, K.; Utsunomiya, K. Dyslipidemia in diabetic nephropathy. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2016, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagar, G.M.; Elseweidy, M.M.M.; Elkomy, N.M.; Keshawy, M.M.; Fathy, O.M.; Sobh, M.S.; Mahmoud, Y.K. Policosanol ameliorates renal inflammation and pyroptosis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits via modulation of HMGB1/PI3K/mTOR/NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 97, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Q.; Tian, W.; Liu, X.-X.; Zhang, K.; Huo, J.-C.; Liu, W.-J.; Li, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhao, M.-G.; Cao, W. Corosolic acid inhibits the proliferation of glomerular mesangial cells and protects against diabetic renal damage. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestry, S.N.; Dhodi, J.B.; Kumbhar, S.B.; Juvekar, A.R. Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by Punica granatum Linn. leaves extract. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Testing. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Bahuguna, A.; Kang, D.-J. Long-term supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil improves dyslipidemia and hepatic inflammation in hyperlipidemic zebrafish: Suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation against carboxymethyllysine toxicity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, M.-S.; Bahuguna, A. Oral supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil augments plasma antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory abilities with enhancement of high-density lipoproteins functionality in rats. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Nam, H.-S.; Baek, S.-H.; Bahuguna, A. Consumption of policosanol (Raydel®) improves hepatic, renal, and reproductive functions in zebrafish: In vivo comparison study among Cuban, Chinese, and American policosanol. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Nam, H.-S.; Kang, D.-J. Efficacy comparison study of human epidermal growth factor (EGF) between Heberprot-P® and Easyef® in adult zebrafish and embryo under presence or absence combination of diabetic condition and hyperlipidemia to mimic elderly patients. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Bahuguna, A.; Kang, D.-J.; Kim, J.-E. Prolonged supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil bestows an antiaging effect, improves blood lipid profile and spinal deformities, and protects vital organs of zebrafish (Danio rerio) against age-related degeneration: Two-years consumption study. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, L.C.; Sen, R.; Menzel, J.; Goyama, S.; Kurokawa, M.; Artinger, K.B. The conserved and divergent roles of Prdm3 and Prdm16 in zebrafish and mouse craniofacial development. Dev. Biol. 2020, 461, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, K.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E. Synergistic Efficacy of Policosanol (Raydel®) and Banaba Leaf Extract to Treat Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic and Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Protection of Liver and Kidney with Enhanced Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030362
Cho K-H, Lee SH, Lee Y, Bahuguna A, Kim J-E. Synergistic Efficacy of Policosanol (Raydel®) and Banaba Leaf Extract to Treat Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic and Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Protection of Liver and Kidney with Enhanced Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(3):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030362
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Kyung-Hyun, Sang Hyuk Lee, Yunki Lee, Ashutosh Bahuguna, and Ji-Eun Kim. 2025. "Synergistic Efficacy of Policosanol (Raydel®) and Banaba Leaf Extract to Treat Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic and Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Protection of Liver and Kidney with Enhanced Tissue Regeneration" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 3: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030362
APA StyleCho, K.-H., Lee, S. H., Lee, Y., Bahuguna, A., & Kim, J.-E. (2025). Synergistic Efficacy of Policosanol (Raydel®) and Banaba Leaf Extract to Treat Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic and Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Protection of Liver and Kidney with Enhanced Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceuticals, 18(3), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030362





