Improved Production of Streptomyces sp. FA1 Xylanase in a Dual-Plasmid Pichia pastoris System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Chemicals
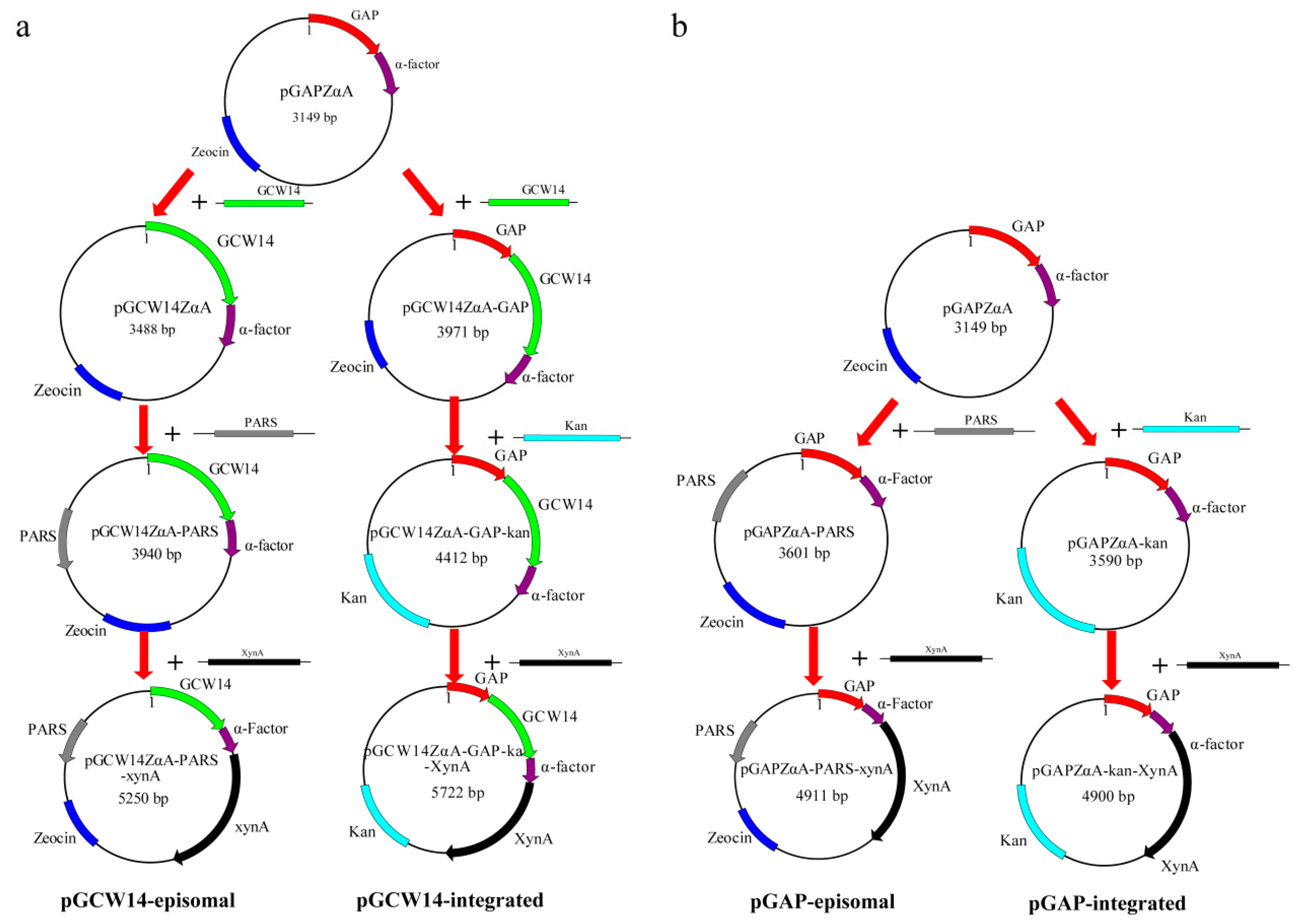
2.2. Construction of the Episomal Vector pGCW14ZαA-PARS
2.3. Construction of the Integrated Vector pGCW14ZαA-GAP-Kan
2.4. Construction of the Episomal Vector pGAPZαA-PARS and the Integrated Vector pGAPZαA-Kan
2.5. Construction of Recombinant Vectors for Xylanase Expression
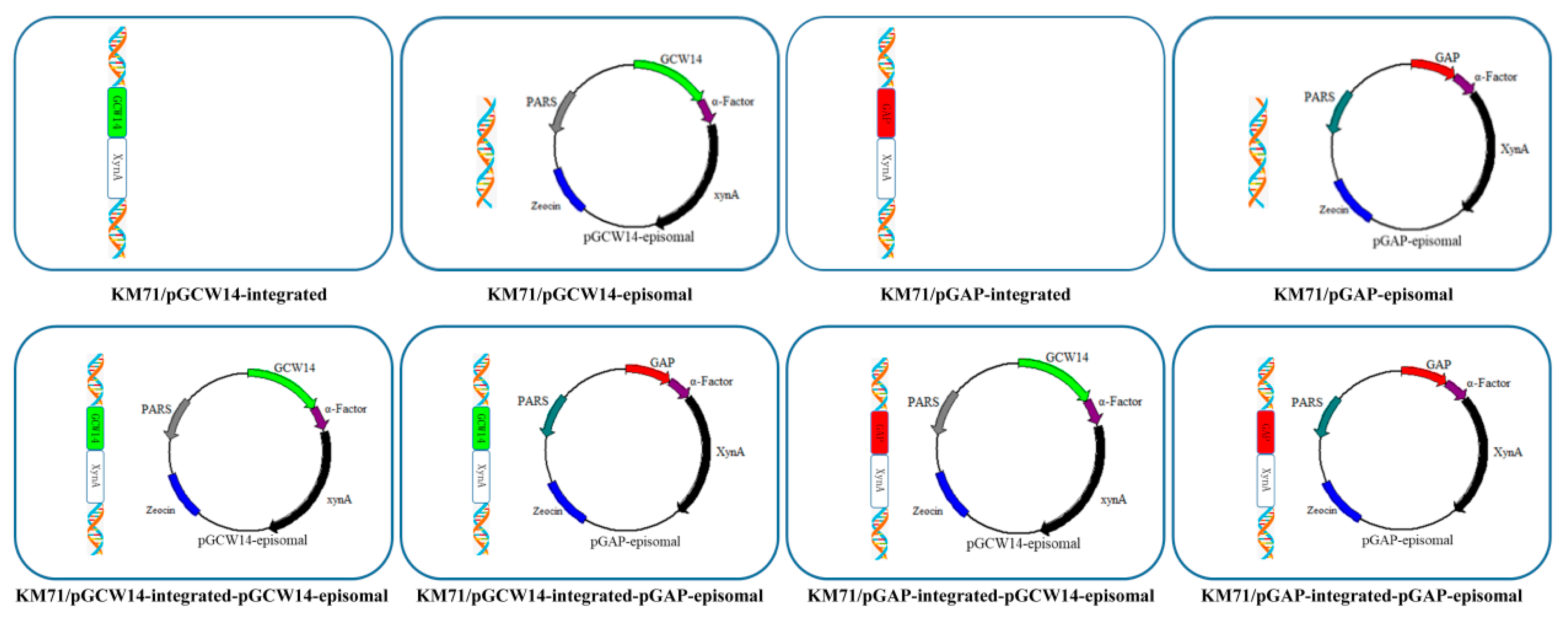
2.6. Construction of Recombinant Strains
2.7. Culturing Recombinant Strains in Shake Flasks
2.8. Determination of Genetic Stability of Episomal Vectors
2.9. High Density Fermentation in a 3.6 L Bioreactor
2.10. Enzyme Activity Assay and Protein Concentration Assay
2.11. Genomic DNA Extraction and Gene Copy Number Analysis by qPCR
3. Results
3.1. XynA Expressions in Single-Promoter Strains in Shake Flasks
3.2. Stability of the pGCW14-Episomal Vector in the Host Cell
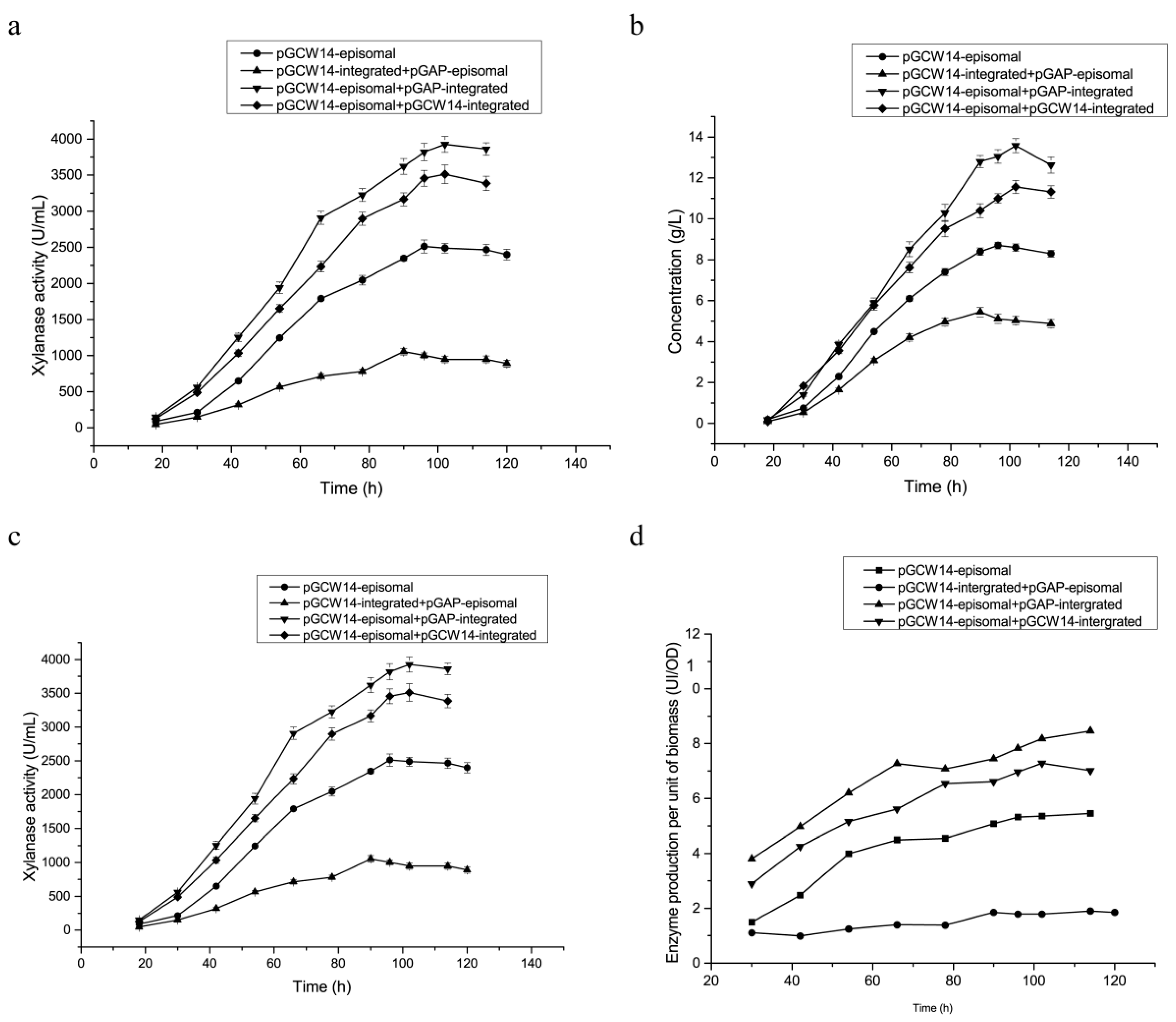
3.3. Enhanced XynA Expressions in Dual-Plasmid Strains in Shake Flasks
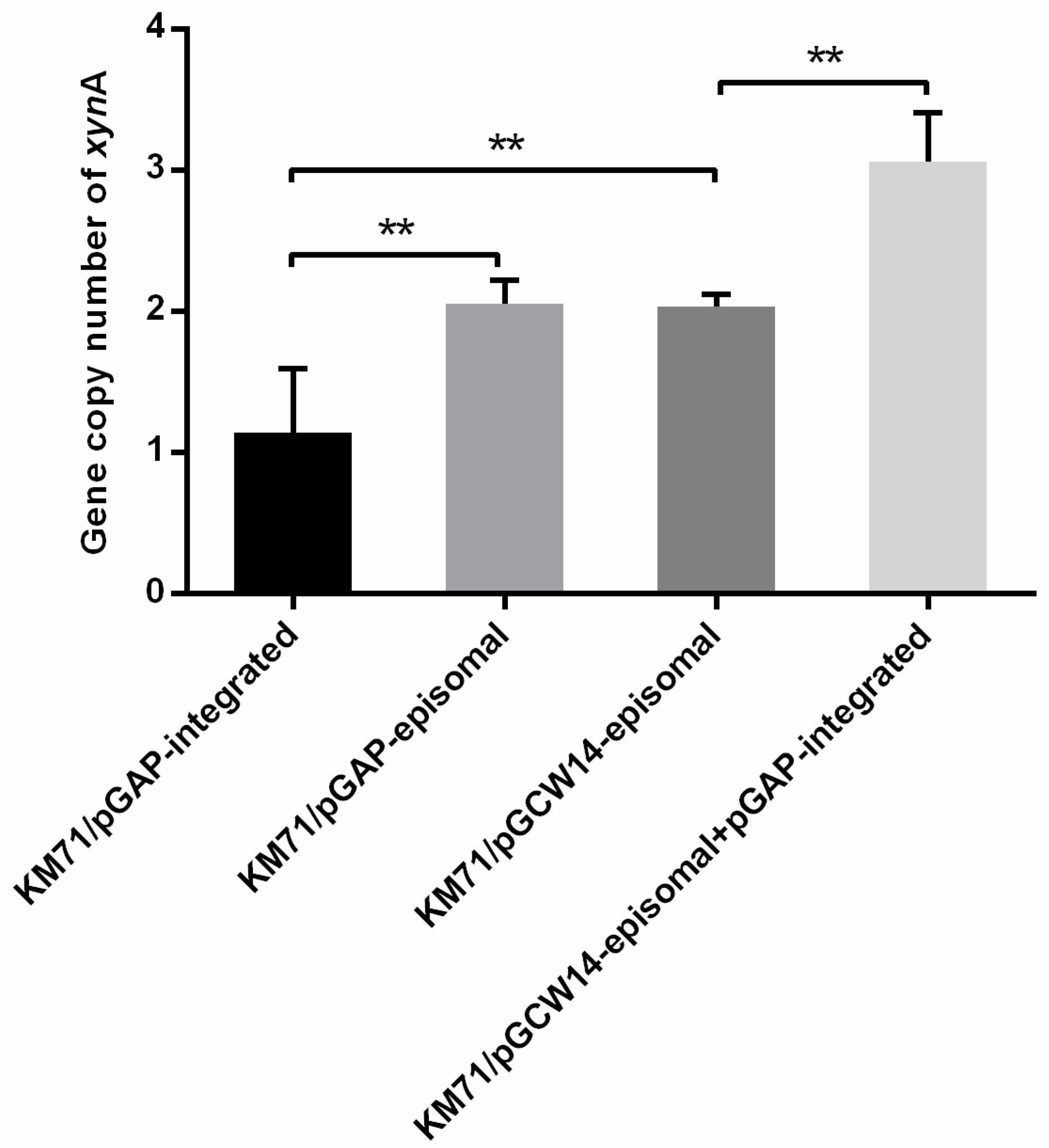
3.4. Gene Copy Number Analysis
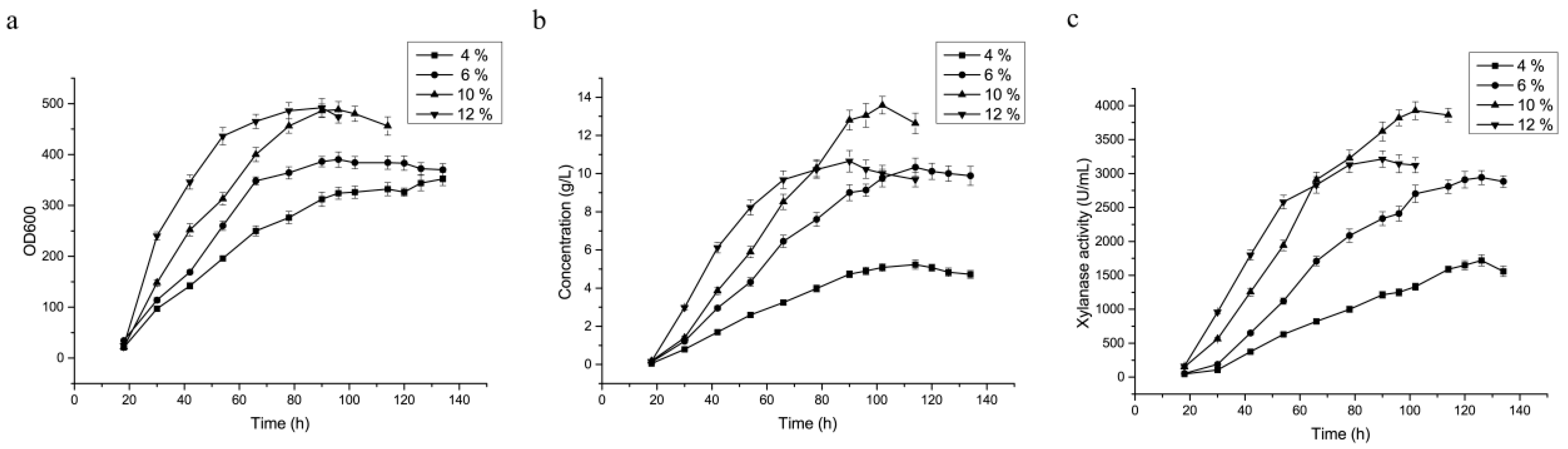
3.5. Optimization of Feed-Flow Rate of the Carbon Source during Fermentation in the 3.6 L Fermenter
3.6. Fermentation of Highly Efficient Recombinant Strains in 3.6 L Fermenter
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Engineering strategies for enhanced production of protein and bio-products in Pichia pastoris: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Hirz, M.; Pichler, H.; Schwab, H. Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: Recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5301–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baghban, R.; Farajnia, S.; Rajabibazl, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Mafi, A.; Hoseinpoor, R.; Rahbarnia, L.; Aria, M. Yeast expression systems: Overview and recent advances. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heistinger, L.; Gasser, B.; Mattanovich, D. Microbe profile: Komagataella phaffii: A methanol devouring biotech yeast formerly known as Pichia pastoris. Microbiology 2020, 166, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, A.; Arun, K.B.; Sindhu, R.; Krishnamoorthy, J.; Reshmy, R.; Sirohi, R.; Pugazhendi, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Szakacs, G.; Binod, P. Customized yeast cell factories for biopharmaceuticals: From cell engineering to process scale up. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohner, S.C.; Muller, H.; Quitmann, H.; Czermak, P. Expression of enzymes for the usage in food and feed industry with Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 202, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, K.R.; Dalvie, N.C.; Love, J.C. The yeast stands alone: The future of protein biologic production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 53, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschmanová, H.; Weninger, A.; Knejzlík, Z.; Melzoch, K.; Kovar, K. Engineering of the unfolded protein response pathway in Pichia pastoris: Enhancing production of secreted recombinant proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4397–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juturu, V.; Wu, J.C. Heterologous Protein Expression in Pichia pastoris: Latest Research Progress and Applications. Chembiochem A Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2018, 19, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roghayyeh, B.; Safar, F.; Younes, G.; Mojtaba, M.; Nosratollah, Z.; Naser, S. New developments in Pichia pastoris expression system, review and update. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krainer, F.W.; Gerstmann, M.A.; Darnhofer, B.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Glieder, A. Biotechnological advances towards an enhanced peroxidase production in Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 233, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Bai, Y.; Cui, Y.; Xu, X.; Qian, L.; Shi, P.; Zhang, W.; Luo, H.; Zhan, X.; Yao, B. Functional diversity of family 3 beta-glucosidases from thermophilic cellulolytic fungus Humicola insolens Y1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Xu, X.; Qian, L.; Shi, P.; Bai, Y.; Luo, H.; Ma, R.; Yao, B. Engineering a highly active thermophilic beta-glucosidase to enhance its pH stability and saccharification performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahaya, R.S.R.; Normi, Y.M.; Phang, L.Y.; Ahmad, S.A.; Abdullah, J.O.; Sabri, S. Molecular strategies to increase keratinase production in heterologous expression systems for industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 3955–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, C.A.; Huang, A.; Nattestad, M.; Oshiro, K.T.; Ray, L.E.; Mulye, T.; Li, Z.H.; Le, T.; Stephens, J.J.; Gomez, S.R.; et al. Analysis of the 5’ untranslated region (5’UTR) of the alcohol oxidase 1 (AOX1) gene in recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Gene 2012, 496, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterham, H.R.; Digan, M.E.; Koutz, P.J.; Lair, S.V.; Cregg, J.M. Isolation of the Pichia pastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and regulation and use of its promoter. Gene 1997, 186, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, S.; Ye, Y.; Lin, Y. Key regulatory elements of a strong constitutive promoter, PGCW14, from Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Xing, Y.; Cai, M.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y. Identification and characterization of novel promoters for recombinant protein production in yeast Pichia pastoris. Yeast 2018, 35, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogl, T.; Glieder, A. Regulation of Pichia pastoris promoters and its consequences for protein production. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.; Ruth, C.; Pitzer, J.; Kickenweiz, T.; Glieder, A. Synthetic core promoters for Pichia pastoris. ACS Synth. Biol. 2014, 3, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.; Sturmberger, L.; Fauland, P.C.; Hyden, P.; Fischer, J.E.; Schmid, C.; Thallinger, G.G.; Geier, M.; Glieder, A. Methanol independent induction in Pichia pastoris by simple derepressed overexpression of single transcription factors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.L.; Luo, J.X.; Zhang, T.Y.; Pan, Y.W.; Tan, Y.H.; Fu, C.Y.; Tu, F.Z. Recent advances on the GAP promoter derived expression system of Pichia pastoris. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Shi, G. Constitutive expression of a novel isoamylase from Bacillus lentus in Pichia pastoris for starch processing. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Sun, H.; Li, P.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. Constitutive expression of alkaline β-mannanase in recombinant Pichia pastoris. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 2025–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Yin, H.X.; Yi, X.P.; Zhang, A.L.; Luo, J.X.; Zhang, T.Y.; Fu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Shen, J.C.; Chen, L.P. Constitutive expression of barley alpha-amylase in Pichia pastoris by high-density cell culture. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 5805–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Luo, J.X.; Chen, S.C.; Guan, W.J.; Fu, C.Y.; Peng, S.Q.; Li, H.L. Constitutive expression of human angiostatin in Pichia pastoris by high-density cell culture. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 34, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ke, F.; Zhao, H.; Liu, T.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y. Constitutive expression of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase LIP2 in Pichia pastoris using GAP as promoter. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zou, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y. Identification and characterization of P GCW14 : A novel, strong constitutive promoter of Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinacker, D.; Rabert, C.; Zepeda, A.B.; Figueroa, C.A.; Pessoa, A.; Farías, J.G. Applications of recombinant Pichia pastoris in the healthcare industry. Braz. J. Microbiol. Publ. Braz. Soc. Microbiol. 2014, 44, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariz, F.C.; Coimbra, E.C.; Jesus, A.L.; Nascimento, L.M.; Torres, F.A.; Freitas, A.C. Development of an IP-free biotechnology platform for constitutive production of HPV16 L1 capsid protein using the Pichia pastoris PGK1 promoter. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 594120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, R.; Mu, W.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T. Efficient secretion of inulin fructotransferase in Pichia pastoris using the formaldehyde dehydrogenase 1 promoter. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.; Gebbie, L.; Palfreyman, R.W.; Speight, R. Effect of plasmid design and type of integration event on recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02712-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin-Cereghino, J.; Wong, W.W.; Xiong, S.; Giang, W.; Luong, L.T.; Vu, J.; Johnson, S.D.; Lin-Cereghino, G.P. Condensed protocol for competent cell preparation and transformation of the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. BioTechniques 2005, 38, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.M.; Lin, J.C.; Chieng, L.L.; Lee, C.K.; Hsu, T.A. Combined use of GAP and AOX1 promoter to enhance the expression of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Luo, W.; Wang, Z.; Lv, P.; Yuan, Z. Combined use of GAP and AOX1 promoters and optimization of culture conditions to enhance expression of Rhizomucor miehei lipase. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-D.; Guo, J.; Li, J.-F.; Wei, X.-H.; Hu, D.; Gao, S.-J.; Yin, X.; Wu, M.-C. Enhancing expression level of an acidophilic β-mannanase in Pichia pastoris by double vector system. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 64, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, D.; Satyanarayana, T. Enhancing the production of recombinant acidic α-amylase and phytase in Pichia pastoris under dual plasmids [constitutive (GAP) and inducible (AOX)] in mixed fed batch high cell density cultivation. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Ma, Y. Inducible and constitutive expression of a novel thermostable alkaline β-mannanase from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. N16-5 in Pichia pastoris and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2008, 43, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Guo, M.; Sun, C.; Qian, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhang, S. A systematical investigation on the genetic stability of multi-copy Pichia pastoris strains. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, M.O.; Reis, V.C.B.; Nicola, A.M.; De Marco, J.L.; de Moraes, L.M.P.; Torres, F.A.G. Multicopy plasmid integration in Komagataella phaffii mediated by a defective auxotrophic marker. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, T.; Guo, M.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhang, S. Efficient generation of multi-copy strains for optimizing secretory expression of porcine insulin precursor in yeast Pichia pastoris. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzhans, J.P.; Luttermann, T.; Wibberg, D.; Winkler, A.; Hubner, W.; Huser, T.; Kalinowski, J.; Friehs, K. A mitochondrial autonomously replicating sequence from Pichia pastoris for uniform high level recombinant protein production. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, L.C.; Bentacur, M.O.; Reis, V.C.B.; De Marco, J.L.; Moraes, L.M.P.; Torres, F.A.G. Molecular strategies to increase the levels of heterologous transcripts in Komagataella phaffii for protein production. Bioengineered 2017, 8, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, Y.; Nishi, T.; Noguchi, R.; Ito, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Nishiyama, T.; Aikawa, S.; Hasunuma, T.; Ishii, J.; Okubo, Y.; et al. A Stable, Autonomously replicating plasmid vector containing Pichia pastoris centromeric DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02882-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liachko, I.; Bhaskar, A.; Lee, C.; Chung, S.C.C.; Tye, B.-K.; Keich, U. A comprehensive genome-wide map of autonomously replicating sequences in a naive genome. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camattari, A.; Goh, A.; Yip, L.Y.; Tan, A.H.; Ng, S.W.; Tran, A.; Liu, G.; Liachko, I.; Dunham, M.J.; Rancati, G. Characterization of a panARS-based episomal vector in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris for recombinant protein production and synthetic biology applications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y. High-level expression of Thermomyces dupontii thermo-alkaline lipase in Pichia pastoris under the control of different promoters. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moumita, B.; Vishal, K.; Pratyoosh, S. Recombinant approaches for microbial xylanases: Recent advances and perspectives. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg Karlsson, E.; Schmitz, E.; Linares-Pastén, J.A.; Adlercreutz, P. Endo-xylanases as tools for production of substituted xylooligosaccharides with prebiotic properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9081–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Dangi, A.K.; Shukla, P. Engineering thermostable microbial xylanases toward its industrial applications. Mol. Biotechnol. 2018, 60, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zheng, K.; Wu, D. A xylanase from Streptomyces sp. FA1: Heterologous expression, characterization, and its application in Chinese steamed bread. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.P.; Gay, H.; McDonald, M.R. Organizational patterns within chromosomes. In International Review of Cytology; Bourne, G.H., Danielli, J.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1960; Volume 9, pp. 77–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Ma, D.; Hao, Y.Y.; Chu, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhuang, Y.P.; Zhang, S.L. Incomplete formation of intramolecular disulfide bond triggers degradation and aggregation of human consensus interferon-alpha mutant by Pichia pastoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, D.; Wu, J. Improving the expression of recombinant xylanase in Pichia pastoris with episomal expression plasmid. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao = Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 712–721. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.; Ergun, B.G.; Calik, P. Double promoter expression systems for recombinant protein production by industrial microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7459–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, N.; Lin, F.; Tian, J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, H. Development of an industrial medium and a novel fed-batch strategy for high-level expression of recombinant beta-mananase by Pichia pastoris. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Várnai, A.; Tang, C.; Bengtsson, O.; Atterton, A.; Mathiesen, G.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Expression of endoglucanases in Pichia pastoris under control of the GAP promoter. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, B.; Cao, Y. Improved thermostability of an acidic xylanase from Aspergillus sulphureus by combined disulphide bridge introduction and proline residue substitution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.; Fan, G.; Yan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, Z. High-level expression of a hyperthermostable Thermotoga maritima xylanase in Pichia pastoris by codon optimization. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2012, 78, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoglan, M.; Karaoglan, F.E.; Inan, M. Comparison of ADH3 promoter with commonly used promoters for recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 121, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
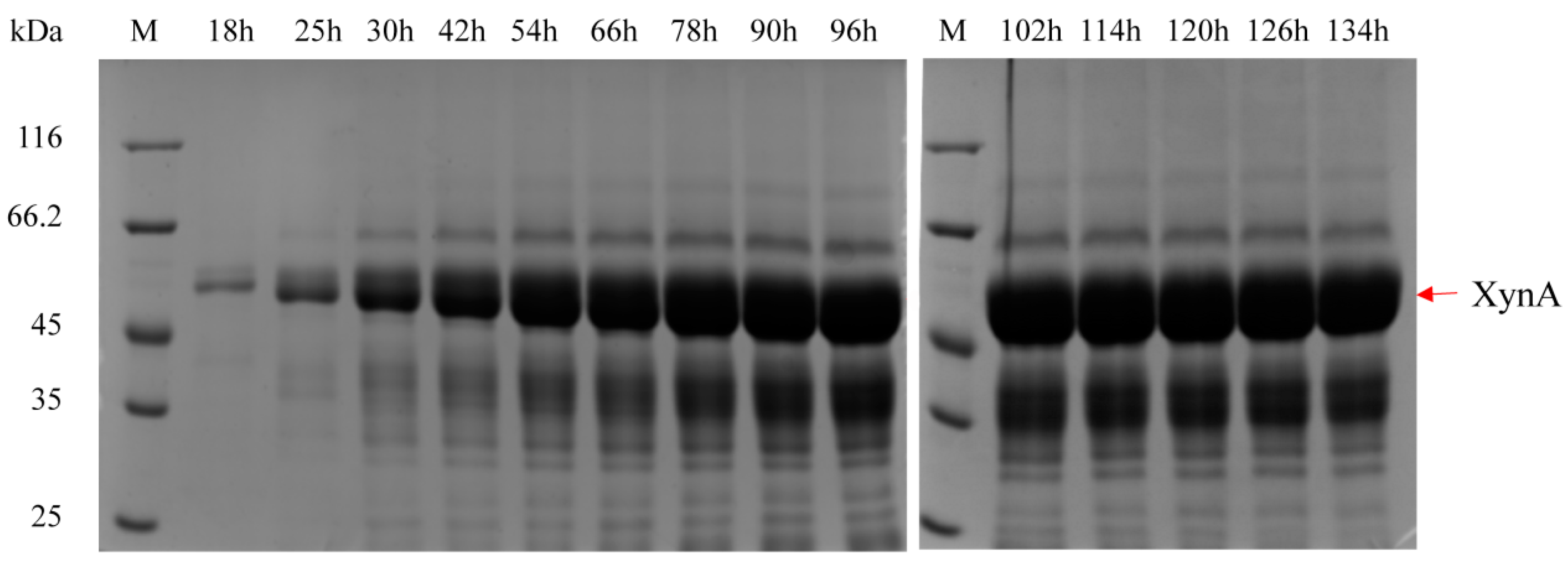
| Strains | pGCW14-Episomal | pGCW14-Integrated | pGAP-Episomal | pGAP-Integrated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity (U·mL−1) | 94.3 ± 7.6 a | 33.4 ± 2.1 b | 32.3 ± 2.5 b | 27.8 ± 1.9 c |
| Generations | Number of Colonies | Gene Losing Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Selective | Resistance Selective | ||
| 30 | 143 | 140 | 2.1% |
| 60 | 144 | 133 | 7.64% |
| 90 | 170 | 144 | 15.29% |
| Strains | pGCW14-Integrated -pGAP-Episomal | pGAP-Integrated -pGCW14-Episomal | pGAP-Integrated -pGAP-Episomal | pGCW14-Integrated -pGCW14-Episomal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity (U·mL−1) | 49.1 ± 3.5 a | 132.7 ± 9.7 b | 49.8 ± 3.7 a | 112.9 ± 7.2 c |
| Yield | Feed Flow Rates of Glycerol | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% | 6% | 10% | 12% | |
| DCW (g·L−1) | 162.68 | 191.1 | 239.12 | 241.08 |
| Protein Conc. (g·L−1) | 5.2 ± 0.37 a | 10.1 ± 0.95 b | 13.6 ± 1.1 c | 10.65 ± 0.87 b |
| Enzyme activity (U·mL−1) | 1720.3 ± 153.5 a | 2940.4 ± 210.1 b | 3925 ± 323.8 c | 3214 ± 276.9 b |
| Specific activity (U·mg−1) | 330.8 ± 25.2 a | 291.1 ± 22.3 b | 303.3 ± 28.1 ab | 301.7 ± 27.7 ab |
| Yield a | DCW (g·L−1) | Protein Conc. (g·L−1) | Enzyme Activity (U·mL−1) | Specific Activity (U·mg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KM71/pGAP-integrated b | 218.3 | 2.7 | 235 | 87 |
| KM71/pGCW14-episomal | 232.24 | 8.7 ± 0.52 a | 2512 ± 193.7 a | 298.1 ± 23.5 a |
| KM71/pGCW14-episomal-pGAP-integrated | 239.12 | 13.6 ± 1.1 b | 3925 ± 323.8 b | 303.3 ± 28.1 a |
| KM71/pGCW14-integrated-pGAP-episomal | 276.36 | 5.4 ± 0.37 c | 1056 ± 89.2 c | 195.6 ± 15.6 b |
| KM71/pGAP-integrated-pGAP-episomal | 251.86 | 5.08 | 968.3 | 190.6 |
| KM71/pGCW14-integrated | 237.65 | 4.86 | 847.6 | 174.4 |
| KM71/pGCW14-episomal-pGCW14-integrated | 243.04 | 11.56 ± 0.92 b | 3512 ± 290.3 b | 303.8 ± 22.9 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, W.; Hu, M.; Pan, Y.; Wu, D.; Wu, J. Improved Production of Streptomyces sp. FA1 Xylanase in a Dual-Plasmid Pichia pastoris System. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 2289-2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030161
Xia W, Hu M, Pan Y, Wu D, Wu J. Improved Production of Streptomyces sp. FA1 Xylanase in a Dual-Plasmid Pichia pastoris System. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2021; 43(3):2289-2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030161
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Wei, Mengkai Hu, Yang Pan, Dan Wu, and Jing Wu. 2021. "Improved Production of Streptomyces sp. FA1 Xylanase in a Dual-Plasmid Pichia pastoris System" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 43, no. 3: 2289-2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030161
APA StyleXia, W., Hu, M., Pan, Y., Wu, D., & Wu, J. (2021). Improved Production of Streptomyces sp. FA1 Xylanase in a Dual-Plasmid Pichia pastoris System. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 43(3), 2289-2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030161






